Human Genome
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
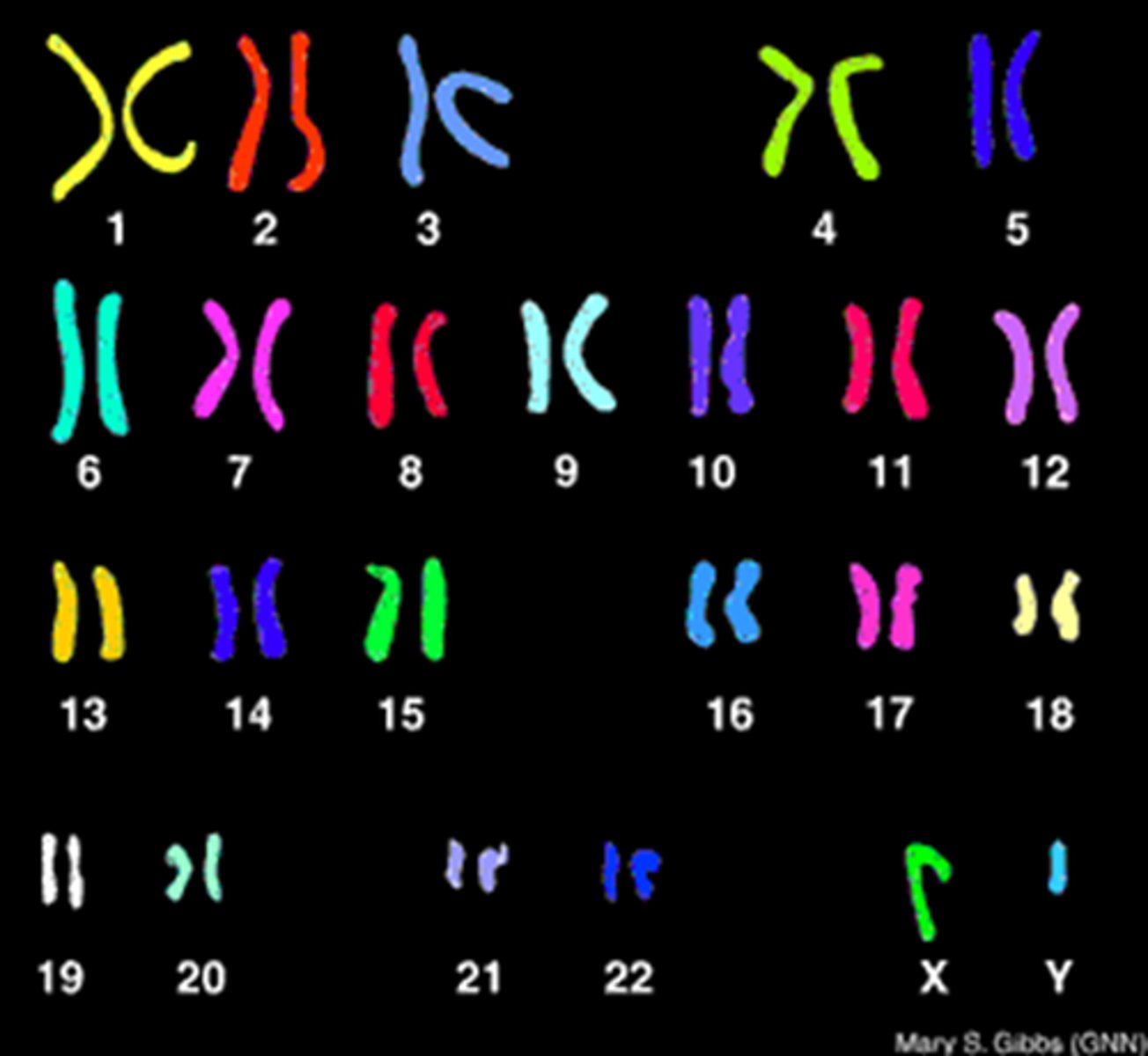
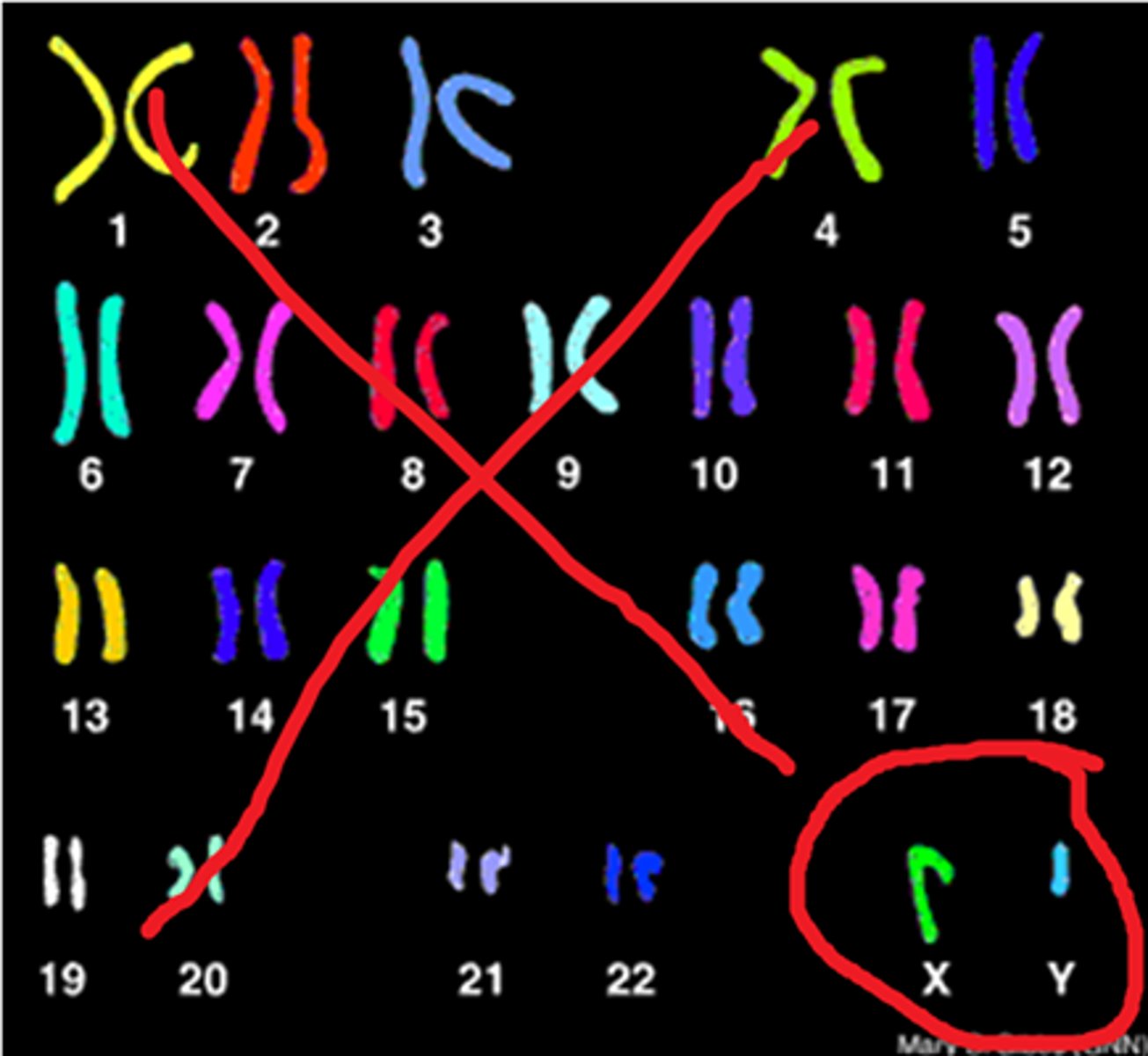
Human Karyotype
46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
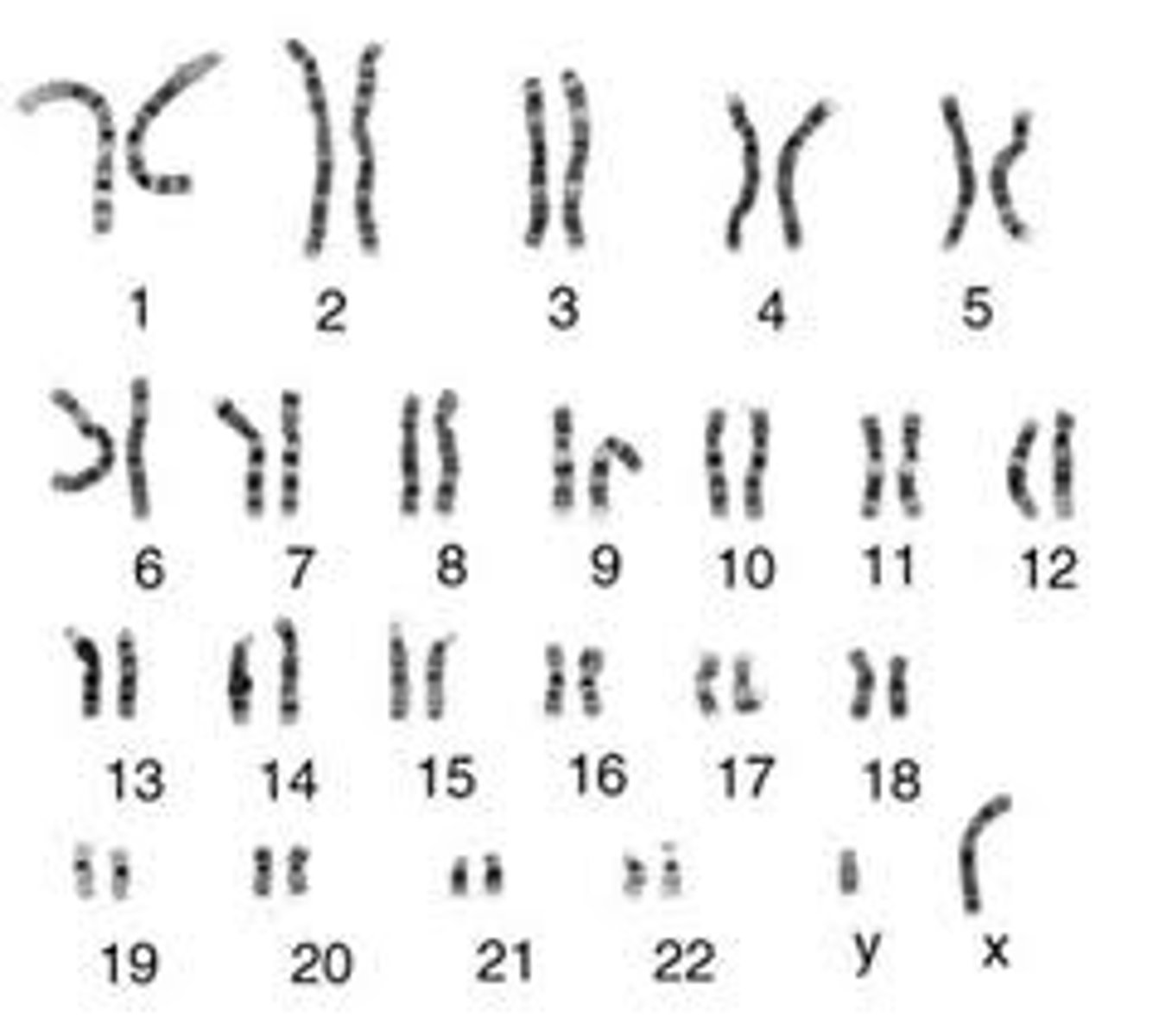
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape. Shows autosomes, sex chromosomes, and homologous chromosomes.
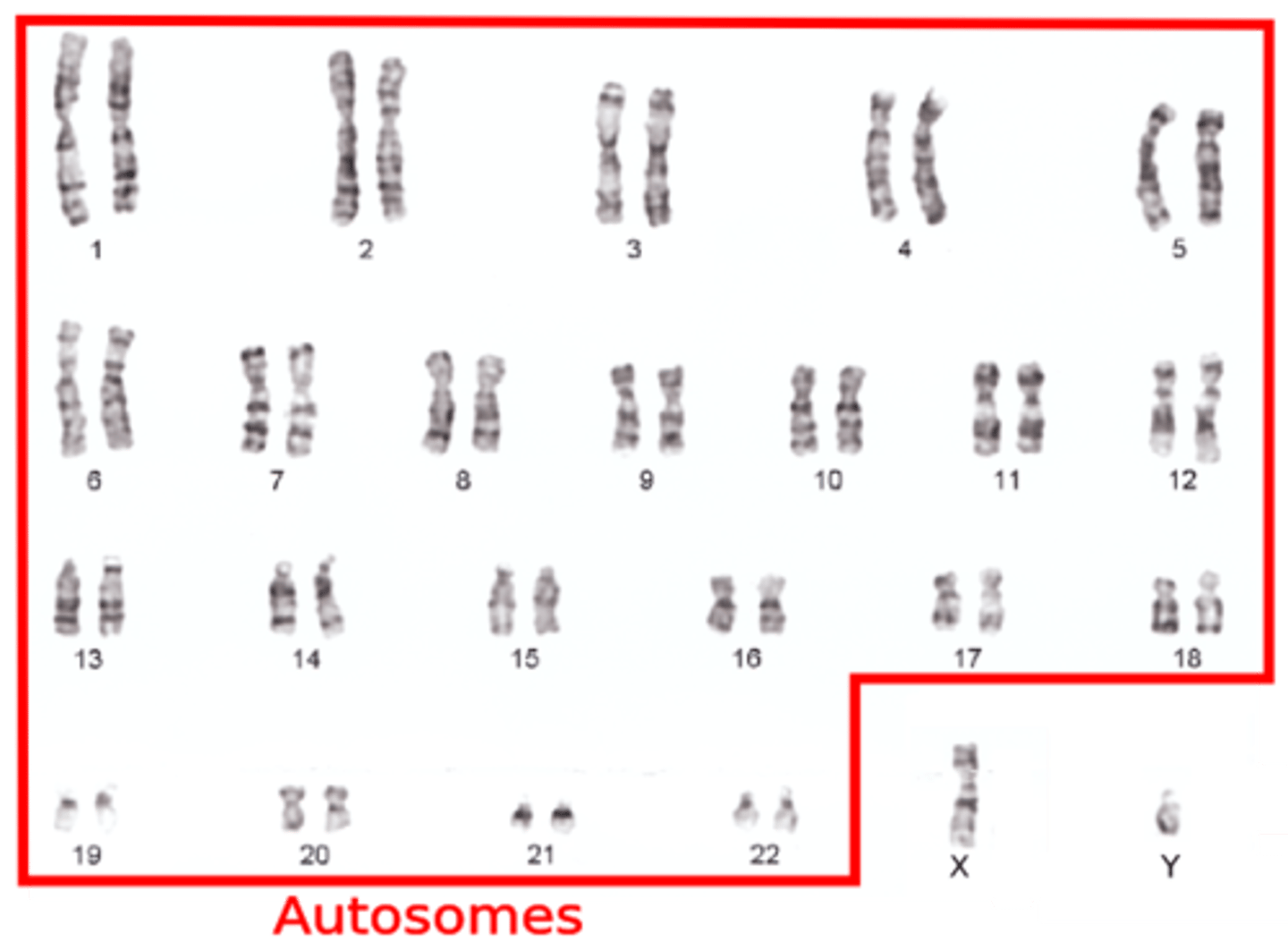
Autosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
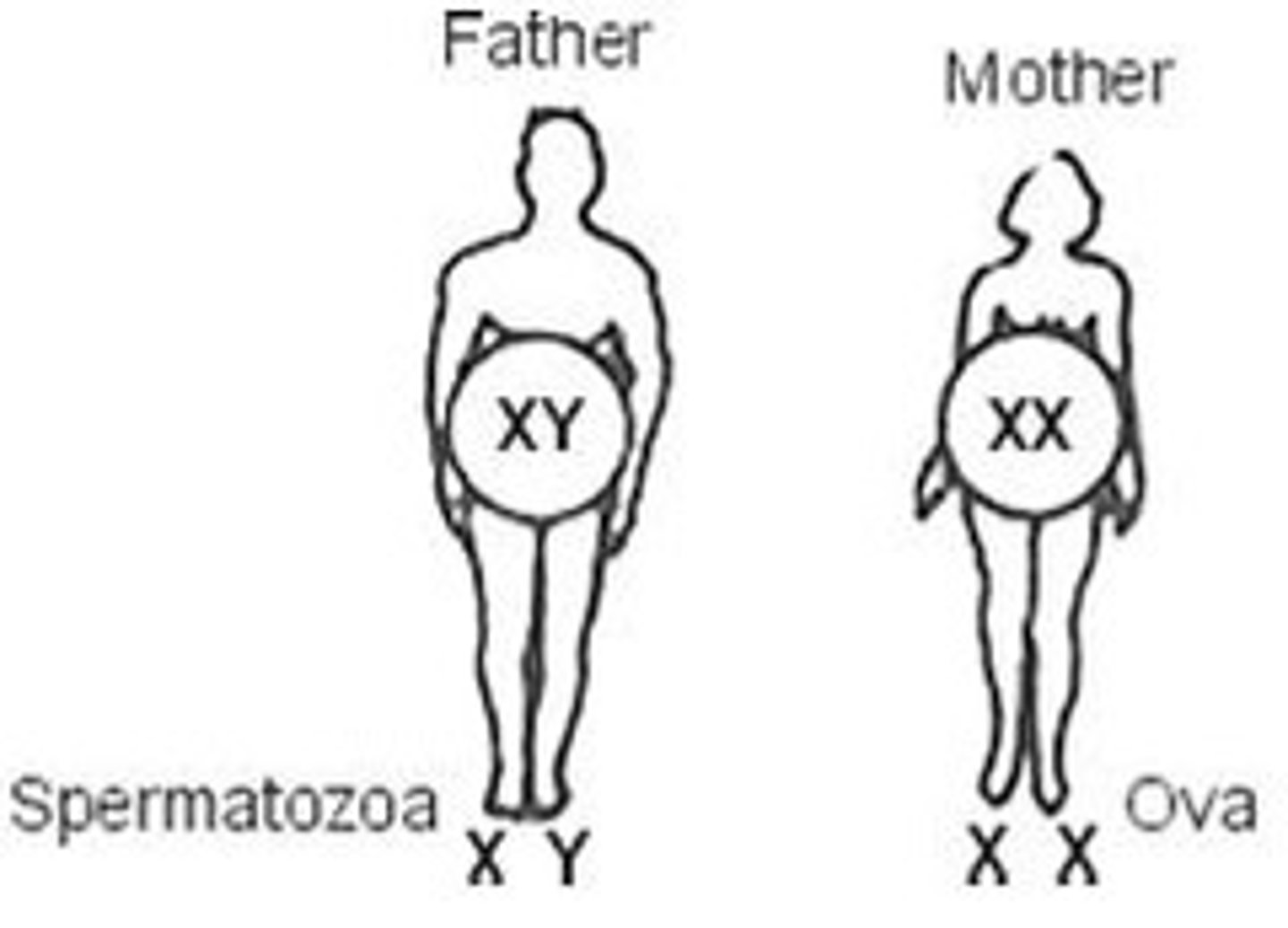
sex chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes.
XX
female sex chromosomes
XY
male sex chromosomes

sex-linked traits
traits controlled by genes located on the X chromosome.
pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait, either dominant or recessive, in several generations of a family.
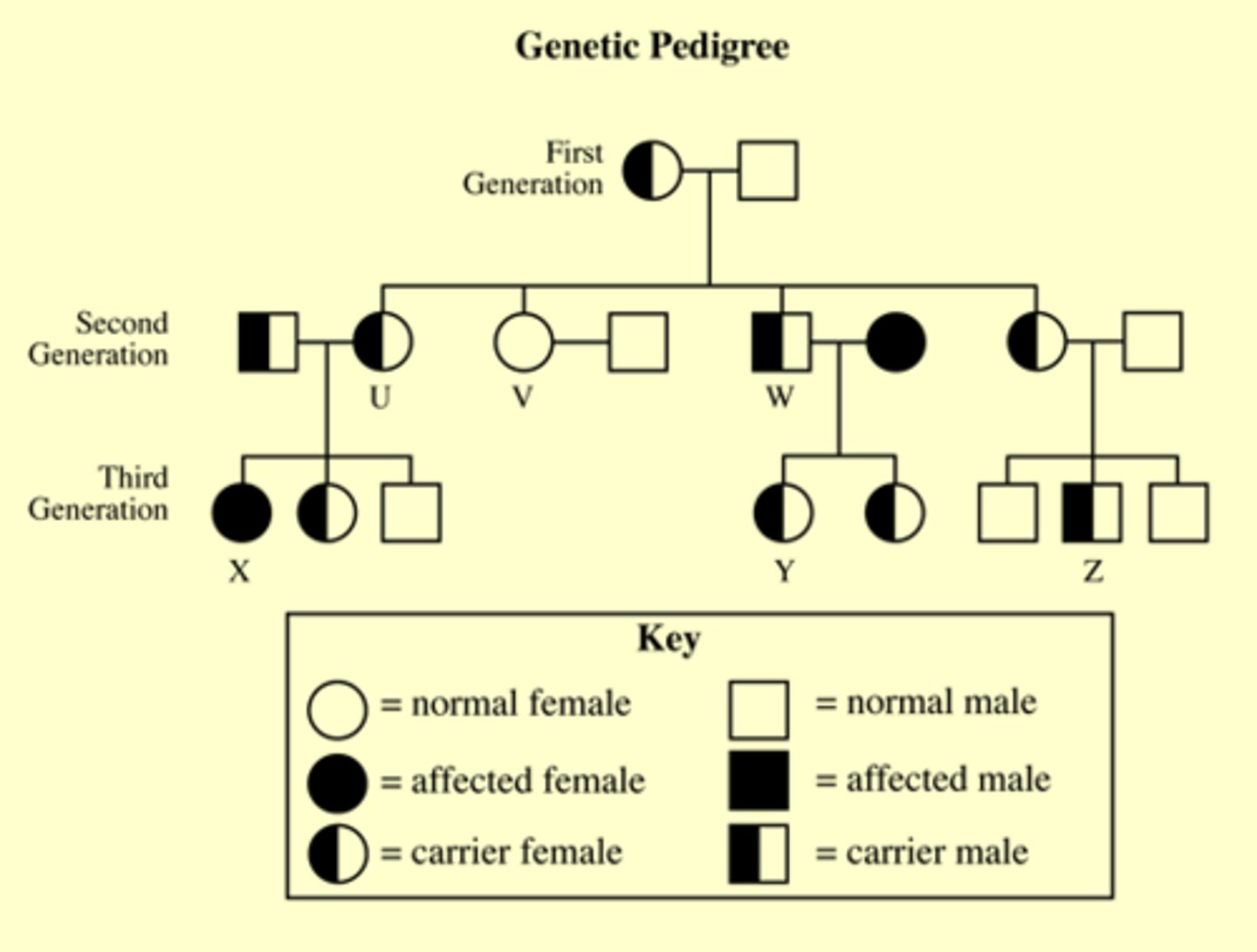
Circle represents
female
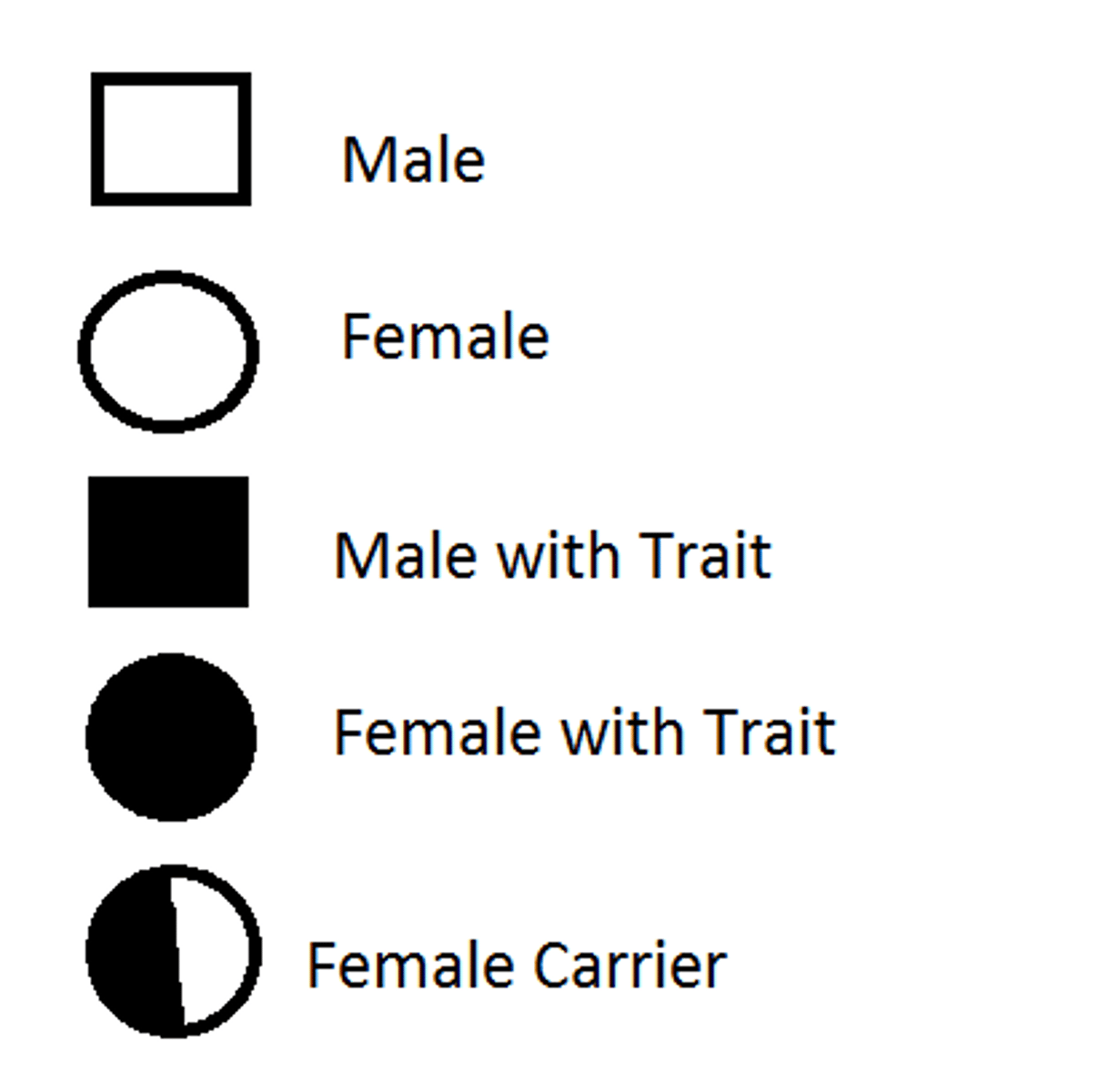
Square represents
male
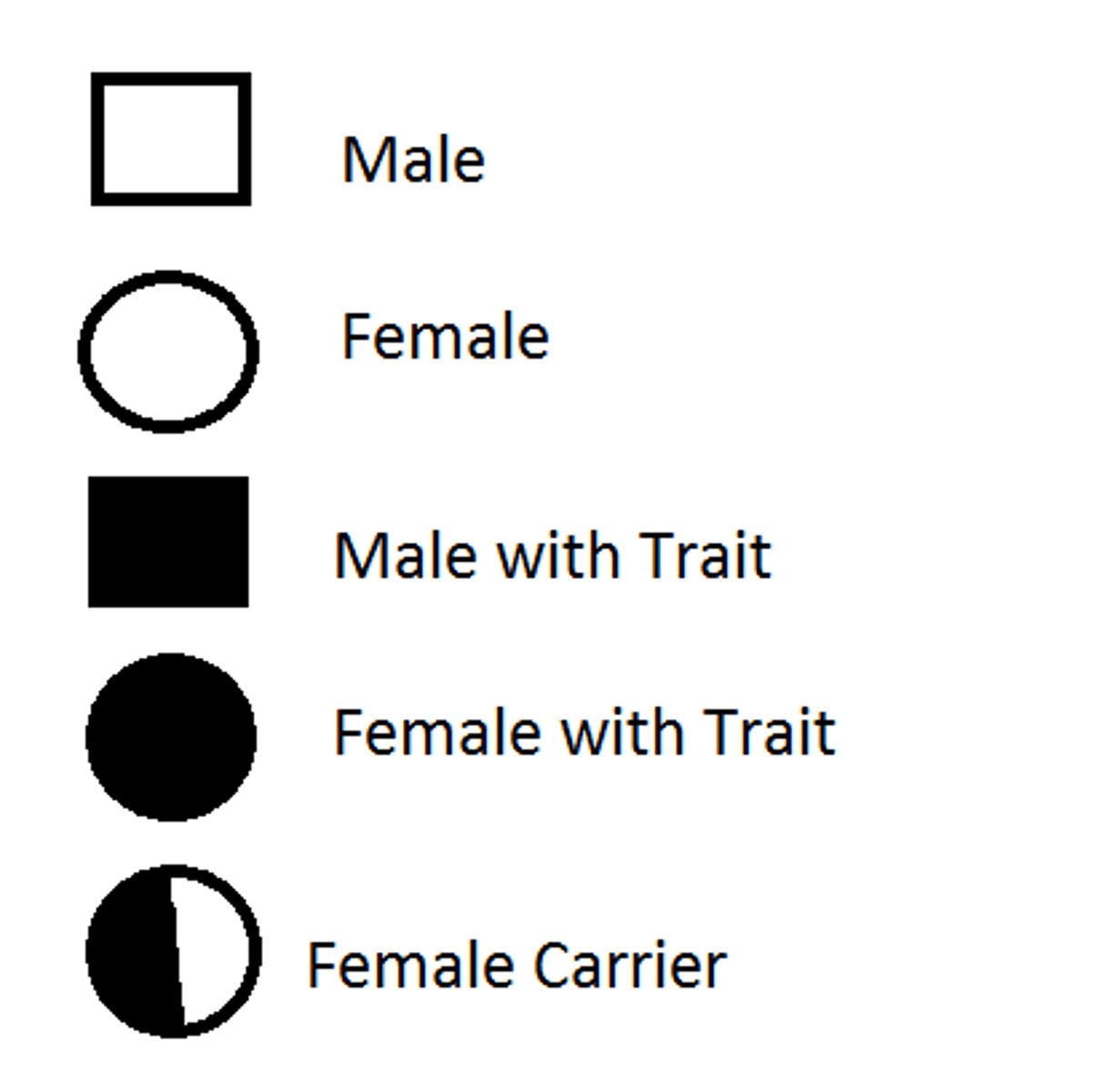
Half shaded circle or square
carrier
genetic disorder
An abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes caused by mutations in DNA
Huntington's disease
A human genetic disease caused by a dominant allele; characterized by uncontrollable body movements and degeneration of the nervous system at 30 to 40 years old.
PKU
A human metabolic disease caused by a mutation in a gene coding for a phenylalanine processing enzyme.
Tay-Sachs disease
A human genetic disease caused by a recessive allele that leads to the accumulation of lipids in the brain.
Allelles
specific versions of a gene
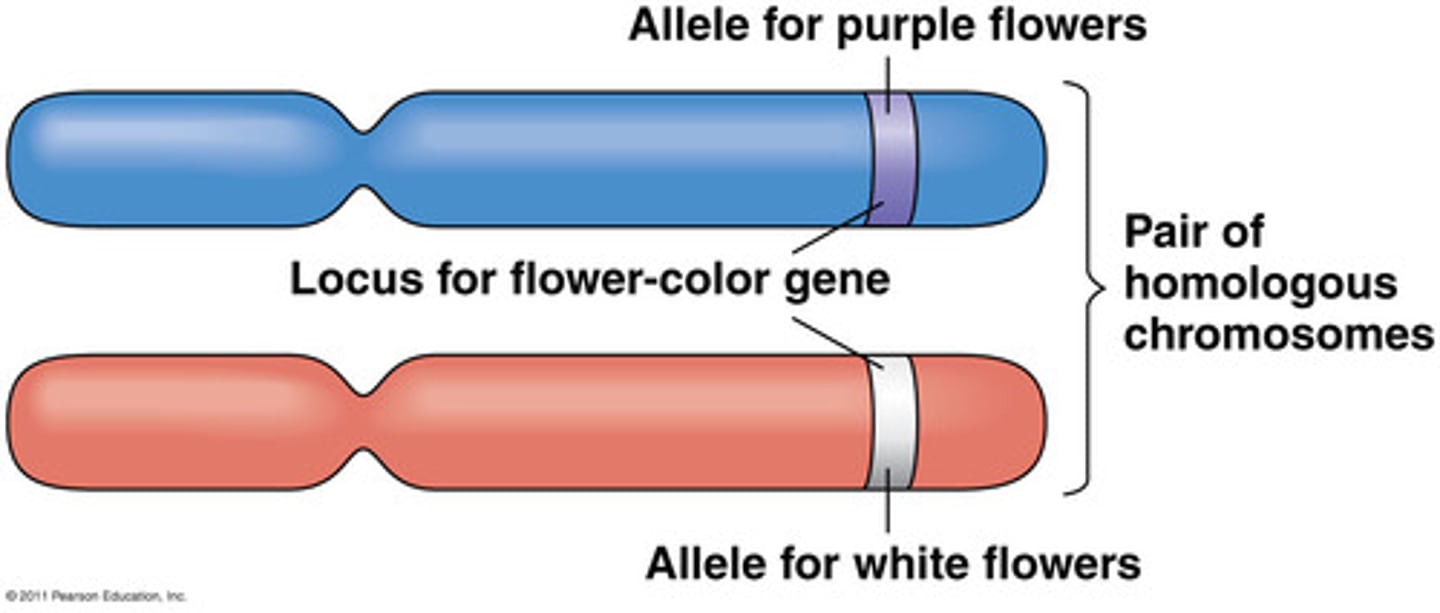
multiple alleles
traits that are controlled by more than two alleles (ex. ABO blood typing = A allele, B allele, & O allele)

dominant allele
represented by a capital letter

recessive allele
represented by a lowercase letter
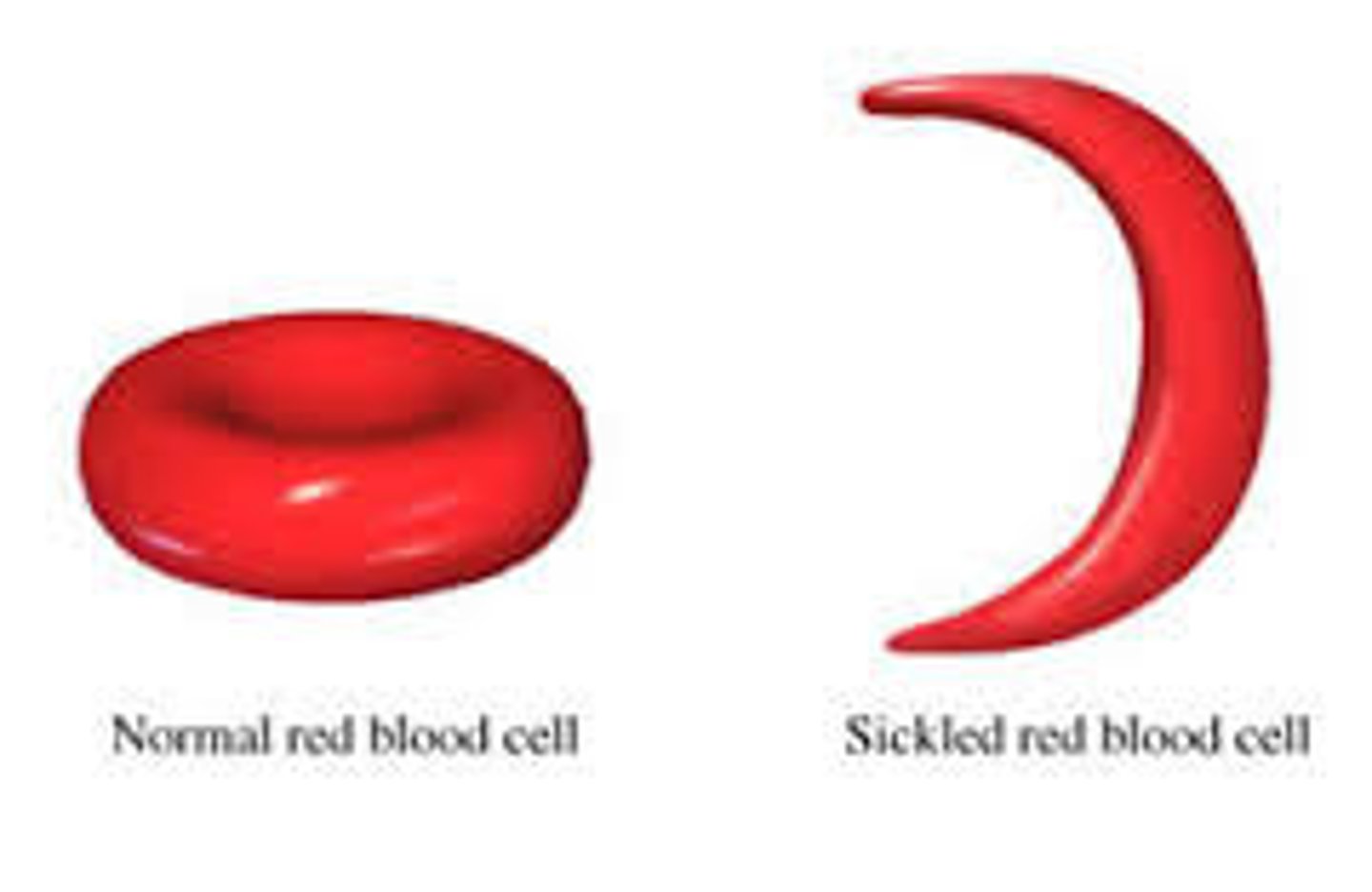
Sickle-Cell Disease
Genetic disorder in which red blood cells have abnormal hemoglobin molecules and take on an abnormal shape. Caused by a change in one DNA base.
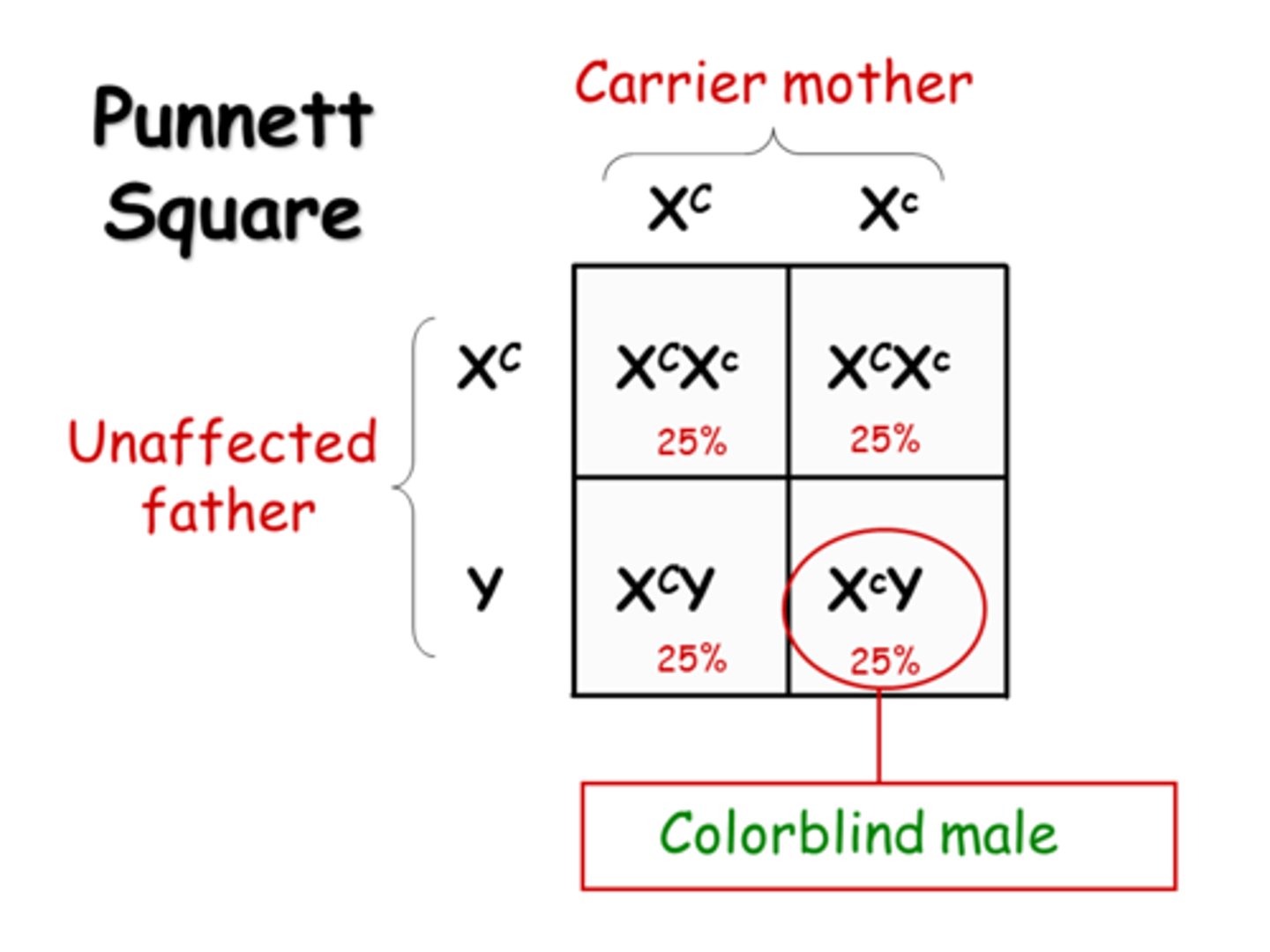
Colorblindness
a recessive x-linked disorder in which an individual cannot distinguish between certain colors. Allele inherited from mother.
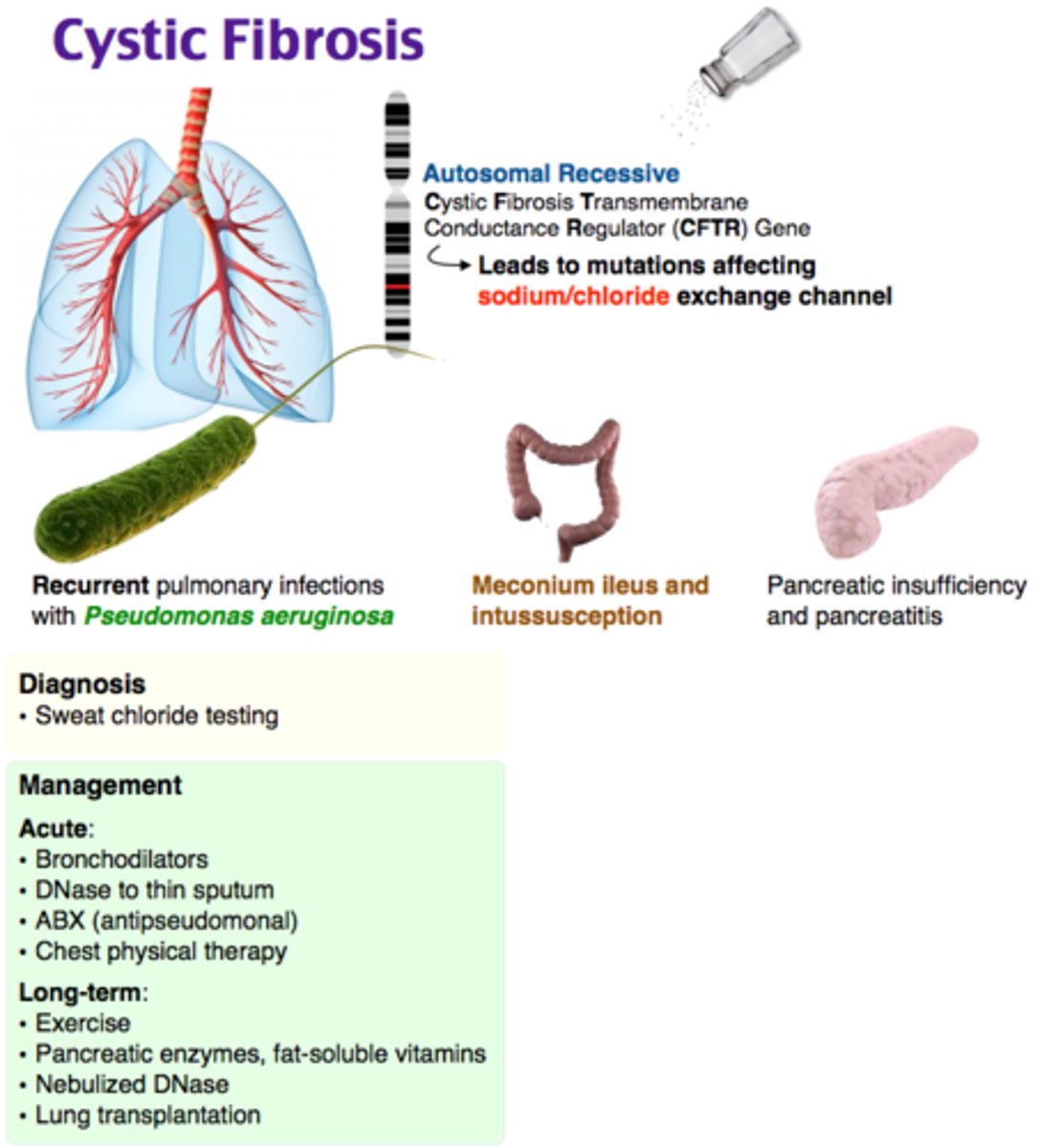
Cycstic Fibrosis
human genetic disorder caused by a recessive allele. It causes a single gene to fail to produce a protein that moves ion across the cell membrane. Body produces thick mucus in lungs.
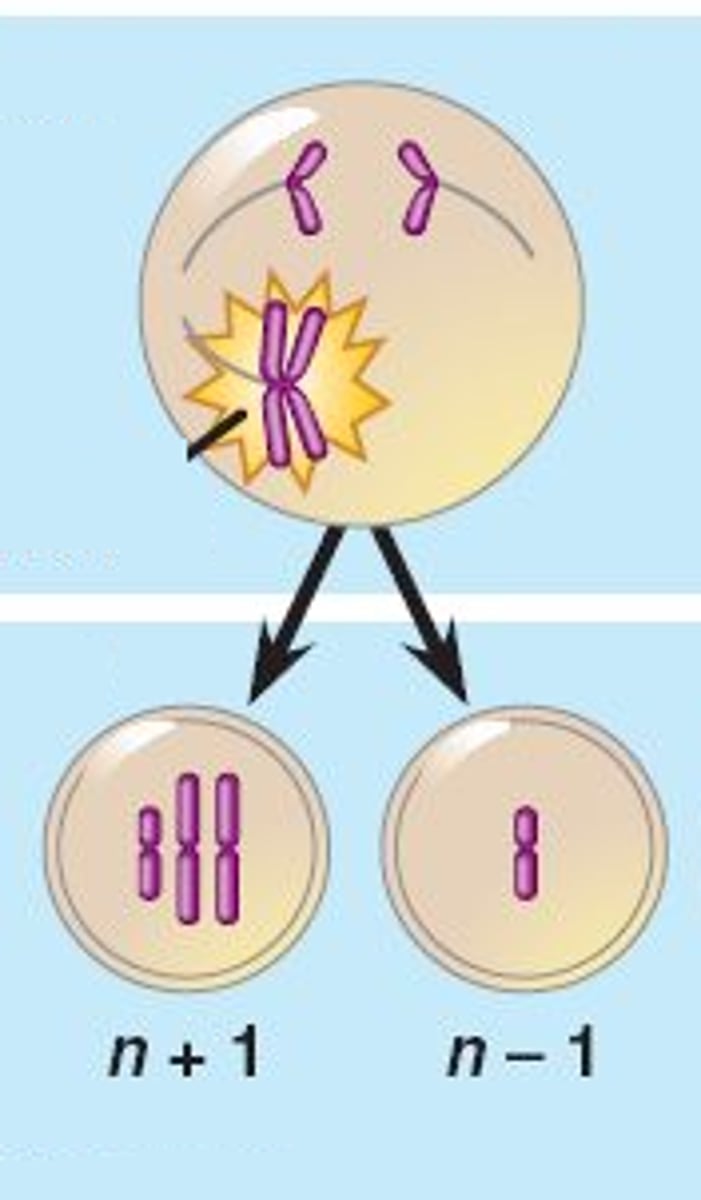
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
Achondroplasia
A form of human dwarfism caused by a single dominant allele

Sex probability of offspring
50% male 50% female

Phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
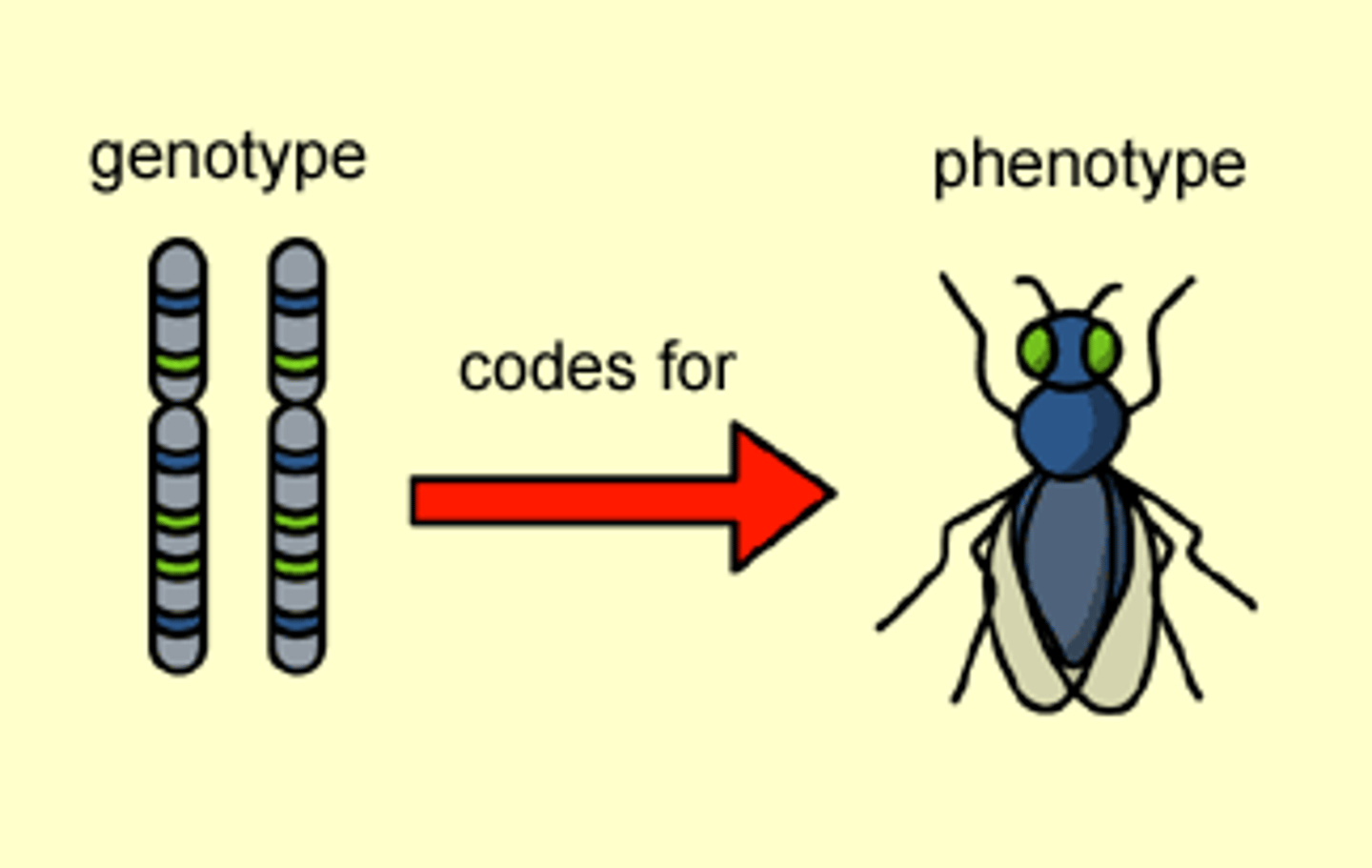
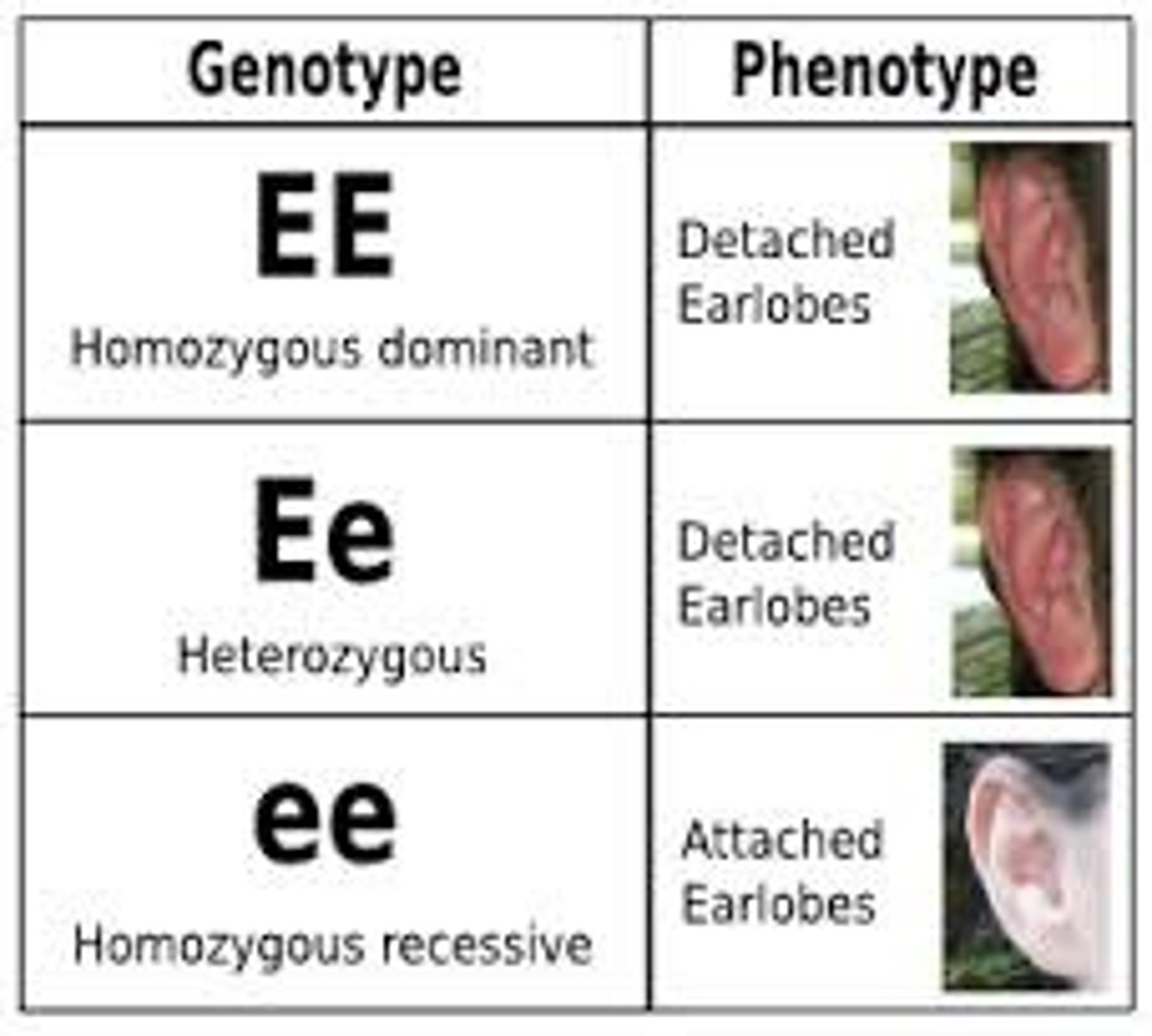
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Down Syndrome
a condition of intellectual disability and associated physical disorders caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21.
