Gen Chem quiz 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
General Chemistry
explains the nature and changes of matter
General Chemistry
useful in everyday life and many professions
Matter
what everything around you is made out of
Solids
the strong ones, does not change unless broken or melted, keeps their shape, particles are super close together
Liquids
the flowing friends, does not have a fixed shape, takes the shape of their container, little loose particles and can move around
Gases
the invisible explorers, gases spread out everywhere, cant always be seen but they are around us, particles move super fast and far apart
Melting
solid to liquid changing state of matter
Vaporization
liquid to gas changing state of matter
Condensation
gas to liquid changing state of matter
Solidification
liquid to solid changing state of matter
Physical Property
odor, color, state, density, melting/boiling point
Chemical Property
ability to form new substances
Element
one kind of atom
Compound
chemically combined elements
Mixture
variable composition, can be solid, liquid, or gas
Homogeneous Mixture
uniform through (e.g., saltwater, air)
Heterogeneous Mixture
non-uniform, distinct parts (e.g., sand and water)
Pure Substances
consistent composition
sodium bicarbonate
Baking Soda
sodium tetraborate decahydrate
Borax
sodium hydroxide
Caustic Soda
calcium carbonate
Chalk
calcium carbonate
Marble
calcium sulfate
Plaster of Paris
sucrose
Table Sugar
monosodium glutamate
MSG/Vetsin
Decanting
separates dense solids from liquids, only useful when solid settles quickly, sand and water are a common example
Sieving
based on particle size, can separate solids from liquids, rocks and sand as example
Filtration
fine solid particles from liquids, uses filter paper or similar material, produces filtrate and residue
Separating Funnel
for non-miscible liquids, based on density experiences, example is oil and water
Centrifugation
spins mixture at high speed, separates based on density, used in milk, blood, and washing machines
Magnetic Separation
separates magnetic from non-magnetic, iron from soil, used in mining and recycling
Evaporation
recovers dissolved solids, solvent evaporates, example is making sea salt
Distillation
like evaporation, collects the vapor (distillate), used in making alcohol, perfumes, and purified water
Chromatography
separates and analyzes mixtures, uses small amounts, based on substance attraction
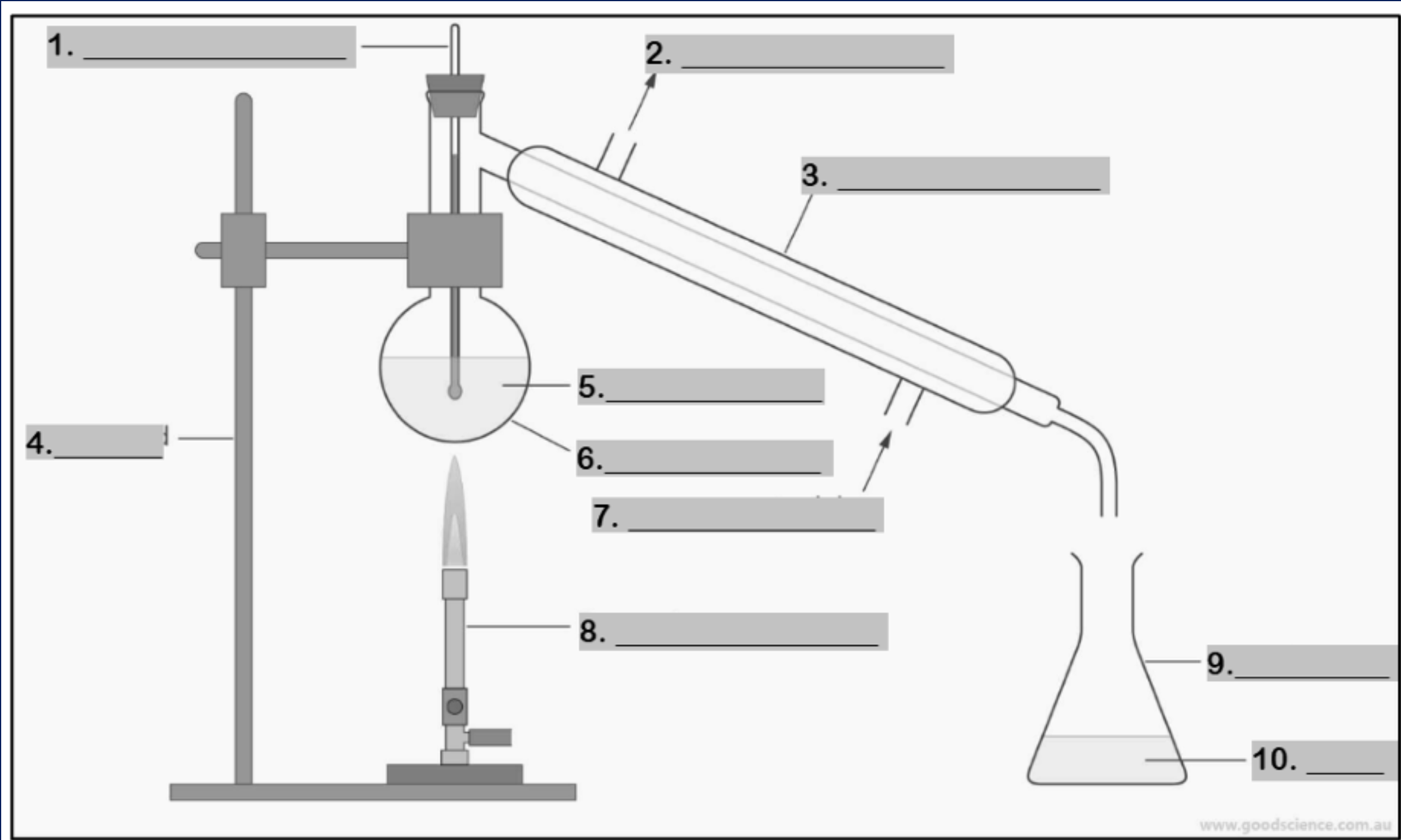
thermometer
Number 1
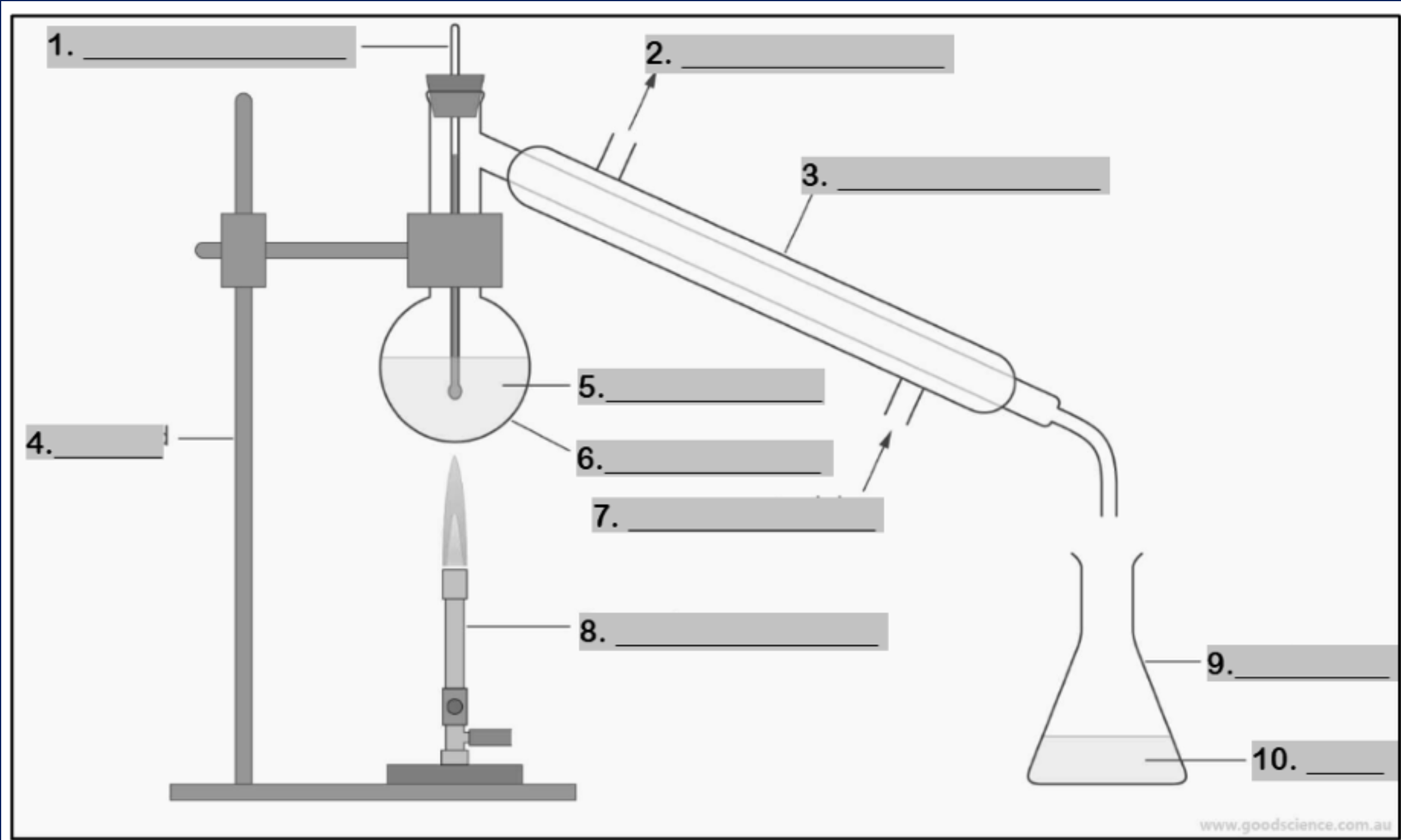
water outlet
Number 2
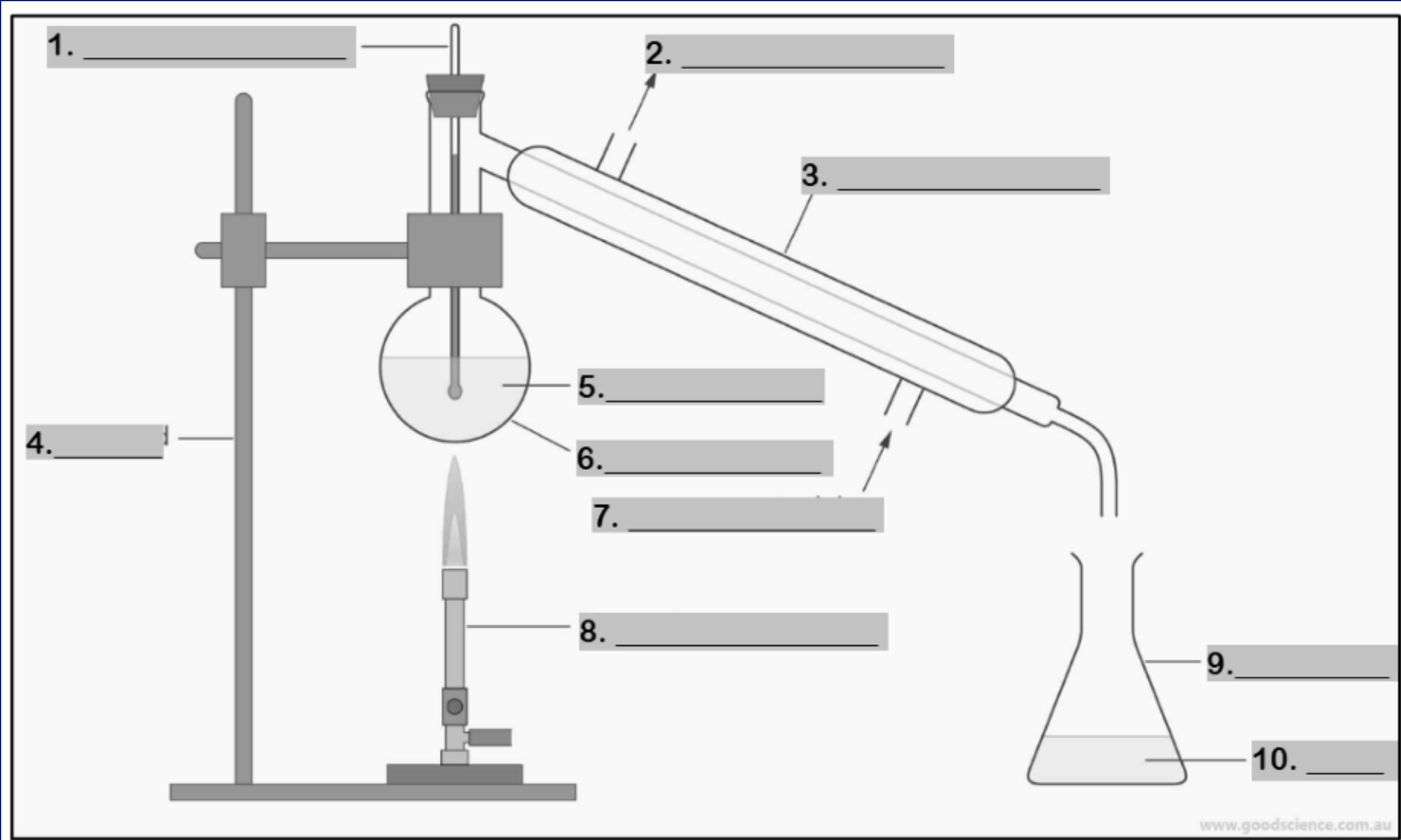
condenser
Number 3
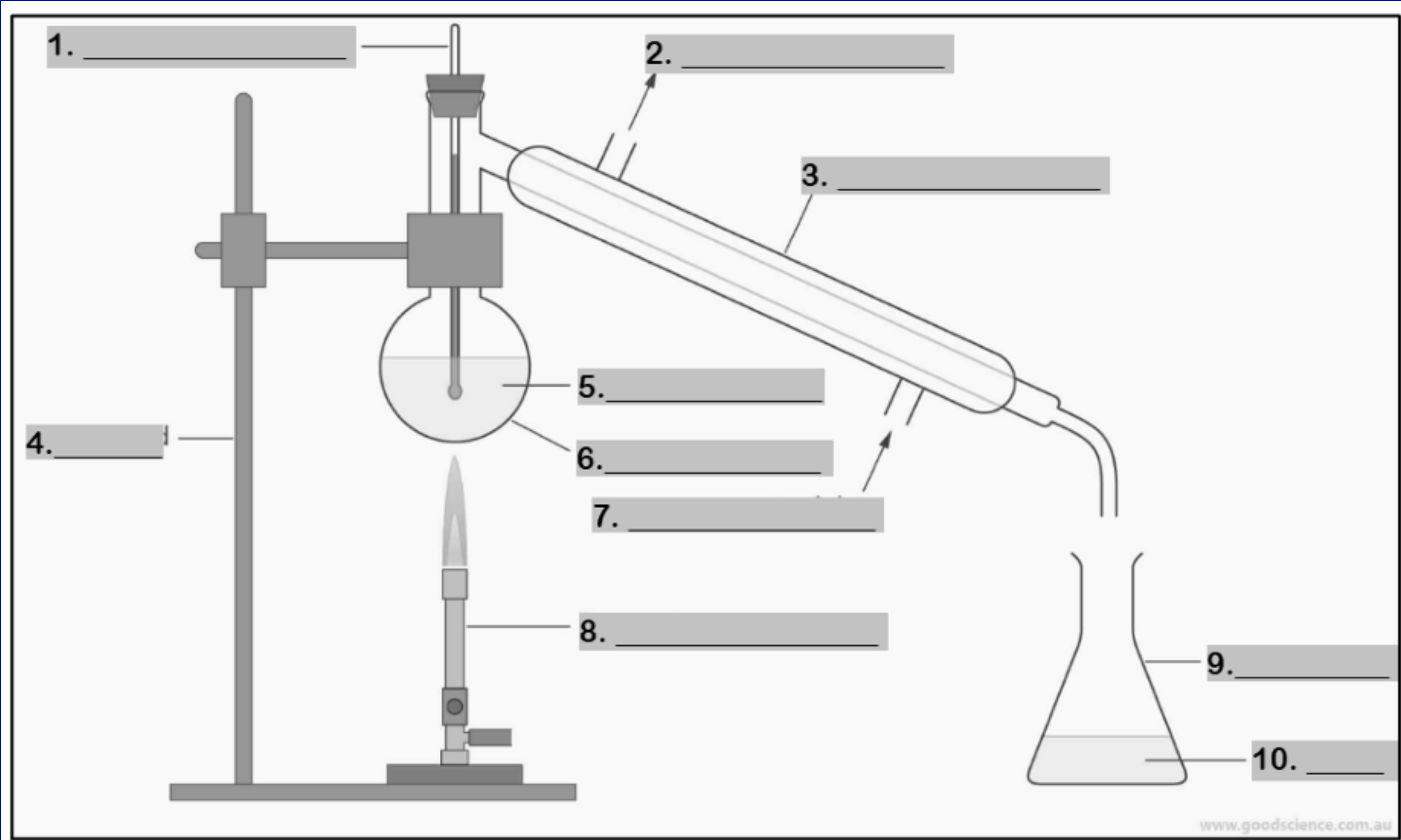
retort stand
Number 4
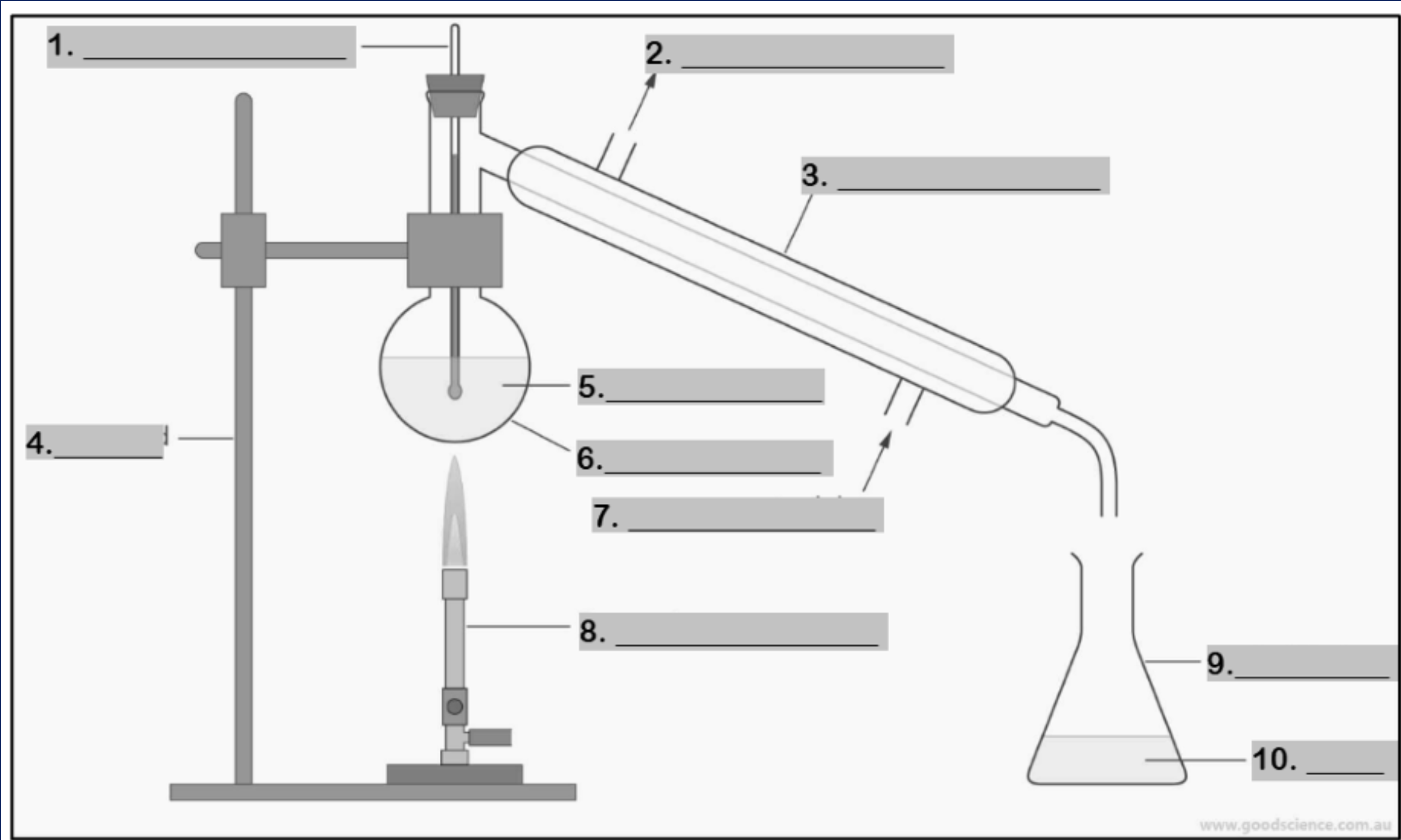
mixture
Number 5
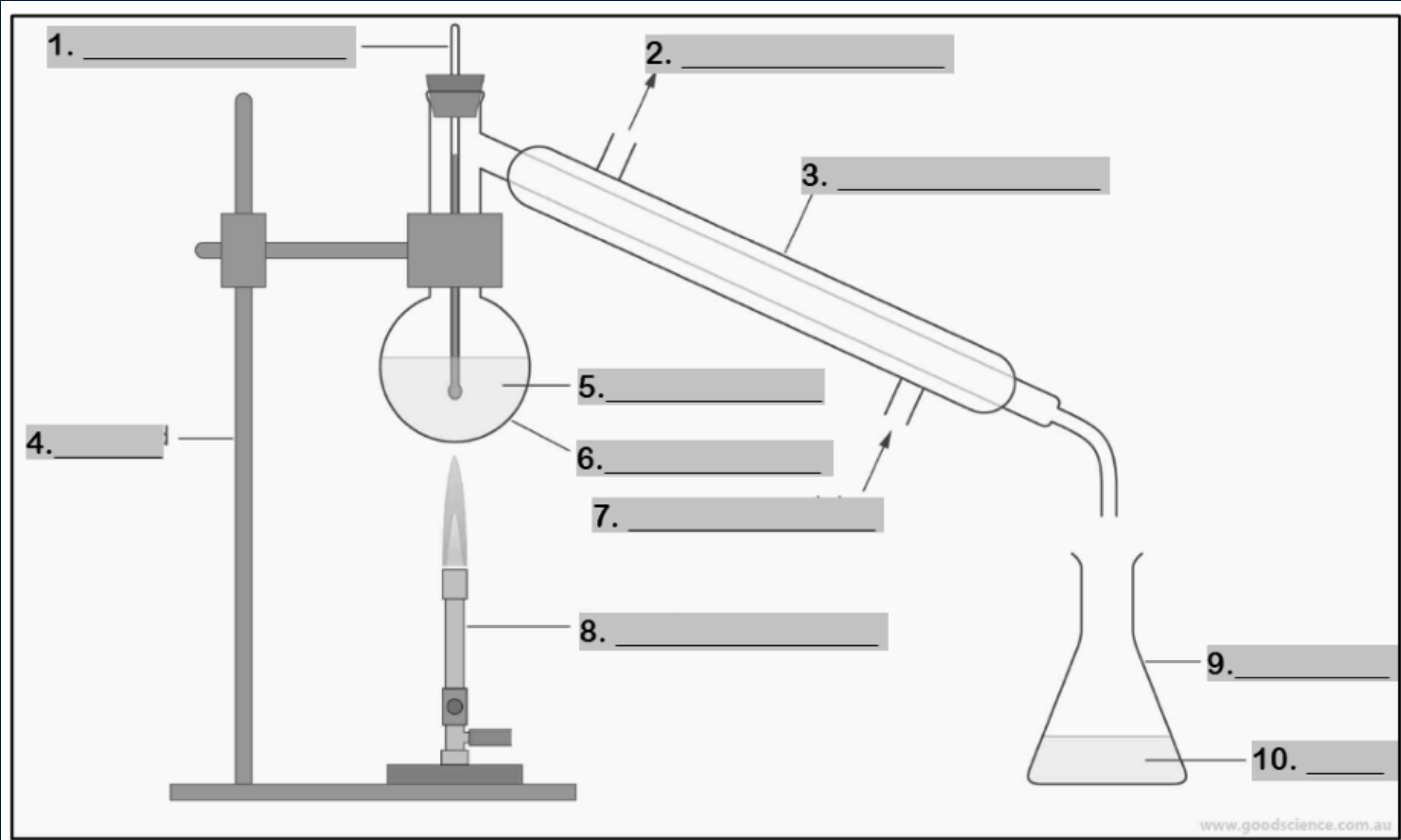
round bottom flask
Number 6
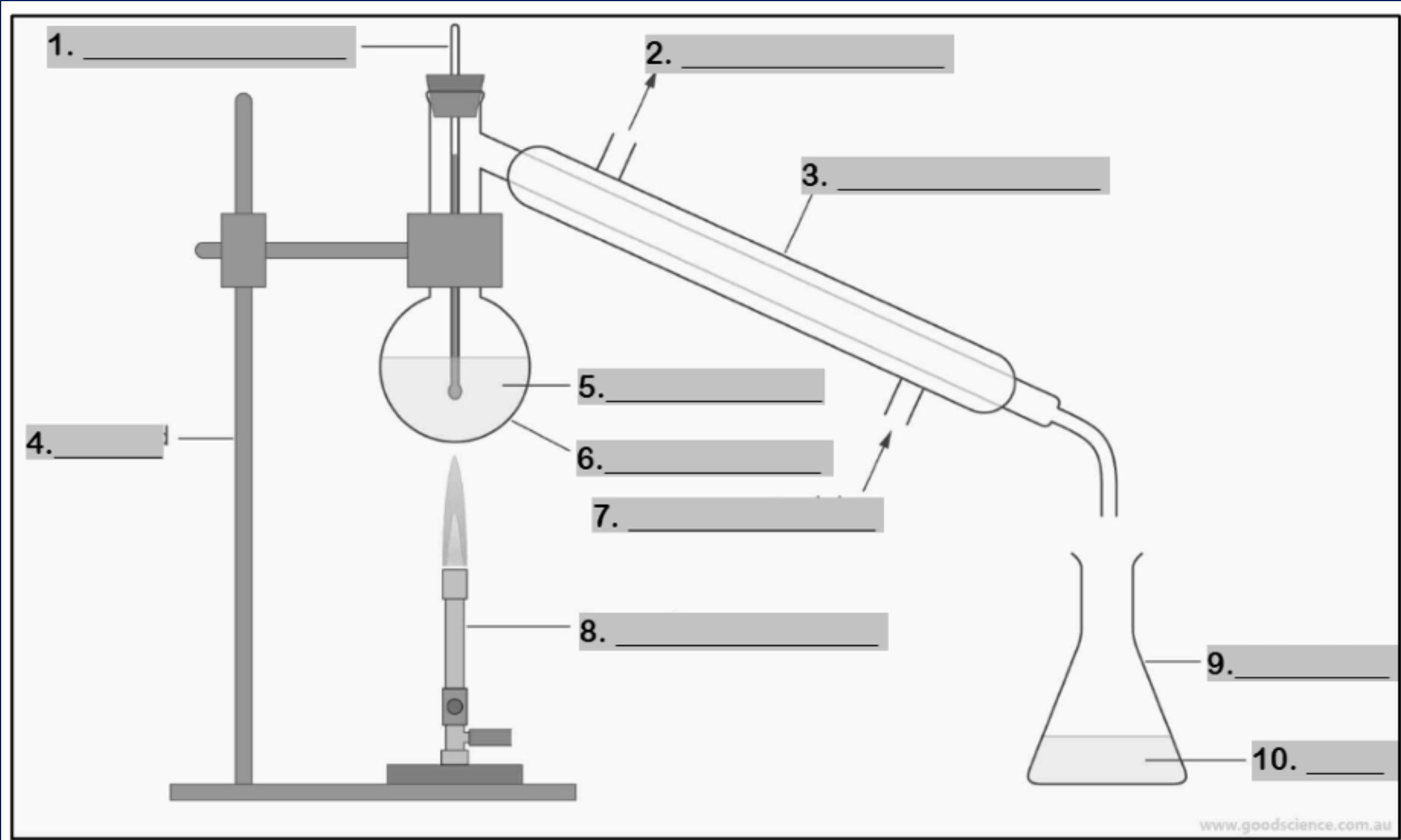
water inlet
Number 7
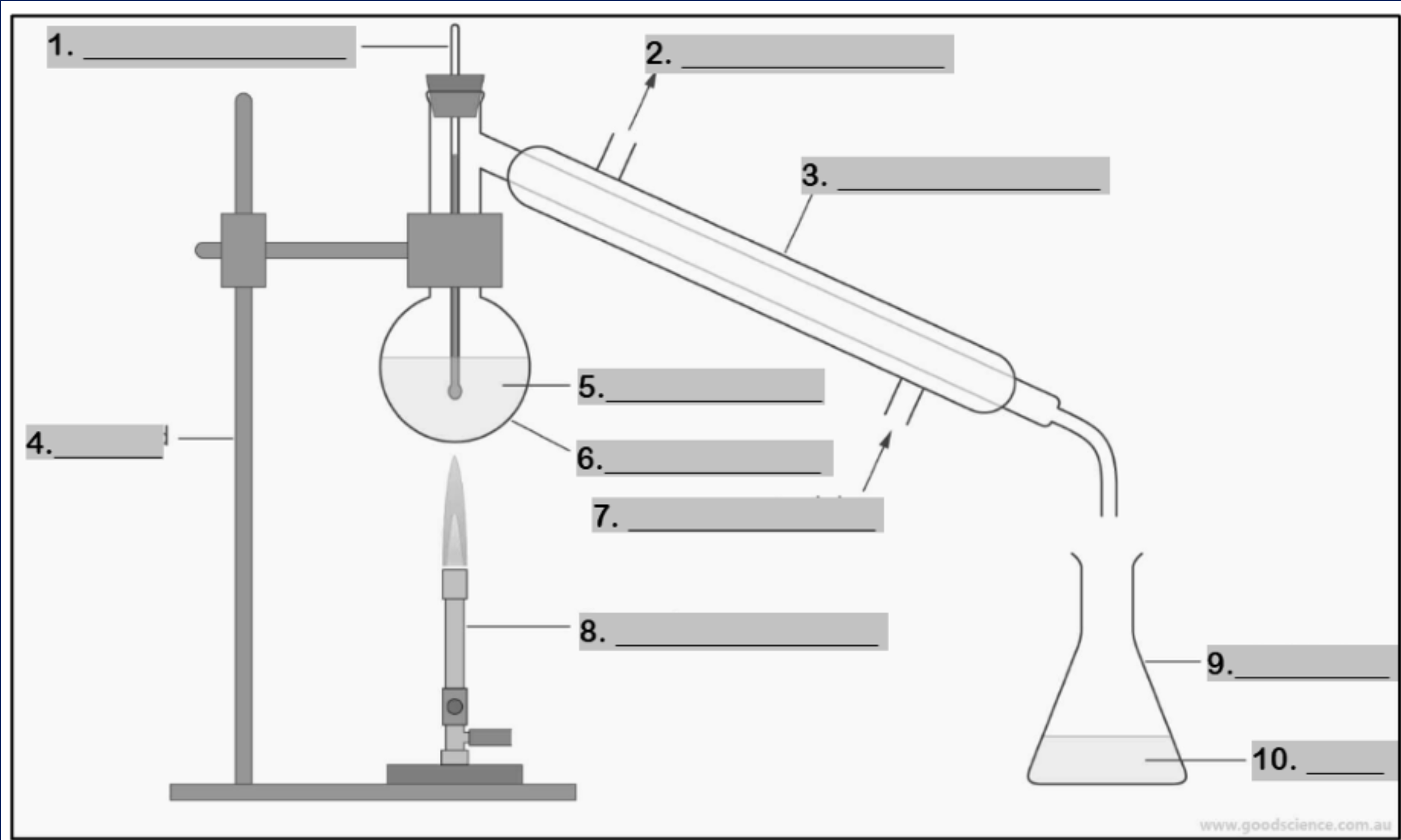
Bunsen burner
Number 8
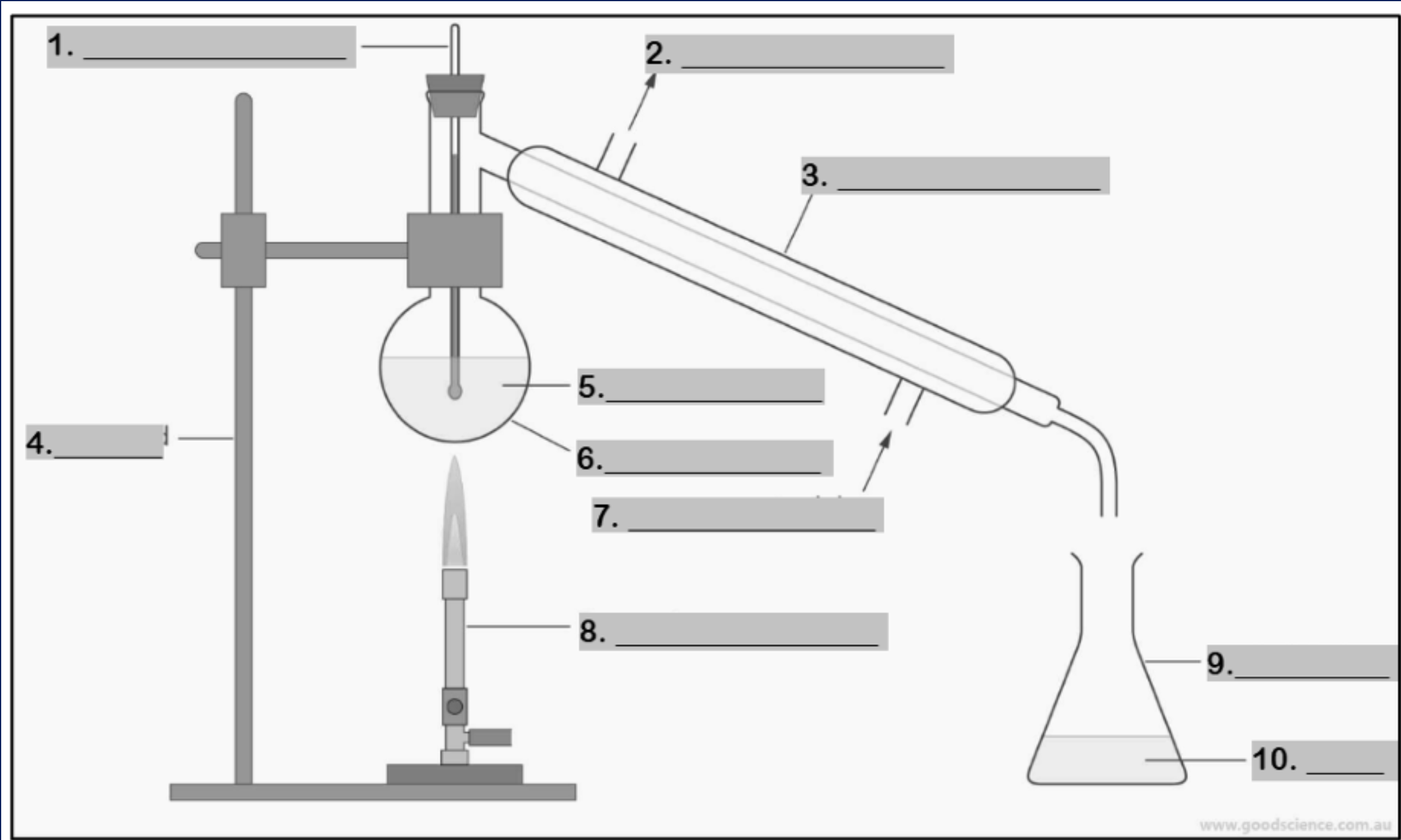
conical flask
Number 9
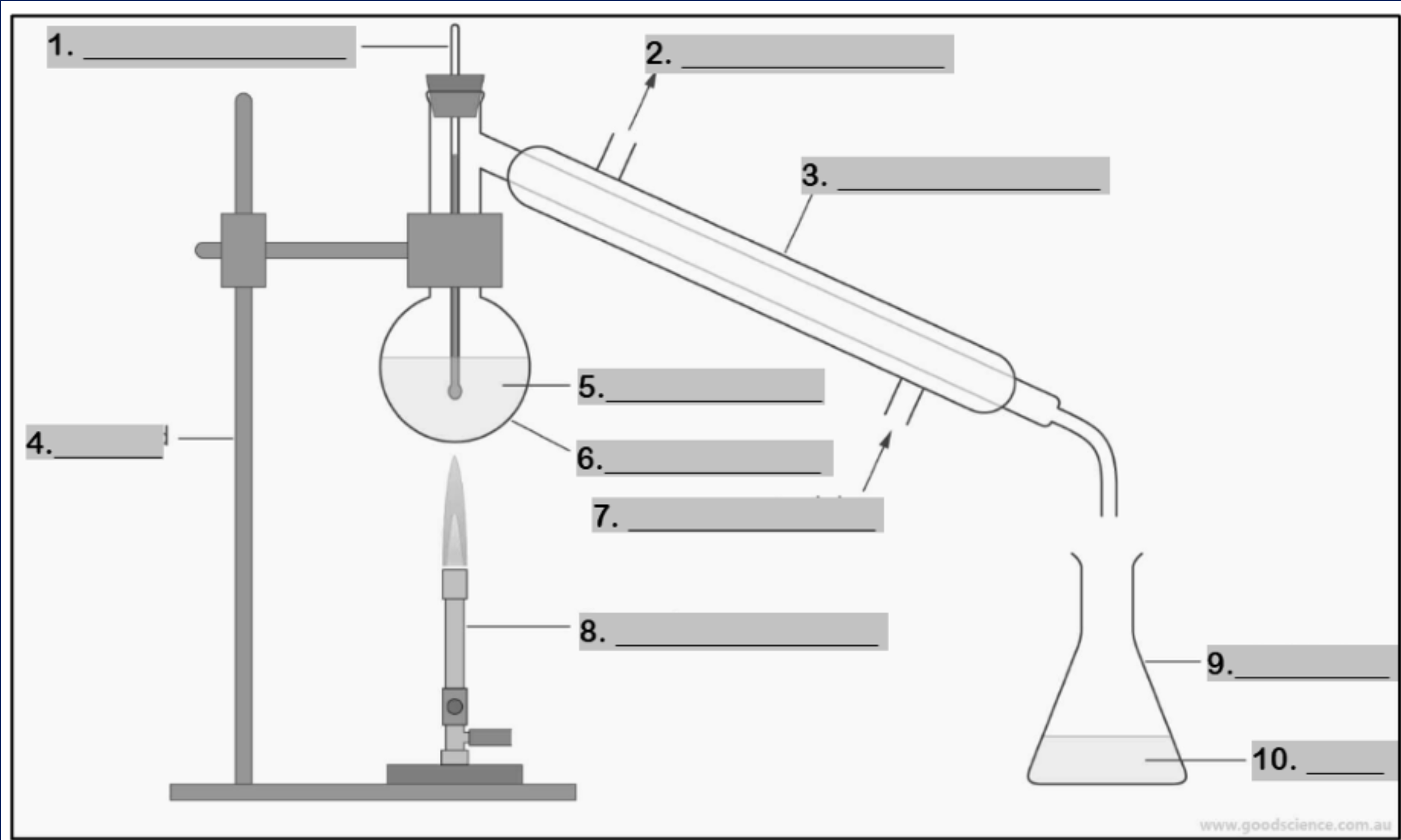
distillate
Number 10
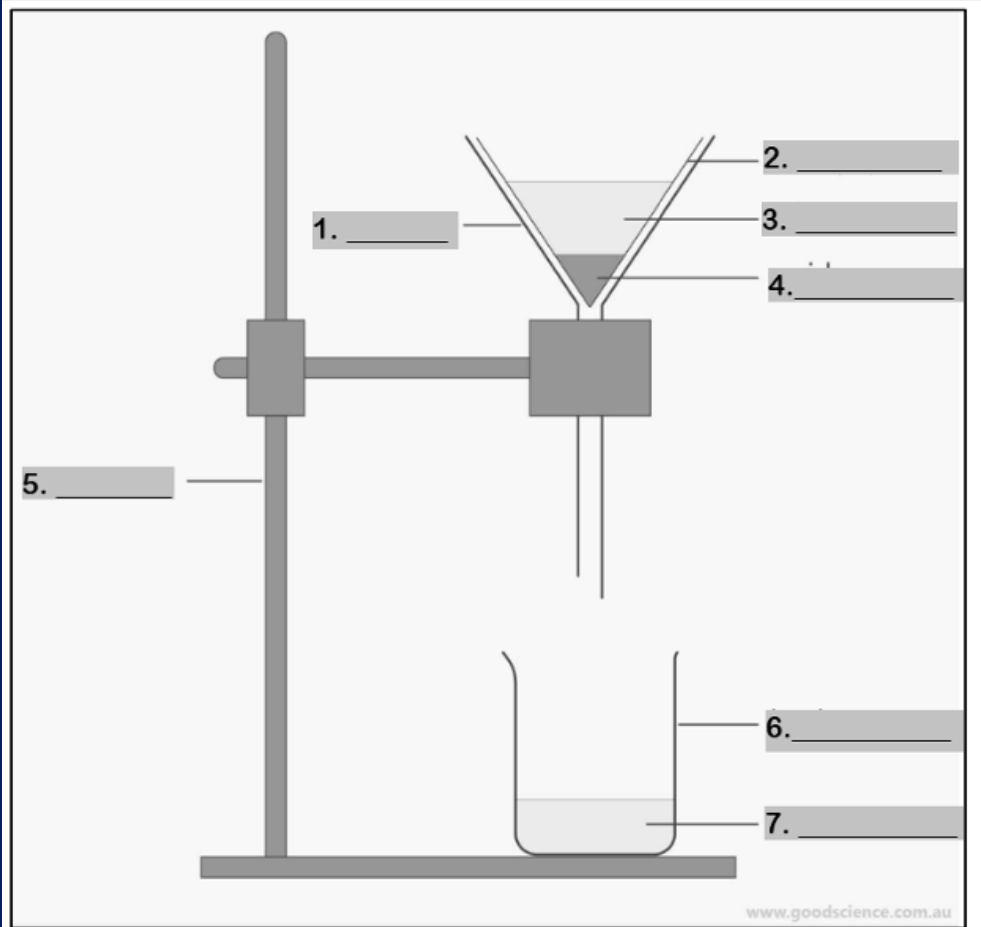
funnel
Number 1
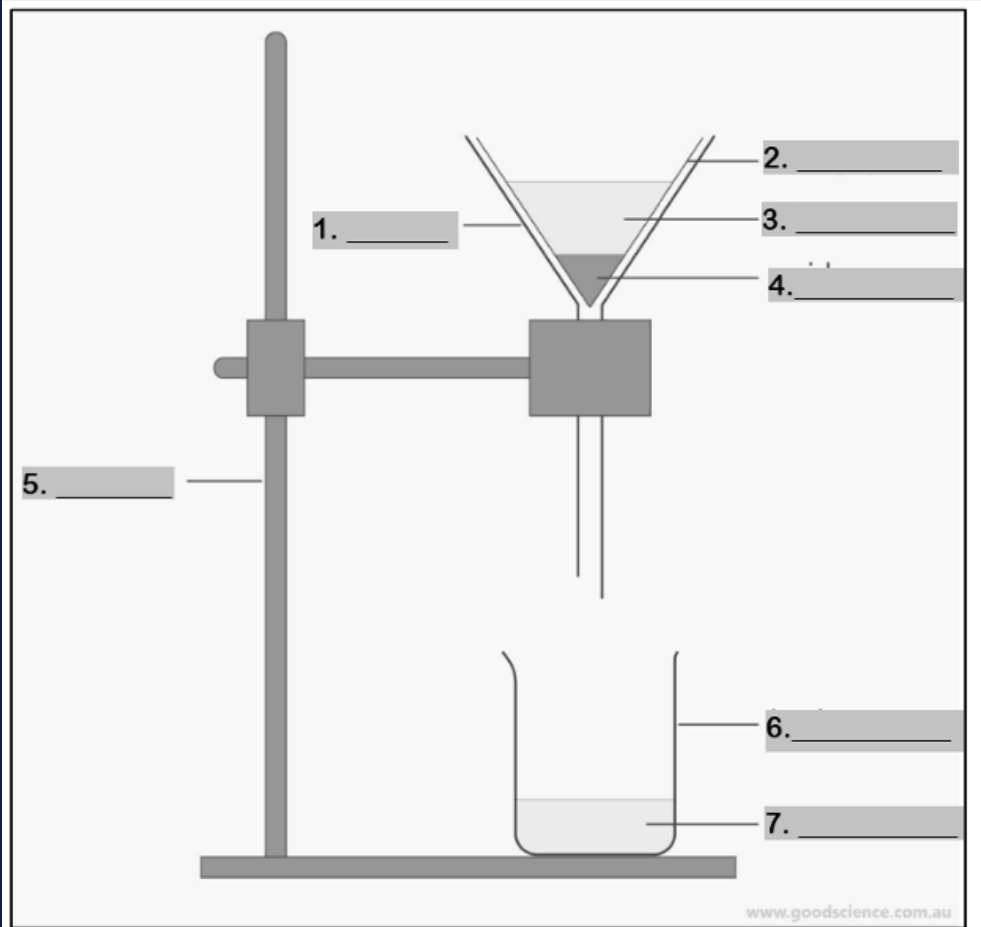
filter paper
Number 2
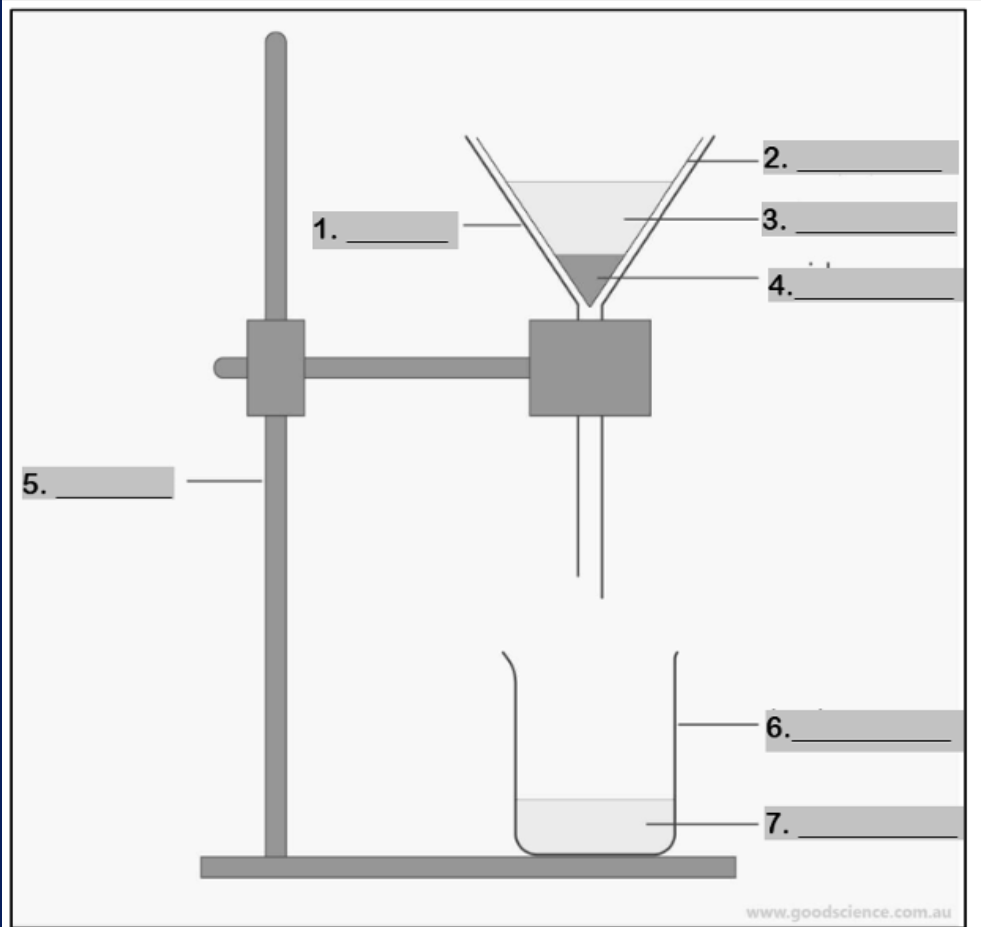
mixture
Number 3
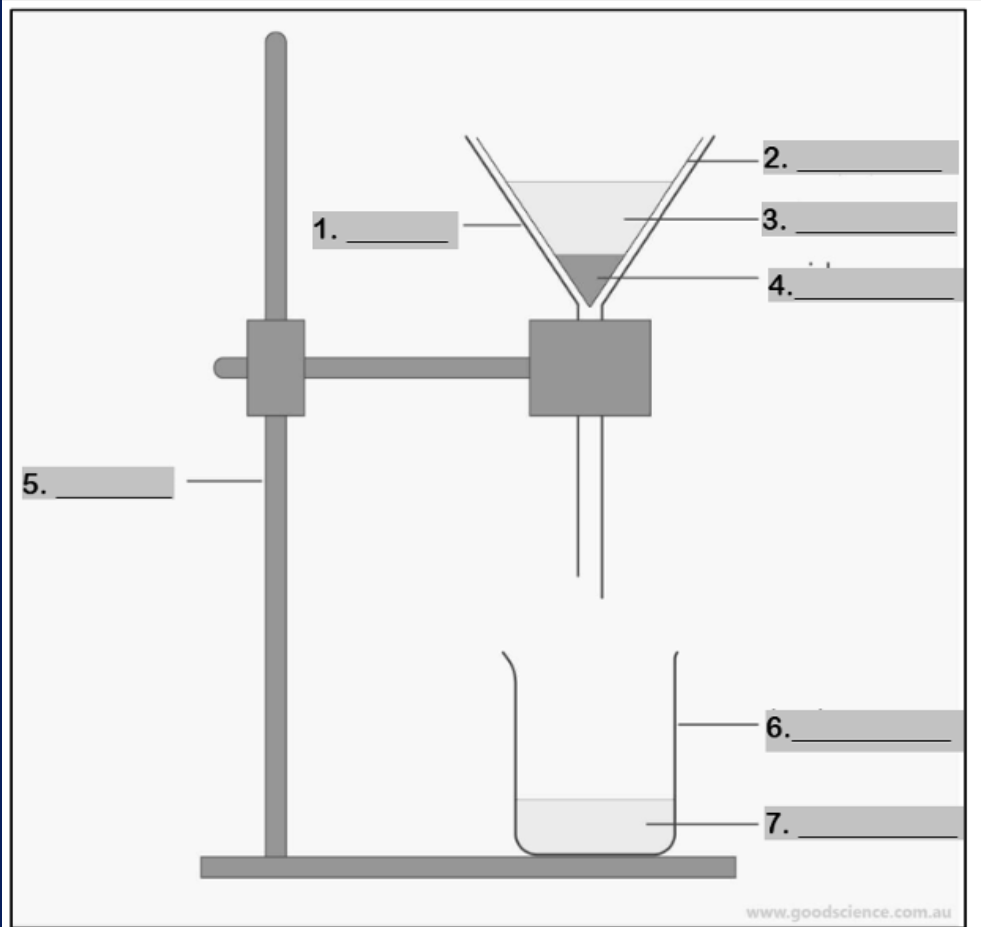
residue
Number 4
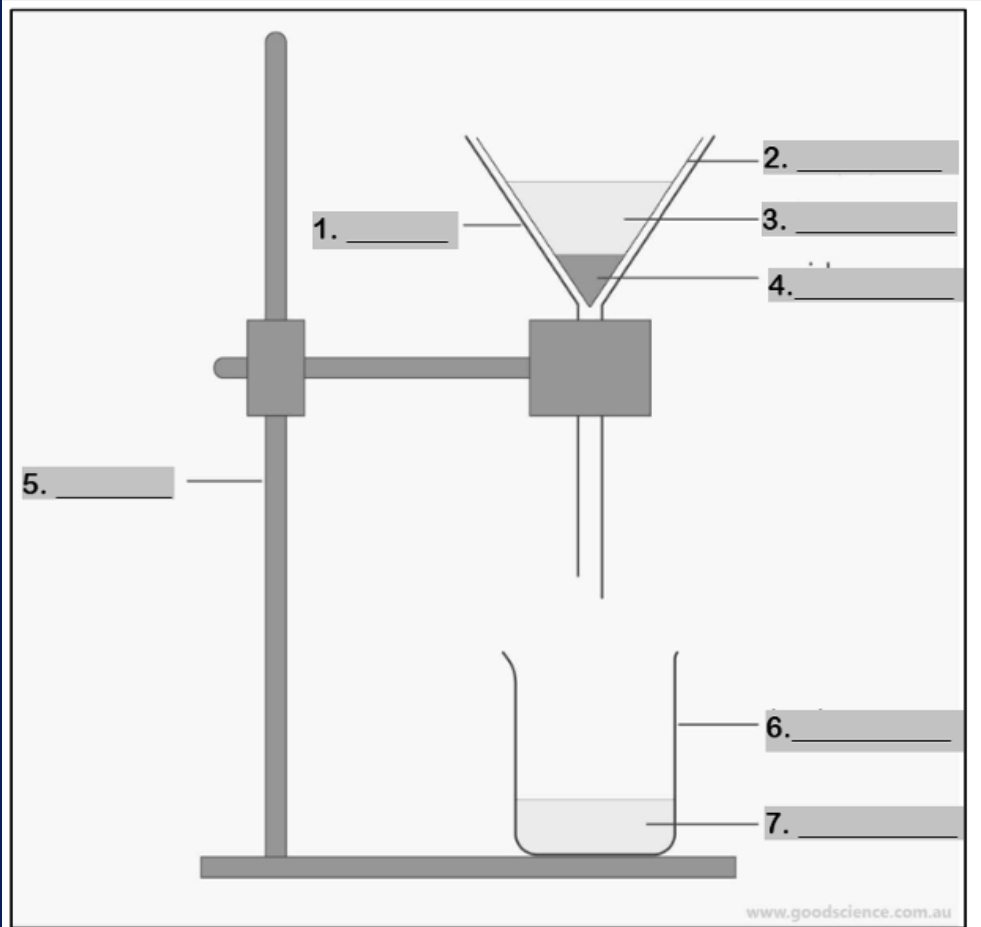
retort stand
Number 5
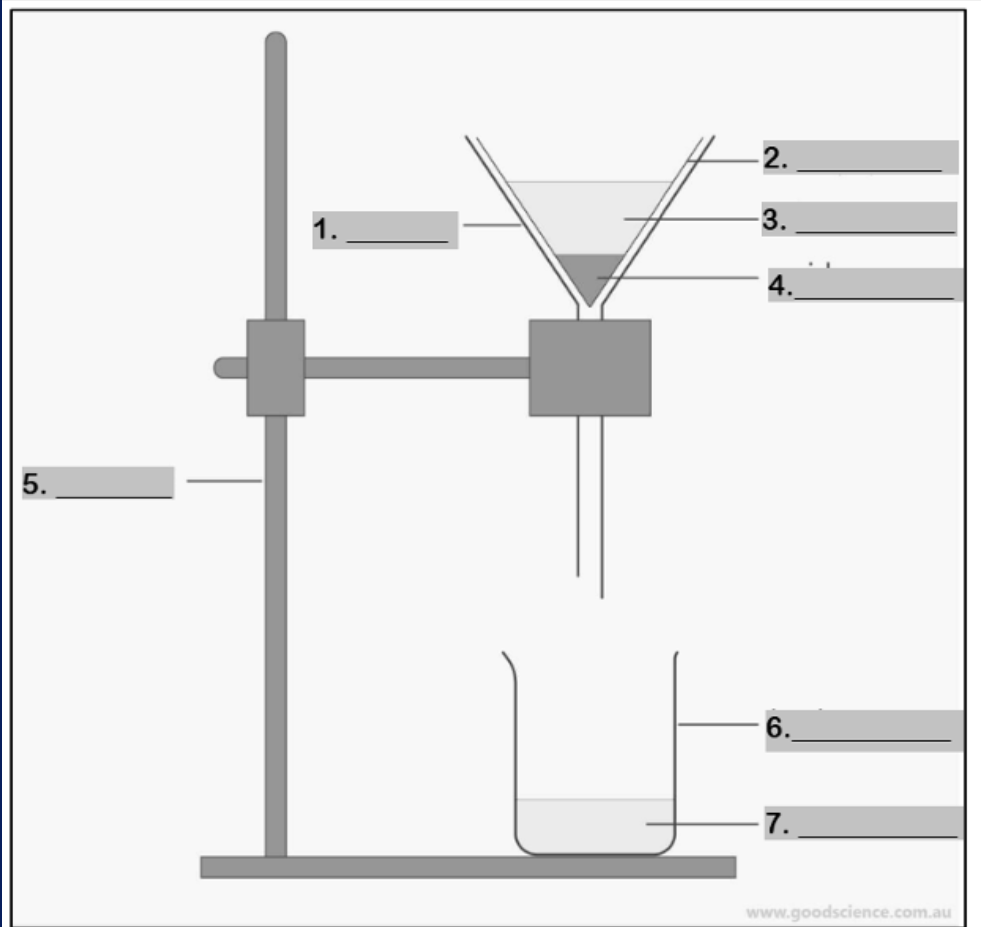
beaker
Number 6
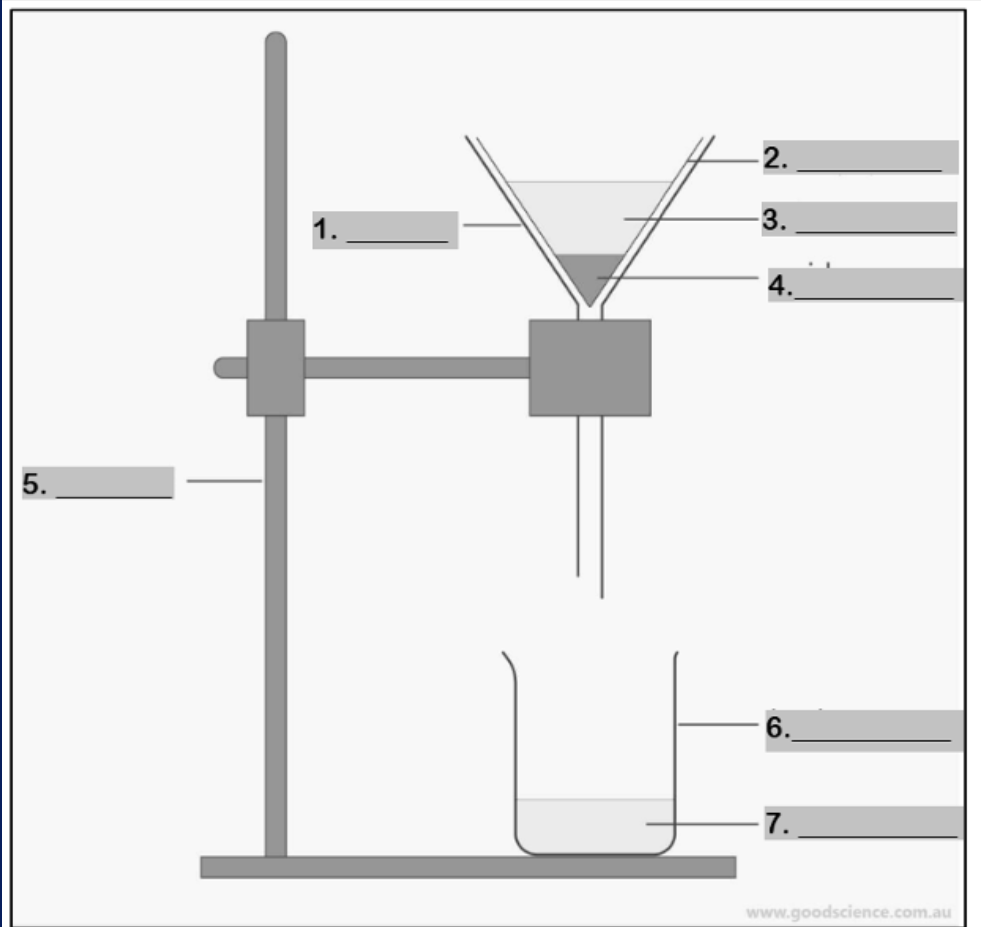
filtrate
Number 7