Earth and space regents prep
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
The three plane boundaries
Divergent plate boundary
Convergent plate boundary
Transform plate boundary
What is divergent plate boundary
Where the plates move away from each other
what is the convergent plate boundary
Where plates collide and one slides underneath the other
What is transform plate boundary
Where the plates slide past each other
What makes up the lithosphere
The mantle and crust
What is ridge push
During sea floor spreading where the new crust pushes away the old crust from the ridge
What is slab pull
When the subduction of the plates make one sink underneath the astheonosphere and as the edge of the plate sinks, it brings the whole plate along with it.
What is subduction
When a plate sinks underneath the asthenosphere
What happens wen high density materials are mixed with low density materials
The high density materials sink while the low density materials float to the top.
What is high density
When something has more compact molecules
what is low density
When something has less compact molecules.
how do p and S waves differ in there movement and the materials they travel through? How does this effect their movement through the earths layers
P waves go through solids, liquids, and gases while S waves only go through solids and p waves also move faster then S waves. P waves can go through all the layers of earth while S waves stops before hitting the outer layer.
How does the density of earths materials effect there position sit in earth?
The less materials would float on top like earths crust and mantle while the more denser materials would sink to the bottom like the core of the earth.
How does an oceanic-continental convergent boundary create volcanos?
When the oceanic plate sinks underneath the asthenosphere, the heat and pressure rises and the water mix’s with the rock. The melted rock then rises and erupts.
What type of plate boundary is most commonly associated with deep ocean trenches?
Convergent
In which earths layer does convection occur?
Earths mantle
Describe two pieces of evidence that support the theory of sea floor spreading?
During sea floor spreading, the new crust pushes old crust away from the ridge. North and South are reversed, which is called magnetic patterns. Magnetic patterns on one side of a mid ocean ridge match’s with the other side.
Convection
Warm less dense materials rise and cold more dense materials sink
How does convection inside the earth drive the movement of tectonic plates?
In the mantle, underneath the mid ocean ridges hot magma rises which creates new crust that pushes old crust away. The colder crust moves away from the ridge and subducts back into the mantle as an ocean trench.
How are oceanic plates different from continental plates
Oceanic are thinner and more dense.
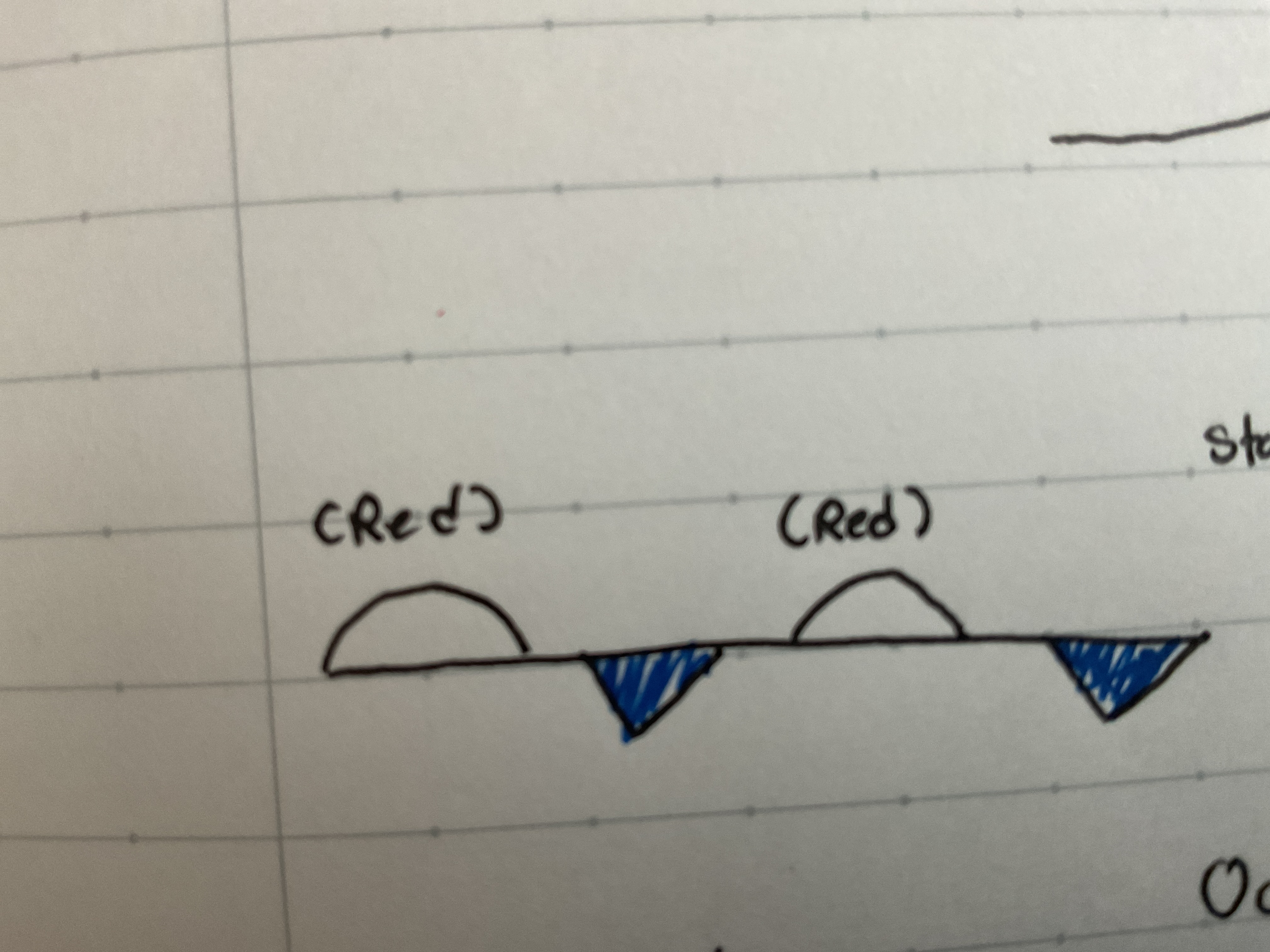
Cold front
When a cold air mass moved into warm air mass pushing it up. Creates rain.
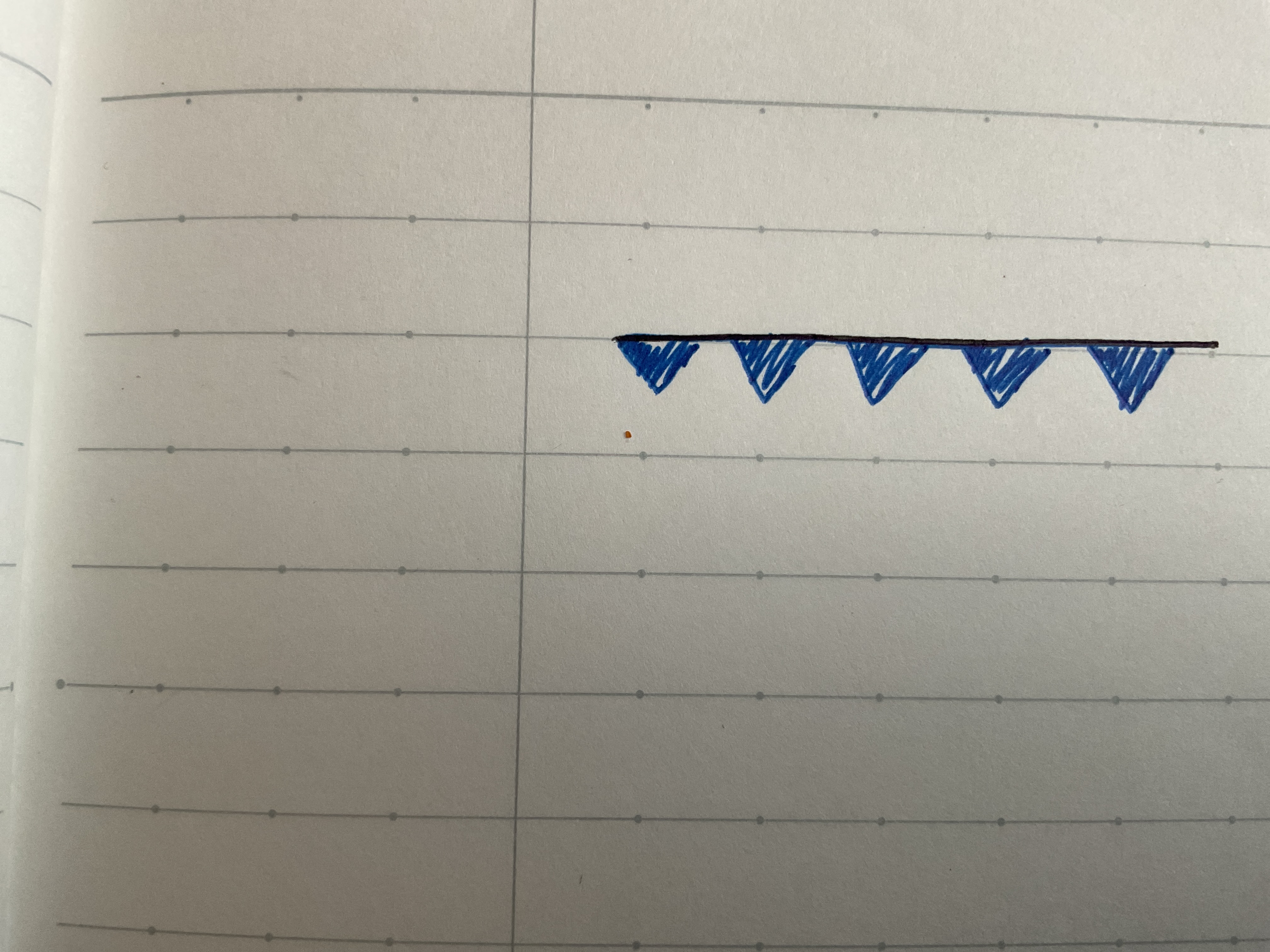

Warm front
Warm air mass overtakes a cold air mass and rises up
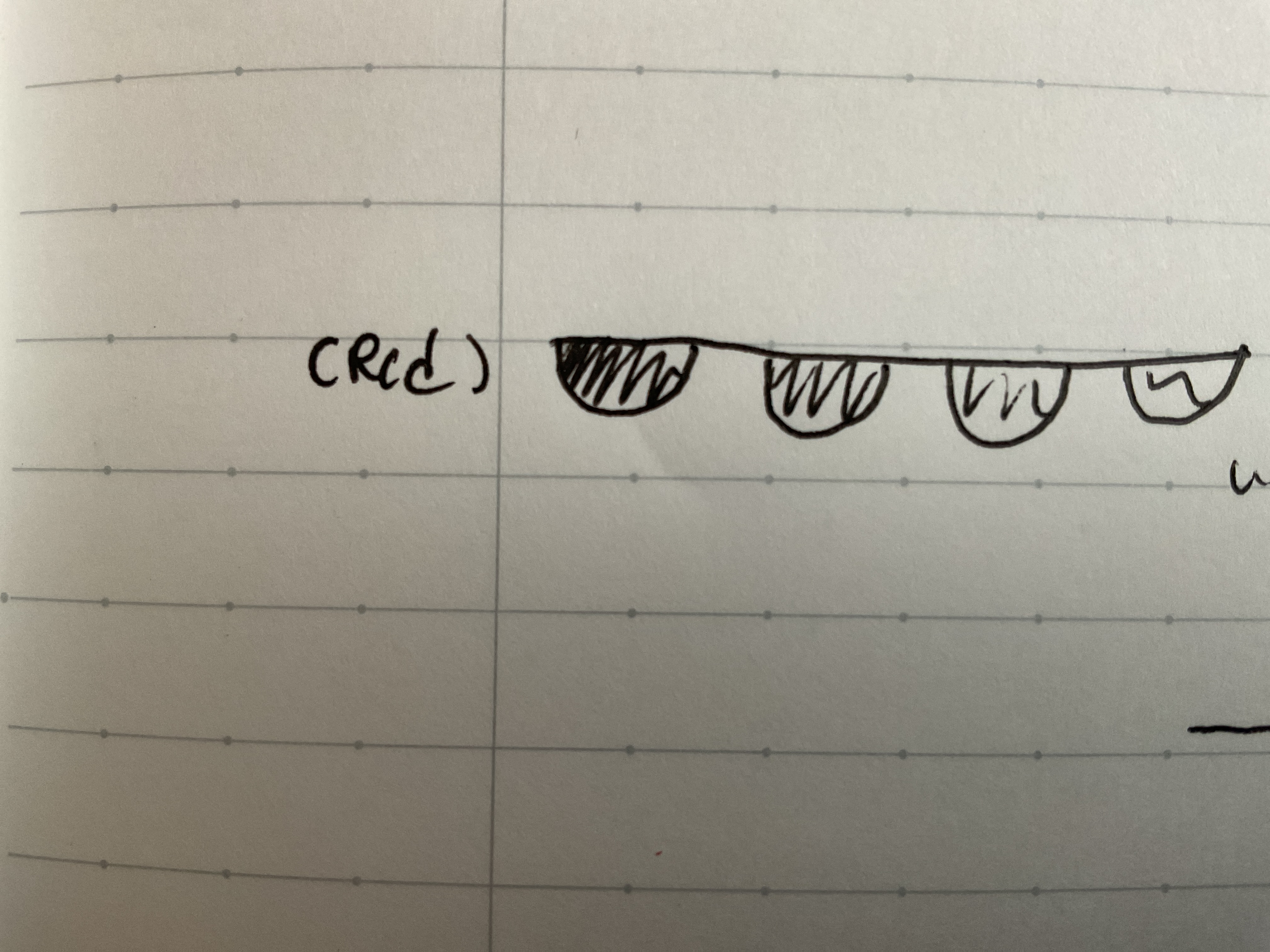
Stationary front
Warm and cold air mass meet but don’t push
Occluded front
When a air mass separates from the ground.
Air mass
Large body of air with the same temperature and humidity
Prevailing winds
Wind that blows consistently in the direction over a certain region.
Weather front
Boundary between 2 air masses
Air masses
Hot & dry
Hot & wet
Cold & dry
Cold & wet
Warm air masses
Near the equator
Cold air masses
Far from equator
Dry
Over land
Wet
Over water
Minerals must be..
solid
Inorganic
Naturally occurring
Definite chemical composition
Unique crystalline structure
Minerals can be identified by..
color (not reliable)
Hardness (1-10)
Luster (metallic, nonmetallic)
Streak (color as powder)
Cleavage/fracture (how it breaks)
Other (taste,smell,magnetism)
Cleavage
Breaks in a more predictable manner
Fracture
Breaks randomly
Three types of rocks…
-igneous rocks
-Metamorphic rock
-sedimentary rock
Igneous rocks
Formed as a result of the cooling and solidification of magma or lava
Metamorphic rocks
Formed as a result of exposure to intense heat and/or pressure
Sedimentary rocks
Formed as a result of compaction and cementation of sediments.
Weathering
Breaking down and changing of rocks as a result of exposure to environment
Erosion
The movement of sediments that have been broken down by weathering
Deposition
Dropping off of sediments that have been eroded and weathered
Physical weathering
Breakdown of rocks into sediments without changing their composition
Chemical weathering
The altering of rocks due to a result of exposure of different substances
Albedo
The reflectivity of a surface; High albedo surfaces reflects more sunlight
Dark objects…
Low albedo
Light objects
High albedo