honors bio unit 3
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Cell theory
All living things are composed of cells and all cells come from other cells
Light microscope
Microscope where visible light is passed through a specimen, then a glass lense
Prokaryote
Type of cell that lacks a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles
found only in domains Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryote
Type of cell that has a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles
Chromosomes
Gene-carrying structure, all cells have one or more of these
Ribosomes
Tiny structures that make protein according to instructions from genes
Cytoplasm
(Cytosol) the thick, jellylike fluid inside both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
refers only to the region between nucleus and plasma membrane in eukaryotes
Nucleoid
Non-membrane bounded region in a prokaryote where the DNA is concentrated
Organelle
A membrane-enclosed structure with a specialized function within a cell
Nucleus
Organelle of eukaryotes that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes, made of chromatin
Endomembrane system
A network of membranes inside and surrounding a eukaryote, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
The portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that lacks ribsosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
The portion of the endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes attached that make membrane proteins and secretory proteins
Vacuoles
Large vesicles with a variety of functions
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Dutch scientist and “father of microbiology”, first person to observe and describe single-celled organisms like bacteria
Cell membrane
(Plasma) the semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell
Cell wall
A rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane of a plant, fungi, bacteria, and some other organisms, providing structural support, protection, and a fixed shape
Cell
The basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms
Coarse adjustment
Used to bring a specimen into approximate focus by moving the stage up and down in large increments
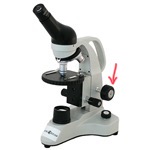
Diaphragm
Eyepiece
Field of view
Fine adjustment
Light source
Magnification
Matthias Schleiden
Objective lens
Ratio
Rotating nosepiece
Robert Hooke
Rudolf Virchow
Stage
Stage clips
Surface area
Theodor Schwann
Turgidity
Volume
Wet-mount slide
Scale formula
Magnification = Image / Actual