Lab 2 - Calorimetry
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Enthalpy (H)
The amount of heat absorbed/evolved in the reaction under conditions of constant pressure
Endothermic Reaction
Reaction has a positive ΔH and system absorbs heat from surroundings. Cold to the touch.
Exothermic Reaction
Reaction has a negative ΔH and system releases heat into surroundings. Warm to the touch.
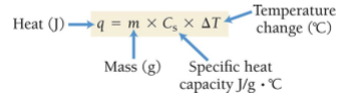
Heat Capacity
Measure of how much heat an object can absorb before its temperature increases by a certain amount
Greater heat capacity results in _____ temperature rise for a given amount of heat
smaller
The heat capacity of an object is proportional to its _____ and _____
Mass and the specific heat of the material
What are some things that affect heat capacity?
Specific heat capacity
Mass of substance/Amount of matter
Temperature change
Type of substance
Specific Heat Capacity (Cs)
The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by 1°C
What are the units for Specific Heat
J / (g ⋅ °Celsius)
The amount of heat lost by the hot material equals the amount of heat __________ by the cold material
Gained
q of system = - q of surrounding
Transfer of heat is always in what direction?
From hot object to cold object
Calorimetry
The process of transferring heat (q) from a hot substance (usually a metal) to a cool substance (usually water) until both are at the same temperature. A calorimeter (usually a foam cup) is used to measure the change in temperature.
Reactions carried out in aqueous solutions are at constant ________
Pressure
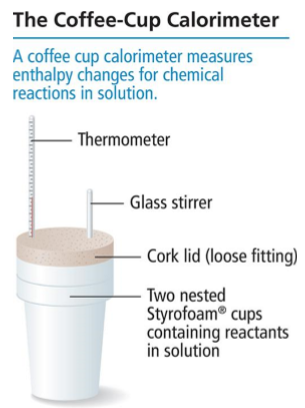
Coffee-Cup Calorimeter
Most common calorimeter used to measure enthalpy changes; Involves two nested foam cups, thermometer, glass stir, and a cork lid.
Formula to find q (Heat in Joules)
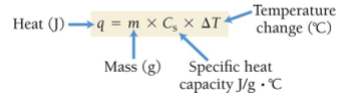
You submerge a hot alloy (120 grams & 150°C) into a coffee cup calorimeter containing a coolant fluid (180 grams & 18°C). When the system reaches thermal equilibrium, the final temperature is 22°C. The specific heat capacity of the coolant is 3.9 J/g⋅K . Calculate the specific heat capacity of the alloy.
Specific Heat = 12.67 J/g⋅ °C
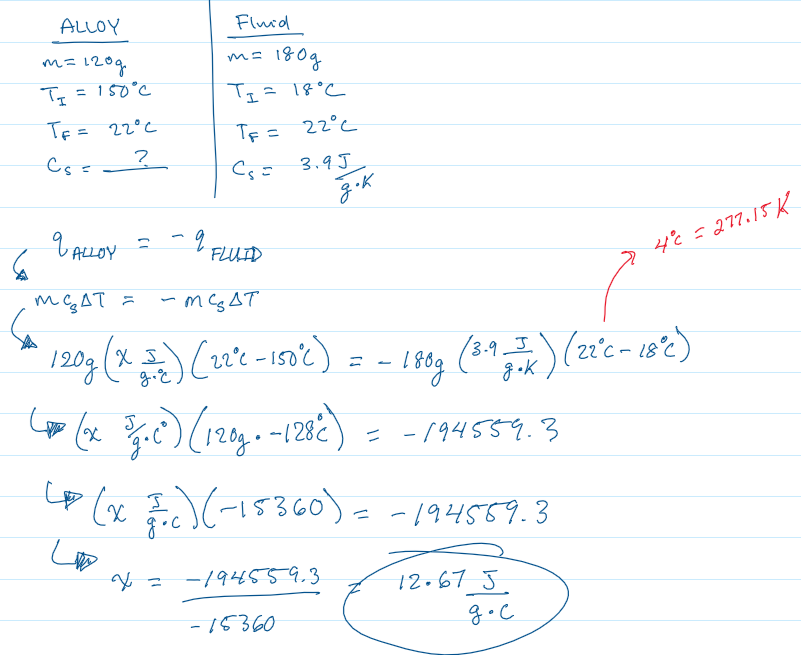
In a coffee cup calorimetry experiment, 50.0 mL of 0.100 M NaOH is added to 50.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl. The temperature of the solution increased by 14.9°C. Calculate ΔH for the reaction. Use 1.00 g/mL as the density of the solution and 4.18 J/ g °C as the specific heat capacity.
ΔH = 1250 kJ/mol
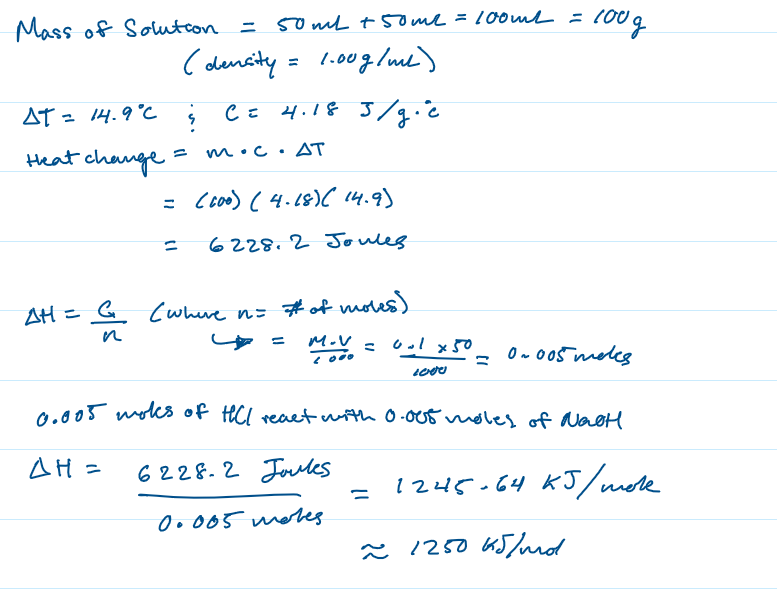
What is the main purpose of using a calorimeter in this experiment?
a. To observe the color change of the metal
b. To find the boiling point of water
c. To measure the volume of the metal
d. To determine the specific heat of the metal
To determine the specific heat of the metal
In the experiment, if the final temperature of the water-metal system is lower than the initial temperature of the water, what does it indicate?
a. The metal and water did not interact
b. The metal absorbed heat from the water
c. There was no heat exchange in the system
d. The water absorbed heat from the metal
The metal absorbed heat from the water
Why is it important to quickly transfer the heated metal to the calorimeter?
a. To make the experiment quicker
b. To increase the temperature of the water
c. To prevent the metal from cooling down
d. To avoid measuring the temperature
To prevent the metal from cooling down
What assumption is made about the calorimeter in this experiment regarding heat transfer?
a. The calorimeter increases the heat of the metal
b. The calorimeter does not absorb any significant amount of heat
c. The calorimeter absorbs all the heat from the metal
d. The calorimeter only measures the heat of the water
The calorimeter does not absorb any significant amount of heat
Which factor is crucial for ensuring accurate measurement of the metal's specific heat capacity in this experiment?
a. The precision in measuring the mass and temperature
b. The speed of stirring the water in the calorimeter
c. The color of the calorimeter
d. The shape of the metal sample
The precision in measuring the mass and temperature