43. Congenital malformations, inflammations and tumors of the penis
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Congenital malformations of the penis?
3 are important:
- Diphallus
- Epispadias
- Hypospadias
Diphallus?
Presence of an accessory penis.
- Extremely rare
Epispadias?
Distal urethral orifice is present on the dorsal aspect of the penis
- Occurs when the genital tubercle fails to close
- Is associated with bladder exstrophy
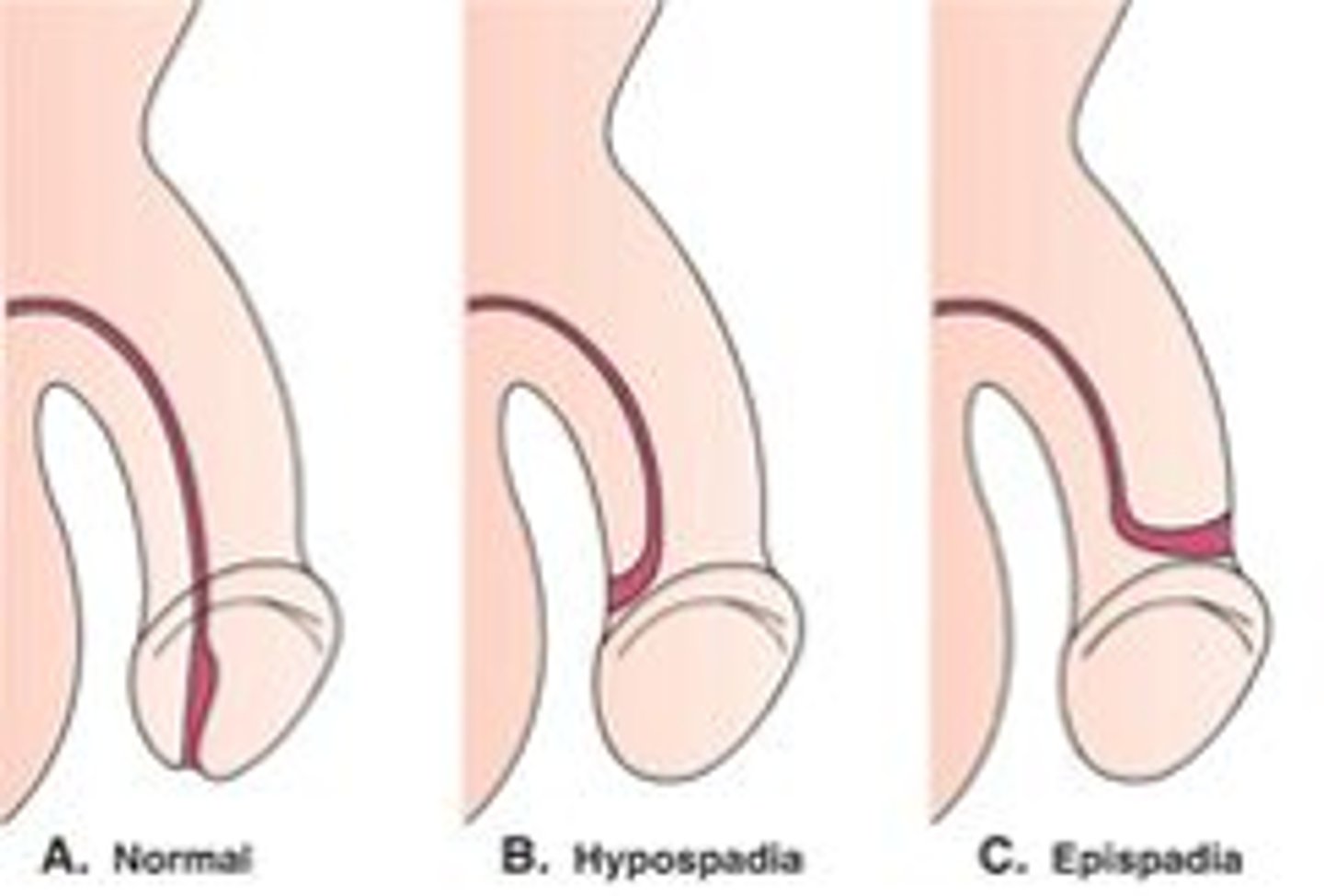
Hypospadias?
Distal urethral orifice is present on the ventral/inferior aspect of the penis
- More common than epispadias
- Occurs when urethral folds fail to close
Inflammation of the penis?
- Balinitis/Balanoposthitis
- Phimosis/Paraphimosis
- Plasma cell balanitis
- Lichen sclerosus/penile Lichen sclerosus
- Peyronie disease
- Priapism
Balanitis/Balanoposthitis?
Balanitis: Inflammation of the glans
Balanoposthitis: Inflammation of the glans and prepuce
Often due to:
- Candida albicans
- Anaerobic bacteria
Phimosis/paraphimosis?
Phimosis: Tight foreskin that cannot be retracted completely
- Is physiological in young children
- Pathological in anyone older
Paraphimosis: Foreskin that has been retracted and cannot be returned to original position
- Often happens during medical procedures
- Improper blood supply to the glans penis -> cause it to swell and worsens the situation
- May become medical emergency to prevent gangrene
Reasons for phimosis to develop?
It can be congenital, but is in most cases acquired
Acquired form:
- Due to fibrosis of the prepuce as a complication of a balanitis/balanoposthitis
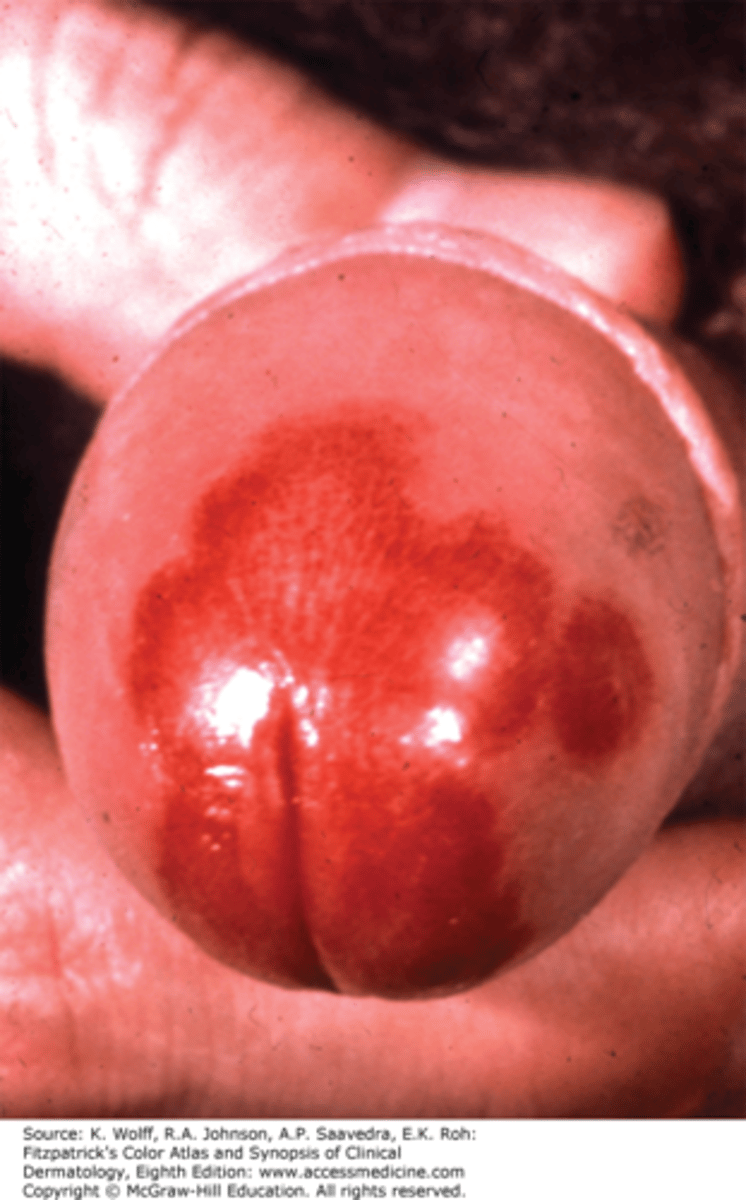
Plasma cell balanitis?
Uncommon condition that causes red patches on the penis
- Cause is unknown
- Condition may resemble precancerous lesion
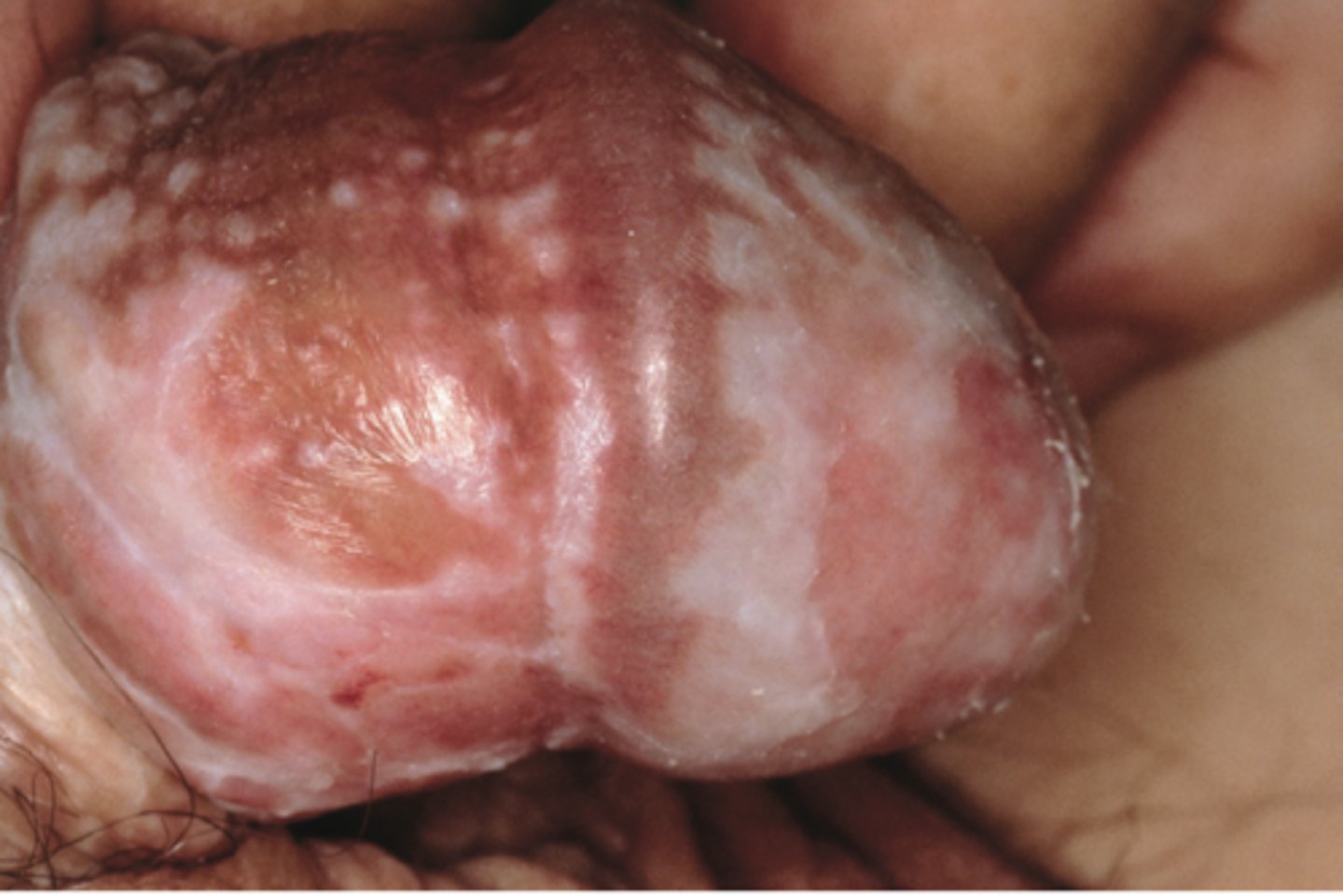
Lichen sclerosus?
Chronic, progressive, inflammatory condition of the skin with characteristic white plaques
- Often affects the genital regions
Penile Lichen sclerosus:
- May cause scarring of the glans and prepuce
- Is a precancerous lesion & therefore increase risk of cancer
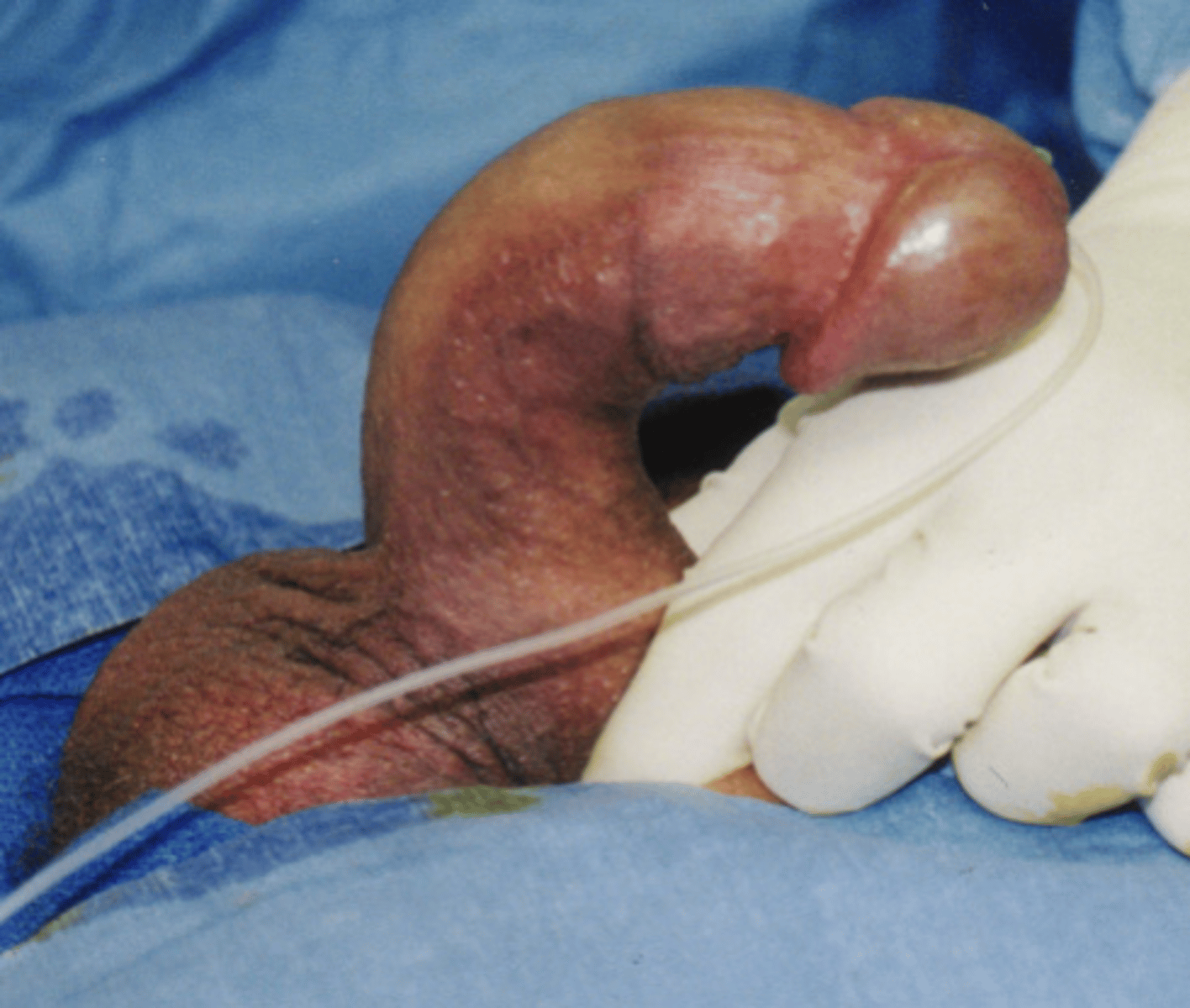
Peyronie disease (Penile fibromatosis)?
Type of fibromatosis -> fibrous growth
- Forms fibrous plaques on the penis
= Causes abnormal bending of the penis and painful erections
Priapism?
Any prolonged erection that occurs without or after stimulation has ceased
May occur due to:
- Sickle cell disease
- Trauma
- Embolization
- Drugs
- Neurological defects
What can priapism cause?
- Ischemia of the penis -> causing necrosis after 48h
= Should be treated as medical emergency
Tumor-like conditions of the penis?
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Trancho nodules/paraffin granuloma/paraffinomas
- Fournier gangrene
Condyloma acuminatum?
Genital warts - can occur on the penis
- Occurs after infection by HPV 6 or 11
- Characterized by koilocytic change
- Most frequently seen in sexually active young adults
How can Condyloma acuminatum lesions look like?
- Flat
- Papillary
- Warty
They regress spontaneously in 50% of patients
Tancho nodules/paraffin granulomas/paraffinomas?
Nodules that occur as a part of granulomatous inflammation
After injection of certain materials into the penis, like:
- Paraffin
- Vaseline
- Silicone
May be performed as a form of penile enlargement
May cause necrosis due to decreased circulation
Fournier gangrene?
Type of necrotizing fasciitis - occurs in the external genitalia or perineum
= Most commonly in scrotum
Life-threatening condition that can lead to sepsis
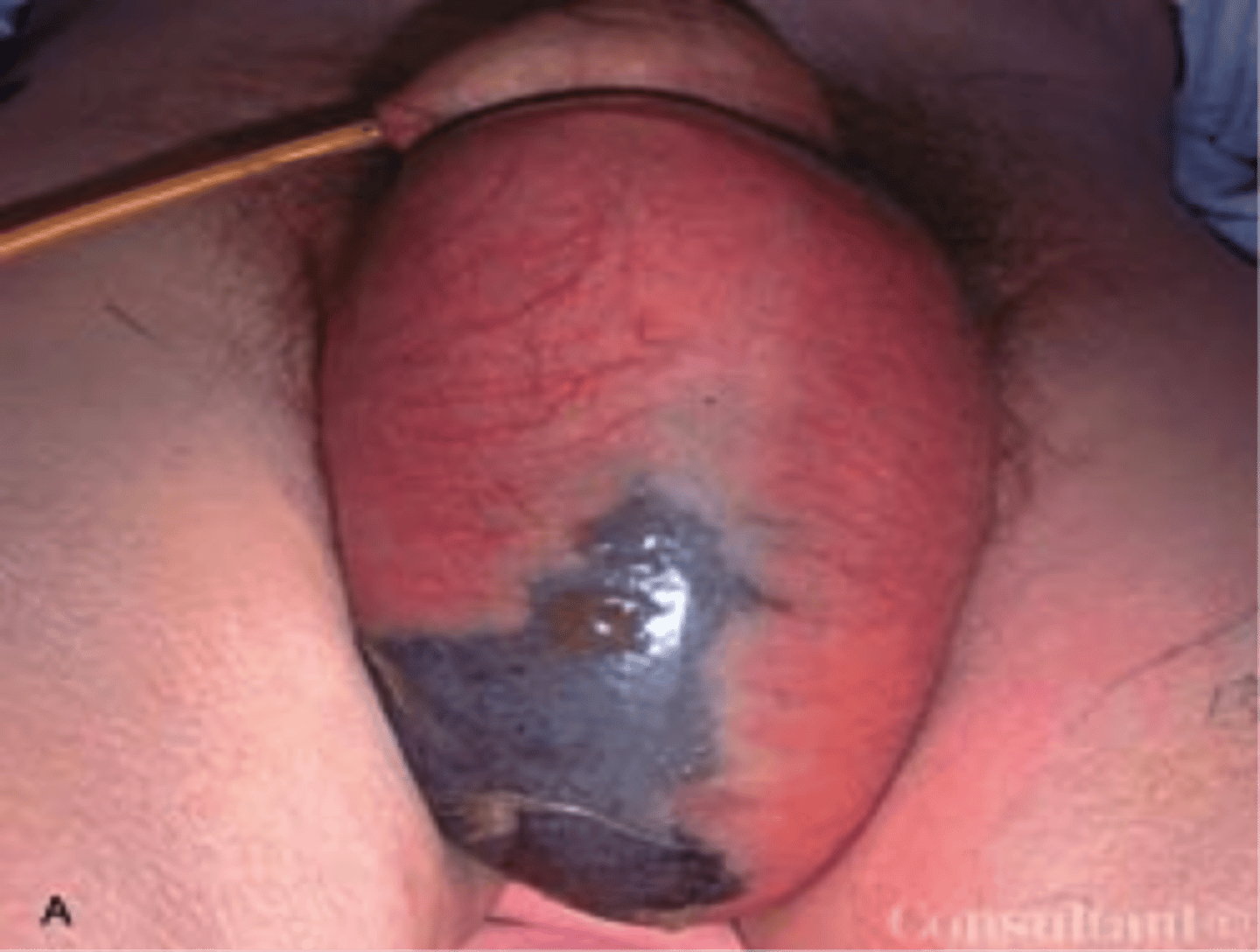
Why does fournier gangrene occur?
Occurs due to:
- Staphylococcal
- Streptococcal
infection
Predisposing factors of Fournier gangrene?
- DM (decrease wound healing)
- Alcoholism
- Immunosuppression
What is necrotizing fasciitis?
Bacterial infection of underlying fascia
- Flesh-eating bacteria
Four precancerous lesions (carcinoma in situ) of the penis?
- Penile lichen sclerosus
- Bowen disease
- Erythroplasia of Queyrat
- Bowenoid papulosis
Bowen disease?
Very early form of skin cancer, which is easily curable and characterized by a scaly patch lesions
Erythroplasia of Queyrat?
Appears as reddish plaques of the glans of the penis
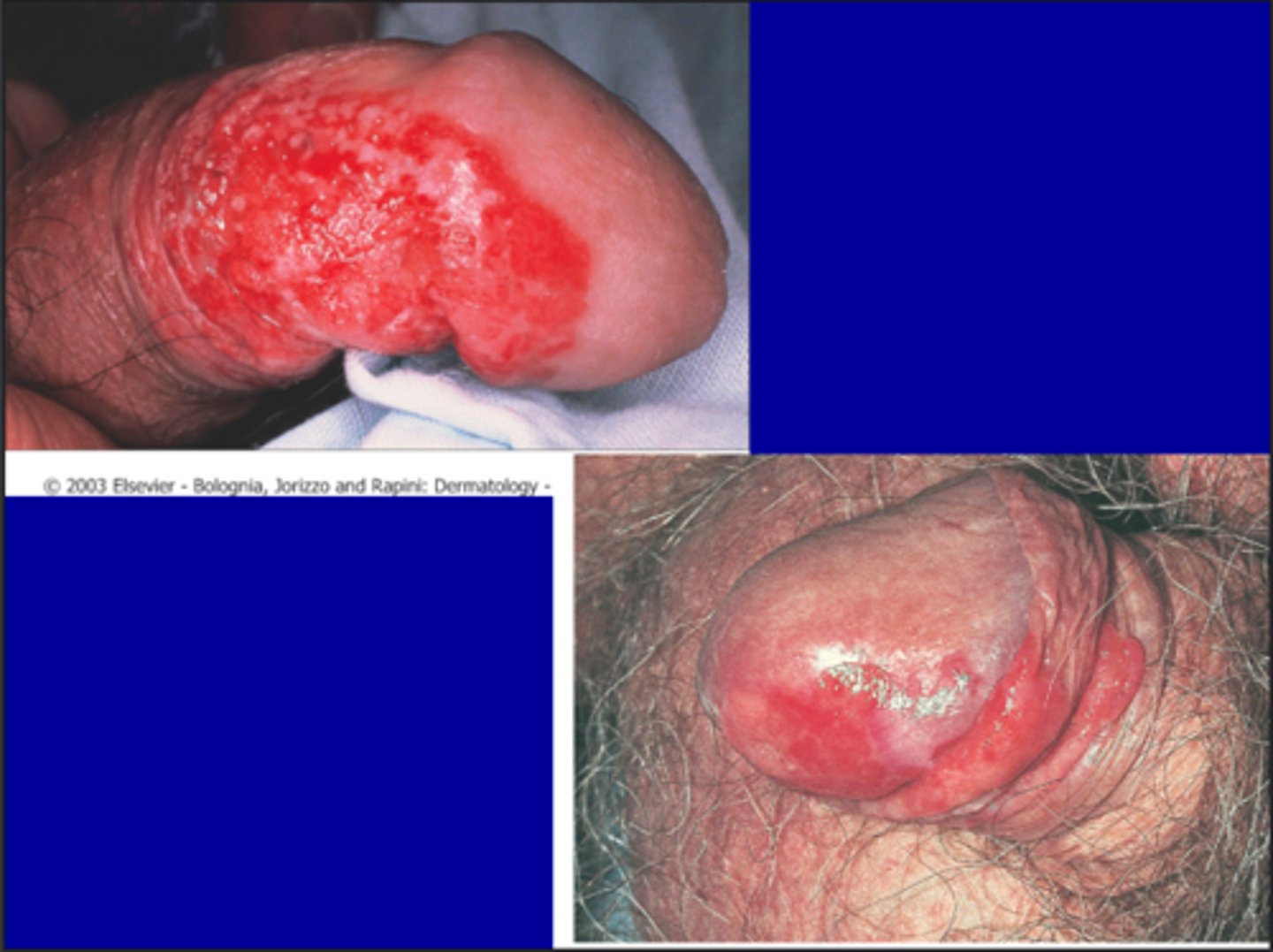
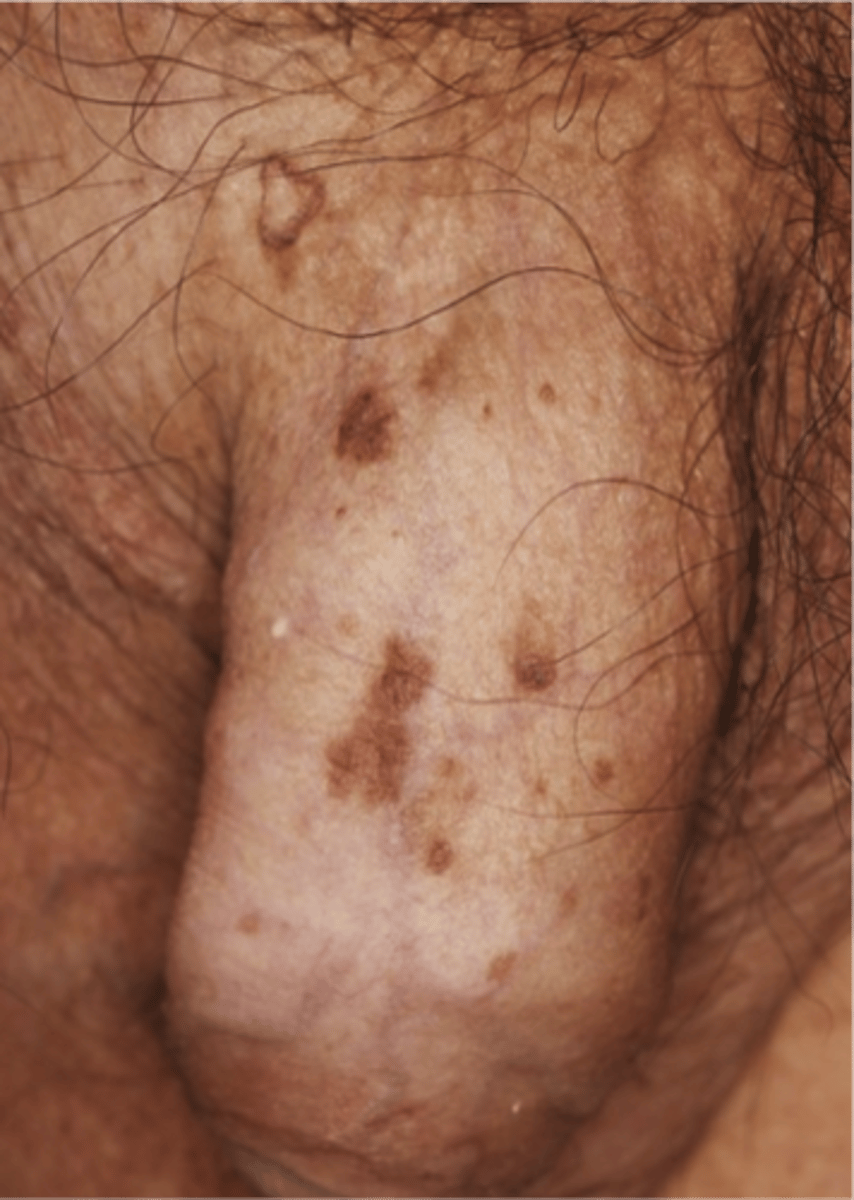
Bowenoid papulosis?
Appears as reddish papules on the shaft
- Rarely progresses into invasice carcinoma
What cancer is most common in the penis?
Squamous cell carcinoma - accounts for 95% of cases of penile cancer
Who are most frequent to have penile cancer?
Older uncircumcised men with poor hygiene
Risk factors - squamous cell carcinoma of the penis?
- Poor hygiene (especially under the prepuce)
- HPV 16 and 18 infection
- Smoking
How can poor hygiene lead to cancer of the penis?
Poor hygiene of the glans -> retention of smegma -> causes balanitis
= Chronic balanitis predispose to squamous cell carcinoma
Morphology of penile carcinoma?
Begin as a grey, crusted and papular lesion
- Most commonly on the glans/prepuce
= Eventually tumor becomes ulcerated
Where can penile carcinoma spread?
- Spreads to inguinal lymph nodes by lymphatic dissemination
- Can spread to lungs by hematogenous dissemination
Tumor of the scrotum?
"Oscheoma"
- Most commonly squamous cell carcinoma
Has historical significance - as it was the first cancer to be associated with an environmental factor
= Chimney sweepers developed scrotal cancer more frequently, due to their exposure to soot