Bio Unit 2 Quiz Questions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:22 AM on 5/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following is **NOT** one of the classes of lipids found in membranes?
A. glycoproteins
B. glycolipids
C. phospholipids
D. sterols (like cholesterol)
A. glycoproteins
B. glycolipids
C. phospholipids
D. sterols (like cholesterol)
A. glycoproteins
2
New cards
A phospholipid is amphipathic which means....
A. Having both cholesterol and phospholipids
B. Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
C. Having both protein and lipid components
A. Having both cholesterol and phospholipids
B. Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
C. Having both protein and lipid components
B. Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
3
New cards
A phospholipid has a polar head group, a phosphate, and...
A. fatty acids
B. nucleic acids
C. amino acids
D. none of these
A. fatty acids
B. nucleic acids
C. amino acids
D. none of these
A. fatty acids
4
New cards
Proteins with hydrophobic regions that cross the cell membrane are called
A. cytoplasmic
B. GPI-anchored
C. integral
D. peripheral
A. cytoplasmic
B. GPI-anchored
C. integral
D. peripheral
C. integral
5
New cards
When cholesterol is added to the phosopholipid bilayer, the membrane...
A. does not change fluidity
B. becomes more fluid
C. becomes less fluid
A. does not change fluidity
B. becomes more fluid
C. becomes less fluid
C. becomes less fluid
6
New cards
A fatty acid tail with one or more double bonds is
A. Unsaturated
B. Saturated
A. Unsaturated
B. Saturated
A. Unsaturated
7
New cards
Active transport
A. Requires ATP
B. Moves molecules against their concentration gradient (low concentration to high concentration)
C. Moves molecules down their concentration gradient (from high concentration to low concentration)
D. A and B
E. A and C
A. Requires ATP
B. Moves molecules against their concentration gradient (low concentration to high concentration)
C. Moves molecules down their concentration gradient (from high concentration to low concentration)
D. A and B
E. A and C
D. A and B
8
New cards
The Na+/K+ (sodium-potassium) pump pumps _____ INTO the cell.
A. K+
B. Na+
C. ATP
D. ADP
A. K+
B. Na+
C. ATP
D. ADP
A. K+
9
New cards
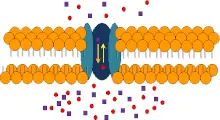
The following image is a representation of:
A. Osmosis
B. Symport
C. Uniport
D. Antiport
A. Osmosis
B. Symport
C. Uniport
D. Antiport
D. Antiport
10
New cards
A potassium channel is an example of
A. active transport
B. osmosis
C. facilitated diffusion
D. more than one of the above
A. active transport
B. osmosis
C. facilitated diffusion
D. more than one of the above
C. facilitated diffusion
11
New cards
In general, ion channels are...
A. Integral membrane proteins
B. Selective to certain ions
C. Gated
D. All of the above
A. Integral membrane proteins
B. Selective to certain ions
C. Gated
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
12
New cards
The Na+/K+ pump moves ___________________ of cells.
A. sodium in, potassium out
B. sodium out, potassium in
C. sodium and potassium in
D. sodium and potassium out
A. sodium in, potassium out
B. sodium out, potassium in
C. sodium and potassium in
D. sodium and potassium out
B. sodium out, potassium in
13
New cards
When comparing facilitated diffusion (F) and active transport (A)
A. F uses transmembrane proteins, A does not
B. F does not require energy input, A does
C. ATP is necessary for F, but not for A
D. both F and A move substances down their conc gradient
E. F can only move molecules out of cells, A can only move molecules in to cells
F. more than one of the above
A. F uses transmembrane proteins, A does not
B. F does not require energy input, A does
C. ATP is necessary for F, but not for A
D. both F and A move substances down their conc gradient
E. F can only move molecules out of cells, A can only move molecules in to cells
F. more than one of the above
B. F does not require energy input, A does
14
New cards
Ion channels located in blood vessels open or close in response to levels of CO2 (carbon dioxide) in the blood. These channels would be best described as
A. Ligand-gated (chemically gated) channels
B. Voltage gated channels
C. Leak channels
D. Mechanically gated channels
A. Ligand-gated (chemically gated) channels
B. Voltage gated channels
C. Leak channels
D. Mechanically gated channels
A. Ligand-gated (chemically gated) channels
15
New cards
Which ion contributes the most to the resting potential of the cell?
A. Ca2+
B. Na+
C. Cl-
D. K+
A. Ca2+
B. Na+
C. Cl-
D. K+
D. K+
16
New cards
At the start of the action potential, the neuron becomes more...
A. negative
B. positive
C. myelinated
D. axon
A. negative
B. positive
C. myelinated
D. axon
B. positive
17
New cards
For most neurons, the resting membrane potential is about ___ while the threshold is approximately ___
A. -70 mV, -50 mV
B. -70 mv, 0 mV
C.50 mV, 70 mV
D. -50 mV, -70 mV
A. -70 mV, -50 mV
B. -70 mv, 0 mV
C.50 mV, 70 mV
D. -50 mV, -70 mV
A. -70 mV, -50 mV
18
New cards
During an action potential, repolarization occurs due to the opening of....
A. voltage-gated Na+ channels
B. voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
C. voltage-gated K+ channels
D. K+ leak channels
A. voltage-gated Na+ channels
B. voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
C. voltage-gated K+ channels
D. K+ leak channels
C. voltage-gated K+ channels
19
New cards
The symptoms of pufferfish poisoning include
A. irregular heartbeat
B. numbness
C. paralysis
D. all of the above
A. irregular heartbeat
B. numbness
C. paralysis
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
20
New cards
TTX blocks
A. voltage-gated Na+ channels
B. voltage-gated K+ channels
C. K+ leak channels
D. the Na/K pump
A. voltage-gated Na+ channels
B. voltage-gated K+ channels
C. K+ leak channels
D. the Na/K pump
A. voltage-gated Na+ channels
21
New cards
The action potential flows toward the nerve/axon terminal because
A. The Na+ gradient is depleted behind the AP
B. The Na+/K+ pump is inactivated behind the AP
C. The voltage-gated Na+ channels are in their refractory period (inactivated) behind the AP
D. This is nonsense; APs always go in both directions
A. The Na+ gradient is depleted behind the AP
B. The Na+/K+ pump is inactivated behind the AP
C. The voltage-gated Na+ channels are in their refractory period (inactivated) behind the AP
D. This is nonsense; APs always go in both directions
C. The voltage-gated Na+ channels are in their refractory period (inactivated) behind the AP
22
New cards
During an action potential, the membrane depolarizes when ________ open and ions move _________ the cell
A. voltage gated K+ channels; out of
B. voltage-gated Na+ channels; into
C. voltage-gated Na+ channels; out of
D. voltage-gated K+ channels; into
A. voltage gated K+ channels; out of
B. voltage-gated Na+ channels; into
C. voltage-gated Na+ channels; out of
D. voltage-gated K+ channels; into
B. voltage-gated Na+ channels; into
23
New cards
An inhibitory neurotransmitter...
A. makes an action potential less likely
B. hyperpolarizes the neuron
C. causes an action potential
D. All of the above
E. A and B
F. B and C
A. makes an action potential less likely
B. hyperpolarizes the neuron
C. causes an action potential
D. All of the above
E. A and B
F. B and C
E. A and B
24
New cards
The fusion of synaptic vesicles with the cell membrane in the synaptic terminal is triggered by a rise in the concentration of which ion?
A. Ca2+
B. Na+
C. K+
D. Cl-
A. Ca2+
B. Na+
C. K+
D. Cl-
A. Ca2+
25
New cards
A drug inhibits voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. This drug would
A. not affect the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
B. increase the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
C. decrease the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
D. increase the likelihood of an action potential
A. not affect the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
B. increase the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
C. decrease the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
D. increase the likelihood of an action potential
C. decrease the release of neurotransmitter from the neuron
26
New cards
A neurotransmitter opens K+ channels on the postsynaptic membrane. The neuron becomes
A. hyperpolarized (more negative)
B. depolarized (more positive)
C. the charge doesn't change
D. more likely to have an action potential
A. hyperpolarized (more negative)
B. depolarized (more positive)
C. the charge doesn't change
D. more likely to have an action potential
A. hyperpolarized (more negative)
27
New cards
In the paper by Geffeney et al that you read for today
A. The newts are prey
B. The newts are predators
C. The snakes are prey
D. The snakes are predators
E. A and D are correct
F. B and C are correct
A. The newts are prey
B. The newts are predators
C. The snakes are prey
D. The snakes are predators
E. A and D are correct
F. B and C are correct
E. A and D are correct
28
New cards
Garter snakes that eat newts containing TTX may be resistant to TTX because they have
A. TTX-resistant sodium channels
B. TTX-resistant potassium channels
C. elaborate ways of only eating TTX-free tissue
D. pumps in the plasma membrane of their cells that actively pump TTX out of their cells
A. TTX-resistant sodium channels
B. TTX-resistant potassium channels
C. elaborate ways of only eating TTX-free tissue
D. pumps in the plasma membrane of their cells that actively pump TTX out of their cells
A. TTX-resistant sodium channels