TBI
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
what is a TBI?
- an alteration in brain function, or other evidence of brain pathology caused by an external force
what is the leading cause of injury-related death and disability in the US?
TBI
what are lead causes of TBI?
- falls
> 1. older adults
> 2. 0-4mo infants
> 14-24yo
what is the most common cause of TBI in young adults?
MVAs
what are the chances of return to work post TBI?
- 50% with mod to severe TBI return to work
- only 33% return to their pre-injury employment
is the brain considered an open or closed system
closed
does blood mix well with neurons?
no
does the skull offer adequate protection to the brain?
- skull offers SOME protection
what is included in the gray matter?
- neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, synapses
- cortex
- nuclei
- horns of the spinal cord
what is included in the white matter?
- tracts
- pathways
- columns
does the pia mater come in contact with white or grey matter?
grey
which is more vascularized - grey or white matter?
- grey
what is the corona radiata?
- 2 paired sheets of white matter fibers that transmit afferent and efferent neurons to and from the cerebral cortex
- continuous ventrally with the internal capsule, and dorsally with the centrum semiovale
- associated with the primary motor cortex
what motor tracts are included in the corona radiata?
- corticobulbar
- corticospinal
what is the flow of cerebrospinal fluid? (8)
1. lateral ventricles
2. interventricular foramina (of Monroe)
3. third ventricle
4. cerebral aqueducts (of Sylvius)
5. fourth ventricle
(exits ventricles)
6. subarachnoid space
7. arachnoid granulations
8. venous bloodstream
what are the enlarged areas where CSF is collected?
cisterns
what are the 4 functions of CSF? (4)
- protect brain and spinal cord
> shock absorption
- nourish and remove waste
> delivers nutrients and removes waste
- maintain brain function
> regulate intracranial pressure and provide buoyancy to reduce stress on brain
- circulate chemicals
> distribute hormones and neurotransmitters
what is a primary brain injury?
- damage is immediate
what is secondary brain injury?
- happen gradually over the course of hours, days, weeks
what is the process of primary brain injury? (5 steps)
1. cerebral contusion
2. axonal shearing
3. BBB damage
4. vascular dysfunction
5. cell death
what is the process of secondary brain injury? (8 steps)
1. NT release
2. increased intracerebral pressure
3. oxidative stress (free radicals)
4. inflammation
5. edema
6. ischemia
7. hypoxia
8. cell death (delayed or immediate)
what are causes of primary brain injuries?
- penetrating (open-head)
- nonpenetrating (closed-head)
> acceleration (whiplash, coup, countercoup)
> non-acceleration (blow to the head)
what are some types of primary injury (traumatic)?
- skull fracture
- contusions (brain bleed) lead to hematoma
- concussions
- lacerations
- diffuse axonal injury
what is a diffuse axonal injury?
- widespread shearing and stretching of axons
- leads to tearing of nerve fibers in the white matter tracts
what are the 3 types of diffuse axonal injuries?
- stretching (tensional forces)
- twisting (rotational forces)
- shearing forces
how is TBI classified?
- glasgow coma scale
what is consciousness?
- awareness of ones self and surroundings
> internal awareness
> external awareness
what is alert?
fully aware and attentive
what is clouding of consciousness?
- brain fog
- state characterized by confusion, impaired capacity to think and respond, disorientation, reduced attention, and memory defects
what is delirium?
- mental state in which you are confused, disoriented, and not able to think or remember clearly
- can be due to medications
what is obtundation?
- sleeps often
- when aroused, exhibits decreased alertness and interest in the environment
- delayed reactions
What is stupor?
- unresponsive state from which the patient can be aroused only briefly with vigorous, repeated sensory stimulation
what are disorders of consciousness (DOC)?
- coma
- unresponsive wakefulness (previous vegetative state)
- minimally conscious state
what is a coma?
- arousal system is not functioning
- arousal and awareness are absent
- patients eyes are closed
- there are no sleep/wake cycles
- ventilator dependent
what is unresponsive wakefulness?
- previously vegetative state
- dissociation between arousal and awareness
- higher CNS centers are not integrated with the brainstem
- pt may be aroused but they are not aware of self or environment
what is minimally conscious state?
- evidence of self or environmental awareness
- patients may localize to round and have sustain visual fixation
- inconsistently communicate through yes/no
what is ranchos los amigos?
TBI rating scale
what is an intracranial pressure monitor?
- a catheter is inserted into the ventricle of the brain to monitor ICP
- if pressure is high, CSF can be drained from ventricle
what is a brain oxygen monitor (licox)
- brain oxygen and cerebral blood flow monitor is inserted into the brain tissue and secured to the skill with a bolt
what are 2 surgeries that can be done with TBI?
- craniotomy
- decompressive craniectomy
> bone flap is stored in freezer and replaced when able (cranioplasty)
T/F: TBI rehab is a multidisciplinary approach?
true
what is the frontal lobe responsible for?
- personality
- behaviors
- emotions
- judgement
- speech (broca)
- problem solving
what is the parietal lobe responsible for?
- interpreting language
- sense of touch, pain, temperature
- interpret vision, hearing, memory
- spatial and visual perception
what is the occipital lobe responsible for?
- interprets vision
what is the temporal lobe responsible for?
- understanding language (wernicke)
- memory
- hearing
- sequencing
what is the cerebellum responsible for?
- balance
- coordination
- posture
what is the brainstem responsible for?
- automatic functions
> breathing
> HR
> swallowing, sneezing, coughing
what is anterograde amnesia?
- unable to create new memories
- usually last to recover after a coma
what is post-traumatic amnesia?
- cant remember events from injury to point of recovery
what is retrograde amnesia?
- inability to remember events prior to the injury
- usually decreases with recovery
what causes decorticate and decerebrate posturing?
- damage to the structures that control motor tone associated with CST
what is decorticate posture?
- lesion above the red nucleus
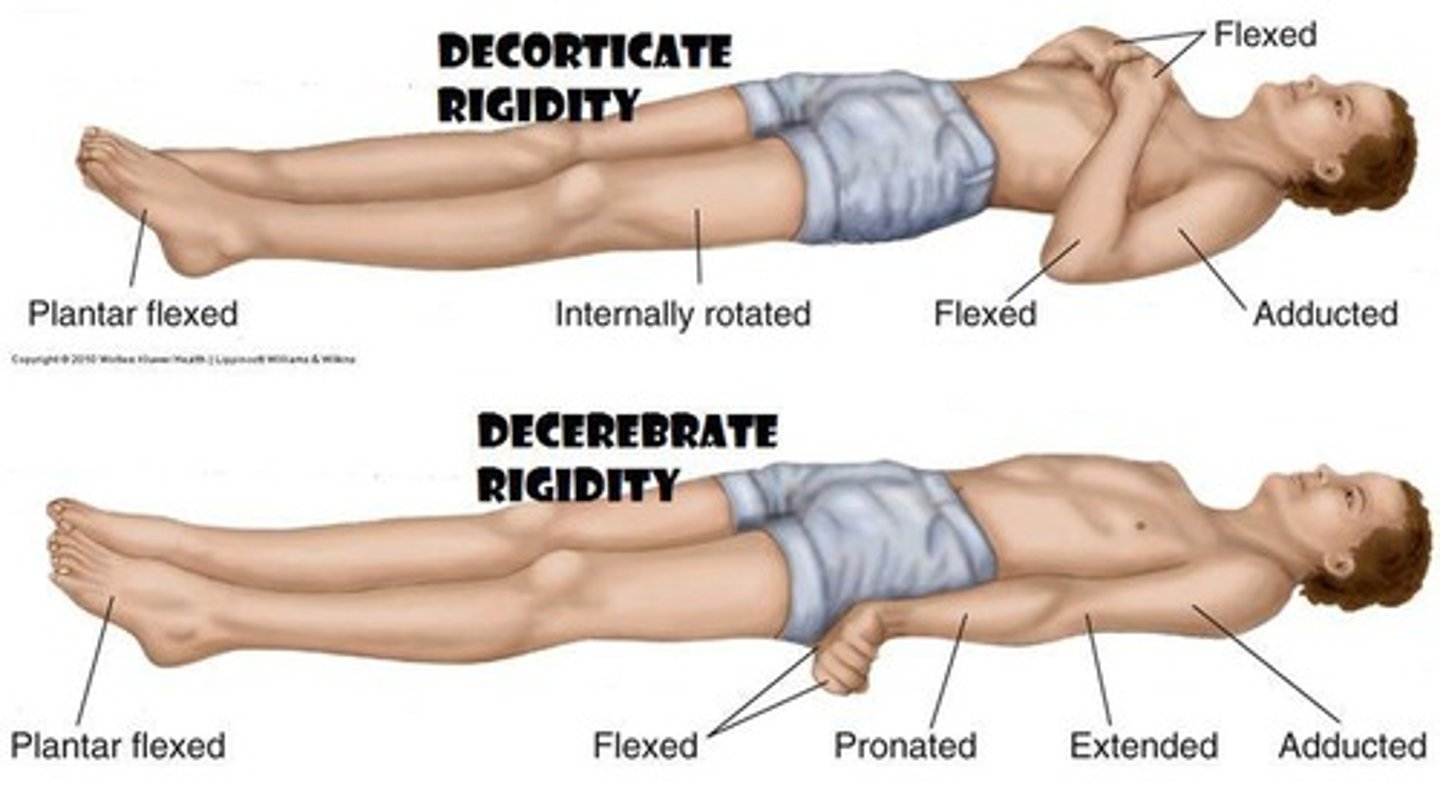
what is decerebrate posture?
- lesion below the red nucleus
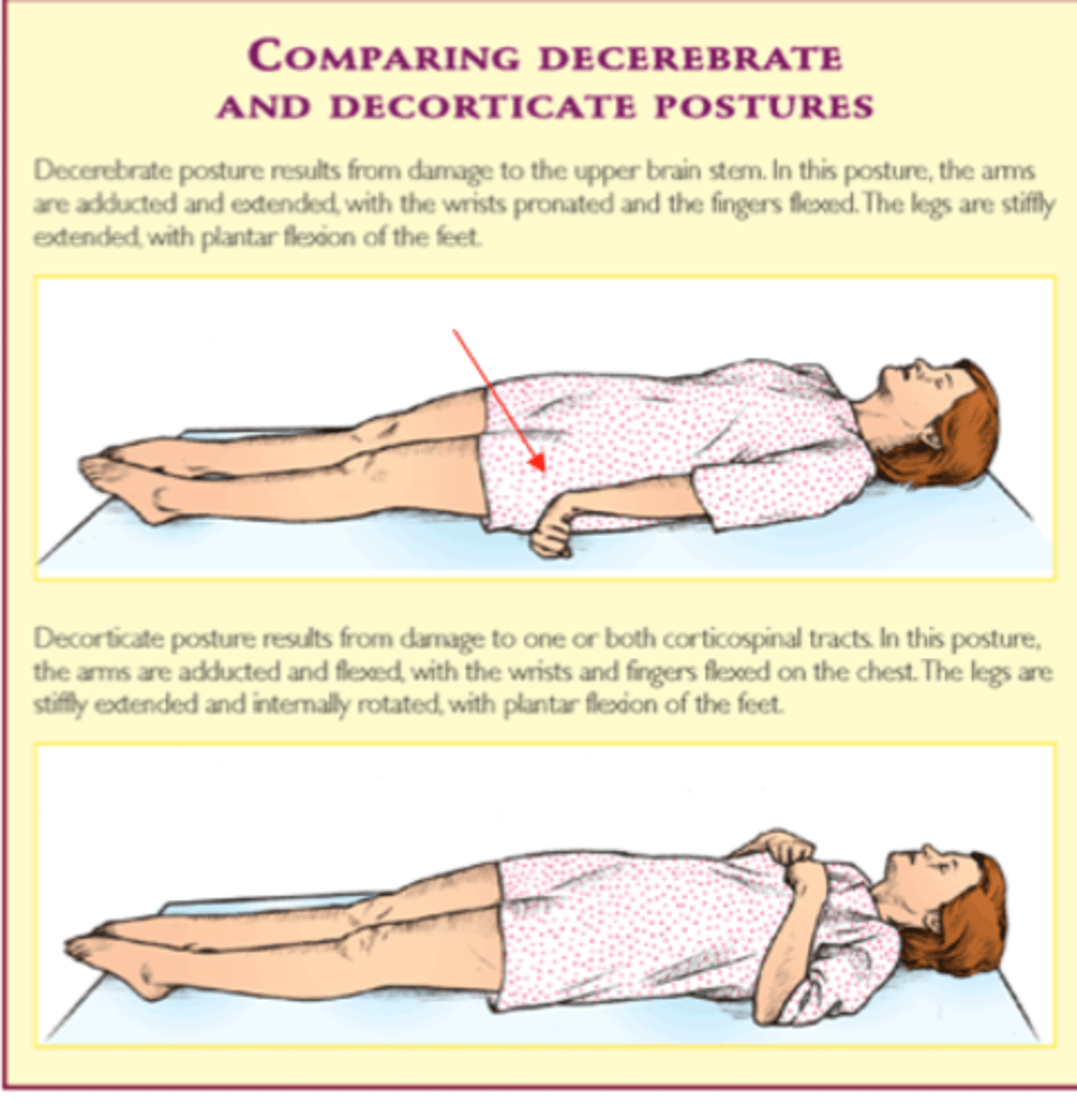
what is the decorticate/decerebrate progression?
- decorticate progresses to decerebrate with progressive destruction/compression of brain structures
what neuromuscular impairments are seen with TBI?
- mostly UMN
- abnormal tone
> initially may be paralytic, then spastic/hyperreflexive
- weakness (hemi/tetra)
what is the JFK coma recovery scale?
- characterise and monitor patients with RLA I-IV
- arousal facilitation protocol
> deep pressure to face, neck, shoulder, arm, hand, chest, back. leg, foot, toes bilaterally
what is community integration questionnaire?
- scales whether the patient does certain community/household/social activities or if they have someone else do it
what are interventions for RLA levels I-III (low level) (4)
- prevent secondary impairments
> prevent contractures, wounds
- monitor changes in status
- provide upright activity challenges
- family education and involvement
T/F: early treatment sessions should be shorter durations, increased frequency?
true
T/F: early exercise post TBI may have adverse effects and impair cognitive recovery?
true
T/F: delayed exercise (2-5wks post) may be more beneficial for neurorehab?
true
does exercise lead to increased or decreased neuroplasticity?
increased
does exercise lead to increased or decreased neuroinflammation?
decreased
does exercise lead to increased or decreased apoptosis?
decreased
does exercise lead to increased or decreased neuroprotection and repair?
increased
what are interventions for RLA levels V-VI (intermediate levels)? (3)
- provide consistent and routine structure
- work on basic mobility and ADL
- improve activity tolerance
what are interventions for RLA levels VII-VIII (high functioning)? (2)
- return to life and community activities
- include cognitive challenges