Biomedical Science - Unit 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Protons
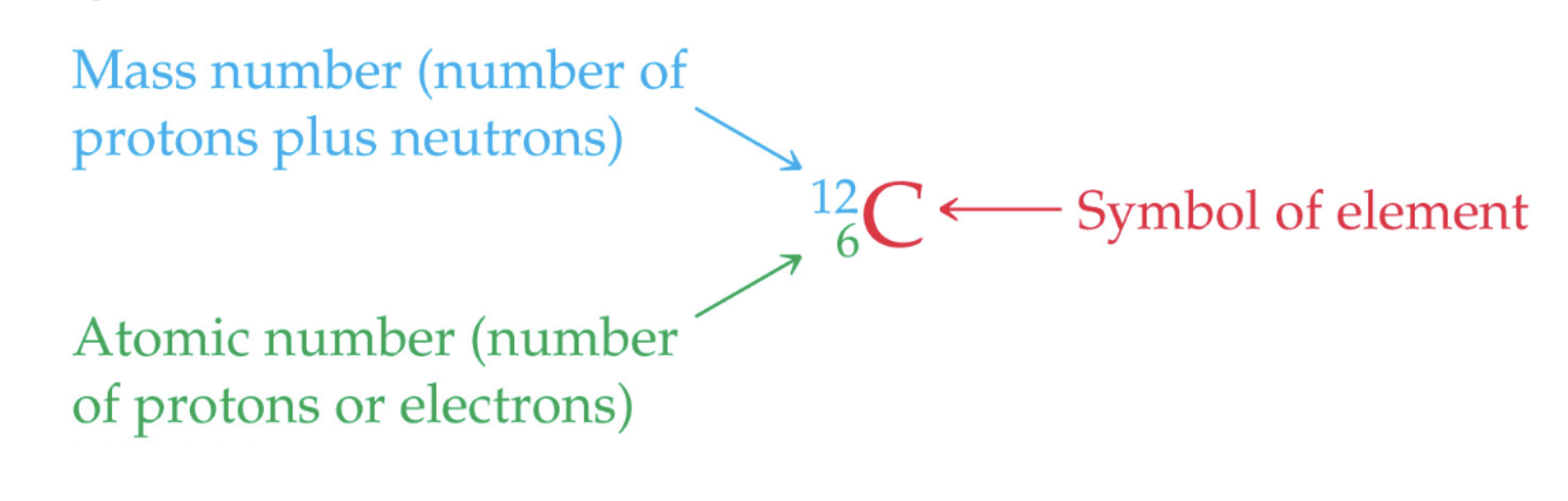
+1, have a mass of about 1, and found in the nucleus. It is the atomic number.
Electrons
-1, have a mass so small we ignore it (about 0), travels around the nucleus, when an atom is neutral this number is the atomic number
Neutrons
Neutral charge, have a mass of about 1, found in the nucleus, mass number is equal to this plus the number of protons
Symbols of Elements
Chemical Formulas
Subscript to the right of the symbol of an element tells the number of atoms of that element in one molecule of the compound
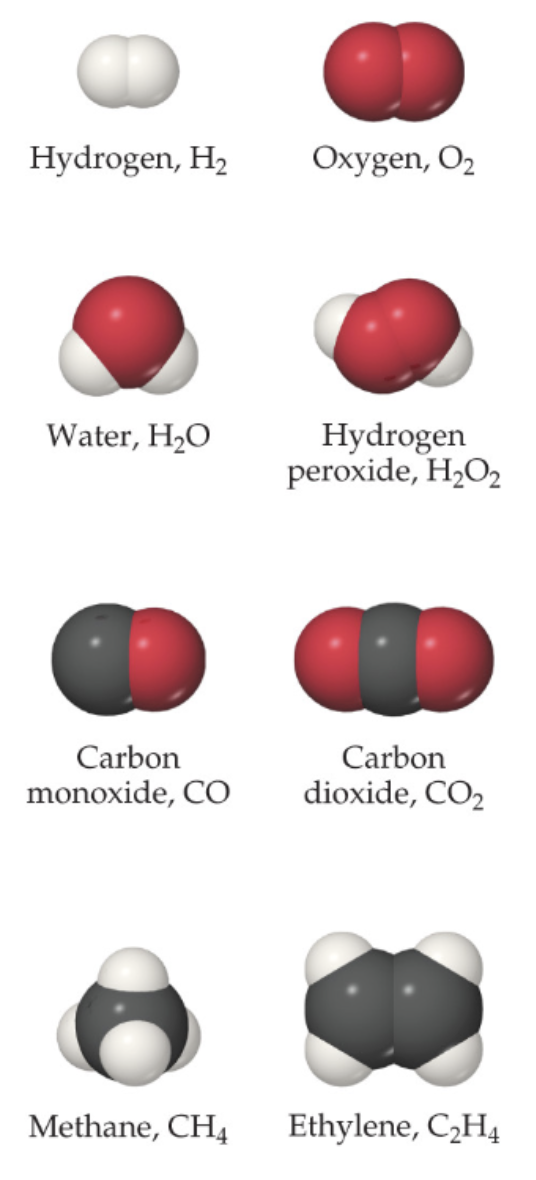
Molecular Compounds
Composed of molecules
Diatomic Molecules
7 elements naturally contain two atoms: H₂, N₂, O₂, F₂, Cl₂, Br₂, I₂
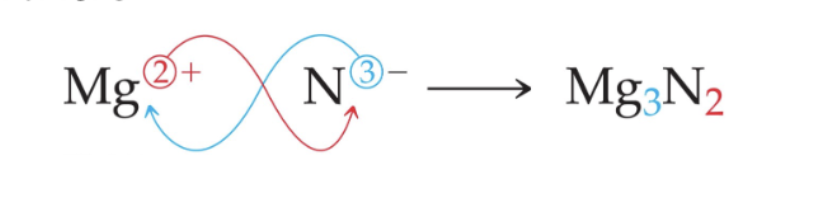
Cations
Formed when at least one electron is lost, monatomic ones are formed by metals
Anions
Formed when at least one electron is gained, monatomic ones are formed by nonmetals
Writing Formulas
Molar Mass
Mass of 1 mol of a substance (g/mol or amu). It is the atomic weight for the element from the periodic table. If it is diatomic, it is twice that atomic weight.
Avogadro’s Number
In a lab, we can’t work with individual molecules because they are too small. 6.02 × 10²³ atoms or molecules is an amount that brings us to lab size and is one mole. (ex. one mole of ¹²C has a mass of 12.000 g.)
Molecular Mass
Sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule
Formula Mass
The sum of the atomic weights for the atoms in a chemical formula. What ionic compounds use.
Solutions
Homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances
Solvent
Component with a concentration significantly greater than the others
Solute
Component of a solution that is present at a much lower concentration than the solvent.
Aqueous Solution
When water is in the solvent
Unsaturated
Solution that has not reached its limit of solubility at a given temperature so more solute dissolves
Saturated
Solution that has reached its limit of solubility at a given temperature so no more solute dissolves
Supersaturated
Solution that has reached its limit of solubility at a given temperature and crystals may grow
Non-electrolyte
Doesn’t contain ions, bulb doesn’t light
Weak electrolytes
Contains a small amount of ions, bulb is dimly lit
Strong Electrolyte
Contains large amount of ions, bulb is brightly lit
Miscible
Substance that fully mixes in all proportions. Nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes and polar solvents dissolve polar solutes. (ex. alcohol and water)
Immiscible
Substance that never fully mixes in any proportions (ex. oil and water)
Molarity (M)
Amount dissolved is concentration, and this is how we measure the concentration of a solution. Equation is (moles of solute)/(volume of solution in liters)
Dilution
Lower concentration, molarity of new solution determined from the equation: Mc x Vc = Md x Vd
Mass Percentage (m/m)
(Mass of solute (g))/(mass of solution (g)) x 100%
Mass/Volume Percentage (m/v)
(mass of solute (g))/ (volume of solution (mL)) x 100%