NSCI 2101 Exam 1
1/246
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
247 Terms
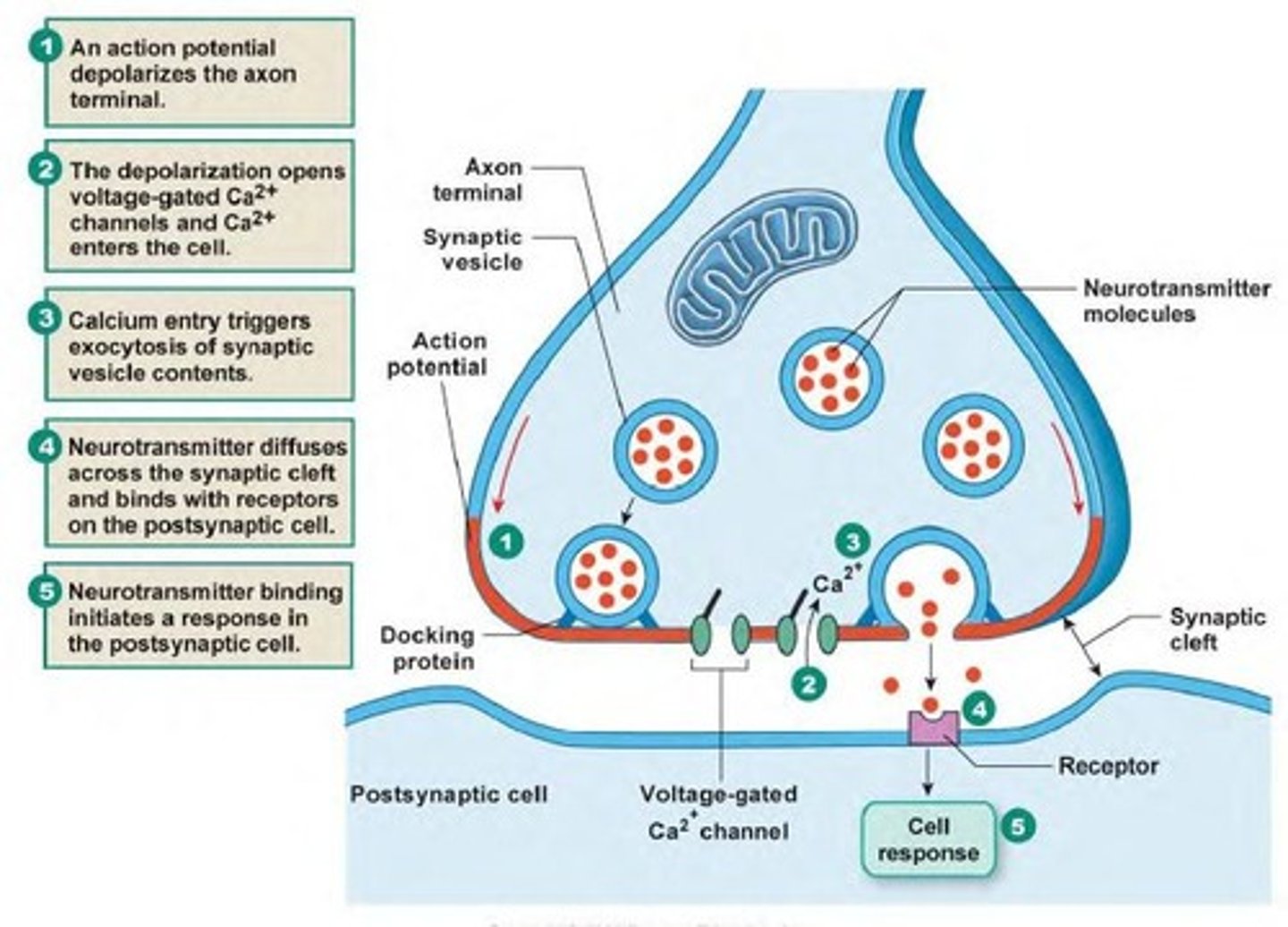
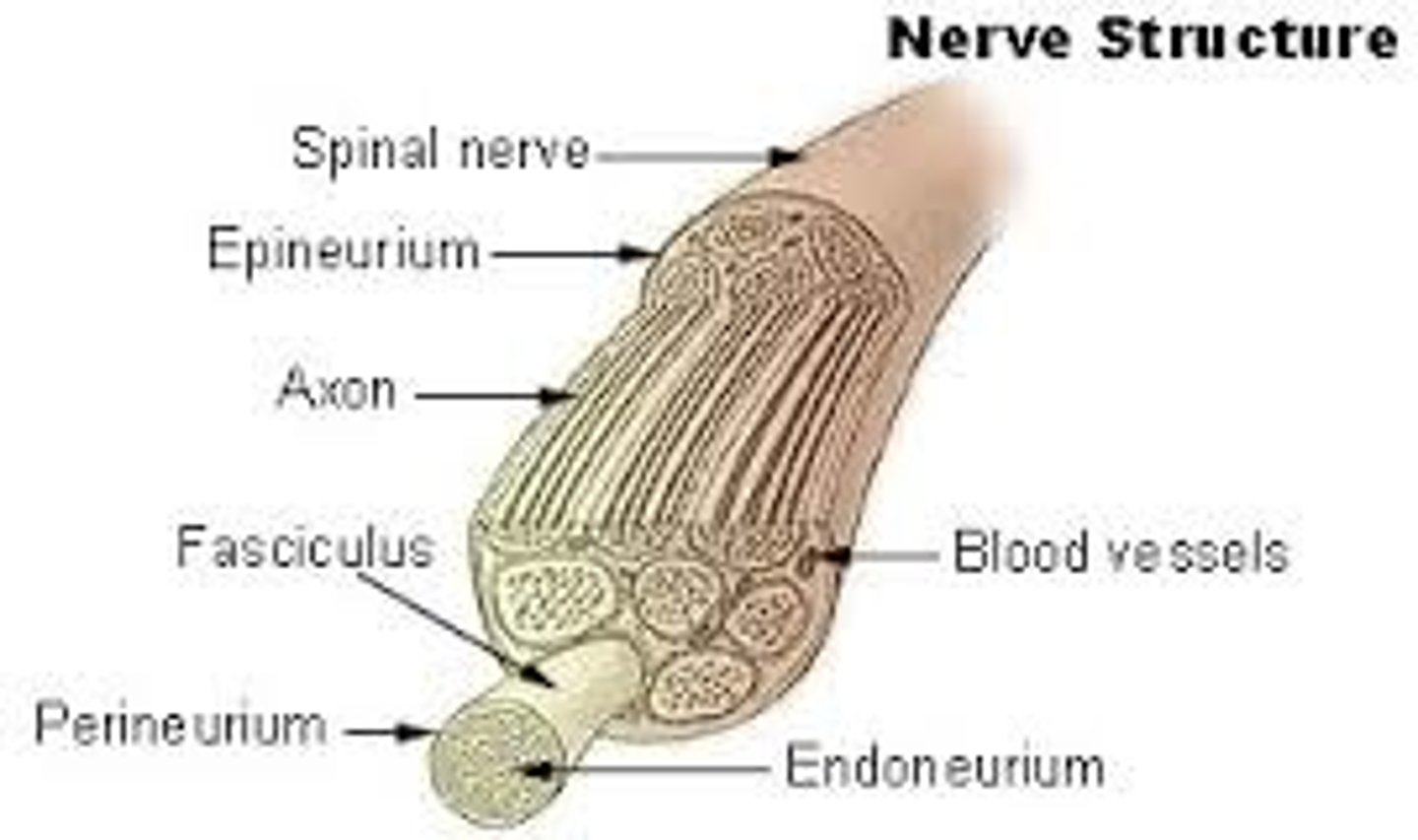
Axon ("nerve fibers")
- carry nerve impulse (action potential)
- Myelin speeds up conduction
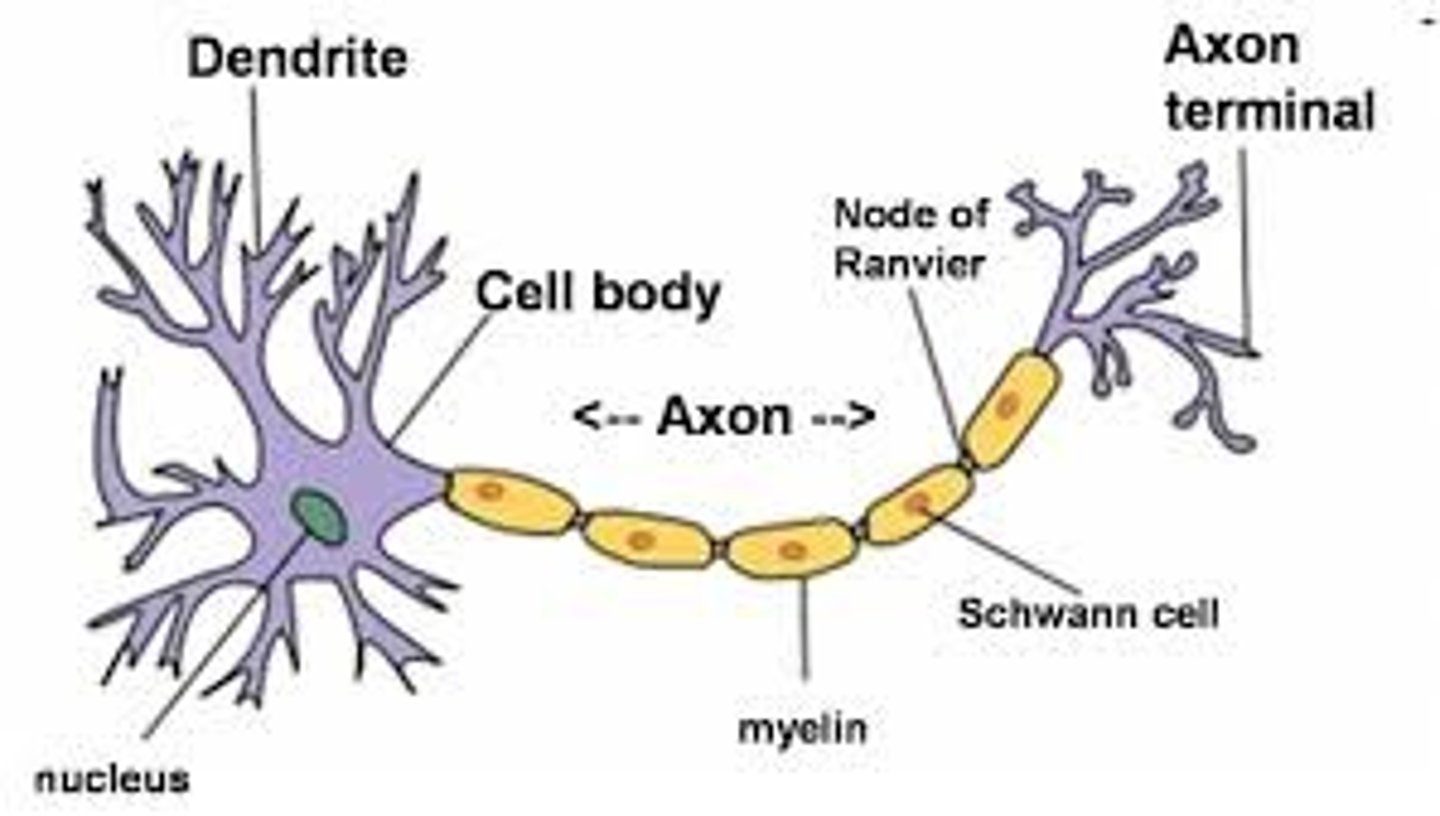
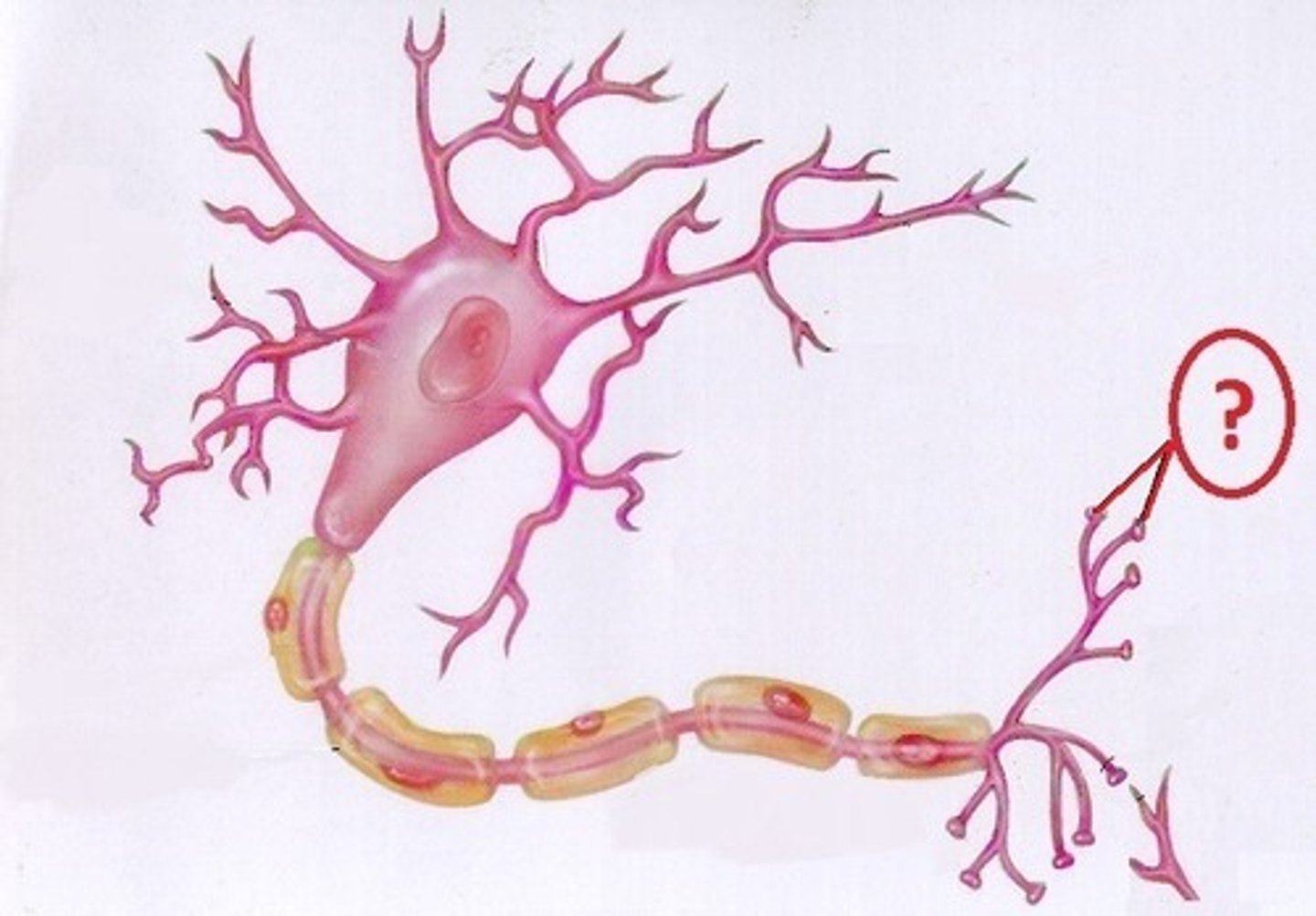
axon terminal
release neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft and onto other neurons at synapse.
dendrites
- receive synapses from axon terminal
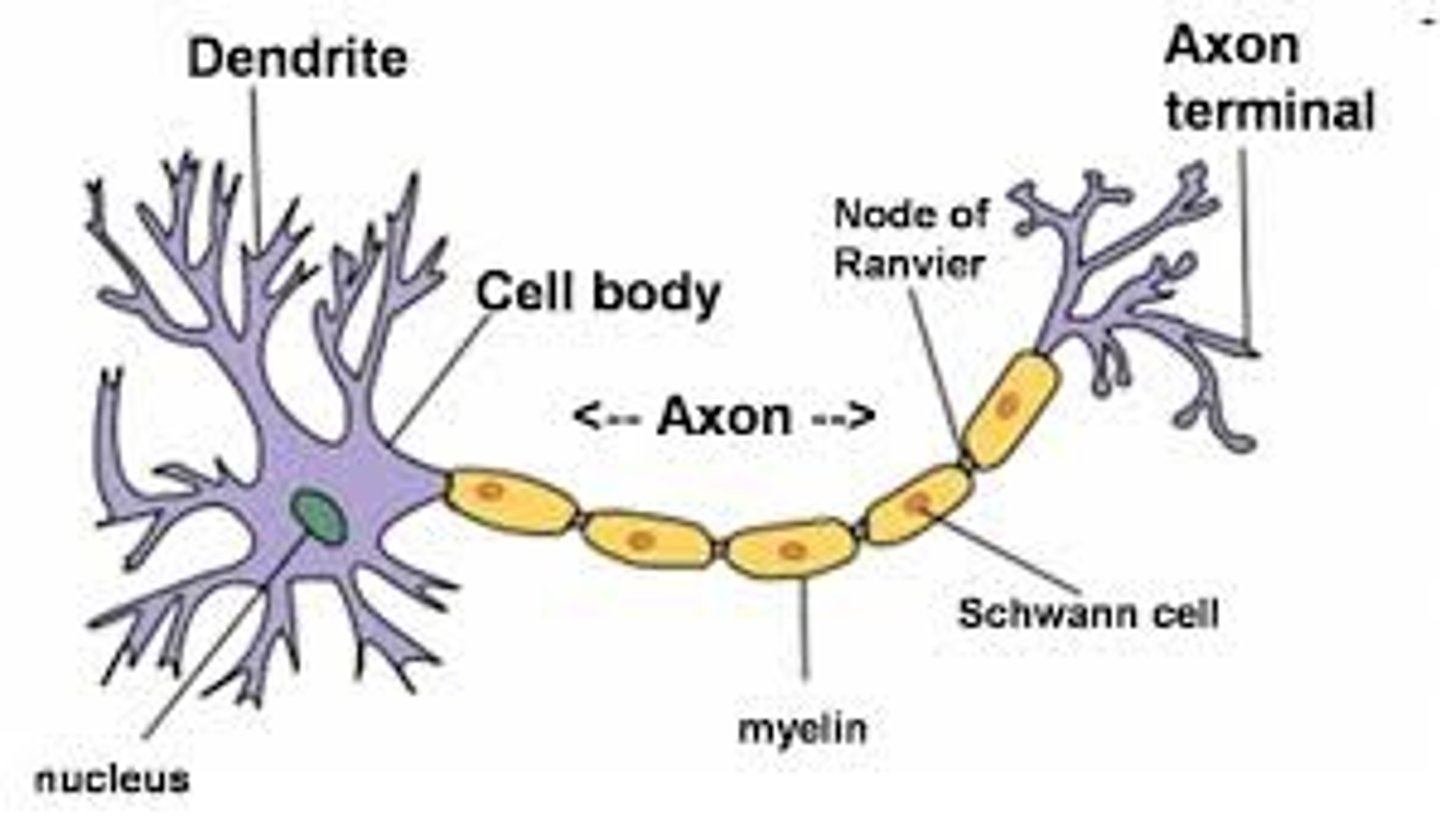
Synaptic Cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
Cerebral cortex
- sparse branching dendrites
- emerge from apex and base of cell soma
Cerebellar cortex
- extensive branching
- emerging only from peripheral half of cell
cell
-surrounded by cell membrane (lipid bilayer)
-require metabolic energy
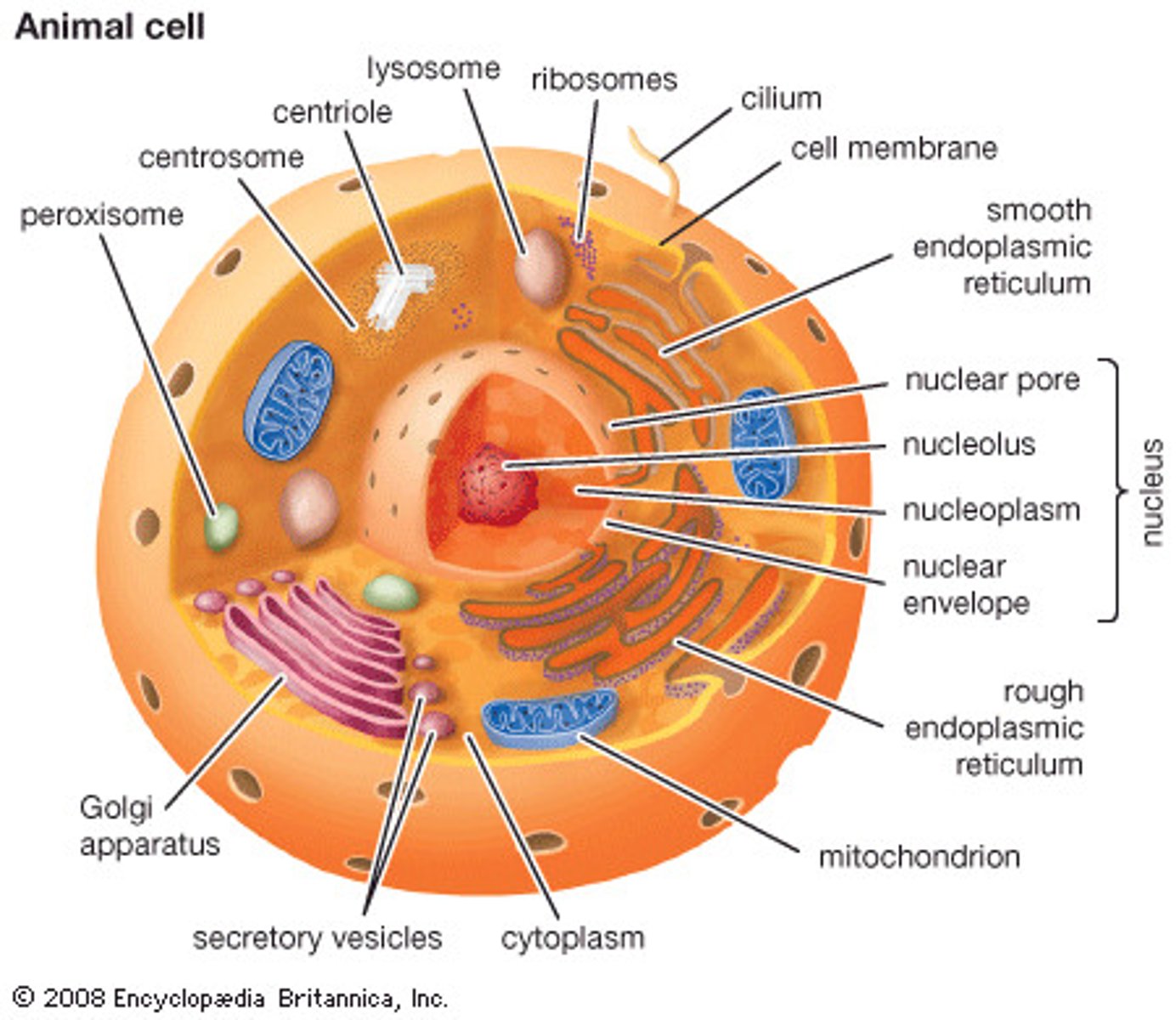
types of cells in the nervous system
neurons and glial cells
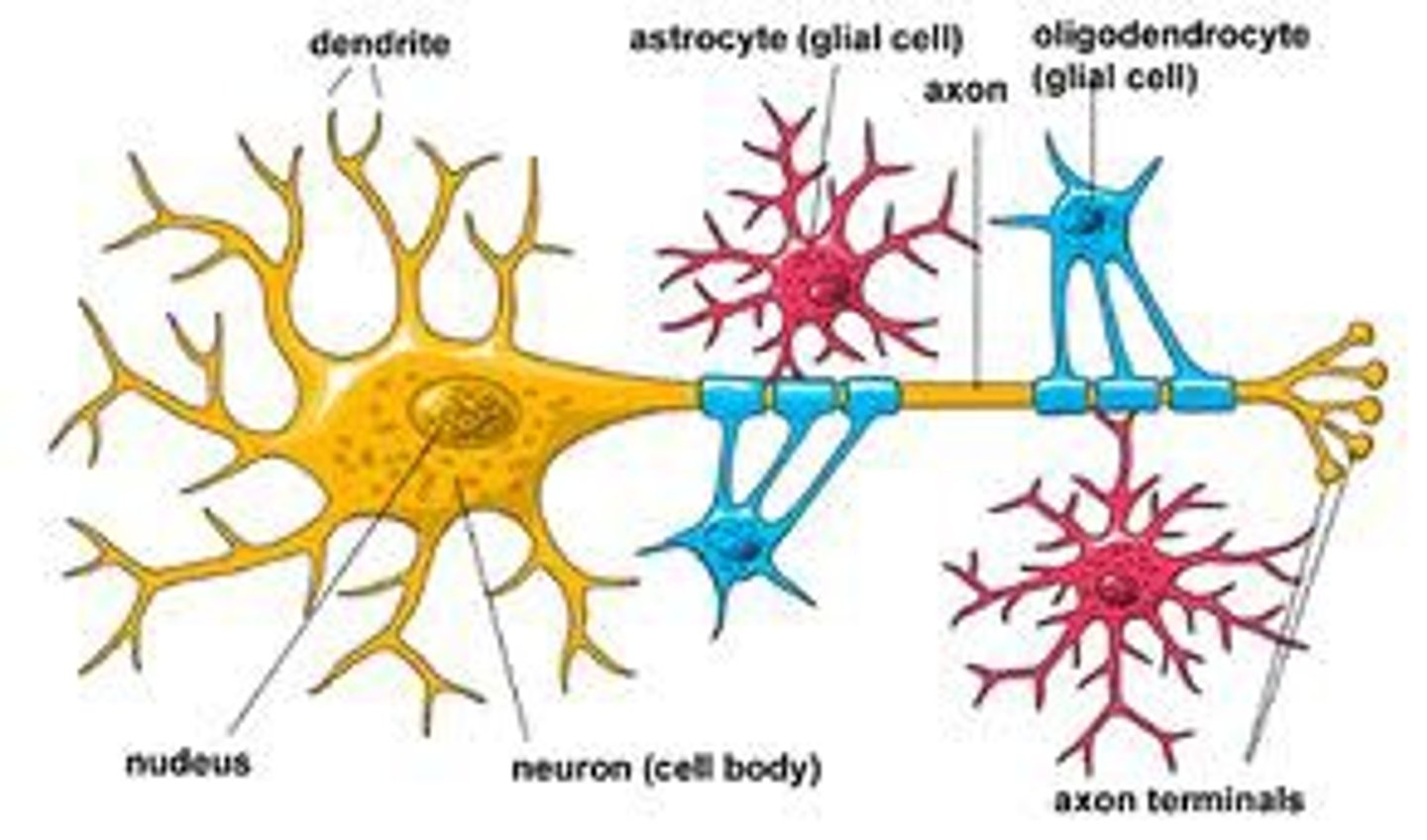
parts of neuron
cell body, axon, axon terminal, myelin sheath, dendrites
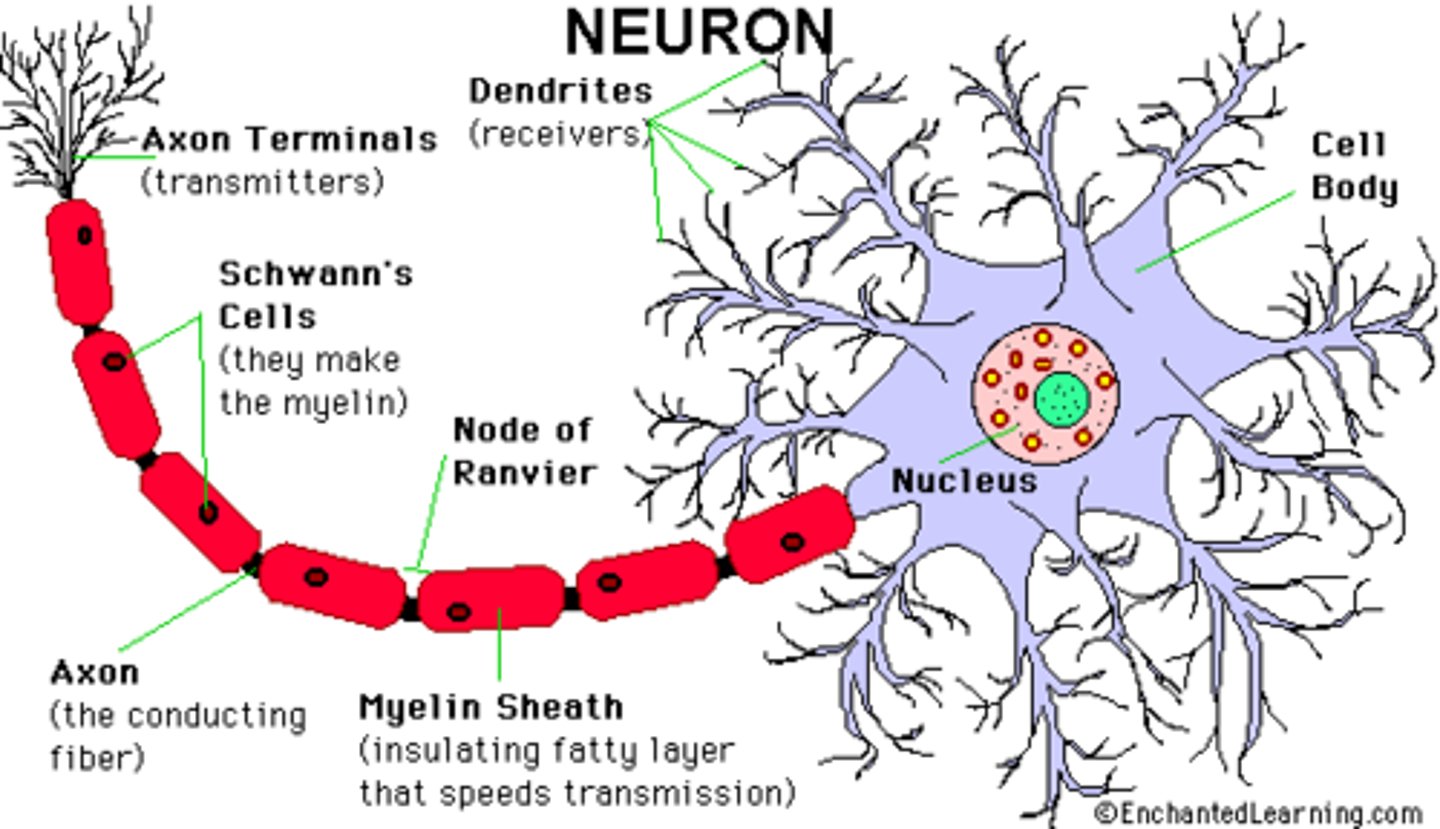
cell soma
-contains nucleus
- synthesizes macromolecules/organelles
- integrate electrical activity
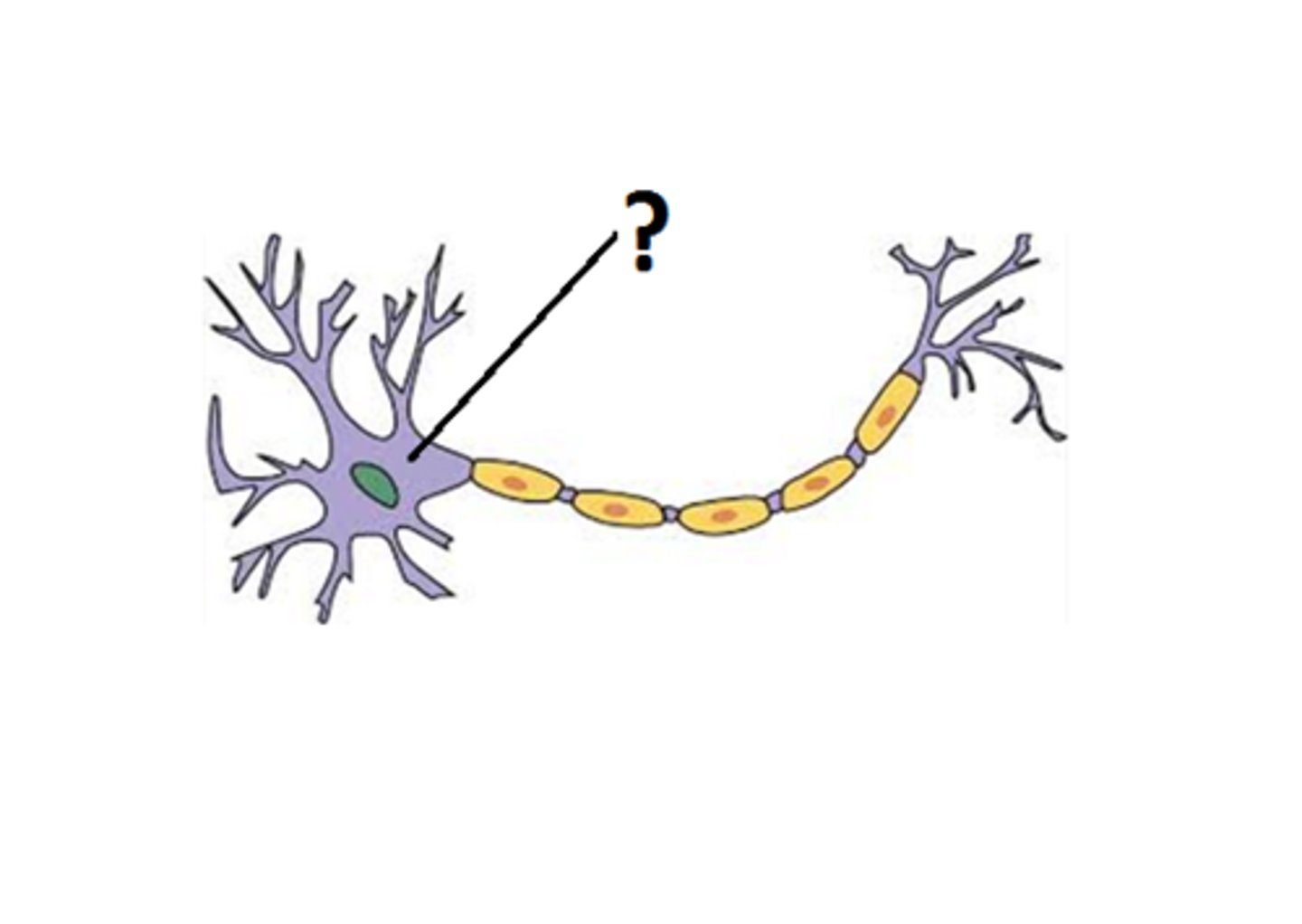
Types of Glia cells
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependyma
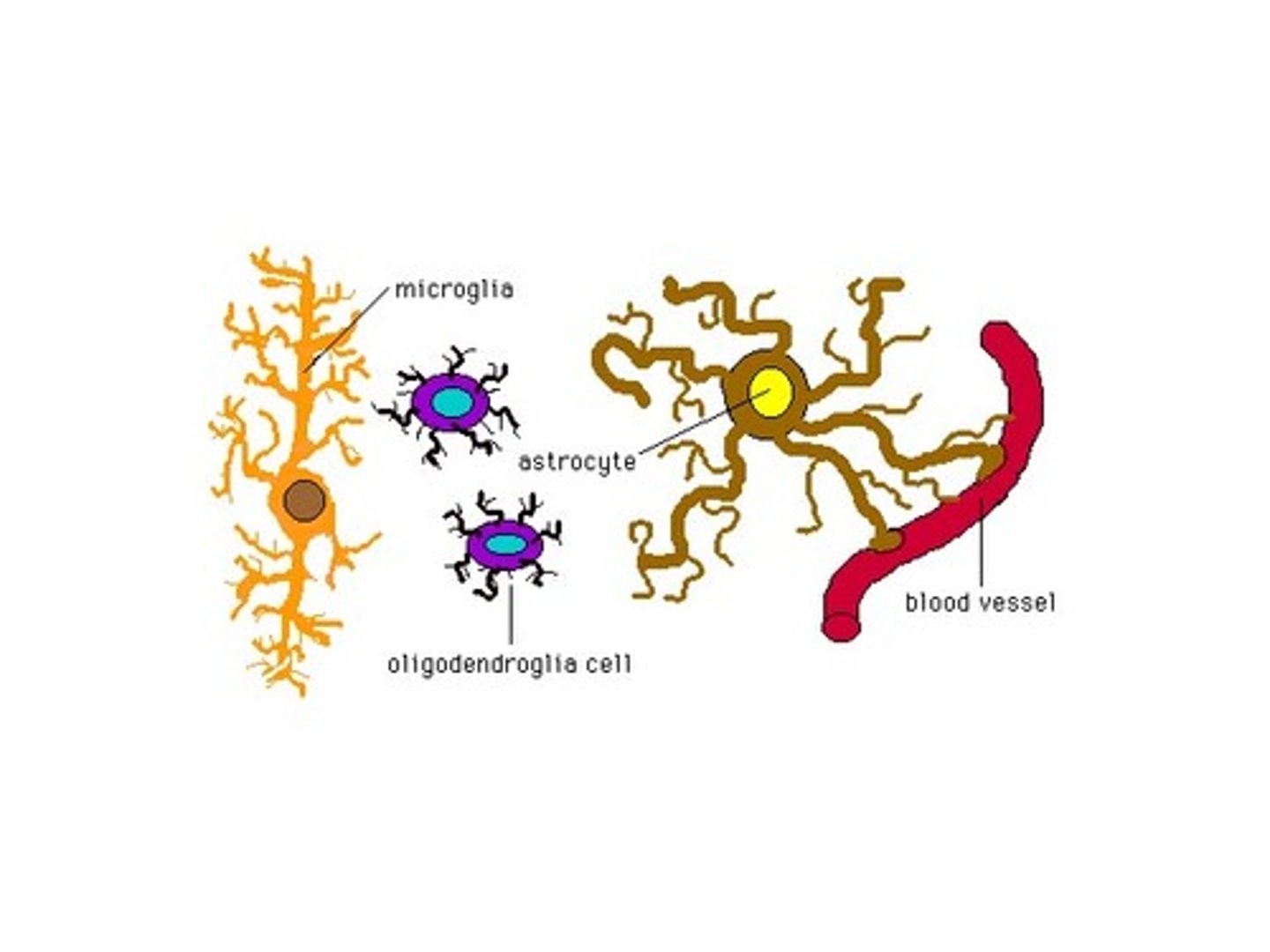
function of glia
- slow, local modulation (not rapid or over long distances)
- create myelin around axon
- scavenge dead cells
- line ventricles
(NO AXONS = SLOW) Glia have no axons
Division of the nervous system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
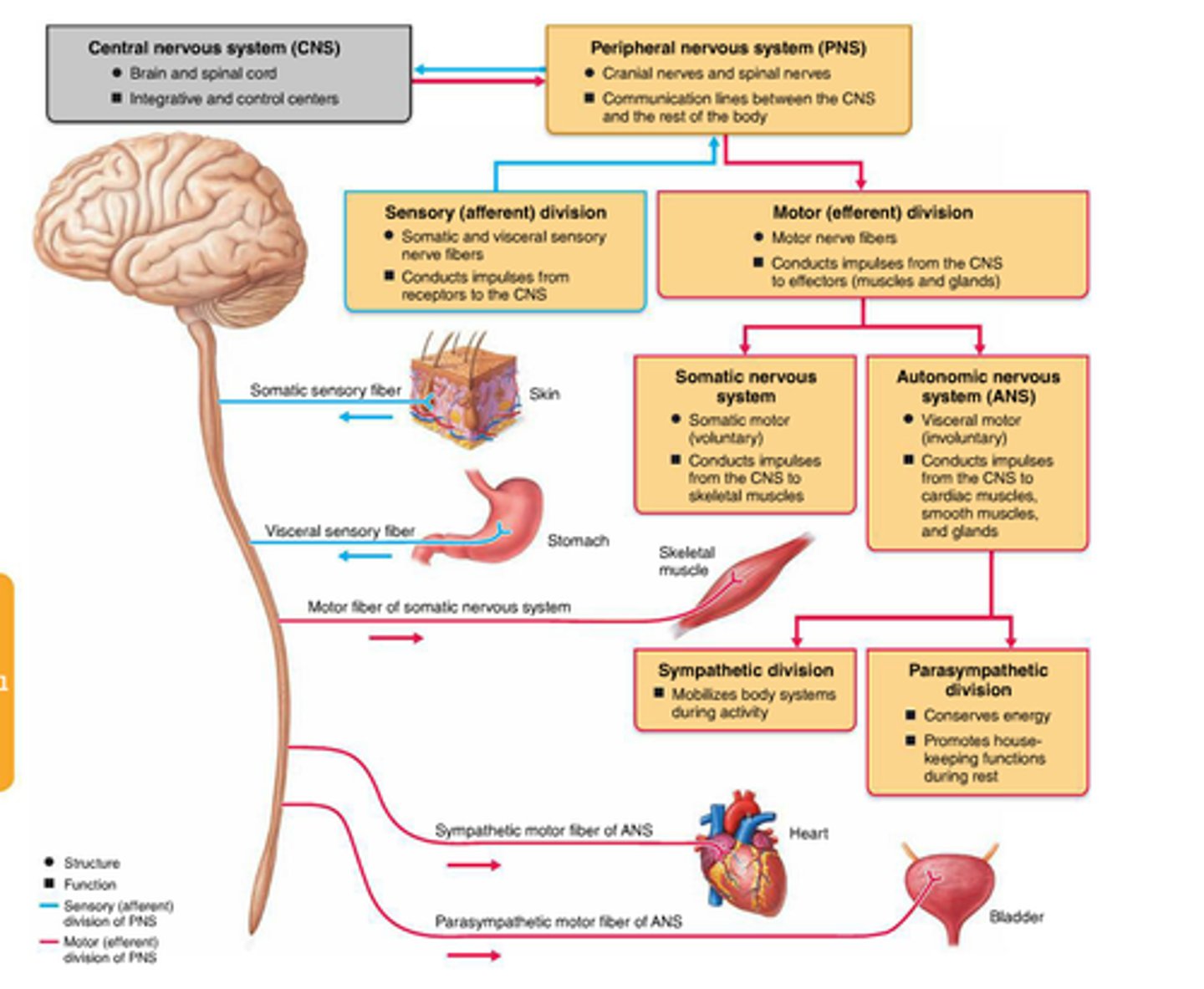
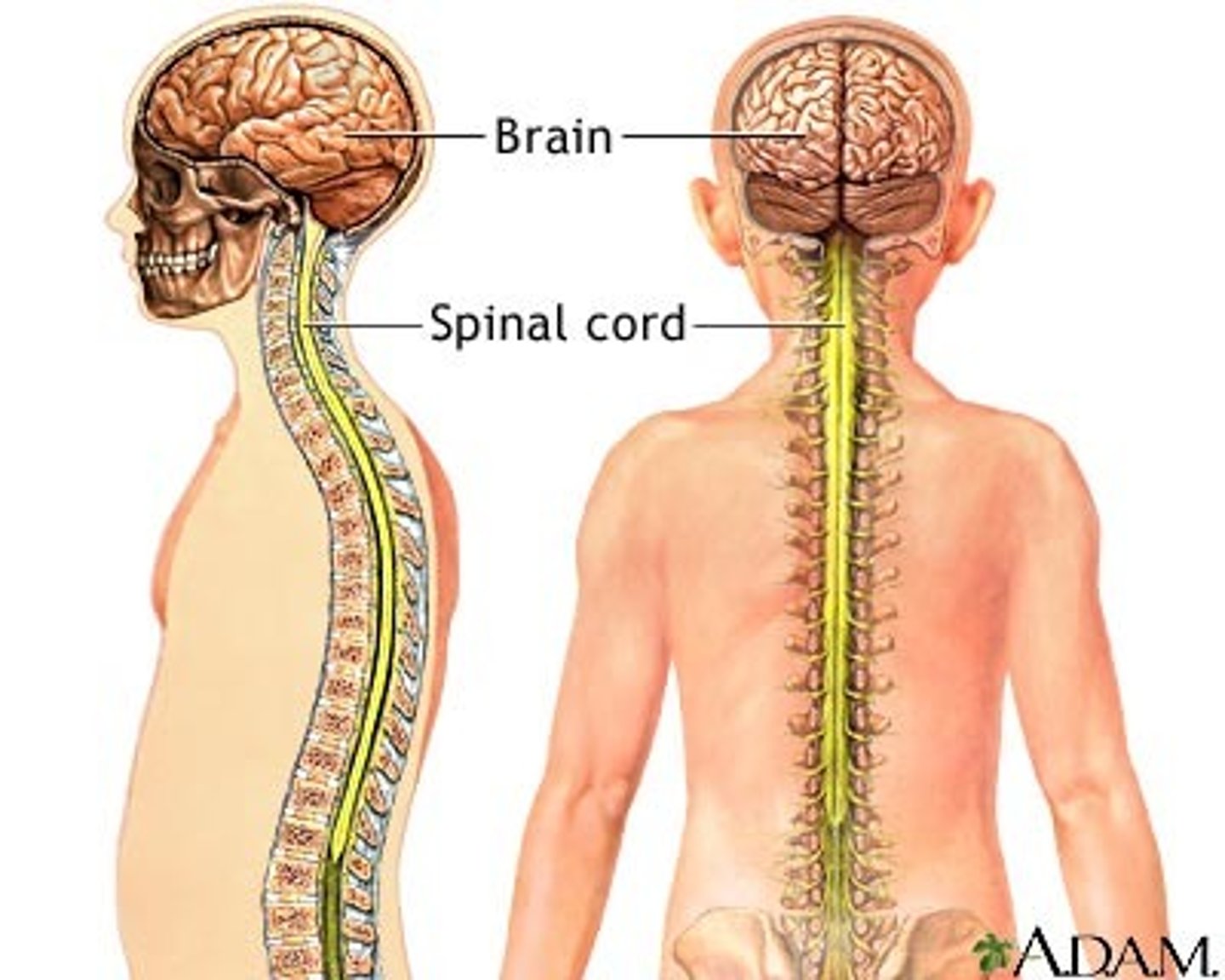
Central nervous system
Brain, spine
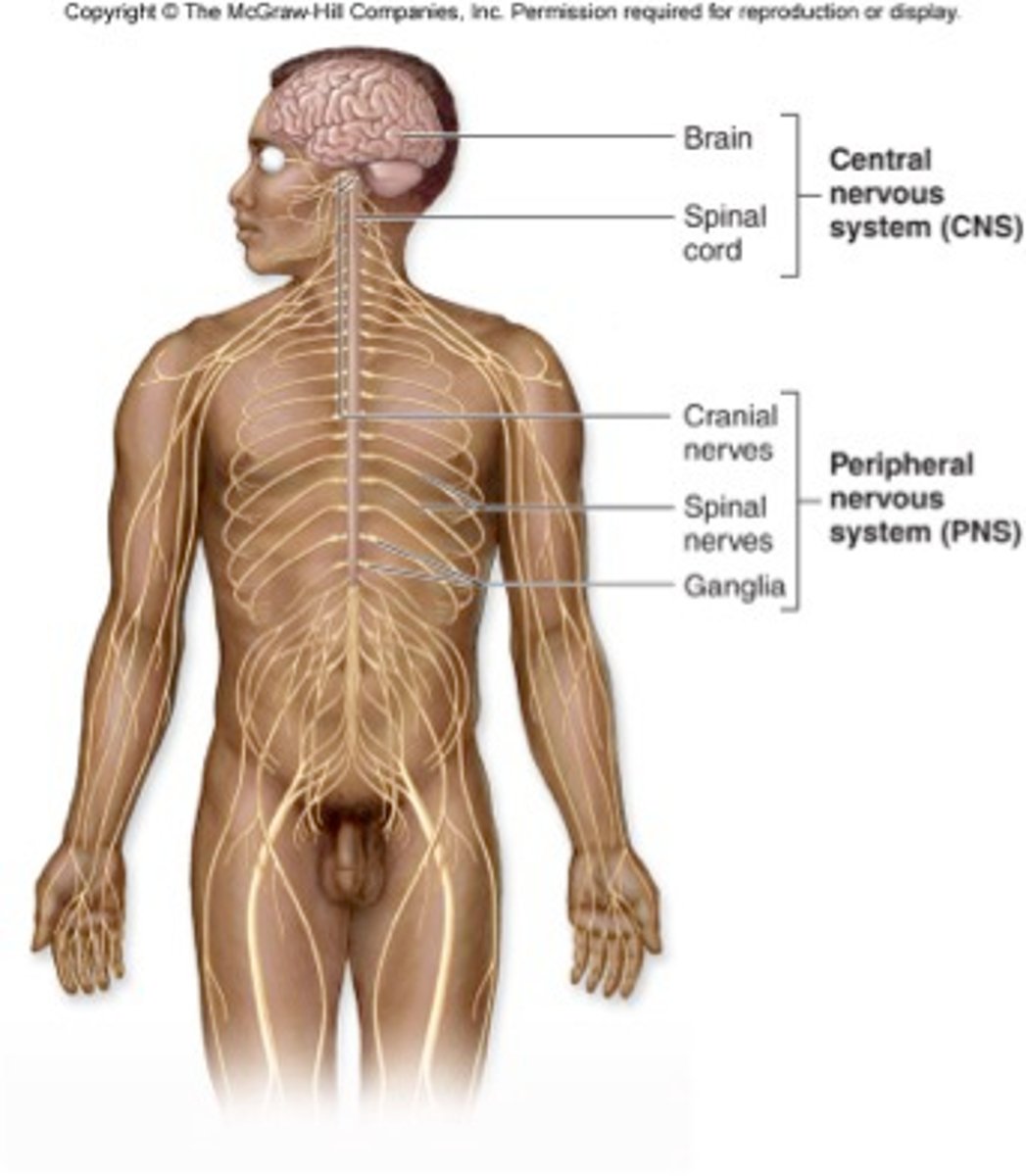
peripheral nervous system
-sensory neurons (from skin, bone, viscera to CNS0
-Motoneurons (from CNS to muscle)
Division of the Peripheral Nervous System
somatic (sensory/moto), autonomic
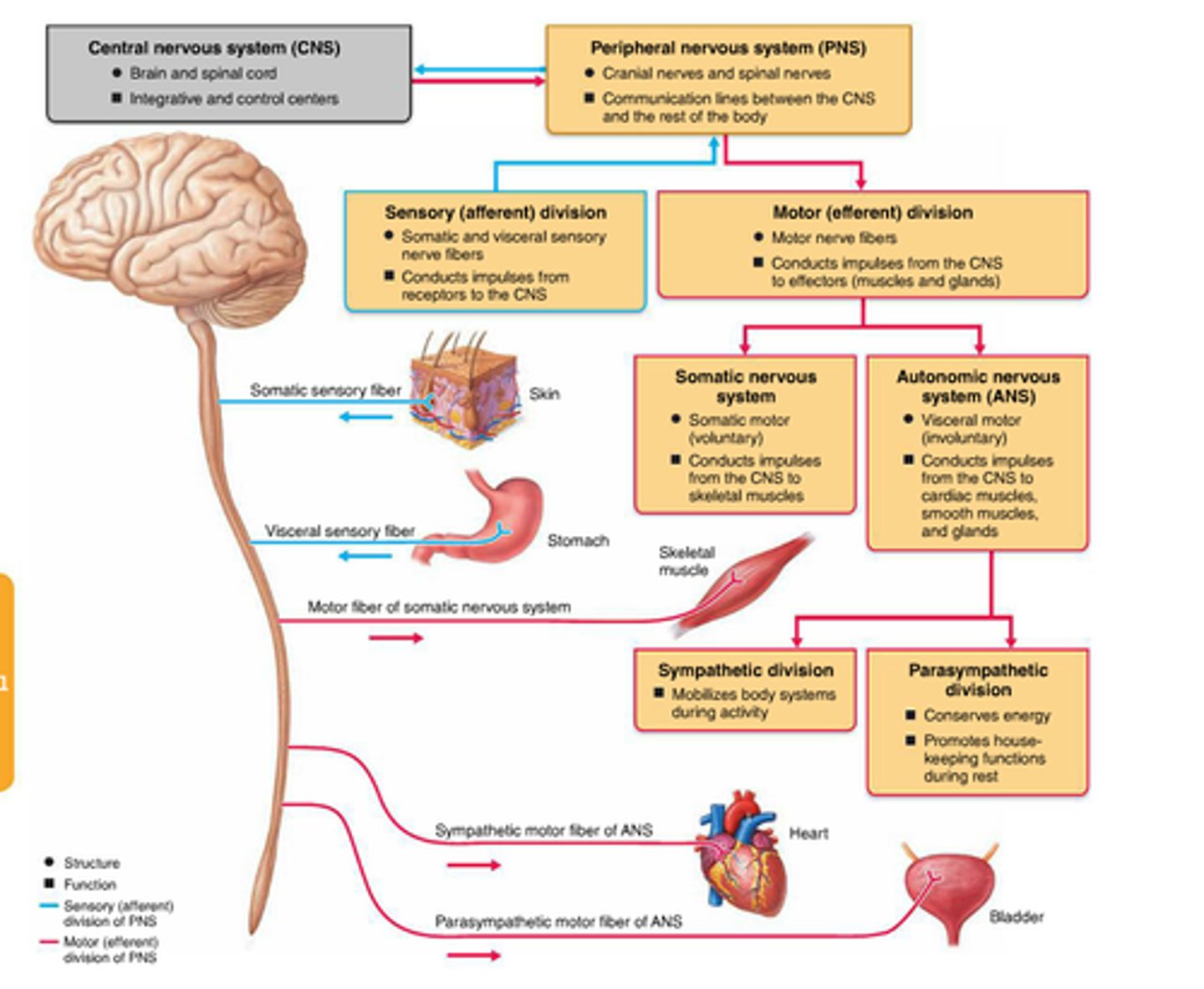
autonomic nervous system
controls vasculature and viscera
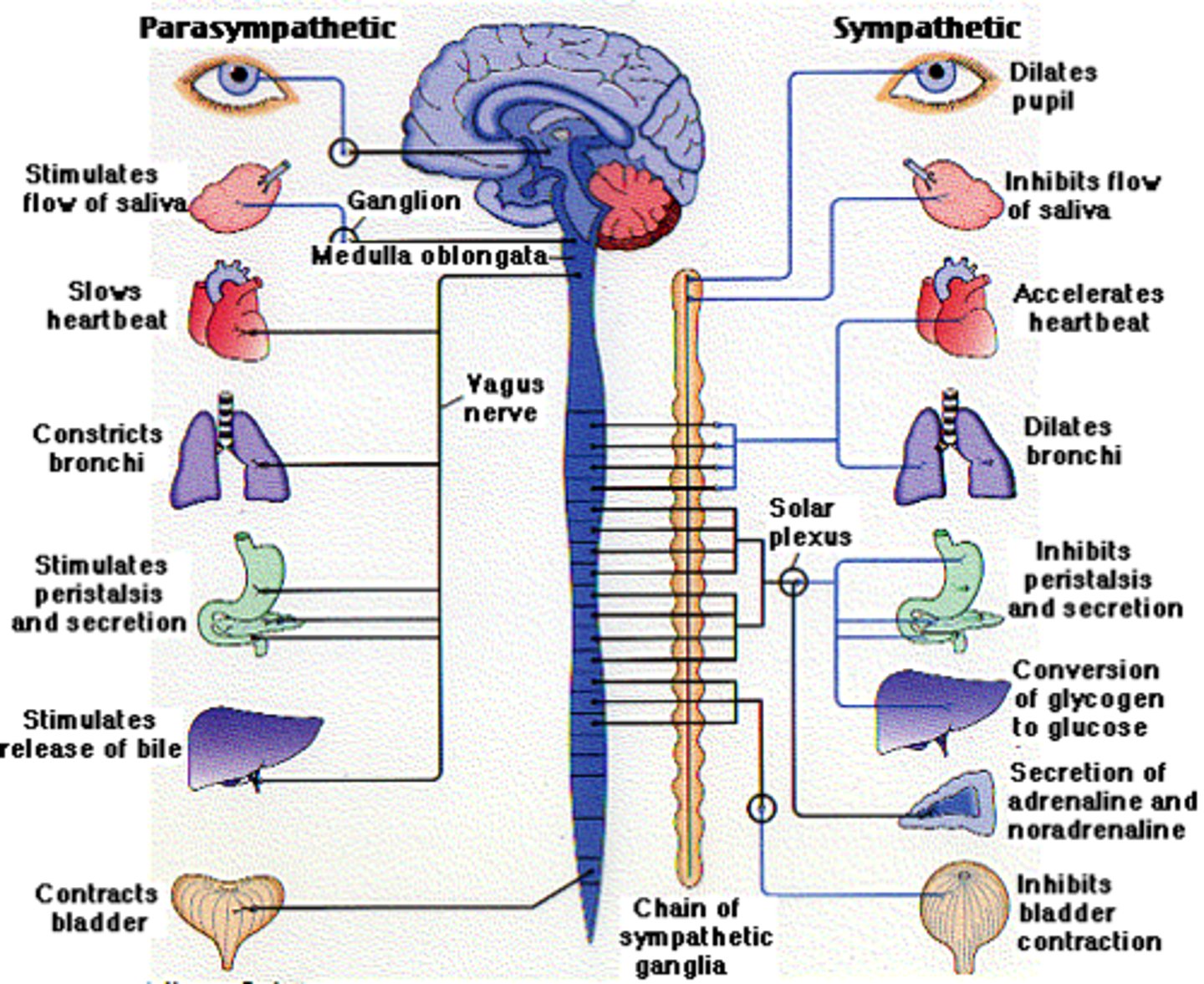
Division of autonomic nervous system
sympathetic and parasympathetic, enteric
sympathetic nervous system
"fight or flight" - arises from thoracic spinal cord
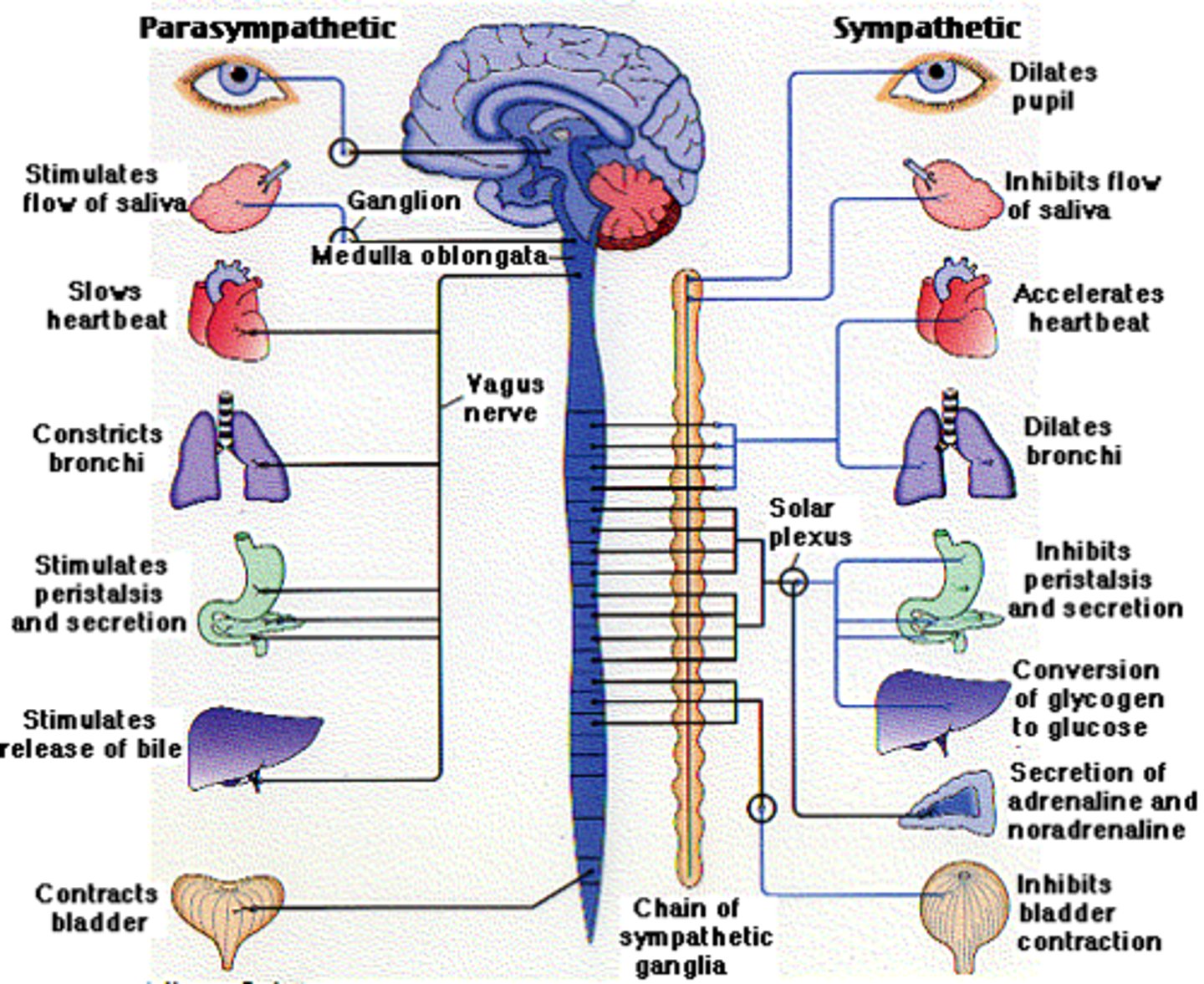
parasympathetic nervous system
"rest and digest" - arises from brain or sacral spinal cord
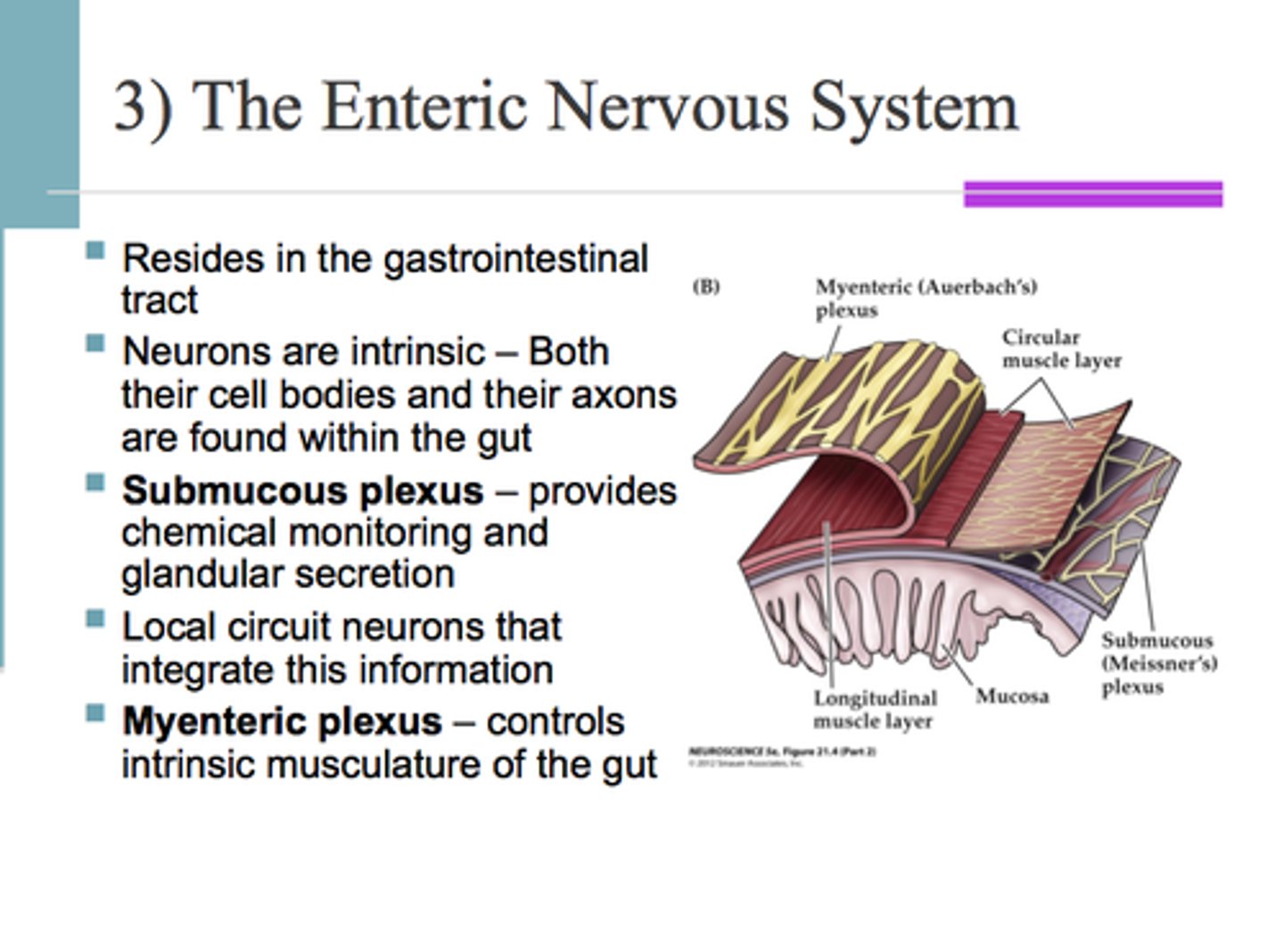
enteric nervous system
secretions and motility of the gut (as many neurons as spinal cord)
tract
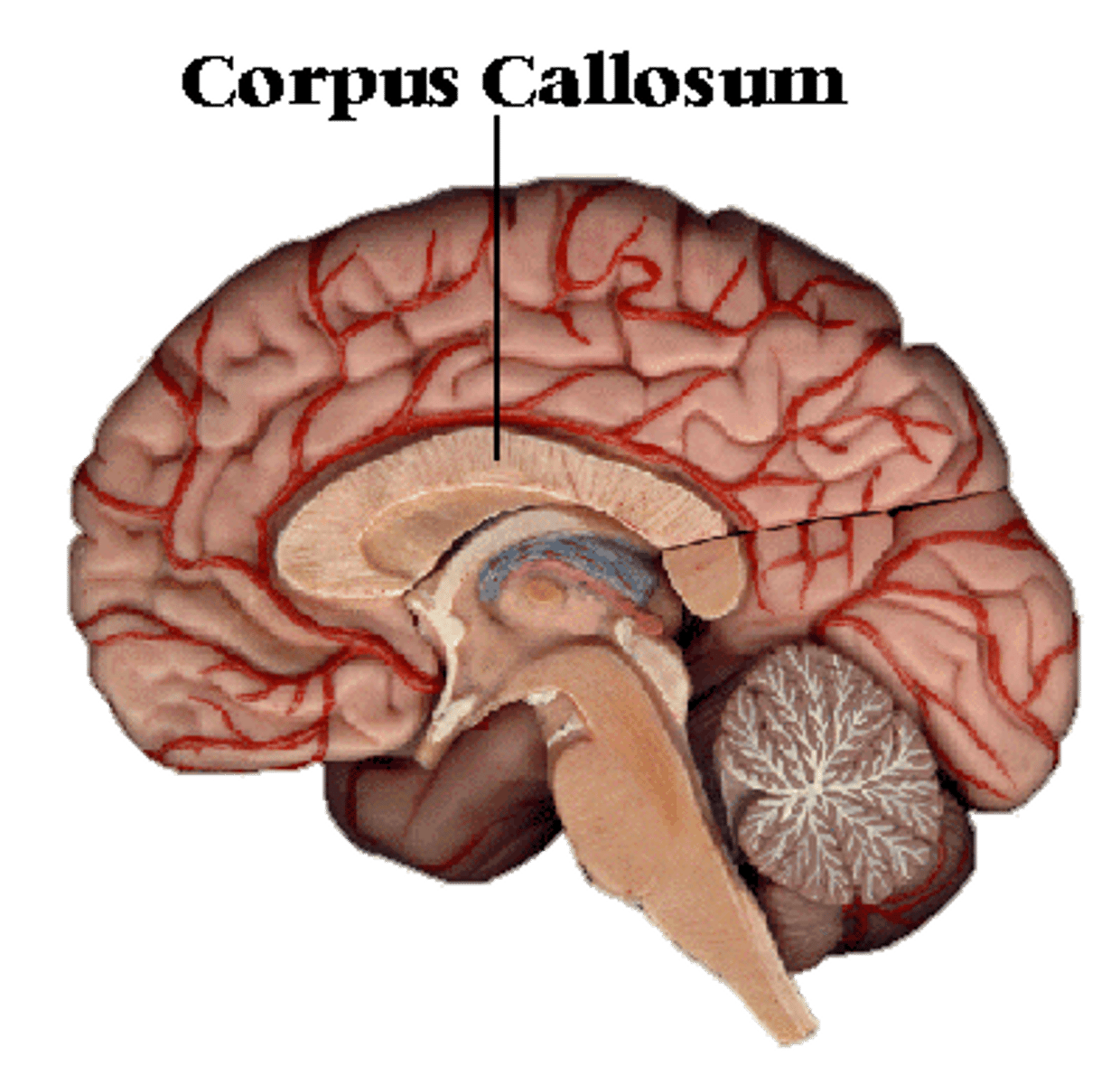
bundle fibers of axon (cns) example is corpus callosum.
Nuclei
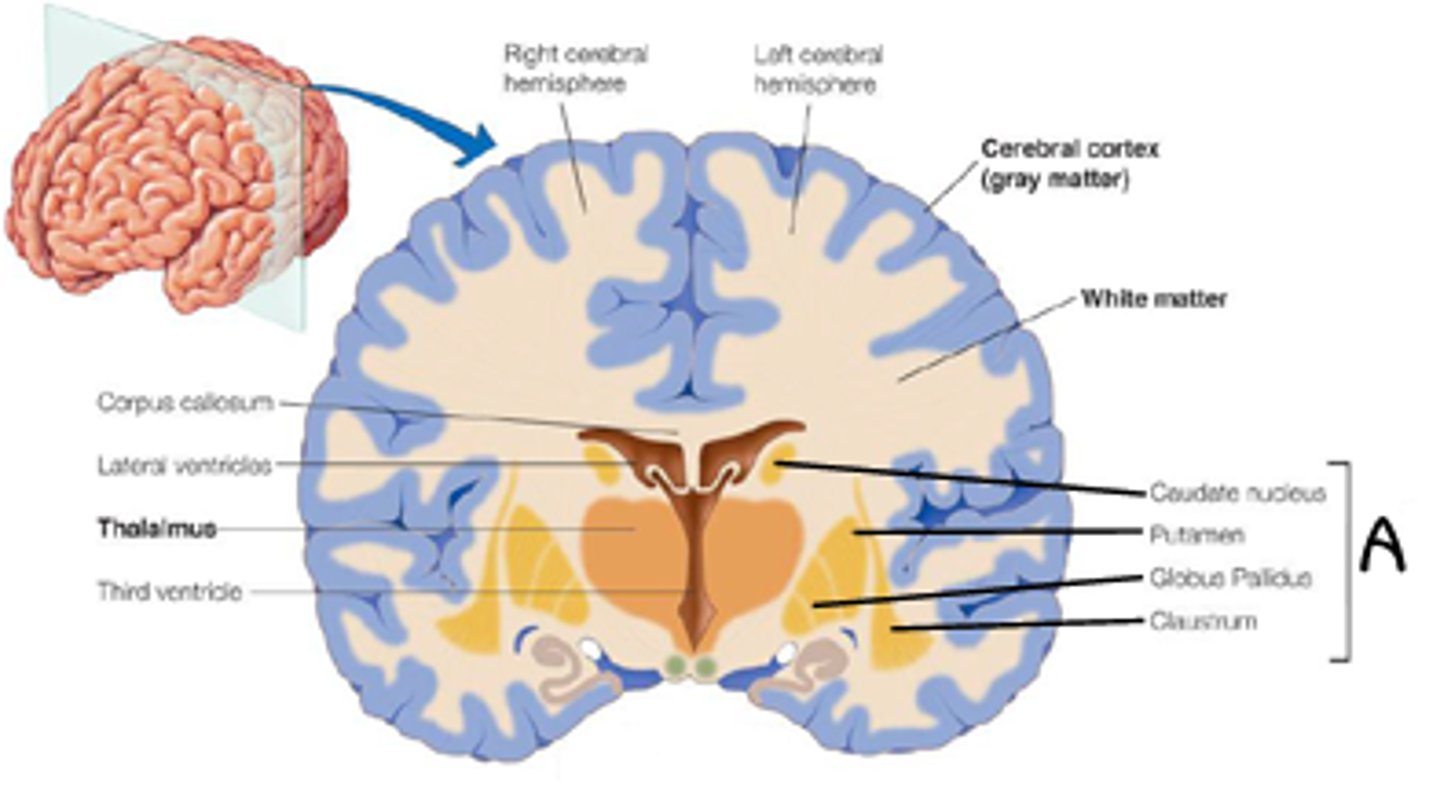
group of neurons outside cortex (CNS)
Cortical Layers
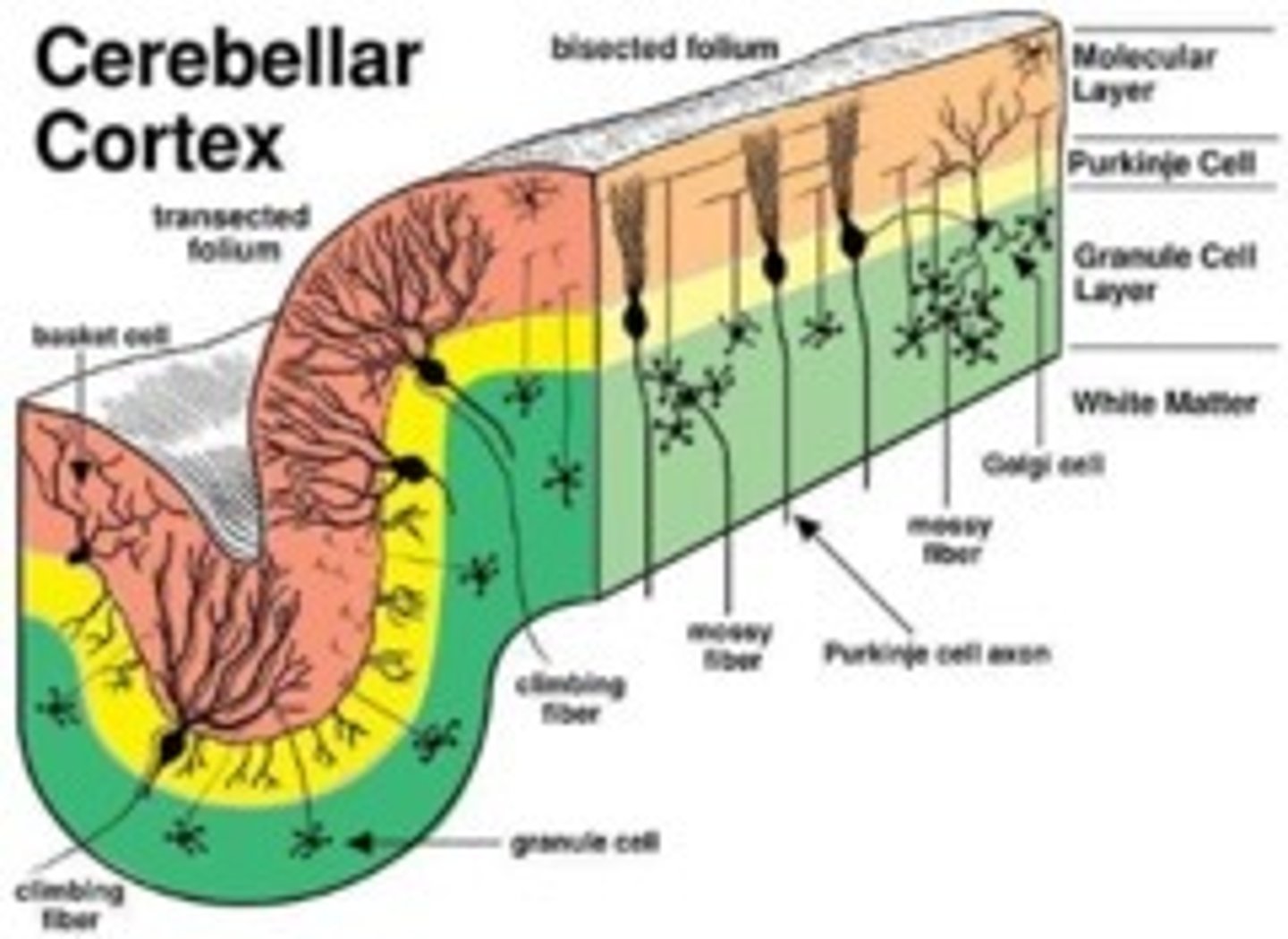
Group of Neurons within cortex (CNS)
ganglia
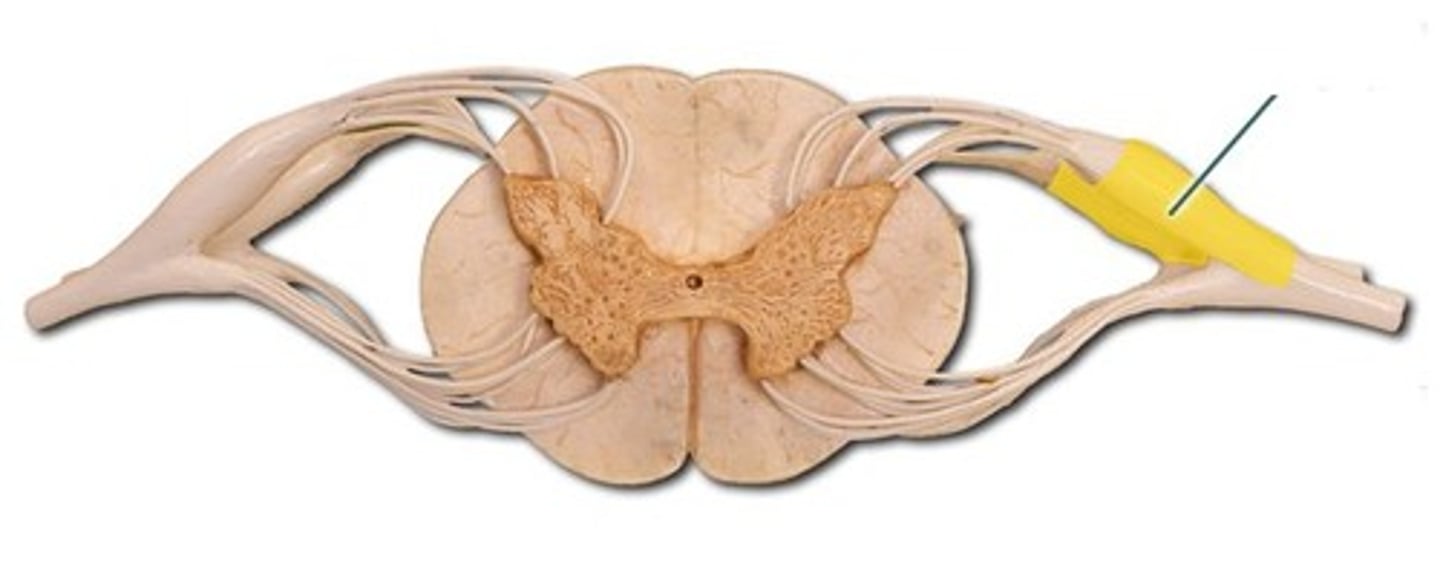
group of neuronal somata (PNS)
nerves
bundle of axons (PNS)
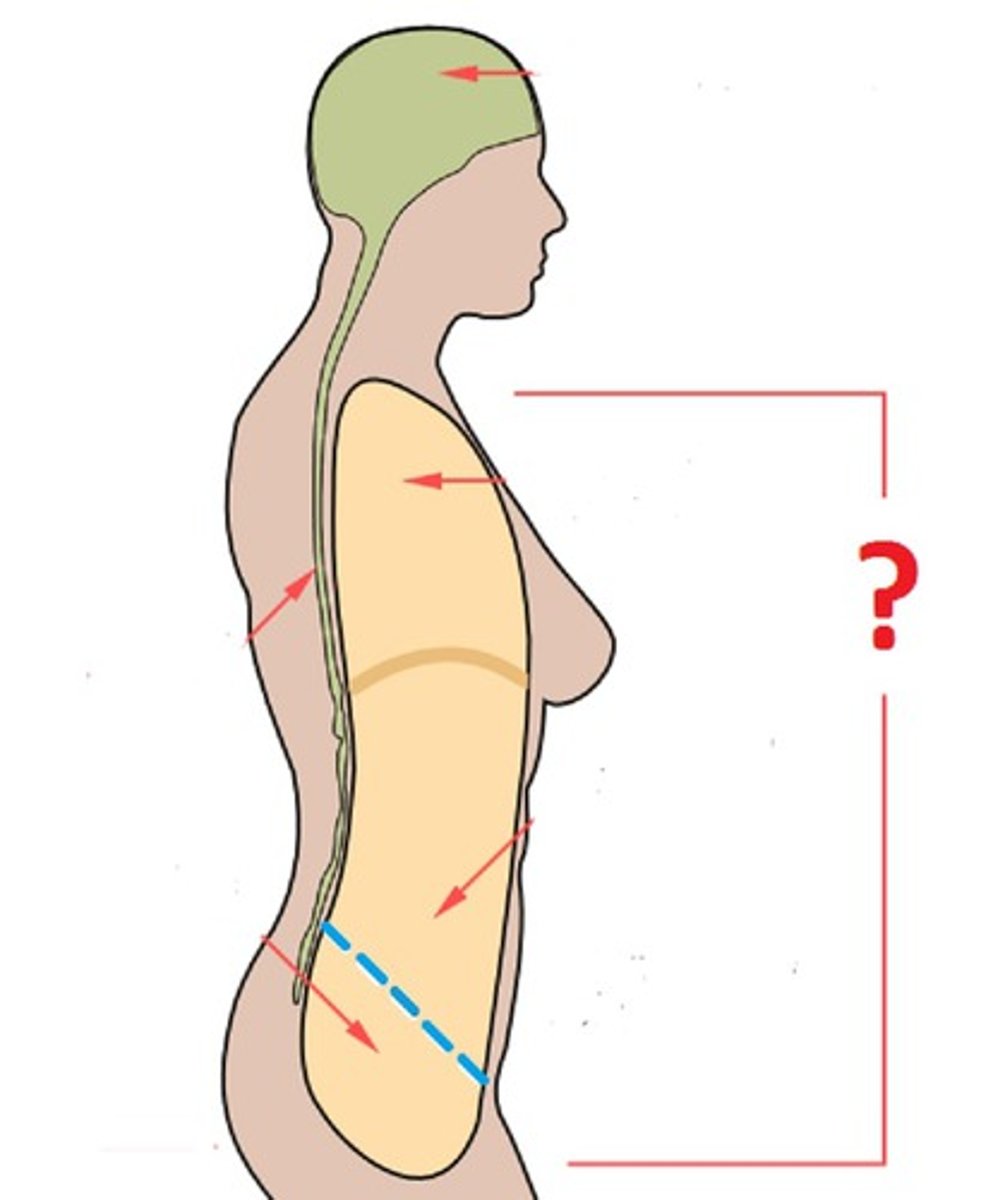
Ventral
Toward the belly
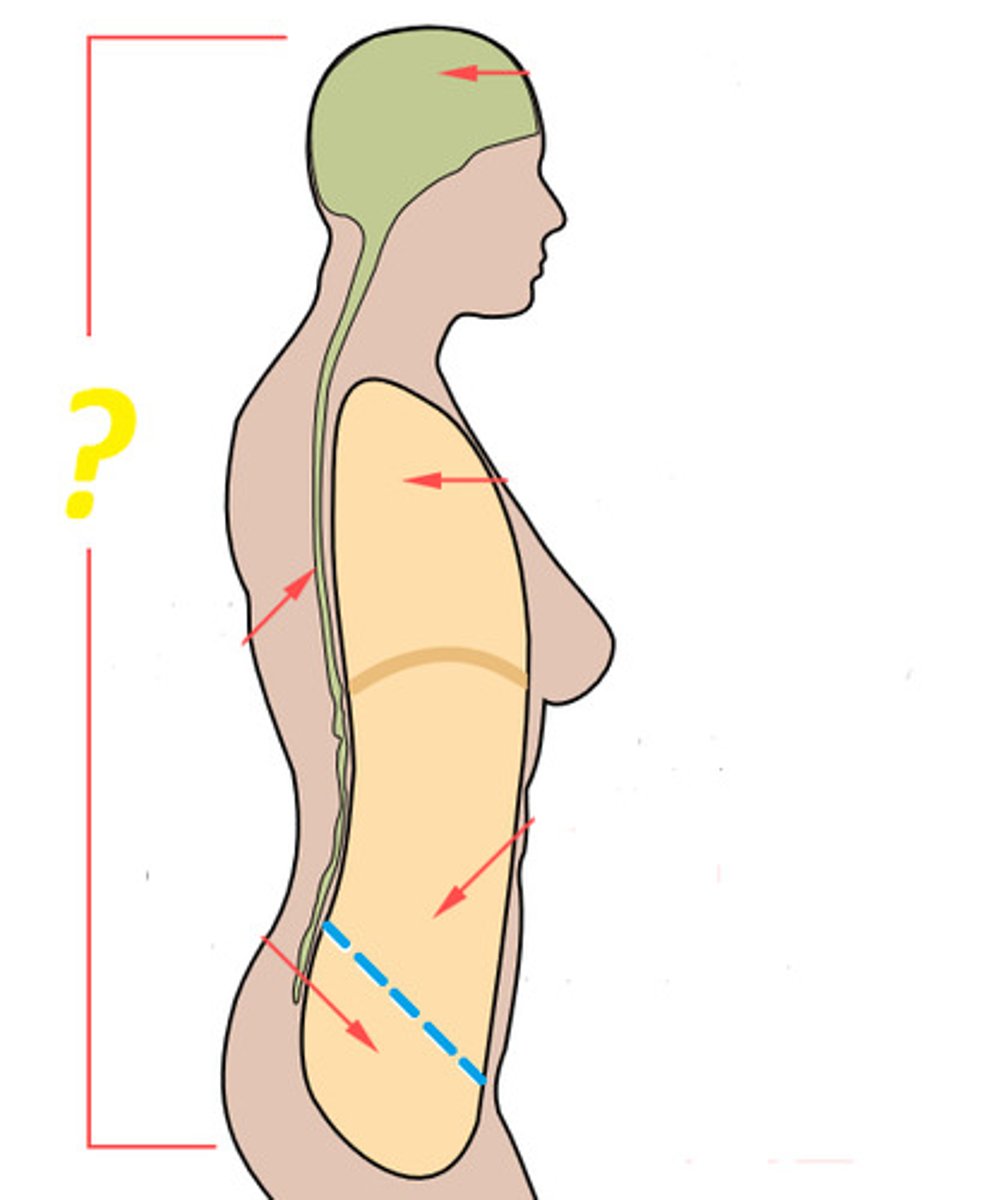
Dorsal
toward the back
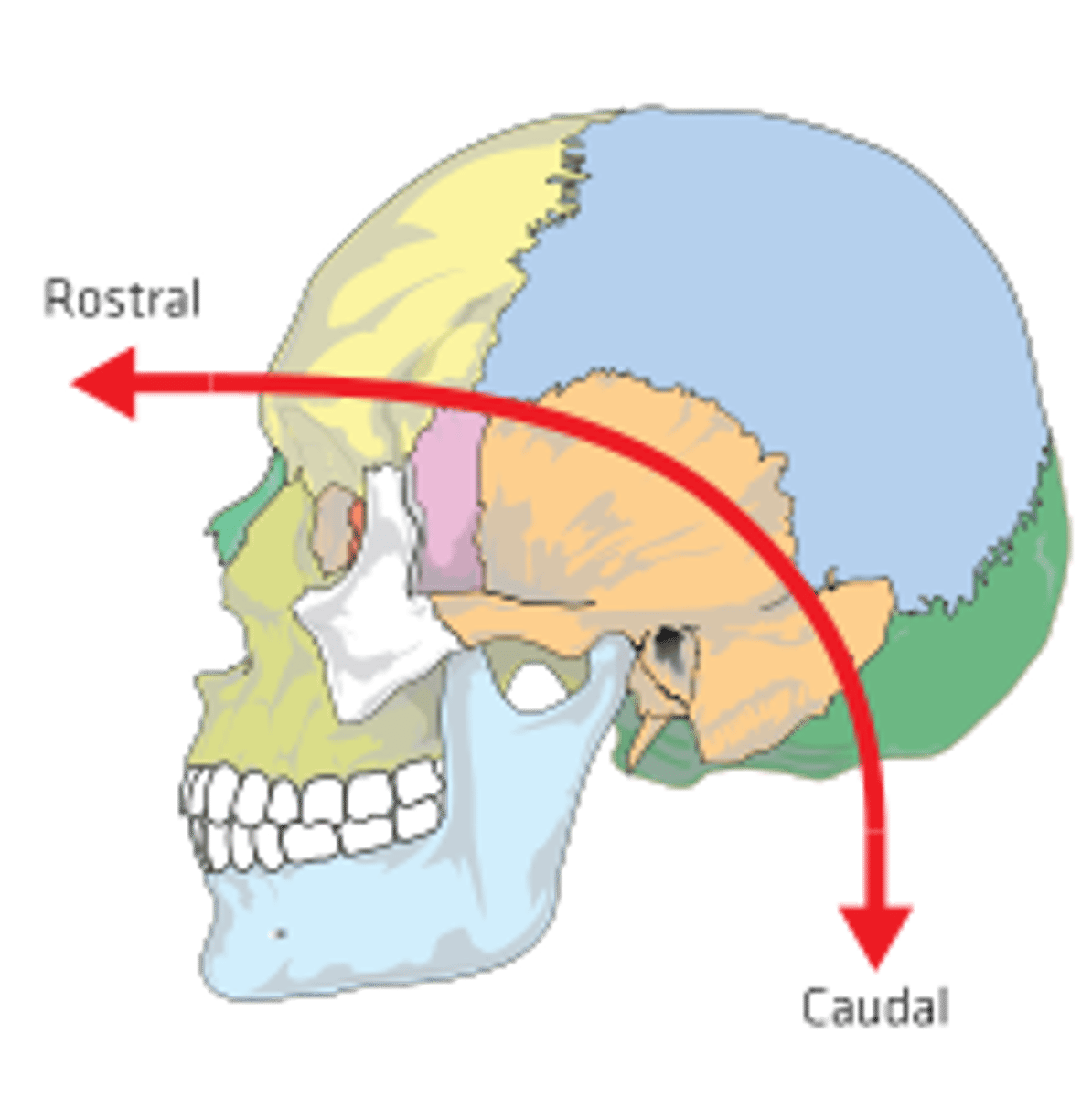
Rostral
toward the beak
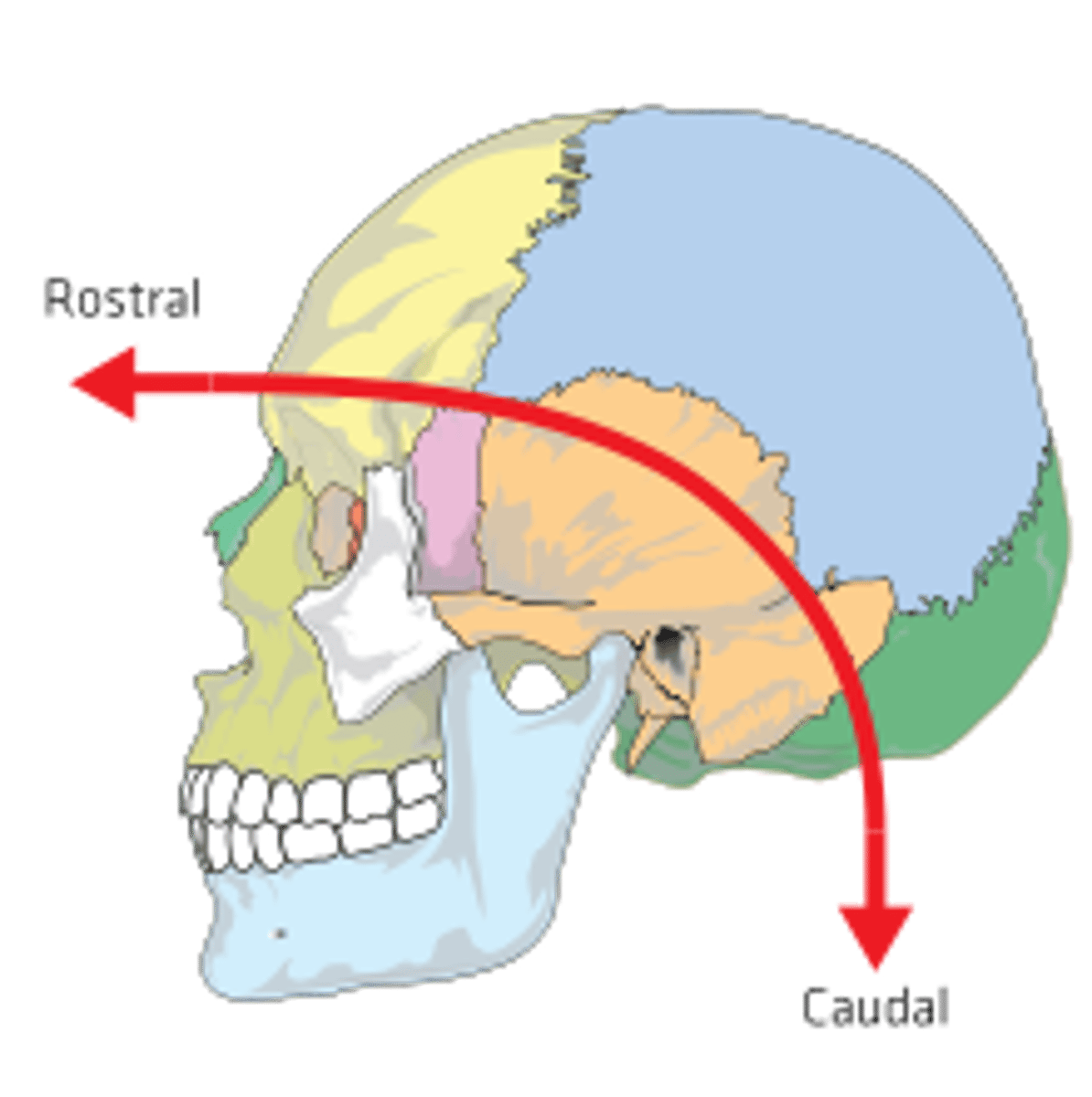
Caudal
towards the tail
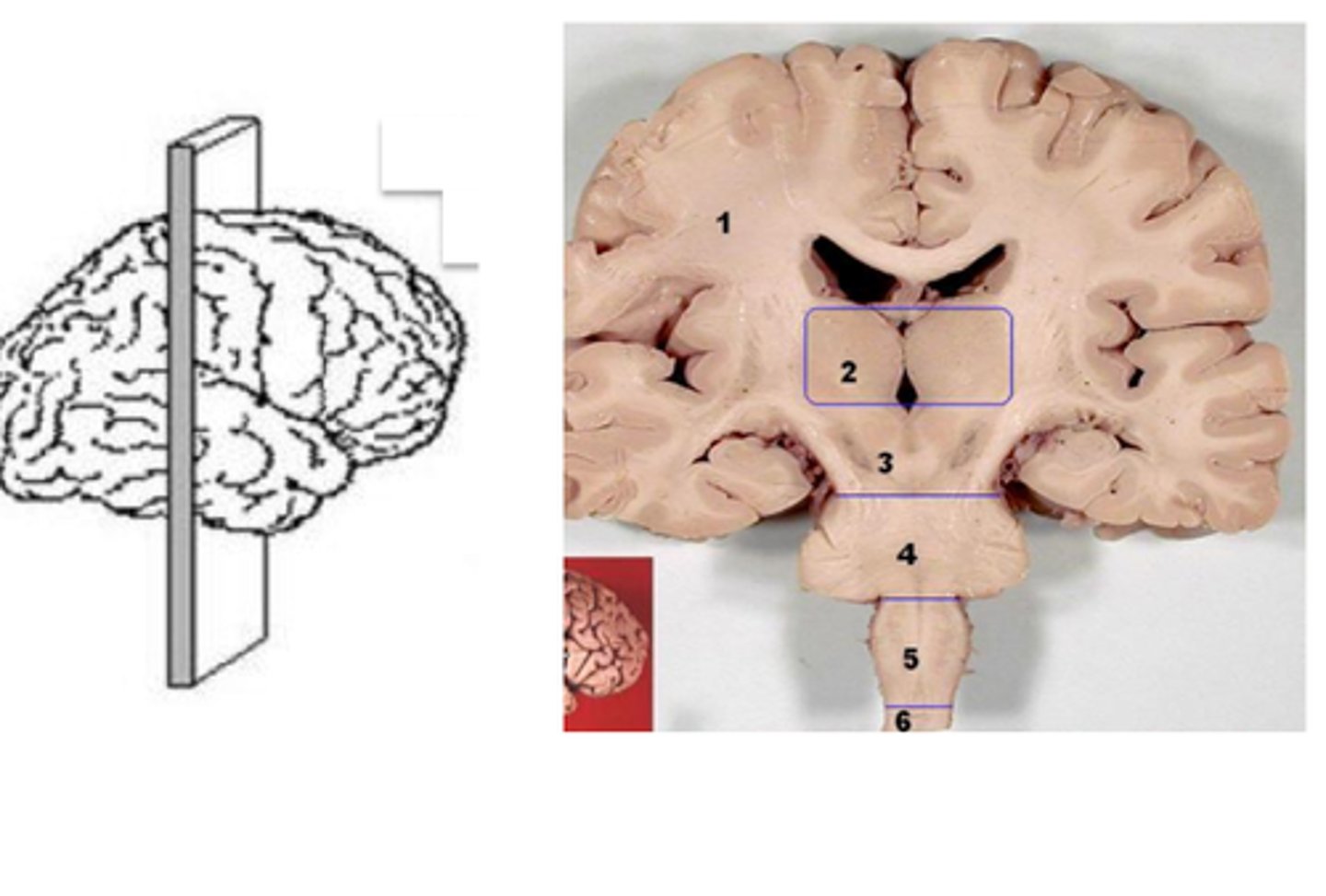
coronal plane
divides body into front and back
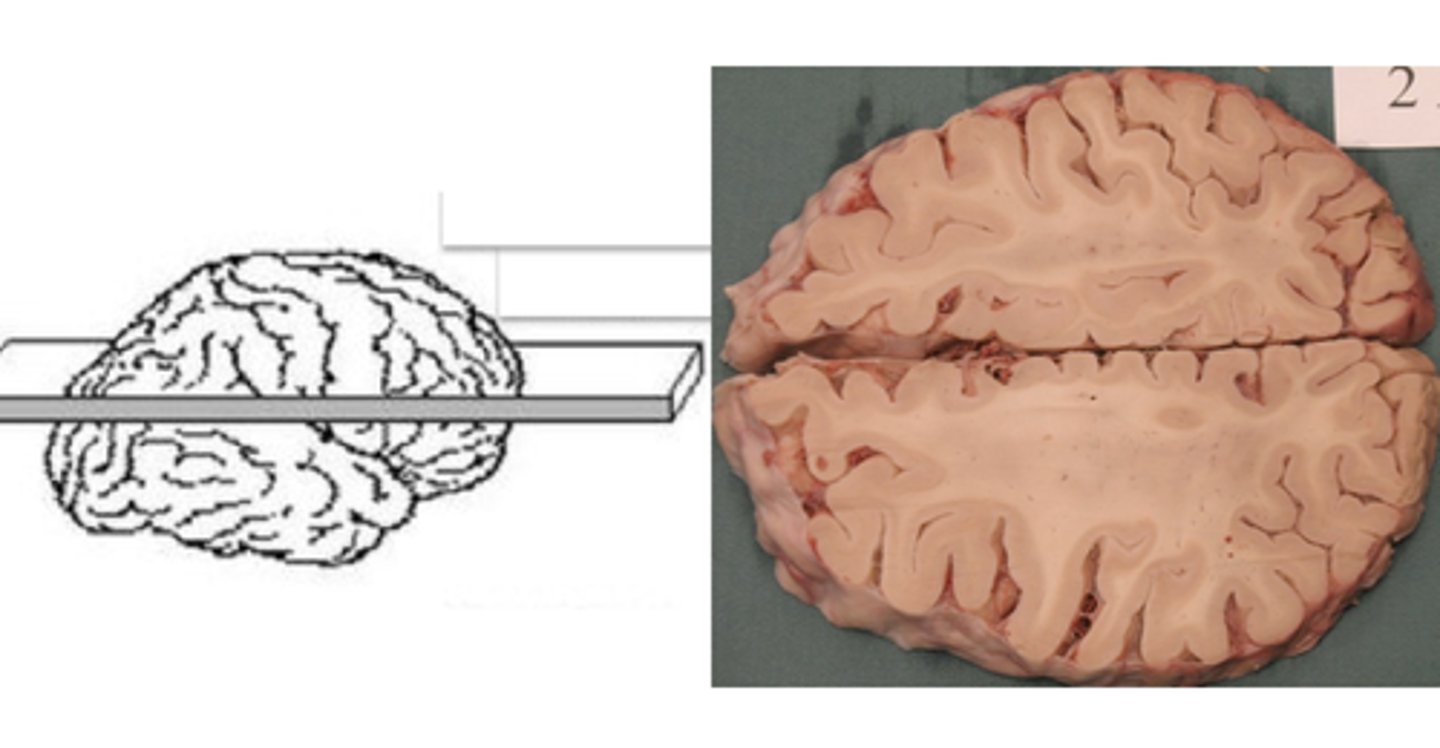
horizontal plane
flat crosswise plane
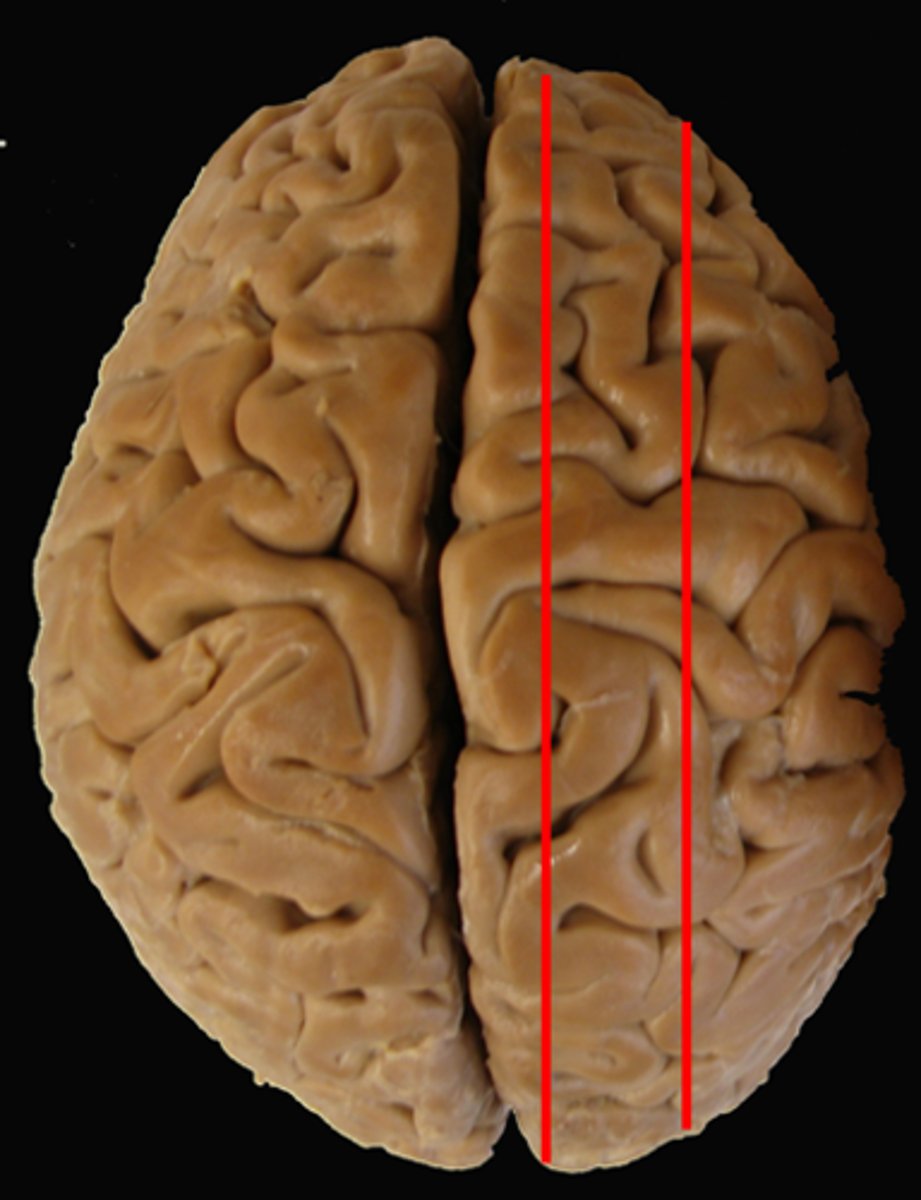
parasagittal plane
not on midline - divides left to right
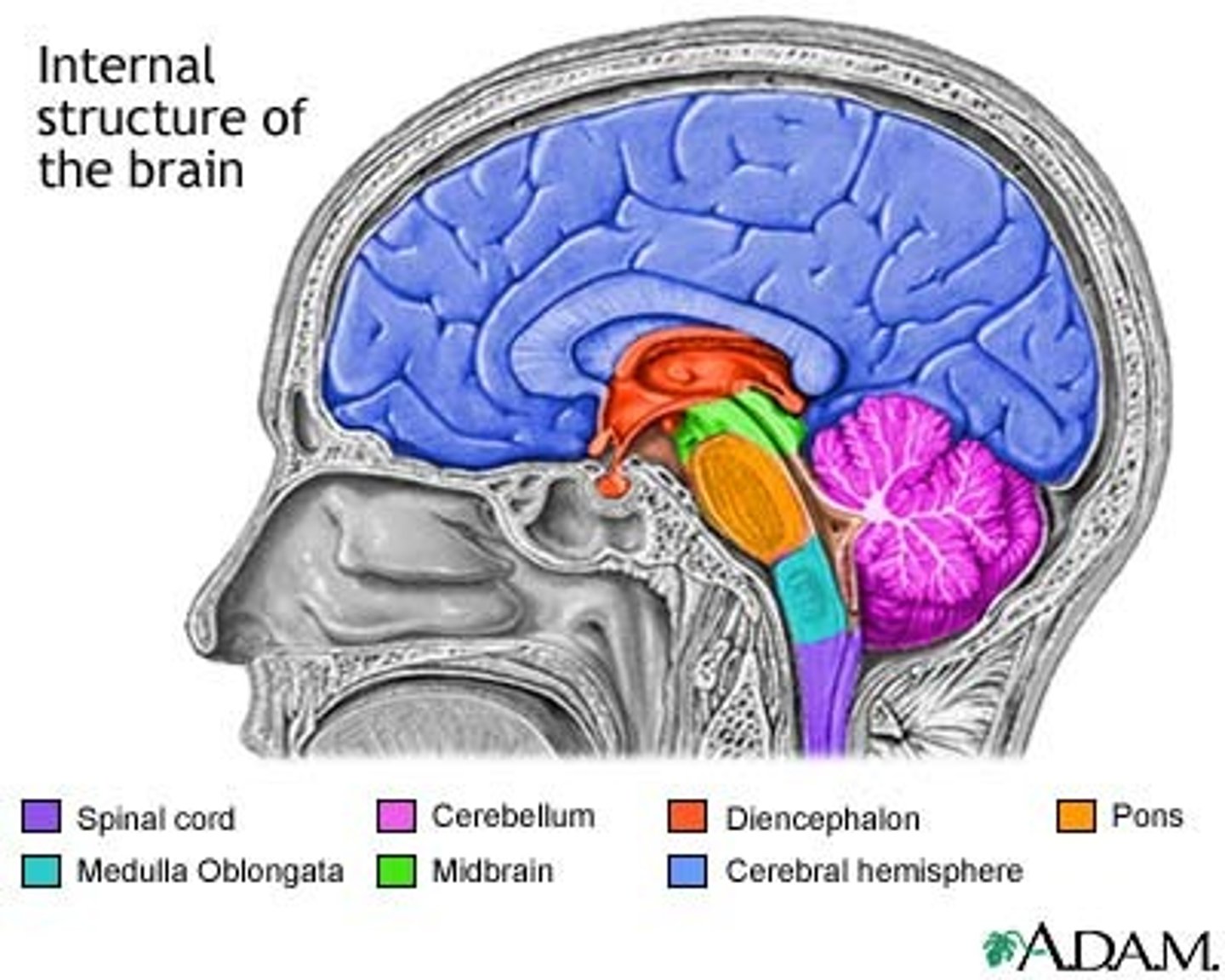
medulla oblongata
- between bottom of skull and top of spine
- most caudal part of brain stem
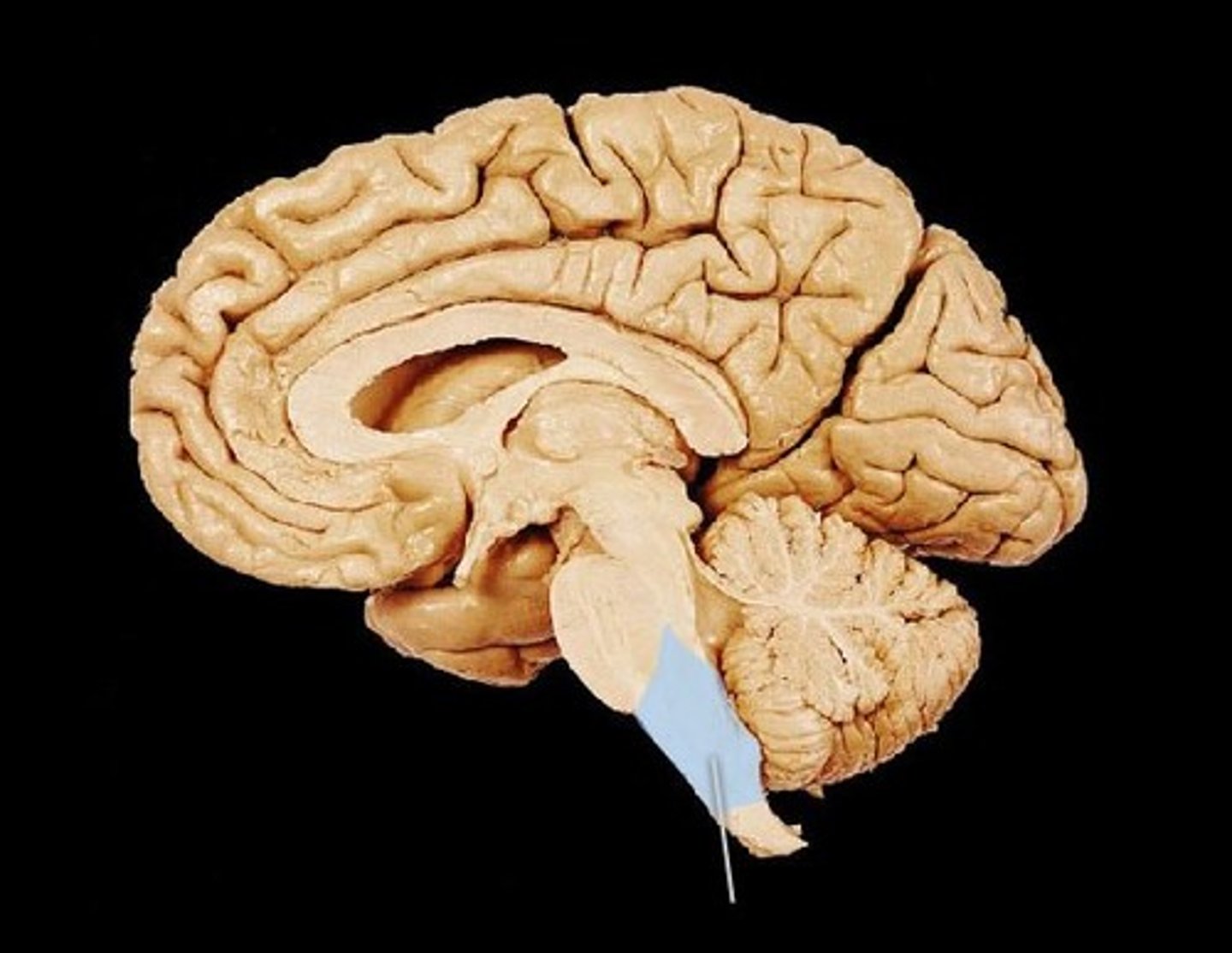
pons
bridge over brain stem connecting cerebellum
- between midbrain and medulla
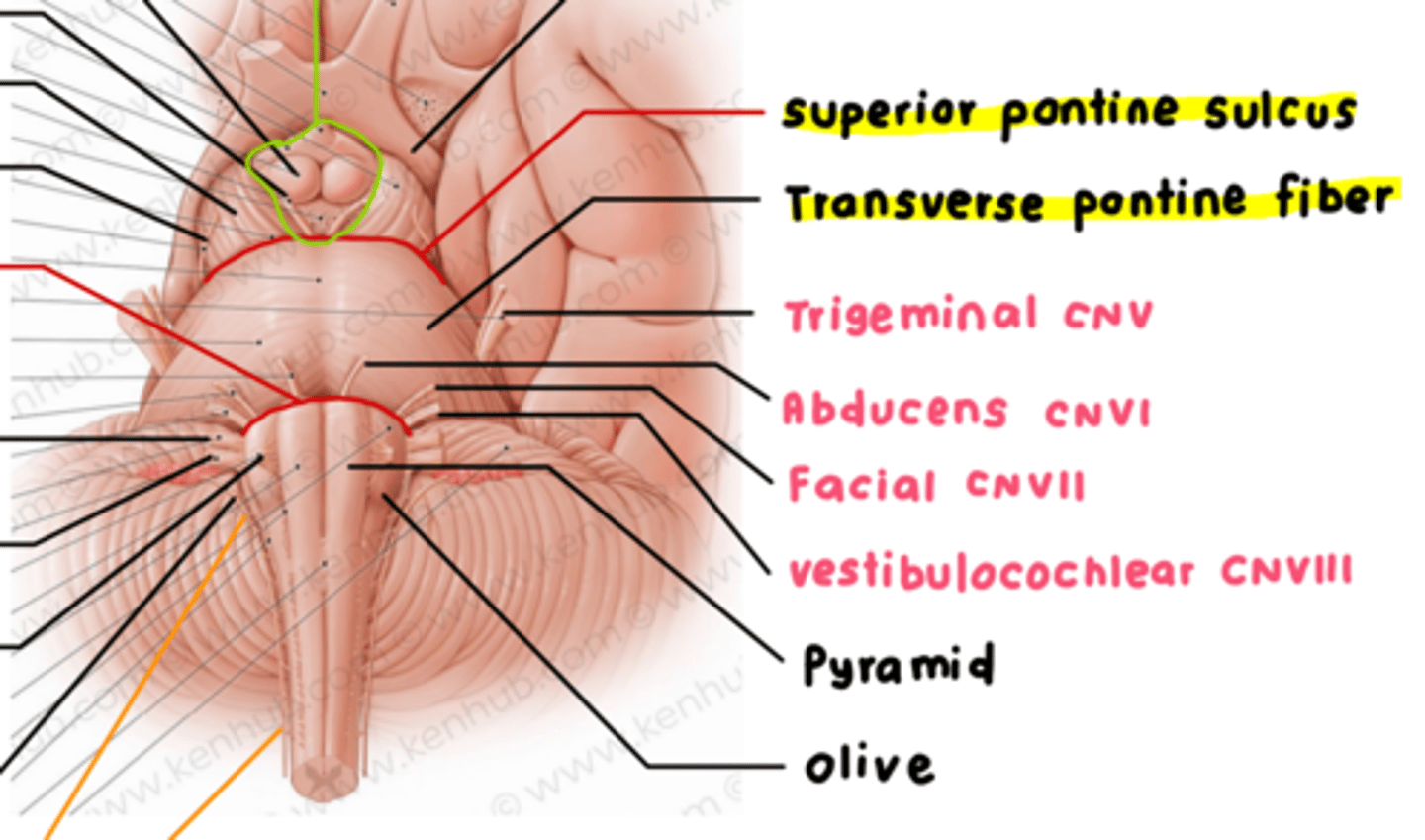
Inferior/Superior pontine sulcus
rostral and caudal sulcus around pons
cerebellum
large, rigid masses on either side of pons
Midbrain
rostral from pons
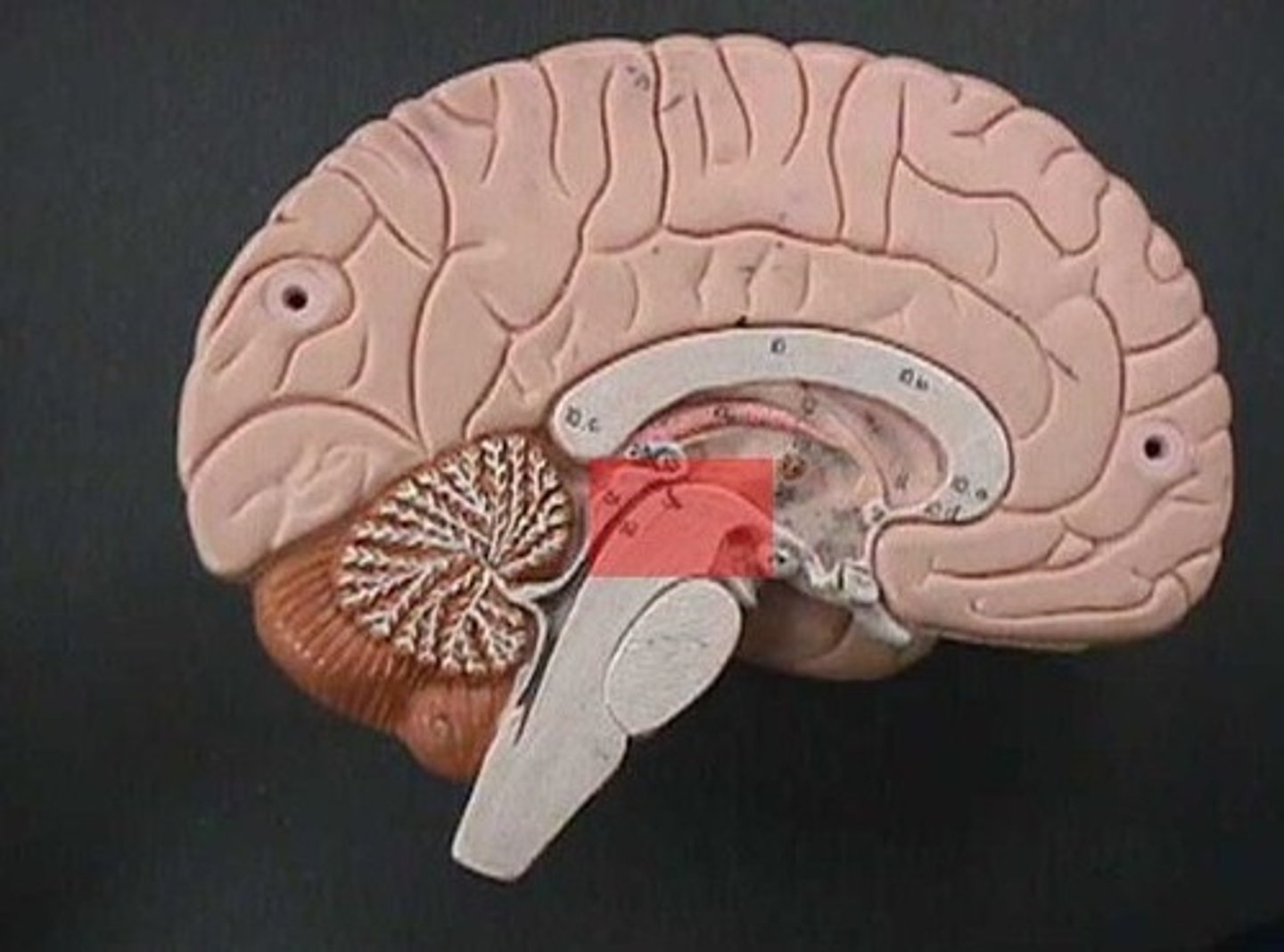
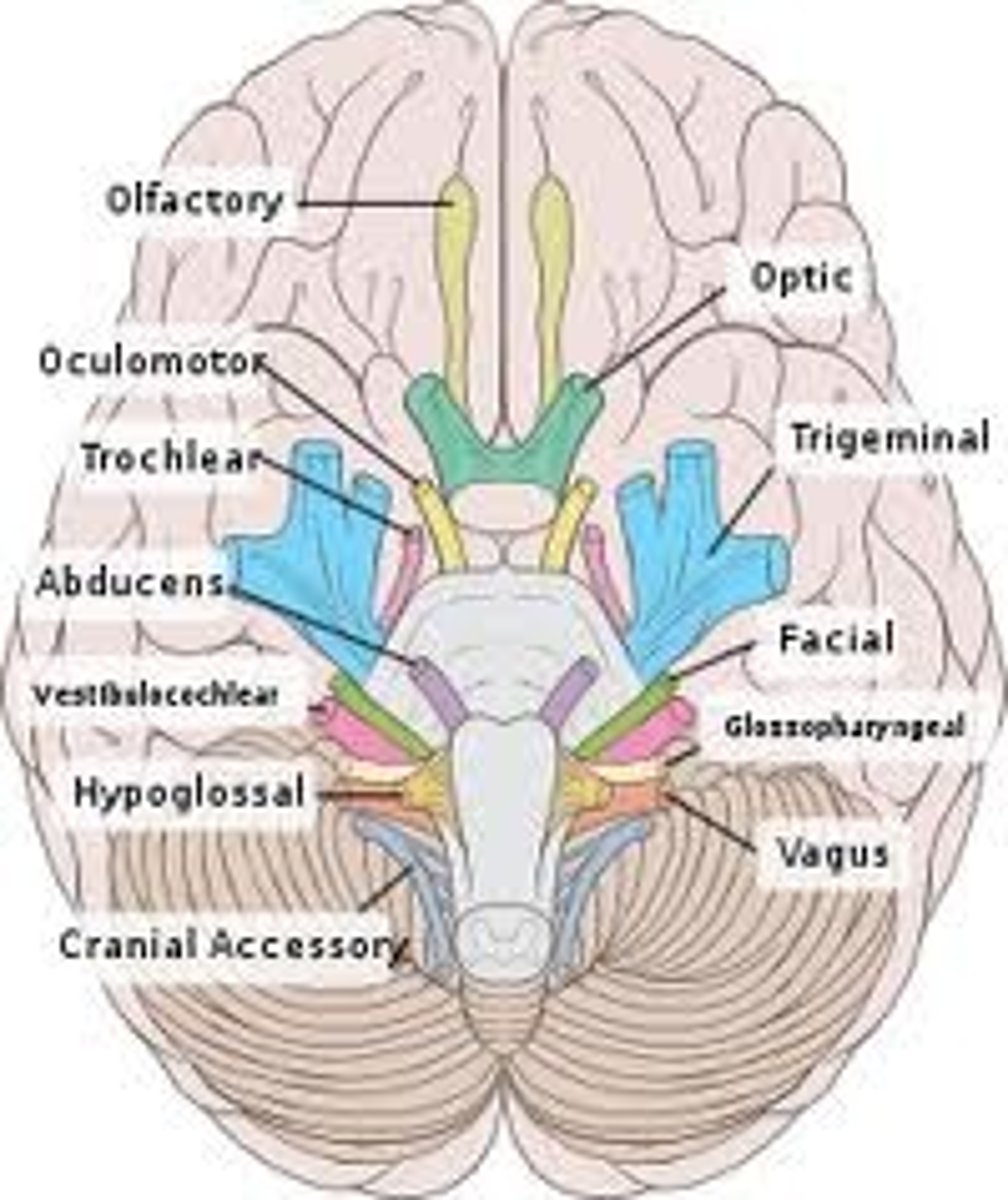
Cranial Nerve 3: Oculomotor
- emerges from the midbrain
- controls ocular movement
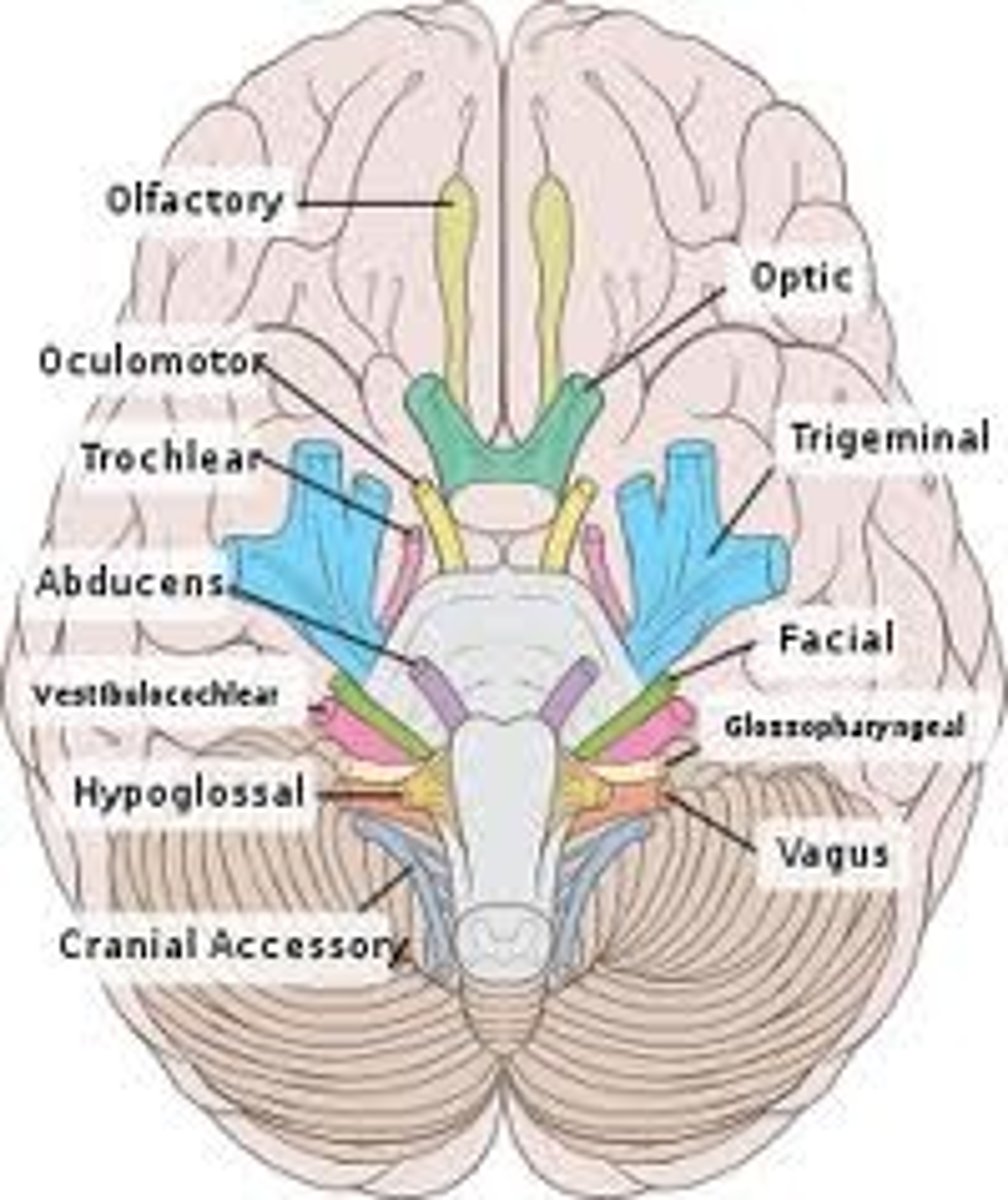
Cranial Nerve 4: Trochlear
emerges from dorsal border of pons and midbrain
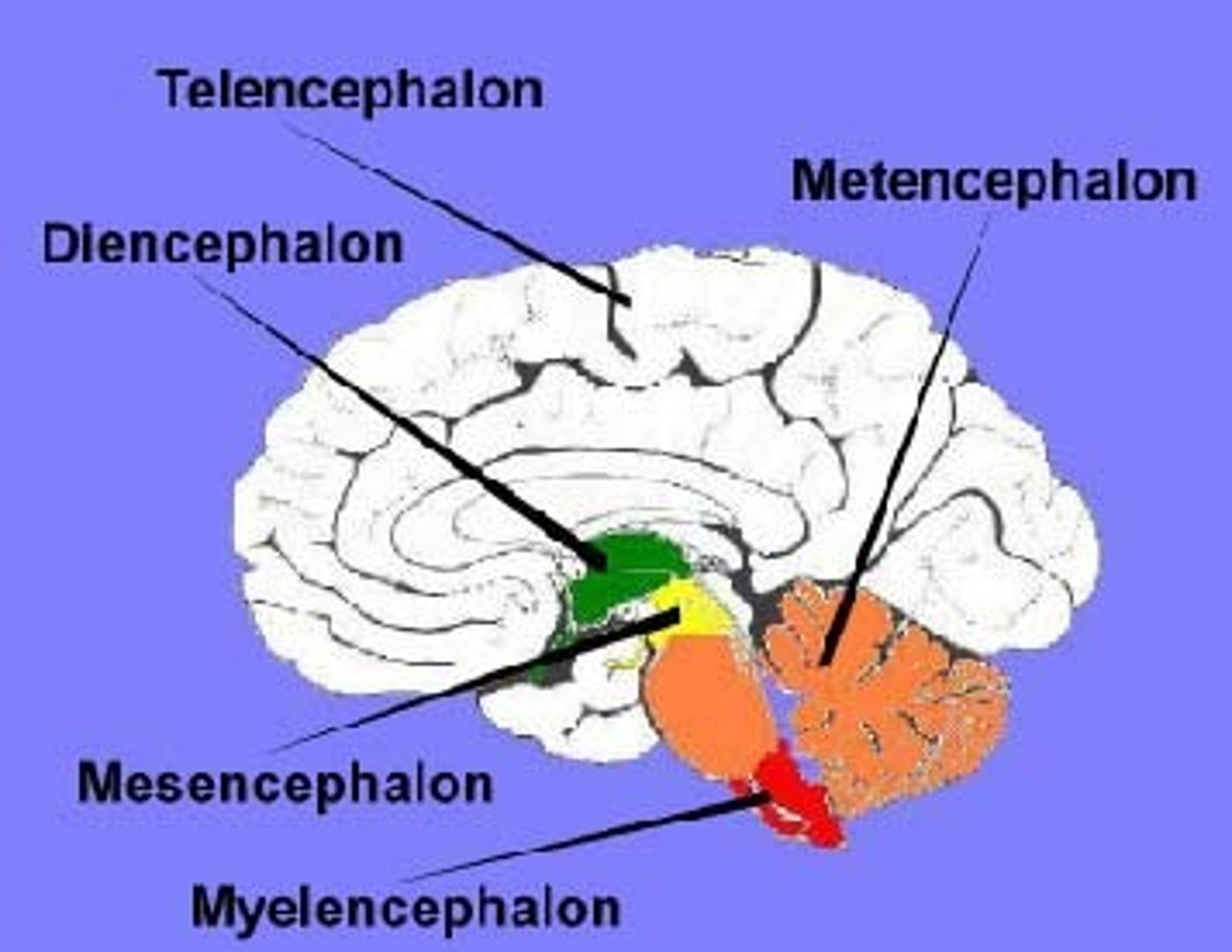
Diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
ventral surface of diencephalon
Telencephalon
cerebral cortex and basal ganglia, amygdala, putamen, caudate nucleus
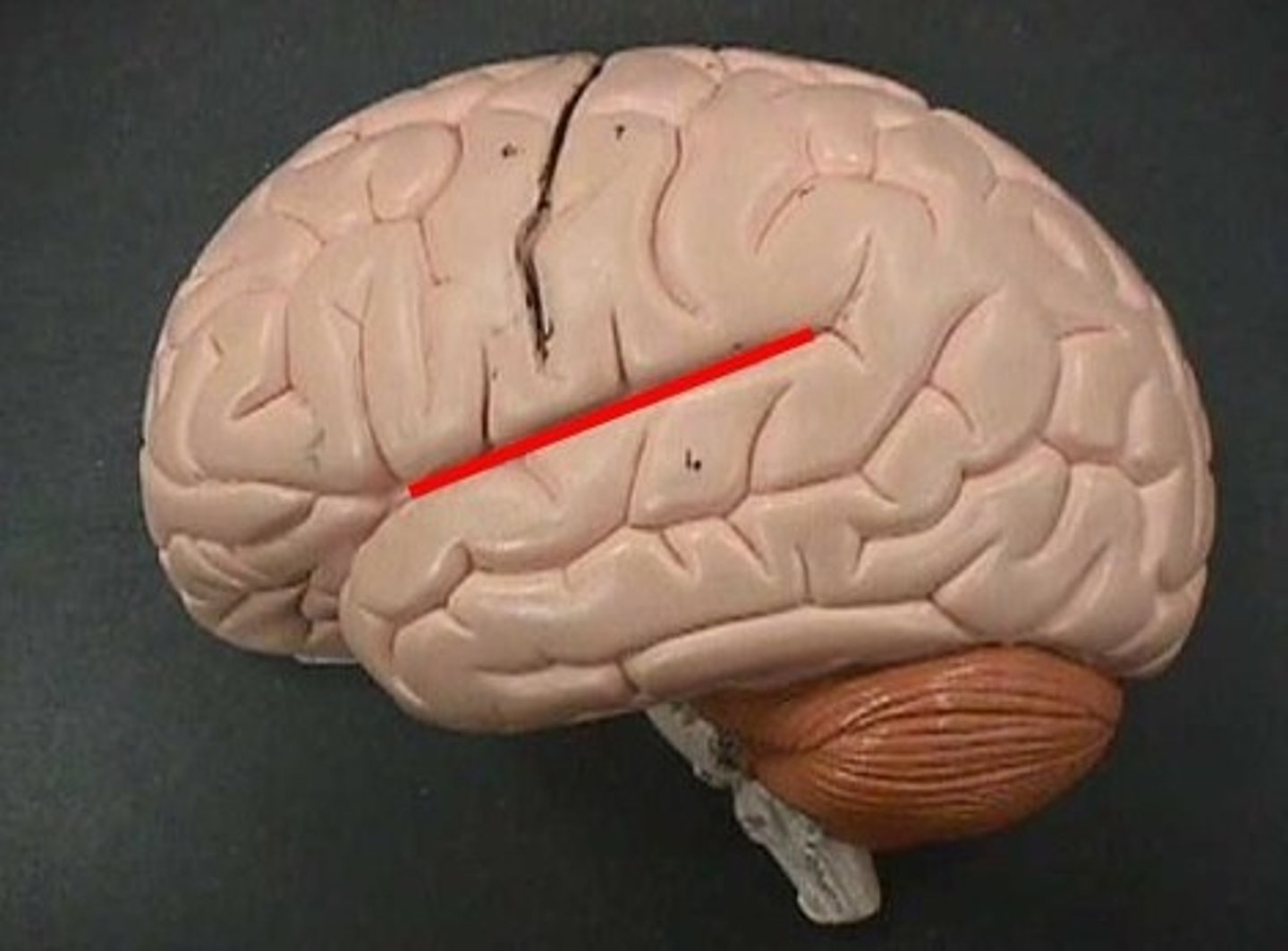
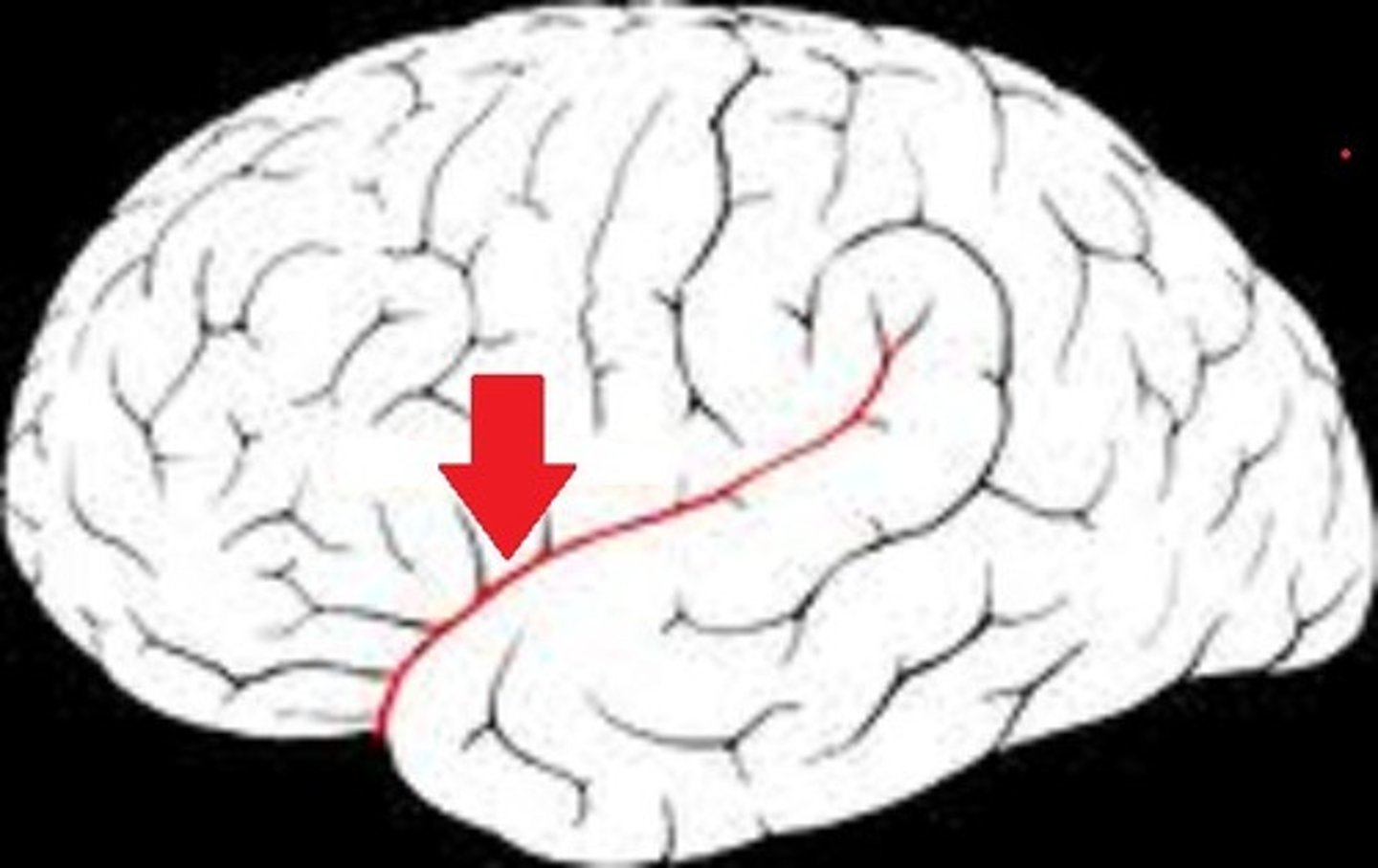
lateral sulcus/fissure
location of pons/medulla
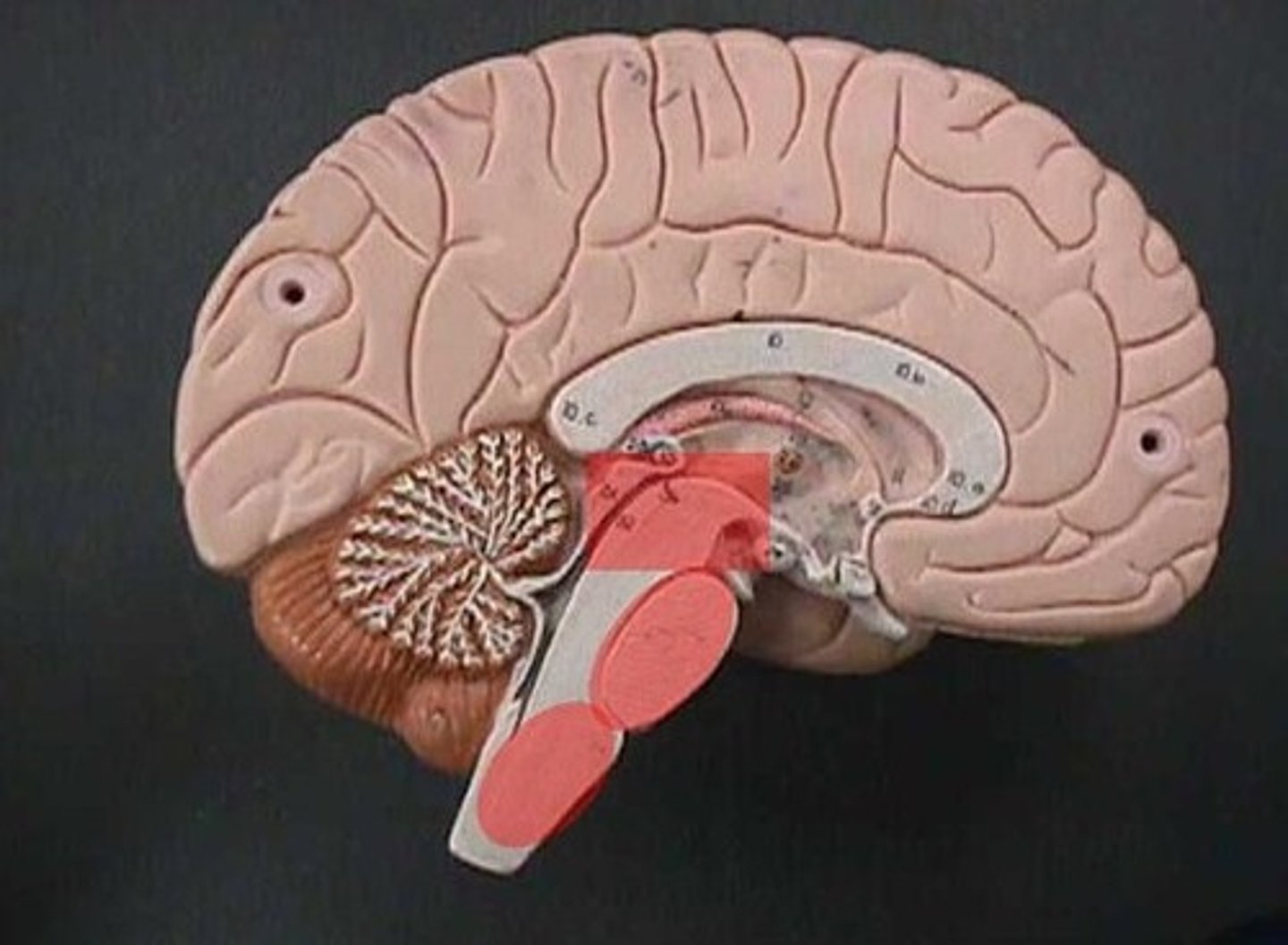
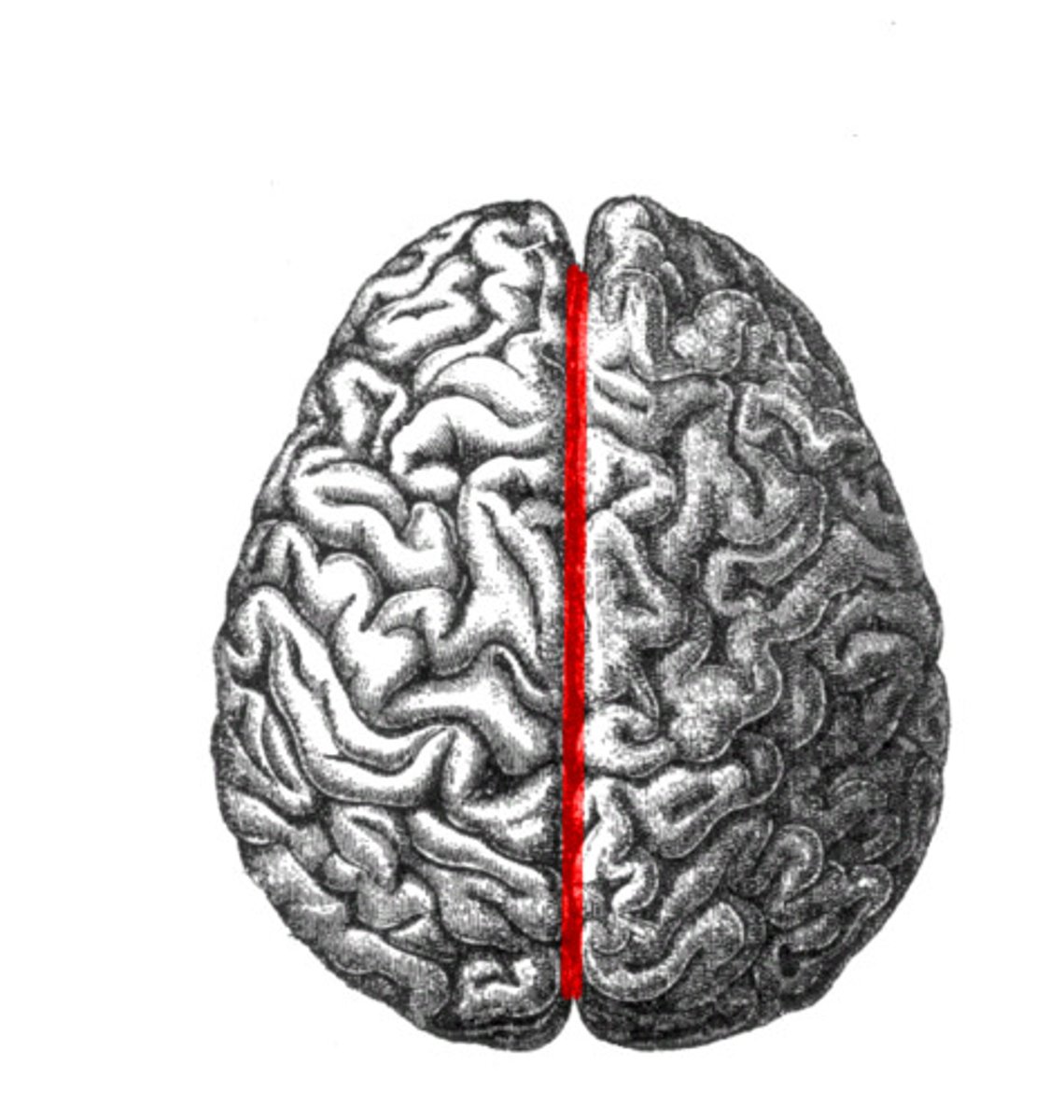
medial longitudinal fissure
separates hemispheres
Purpose of gyri/sulcus
increase surface area of the cortex
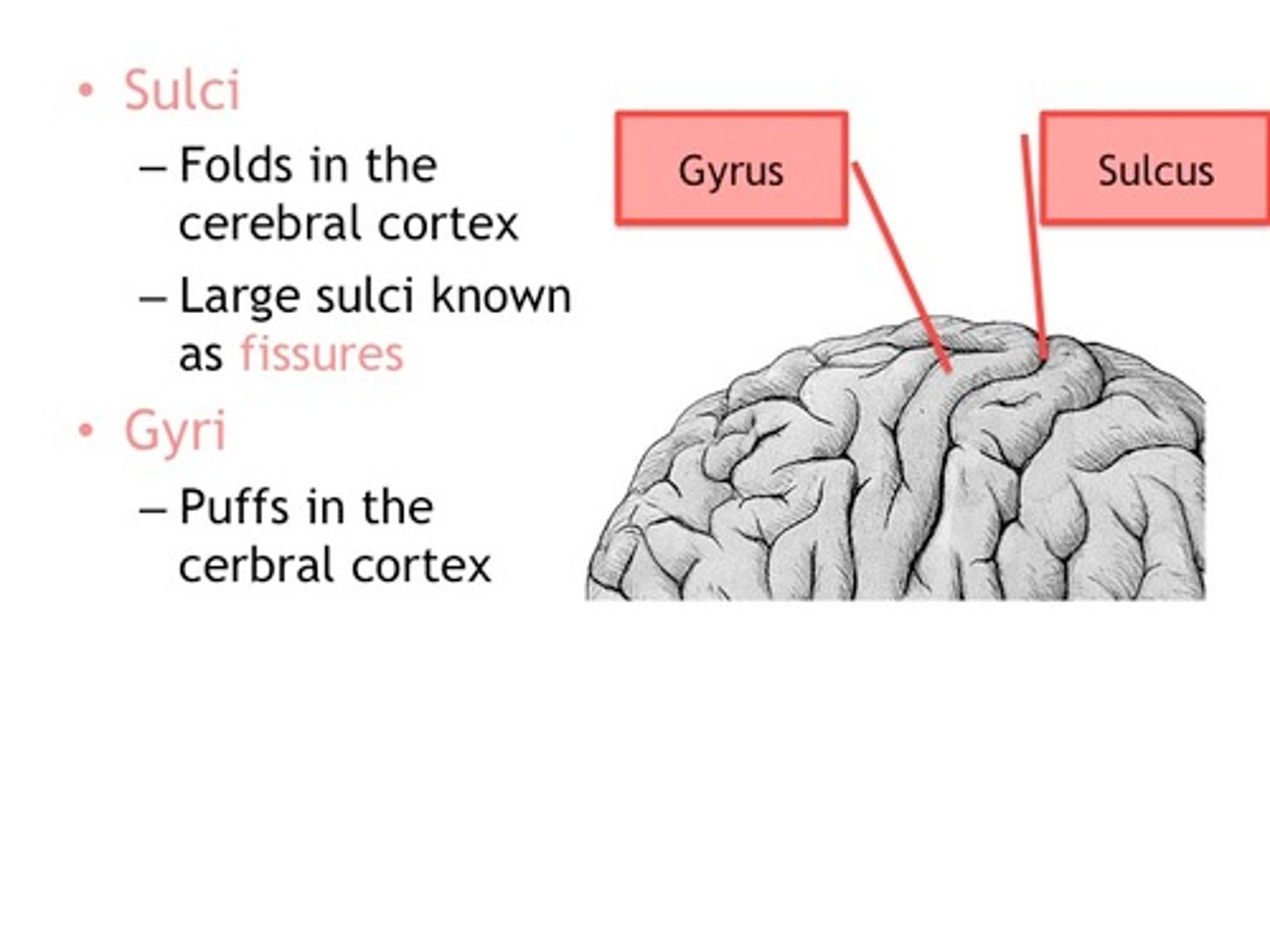
sulcus/fissure
groove in brain surface. Fissure is a deep groove.
gyrus
bump or ridge on brain surface
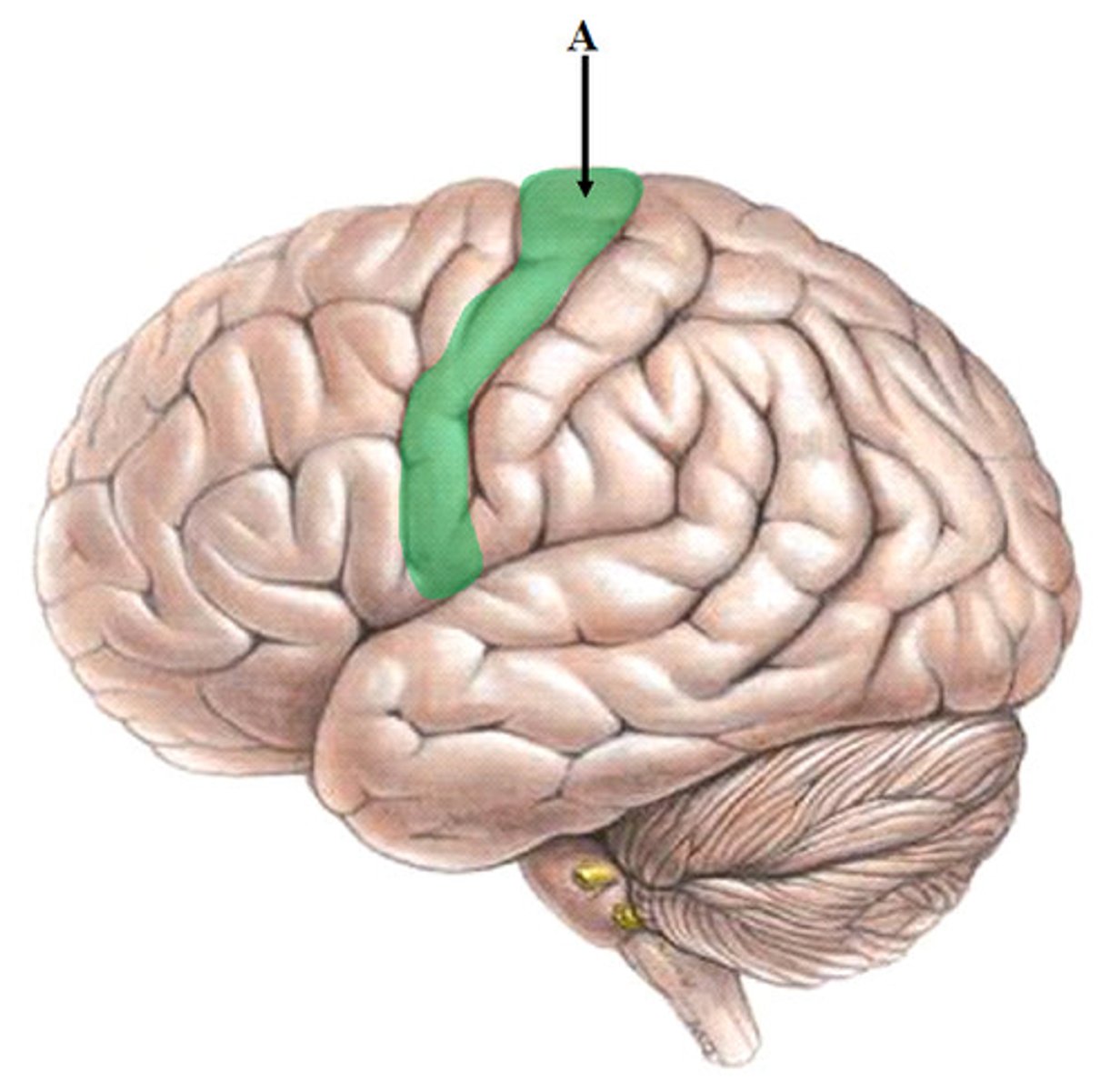
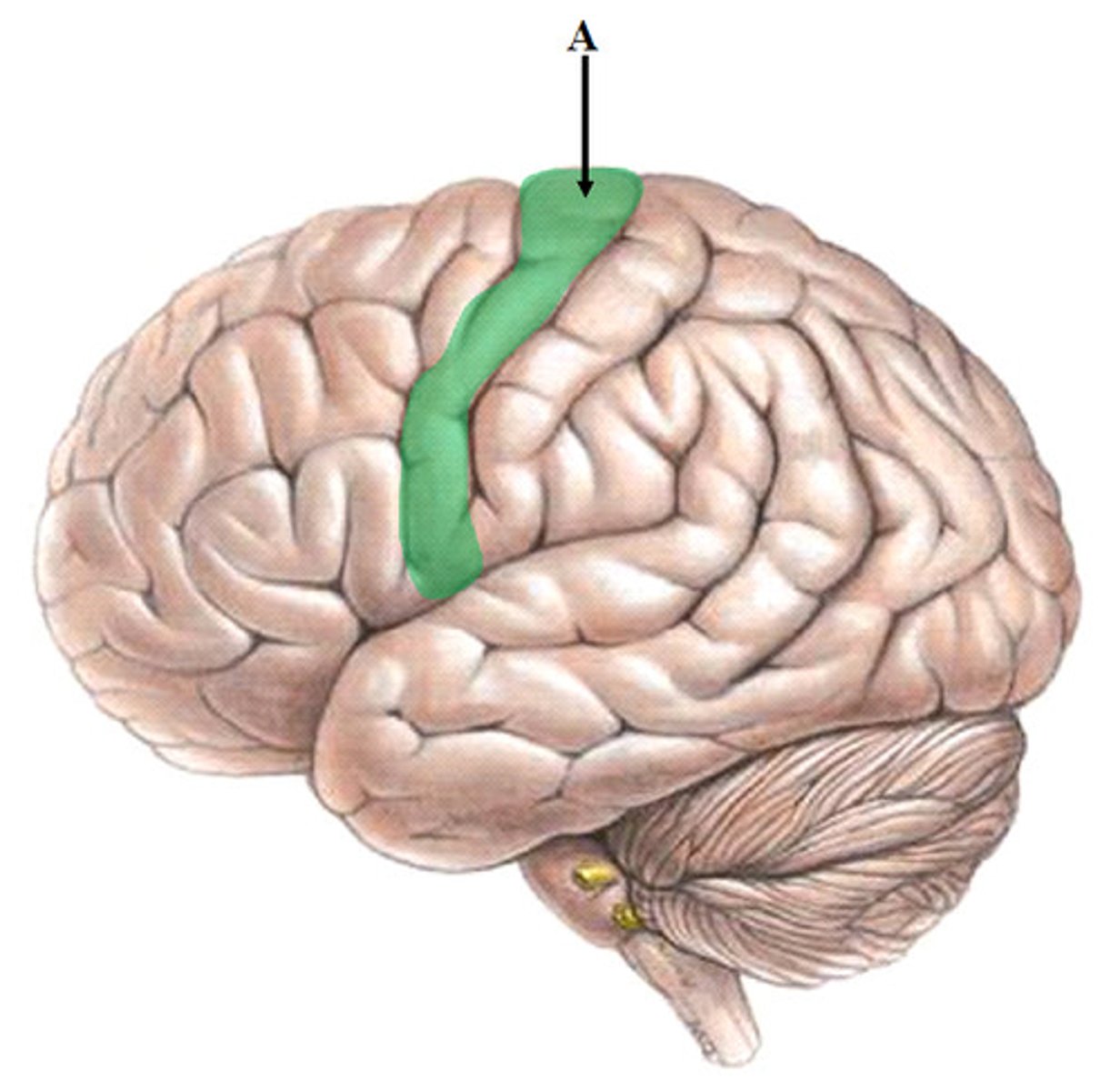
pre-central gyrus
movement/motor
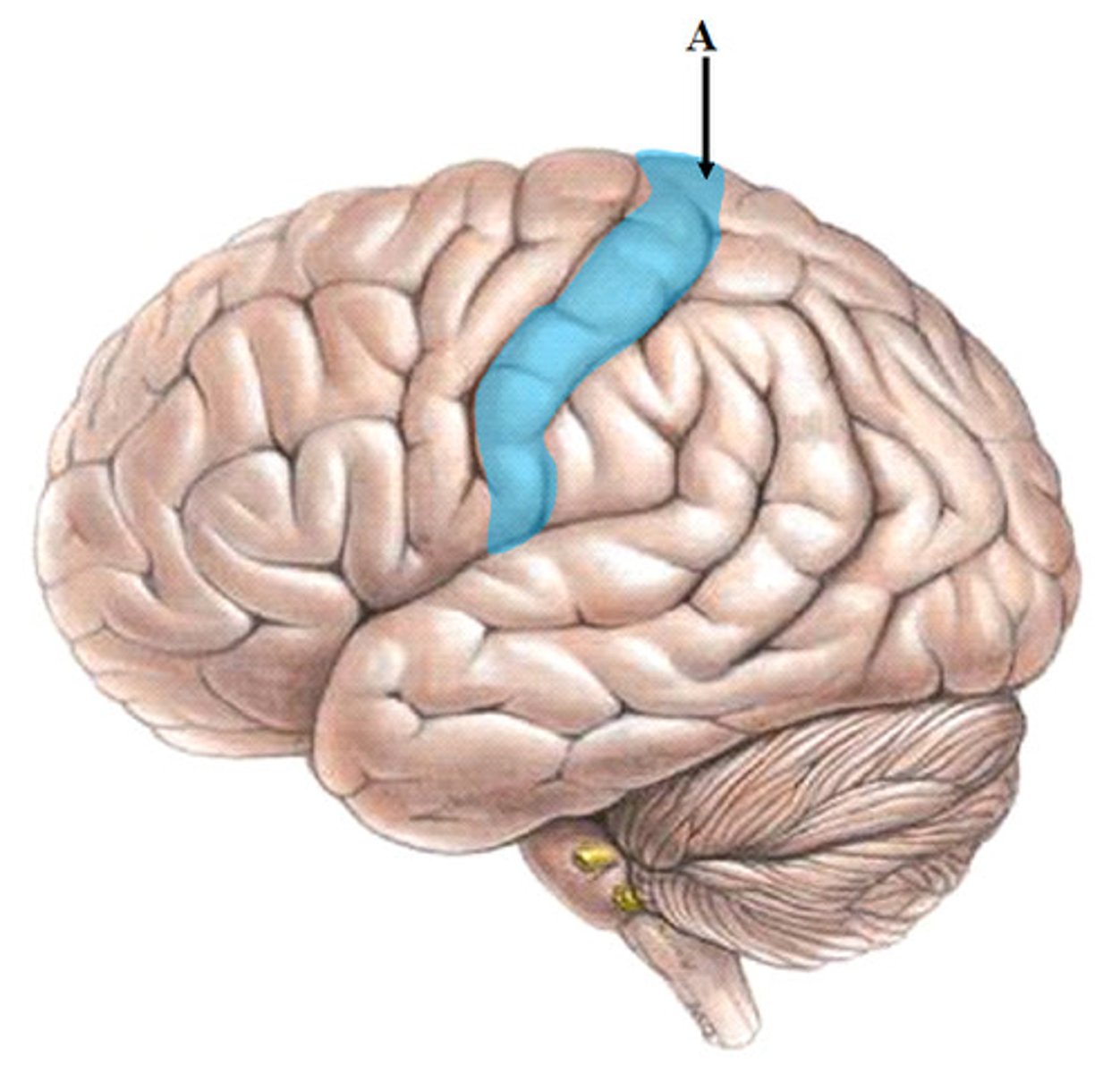
post central gyrus
(touch)/sensory
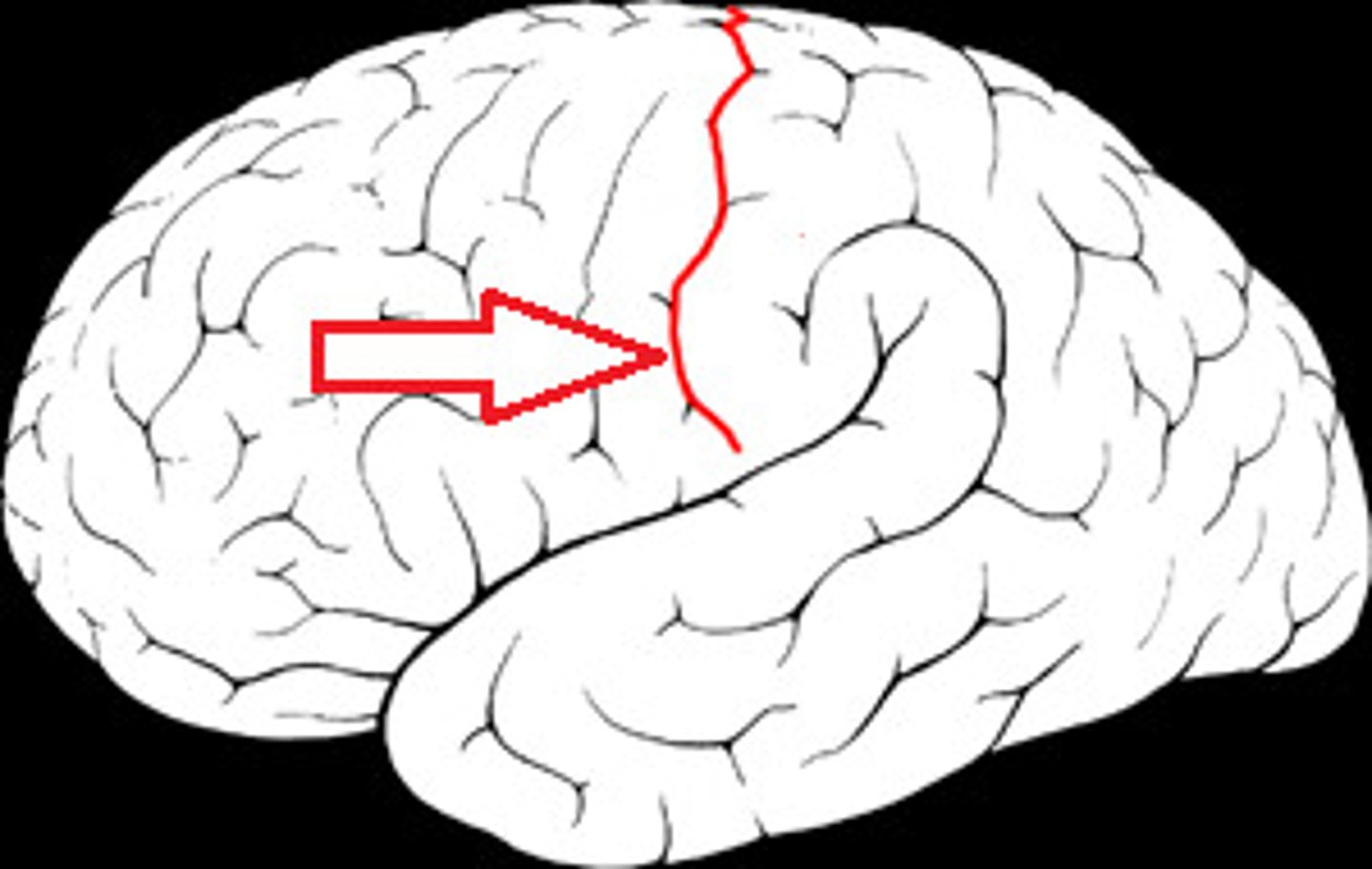
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
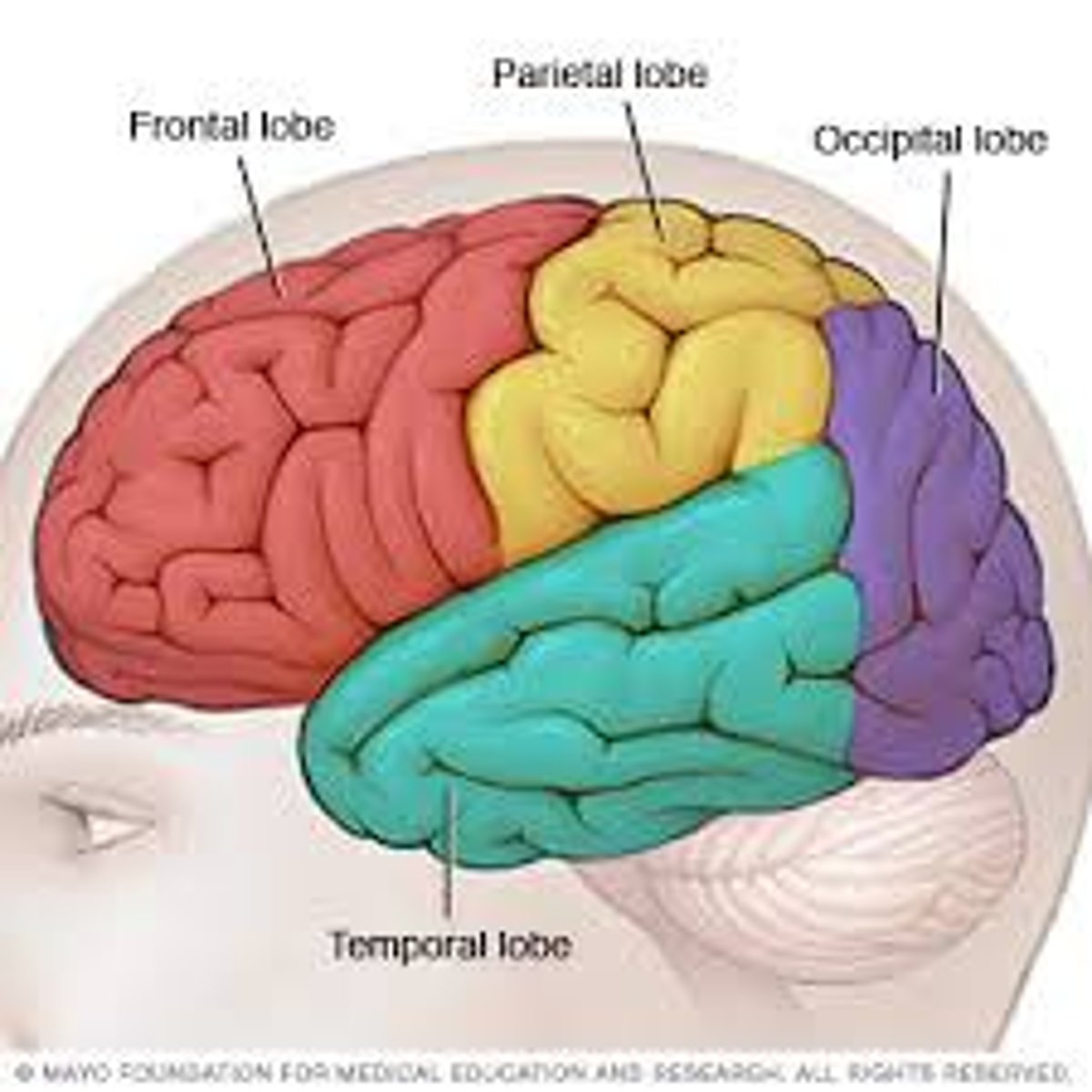
Lobes of the cerbral cortex
limbic is deep medial, surrounding corpus callosum
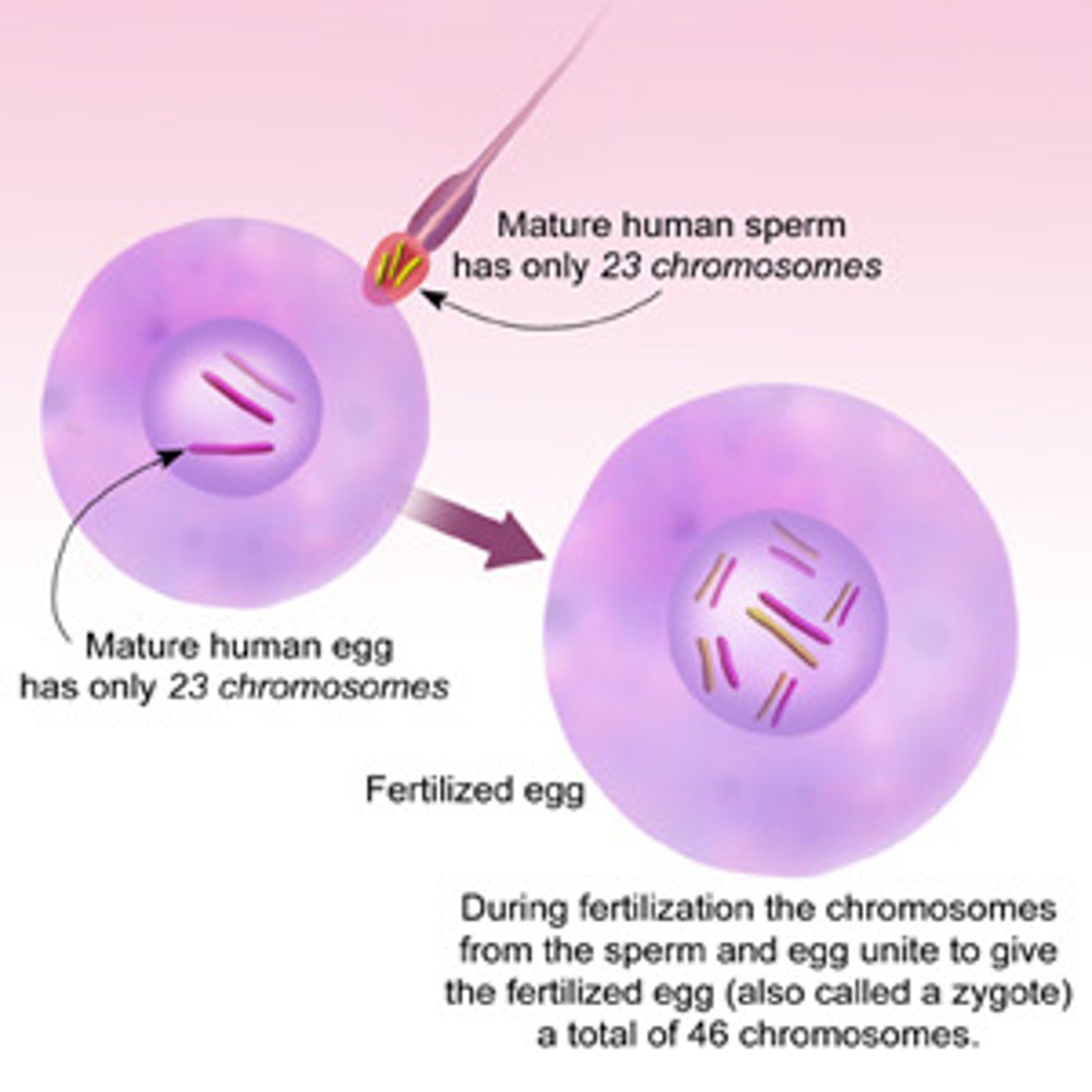
Fertilized egg
zygote, after the sperm and the egg unite
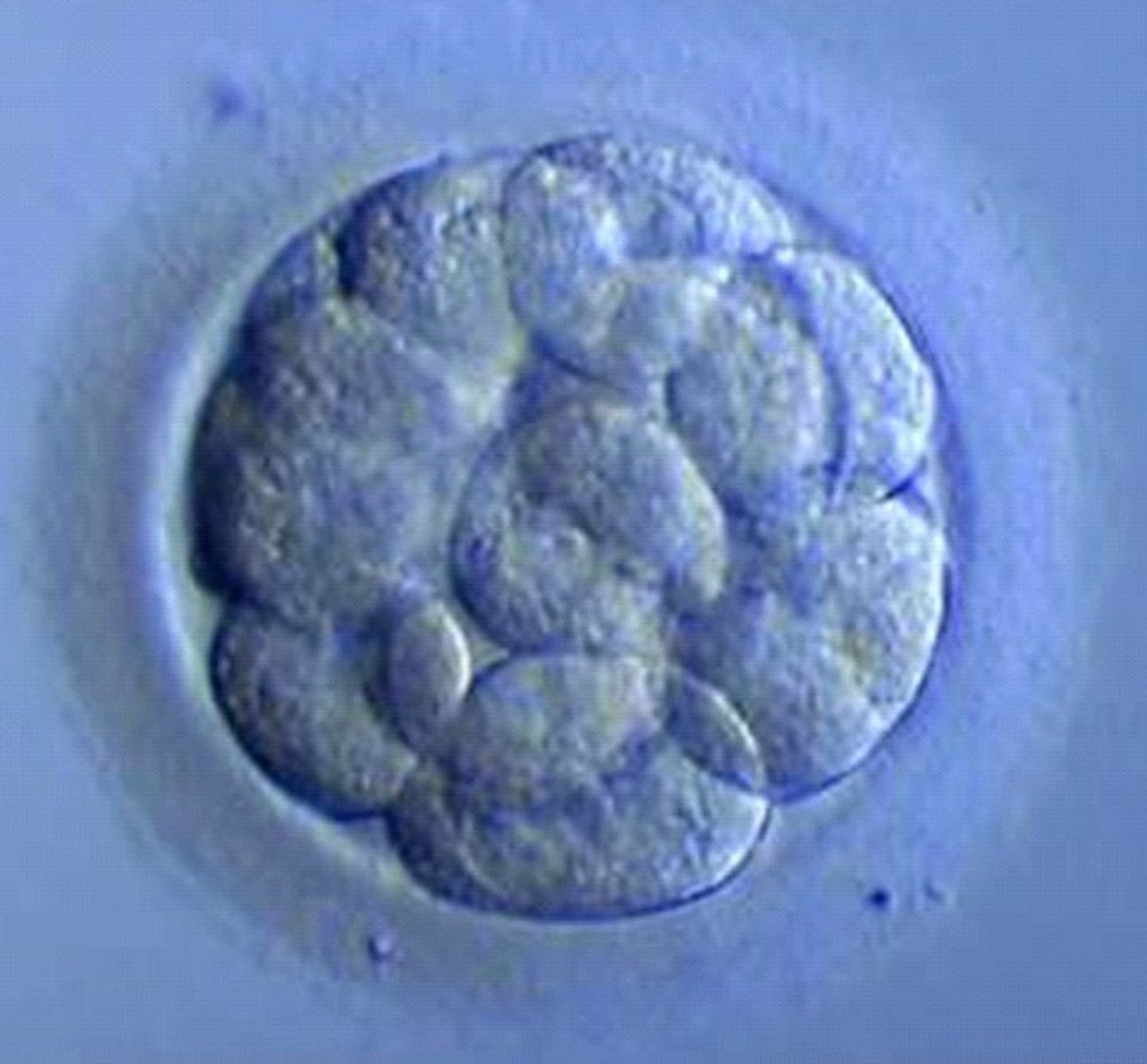
Morula
A solid ball of cells that makes up an embryo; in humans, this stage occurs within four days of fertilization. zygotes divides 2-3 days after fertilization
inner cell mass
forms embryo
embryonic age
time after fertilization (used by Biologist and us)
gestational age
time after last menstruation (embryonic + 2 weeks)
*used by clinicians
embryo invades uterus
day 6-15
develops into embryonic disk
embryonic disk
- composed of ectoderm and endoderm
- part of the inner cell mass
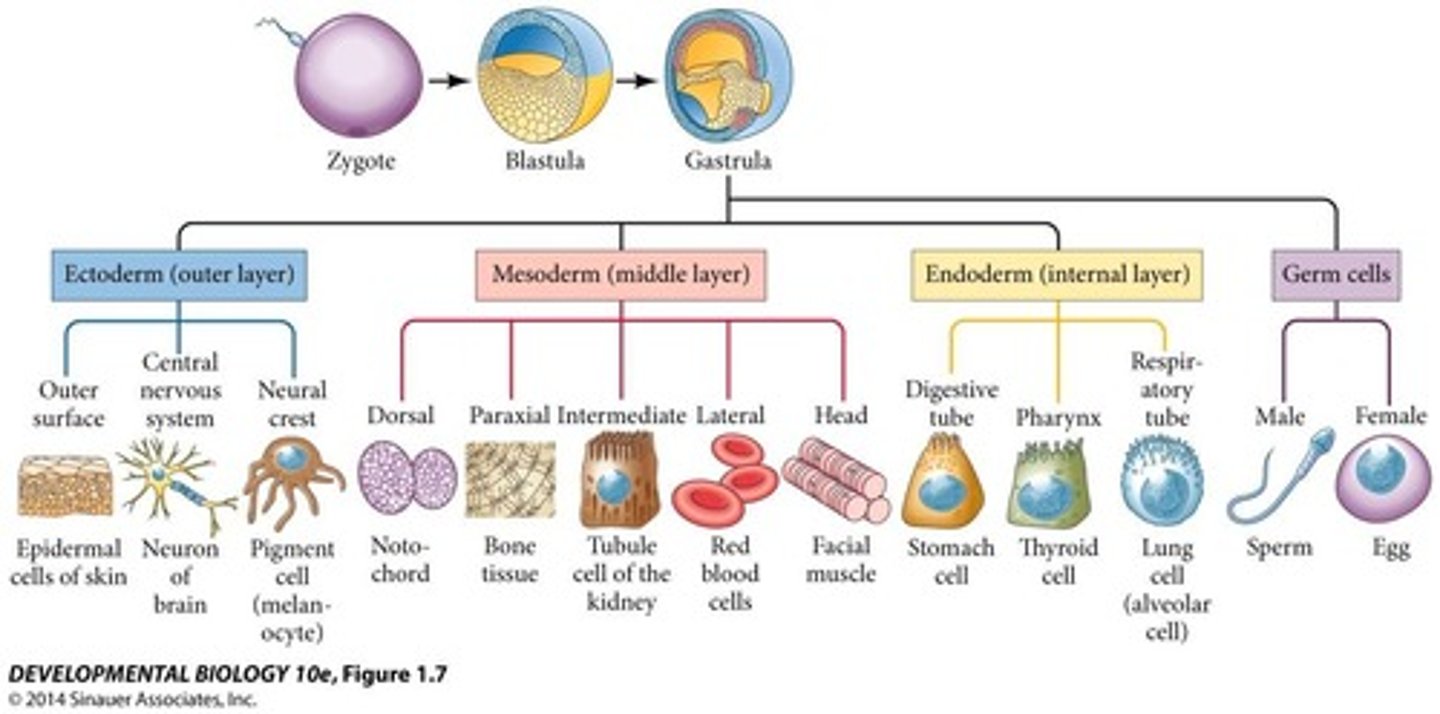
Primary germ layers
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
primitive streak
- defines 2 sides
-first midline
-develops in embryonic disk
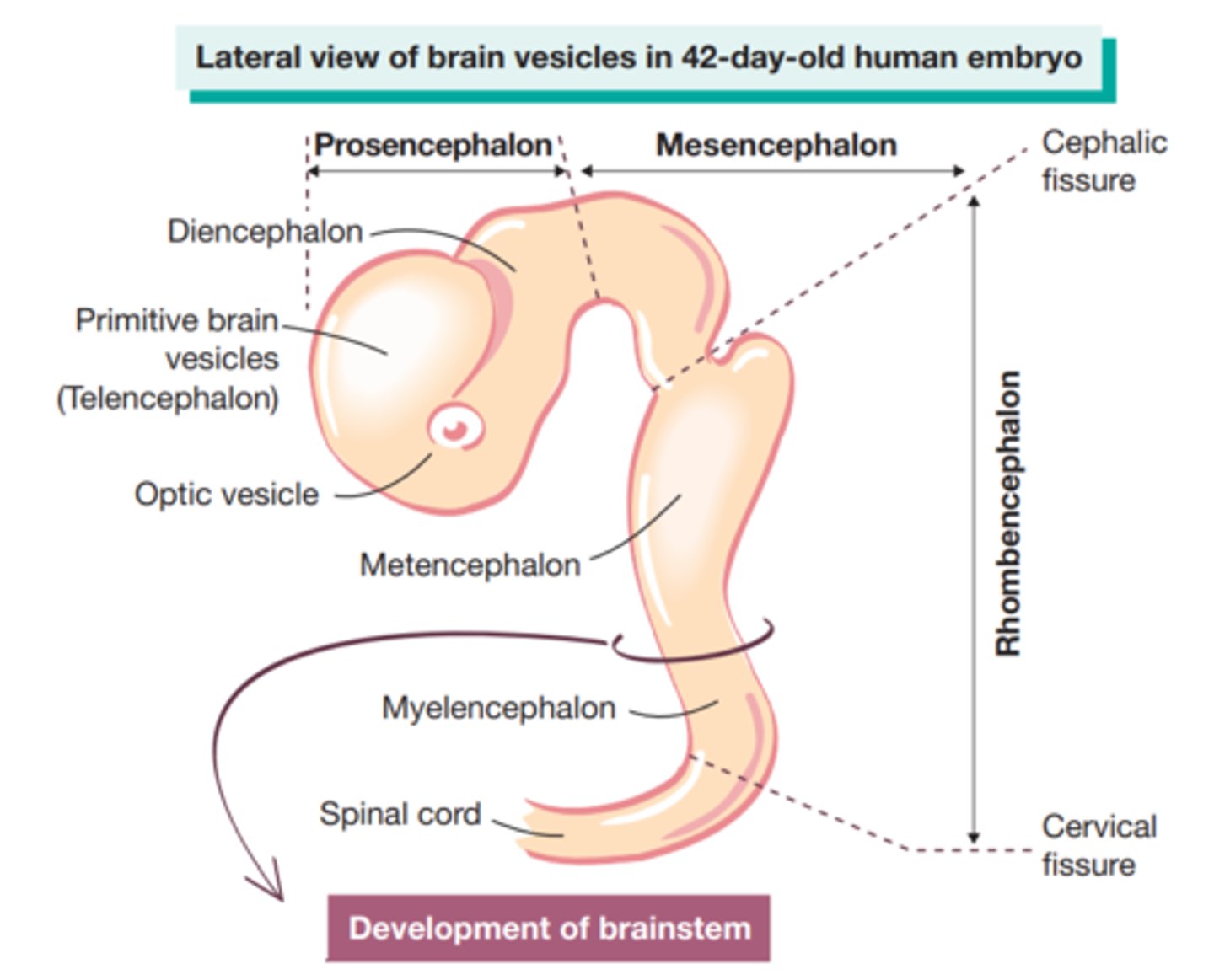
cephalic fissure
curve in midbrain of the embryo that positions the forebrain ventrally
mesoderm
- bone, muscle, and organs
-develops after other primary germ layers
- forms from cell migration from the ectoderm
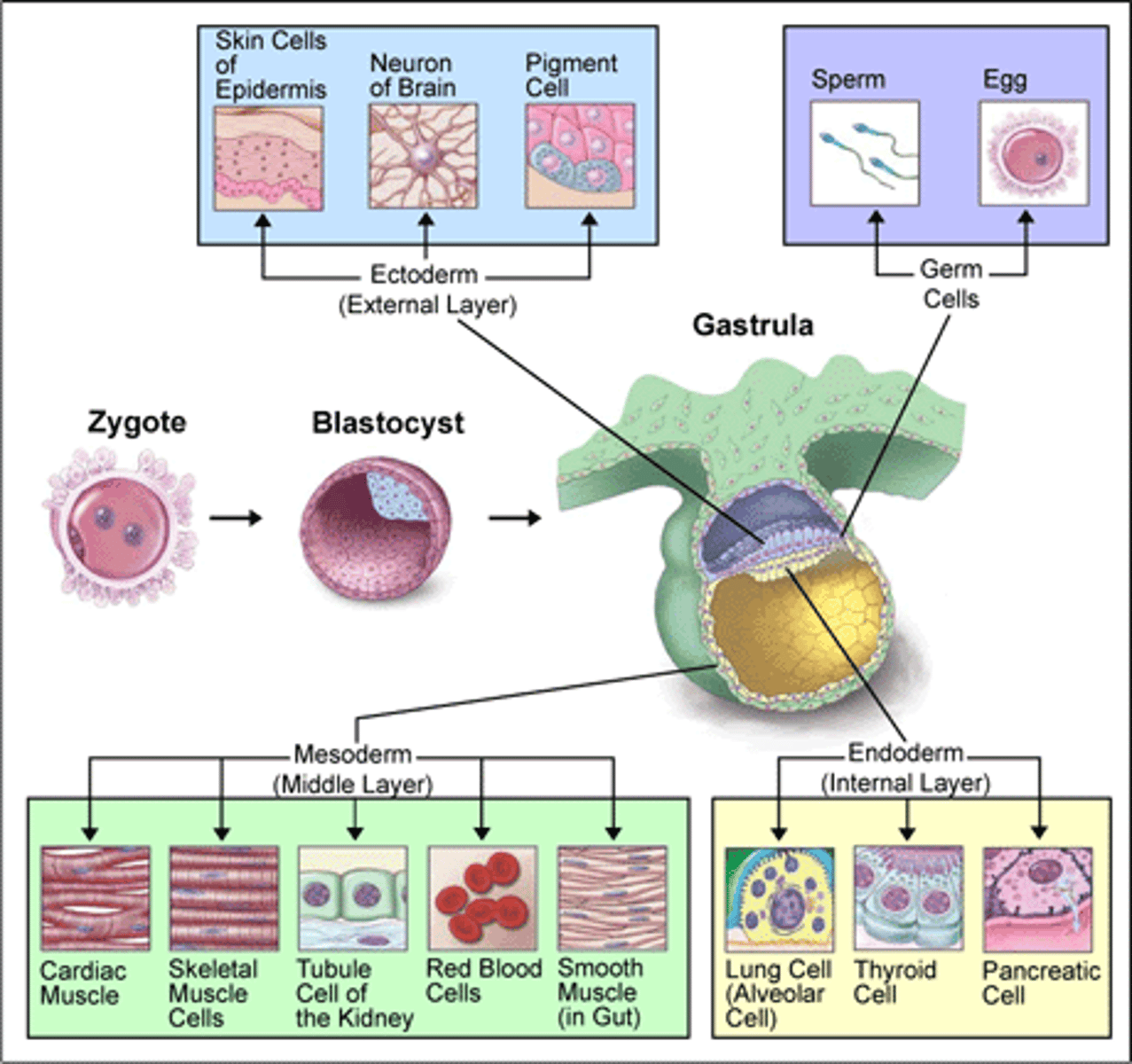
ectoderm
skin and nervous system
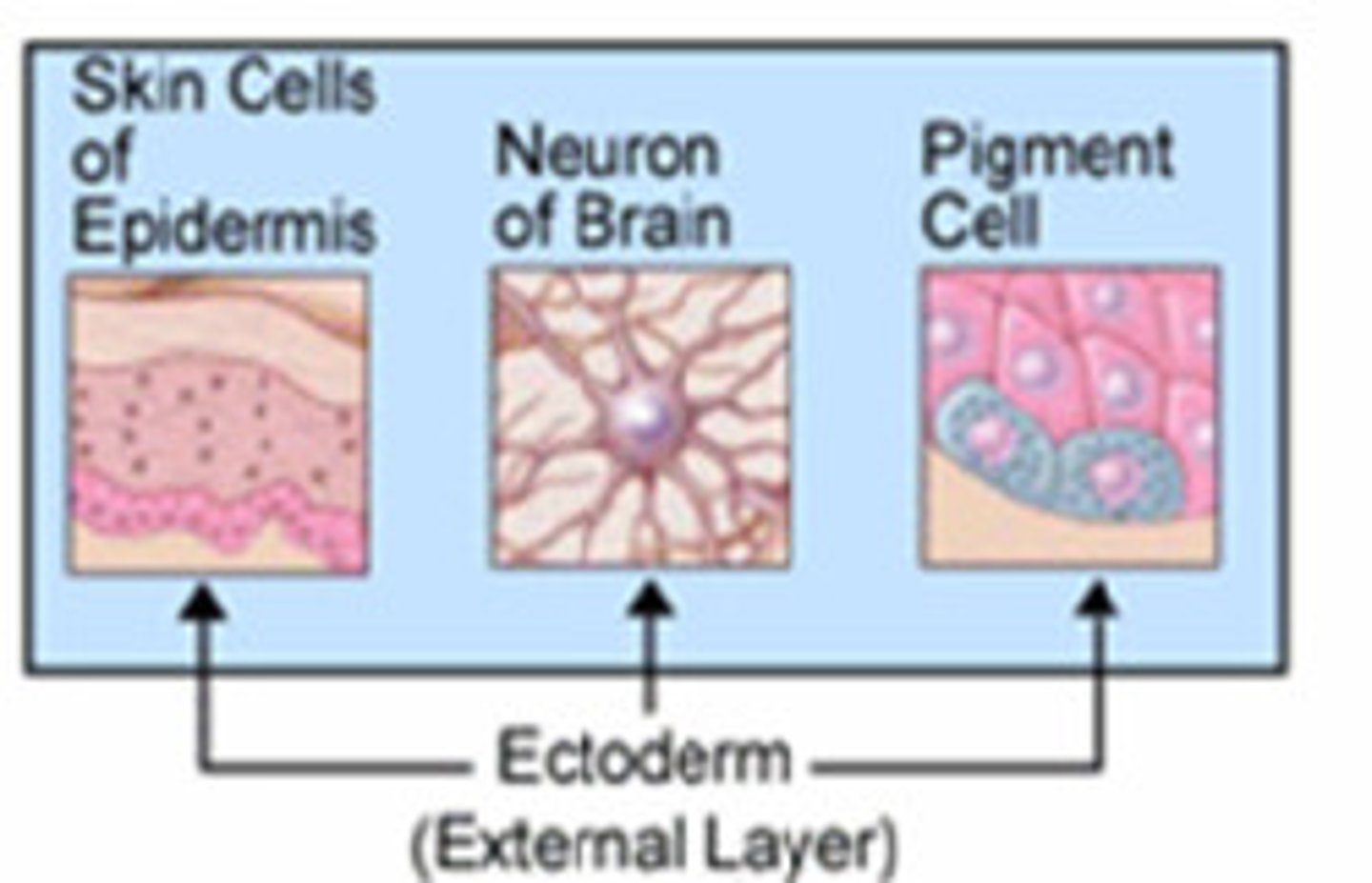
Endoderm
gut, glandular organs, liver
primary germ cell layers forms from...
cell migration
neural plate formation
cell migration from ectoderm forms mesoderm, forming neural plate
Neurulation
formation of the neural tube
( neural plate -> neural groove -> neural tube)
neural groove
before closure - hallow inside
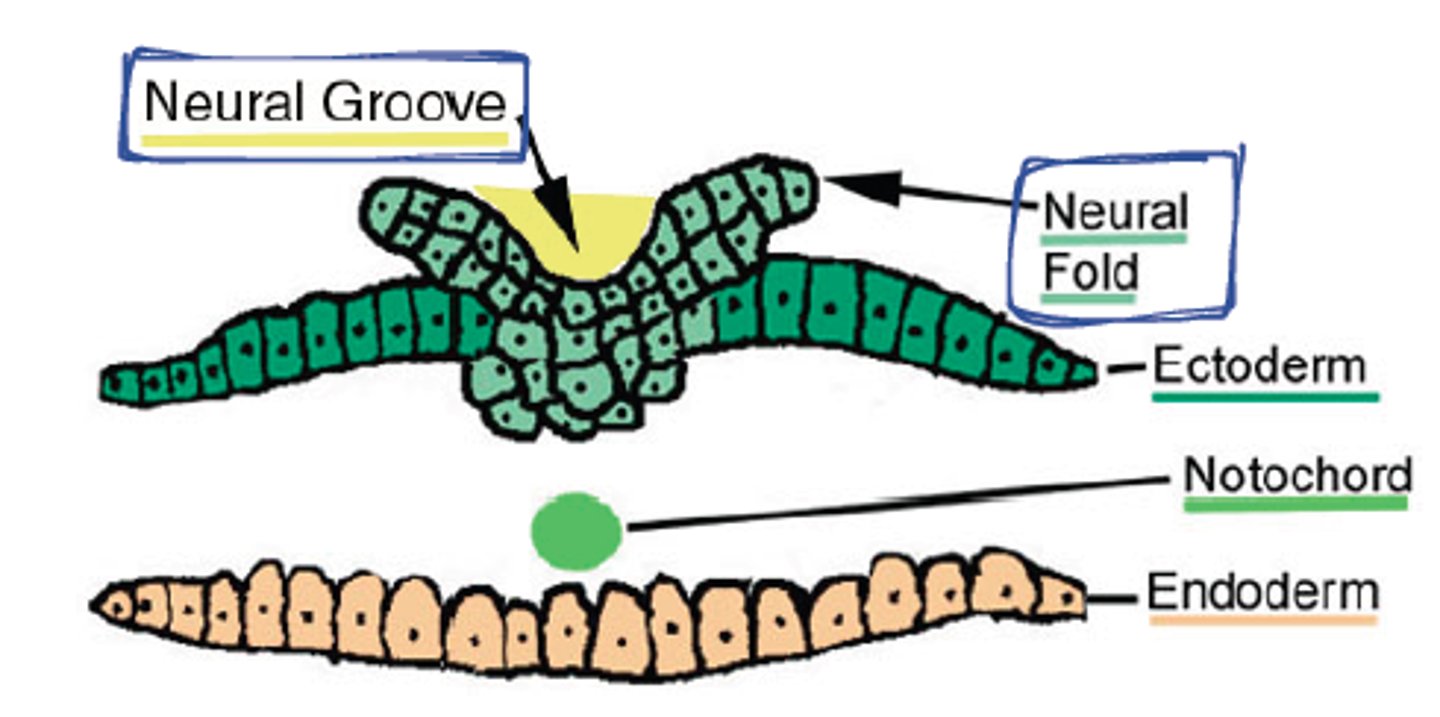
formation of neural crest
fusion above neural tube/groove
- will become the PNS
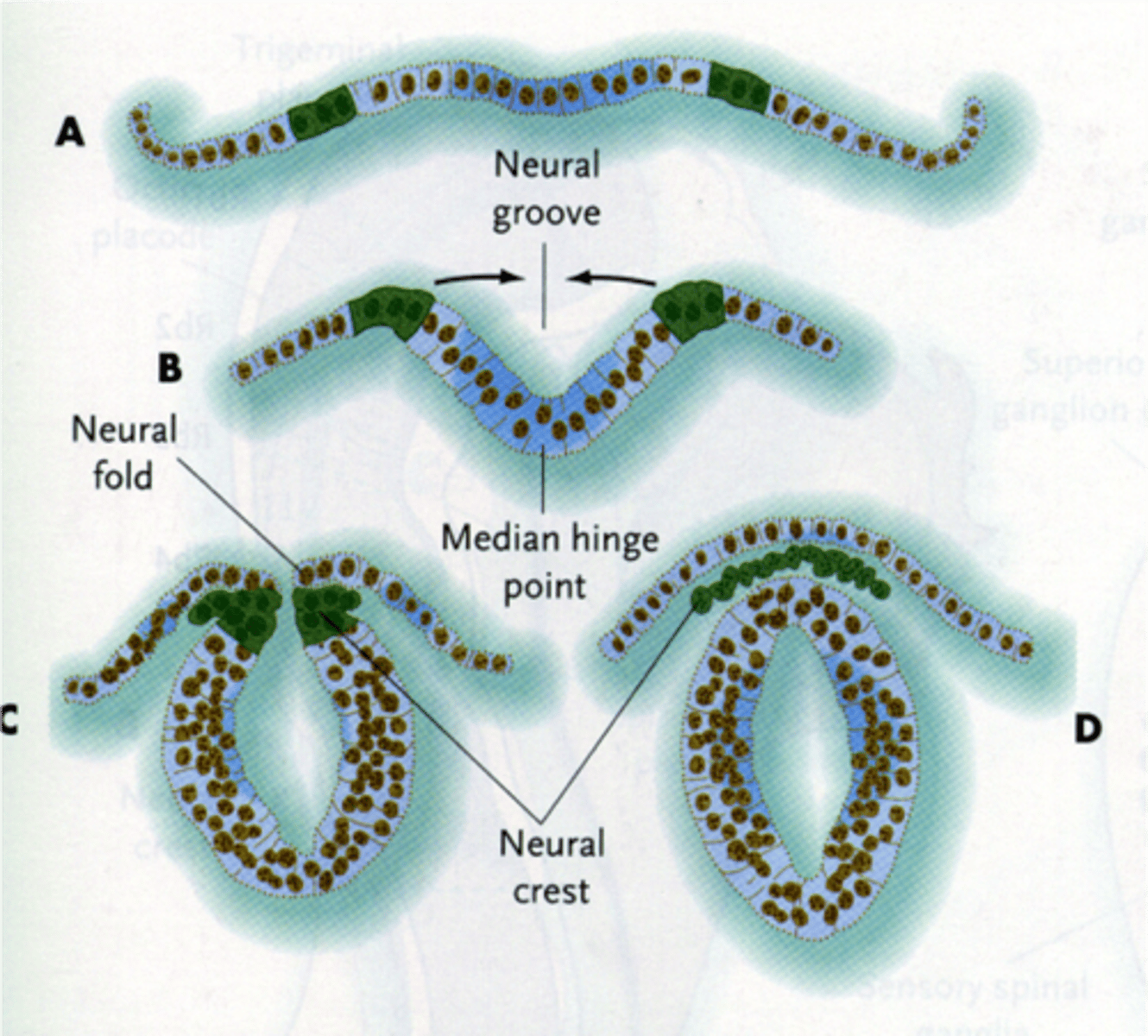
nueral tube
will become the CNS
- hollow tube that is inside
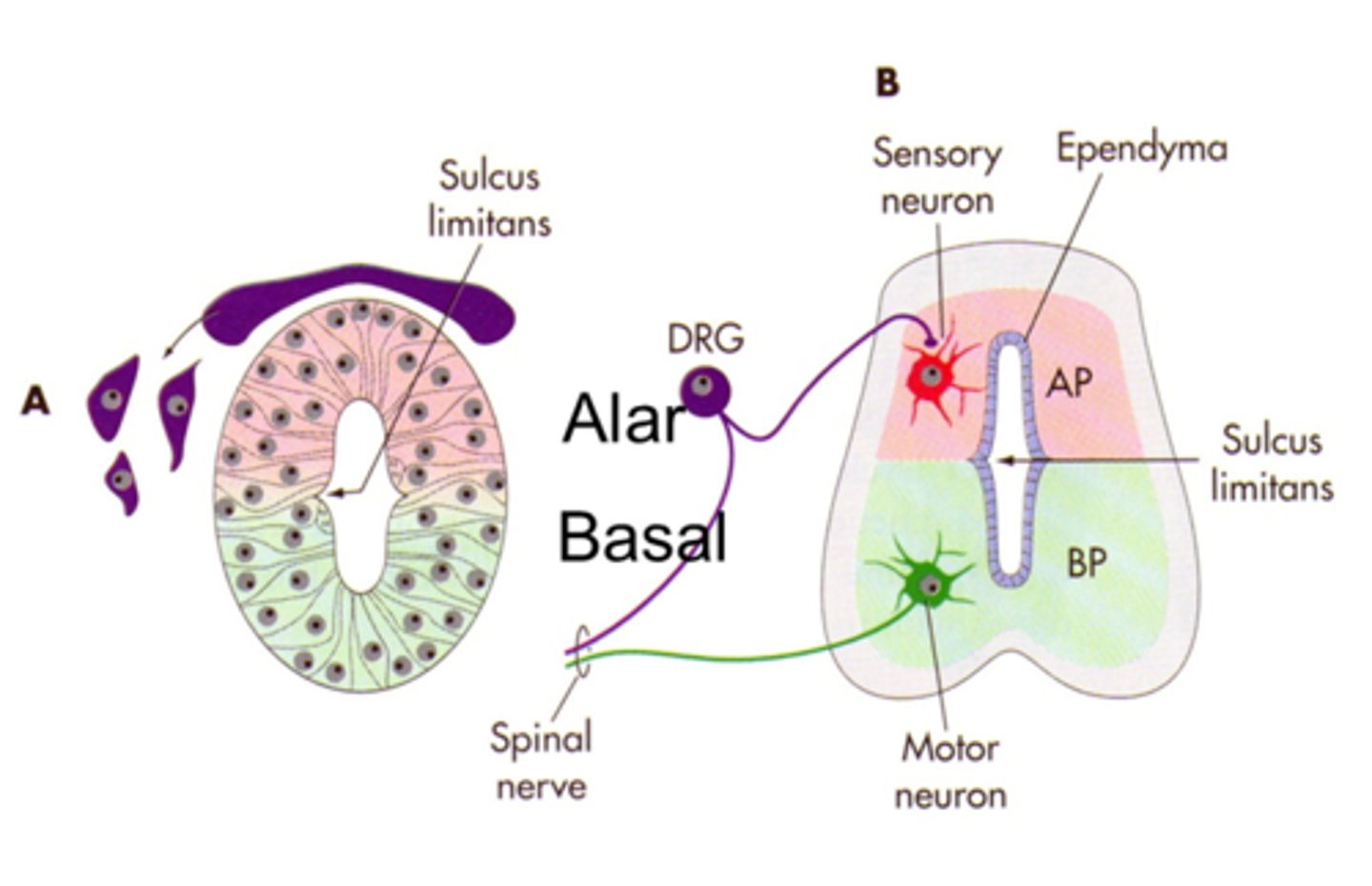
basal plate
motor (output)
ventral plate on neural tube
alar plate
sensory (input)
dorsal plate on neural tube
neural tube defects
spina bifida and anencephaly
spina bifida
- neural tube defect
- failure of closure at the caudal end of neural tube
- results in meninges forming outside the body
- prevented by B-12 during pregnancy
Anencephaly
failure of fusion of neural tube on rostral end
formation of the nervous system relies on
mitosis (cell division), cell migration
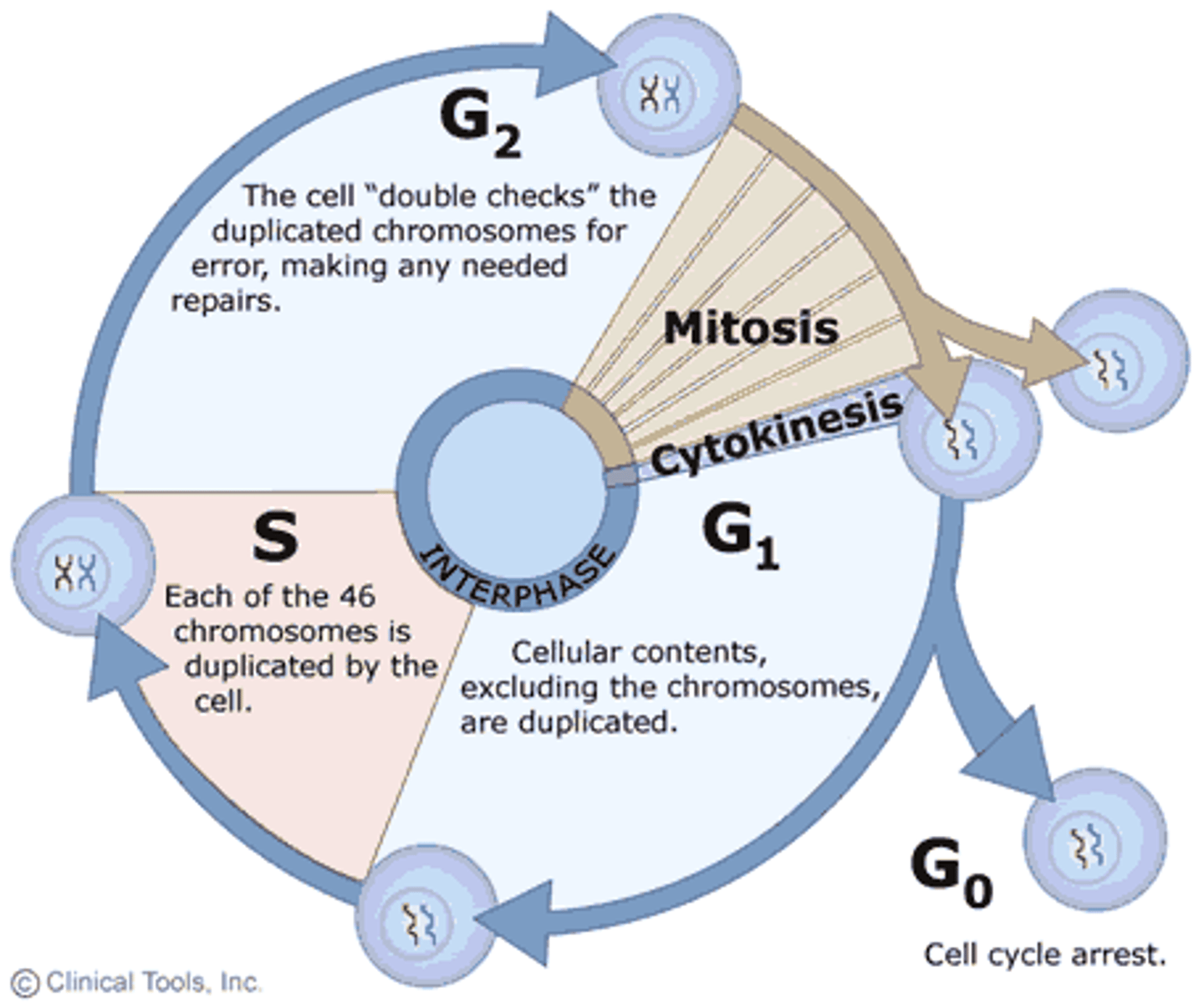
Mitosis allows
Growth
Differentiation
cell migration
cells move to their destinations
Cell Cycle
neurons terminally differentiate and enter Go
PNS forms from
neural crest (spinal column) and neurogenic placodes (developing head)
neural crest forms...
sensory ganglia
autonomic ganglia
schwann cells
enteric NS
melanocytes
Neurogenic placodes form...
-sensory ganglia (nerves)
-olfactory epithelium
-hair cells in ear
-anterior pituitary gland
-lens of eye
Formation of CNS relies on
migration and mitosis
spinal cord develops from
neural tube
2 important functions of placodes
1- cells can source important cells and tissue
2 - can induce changes in neighboring cells/tissues (lens)
neural vesicles
hallow swelling that occur around 26 days
primary vesicles
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
secondary vesicles
telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon
*divide around 40 days
pontine flexure
-between the mete- and myelen-
-opens the fourth ventricle
sulcus limitans
separates alar and basal plates
Development of cerebellum
Rhombic lip - divides and grows into..
around 20 weeks
development of forebrain
-telencephalon enlarges most
- outward expansion results in C-shape
Temporal lobe grows over
insular cortex
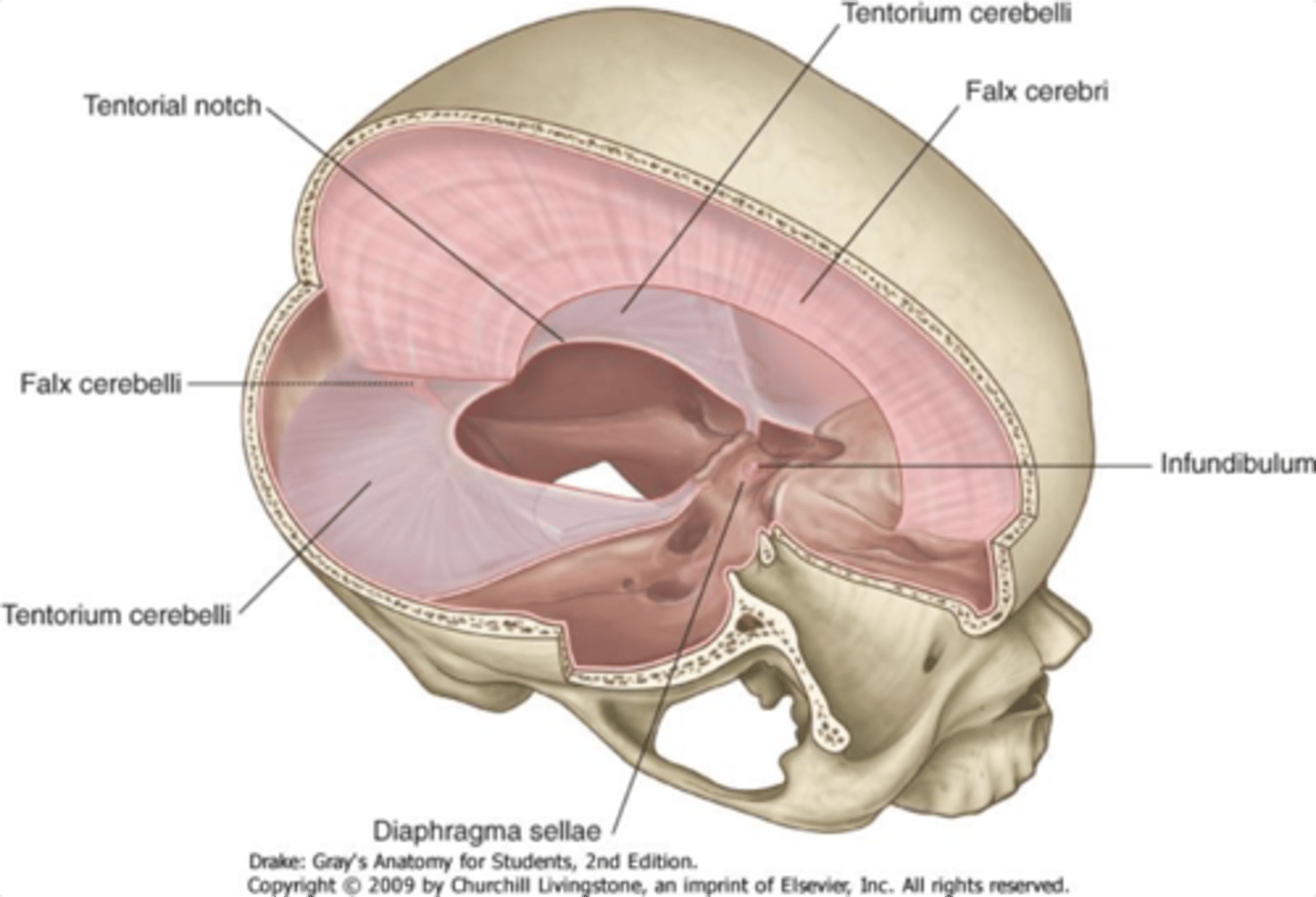
function of meninges
protect brain and spinal cord - suspension system
3 layers of meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Dura Mater
adheres to inside of skull
- has one blood supply (meningeal arteries)
-has pain sensing nerve fibers
arachnoid trabeculae
little beans between pia and arachnoid
dural folds
falx cerebri
- stabilizes brain from forces from sides