Sensation and Perception Quiz 3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
How we hear
every natural sound we hear is composed of multiple frequencies, we hear a lot at once
wavelength is the inverse of
frequency
Sinusoid wave
represents pure tones, regular periods of sound condensation
sound waves
created by alternating patterns of high and low density air molecules generated by movement of a stimulus
Unit of frequency
measured in Hertz (Hz)
Frequency
number of waves per unit of time
frequency is the inverse of
wavelength
frequency is determined by
rate at which air is compressed (ex. speaker diaphragm)
Well spaced molecules
low frequency
Closer together molecules
high frequency
we hear different frequencies as having different
pitches
Amplitude
amount of energy in the wave, how big it is
how we perceive amplitude
loudness
Phase
sound waves position in the cycle, technology behind noise cancelling headphones
how noise cancelling headphones work
match incoming noise with complete opposite phase noise, which cancel each other out and we perceive nothing
constructive interference
two sounds add together and we get a louder sound than two original, occurs when waves are in phase
Deconstructive interference
we add two sounds out of phase 180 degrees we get no sound (noise cancelling headphones)
Timbre
distinguished sound quality: ev vocal note vs guitar note
Waveform
graphical representation of a wave against time
Spectrum
amplitude against frequency (shows amplitude on y axis and frequency on x axis)
how speakers work
produce sound by moving diaphragm inward and outward, alternating pattern of refraction and compression that creates wave
compression
high density sound
refraction
low density sound
Sound level
an vary from whisper to explosion, expressed on decibel scale
Every change in 10db is a tenfold increase in sound power
humans are most sensitive to what range
20-20 000 Hz, mostly around the 3-4 thousand range
Pinna
outermost part of ear, funnels sound into ear canal, varies across species (elaphans have huge ears)
Ear Canal and drum
pinna funnels sound into ear canal, vibration vibrates eardrum that creates the signal sent to brain
Ossicles
3 smallest bones in body
hammer, anvil, stirrup
role of the ossicles
Transmits and amplifies sound even more because inner ear is fluid filled
fluid makes it harder to translate into signals
how sound gets amplified by ossicles
small movements of malleus amplified into larger movement by the time they reach the stapes
Stapes rests on the oval window, pushes it in and out in response to tympanic membrane
how sound gets transducted
Movement of oval window causes cochlear fluid to move like waves
Movement causes displacement of basilar membrane
Basilar membrane lined with hair cells that respond to waves and generate electric potentials
basilar membrane located in
the center of cochlea
Hair cells at base sensitive to
high frequencies
Apex has hair cells sensitive to
low frequency
Organ of Corti
Region of sound transduction
contains rows of hair cells
Inner hair cells
depolarize and send signals in response to their preferred frequency
outer hair cells
amplify sound signals
organ of court is covered by
techtorial membrane
Spiral ganglia
first neurons in auditory pathway, they exit cochlea at auditory nerve
Audiogram
measure of how well someone can hear
Uses method of limits
hearing loss due to noise exposure (audiogram)
has higher threshold
Presbycusis
age related hearing loss, hair cells degrade over time especially for high frequency sounds,
Hyperacusis
makes everyday sounds feel too loud, caused by a variety of things like drugs, head injury, mental health, surgery, infection
Tinnitus
hearing sounds that aren't there, ears ringing
Amplification
a hearing aid to help amplify sounds and reverse hearing loss
compression technology
compress sound info to lower its pitch so it's received by an intact region of the ear, distorts harmonic arrangement of a sound and affects its timbre
Cochlear implants
microphone worn on back of ear, transmits sound info through skull to electrode in cochlea, directly stimulates spiral ganglion initiating signaling. For people whose hair cells don't work
Ascending auditory pathway
Neurons of cochlear nucleus project to superior olivary complex on contralateral side
Then project to inferior colliculus
And then to medial geniculate nucleus
More crosstalk than visual pathway
Efferent fibres
carry info away from brain
Afferent fibres
carry info toward the brain
8th cranial nerve
vestibular and cochlear area, transmits sound and balance and orientation
Tonotopic organization
different sound frequencies are processed by different neurons located in specific places
Present at each point along pathway to preserve brain's ability to discriminate sounds based on pitch
Where pathway
heads toward parietal lobe to integrate with visual stream, tracks location and movement
What pathway
travels along ventralateral temporal lobe to the front brain, integrates with attention memory and emotion discernation
Cues to segregation/fusion
Other parameters can affect whether they are bound or separated
When the time between them is short were more likely to perceive two sounds
If theyre more slow we perceive a single sound source
ADD INFO!
Harmonic structure/ timing cues
Most sounds harmonic in nature
If they all have the same onset and onset times, we perceive them as together
If we change spacing of a frequency so its not a multiple of the harmonic we’ll perceive two diff sounds
Sound Localization
How we tell where things are
Interaural time difference cues
etween ears, there are time differences between what we hear by a 10th of a second because one ear is closer, the head also blocks some noise (acoustic shadow)
location with biggest ITD
Source 90 degrees to right or left
Interaural difference in the superior olive
Give our brain ability to encode interaural time differences
Jeffers Model
If a sound is on your right, it'll reach right ear before left
if Electrical activity at right superior olive arrives first it results in electrical activity at ITD sensitive cell in that location
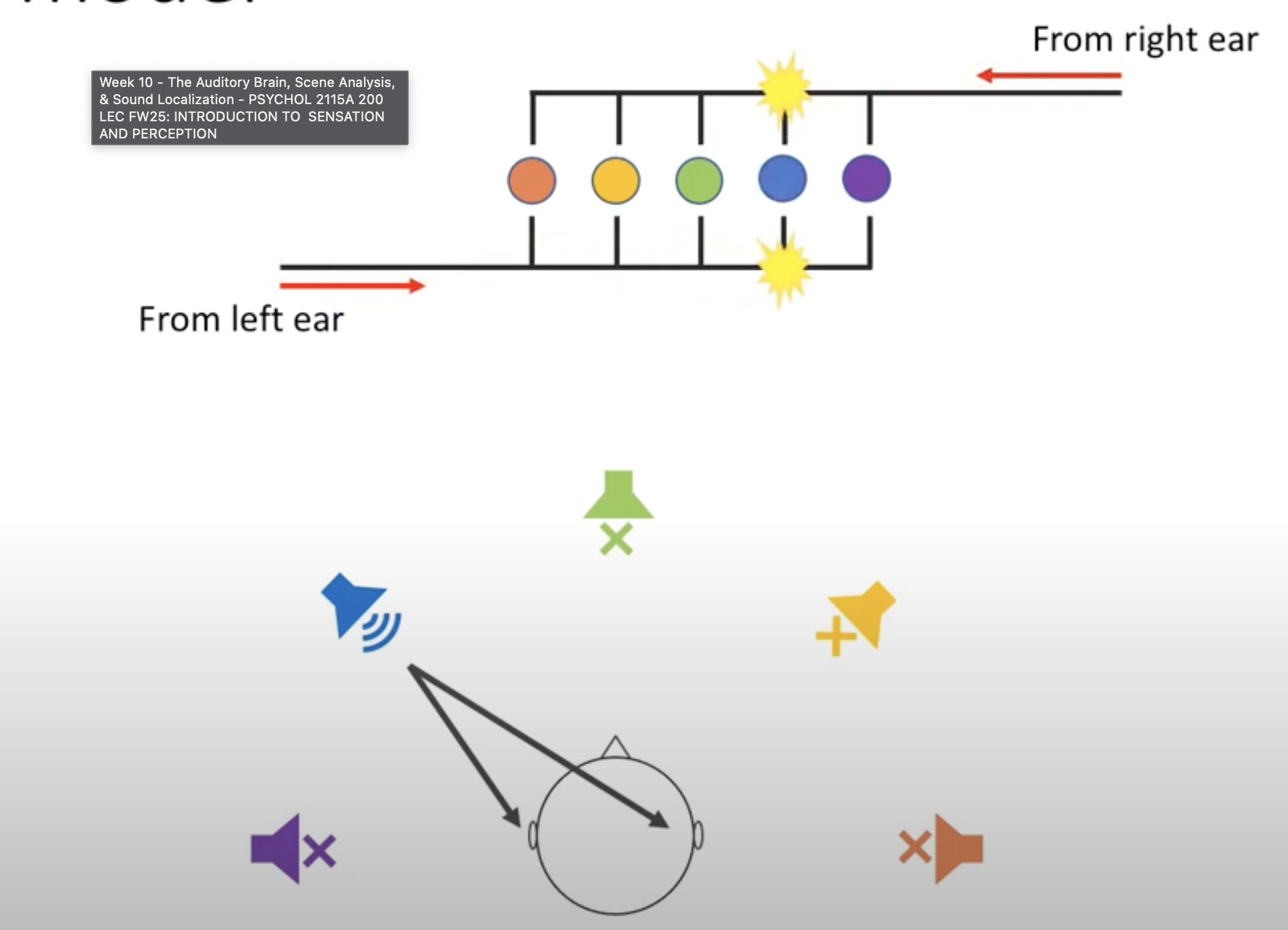
Source Confusion
There are places we can't discriminate between ex. 60 degrees and 120 degrees on the same side since they have the same Interaural difference
We have to use other cues like prior knowledge
Human pinna helps because it funnels info differently from different elevations, helps judge adobe and below
High frequency sound and object tracking
Some species are better than others ex. bats and echolocation