HSC Biology Trial Exam Revision Guide
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
A reproductive process involving a single parent, resulting in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
Sexual Reproduction
A reproductive process involving two parents, leading to genetically diverse offspring through meiosis and fertilization.
Binary Fission
A form of asexual reproduction where a parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells of equal size.
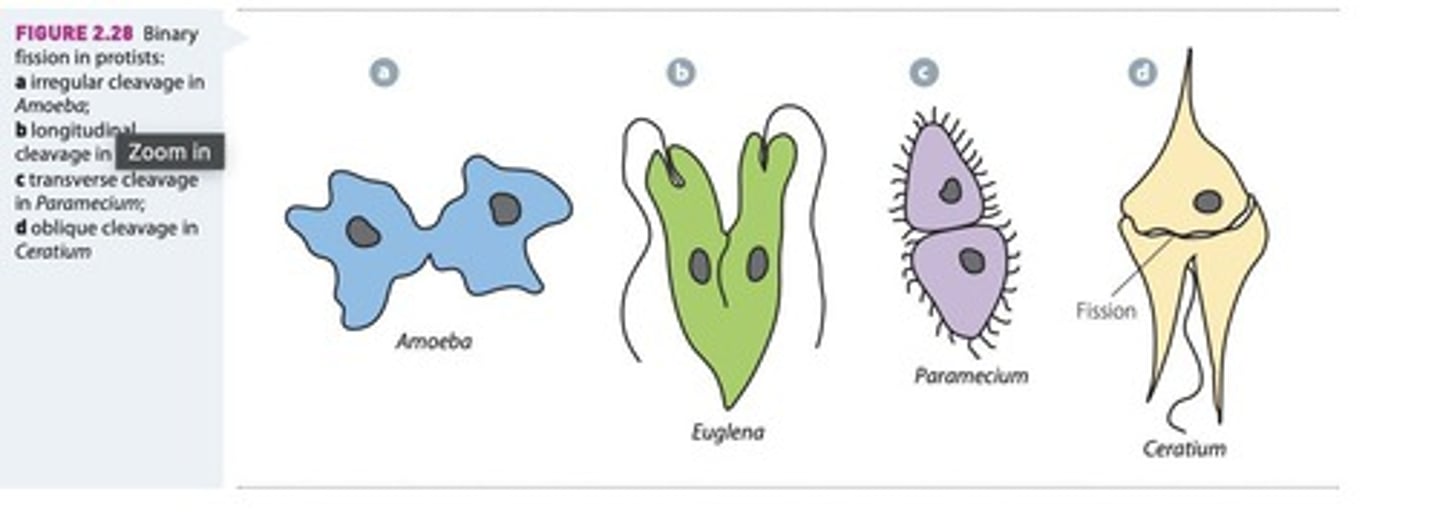
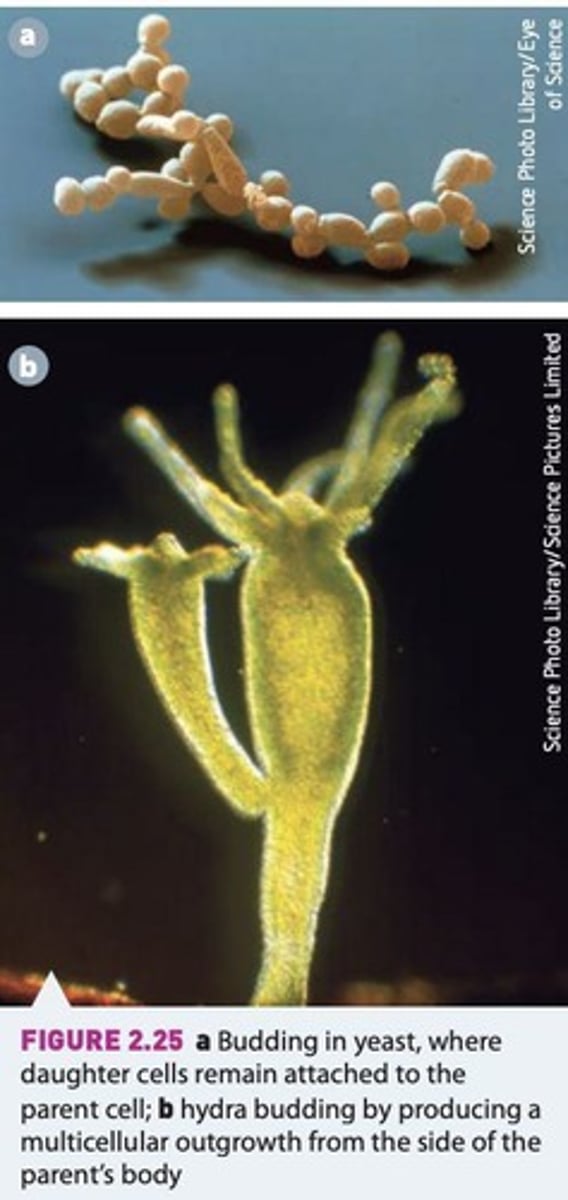
Budding
A method of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth or 'bud' on the parent organism.
Vegetative Propagation
A form of asexual reproduction in plants where new individuals arise from parts of the parent plant, such as stems or roots.

Spores
Tiny, typically unicellular reproductive structures that facilitate dispersal and survival in harsh conditions, produced by various organisms.
Asexual Spores
Spores produced by mitosis that are genetically identical to the parent organism.
Sexual Spores
Spores produced by meiosis, resulting in genetic variation, formed after the fusion of gametes from different organisms.
Sporophyte Stage
The diploid stage in the life cycle of plants, such as ferns, where spores are produced by meiosis.
Gametophyte
The haploid stage in the plant life cycle that develops from spores and produces gametes.
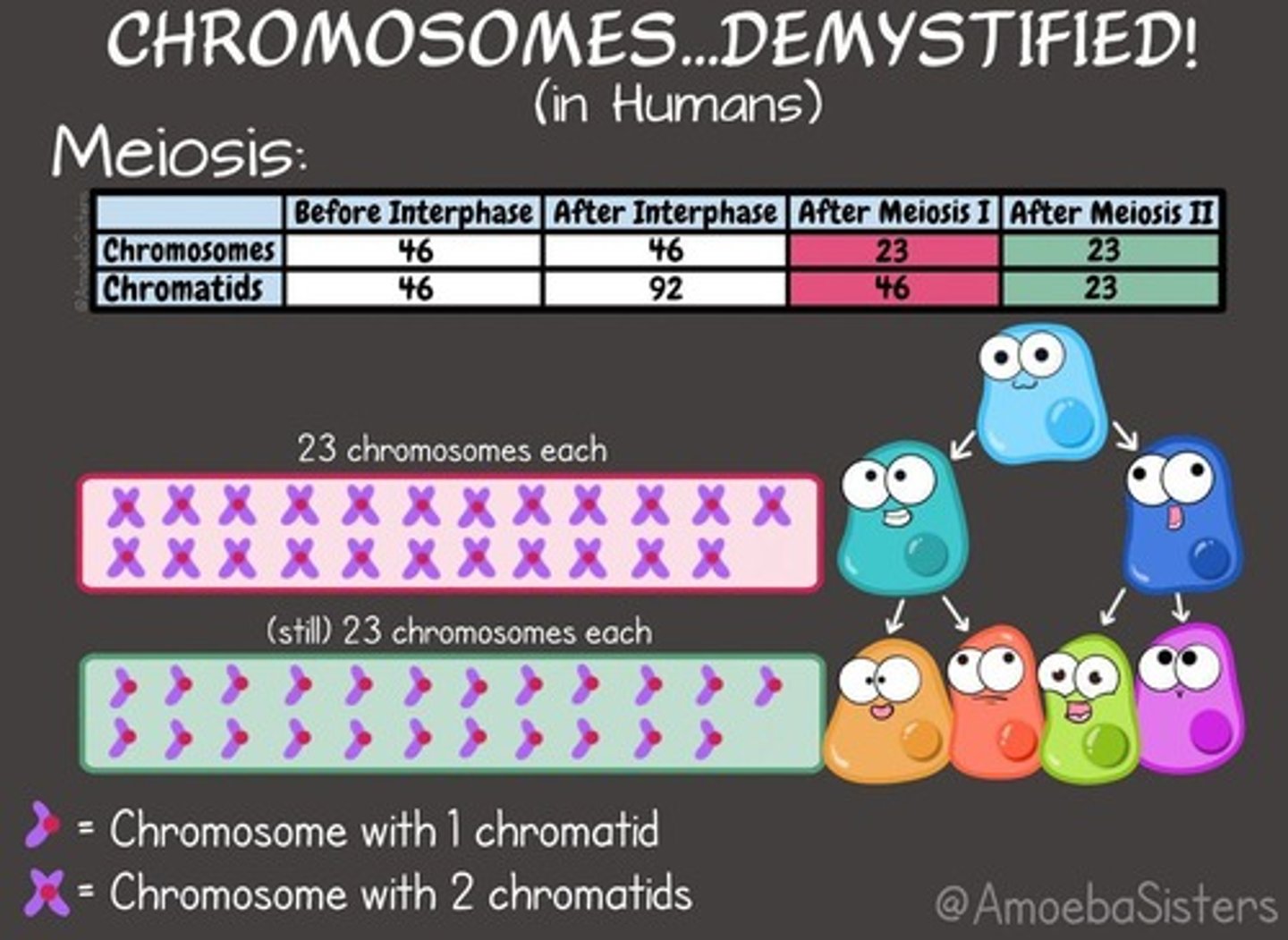
Meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes.
Mitosis
A type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, used in asexual reproduction.
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from the male anther to the female stigma in flowering plants, essential for fertilization.
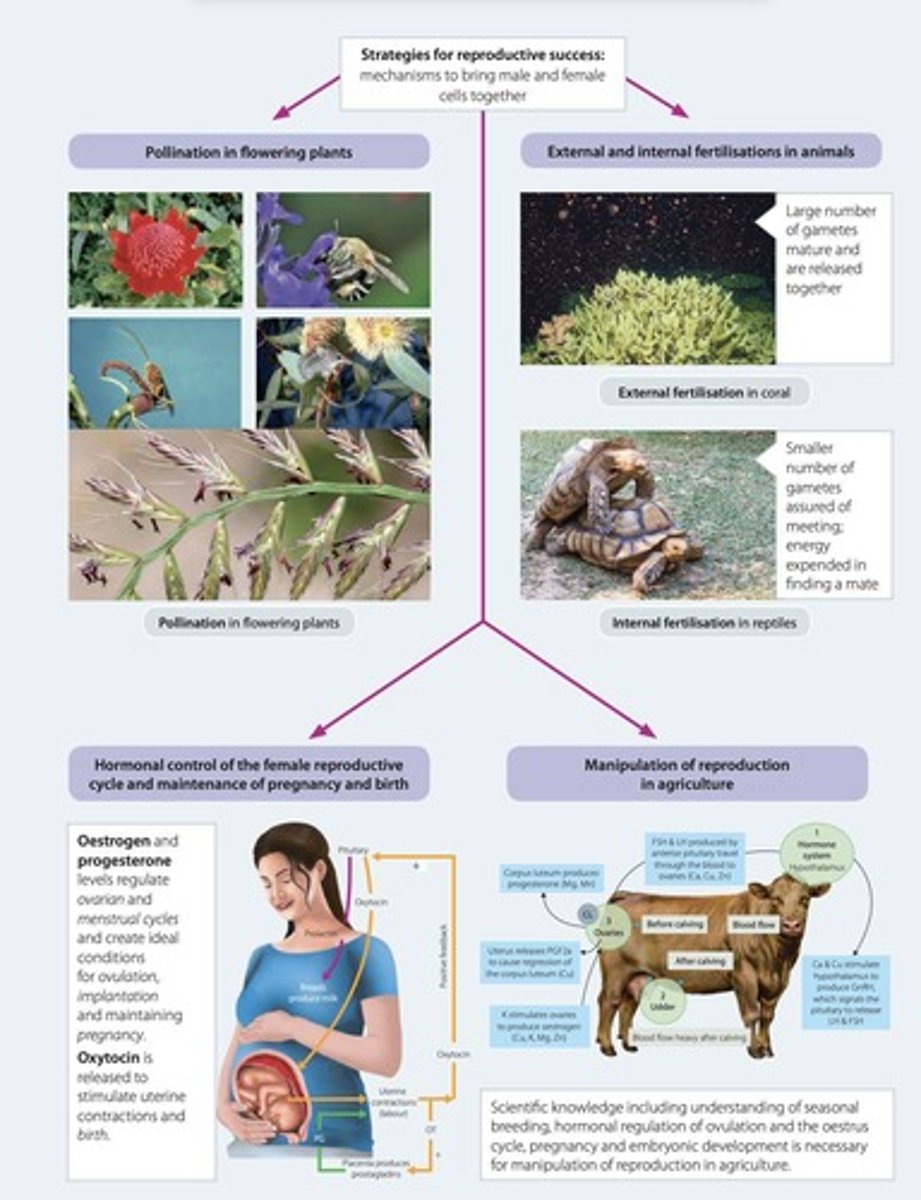
Fertilization
The fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote, leading to the development of a new organism.
Genetic Variation
The diversity in gene frequencies among individuals within a population, crucial for evolution and adaptation.
Inheritance Patterns
The ways in which traits and genetic information are passed from parents to offspring.
Reading Time
The initial 5 minutes of an exam allocated for students to read and understand the questions before answering.
Exam Booklet
An additional writing booklet used during exams for extended answers, which must be clearly indicated to markers.
Gametophyte Stage
The haploid phase in the life cycle of plants where gametes are produced through mitosis.
Fertilisation
The process in which sperm and egg cells fuse to form a diploid zygote.
Follicular Phase
The initial phase of the ovarian cycle, characterized by the maturation of ovarian follicles and increased estrogen production.
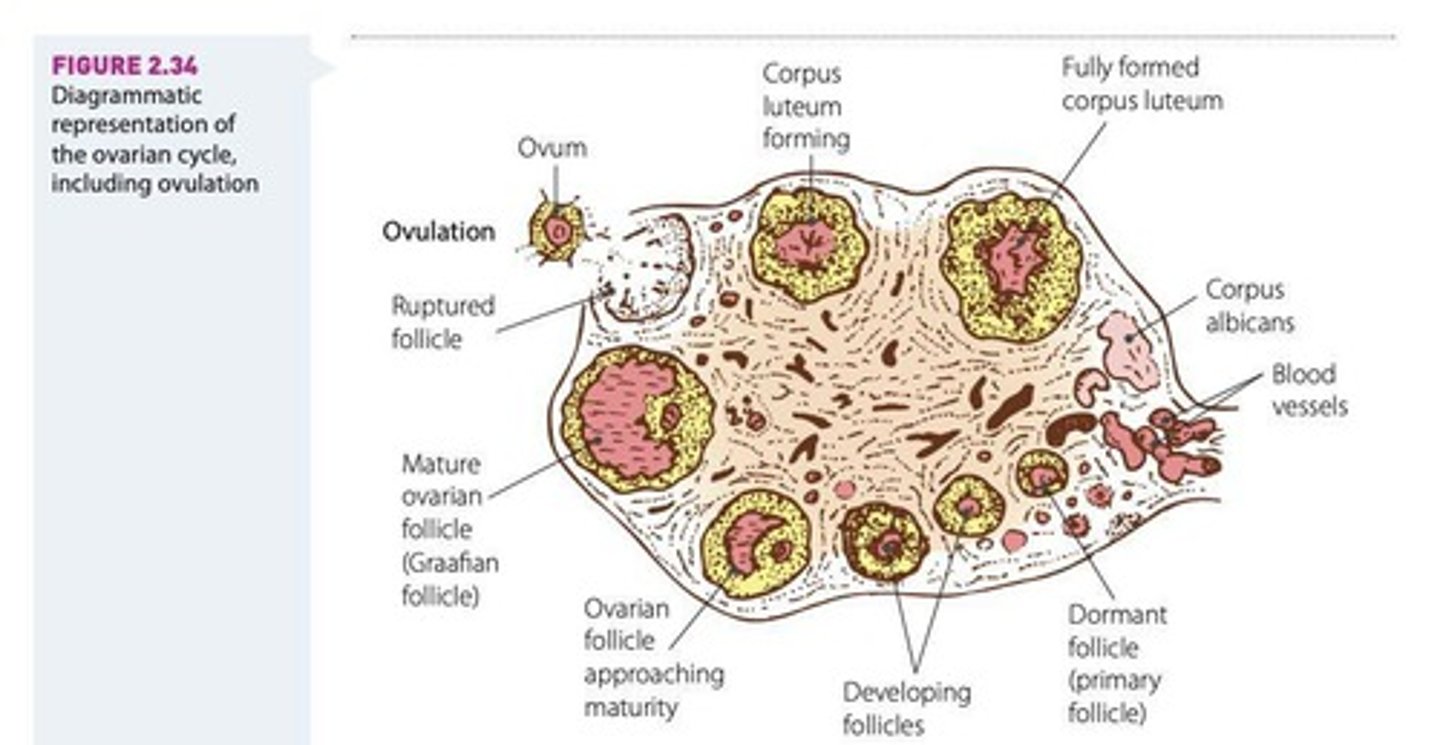
Ovulation
The release of a mature egg from the ovary, triggered by a surge in luteinising hormone.
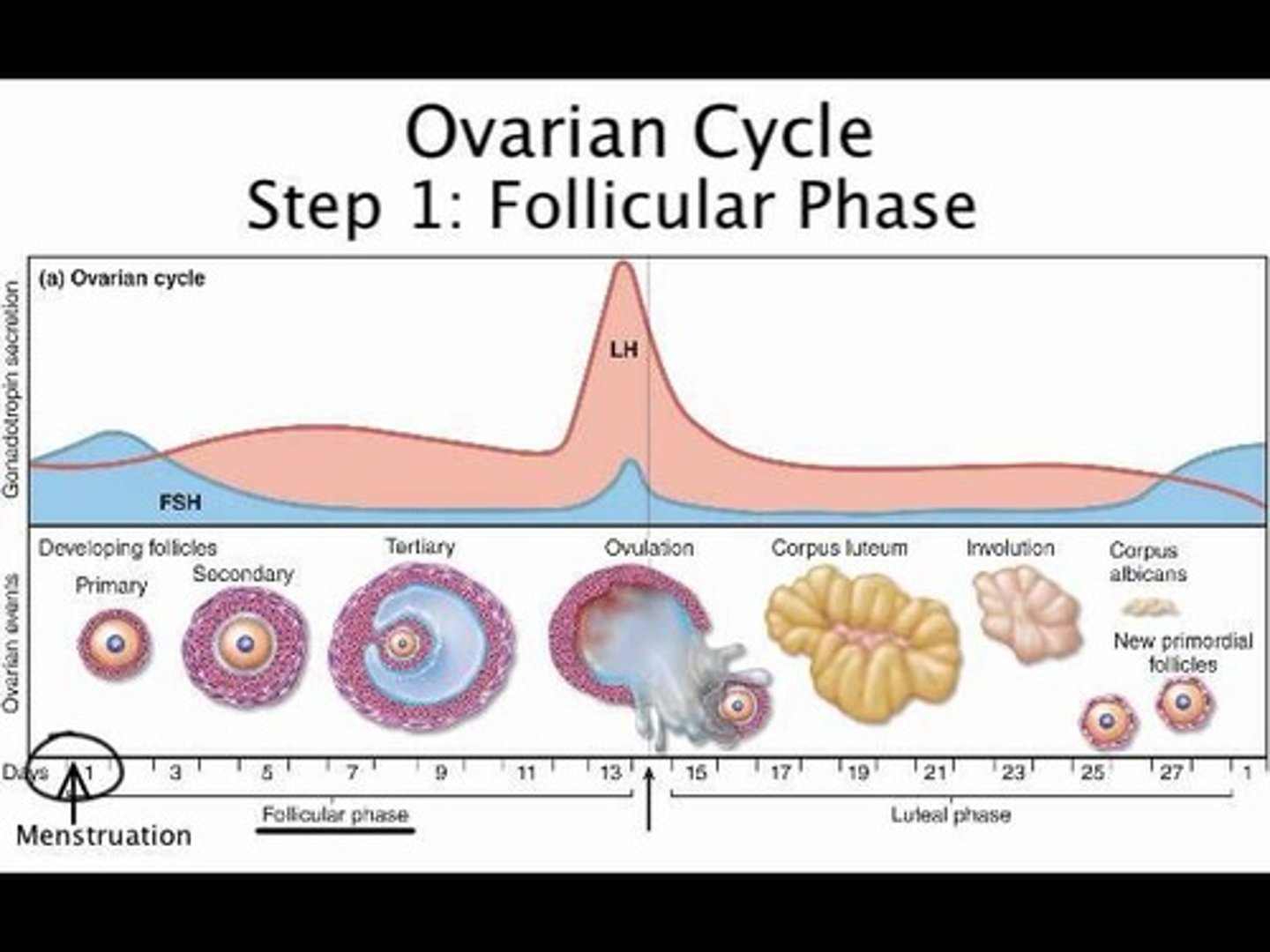
Luteal Phase
The phase following ovulation where the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, secreting hormones to maintain the uterine lining.
Menstruation
The shedding of the uterine lining due to decreased hormone levels, marking the start of a new menstrual cycle.
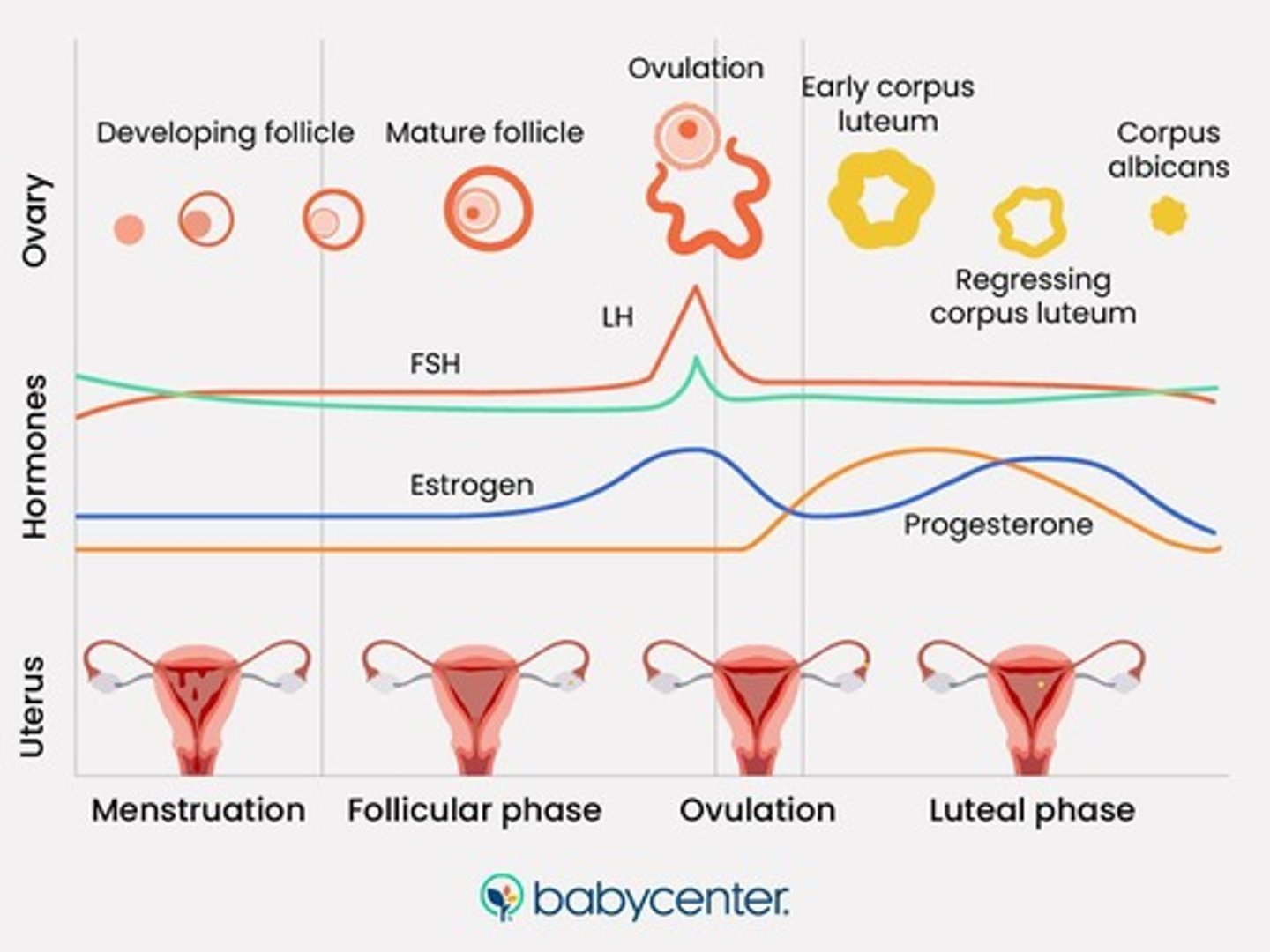
Proliferative Phase
The phase of the menstrual cycle where estrogen stimulates the regeneration of the endometrial lining.
Secretory Phase
The phase where progesterone causes the endometrium to thicken and prepare for potential embryo implantation.
Internal Fertilisation
The process of fertilisation occurring inside the female's body, common in mammals and birds.
External Fertilisation
The process of fertilisation occurring outside the organism, typically in aquatic environments like those of fish and amphibians.
Corpus Luteum
The structure formed from the ruptured follicle that secretes hormones to maintain the uterine lining.
Endometrium
The inner lining of the uterus that thickens in preparation for potential implantation of an embryo.
Oestrogen
A hormone produced by the ovaries that plays a key role in regulating the menstrual cycle and reproductive system.
Progesterone
A hormone secreted by the corpus luteum that helps prepare the uterine lining for a potential pregnancy.
Higher Survival Rates
Increased parental care and protection enhance offspring survival chances.
Less Dependency on Environmental Factors
Reduced risk from external threats such as predators and environmental fluctuations.
Selective Mating
Increased potential for mate choice and genetic fitness.
Energy Cost
High energy investment in fewer offspring and parental care.
Limited Offspring Numbers
Typically produces fewer offspring per reproductive event.
Greater Parental Risk
Parental care can expose parents to predation or resource depletion risks.
Low Survival Rate
Eggs and embryos are vulnerable to environmental hazards, predators, and diseases.
Environmental Dependency
Requires specific environmental conditions, such as aquatic environments or specific temperatures.
Less Selective Mating
Limited control over mate choice can lead to less genetic optimization.
Crossing Over
The exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I, creating new combinations of alleles.
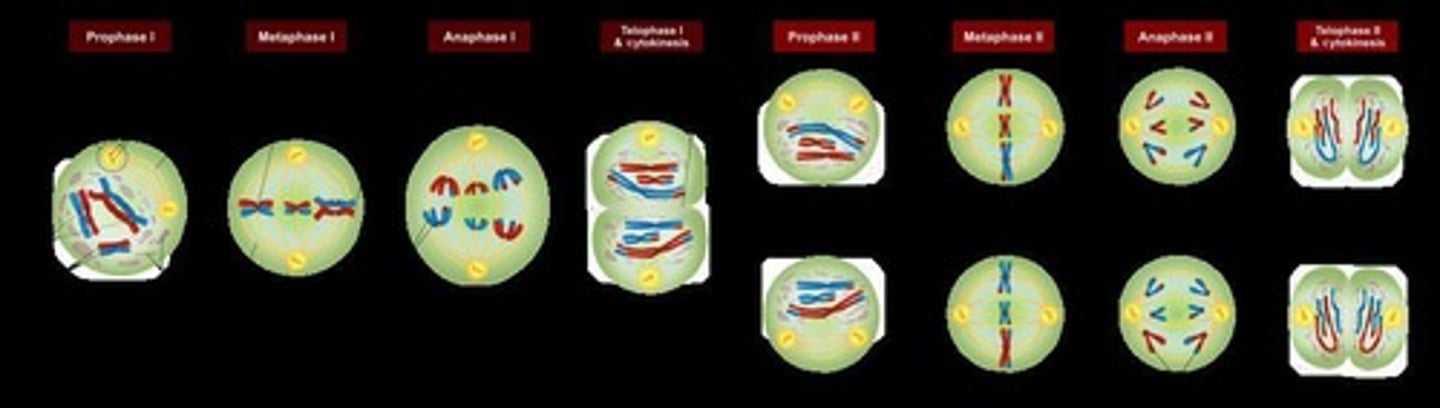
Independent Assortment
The random alignment of homologous chromosome pairs during Metaphase I, leading to varied genetic combinations.
Random Segregation
The random distribution of alleles into gametes during Anaphase I and II.
Random Fertilisation
The process where any sperm can fertilise any egg, increasing genetic variation among offspring.
DNA Structure
Consists of nucleotides made up of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G).
Polypeptide Synthesis
The process where DNA is transcribed into mRNA and then translated into amino acids by tRNA at ribosomes.
DNA Replication
The process of copying DNA to produce two identical DNA molecules, involving initiation, elongation, and termination.
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that relieve torsional stress during the unwinding of the DNA double helix.
DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between bases.
Primase
An enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers essential for initiating DNA replication.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to each original template strand during DNA replication.
Leading Strand
The strand of DNA that is synthesized continuously during replication.
Lagging Strand
The strand of DNA that is synthesized discontinuously, forming short segments known as Okazaki fragments.
DNA Ligase
An enzyme that connects Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
Transcription
The process in which RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA from a DNA template.
Translation
The process where mRNA is translated into a polypeptide chain at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Molecules that carry specific amino acids and pair anticodons with complementary codons on mRNA during protein synthesis.
Peptide Bond
A strong covalent bond that links amino acids together in a polypeptide chain.
Primary Structure
The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein, determined by the gene encoding the protein.
Secondary Structure
Regular folding patterns within polypeptides, such as alpha helices and beta pleated sheets, stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary Structure
The overall three-dimensional shape of a protein formed by interactions between side chains of amino acids.
Quaternary Structure
The structure formed when two or more polypeptide chains interact to form a functional protein.
Mutation
A permanent change in the DNA sequence of a gene, which can affect protein function.
Point Mutation
A type of mutation where one nucleotide base is replaced by another, potentially altering one amino acid in a protein.
Frameshift Mutation
A mutation caused by the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide, shifting the reading frame and altering the entire downstream protein sequence.
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies within a population, which can significantly impact small populations.
Bottleneck Effect
A sharp reduction in population size due to environmental events, leading to a loss of genetic diversity.
Founder Effect
When a small group colonizes a new area, carrying only a fraction of the genetic variation of the original population.
Co-dominance
A genetic inheritance pattern where both alleles are fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygote.
Incomplete Dominance
A genetic inheritance pattern where neither allele is fully dominant, resulting in a blended phenotype in the heterozygote.
Sex-Linked Inheritance
A pattern of inheritance where genes are located on the X chromosome, often affecting males more than females.
Autosomal Dominant
A pattern of inheritance where only one copy of a dominant allele is needed to express the trait.
Autosomal Recessive
A pattern of inheritance where two copies of a recessive allele are required to express the trait.
Polygenic Inheritance
A trait that is controlled by multiple genes, often influenced by environmental factors, such as human height and skin color.
Sex-Linked Traits
Traits that are associated with genes located on sex chromosomes, often affecting one sex more than the other.
Frequency Data
Data that shows how often a particular allele, genotype, or phenotype appears in a population.
SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms)
Variations at a single base pair in the DNA sequence among individuals, used to detect genetic variation and track ancestry.
Patterns
Repeated or consistent distributions of traits, alleles, or genetic markers that suggest selection, inheritance, or population structure.
Trends
Directional changes in allele frequency or trait presence over time, indicating natural selection or genetic drift.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
A mathematical model used to predict allele and genotype frequencies in a population that is not evolving.
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
A formula used to calculate allele and genotype frequencies, expressed as p + q = 1 for alleles and p² + 2pq + q² = 1 for genotypes.
Conditions for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Five conditions necessary for a population to remain in genetic equilibrium: no mutations, no natural selection, no gene flow, large population size, and random mating.
Chromosomal Mutation
Large-scale changes in the structure of chromosomes, including duplications, inversions, and deletions.
Mutagens
Agents that increase the mutation rate, which can be physical, chemical, or biological.
Base Substitution
A type of point mutation where one nucleotide is replaced by another, potentially altering the resulting protein.
Frameshift Mutation (Deletion)
A mutation that involves the removal of a nucleotide, shifting the reading frame and altering downstream codons.
Frameshift Mutation (Insertion)
A genetic alteration where one or more nucleotides are added into a DNA sequence, causing a shift in the reading frame, which can severely impact protein synthesis.
Deletion
The loss or absence of a segment of a chromosome, which can lead to the loss of essential genes and serious developmental issues.
Duplication
A chromosomal mutation where a segment of DNA is copied and inserted again, potentially leading to gene overexpression or disruption of gene function.
Inversion
A chromosomal mutation where a segment of a chromosome breaks off, flips, and reattaches in reverse order, which may cause gene fusion or misregulation.
Translocation
The transfer of a chromosome segment to a non-homologous chromosome, often resulting in aneuploidy and associated genetic disorders.
Coding DNA Mutations
Mutations that occur in exons, which can directly alter the amino acid sequence of proteins, affecting their function.
Non-Coding DNA Mutations
Mutations that occur in introns or regulatory regions, which may not directly change protein sequences but can affect gene expression.
Missense Mutation
A type of coding mutation that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in a protein.
Nonsense Mutation
A mutation that introduces a premature stop codon in the protein-coding sequence, leading to a truncated protein.
Silent Mutation
A mutation that does not change the amino acid sequence of a protein, often occurring in non-coding regions.
Biotechnology
The use of biological processes, organisms, or systems to manufacture products aimed at improving human life quality.
Transgenic Organisms
Organisms that have been genetically modified to contain genes from other species, often to enhance desirable traits.
Recombinant DNA Technology
A method involving the cutting and joining of DNA fragments using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase to create new genetic combinations.