Computer Systems Exam 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
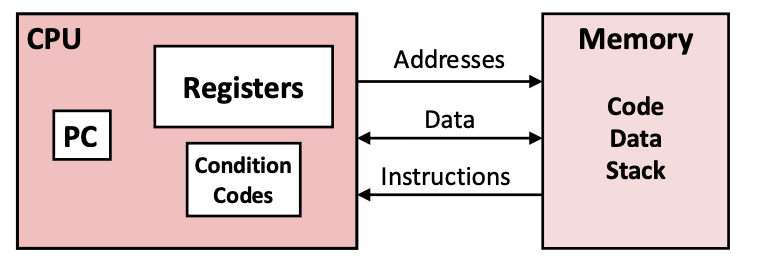
What does PC mean and what does it do?
Program Counter
Stores the address of next instruction
What are condition codes?
They store status information about most recent arithmetic or logical operation
isnt used in MIPS but used in other ISA’s
Register File?
Used in program data
Memory?
A byte addressable array
holds code and user data
stack to support procedures
What is the Assembly/machine code view of CPU and Memory? Draw it !!!
What are computers made of?
They are made of circuits
Use tow symbols to represent information
Low voltage (off, or zero)
High voltage (on, or one)
They are also base 2 (binary)
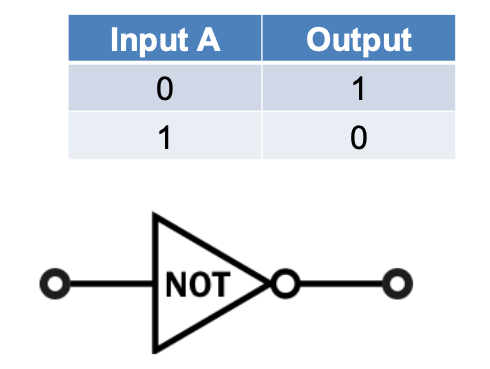
What is a not gate and its truth table?
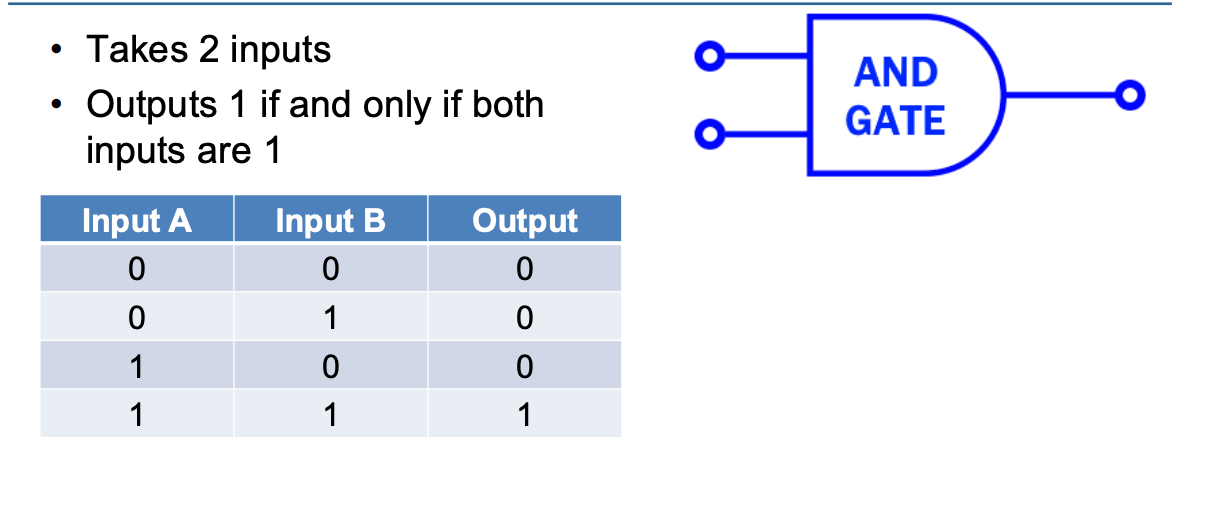
What is an AND gate and its truth table?
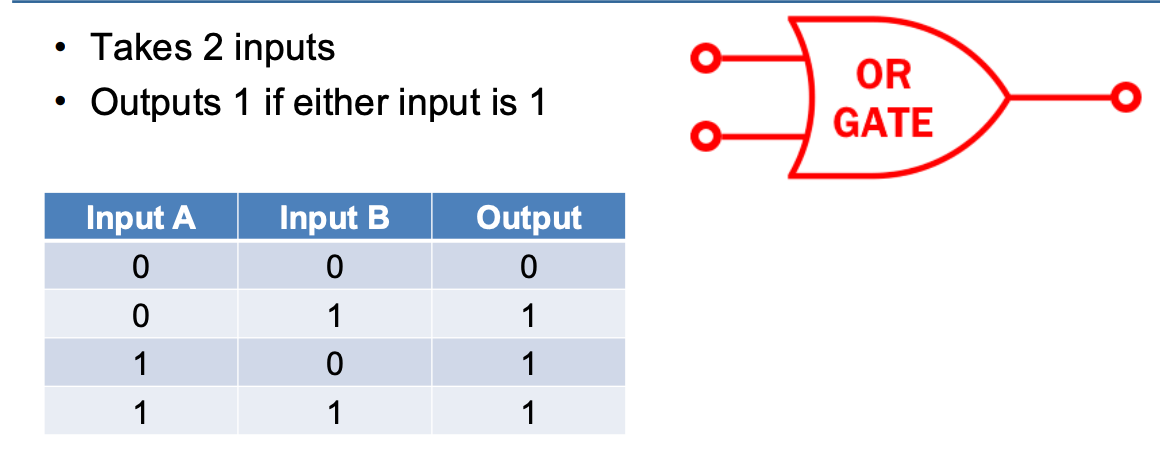
What is does an OR gate look like and whats its truth table?
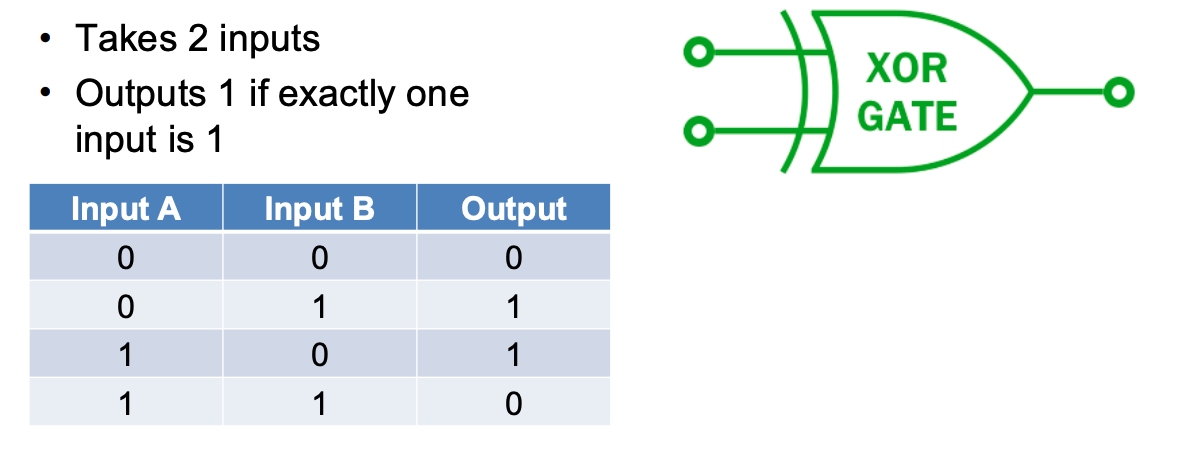
What does an XOR gate look like and whats its truth table?
What are the components of the system?
Processing
Where computation happens
Memory
where data is stored
Peripherals
communication beyond the computer
What are the components of circuits and what do they do?
Power
may act as a 1 and or high voltage (on)
Ground
acts like a 0 and or low voltage (off)
Resistors
allow a change of voltage
Transistors
Are the building blocks of computers
allow all circuits to compute values dynamically
The gate controls the connection between source and drain
sending voltage to the gate connects source and drain
removing voltage to the gate disconnects source and drain
What is a multiplexer?
A hardware unit that acts as selectors
What does a multiplexer do?
Takes multiples inputs
1 selection input
multiple possible choices
1 output
value is equal to the choice input chosen by selection input
They make it possinle for several input signals to share one device or resource
What is a clock signal?
A signal that oscillates between high and low state at a constant frequency (think metronome)
it is used to synchronize actions by using latches
What does a latch (AKA registers) do?
They manage the data transfer between components on rising edges
They store a bit of data temporarily until its updated by new input signals
What are peripherials and name a few examples
They are how computers communicate with the outside world
are used by memory-mapping
Examples:
monitor
mouse
keyboard
internet
printer
speaker
webcam
What is the hardware in a processor?
storage
Instruction memory
fetch 32-bit instructions
Data memory
Load/store 64-bit data
Register Array
storage for 32 integer registers
has 2 read ports/ can read 2 registers at once
1 write port
Functional Units
+4
PC incrementer
Xtnd
sign extender
ALU
Arithmetic and logical instructions
Zero test
detector whether operand == 0
What happens when executing an instruction? (Ex)
The ALU performs the specified operation from the instruction opcode bits on its input values.
What happens when fetching an instruction? (IF)
The required data is fetched from main memory with an increment of +4
What happens when decoding an instruction?(ID)
Read source registers and generate control signals
what happens when using memory with an instruction?(MEM)
Read or write the data memory
What happnes in write back with an instruction?(WB)
Store a result in the desired register
What is latency?
The time between the beginning and completion of an instruction
= number of stages * maximum stage time (ns)
remember when trying to get the maximum stage time include the latch time with that
What is throughput (AKA bandwidth)
The rate of instruction completion
= 1 / maximum stage time (GHz)
What is Amdahl’s Law?
Soverall = T/ T’ = 1/ ((1-Fenhanced) + (Fenhanced/ Senhanced))
What are the 5 stages of pipelining
Fetch (IF)
Decode (ID)
Execute (EX)
Memory (MEM)
Write back (WB)
What is a data hazard?
Events thats occur when the result of a previous instruction and that result of instruction has not yet been computed.
Pairs of instructions that would change output if reversed
What are the types of data hazards?
RAW (read after write)
WAW (write after write)
WAR (Write after read)
what is a control hazard?
When a choice on what instruction to fetch hasnt been made in time for the next instruction
What is stalling?
The idea behind stalling is to delay the dependent instruction until data is ready.
what are pipeline stage transitions?
links between pipeline stages that can be disabled or enabled
bubble
transfer
stall
latches
What is branch prediction?
technique used in hardware to guess the outcome of conditional branch instructions
How does a static prediction work?
Makes a prediction independent of code execution
How does a static not-taken prediction work?
Assumes that a branch will never be taken
How does branch prediction improve performance?
The more successful predictions you have the faster your system can run (usually only good for low-latency systems).
How is correctness maintained in branch prediction?
Store computation without committing it
if wrong, rollback and pay a penalty
otherwise commit it
Why are taken branches harder to predict well then non-taken branches?