chem final 1120
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
nucleophile
electron rich
electrophile
electron lacking
chilarity
connected to 4 different centers
rank the carbocation stability from most → least stable
3 > 2 > 1 > CH bonds
Sn1 reactions
rate = ?
__ step reaction
what are the steps?
overall reaction order = ?
substrate = ?
nucleophile = ?
rate = k [substrate]
two step reaction
Leaving group leaves (step 1)
carbocation leaves (step 2)
overall reaction order = 1st
substrate = 1st order
nucleophile = 0th order
Sn2 reactions
rate = ?
__ step reaction
what are the steps?
overall reaction order = ?
substrate = ?
nucleophile = ?
rate = k [substrate][nucleophile]
one step reaction
LG & carbocation leaves at same time
overall reaction order = 2nd
substrate = 1st
nucleophile = 1st
1st order reactions
how do you determine?
what is the rate equation?
what is the unit?
what is the graph?
if one concentration gets an increase of x2, x3, etc, then the initial rate will be affected in the same manner = x2, x3, etc
EX: [BrO3]= x2 & Rate= x2
rate= k[A]1
unit: s-1
graph = ln[R]
linear
2nd order reactions
how do you determine?
what is the rate equation?
what is the unit?
what is the graph?
if one concentration gets an increase of x2, x3, etc, then the initial rate will be affected by a more of an increase = x4, x6, etc
EX: [BrO3]= x2 & Rate= x4
rate= k[A]2
unit: M-1s-1
graph = 1/[R]
exponential
0th order reactions
how do you determine?
what is the rate equation?
what is the unit?
what is the graph?
if one concentration gets an increase of x2, x3, etc, then the initial rate will NEVER be affected
EX: [BrO3]= x2 & Rate= x1
rate= k
unit: M/s
graph = [R]
straight
oxidative states for a elementary substance = O2 , Cl2 , H2 , etc
always 0
oxidized & reducing agent
what does this mean for the oxidative state
lose e-
oxidative state: INCREASE
ex = 0 → +1
reduction & oxidizing agent
what does this mean for the oxidative state
gain e-
oxidative state: DECREASE
ex = 0 → -1
is anode oxidation or reduction
oxidative
is cathod oxidation or reduction
reduction
how to use cell voltage
Vc - (Va) = Δ V
if ΔV > 0, what does this mean
its POSITIVE (+)
spontaneous which means its better for reducing
if ΔV < 0
its NEGATIVE (-)
non-spontaneous, which means its not good for reducing
oxidative
what weakens a base vs strengthens
weak- e- withdrawing (OH group close to NH), high electronegativity, resonance
strength - e- donating (CH group close to NH), low electronegativity, inductive
how to tell if reaction is PF vs RF
PF = strong —> weak
RF = weak —> strong
if a question gives molarity, pH/Ka what should you do
ICE TABLE
-then the assumption method = concentration / Ka > 400
more acidic =
bigger sixes & large EN
rate of the foward reaction depends on what
products
rate of reverse reaction depends on what
reactants
relationship between pH and pKa @ equivilance point
pH = pKa at 50
more basic
less electronegativity + lone pair of e-
pH and pKa
pH ~ pKa
pH —> pOH
14 = pH + pOH
pH —> [H3O+]
10^-ph = [H3O+]
[H3O+] —> pH
pH = -log[H3O+]
small pKa
big pKa
small = strong acid
big = weak acid
Ka equation
Ka=[A-][H3O+]/[HA]
thermodynamic argument
kinetic argument
thermo - @ equilibrium
kinetic - rate of forward v rate of reverse
large rate of forward > small rate of reverse shift towards…
shift toward PRODUCTS
small rate of forward < large rate of reverse shift towards…
shift toward REACTANTS
relative abundance equation
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
which species would be found in this pH
if the pH’s are LESS than the pKa = it will be found in this area
buffer
weak acid + weak base
only differ by 1 proton
oxidation equation
A —> A^n+ + ne-
reduction equation
B^m+ + me- —> B
mnemonic for cathode and anode
AN OX (oxidation = anode) carried electrons to a RED CAT (reduction = cathode)
what is the anode in the salt bridge
Zinc
what is the cathod in the salt bridge
copper
what is the salt bridge doing
salt bridge doesnt disrupt equilibrium because it creates a closed circuit that helps electrons run thru to get to teh cathode side
rate law
rate = k [A][B]..
how to find intermediate
produced then consumed
how to find overall reaction
reaction WITHOUT intermediates
k =
Ae^(-Ea/RT)
given TWO temps equation
e^(-Ea/R)(1/T2 - 1/T1)
what does a catalyst (enzyme) do
consumed then produced
rate average equation
[A2] -[A1] / ( t2 - t1 )
how would you find the rate of decomposition
rise/run ==> SLOPE
What is a 0th order reaction, and how does its rate depend on the concentration of reactants?
0th order reaction is a reaction whose rate is independent of the concentration of the reactant(s).
Rate law: Rate= k (k = rate constant)
Concentration vs. time: decreases linearly over time:
[A]=[A]0−kt[A] = [A]_0 - kt[A]=[A]0−kt
Half-life: t1/2=[A]02kt_{1/2} = \frac{[A]_0}{2k}t1/2=2k[A]0 (depends on initial concentration)
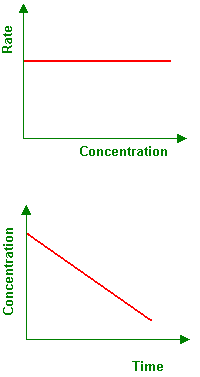
what graph is this: 0, 1, 2 order
0th order
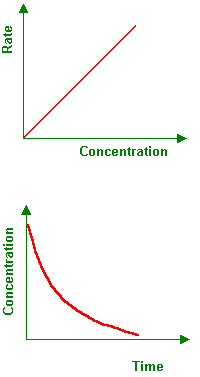
what graph is this: 0, 1, 2 order
1st order
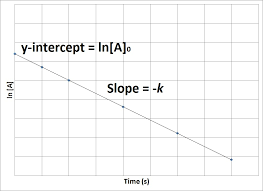
what graph is this: 0, 1, 2 order
1st order
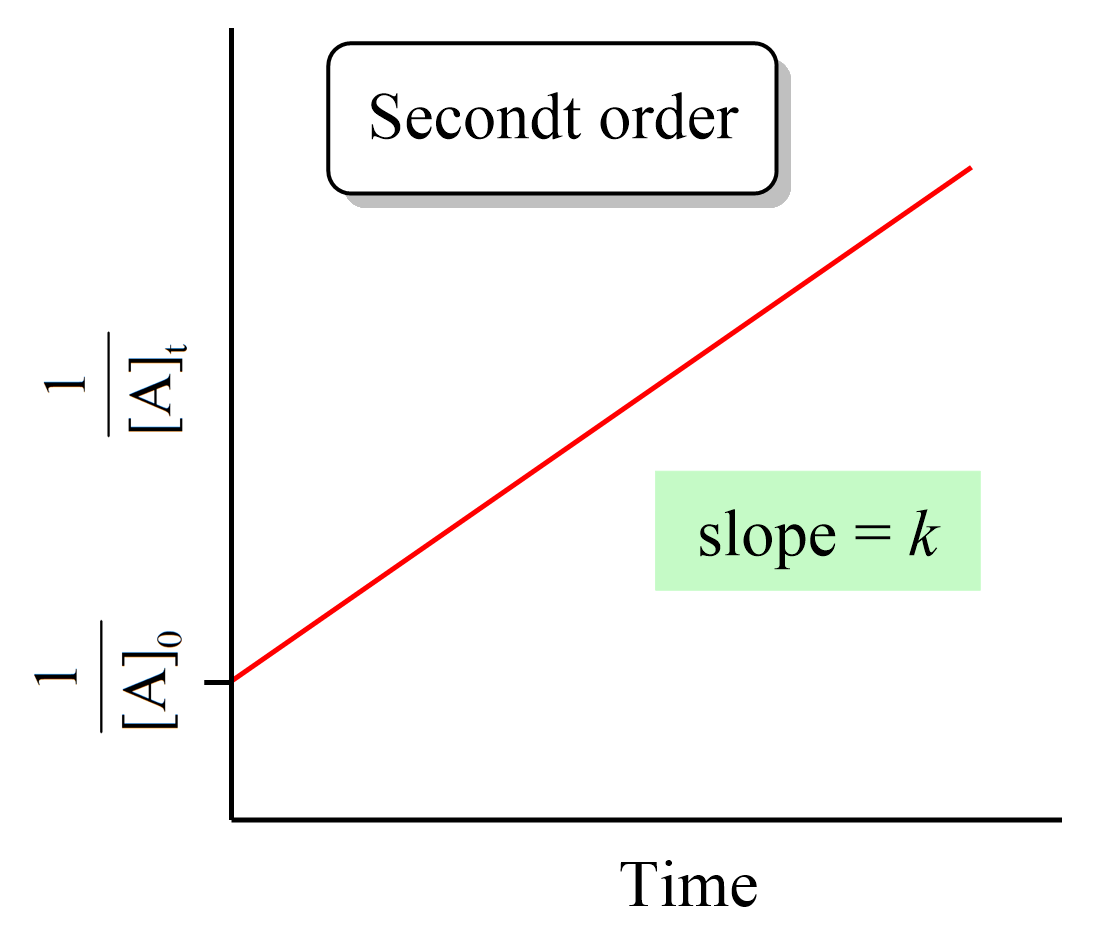
what graph is this: 0, 1, 2 order
2nd order
What are the key features of a first-order reaction?
Rate law: Rate=k
Units of k: s−1
Graph: Straight line when plotting ln[A] v t
What are the key features of a second-order reaction?
Rate law: Rate=k[A]^2 OR Rate=k[A][B]
Units of k: M−1s−1
Graph: Straight line when plotting 1/[A] vs. t
half life of 1st order reaction
ln(2)/t1/2
given three graphs: [R], ln[R], or 1/[R]
two graphs are NOT aligned with the dots and are not lines of best fit = [R] and 1/[R]
one graph is = ln[R]
what order is it and how do you know
1st order
ln[R] —> line of best fit
ln[R] = first order
y = mx + b
y= ln(k)
m = -Ea / R
x = 1/T
ln(a) = b
when drawing the arrows where do the arrows go
high e- density —> low e- density
acid reaction equation
HA (acid) + H₂O (base) ⇌ A⁻ (conjugate base) + H₃O⁺ (conjugate acid)
base reaction equation
B (base) + H₂O (acid) ⇌ BH⁺ (conjugate acid) + OH⁻ (conjugate base)
water autoionization equation
Kw = [OH-][H3O+]
what does both [OH-] & [H3O+] equal
1.0 × 10^-7
what does Kw =
1.0 × 10^-14
pH equation
pH = -log[H3O+]
[H3O+] equation
[H3O+] = 10^-pH
how to find pOH
pOH = 14 - pH
[OH-] = 10^pOH
if Ka / Kb > 1, what does this mean? strong or weak?
product favored (want)
strong because it completely dissociates into the particles in the products
if Ka / Kb < 1, what does this mean? strong or weak?
reactant favored (dont want,, majority is this)
weak because it partially dissociates
acid
donates H+
base
accepts H+
conjugate base
donates H+
goes with acid
conjugate acid
accepts H+
goes with base
exothermic
release heat into surroundings
surroundings = increase temp
inside = decrease temp
freezing, condensation, deposition
endothermic
absorb heat from surroundings
surroundings = decrease temp
inside = increase temp
melting, boiling, sublimation
AA + BB → AB
endo or exo
EXOthermic
weak → stronger bonds
AB → AA + BABY
endo or exo
ENDO thermic
strong → weak bonds
energetics on Ep
low Ep
entropics on configurations
high # of configs
negative H
postive S
product favored → -G
what you want !
postive H
negative S
reactant favored → + G
dont want !