Dermatology - Medical Assistant
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Externship
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
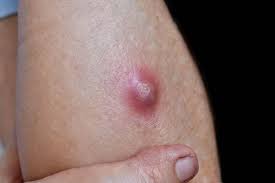
ABSCESS
A closed pocket containing pus. Some abscesses are easily diagnosed clinically, as they are painful and may "come to a head" such that pus becomes visible, but deep and chronic abscesses may just look like a TUMOR clinically and require biopsy to distinguish them from neoplasm.
ATROPHY
A localized thinning of the skin which may cause a depression.

ATYPICAL
The simple, straightforward definition would be "unusual," but "atypical" means much more than that. In a diagnosis, the use of the term atypical is a vague warning to the physician that the pathologist is worried about something, but not worried enough to say that the patient has cancer.
BULLA
A blister greater than 0.5cm in size which contains clear fluid.
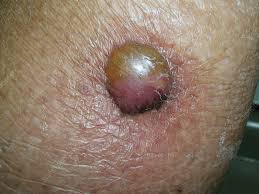
CARCINOMA
A malignant NEOPLASM whose cells appear to be derived from EPITHELIUM. This word can be used by itself or as a suffix. Cancers composed of columnar epithelial cells are often called adenocarcinomas. Those of squamous cells are called squamous cell carcinomas.
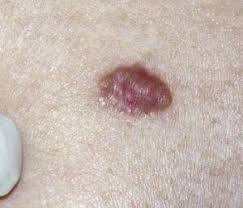
CRUST
A scab, caused by the leaking of blood or plasma through a lesion.
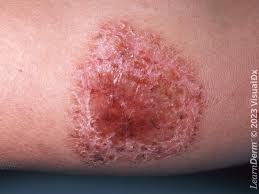
CYST
An enclosed sac in the skin which can contain fluid or solid material.
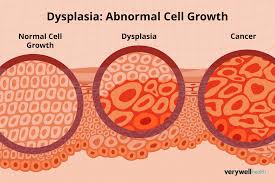
DYSPLASIA
An ATYPICAL proliferation of cells. This may be loosely thought of as an intermediate category between HYPERPLASIA and NEOPLASIA. It finds its best use as a term to describe the phenomenon in which epithelium proliferates and develops the microscopic appearance of cancerous tissue, but otherwise tends to "behave itself" and stays on the body surface without actually invading into it. Not all doctors accept dysplasia as a concept.
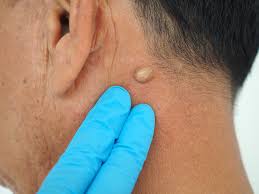
ECCHYMOSIS
A visible large collection of blood in the skin larger than 0.5cm in diameter.
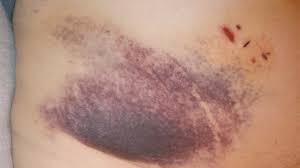
EPITHELIUM
A specialized type of tissue that normally lines the surfaces and cavities of the body.

EROSION
A focal loss of the top surface of skin. Since it is superficial, the skin heals without scarring.
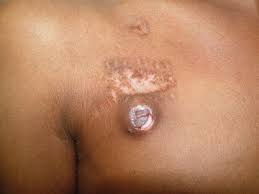
EXCORIATION
An erosion or ulcer caused by scratching.
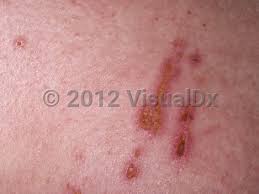
FISSURE
A thin linear crack in the skin which is deeper than it is wide.
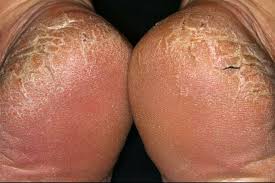
GRANULOMA
A special type of inflammation characterized by accumulations of macrophages, some of which coalesce into "giant cells." Granulomatous inflammation is especially characteristic of tuberculosis, some deep fungal infections, sarcoidosis, reaction to foreign bodies and several skin diseases of unknown cause.
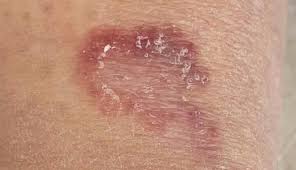
HYPERPLASIA
A proliferation of cells which is reactive and not neoplastic. In some cases, this may be a result of the body's normal reaction to an imbalance or other stimulus, while in other cases the physiologic cause of the proliferation is not apparent. An example of the former process is the enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck as a result of reaction to a bacterial throat infection.
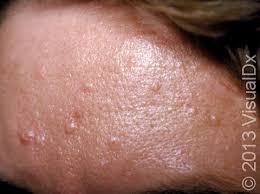
INFLAMMATION
The result of the immune system reacting to unwanted stimulation. It shows as swelling, pain, tenderness, redness and/or heat. Immune system cells are seen in the specimen being examined. These inflammatory cells include 1) neutrophils, which are the white blood cells that make up pus and are seen in acute or early inflammations, 2) lymphocytes, which are typically seen in more chronic or longstanding inflammations, and 3) macrophages (histiocytes), which are also seen in chronic inflammation. Some types of inflammation are readily diagnosable such as an infected skin wound, others require a biopsy to show the cause and prove they are not NEOPLASMS. The suffix "-itis" is appended to a root word to indicate "inflammation of".
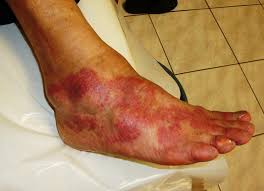
LESION
This is a vague term meaning "the thing that is wrong with the patient." A lesion may be a TUMOR or an area of INFLAMMATION.
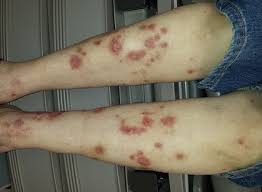
LICHENIFICATION
Area of thickening of the skin caused by chronic scratching. The normal skin lines are easier to visualize.
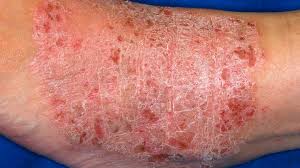
MACULE
A well-defined area with a change in skin color. It is totally flat. If one runs their finger over the area it cannot be felt.

METASTATIC
When cells that can travel through the lymph vessels or blood vessels lodge in some distant organ and grow into tumors, they are called metastasis. There are two major routes of metastasis: 1) hematogenous, in which the cells travel through the blood vessels, and 2) lymphogenous, in which the lymphatic vessels conduct the cancer cells. In the case of lymphogenous metastasis, the metastatic tumors can grow from cancers cells entrapped in the lymph nodes that collect the lymph draining from the organ where the original cancer has developed. Most malignant tumors spread both ways, but prefer to spread one way more often.
NECROSIS
Death of tissue. Necrosis may be seen in INFLAMMATION, as well as in NEOPLASMS.
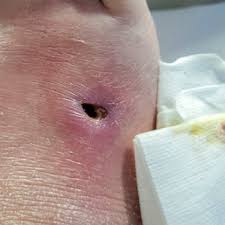
NEOPLASM, or NEOPLASIA
A "new growth" of the body's own cells no longer under normal physiologic control. These may be "benign" or "malignant." Benign neoplasms are typically tumors (lumps or masses) that, if removed, never bother the patient again. Even if they are not removed, they are not capable of destroying adjacent organs or "seeding" out to other parts of the body. Malignant neoplasms, or "cancers," are those whose natural history (i.e., behavior if untreated) is to cause the death of the patient. Malignancy is expressed by 1) local invasion, in which the neoplasm extends into vital organs and interferes with their function, and/or 2) METASTASIS, in which cells from the tumor seed out to other parts of the body and then grow into tumors themselves.
NODULE
A raised solid lesion greater than 0.5cm in diameter. This can be superficial or deep in the skin.
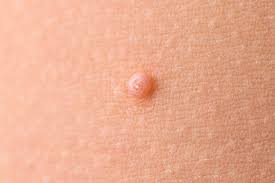
PAPULE
A raised solid lesion which may be up to 0.5cm in size.
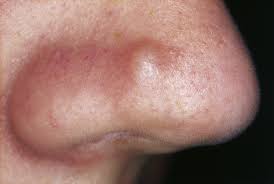
PETECHIA
A visible small collection of blood in the skin smaller than 0.5cm in diameter.
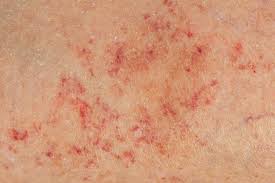
PLAQUE
A well-defined raised flat-topped lesion. It is similar to a plateau seen in geological formations.
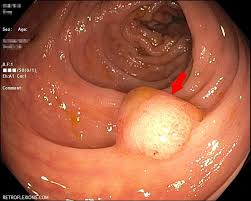
POLYP
A structure consisting of a rounded head attached to a surface by a stalk, mushroom-like. The typical skin polyps that develop ("skin tags") are benign.
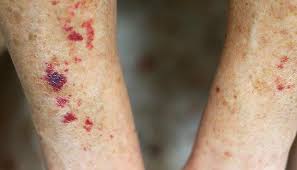
PURPURA
A bleeding into the skin causing small red areas (PETECHIA) or large red areas (ECCHYMOSIS).
SARCOMA
A rare malignant NEOPLASM whose cells appear to be derived from those other than EPITHELIUM. The connective tissues of the body (fibrous tissue, muscle, bone, cartilage, fat, and lining of joints) tend to give rise to sarcomas. CARCINOMAS are much more common than sarcomas.
SCALE
A buildup of dead epidermal (skin) cells caused an abnormal growth rate and shedding.
SCAR
A dense collection of collagen fibers which form after an injury to the skin or from surgery. Scars are usually pink at first, then fade or hyperpigment over time.
SUPPURATION
A type of acute INFLAMMATION characterized by infiltration of neutrophils at the microscopic level and formation of pus at the gross level. ABSCESS is special type of suppurative inflammation.

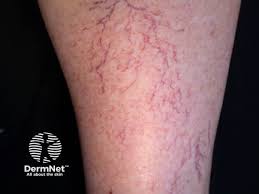
TELANGIECTASIA
Prominent, dilated superficial blood vessels.
TUMOR
A mass or lump that can be felt with the hand or seen with the naked eye. This may be a NEOPLASM, HYPERPLASIA, distention, swelling, or anything that causes a local increase in volume. The thing to remember is that not all tumors are cancers, and not all cancers are tumors.
ULCER
A focal full thickness loss of the skin. This heals with scarring since it is a deep lesion.
VESICLE
A small blister less than 0.5cm in size which contains clear fluid.
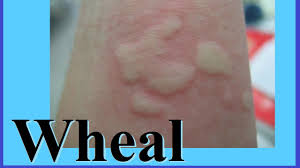
WHEAL
A localized swelling of the upper portion of skin. This is usually pink and itchy.