Hematology 2
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
bone marrow role and what it produces
Role: Primary site for blood cell production (hematopoiesis).
Produces: Red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets
spleen role
Spleen:
Role: Filters blood, removes old RBCs, and stores platelets
Additional: Plays a role in immune response by filtering pathogens.
liver role
Liver:
Role: Produces important plasma proteins (like albumin and clotting factors) and stores iron for hemoglobin production
Detoxifies: Removes waste products and toxins from the blood.
heart role
Heart:
Role: Pumps blood throughout the body, ensuring oxygen and nutrients are delivered to tissues and waste products are carried away.
Circulation: Responsible for systemic and pulmonary circulation.
lymphatic system role
Lymphatic System (Lymph Nodes & Vessels):
Role: Returns excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream and helps fight infections through WBCs (immune function)
kidney role
Kidneys:
Role: Regulate blood volume and pressure by controlling fluid balance and producing erythropoietin (hormone that stimulates RBC production).
Filter: Waste and excess substances from the blood
how common are granulocytes, appearance and role
Granulocytes: most common (50-70%)
Types: Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
Appearance: Have granules in their cytoplasm that stain differently.
Role: phagocytosis, contains enzyme granules that release proinflammatory factors
Neutrophils: First responders to bacterial infections, phagocytize pathogens.
Eosinophils: Fight parasitic infections and allergic reactions.
Basophils: Release histamine during allergic responses and inflammation
Monocytes appearance, role
Monocytes:
Appearance: Larger, kidney-shaped nuclei and abundant cytoplasm
Role: Differentiate into macrophages or dendritic cells when they leave the bloodstream and enter tissues, involved in phagocytosis and antigen processing of foreign particles
Macrophages: Phagocytize pathogens, dead cells, and debris.
Dendritic cells: Present antigens to help activate other immune cells.
Function: Involved in immune response, tissue repair, and inflammation
lymphocytes appearance and role
Lymphocytes:
Types: T cells, B cells, and Natural Killer (NK) cells.
Role: involved in antibody production and immune cell communication, alerting, and targeting through cytokine release
T cells: Kill infected or cancerous cells and help regulate immune responses.
B cells: Produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
NK cells: Kill virus-infected cells and tumors.
Appearance: Smaller with a large nucleus and a thin rim of cytoplasm
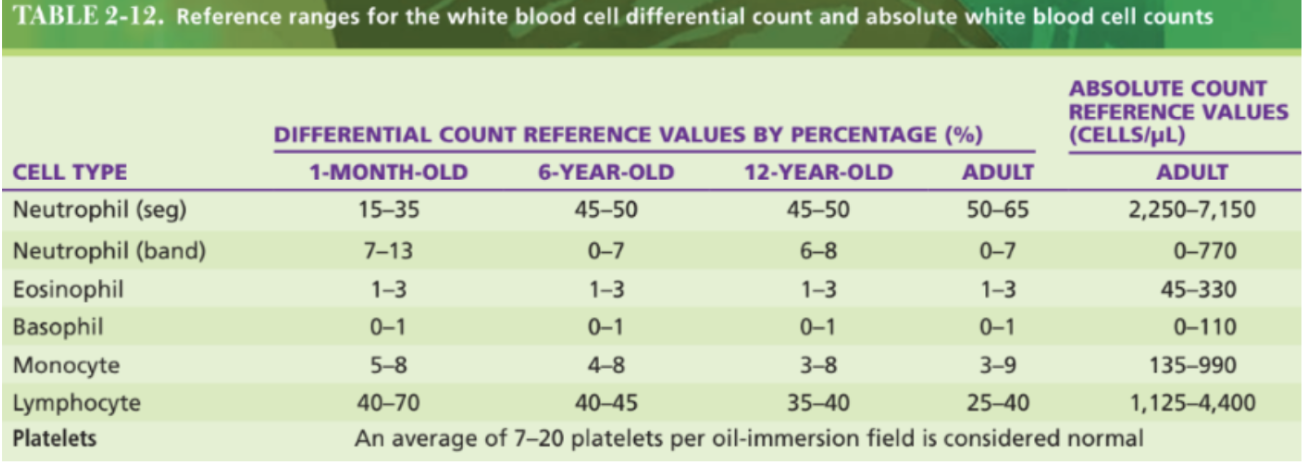
Reference ranges for WBC differentials
1month old
6yr old
12yr old
adult
What factors affect wbc values?
Factors affecting values
Bacterial infections = higher neutrophil amounts
Viral infections = higher abnormal lymphocytes
Parasites and allergies = higher eosinophil counts
Leukemia = increase in one type of WBC
What are reticulocytes? what are they used for to assess
Reticulocytes - immature RBC produced in bone marrow
Used to assess erythropoiesis (RBC production), especially in anemia cases
Reference ranges for immature rbcs to total rbcs%
adult
newborns
Reference ranges
Age | Reference range in % | Upper limit of normal % |
Adults | 0.5-1.5% | 3 |
Newborns | 2.5-6.5% | 10 |
what does erythrocyte sedimentation help detect?
Erythrocyte sedimentation - process of RBcs settling at liquid bottom
Rate can be used to detect inflammation or malignancies
what are the steps?
Steps:
Blood sample is placed in a thin tube
Distance the RBC’s fall from top of liquid is measured (can be high/low)
What factors affect the sedimentation rate?
(aggregate, disease, shape)
Factors affecting sedimentation rate
Erythrocytes can aggregate (combine) = more mass, higher sedimentation rate
Indicates high acute phase proteins, meaning inflammatory/degenerative disease
Disease - macrocytic cells (big RBCs) = higher sedimentation rates
Sickle shaped/spherocytic cells = low sedimentation rates
Amount of RBCs; higher levels of polycythemia (abnormal RBC increase) = lower rate of sedimentation (more viscous/thick)
Reference ranges for sediplast ESR