Aquatic Chemistry V - Water Hardness Intro
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What does alkaline water mean for other particles present?
increased pH to a sufficient alkaline condition will cause transition metals to precipitate and form sediment
Deposition of metals may result in co-precipitation and trace metals are also deposited
When is water considered ‘hard’?
It is hard due to high concentrations of calcium dn magnesium
can be seen as white fur/scum on items
Effects are produced by the presence of polyvalent metal ions in the water from weathering of minerals
What mineral types are often part of water hardness?
Carbonates - e.g. CaCO3
Sulphates - e.g. Gypsum (CaSO4×2H2O)
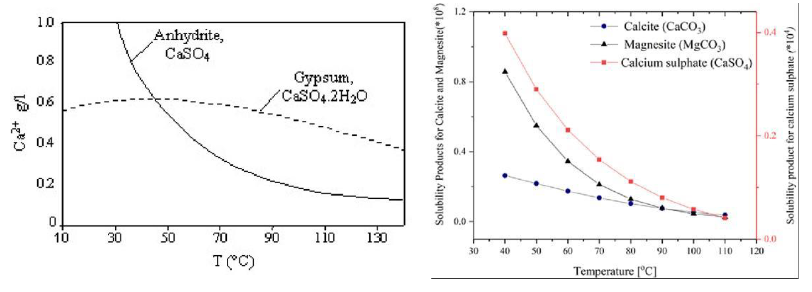
How does temperature affect the solubility of these hard water salts?
their solubility decreases with a temperature increase
Alkalinity also supports the sediment formation as metal solubility decreases with a high/alkaline pH
What are the benefits of alkaline and hard water?
alkalinity in water lower solubility of toxic metals
the buffering action of the salts producing the hardness lessens the effect of acidic pollutants
Hard water is not considered a health hazard, it is just a technical hazard
It provides additional calcium and magnesium in your diet
What is complexation?
A chemical reaction that takes place between a metal ion and a molecular or ionic entity known as a ligand that contains at least one atom with an unshared pair of electrons
What is a complex compound?
A central metal ion surrounded by ligands
These ligands can be ions or neutral
How does bioavailability affect complexation?
complexation increases the total concentration of metal ions in a solution, which then increases bioavailability
Bioavailability is the external availability of a chemical to an aquatic organism
This promotes the transport and cycling of metal in our aquatic environments (biogeochemical cycle)
What is the biogeochemical cycle?
the movement of elements and nutrients between biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living environment shapers) factors
What are chelates/chelating agents?
A polydentate ligand forming ringed structures with metal ions
A chelate is a chemical compound that consists of a metal ion and a chelating agent
A chelating agent is a substance whose molecules can form multiple bonds toa single metal ion
What is a polydentate ligand?
A ligand that can donate multiple electron pairs to the central metal ion
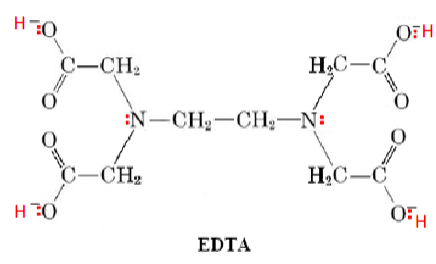
What is the polydentate ligand used in reducing water hardness?
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid - EDTA - a hexadentate ligand, forms six bonds with the central metal ion
Used to reduce water hardness by forming bonds with the metal ions and forming chelating complexes, chelates, therefore removing them from the water
Prevents new sediment from forming
low solubility in water
How does EDTA chelation work?
EDTA forms chelates with transition metals and main group metal ions making it a good remover
It forms complexes with calcium and magnesium - hard water compounds
EDTA can be used as a de-scaler in hard water areas
What is complexometric titration?
Also called chelatometry, it is used to determine water hardness levels through measuring levels of metals like calcium and magnesium
What are the three types of complexometric titration?
Chelation
Precipitation
Ion Exchange
What are other applications of complexometric titration?
Determination of solution pH
Determination of metal ions in solution
Determination of water Hardness of a solution
What are the steps for EDTA chelatometry?
EDTA is the chelate/chelating agent, it also acts as a water hardness sequester so is important for water treatment
Sample of water is collected and stored until use
The sample undergoes titration using aqueous EDTA solution with a specified molar concentration
After completing the titration, you will have a volume of EDTA required for complete complexation of Ca2+ or Mg2+
The data collected can then be used to to calculate the amount of mineral in ppm.
What is the EDTA chemical reaction?
H2Y2- + Mn+ → MY(n-4) + 2H+
where H2Y2- is the dominant form of EDTA in solution
Mn+ is the metal ions
MY(n-4) is the complex
E.g. H2YY2- + Can+ → CaY(2-) + 2H+
The ration of EDTA ion : metal ion = 1:1
What are the steps to find the mineral content in ppm after EDTA chelation?
Recall the equation and the 1:1 ratio: H2Y2- + Mn+ → MY(n-4) + 2H+
Work out the number of moles of EDTA using the equation: (cm3 of EDTA use x Molar conc of EDTA)/volume = mol
As the ratio is 1:1, you have also worked out the mol of metal ion in step 2 and can use this to find the concentration of the sample using mol/volume of sample = conc of mineral in sample
Convert to ppm by multiplying by doing conc x mineral molar mass as this makes it g/l
x1000 to convert to mg/l which is the same as ppm
How is EDTA removed after water treatment?
EDTA is removed using bacteria, and about 80% of it is removed through this process
It is biodegradable but the process is slow
Due to the number of application for EDTA, there are concerns about its impact on the environment as it produces CO2