5. Endo/Repro Exam 2: Physiology: Ovarian and Uterine cycles (Dr. Leavis)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What has the following characteristics:
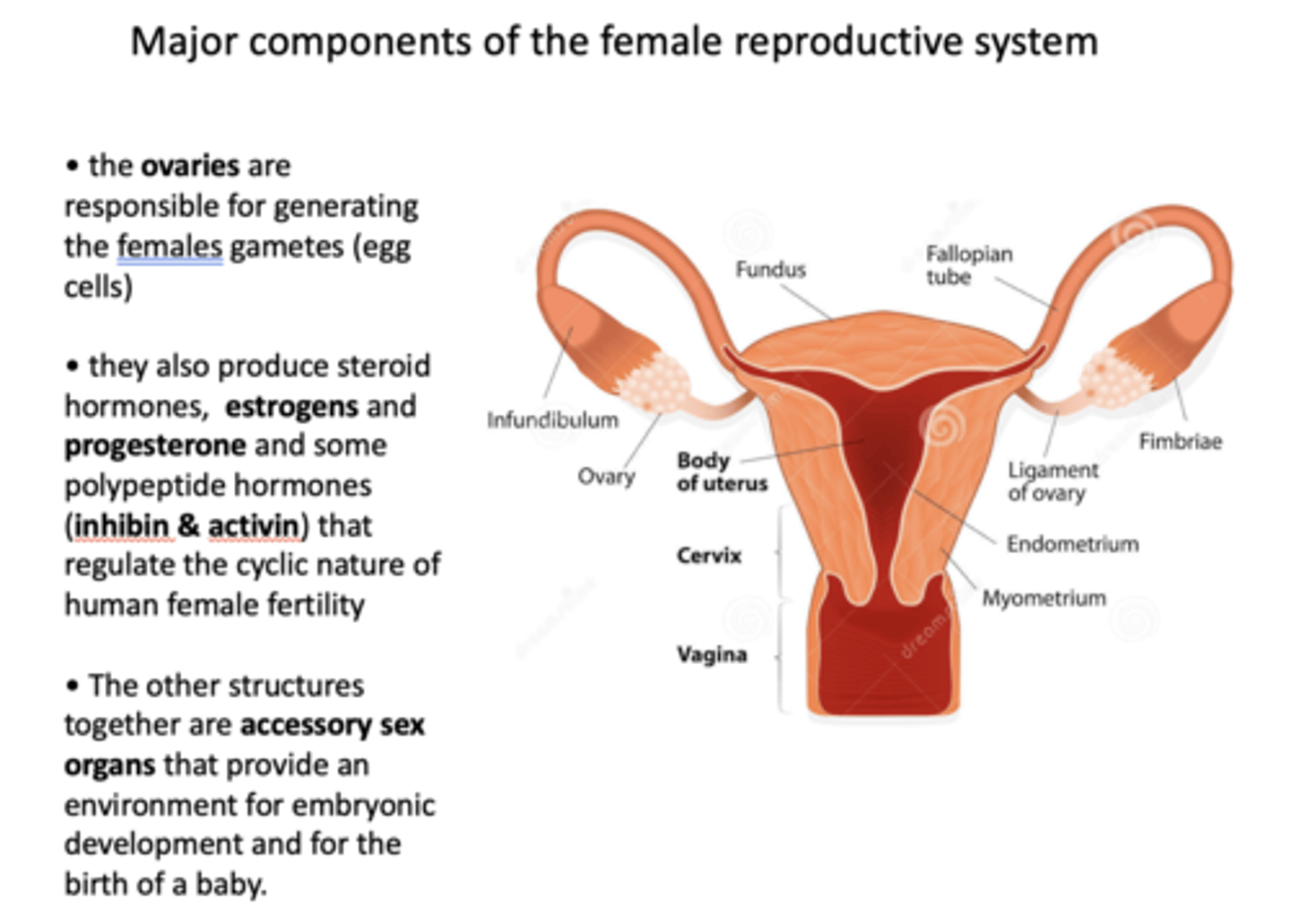
- Responsible for generating the females gametes
- Produce estrogen, progesterone, inhibin & activin that regulate the cyclic nature of female fertility
ovaries
The characteristic _______________ seen in the maturing of a female gamete in an ovarian follicle and releasing it (ovulation) is called the menstrual cycle because it involves the periodic shedding of blood and endothelial tissue from the uterus at monthly intervals.
periodicity

T/F: Changes in the ovary during the cycle is coordinated with changes in the cervix and in the uterine lining or endometrium
True

T/F: The cyclic functions are integrated through hormones secreted from the hypothalamus/pituitary and the ovary
True

In pregnancy, the _________ functions as an endocrine organ, producing hormones that support fetal development
placenta

during fetal development primordial germ cells originate in the yolk sac of the embryo- they migrate to the genital ridge where they become _____________
oogonia (~7 weeks gestation)
What does the number of oogonia increase to by week 15 of the mitotic divison?
~15 million
what is the name of a oogonia that arrests in prophase of meiosis 1?
primary oocyte
The first stage of meiosis in primary oocytes is frozen in what stage?
prophase
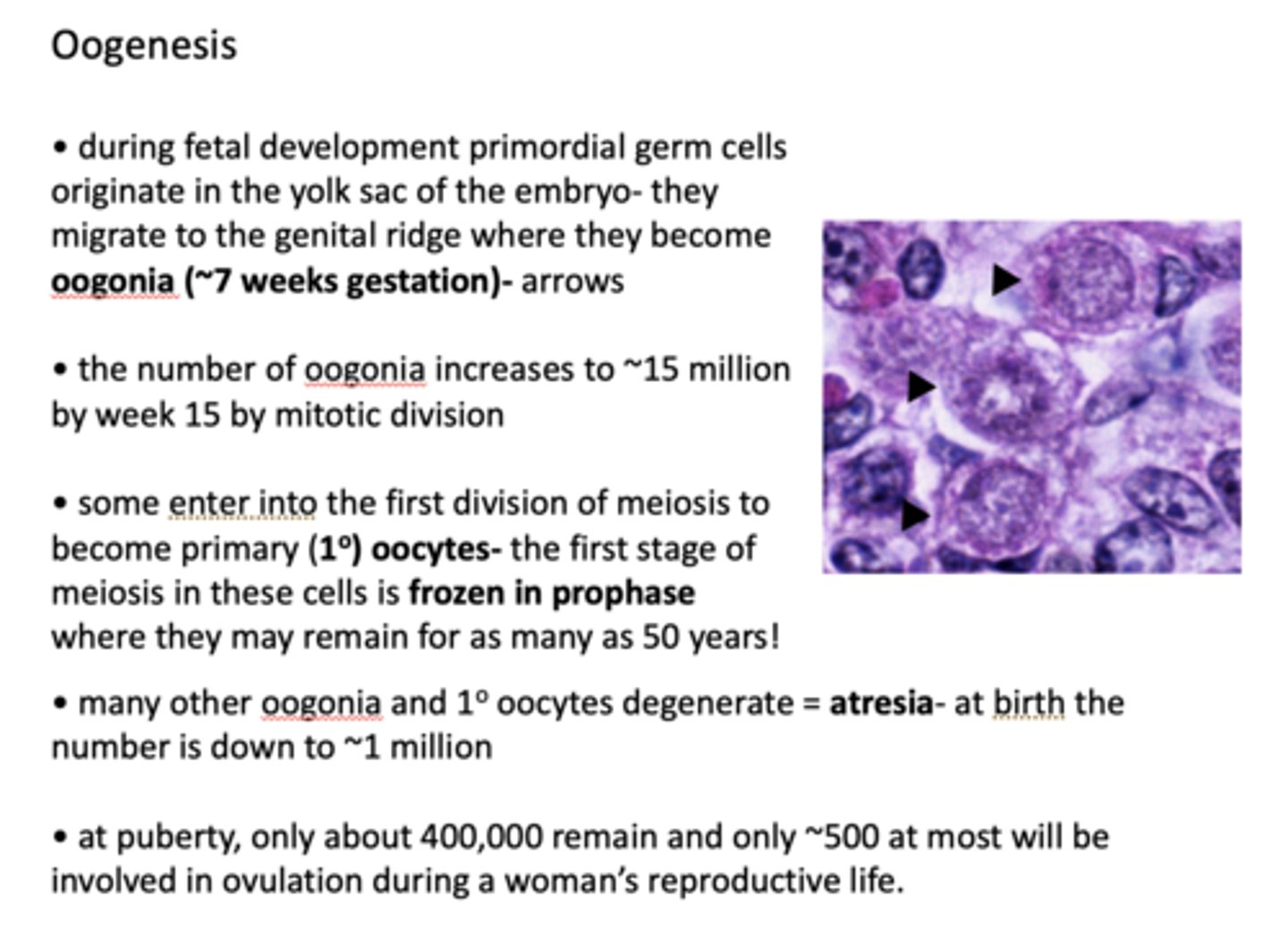
many other oogonia and 1o oocytes degenerate = ___________- at birth the number is down to ~1 million
atresia
T/F: At puberty, only about 400,000 primary oocytes remain and only ~500 at most will be involved in ovulation during a woman's reproductive life.
True
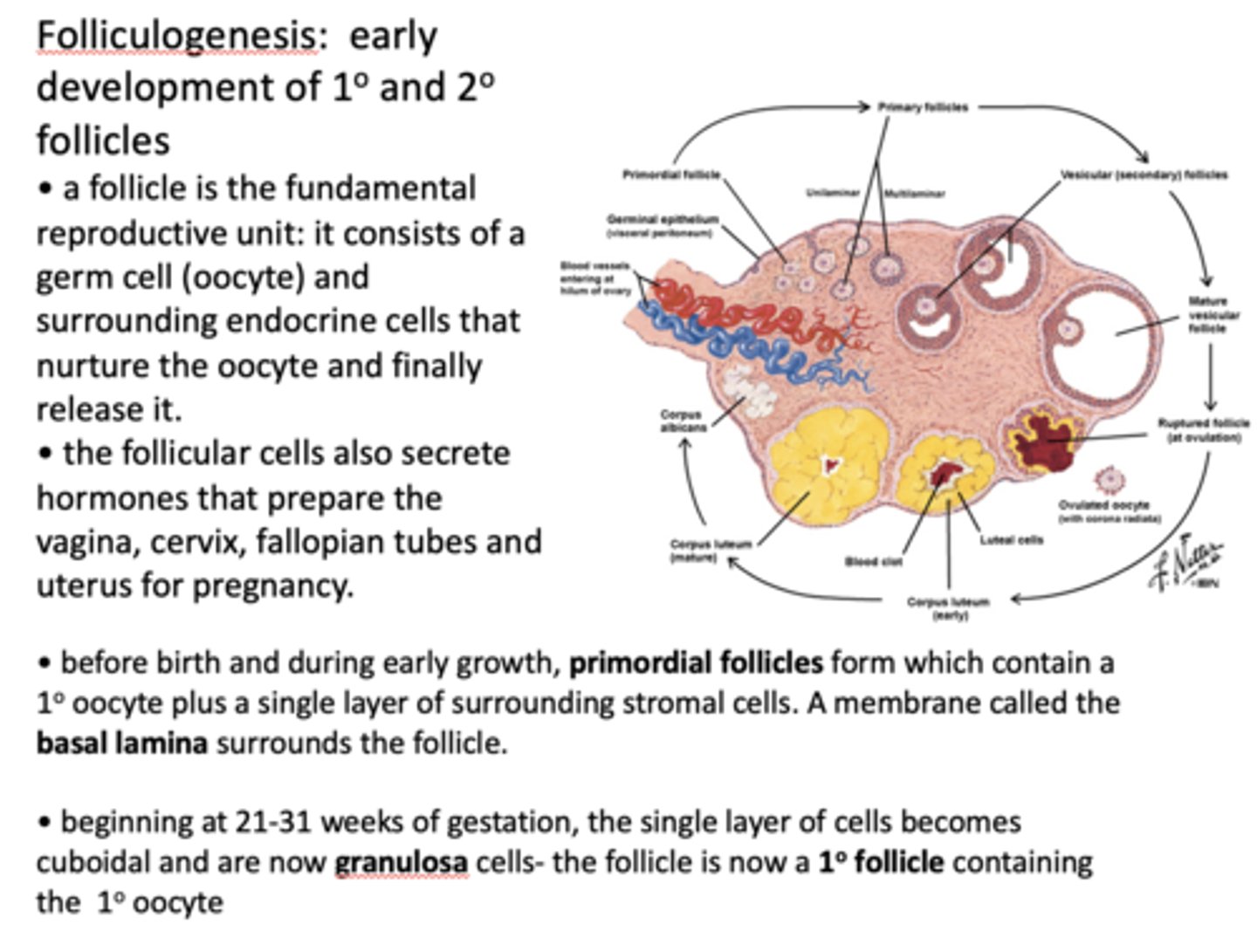
The fundamental female reproductive unit is known as what?
follicle
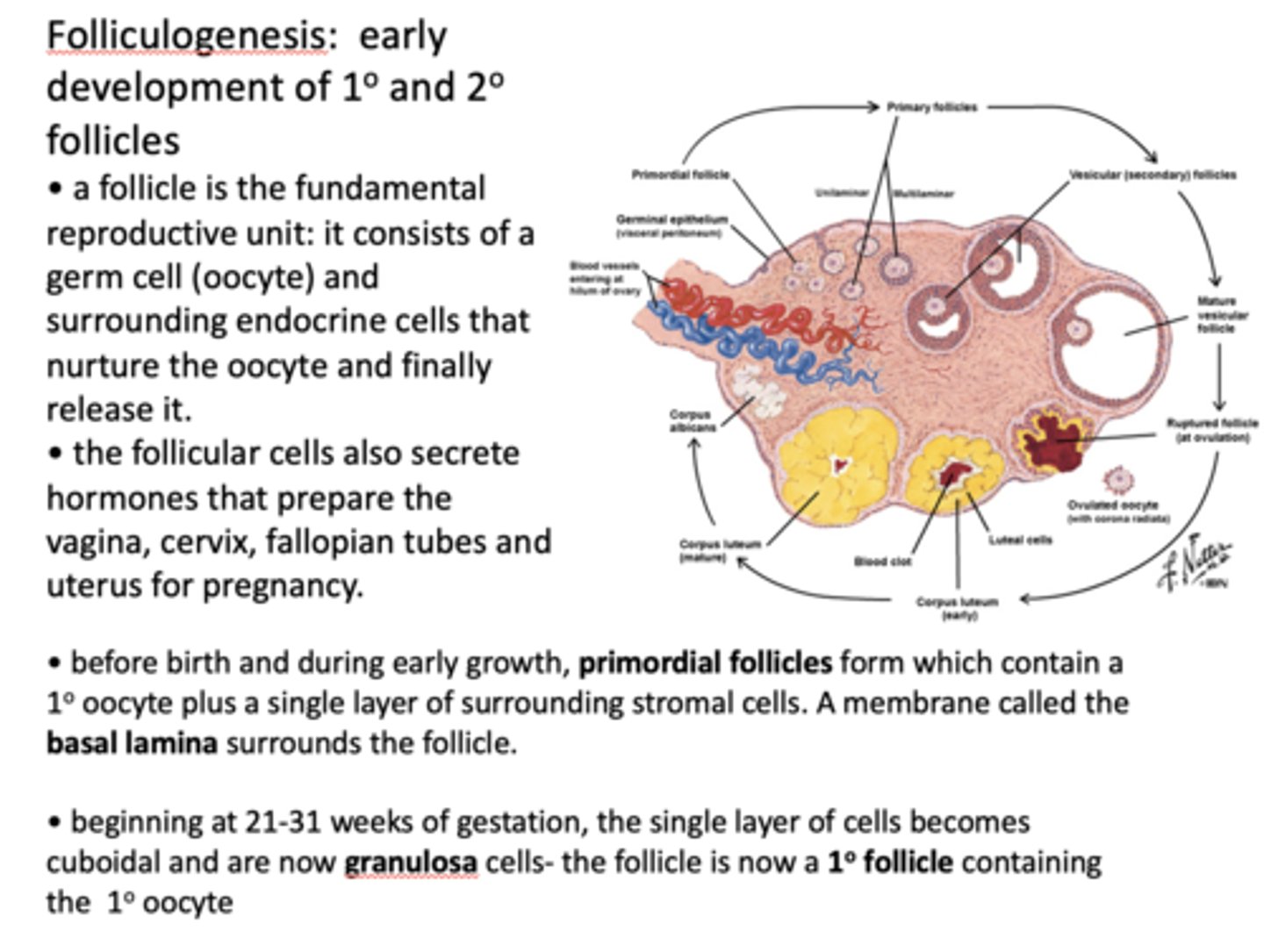
What consists of a germ cell (oocyte) and surrounding endocrine cells that nurture the oocyte and finally release it?
Follicle
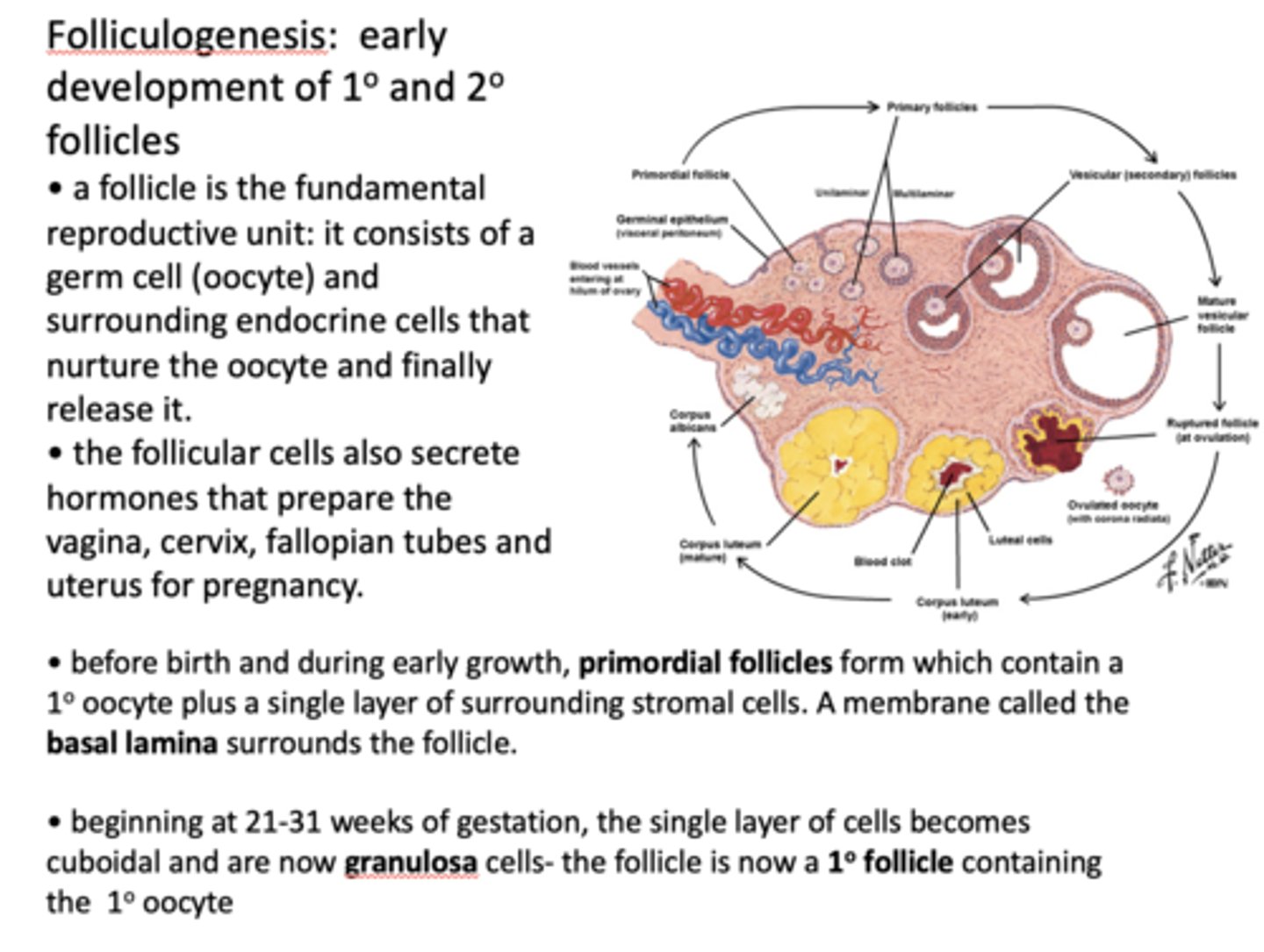
What cells secrete hormones that prepare the vagina, cervix, fallopian tubes and uterus for pregnancy?
Follicular cells
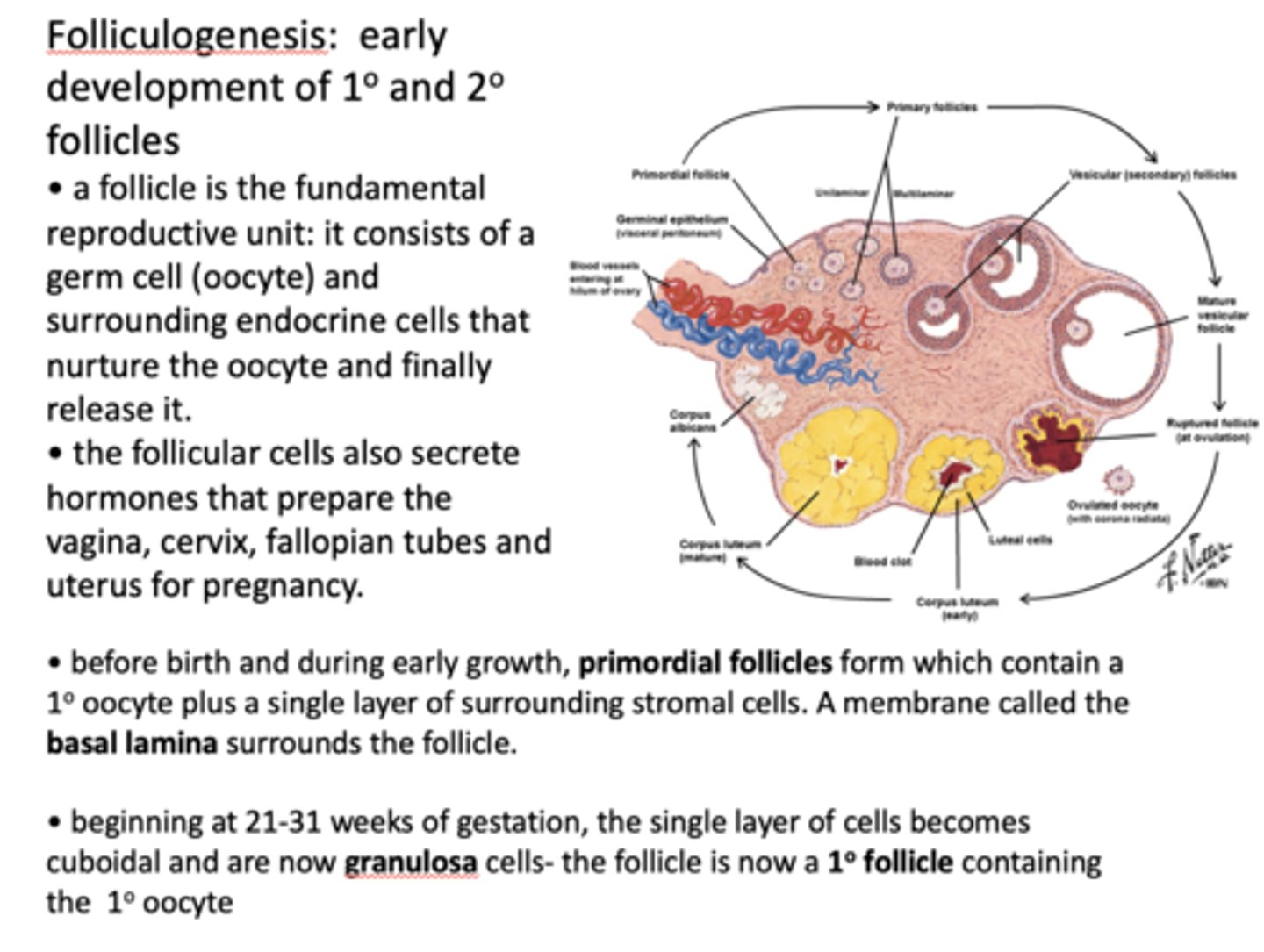
Before birth and during early growth, ______________ form which contain a primary oocyte plus a single layer of surrounding stromal cells.
primordial follicles
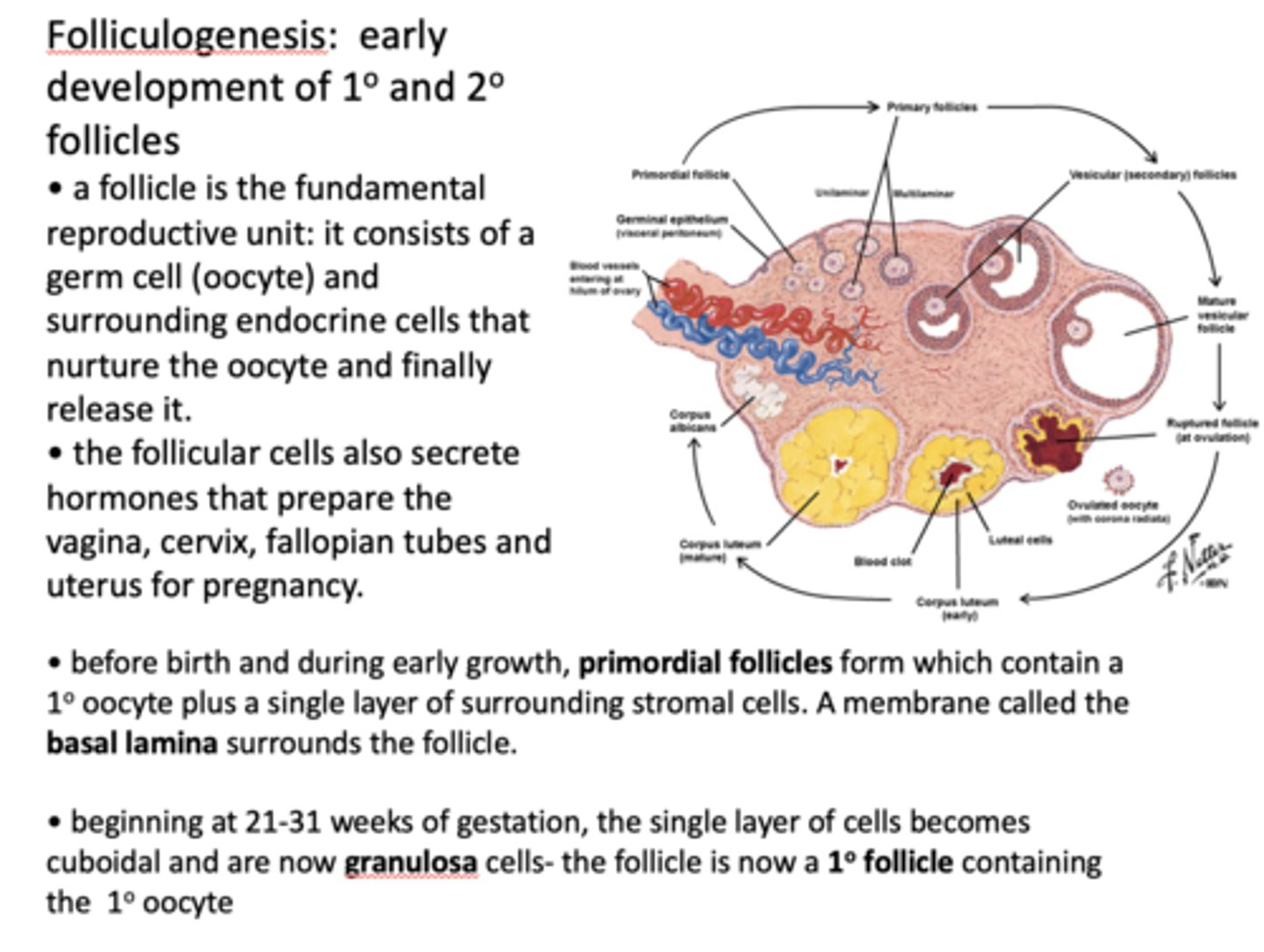
A membrane called the ____________ surrounds the follicle.
basal lamina

beginning at 21-31 weeks of gestation, the single layer of cells becomes cuboidal and are now ___________ cells - the follicle is now a ___________ containing the primary oocyte
granulosa cells, primary follicle
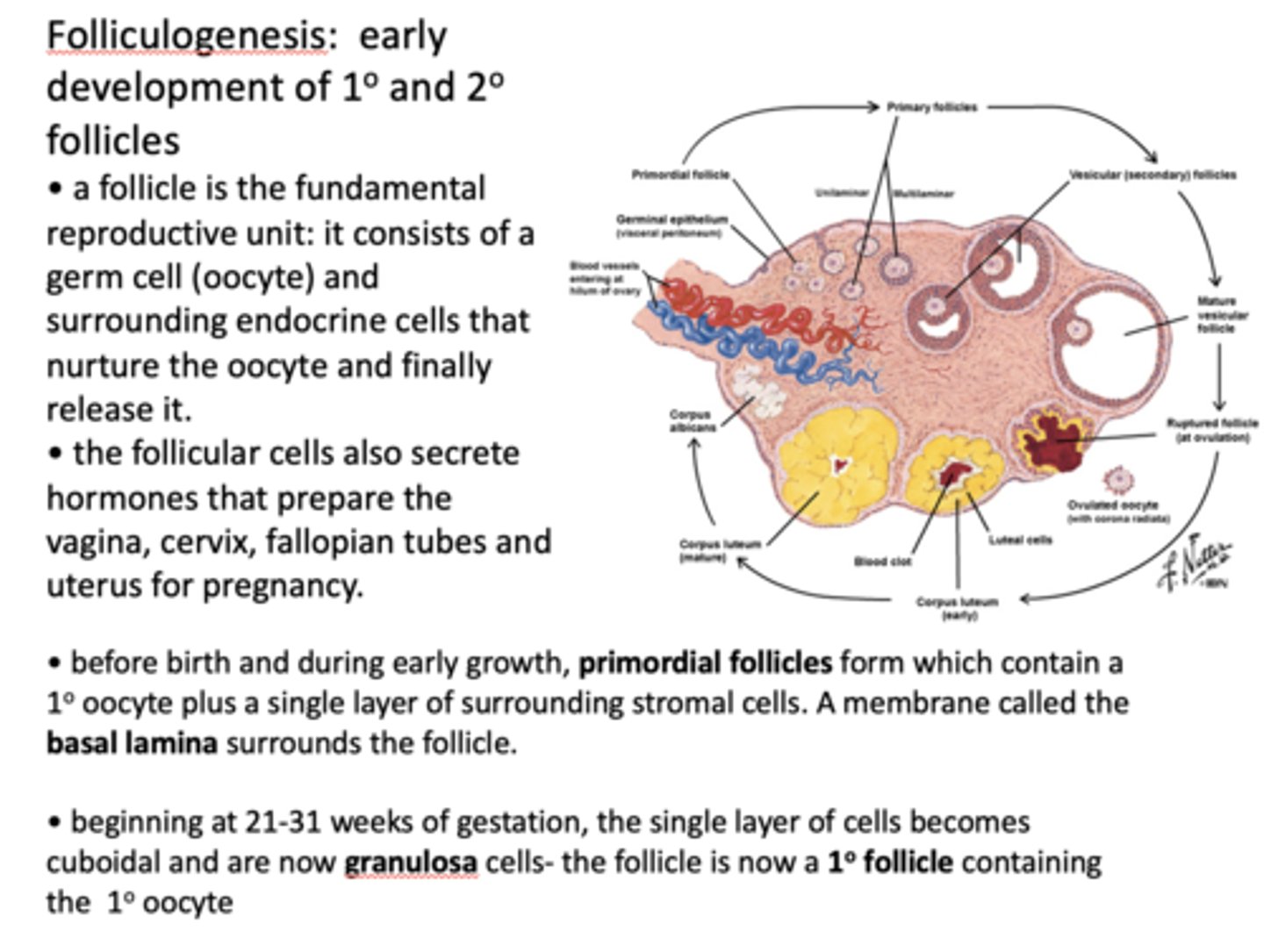
what event indicates a primordial follicle's transition into a primary follicle?
single layer of surrounding stromal cells turns into simple cuboidal granulosa cells
what event indicates a primary follicle's transition into a secondary follicle?
granulosa cells divide to produce several layers
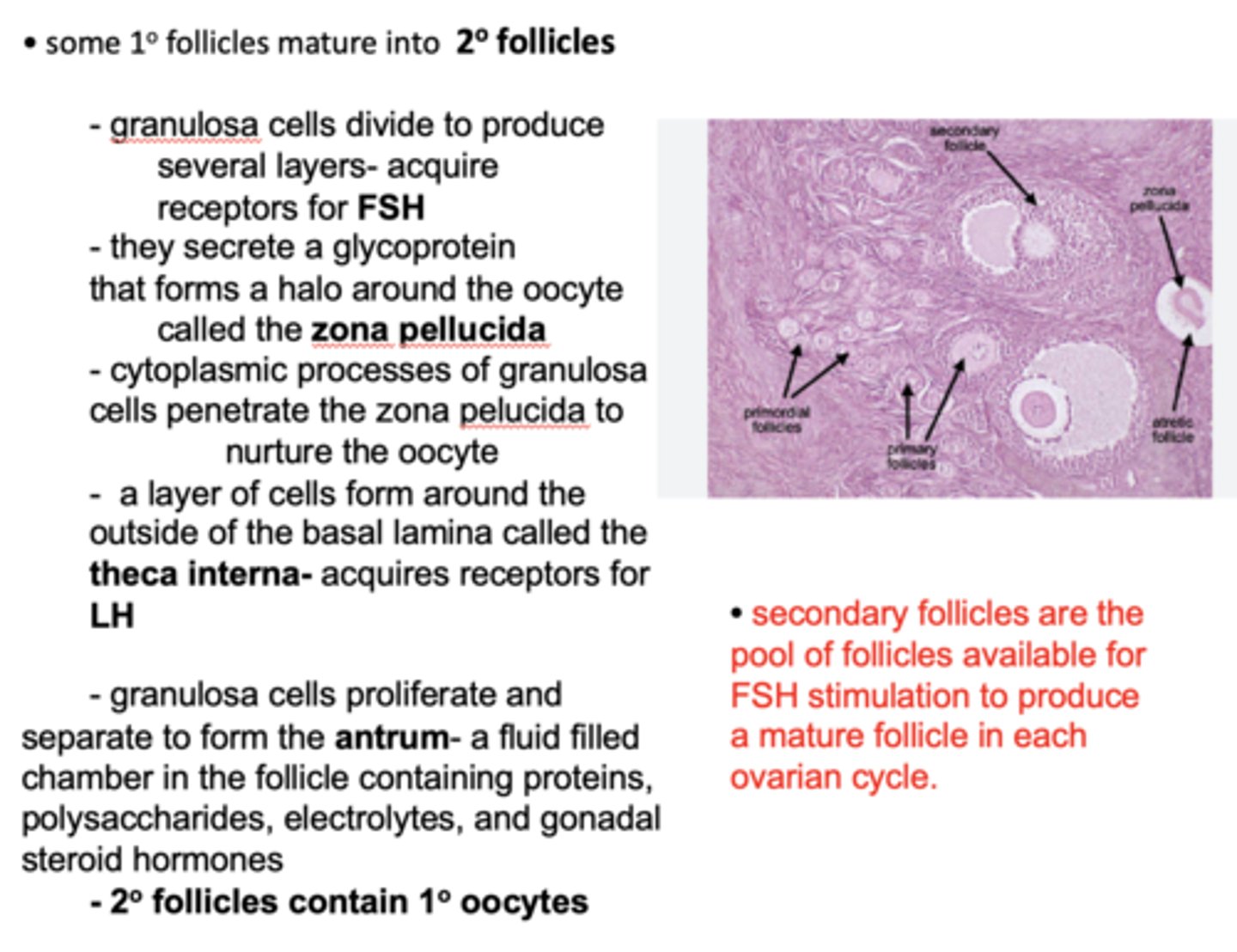
What doe some primary follicles mature into?
Secondary follicles
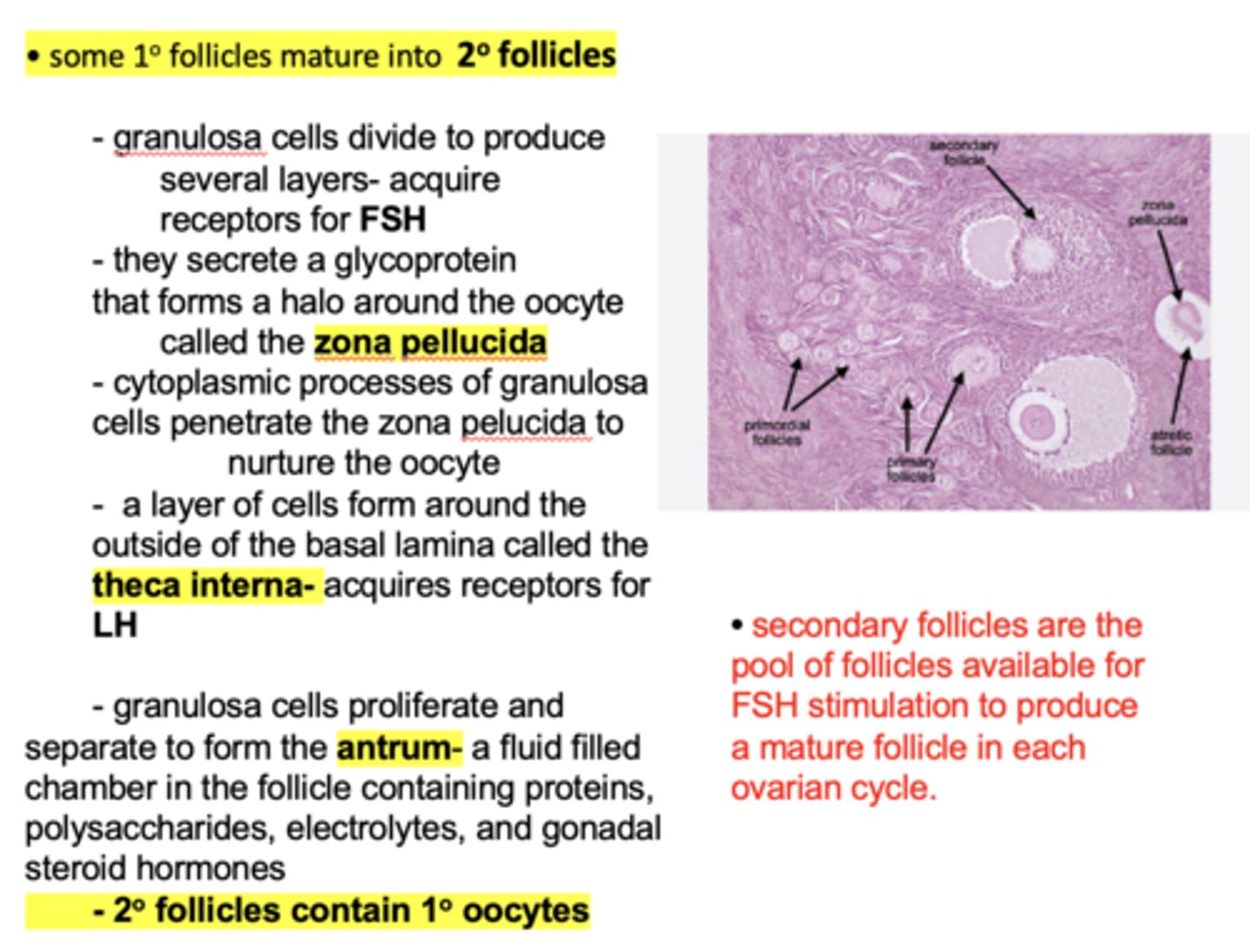
in the secondary follicle, which cells acquire receptors for FSH?
granulosa cells
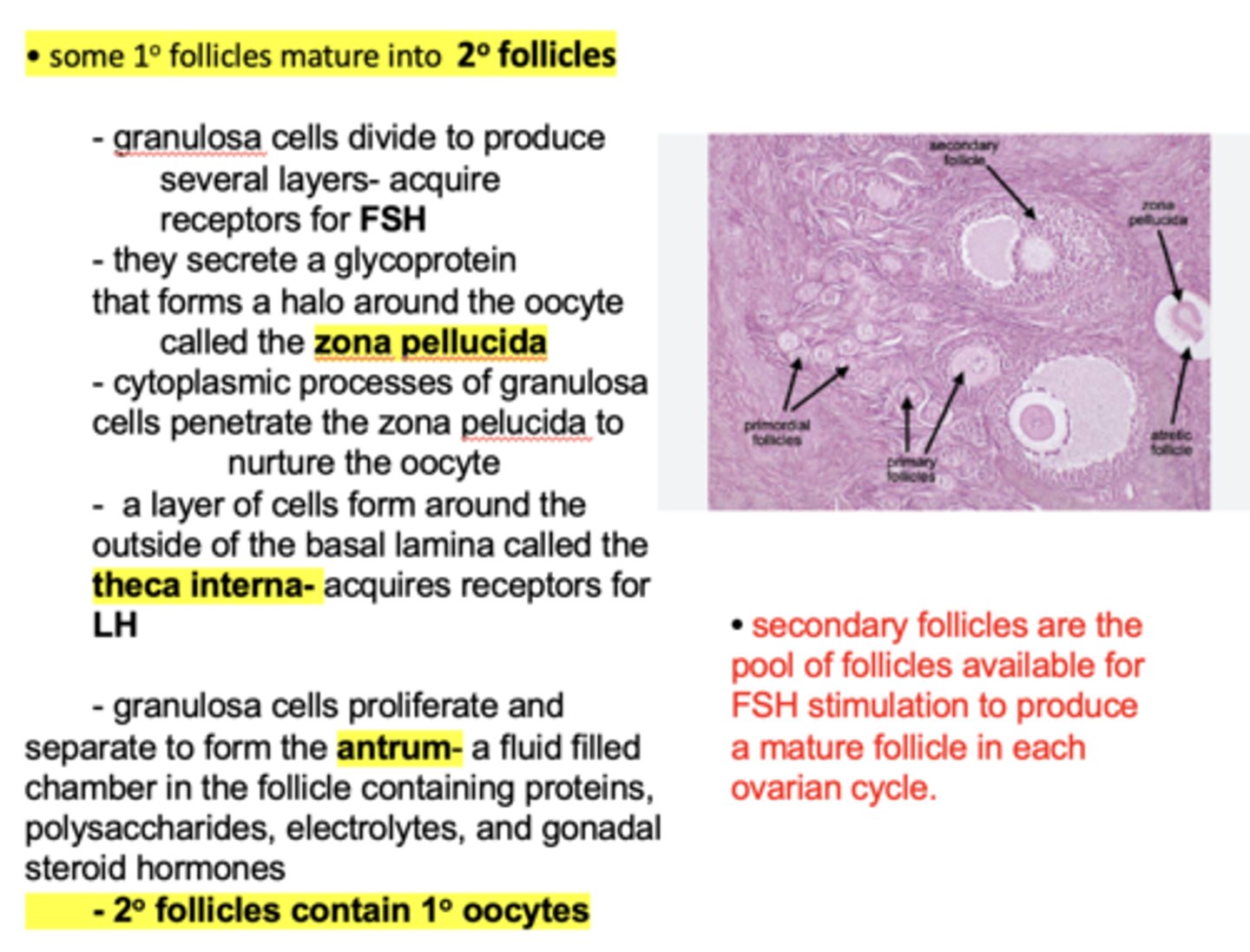
in the secondary follicle, which cells acquire receptors for LH?
theca interna cells
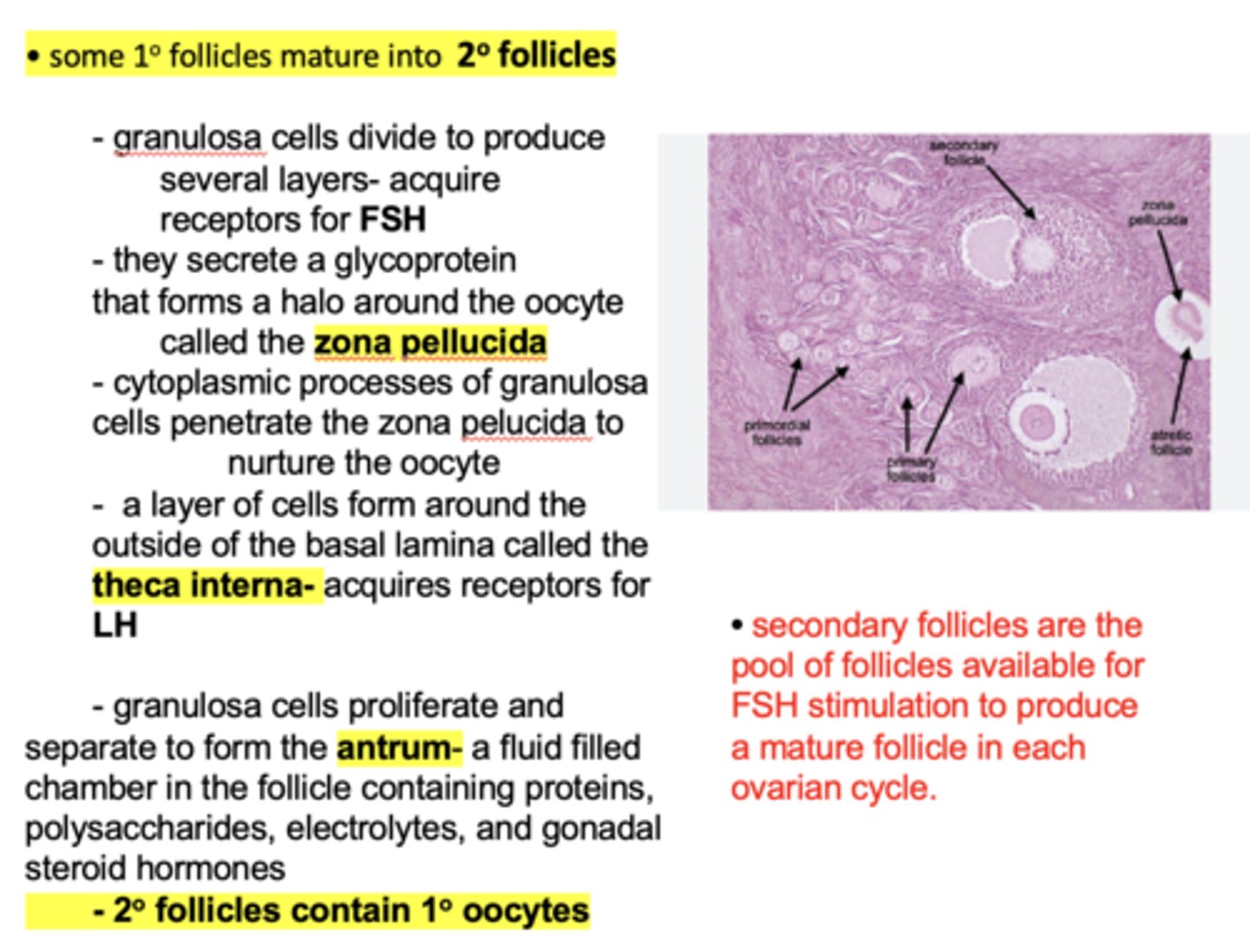
granulosa cells divide and secrete a glycoprotein that forms a halo around the oocyte called the ______________
zona pellucida
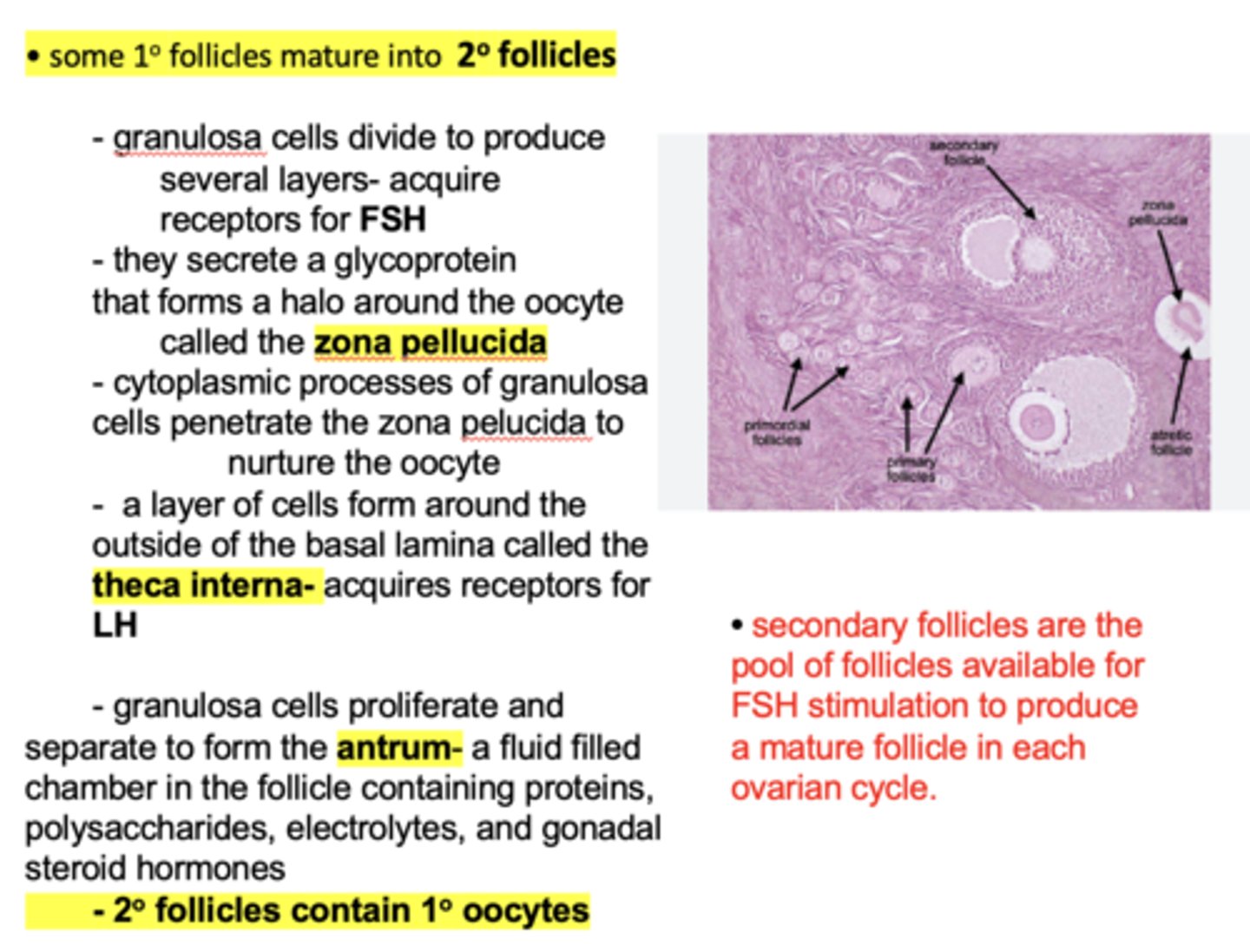
which type of follicles are the pool of follicles available for FSH stimulation to produce a mature follicle in each ovarian cycle?
secondary follicles
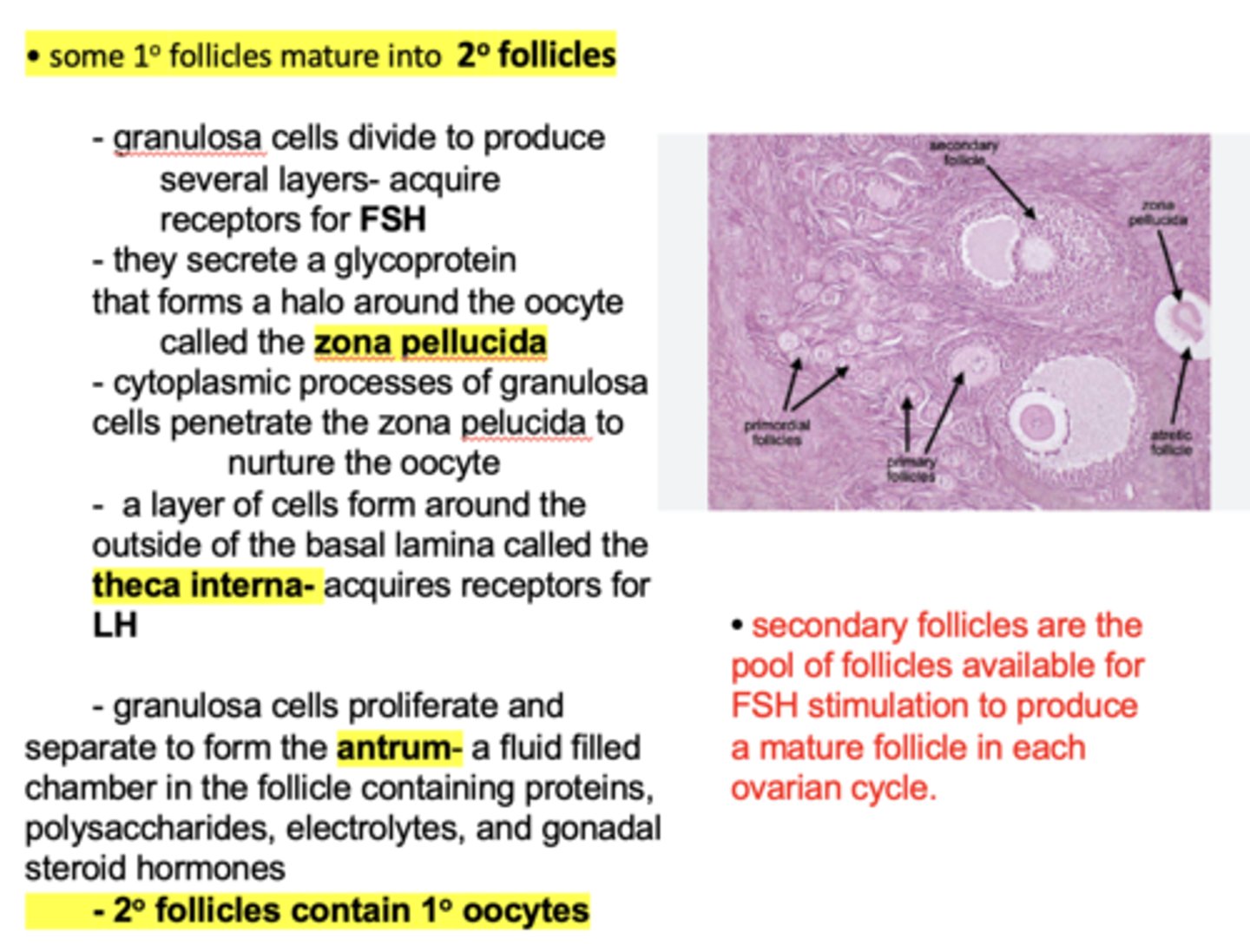
granulosa cells proliferate and separate to form the _____________, a fluid filled chamber in the follicle containing proteins, polysaccharides, electrolytes, and gonadal steroid hormones
antrum
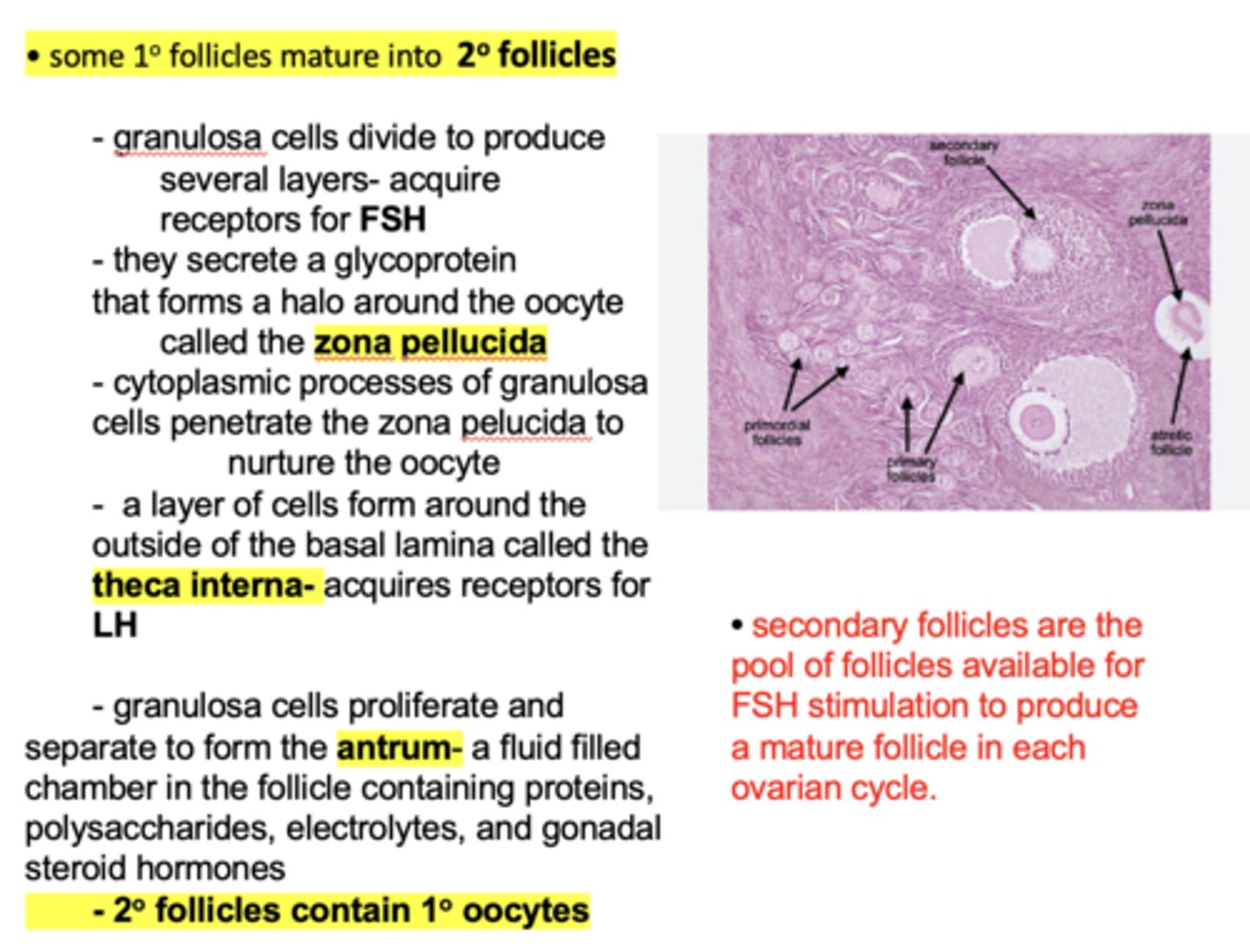
Secondary follicles contain __________ oocytes
Primary
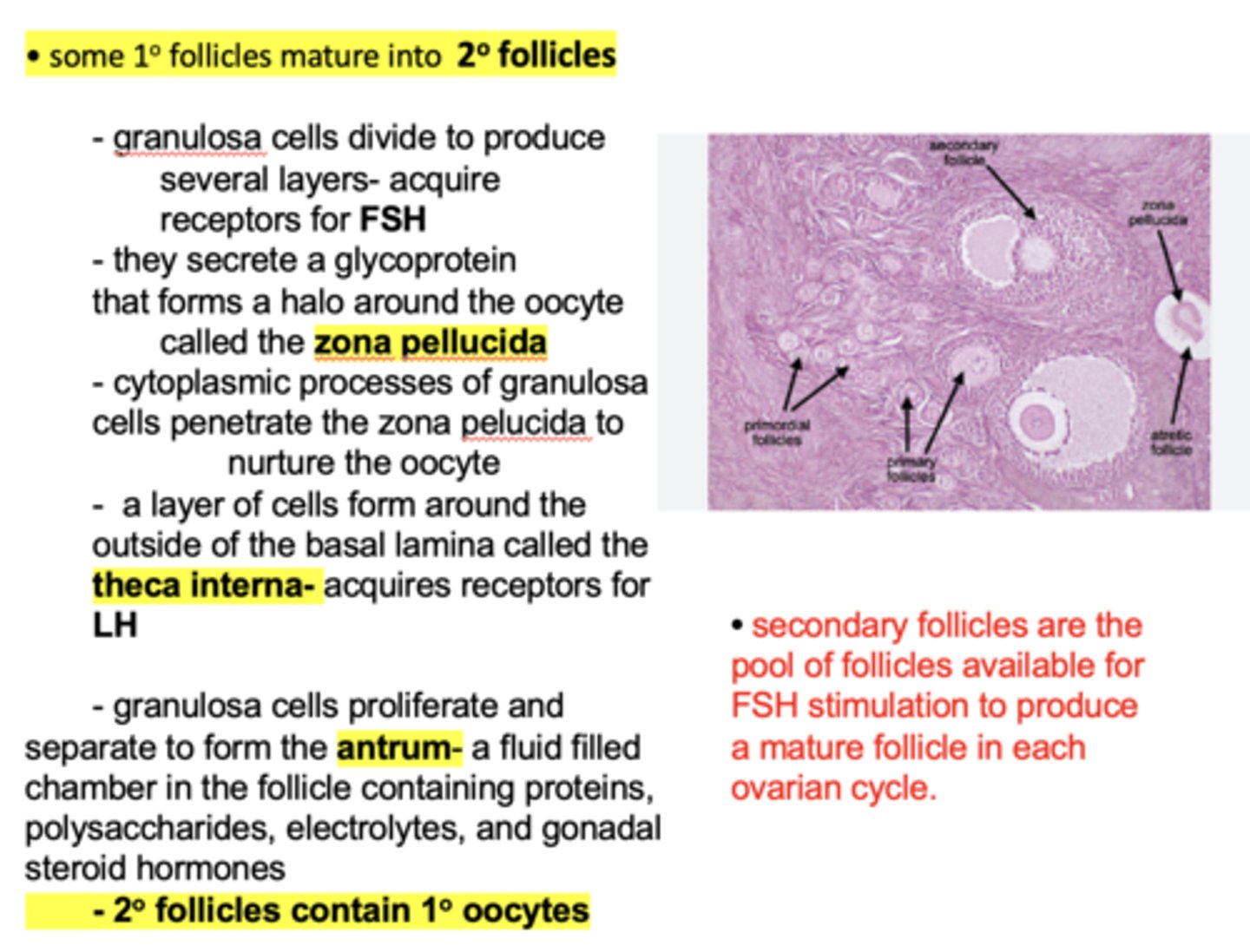
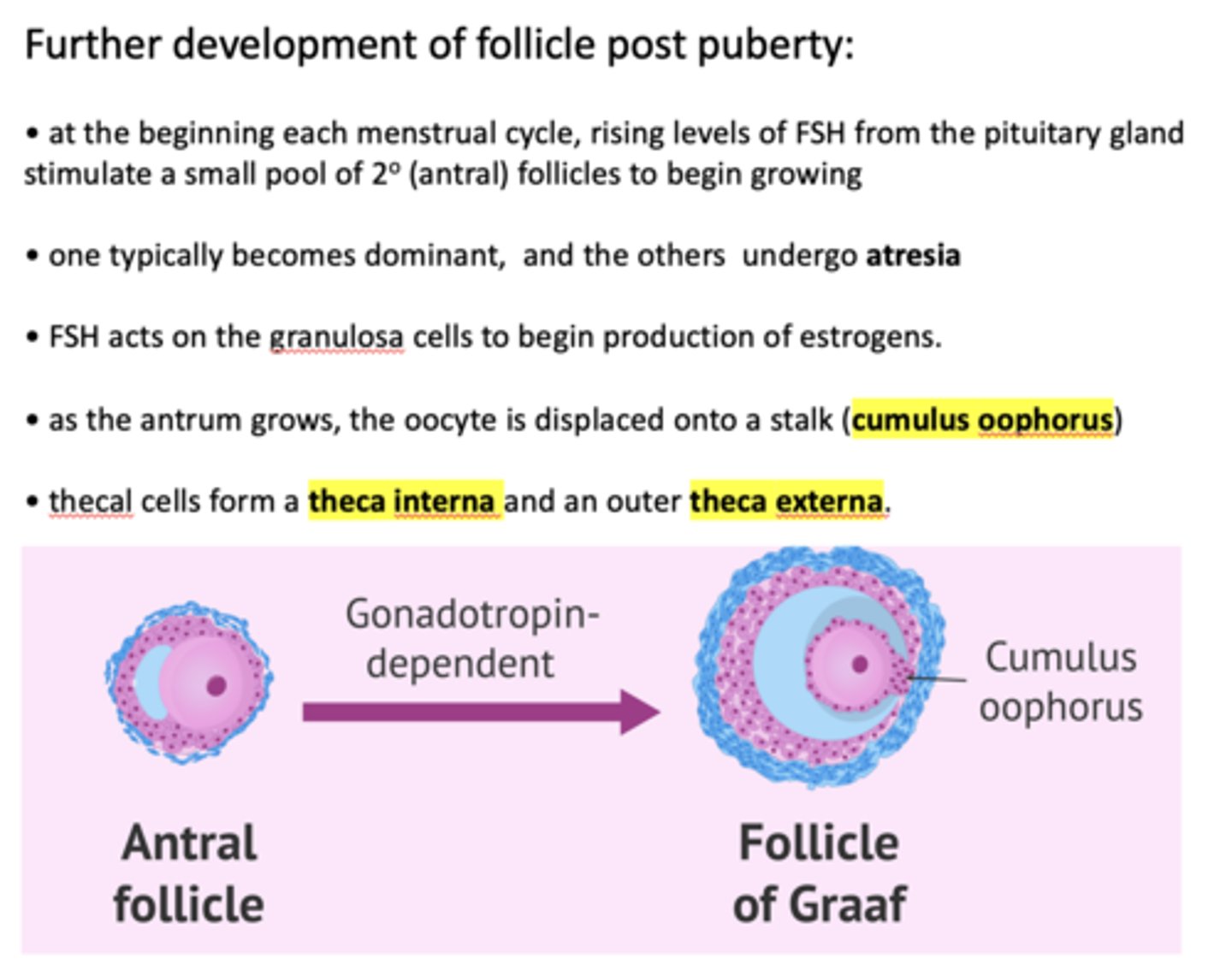
at the beginning each menstrual cycle, rising levels of ___________ from the pituitary gland stimulate a small pool of secondary follicles to begin growing
FSH
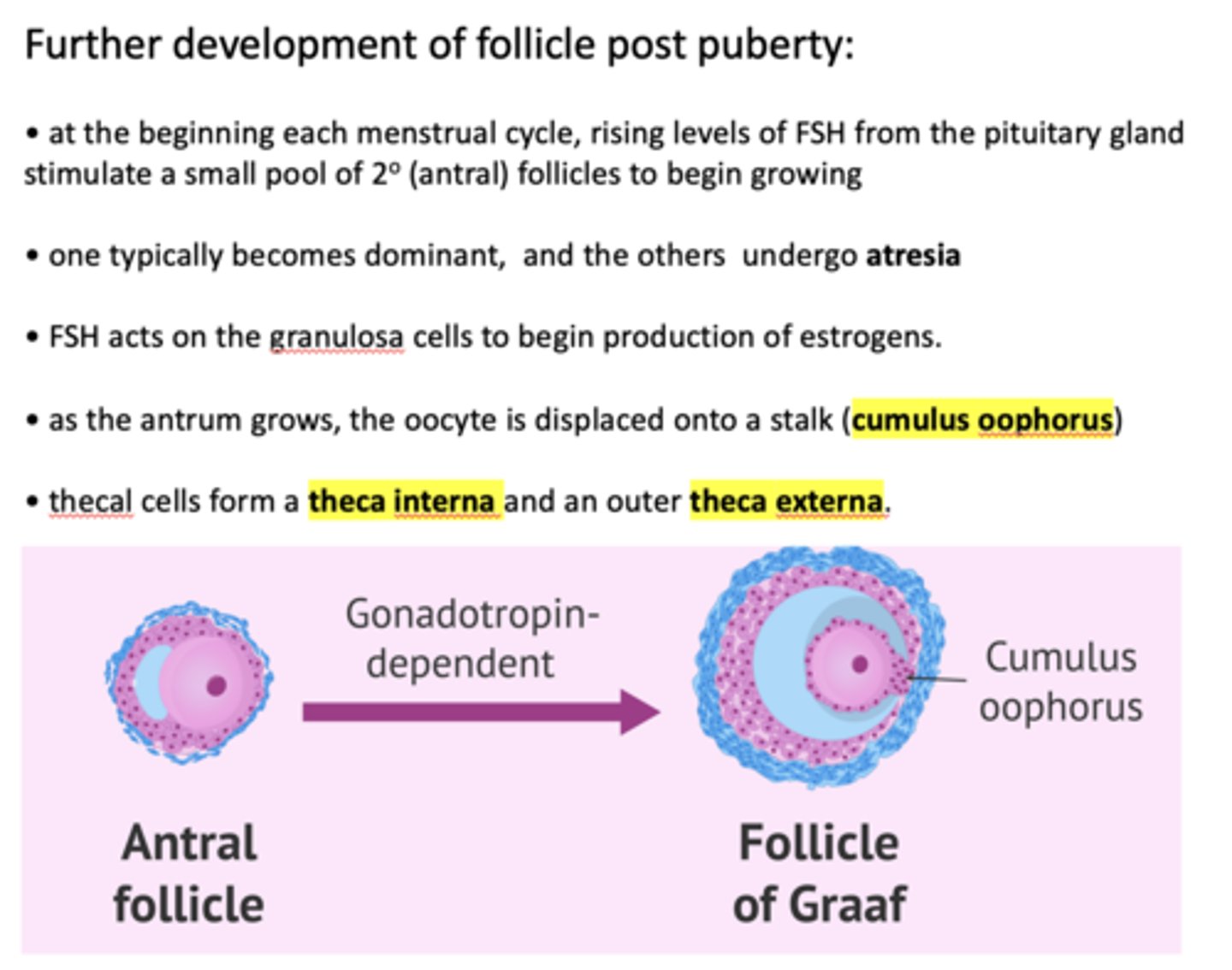
One follicle one typically becomes dominant, and the others undergo _____________
atresia
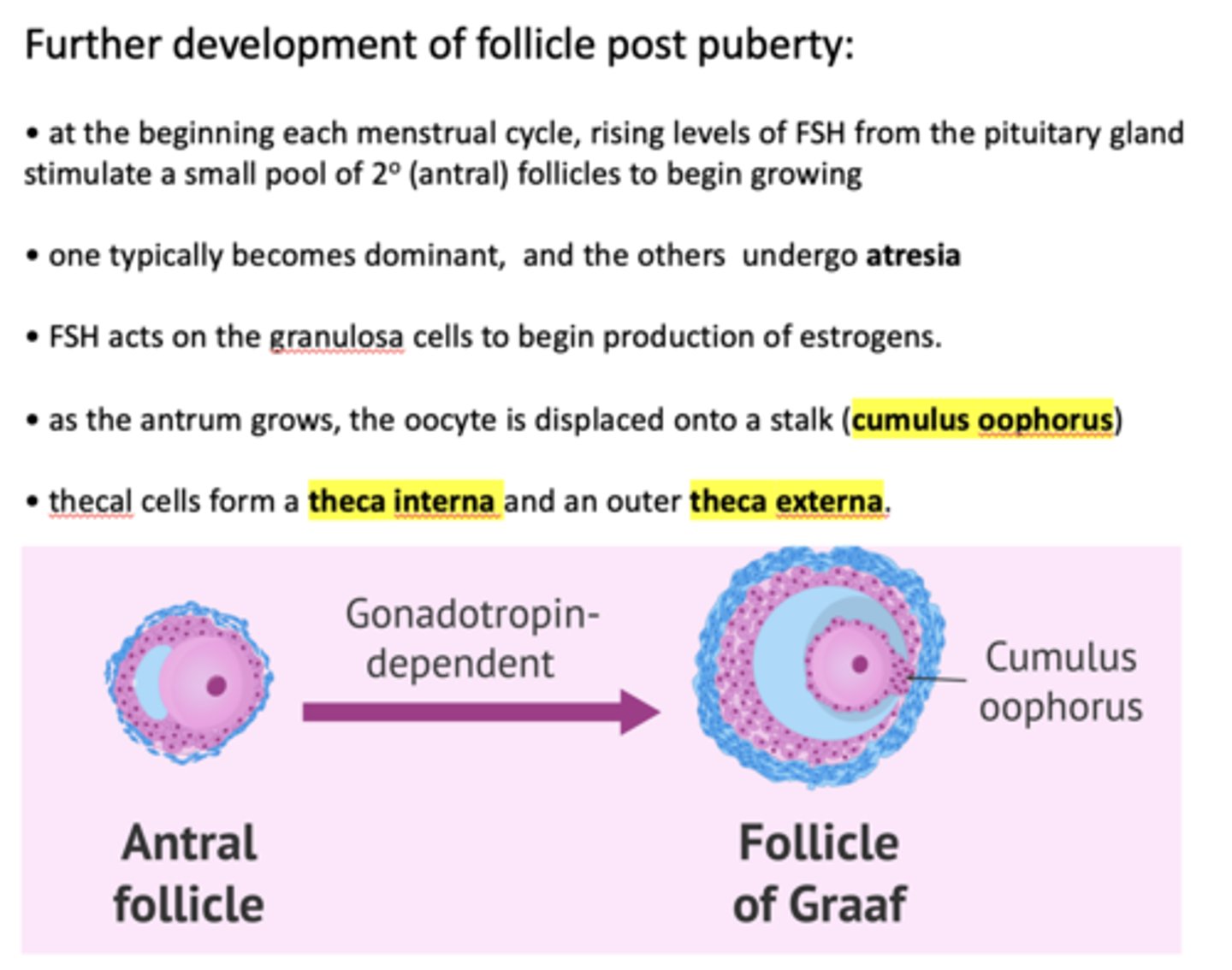
FSH acts on ______ to begin production of estrogens
granulosa cells
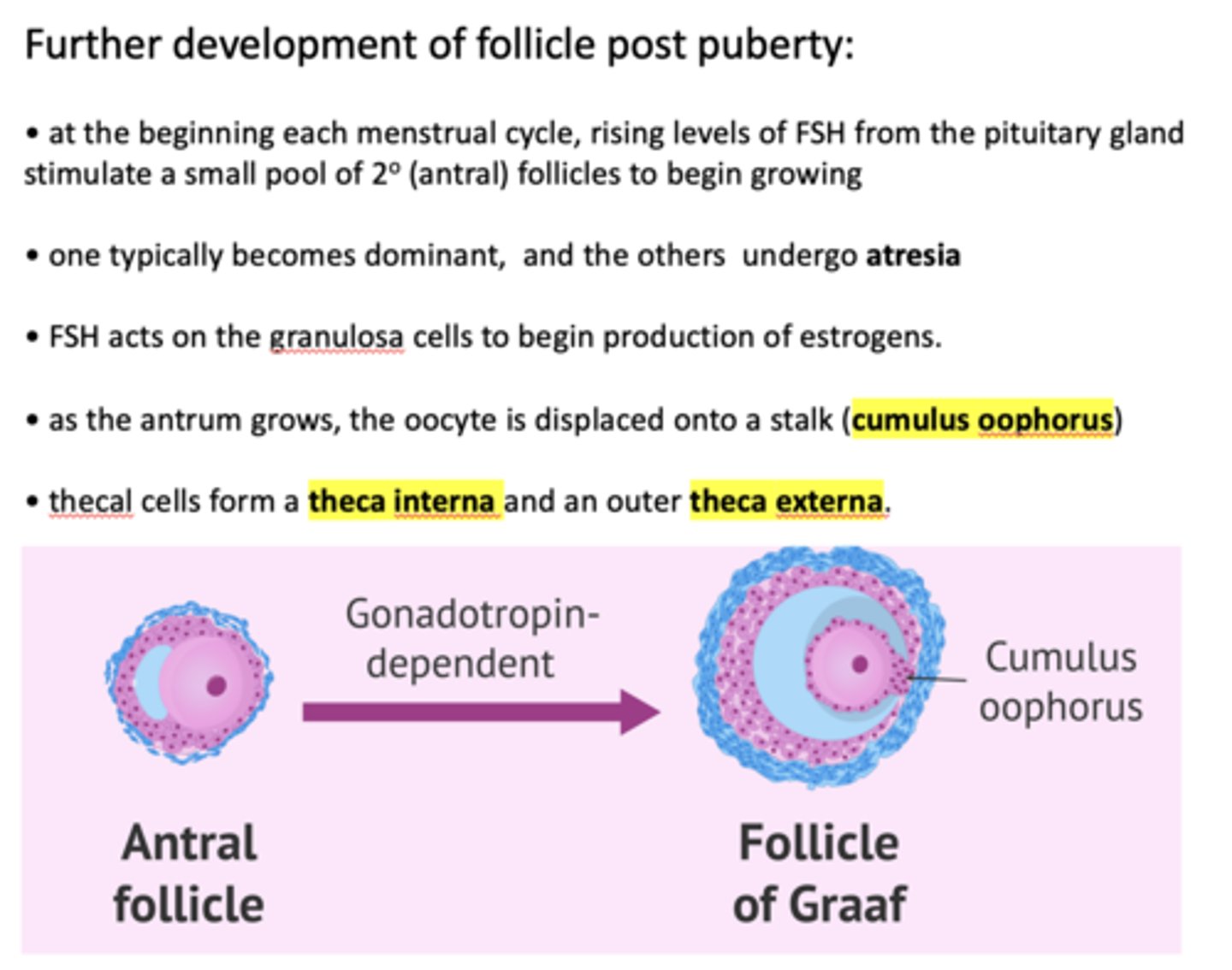
FSH acts on the granulosa cells to begin production of ___________
estrogen
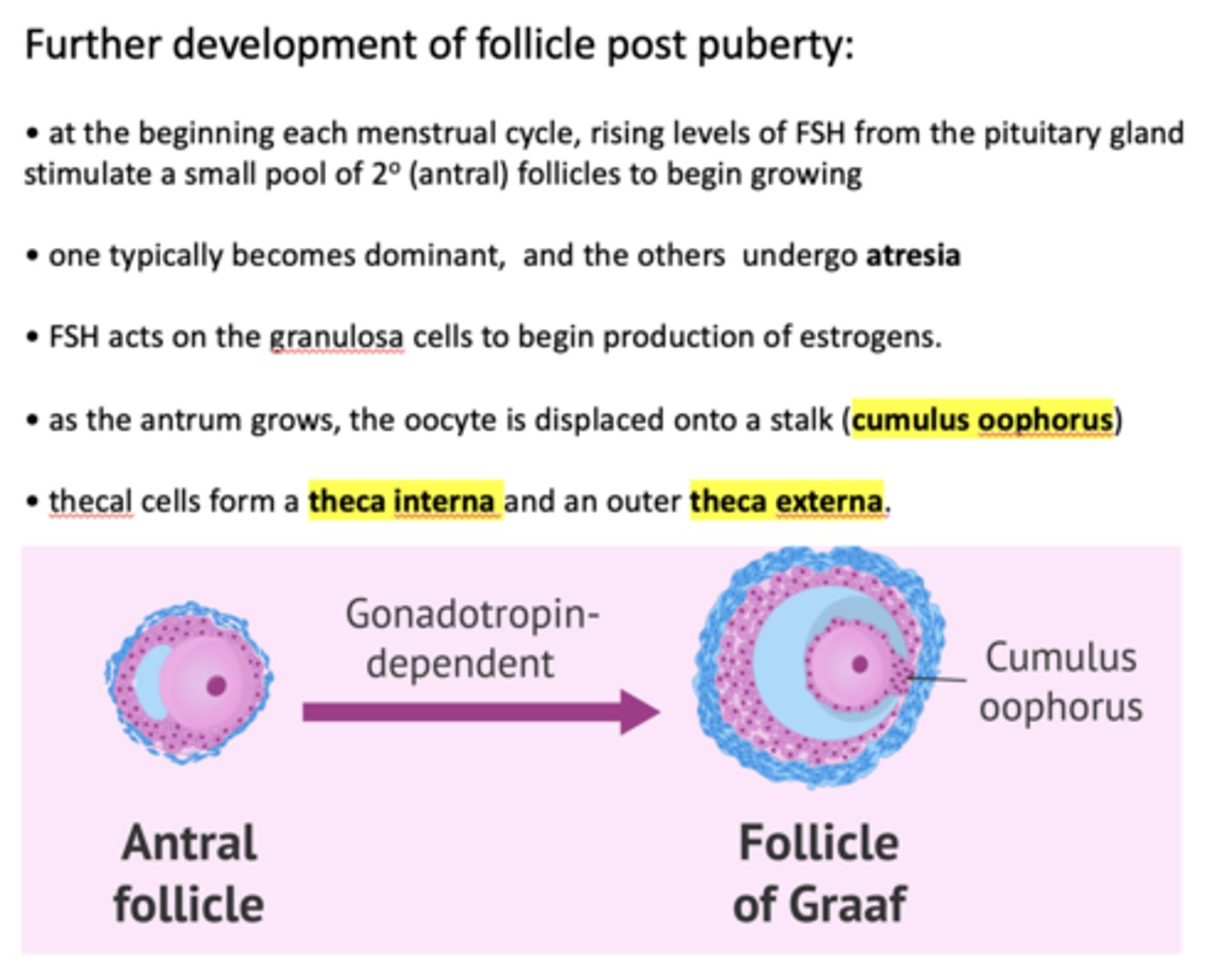
within a Graffian follicle, the oocyte is displaced onto a stalk called the _________
cumulus oophorus
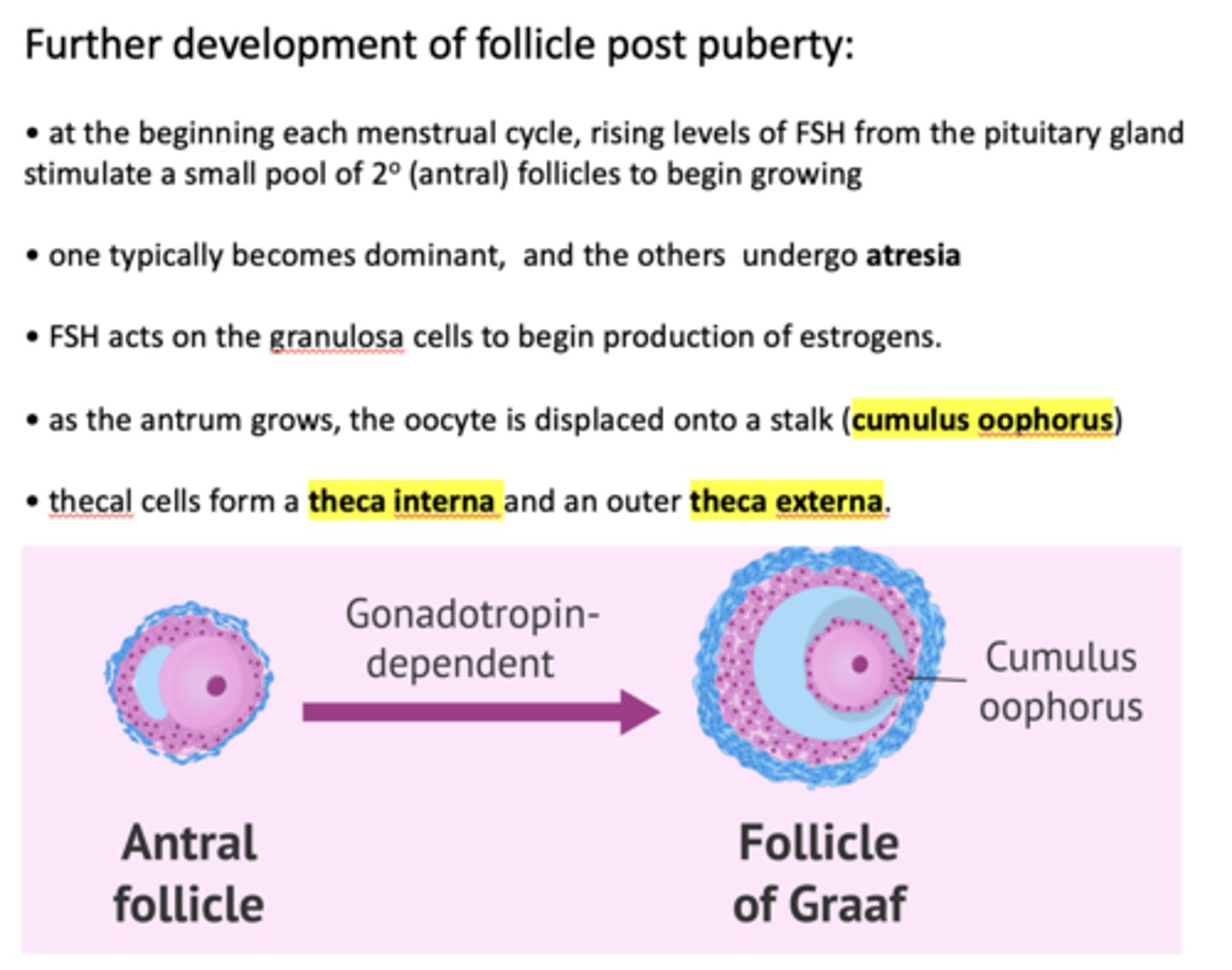
Thecal cells form a theca interna and an outer ___________
Theca externa
when does a primary oocyte become a secondary oocyte?
ovulation

the resulting secondary oocyte immediately begins the second meiotic division but is arrested at what phase?
metaphase
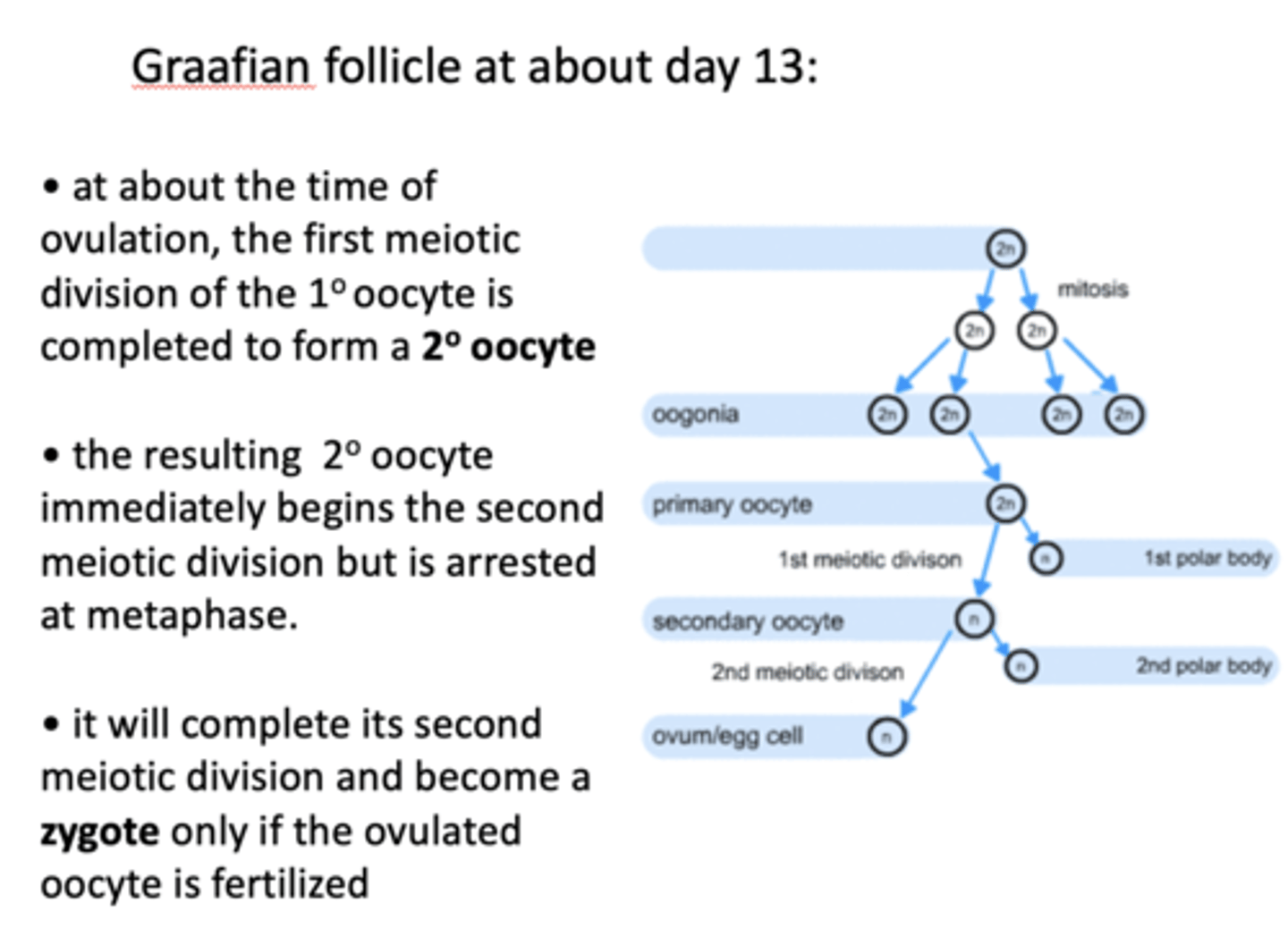
a secondary oocyte will complete its second meiotic division and become a ___________ only if the ovulated oocyte is fertilized
zygote

at about day 13 (of a 28 day cycle), a surge of the pituitary hormone ___________ initiate the process of ovulation or release of the oocyte from the follicle
LH (lesser extent FSH)
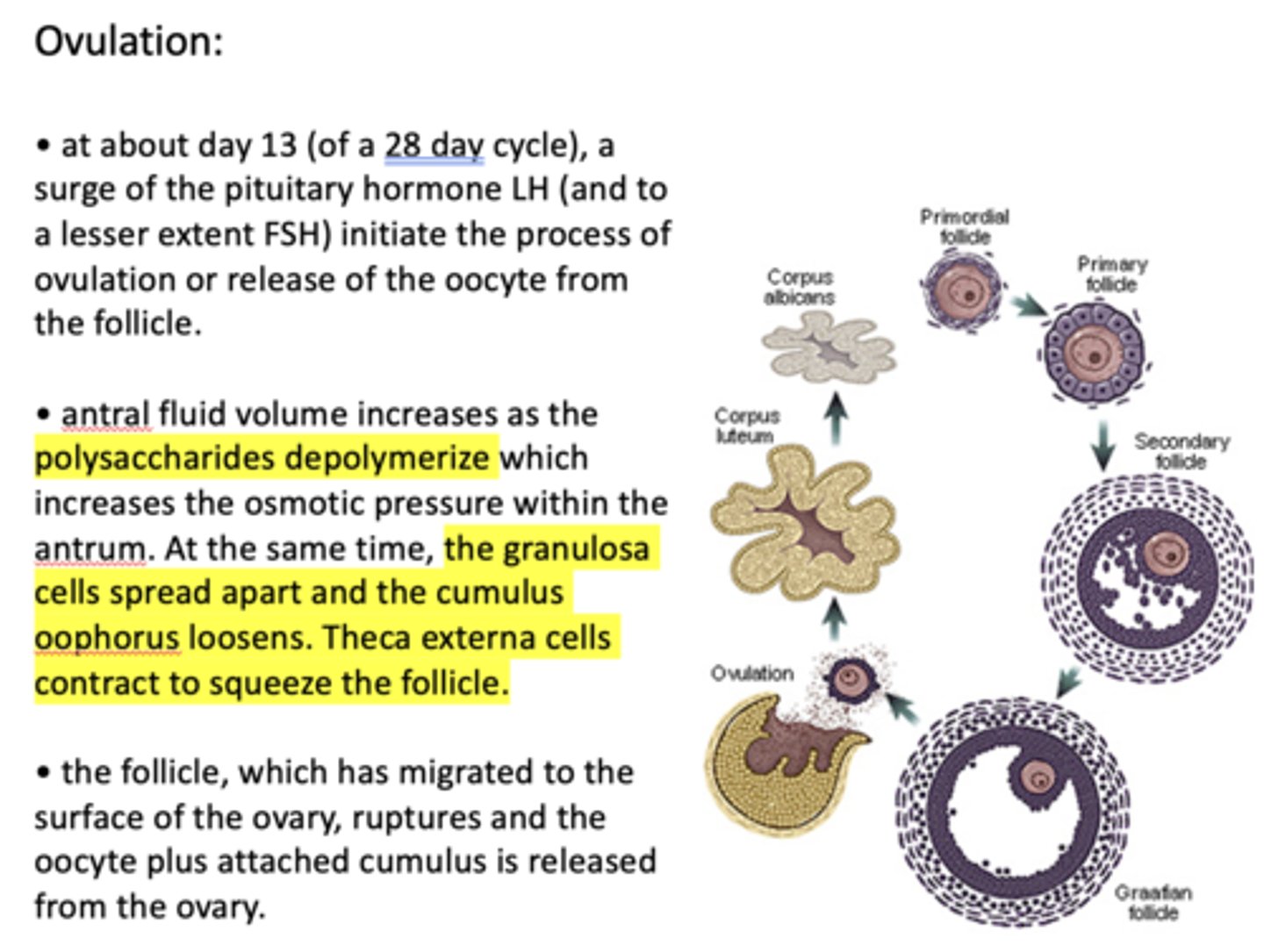
about what day in a 28 day cycle does ovulation occur?
13
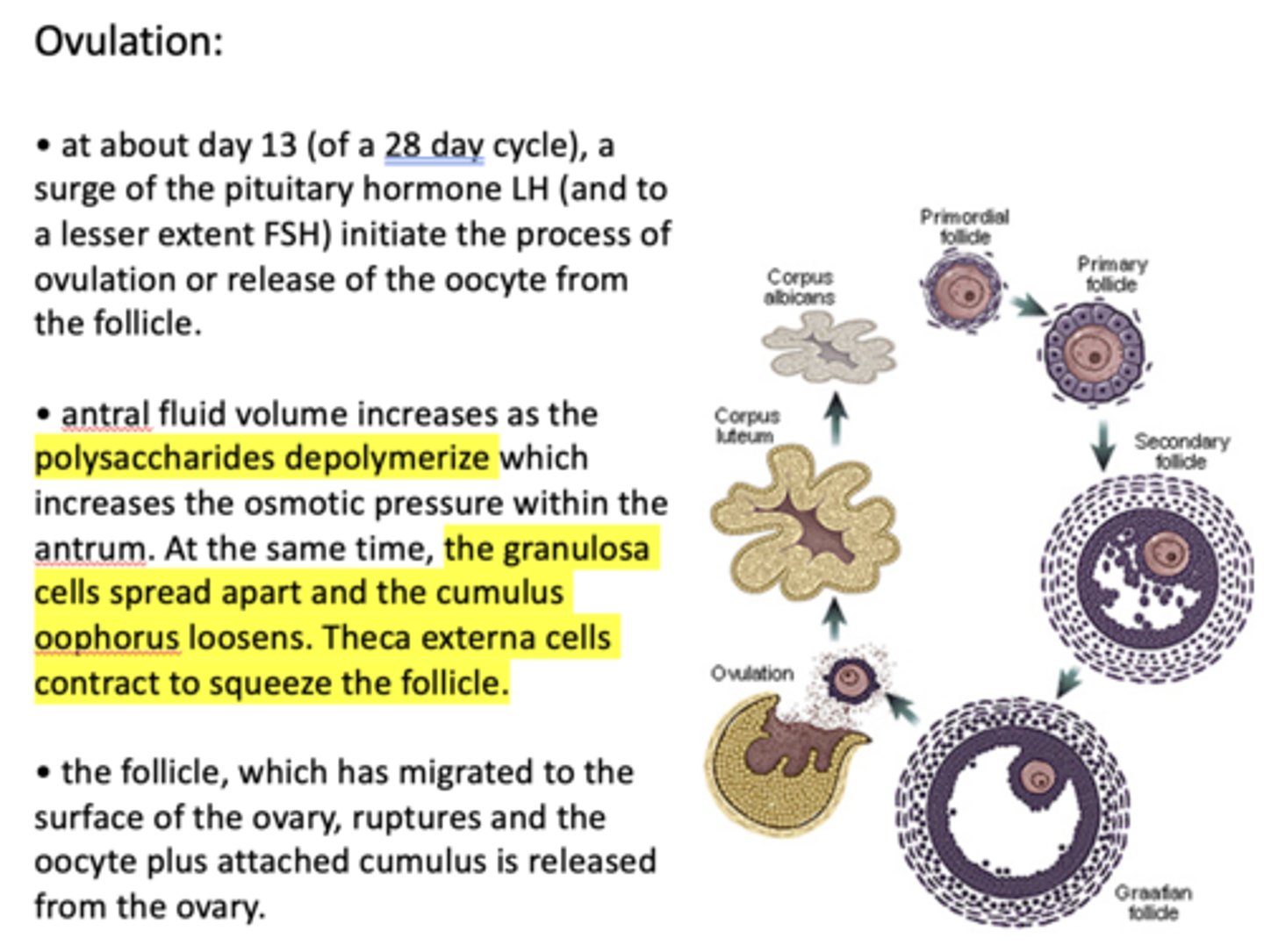
what five factors contribute to the oocyte being released from the follicle?
- Antral fluid volume increases as polysaccharides depolymerize
- Antral osmotic pressure increases
- Granulosa cells spread apart
- Cumulus oophorus loosens
- Theca externa cells contract to squeeze follicle
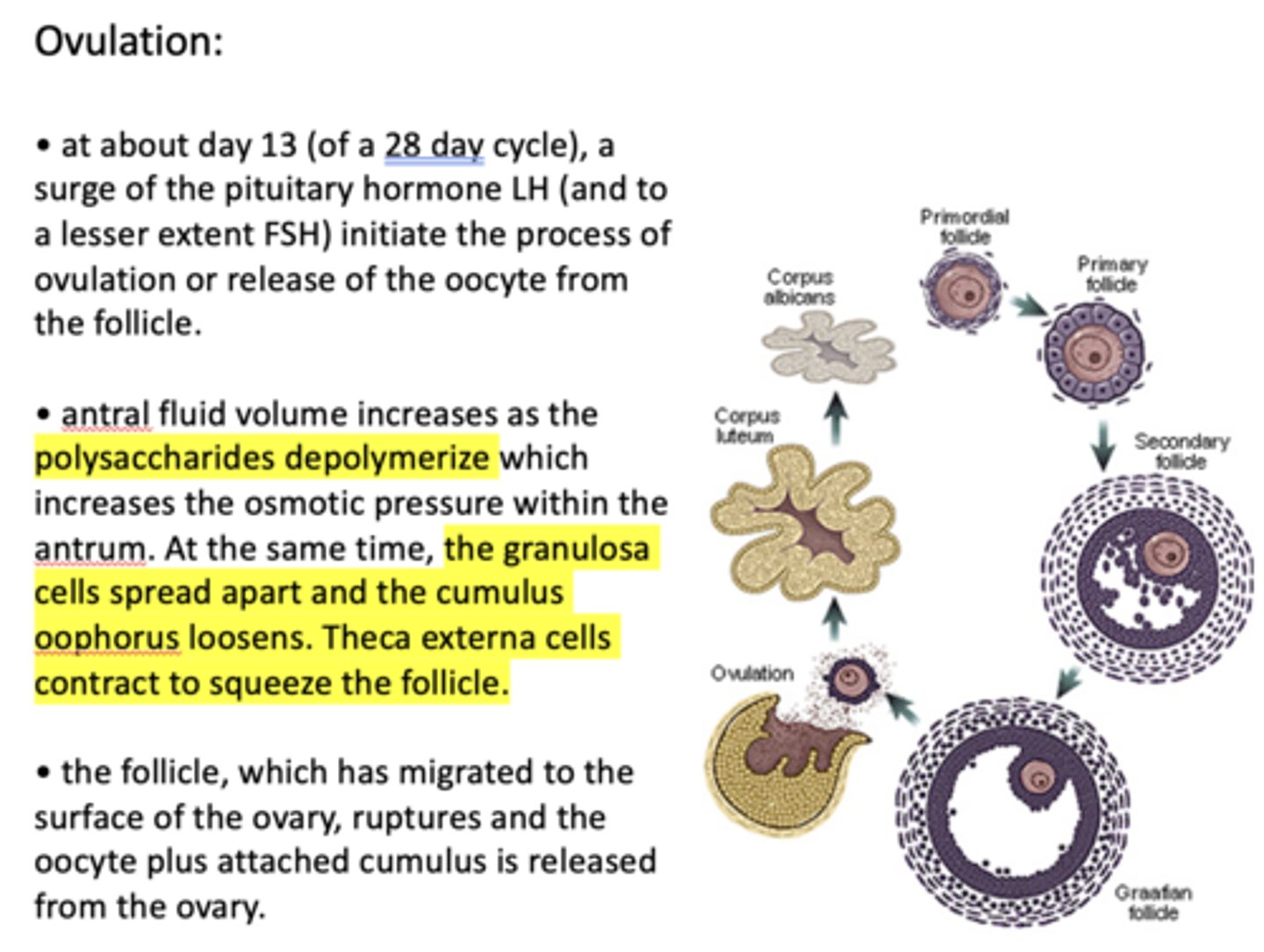
the follicle, which has migrated to the surface of the ovary, ruptures and the oocyte plus attached ___________ is released from the ovary
cumulus
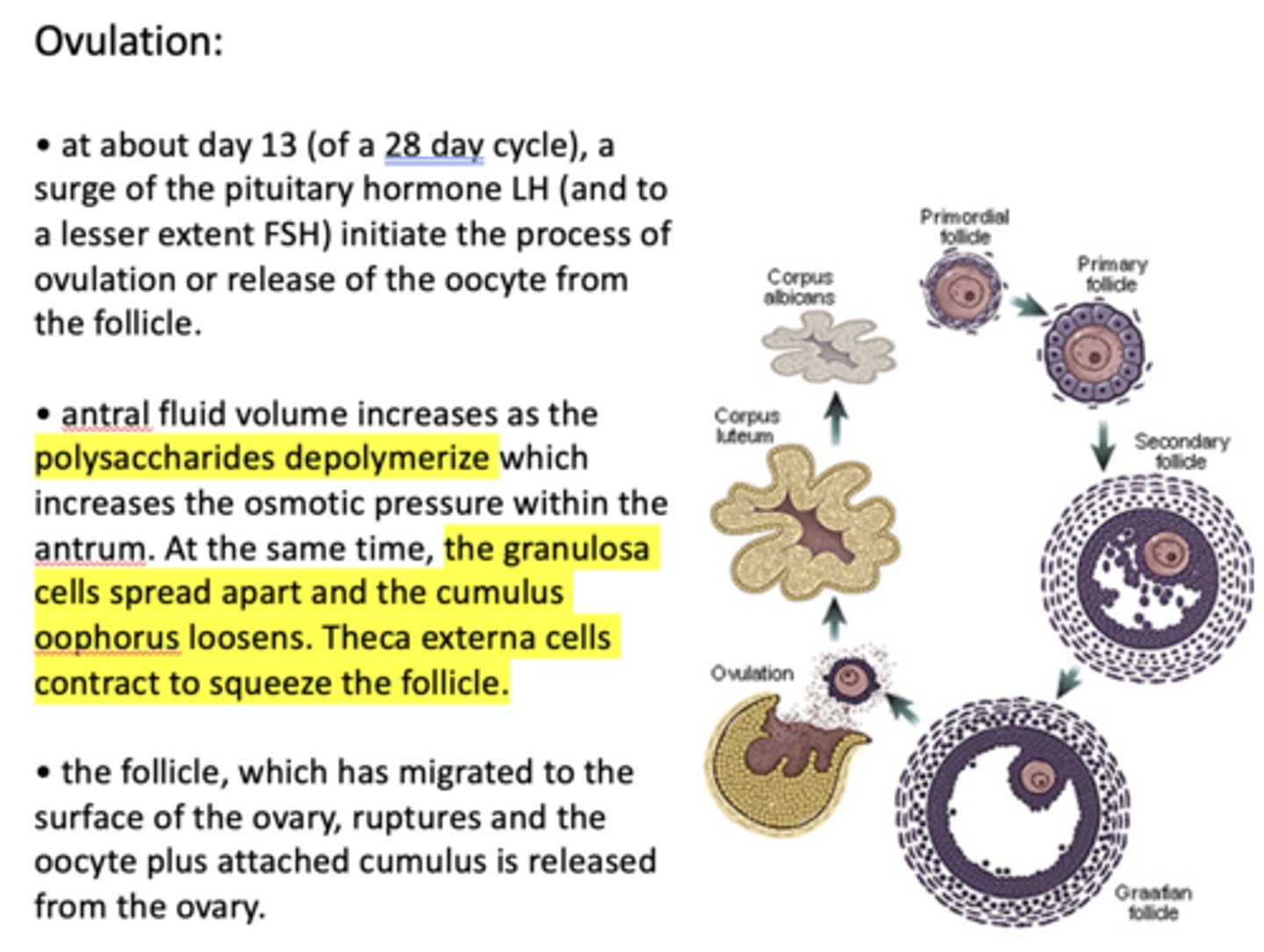
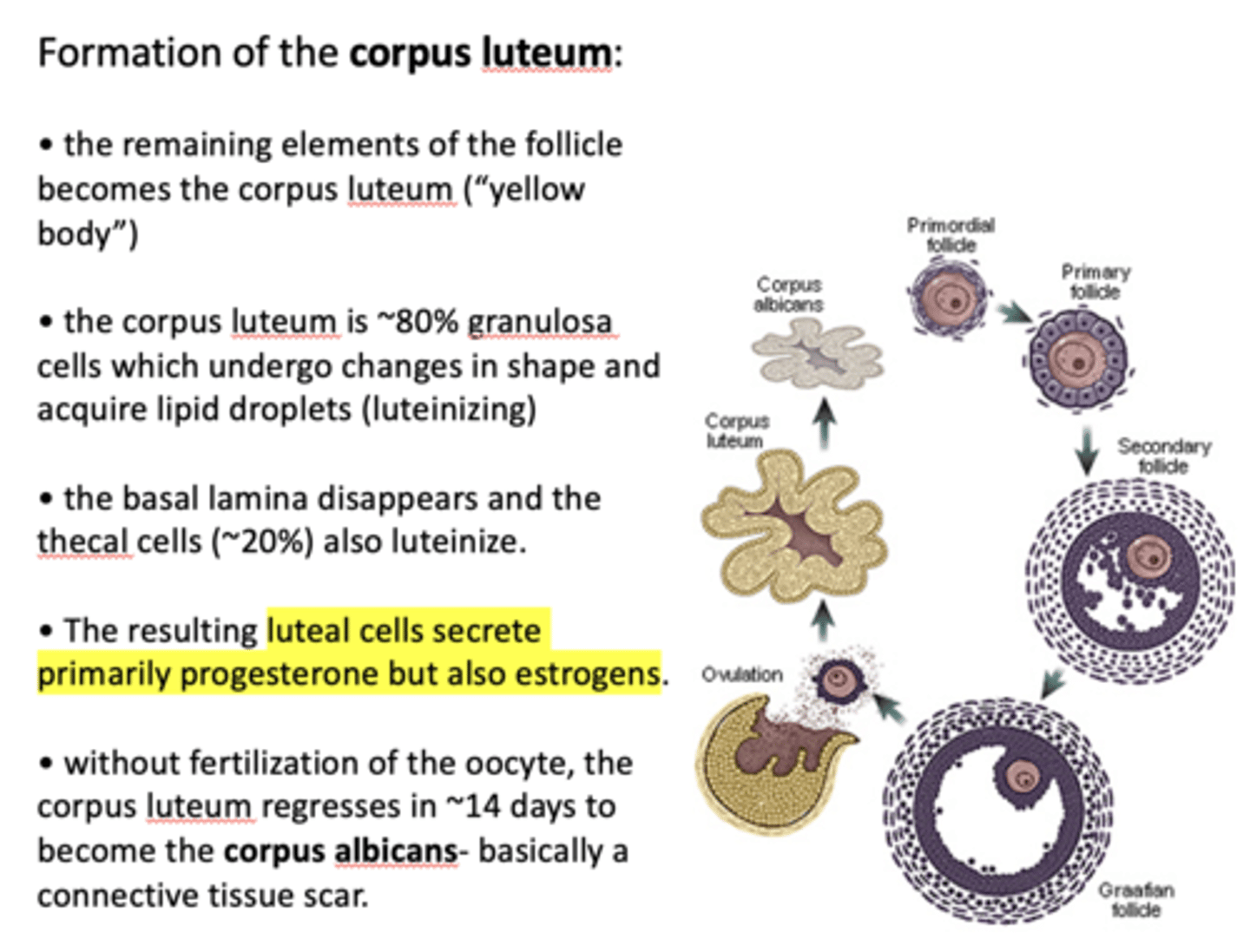
the remaining elements of the follicle becomes the ____________
corpus luteum
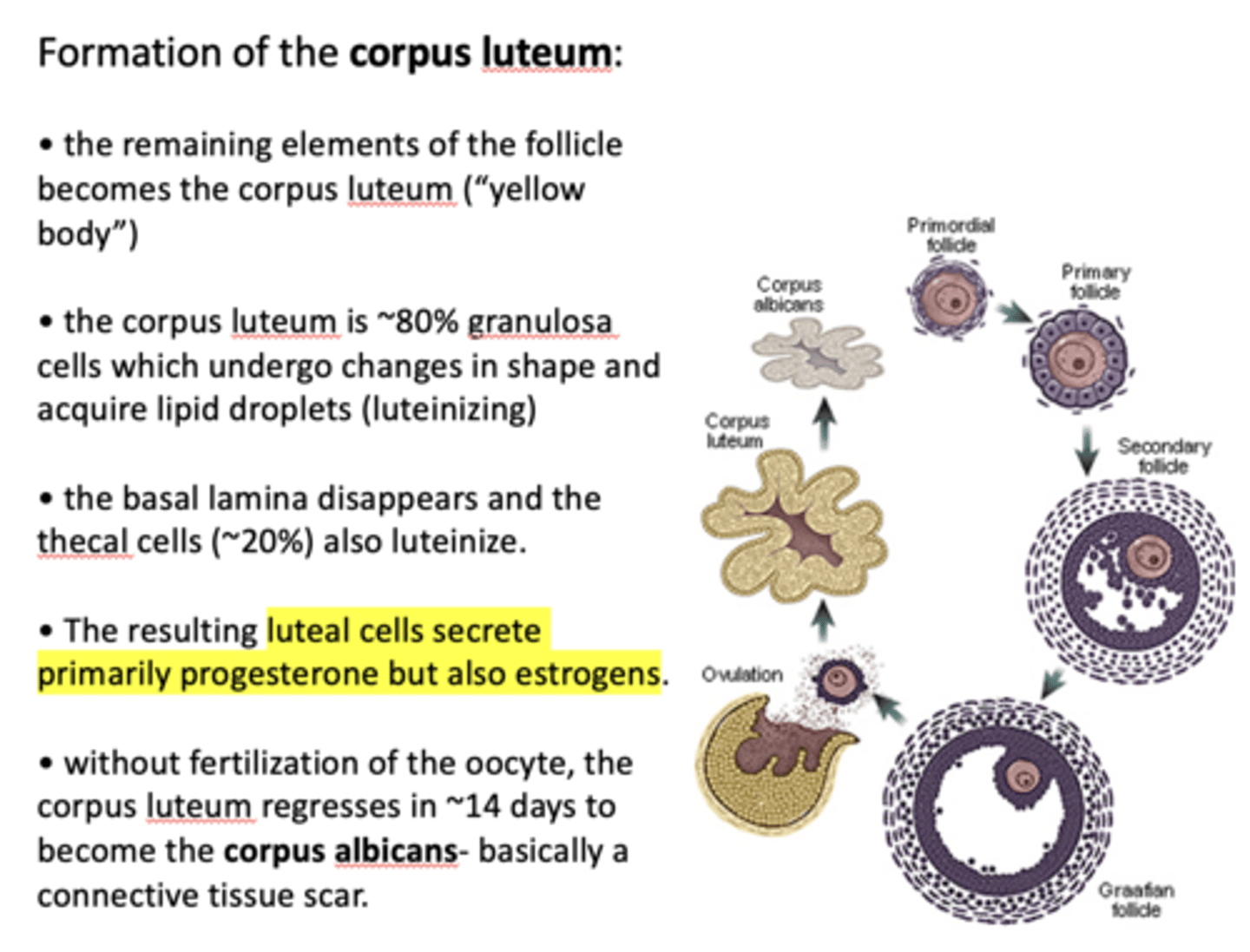
the corpus luteum is ~80% __________ which undergo changes in shape and acquire lipid droplets (luteinizing)
granulosa cells
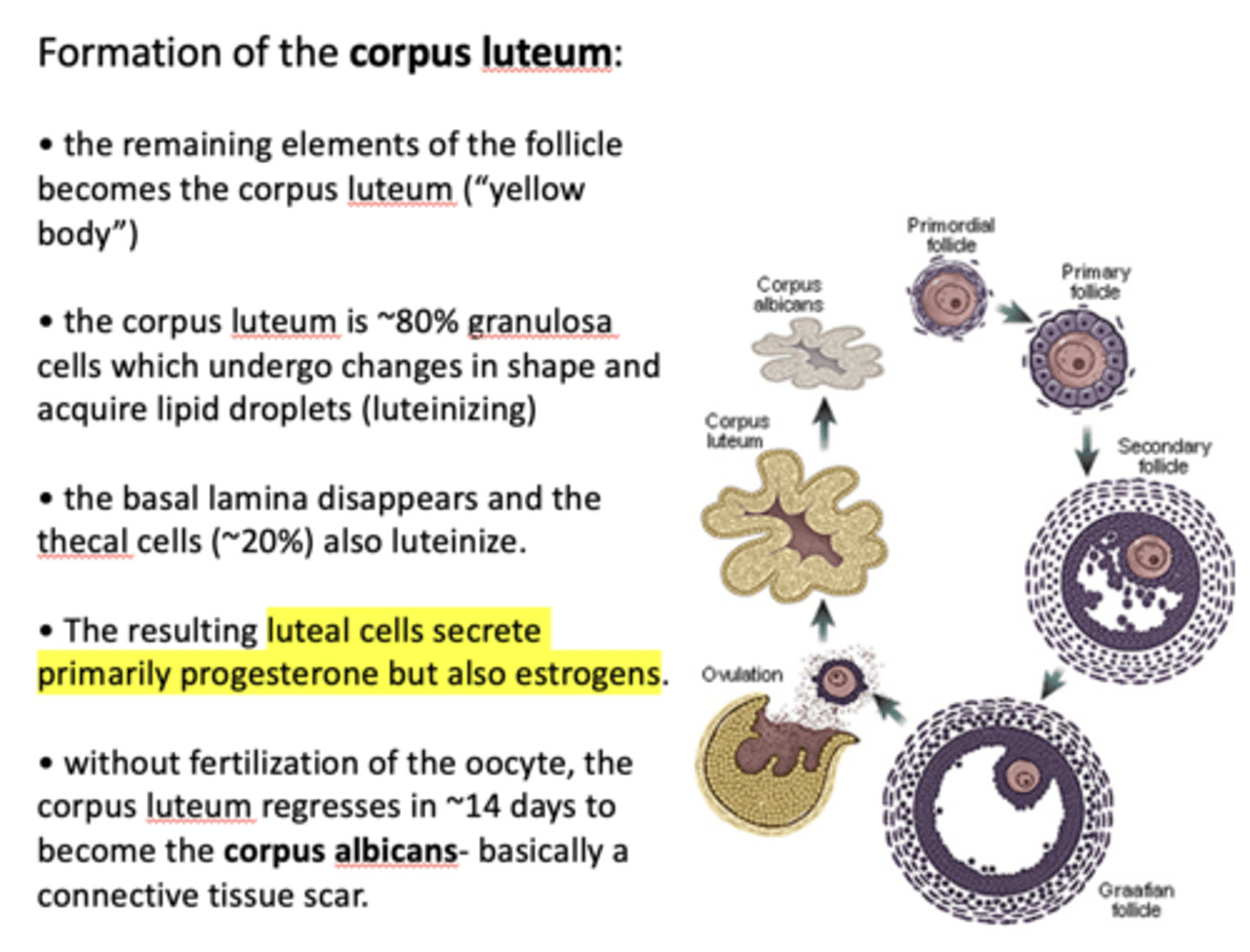
The basal lamina disappears and the ___________ (~20%) also luteinize
thecal cells
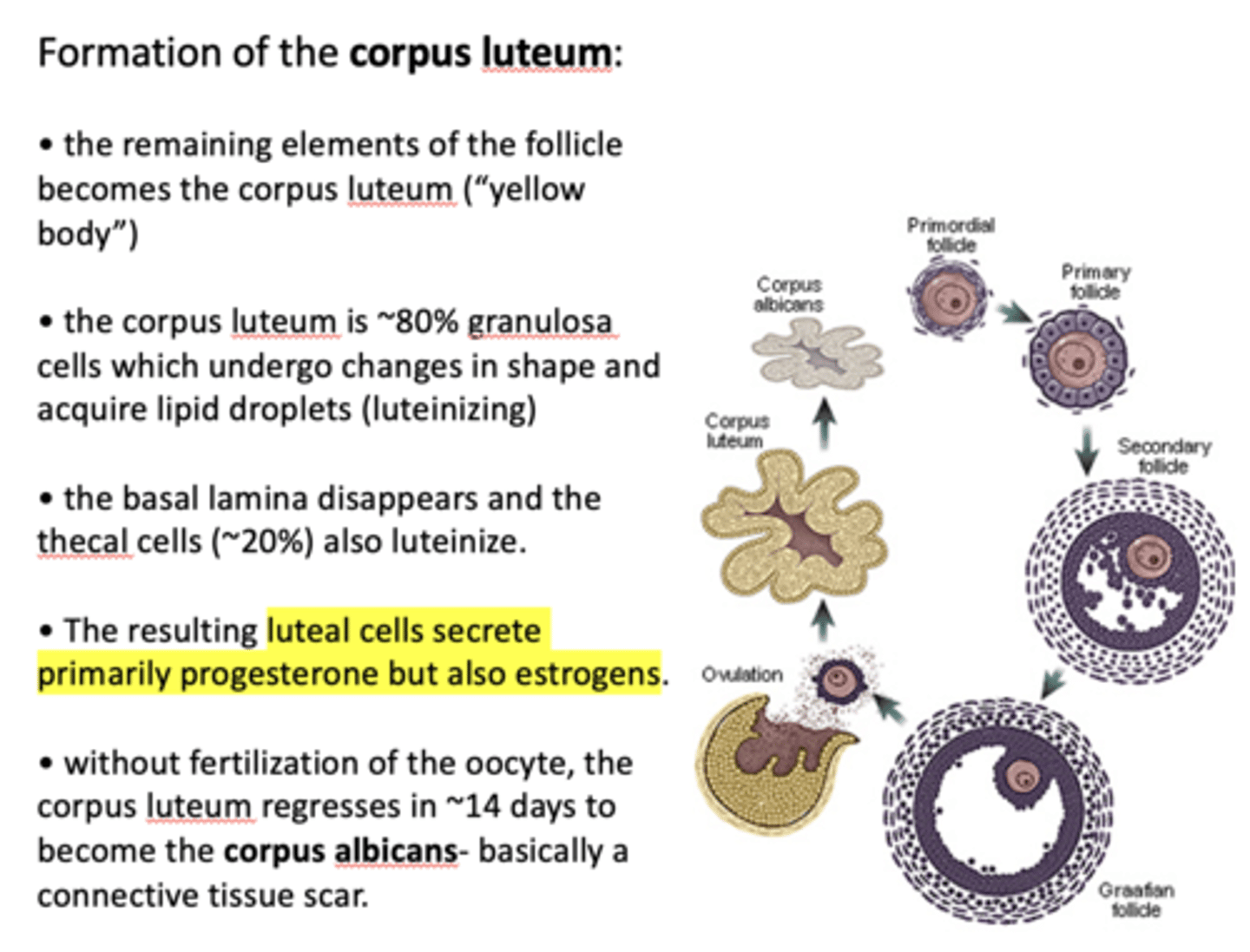
what hormones are secreted from the corpus luteum (resulting luteal cells)?
progesterone (primarily) and estrogen
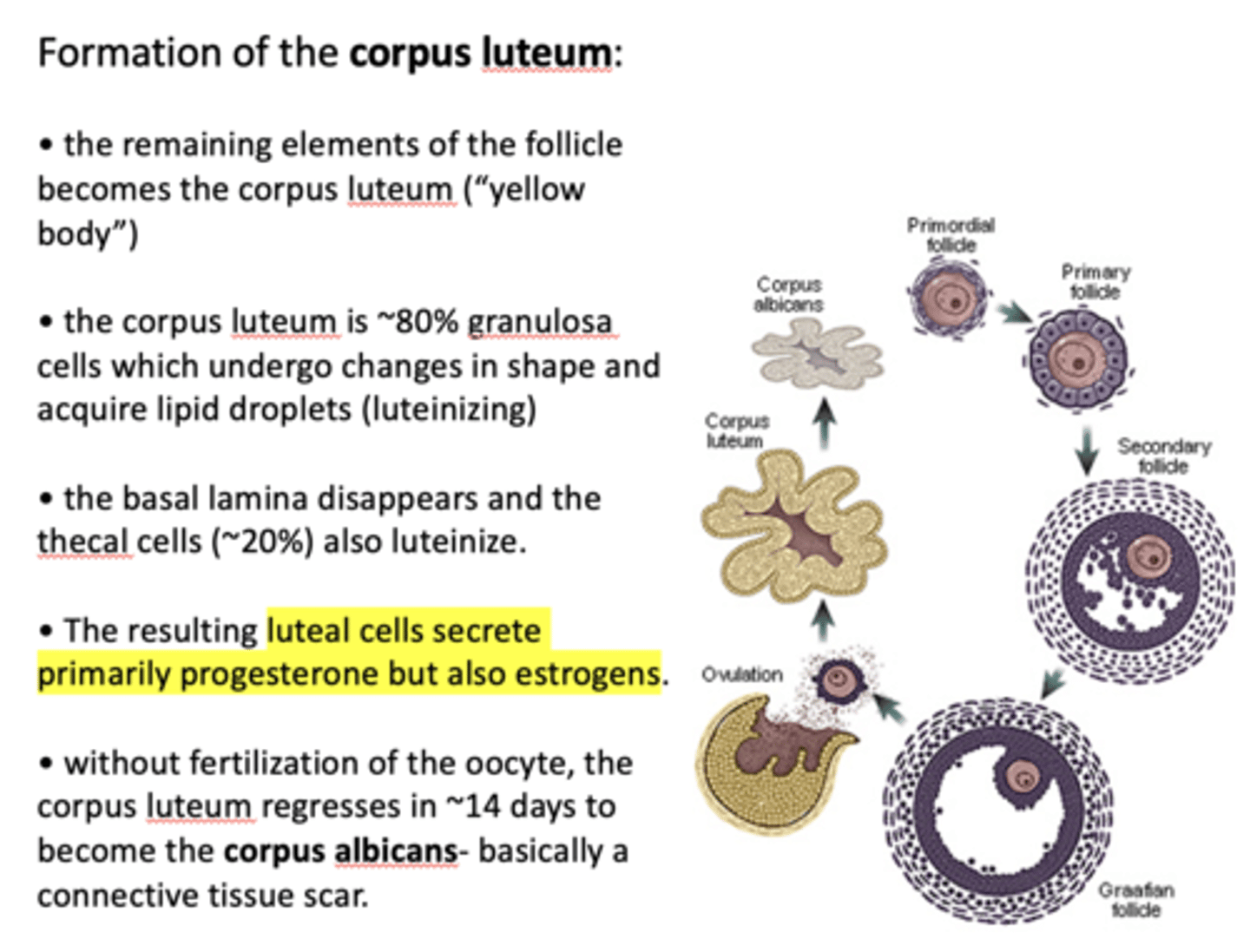
without fertilization of the oocyte, the corpus luteum regresses in ~14 days to become the _________, connective tissue scar
corpus albicans
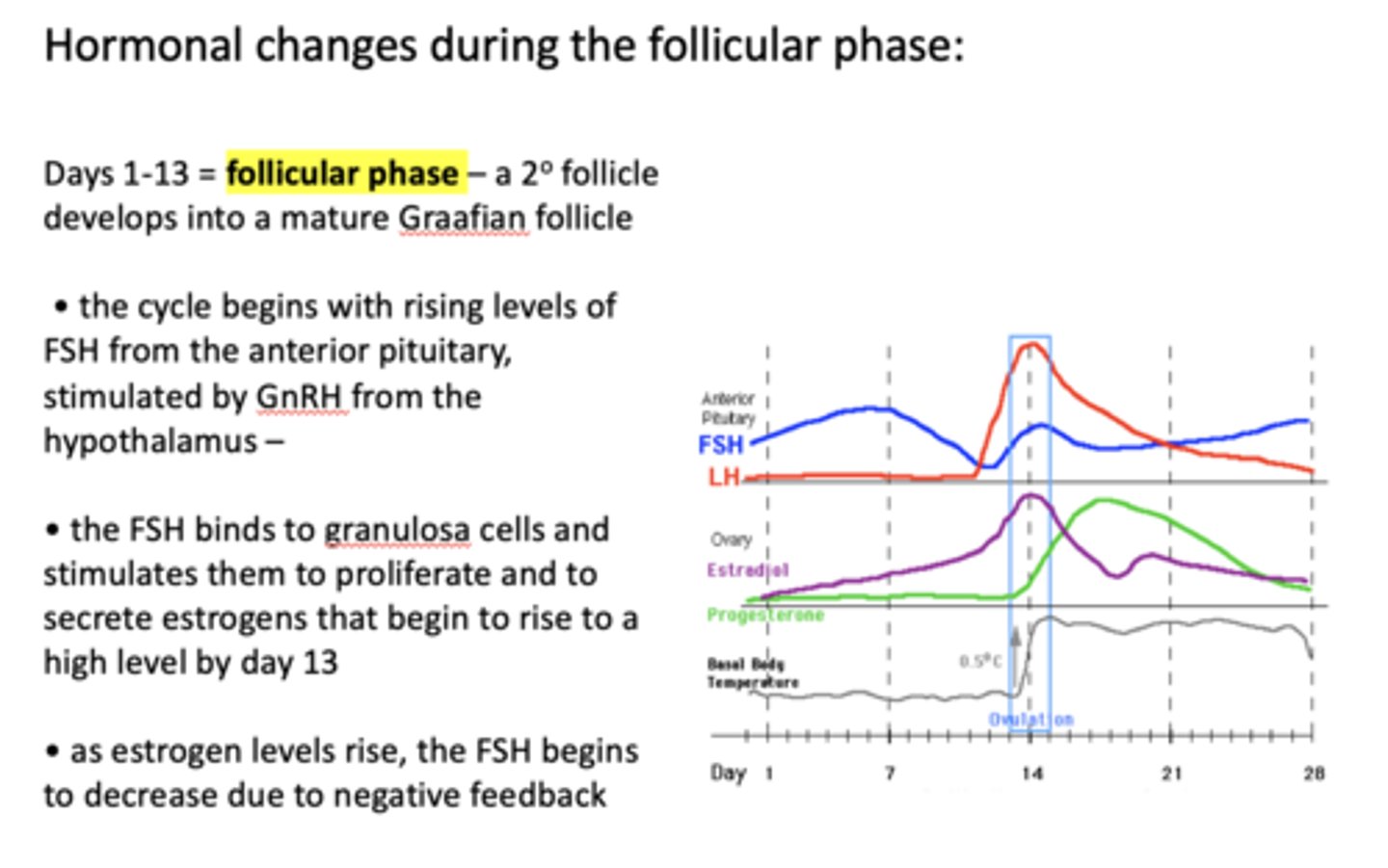
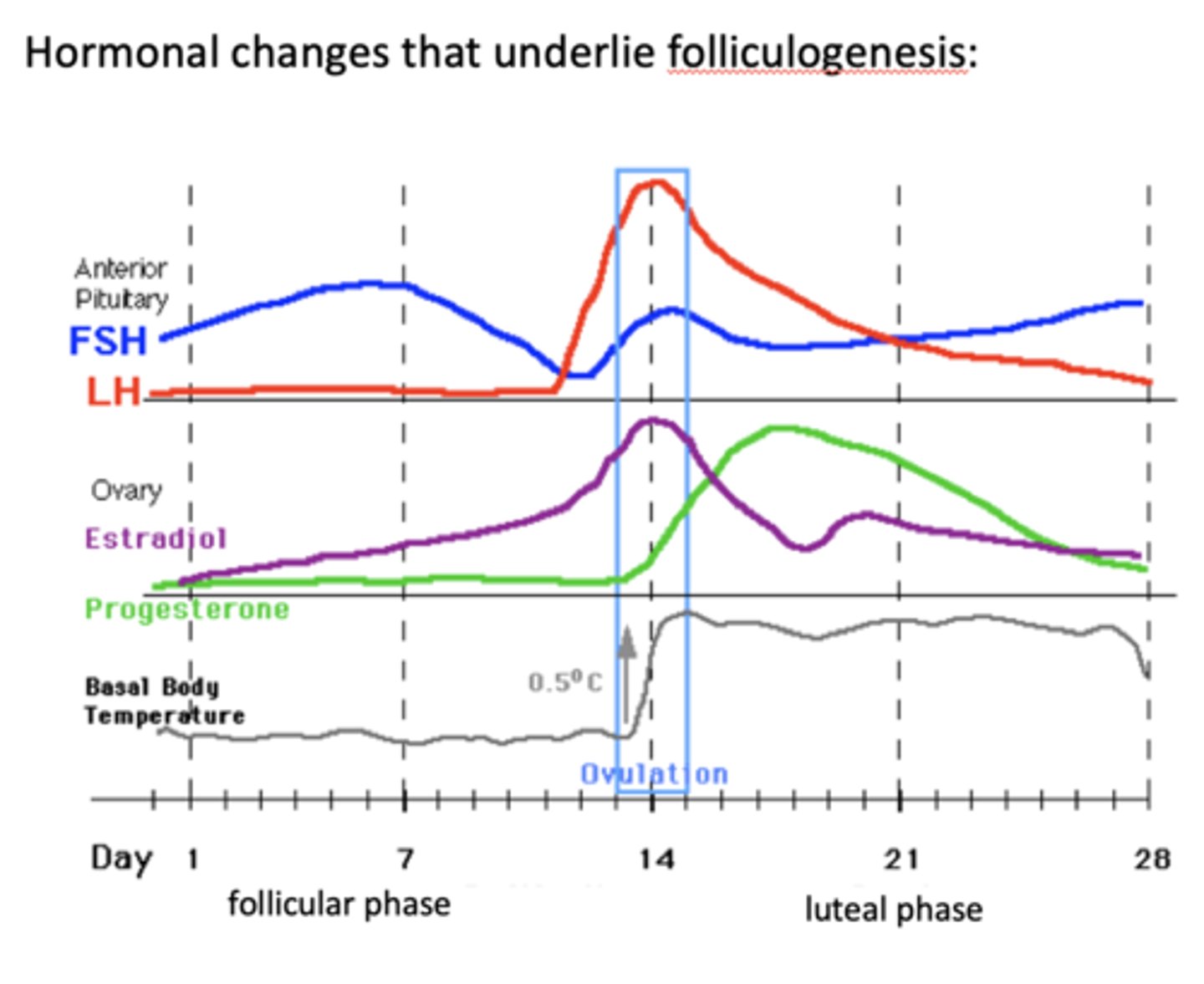
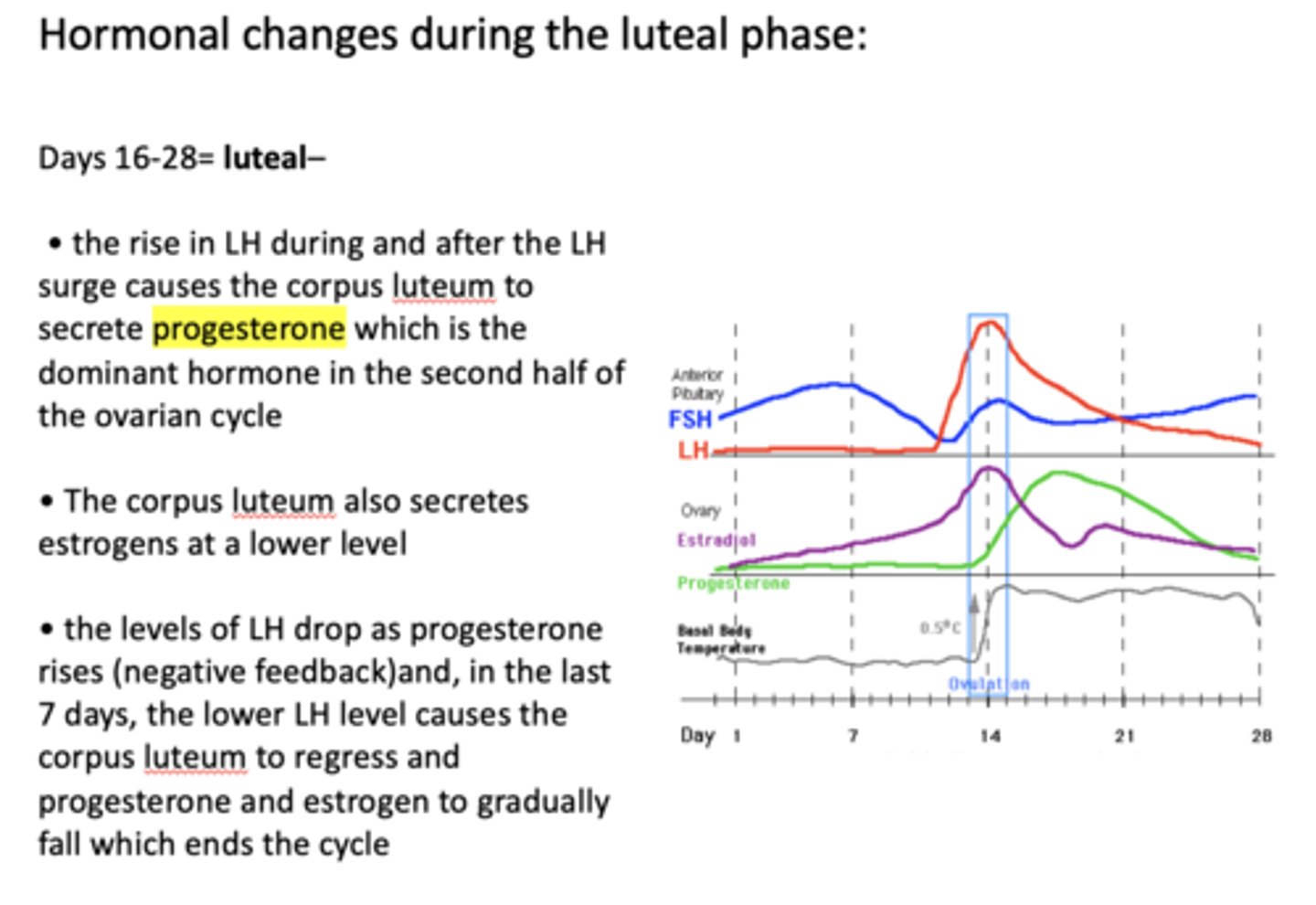
the first 13 or so days of the menstrual cycle are called the ________
follicular phase
the last 15 or so days of the menstrual cycle are called the ________
luteal phase
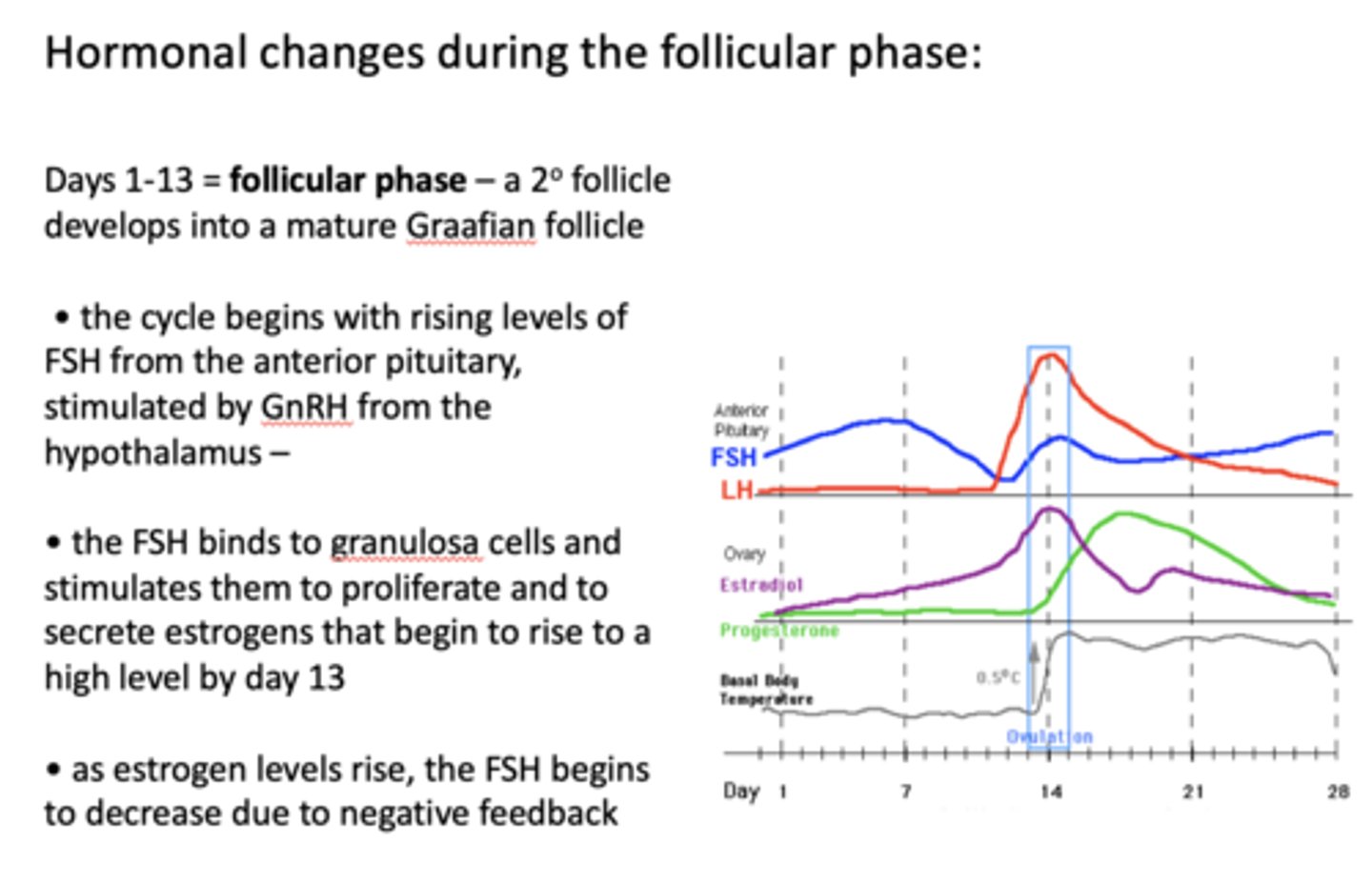
The cycle begins with rising levels of FSH from the anterior pituitary, stimulated by ____________ from the hypothalamus
GnRH
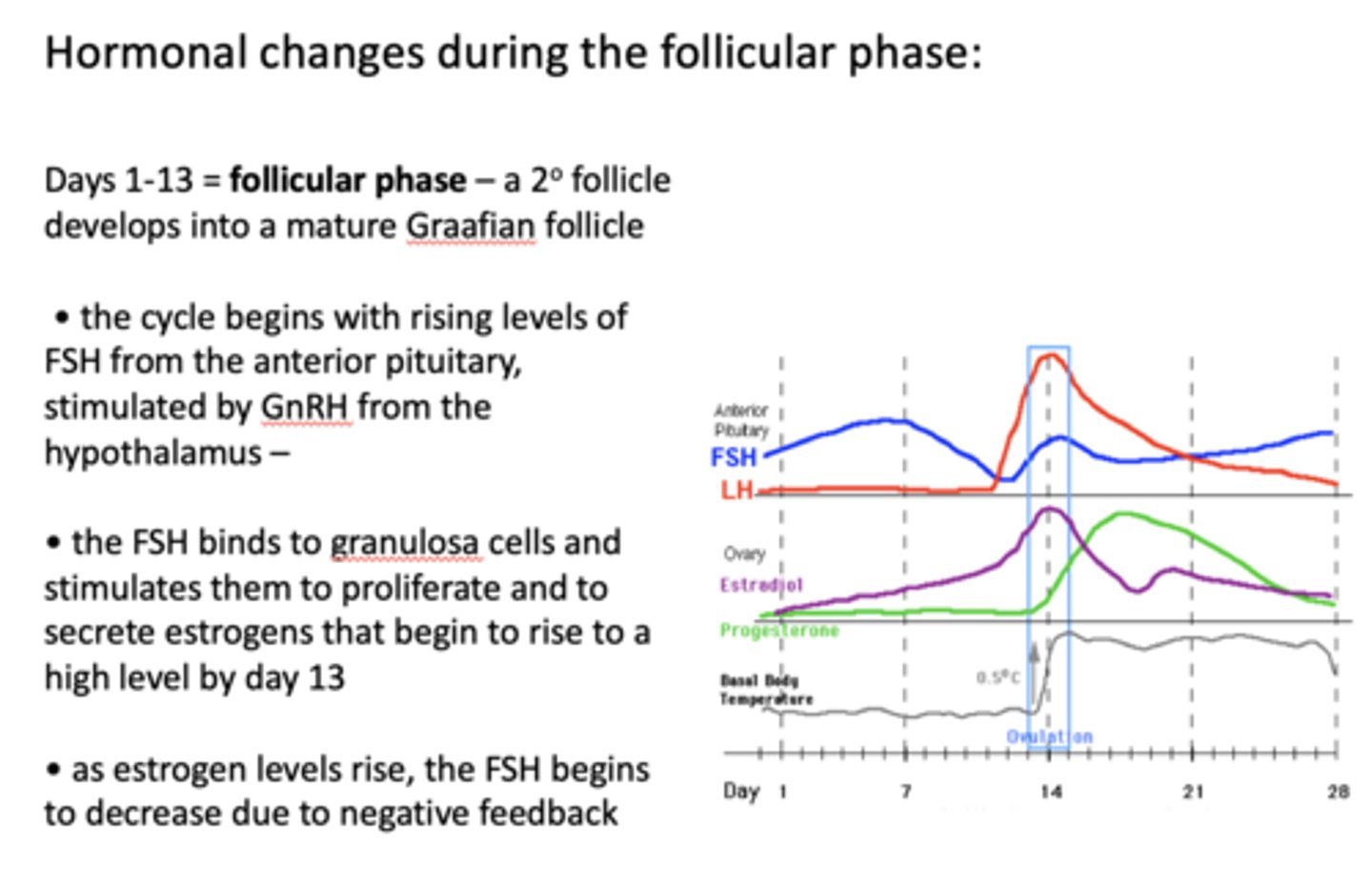
the follicular phase is marked by a rise in what hormone?
FSH
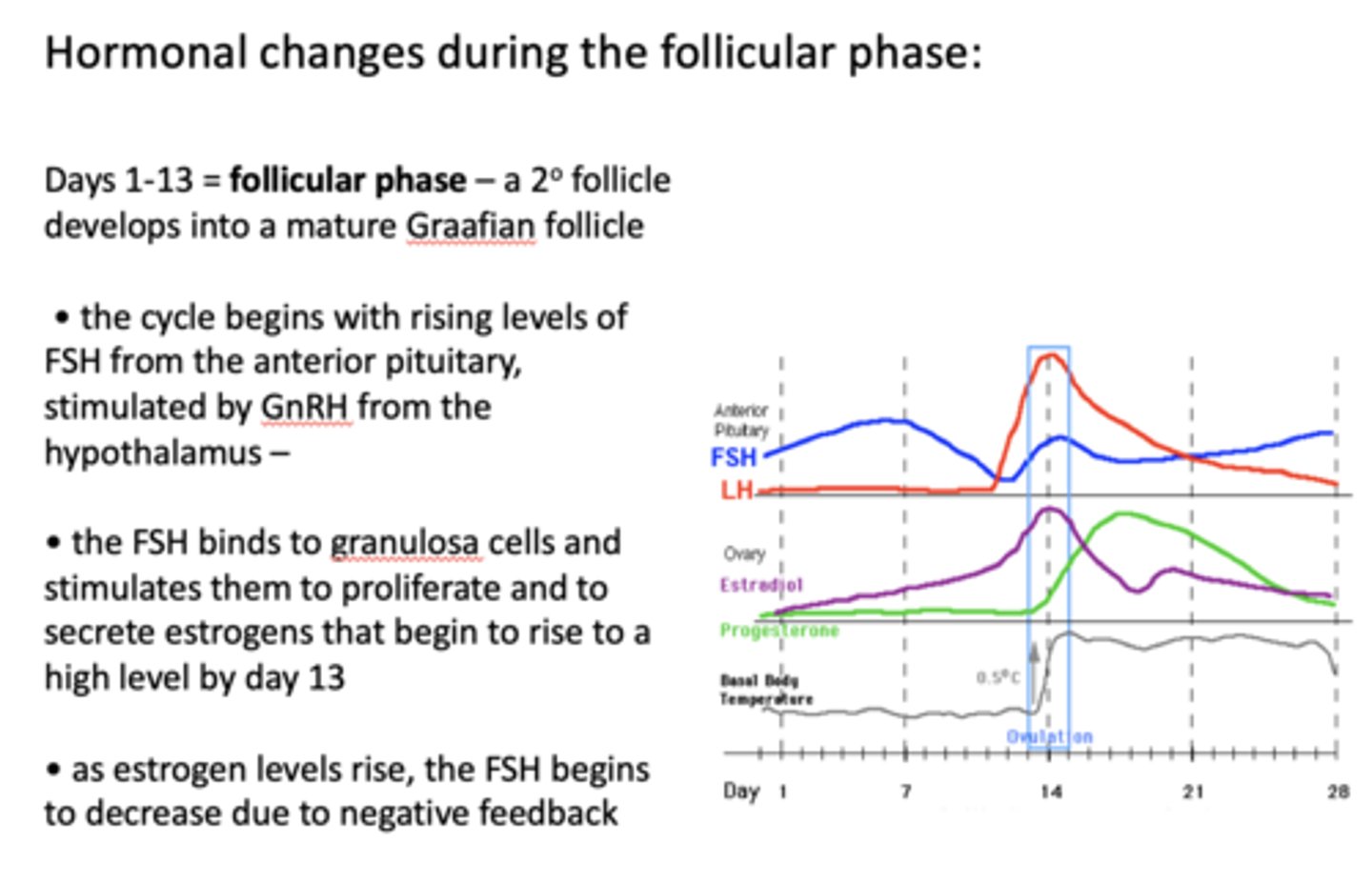
__________ binds to granulosa cells and stimulates them to proliferate and to secrete estrogens that begin to rise to a high level by day 13
FSH
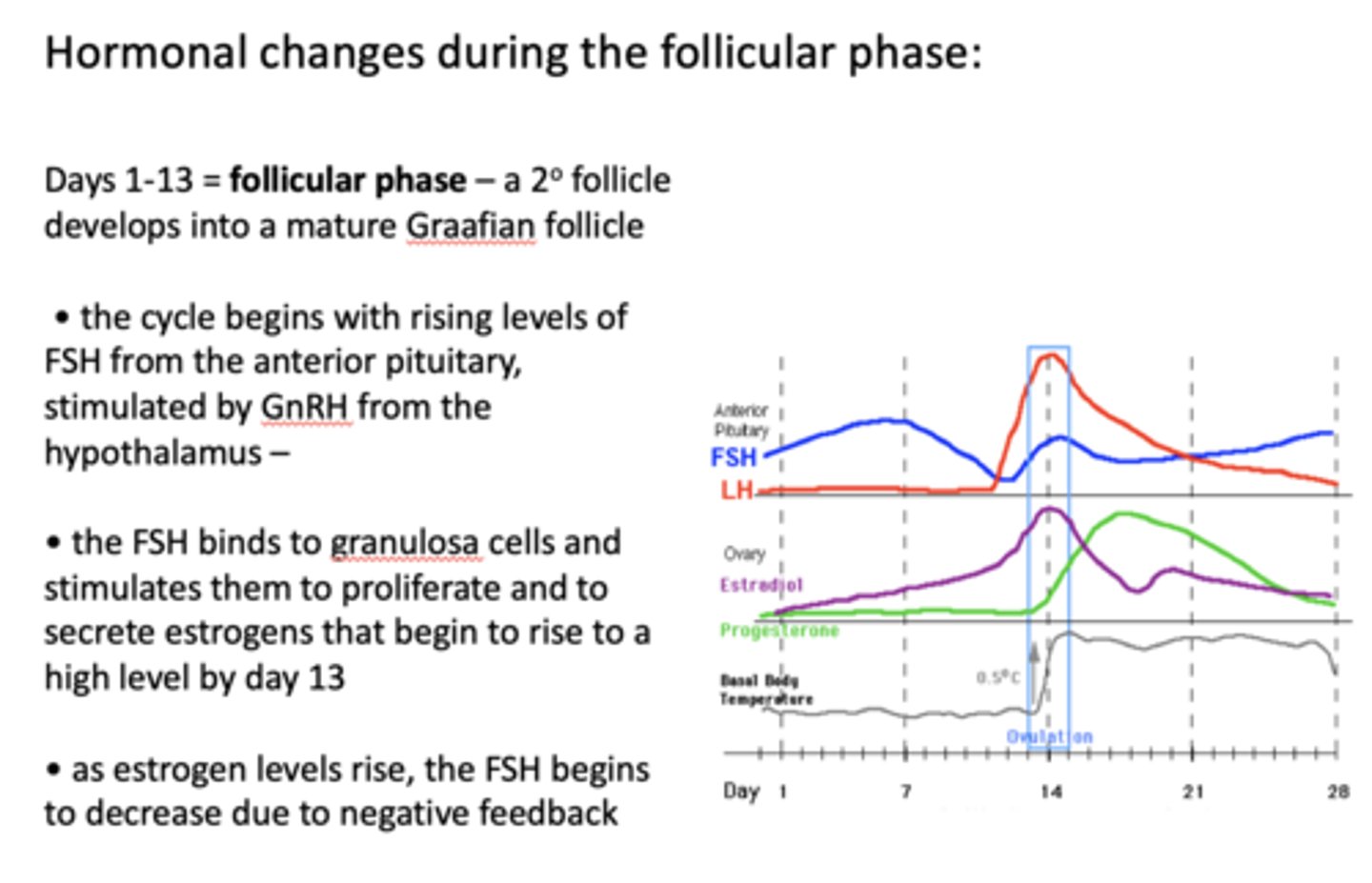
FSH binds to ________ and stimulates them to proliferate and to secrete estrogens that begin to rise to a high level by day 13
granulosa cells
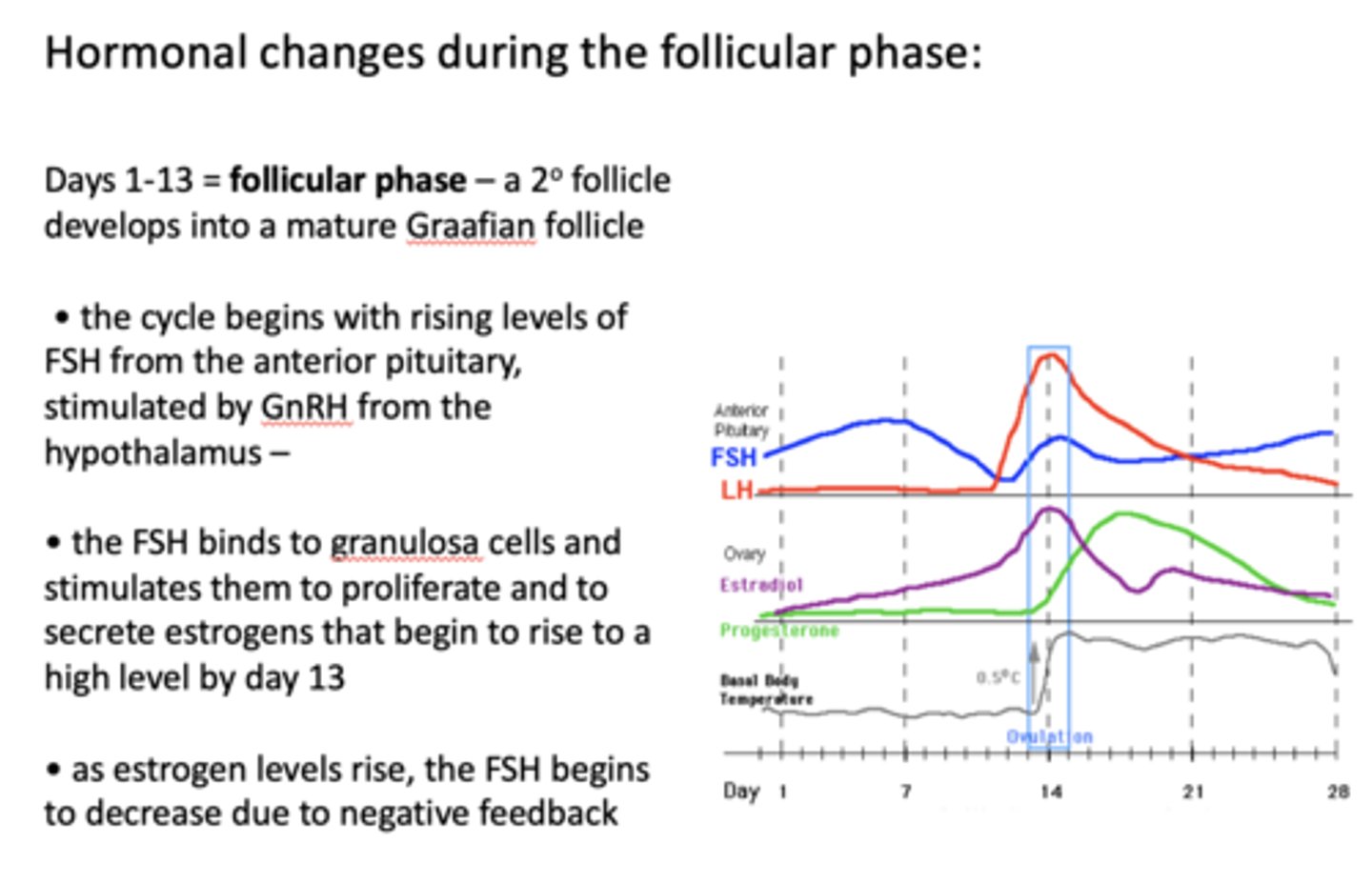
these cell secrete estrogen under FSH stimulation:
granulosa cells

as estrogen levels rise, the ____________ begins to decrease due to negative feedback
FSH
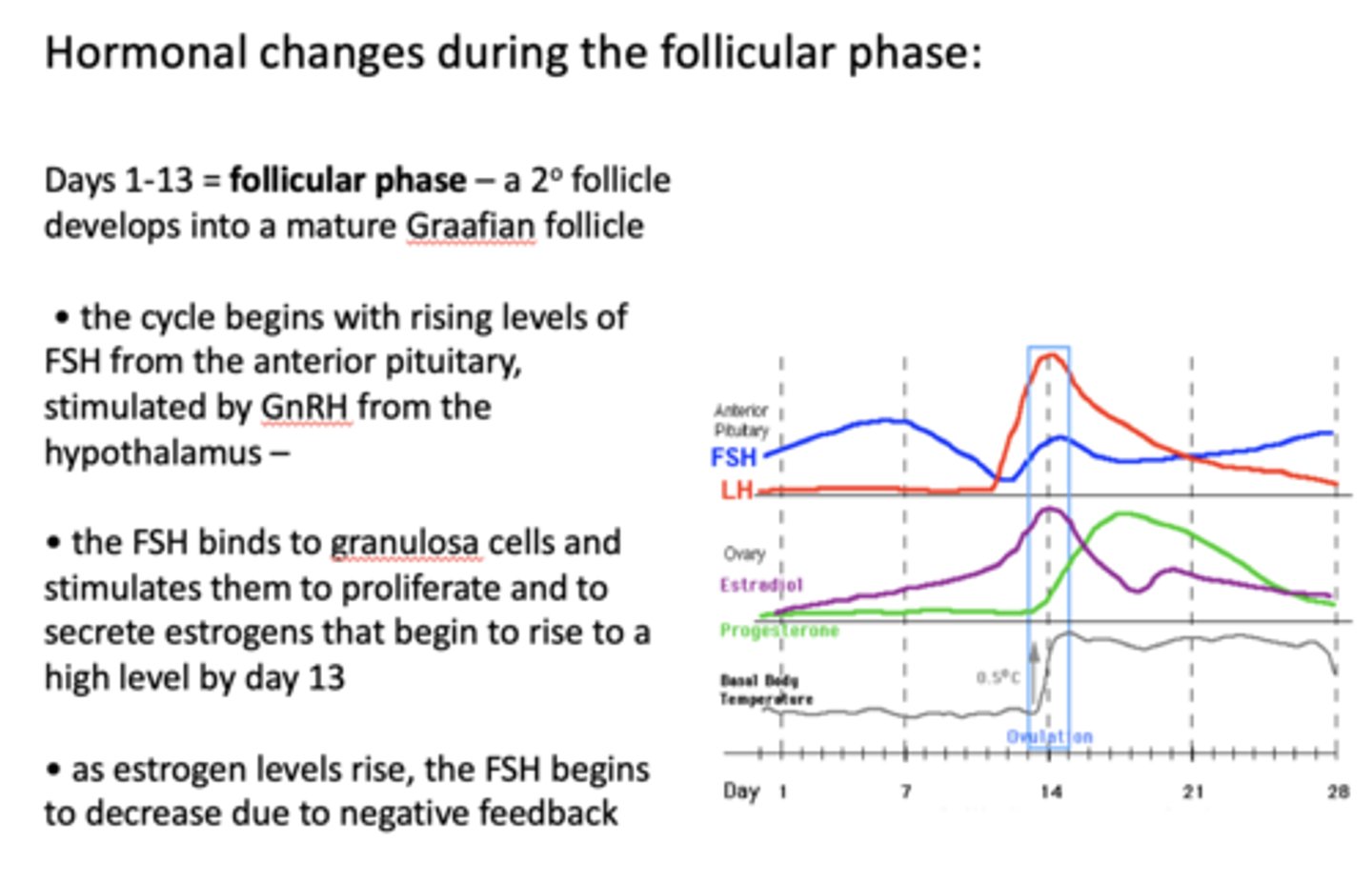
as ________ levels rise, the FSH begins to decrease due to negative feedback
estrogen
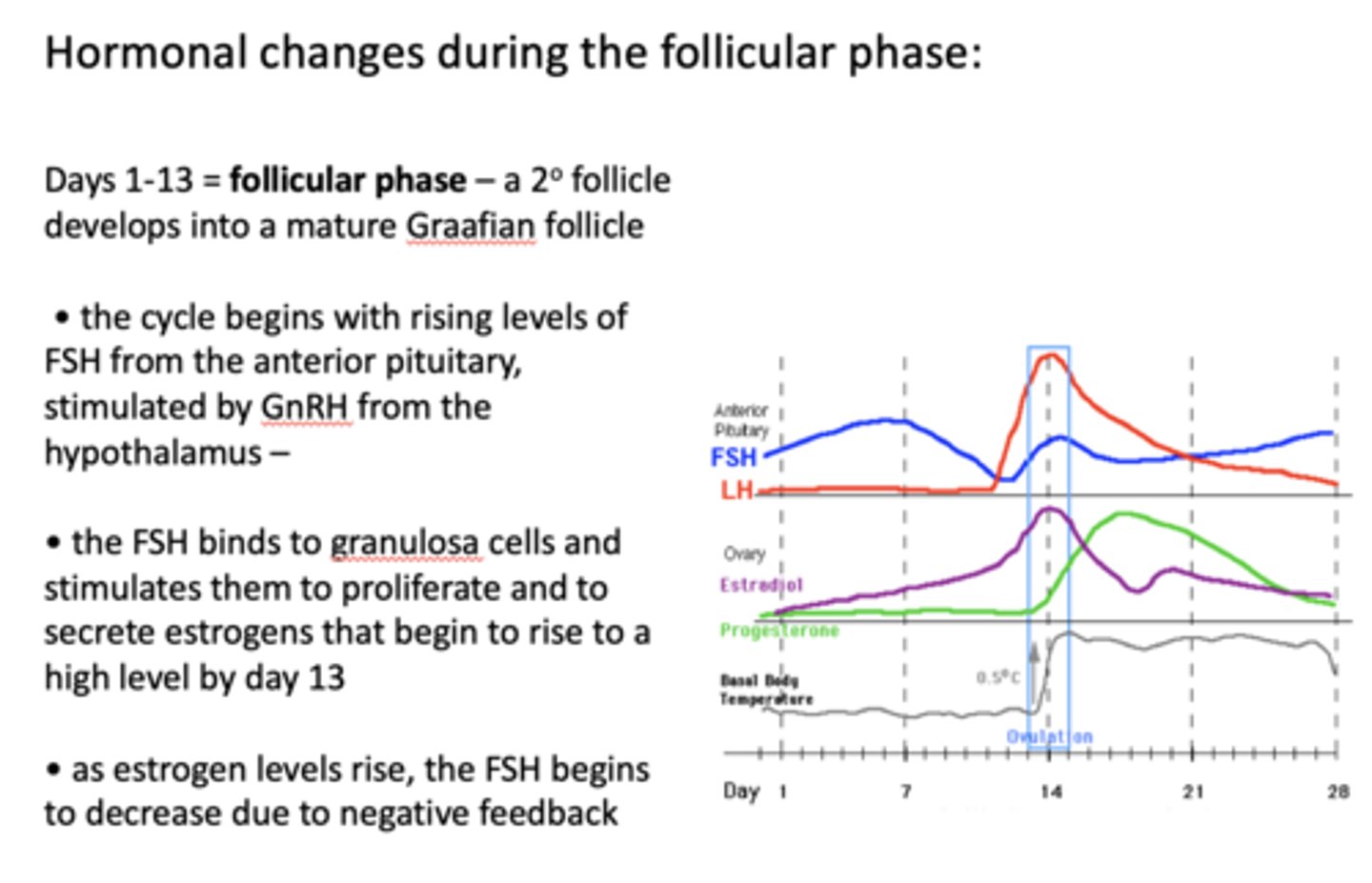
a rise in estrogen exerts BOTH positive and negative feedback on what hormone?
FSH
as estrogen levels rise to a very high level at day 13, the negative feedback on the pituitary becomes a positive feedback, and ___________ and ___________ rise
LH and FSH
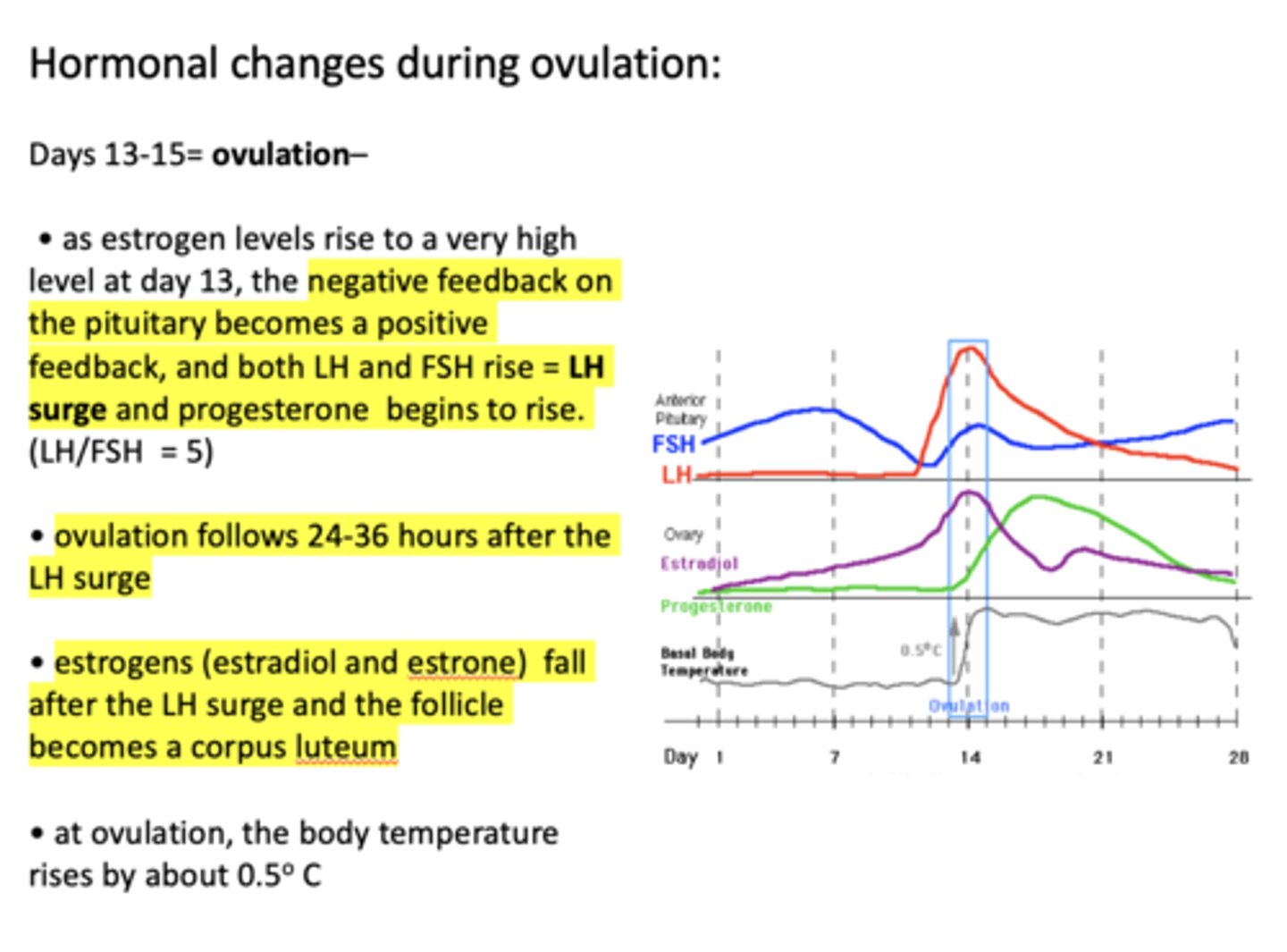
as estrogen levels rise to a very high level at day 13, the negative feedback on the pituitary becomes a positive feedback, and both LH and FSH rise. This is called the ________
LH surge
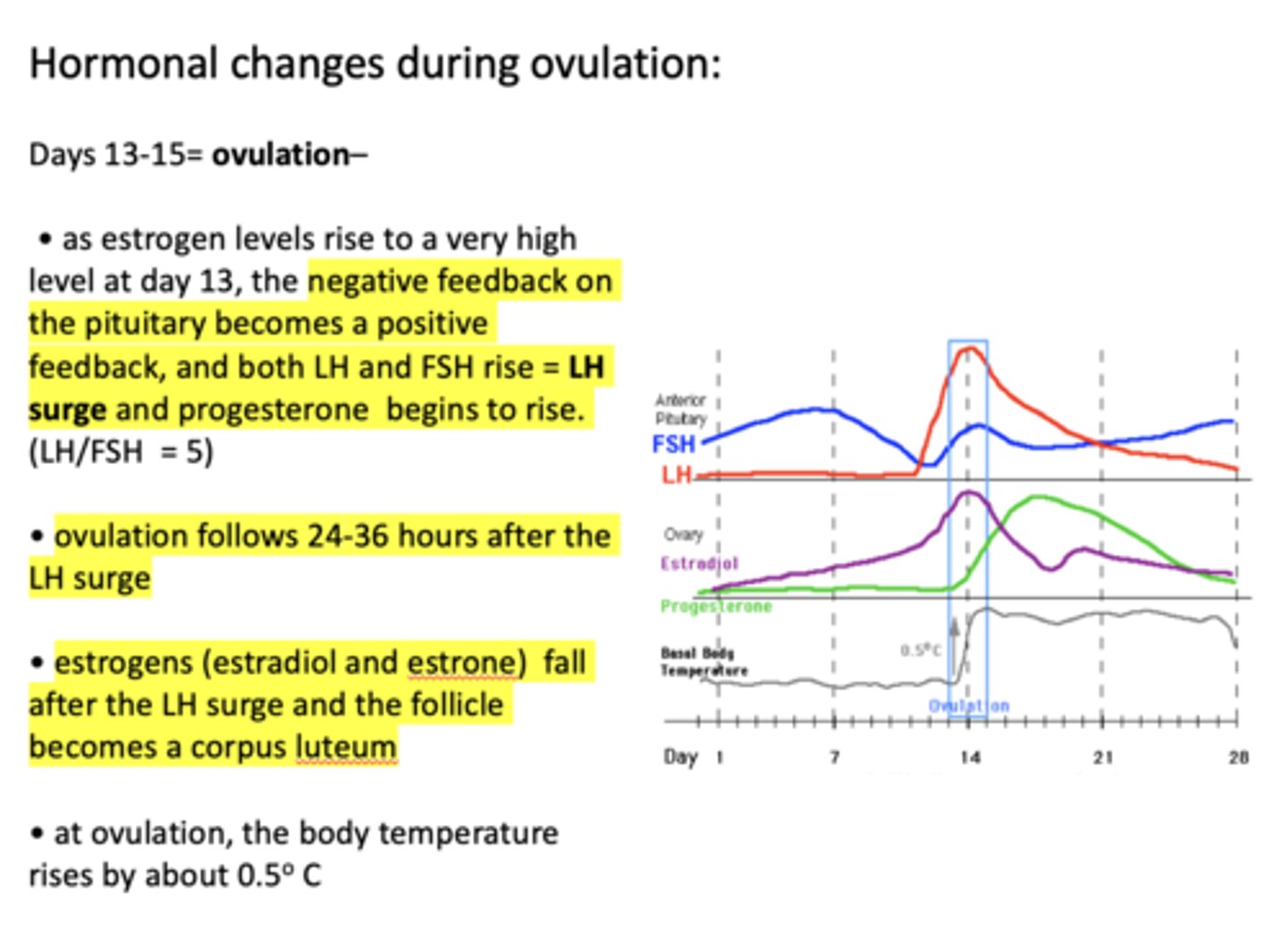
what hormone begins to rise during ovulation?
progesterone
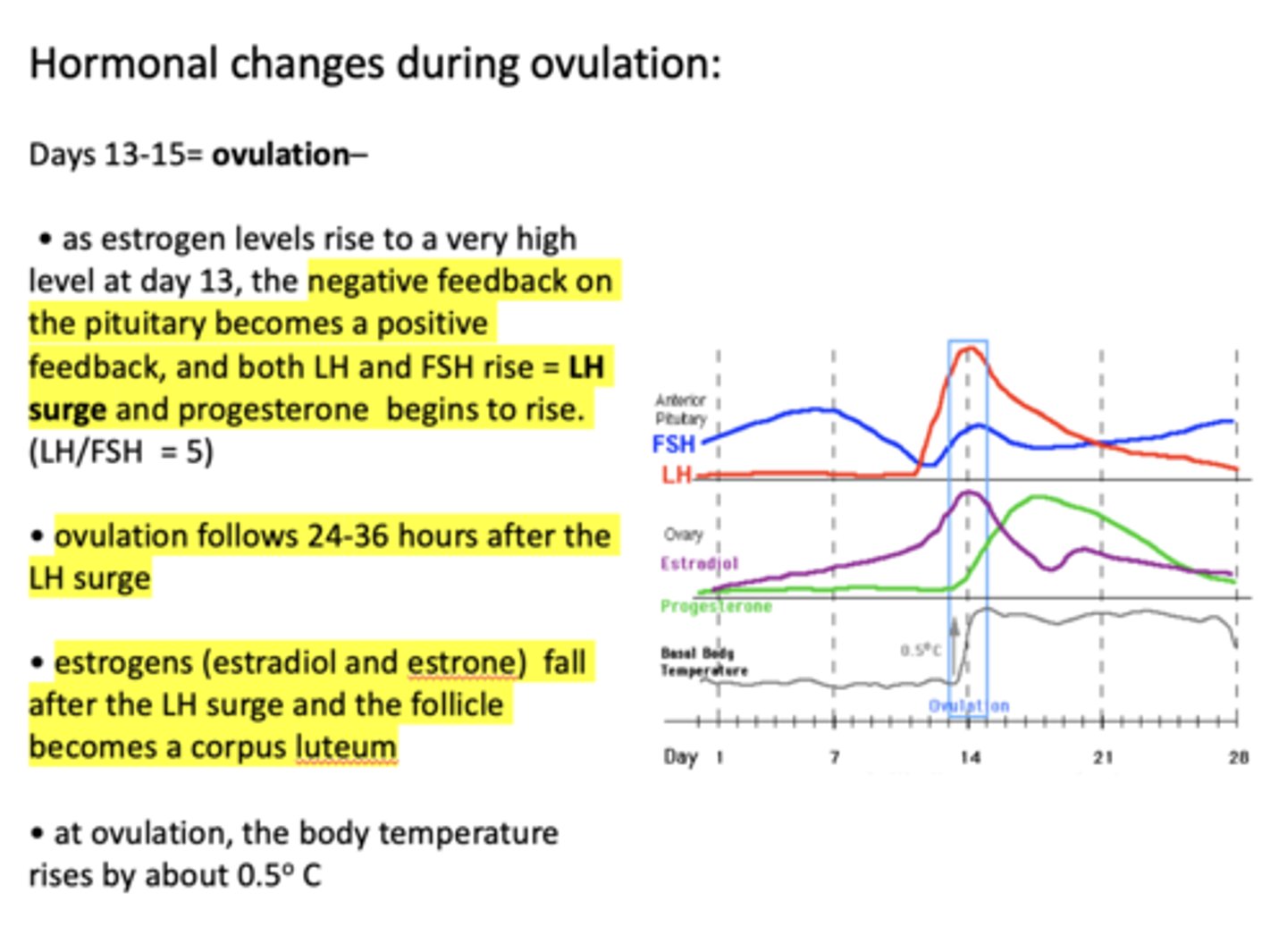
ovulation begins ______-______ after the LH surge
24-36 hours
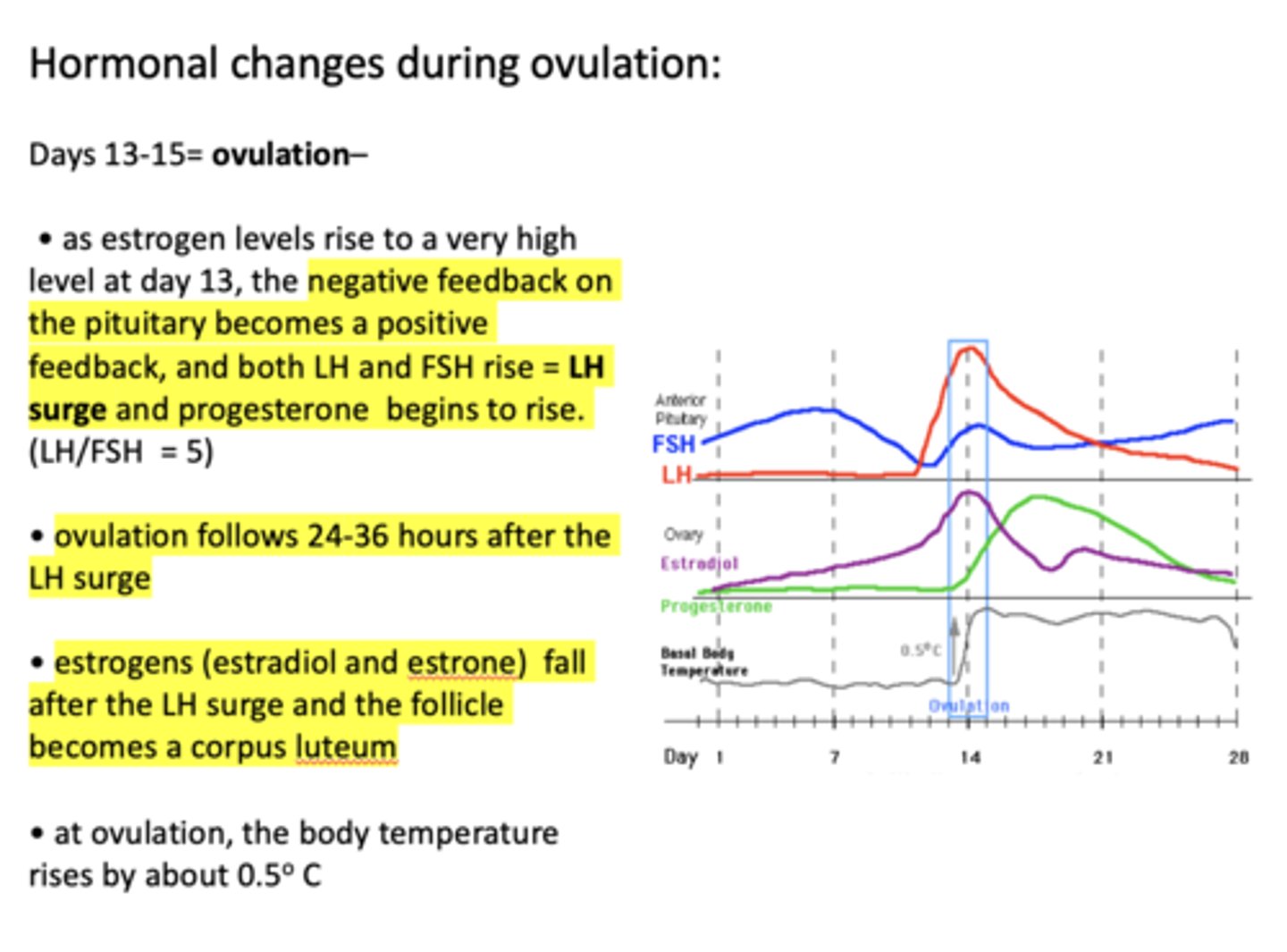
what causes a fall in estrogen after the LH surge?
the follicle becomes a corpus luteum
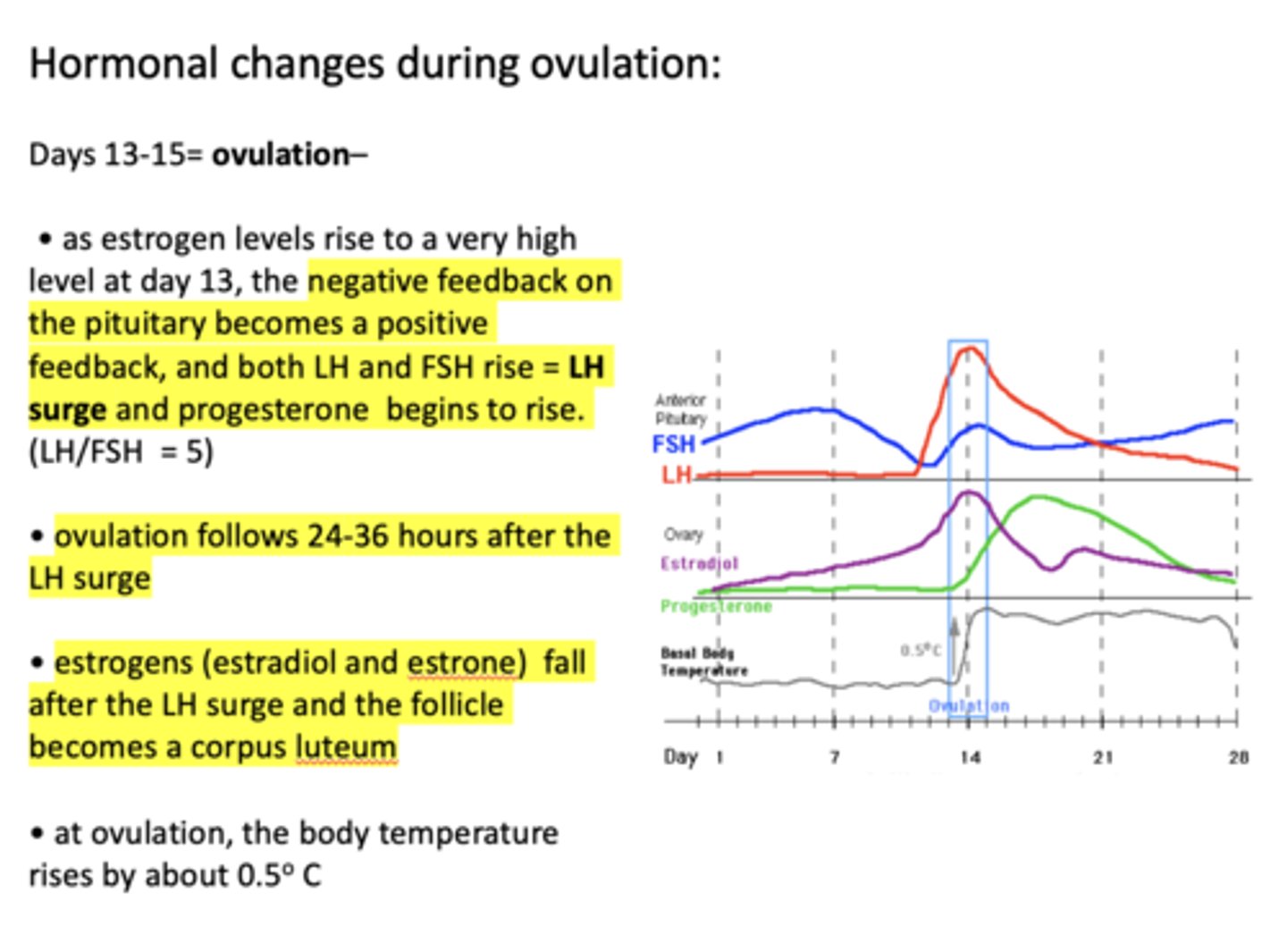
at ovulation, how much does the body temperature rises by?
About 0.5 C
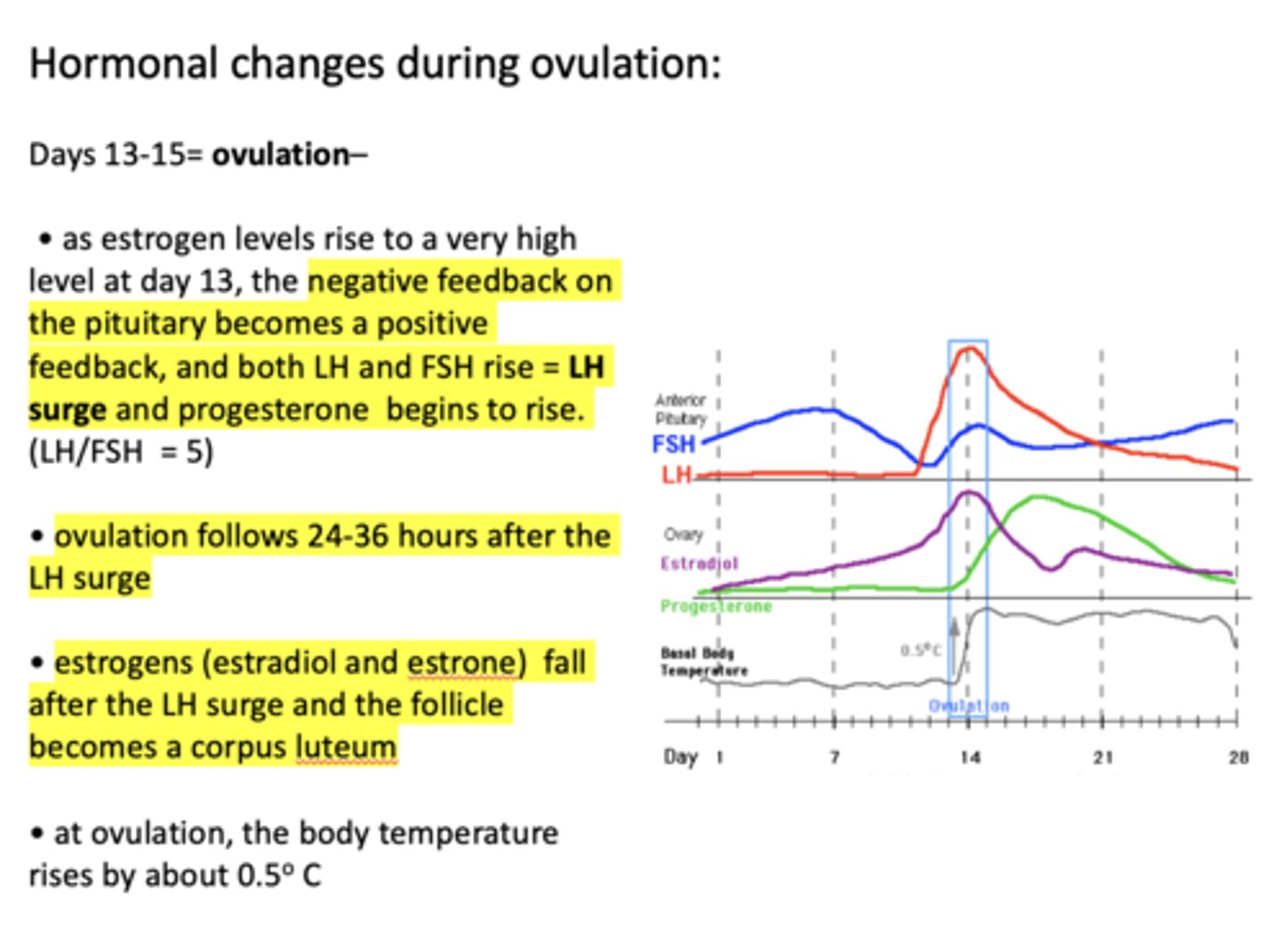
what causes the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone?
the rise in LH
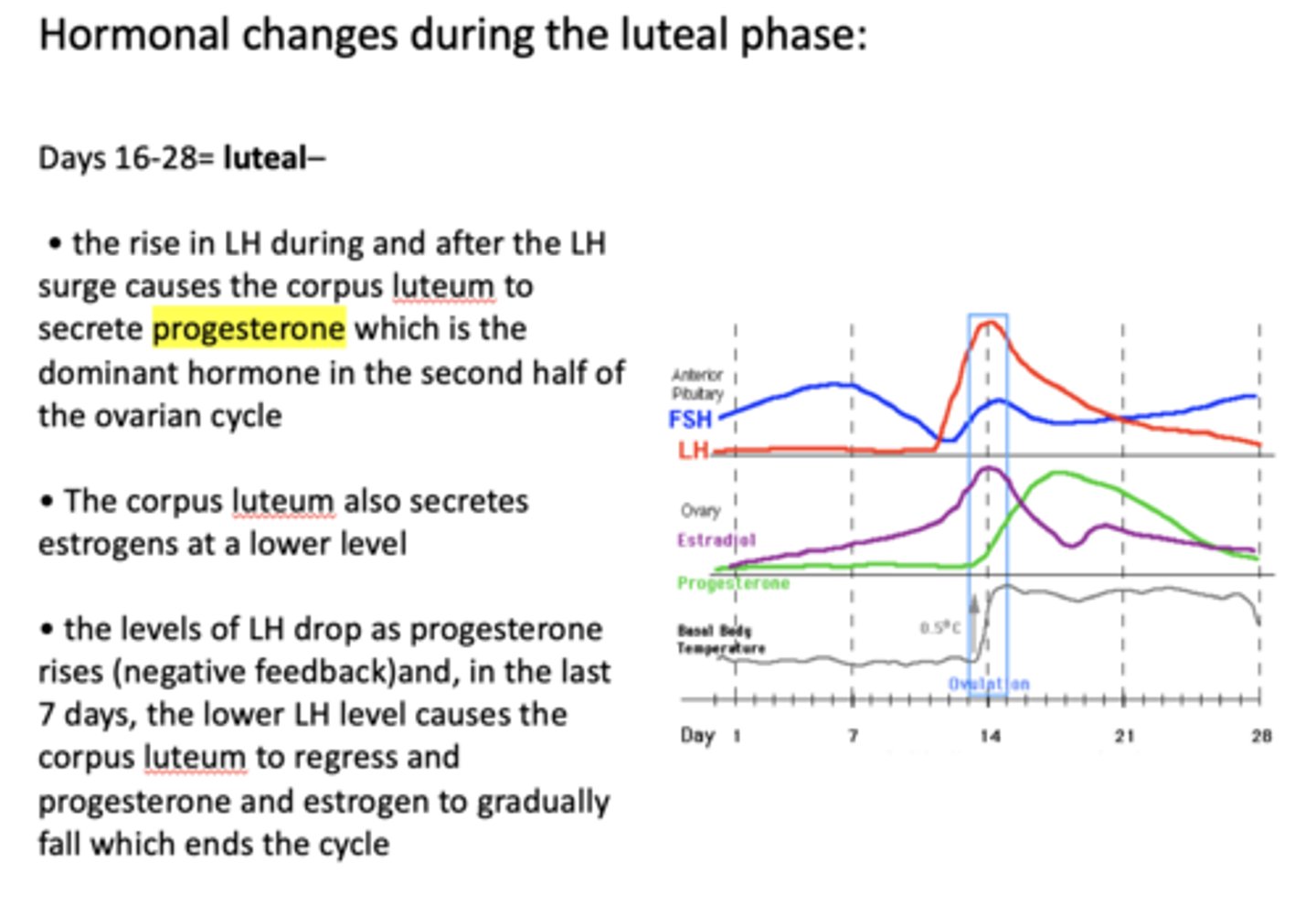
What is the dominant hormone in the second half of the ovarian cycle?
progesterone
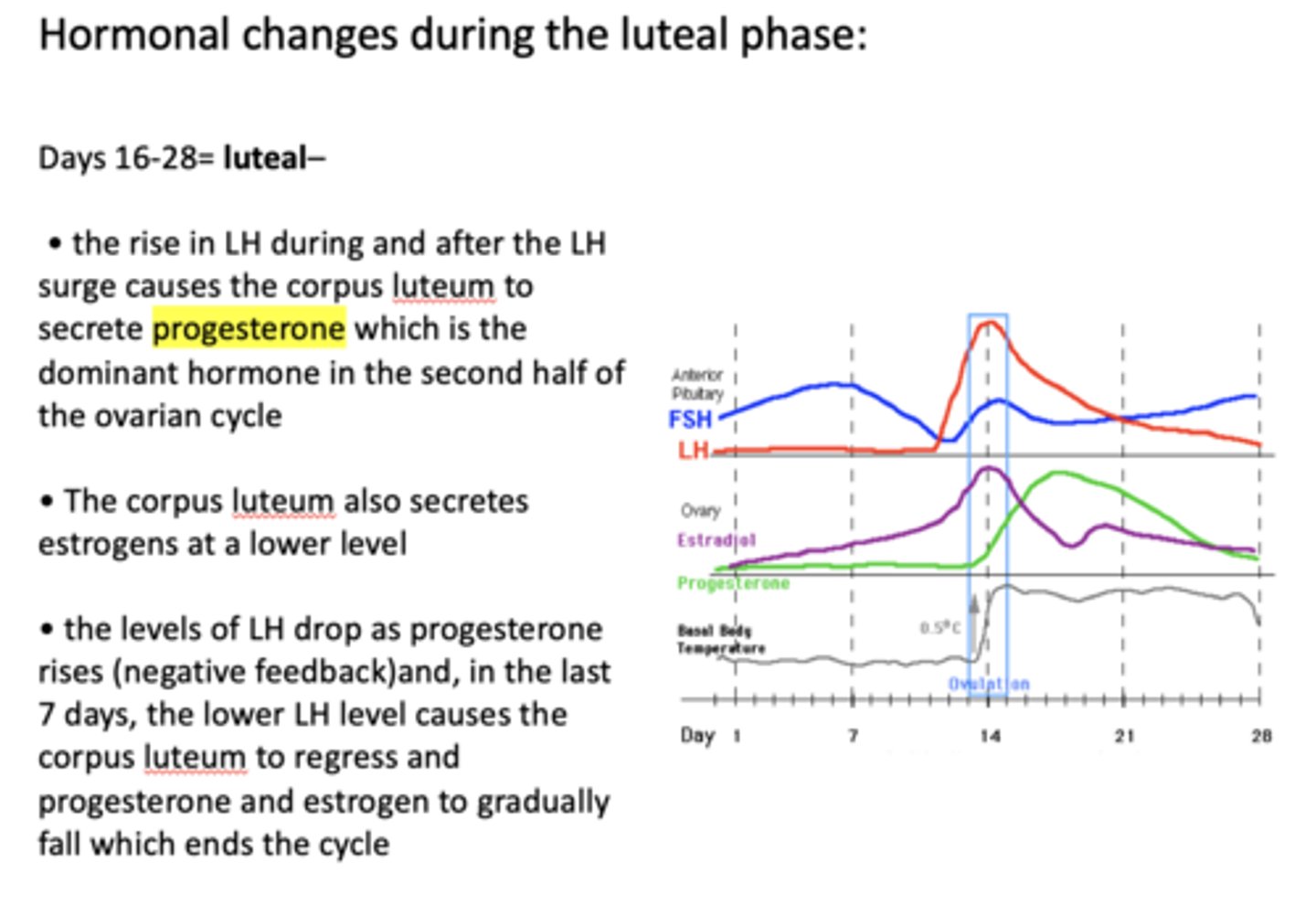
what hormone exerts a negative feedback, causing LH levels to drop?
progesterone
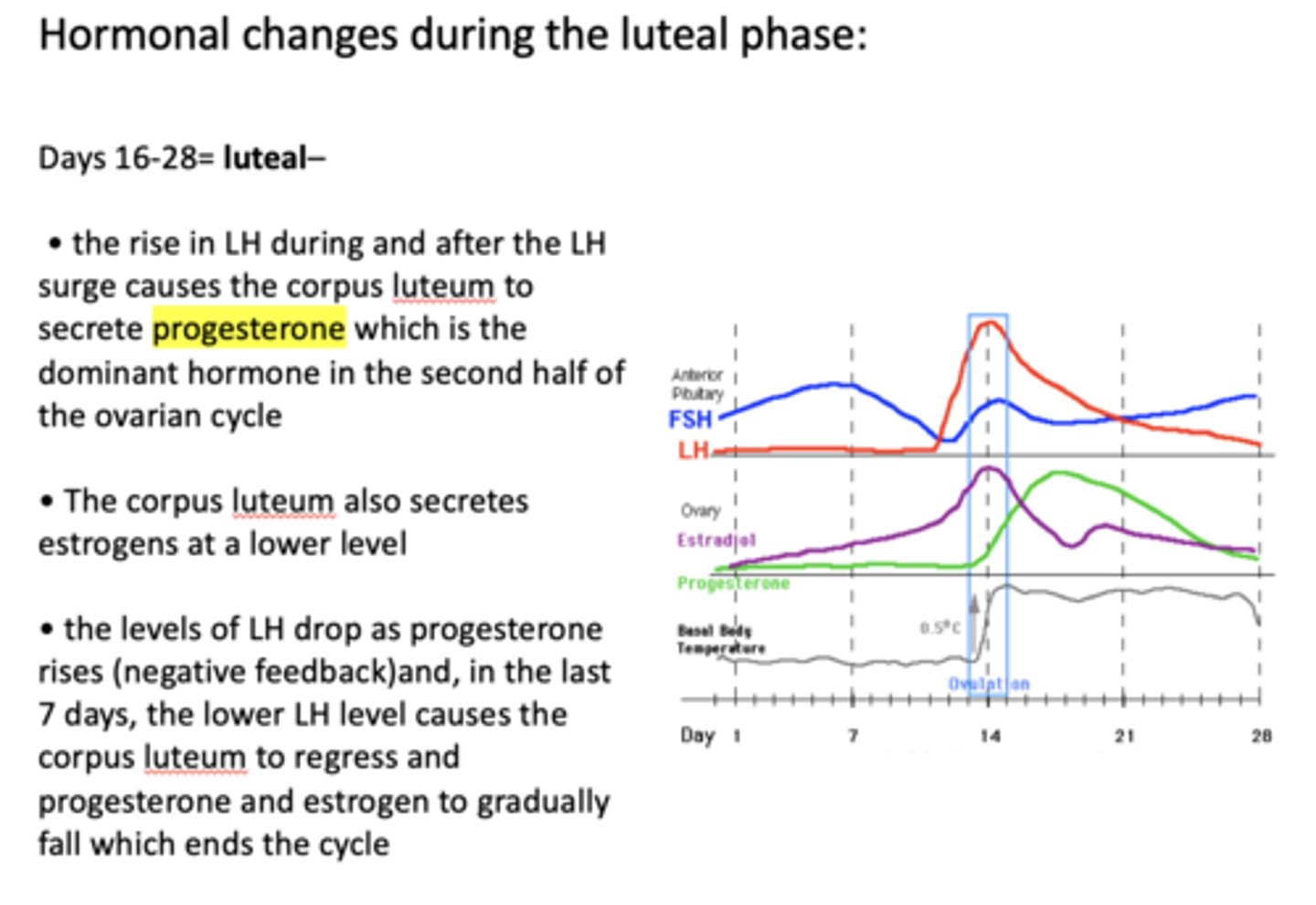
What does the corpus luteum secrete at lower levels?
Estrogens
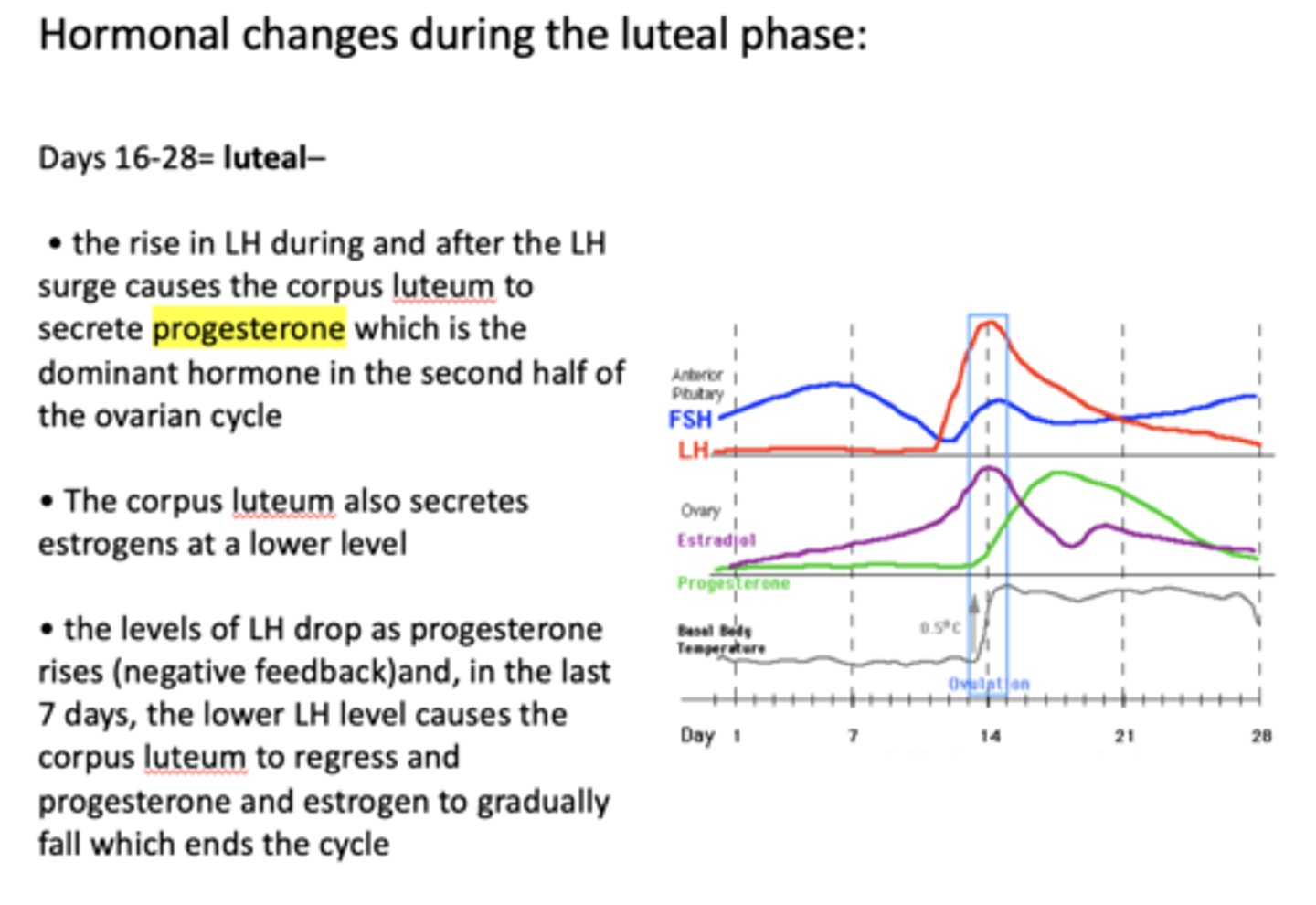
the decrease in ____________ levels causes the corpus luteum to regress and progesterone and estrogen to gradually fall which ends the cycle
LH
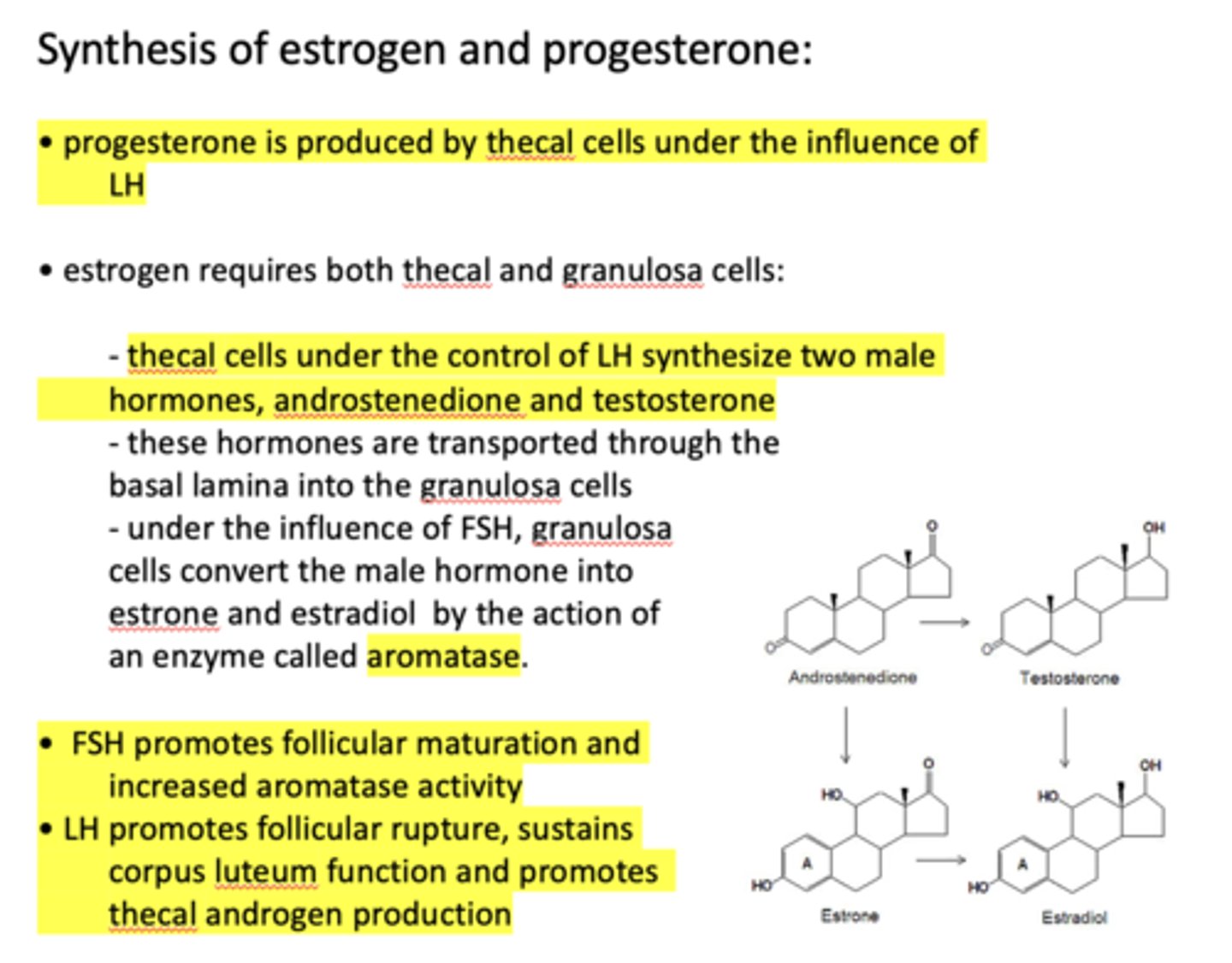
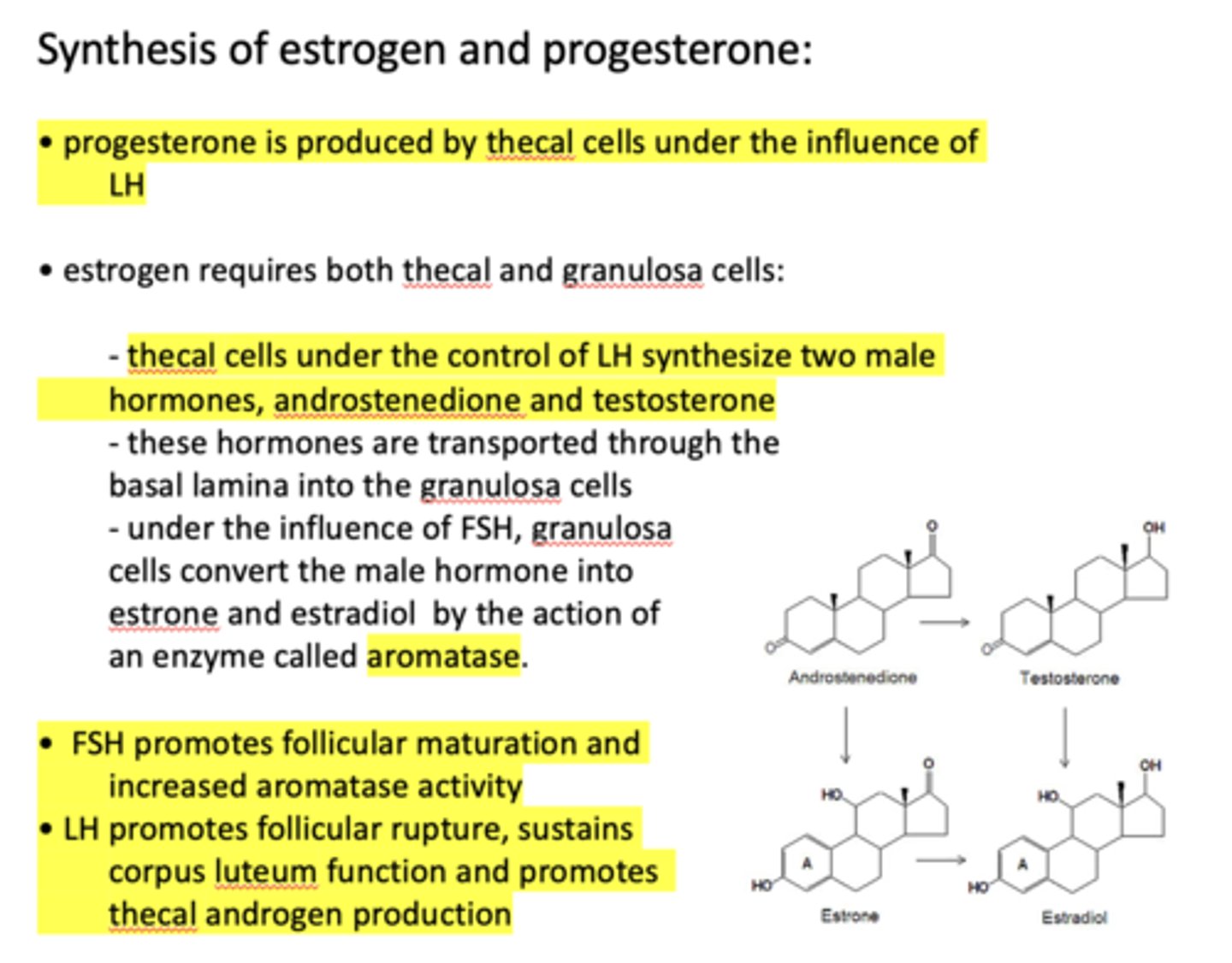
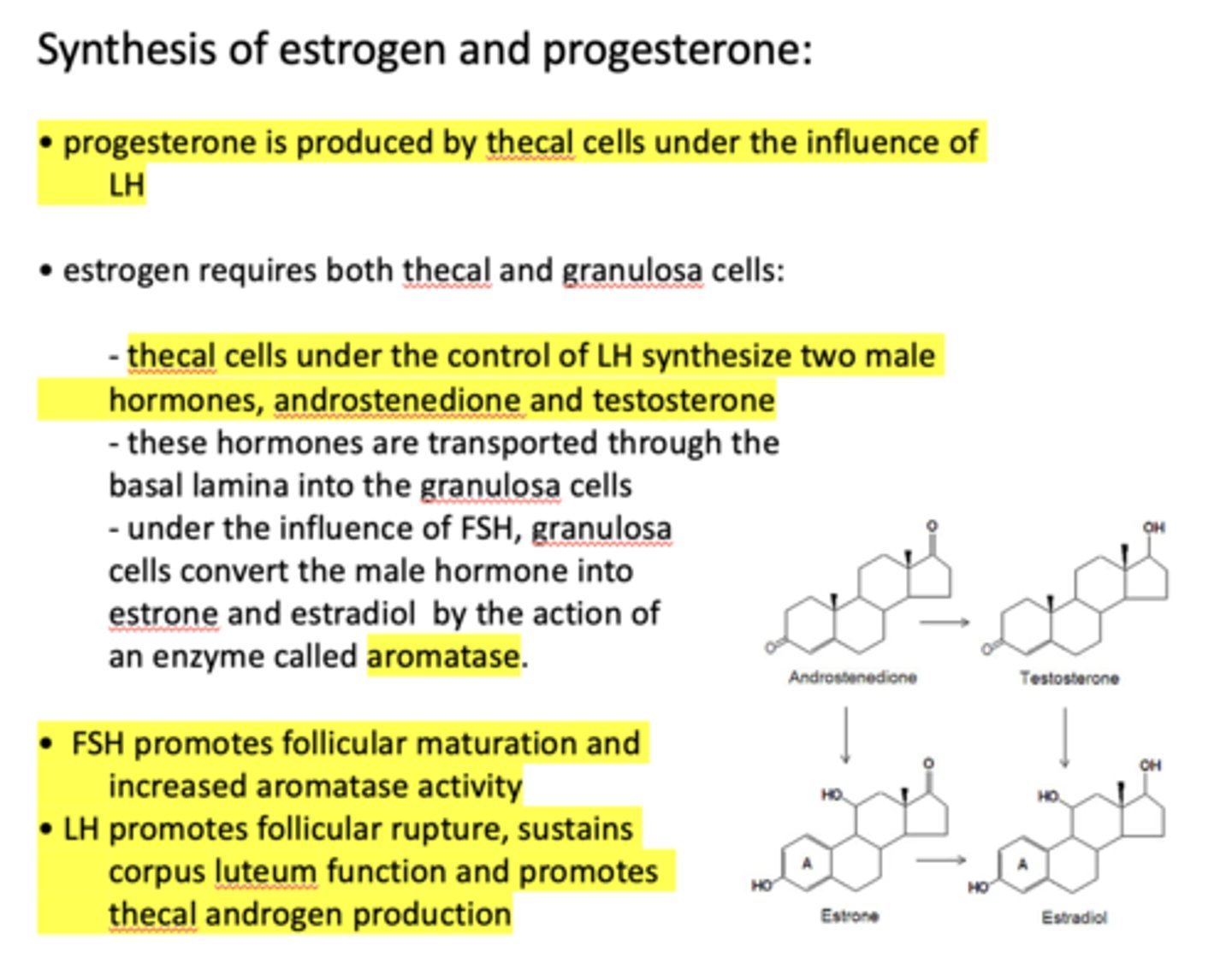
progesterone is produced by ____________ under the influence of LH
thecal cells
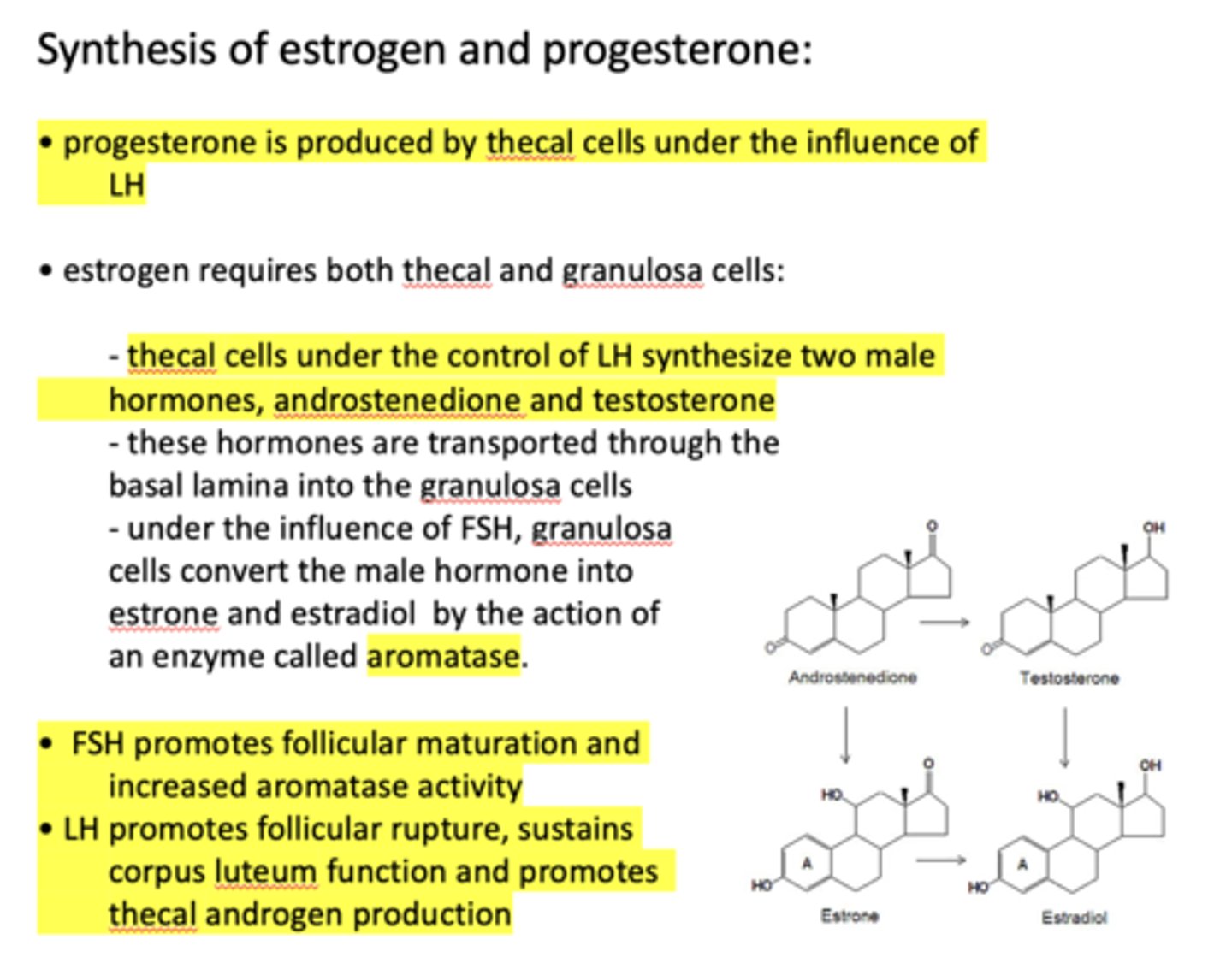
progesterone is produced by thecal cells under the influence of _____________
LH
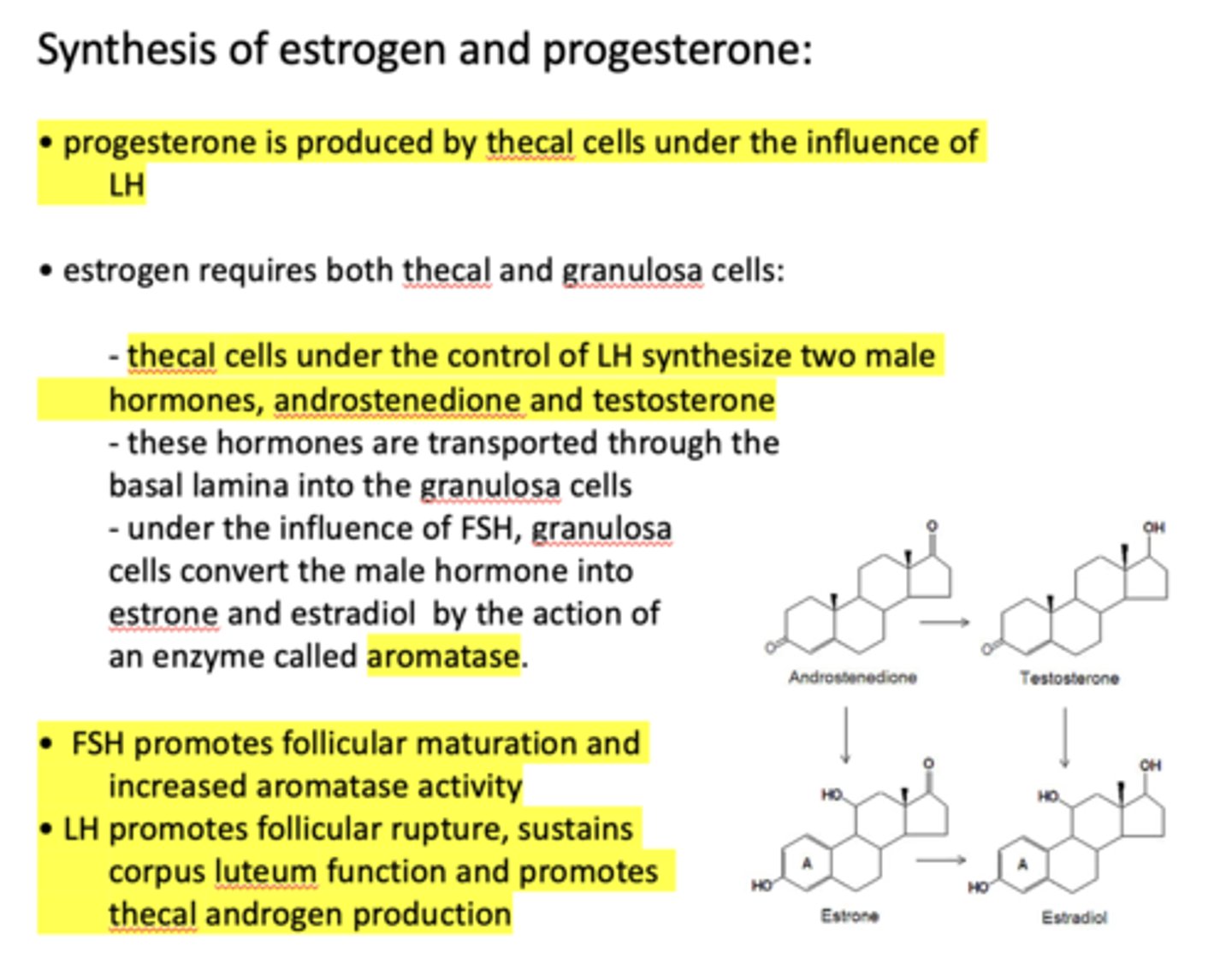
the production of estrogen requires both _____________ and _____________
thecal cells, granulosa cells
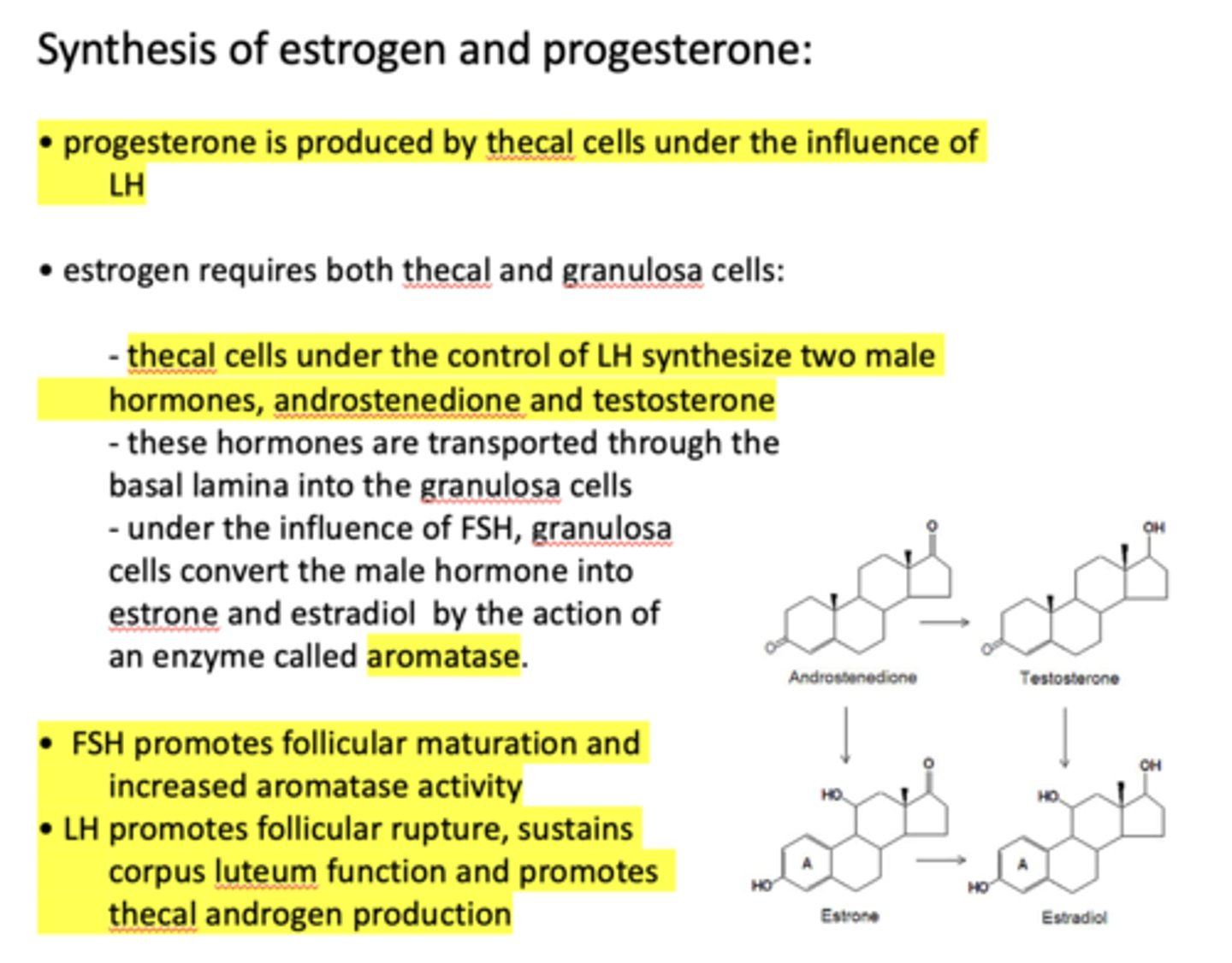
thecal cells under the control of LH synthesize two male hormones, ______________ and ______________
androstenedione, testosterone
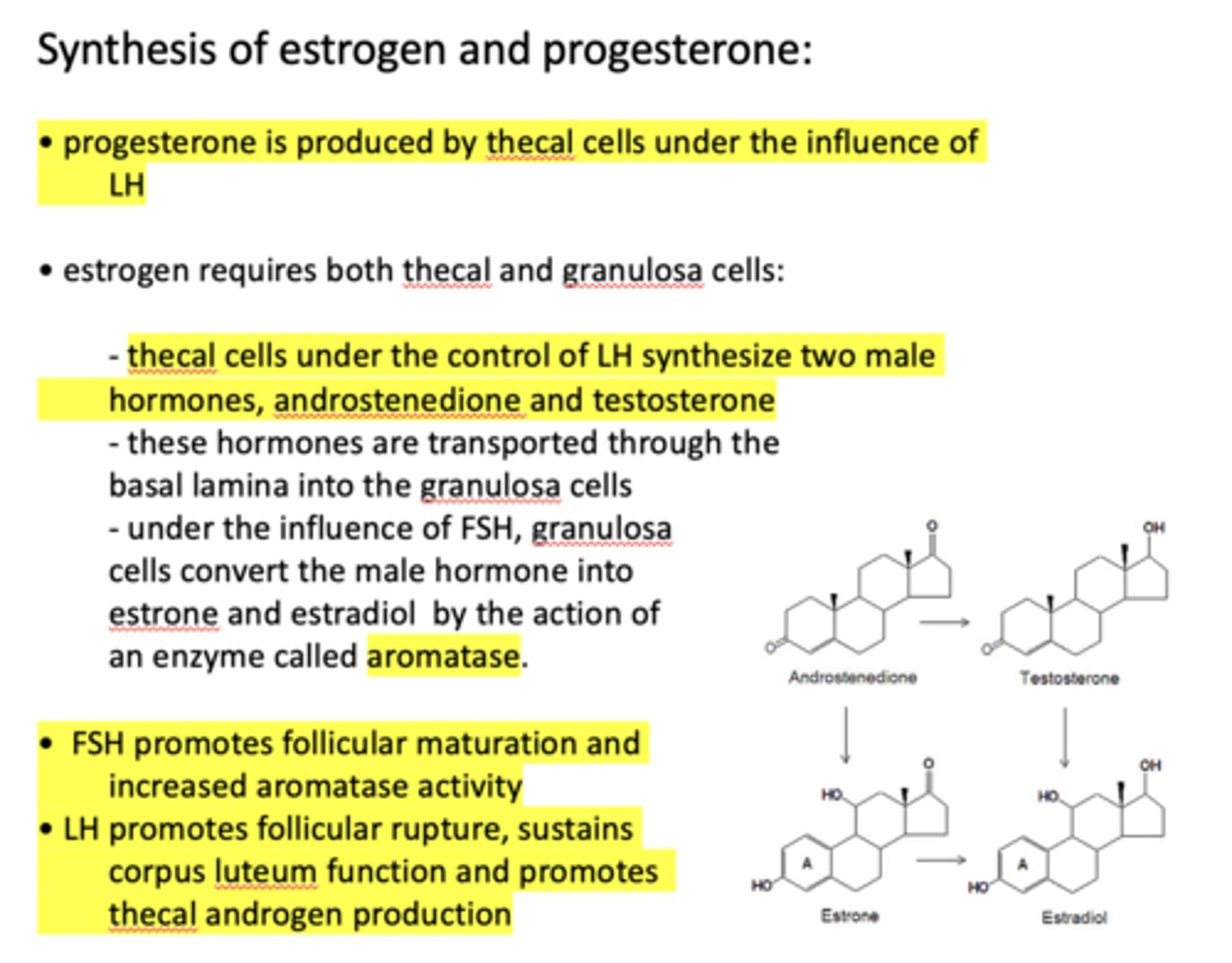
thecal cells under the control of __________ synthesize two male hormones, androstenedione and testosterone
LH
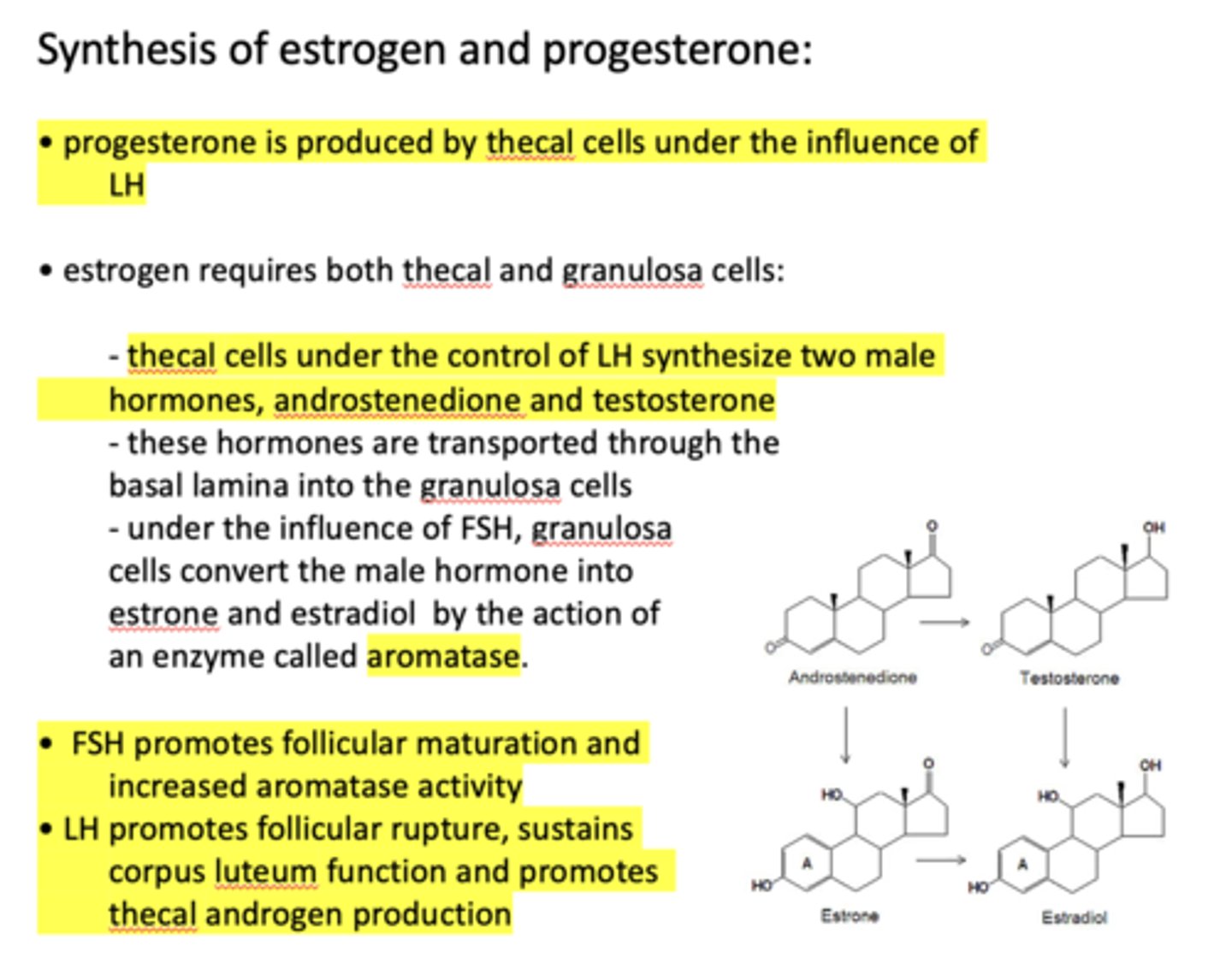
Androstenedione and testosterone are transported through the basal lamina into the ___________
granulosa cells
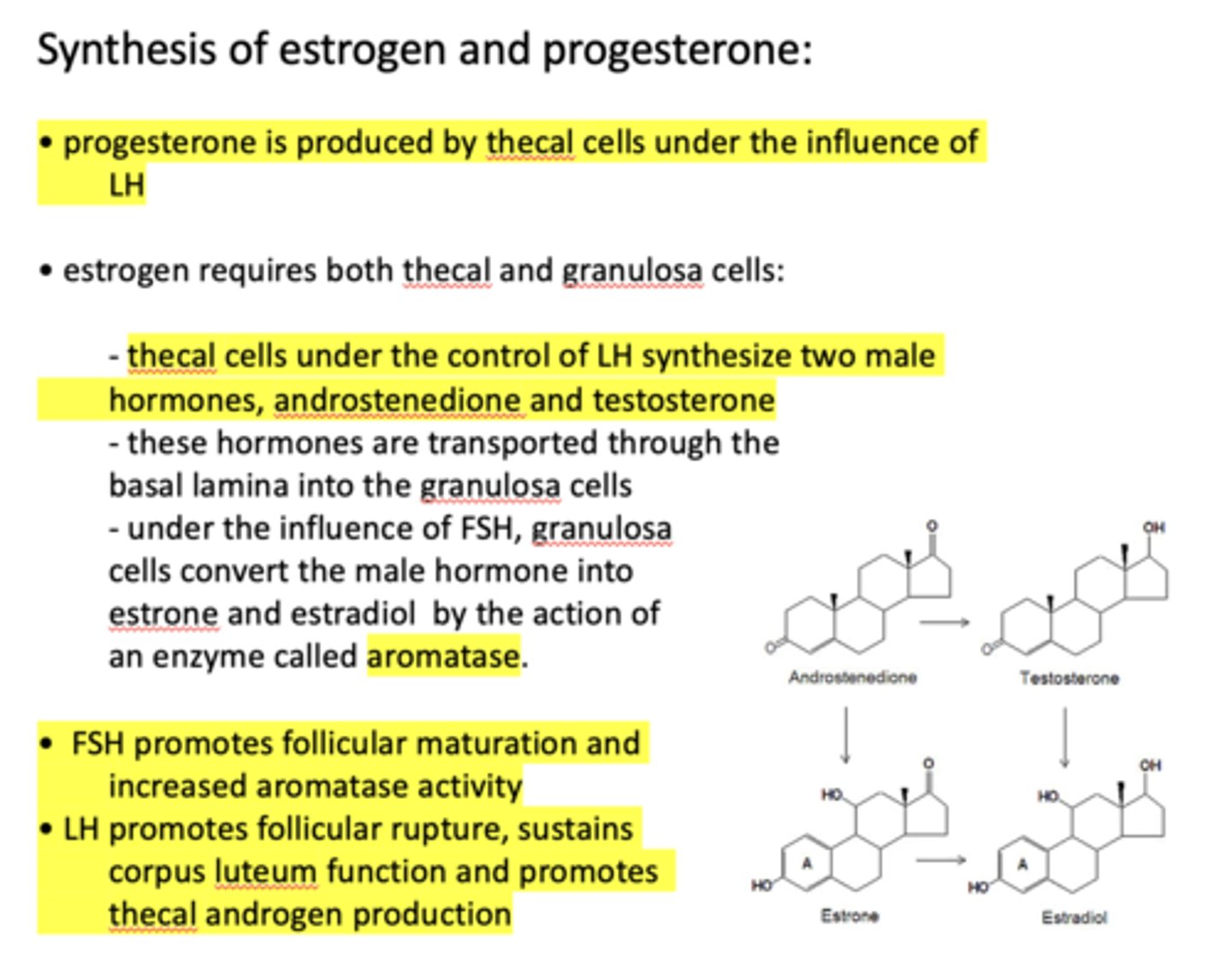
under the influence of _______, granulosa cells convert the male hormone into estrone and estradiol by the action of an enzyme called aromatase
FSH
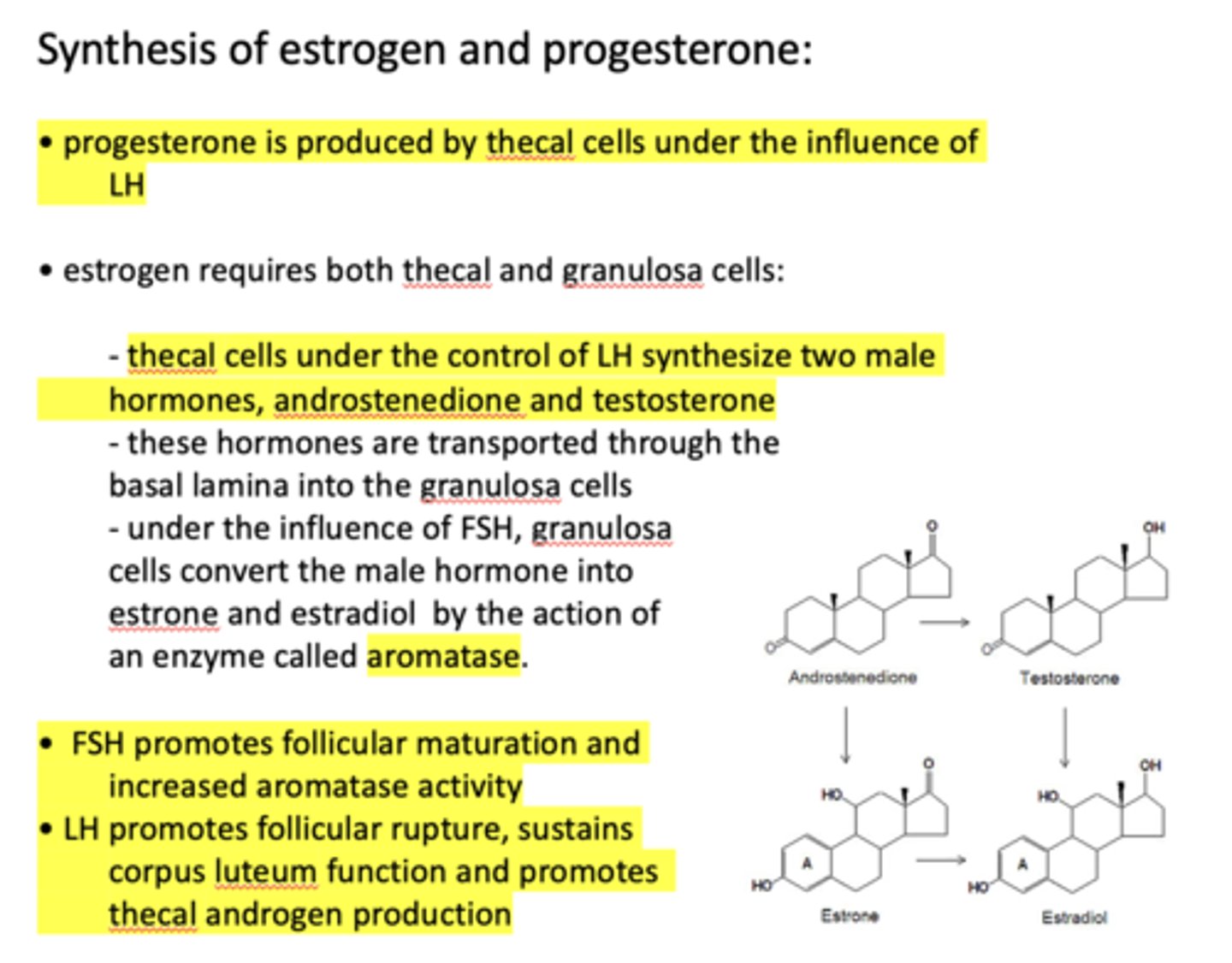
under the influence of FSH, granulosa cells convert the male hormone into estrone and estradiol by the action of an enzyme called ________
aromatase
What hormone promotes follicular maturation and increased aromatase activity?
FSH
What hormone promotes follicular rupture, sustains corpus luteum function and promotes thecal androgen production?
LH
Both estrogen and progesterone act on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to down-regulate _____________ from the former and FSH and LH from the latter
GnRH
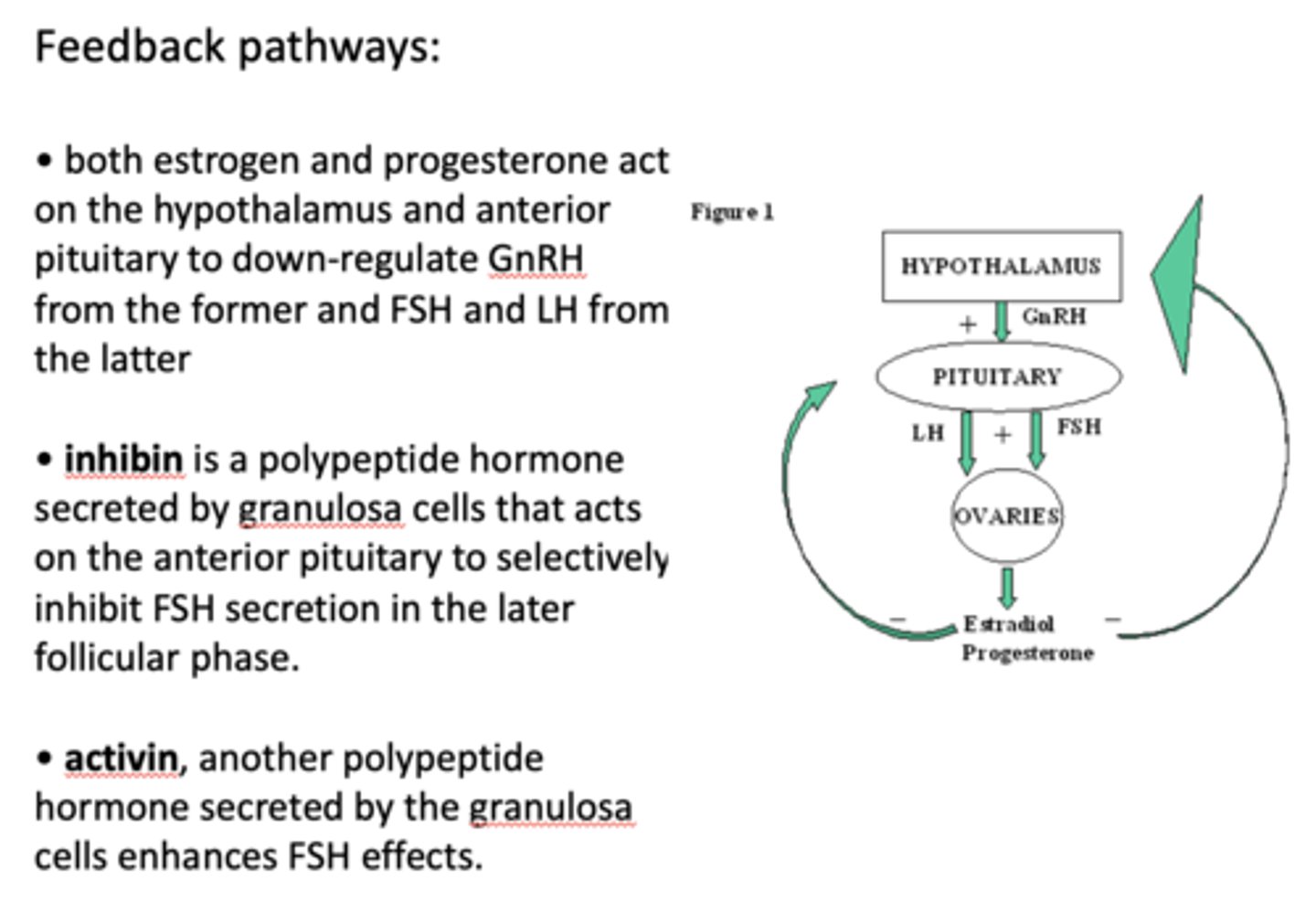
an increase in estrogen will exert a negative feedback on the hypothalamus secretion of GnRH and anterior pituitary secretion of ____________
FSH
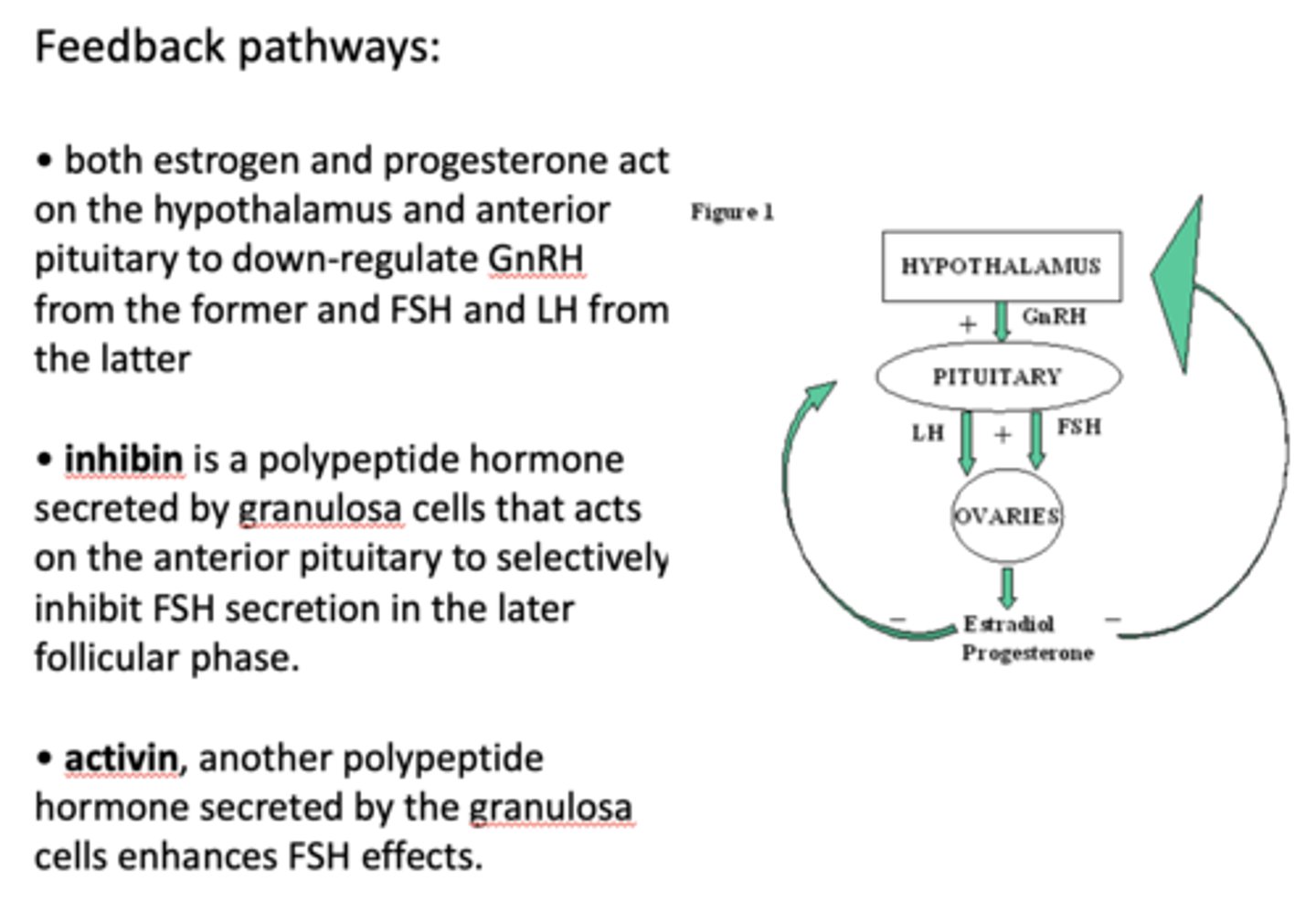
an increase in progesterone will exert a negative feedback on the hypothalamus secretion of GnRH and anterior pituitary secretion of ____________
LH
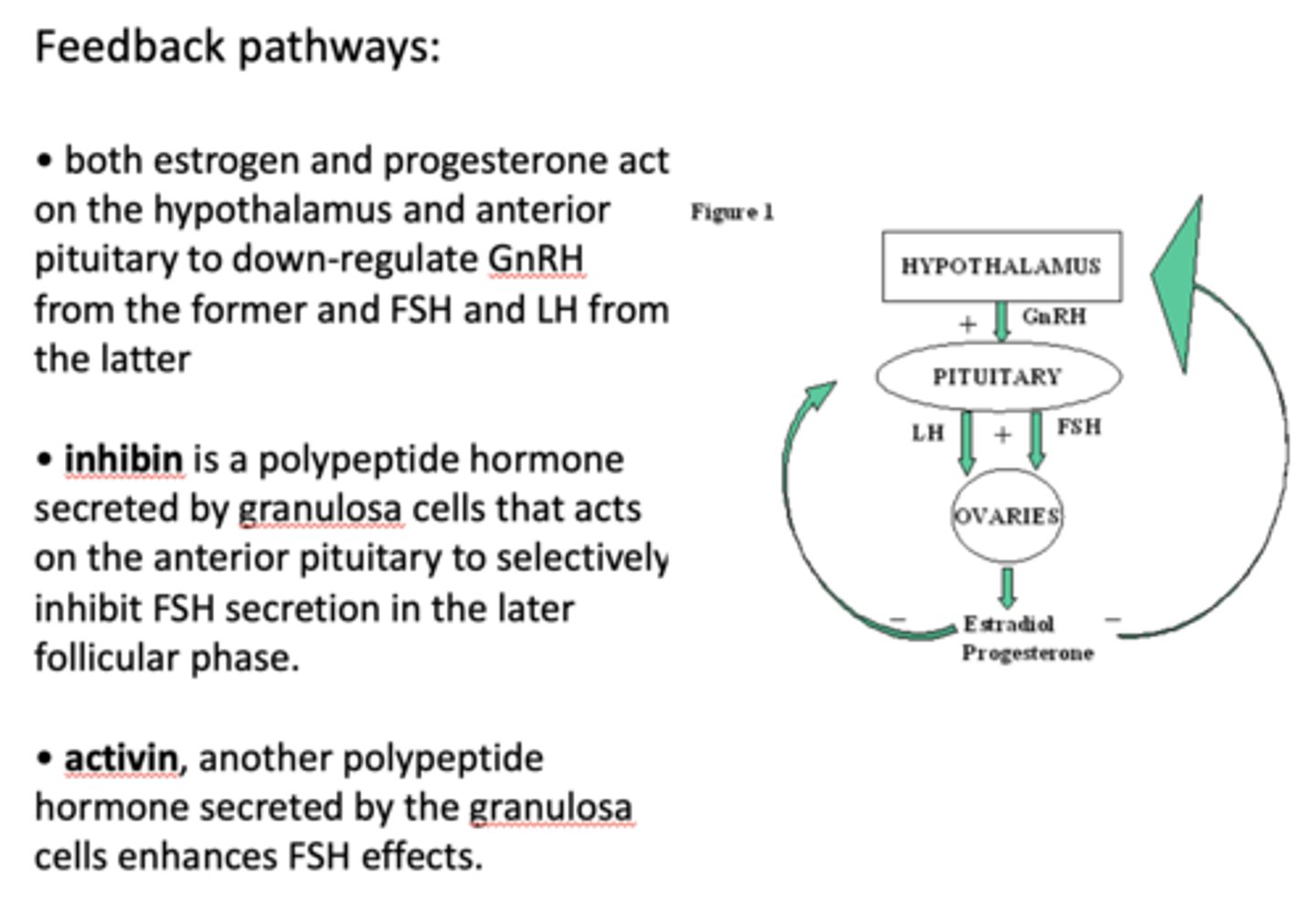
__________ is a polypeptide hormone secreted by granulosa cells that acts on the anterior pituitary to selectively inhibit FSH secretion in the later follicular phase
inhibin
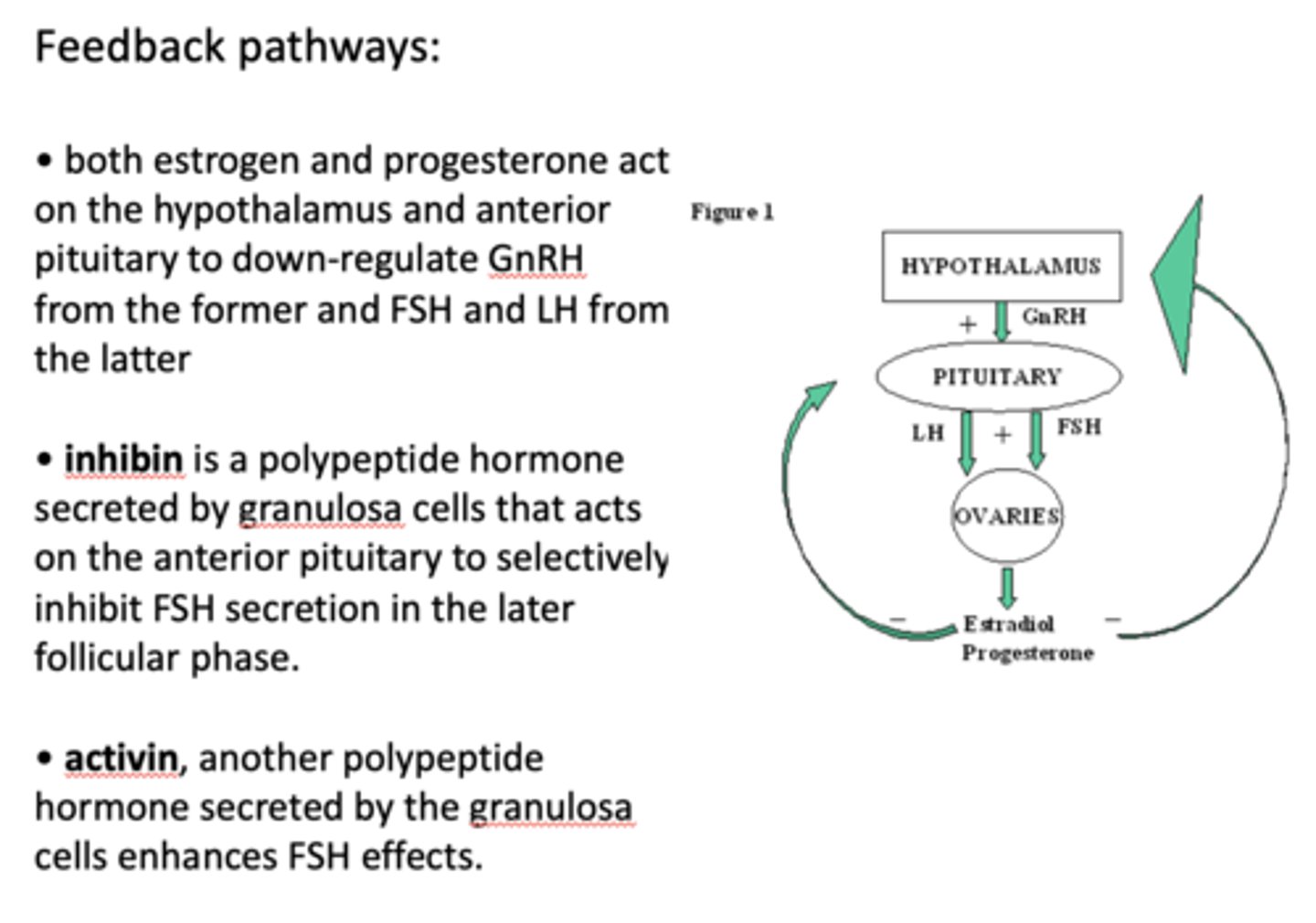
What is another polypeptide hormone secreted by the granulosa cells that enhances FSH effects?
activin
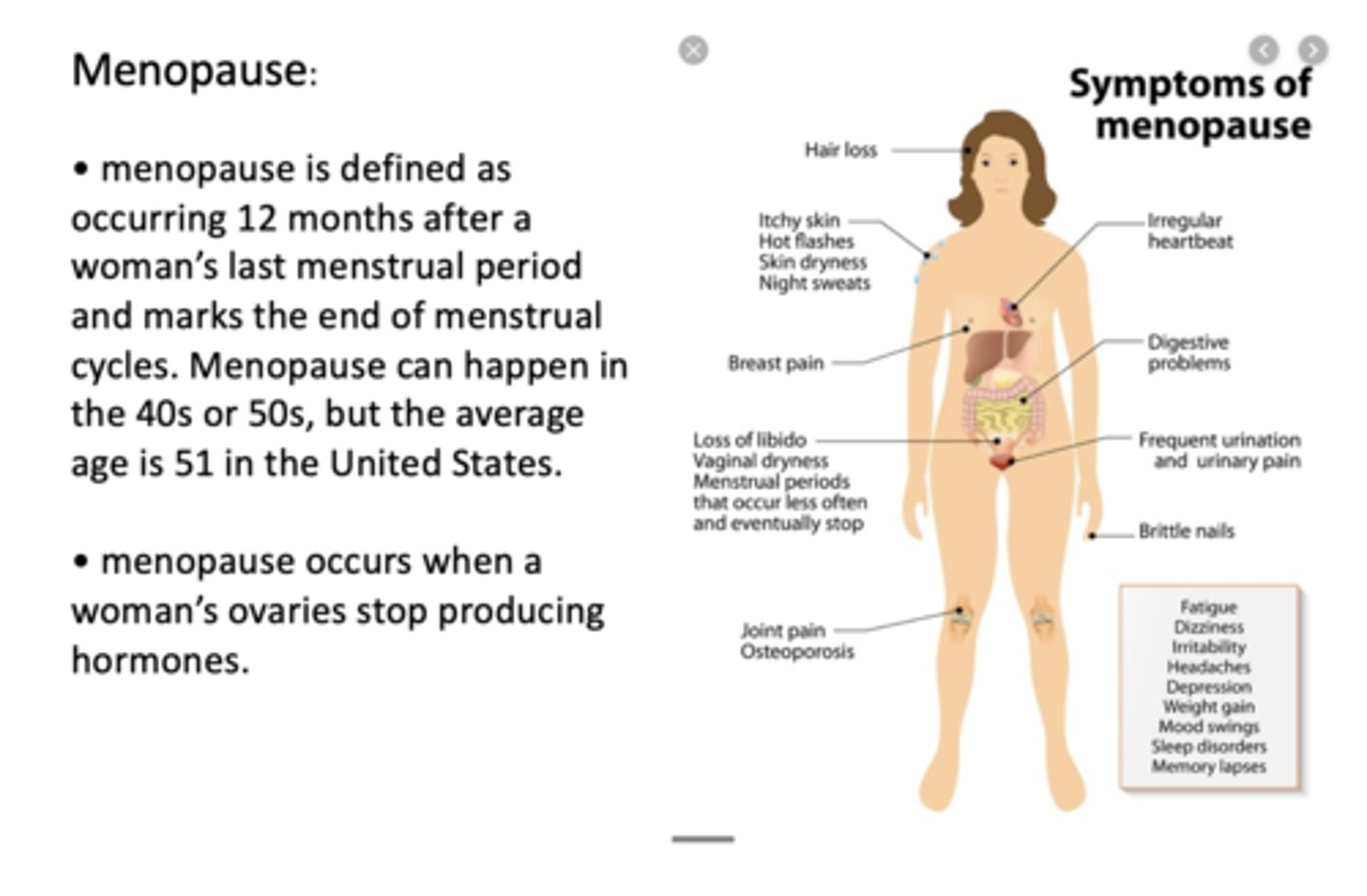
menopause is defined as occurring _________ months after a woman's last menstrual period and marks the end of menstrual cycles. Menopause occurs when a woman's ovaries stop producing hormones
12
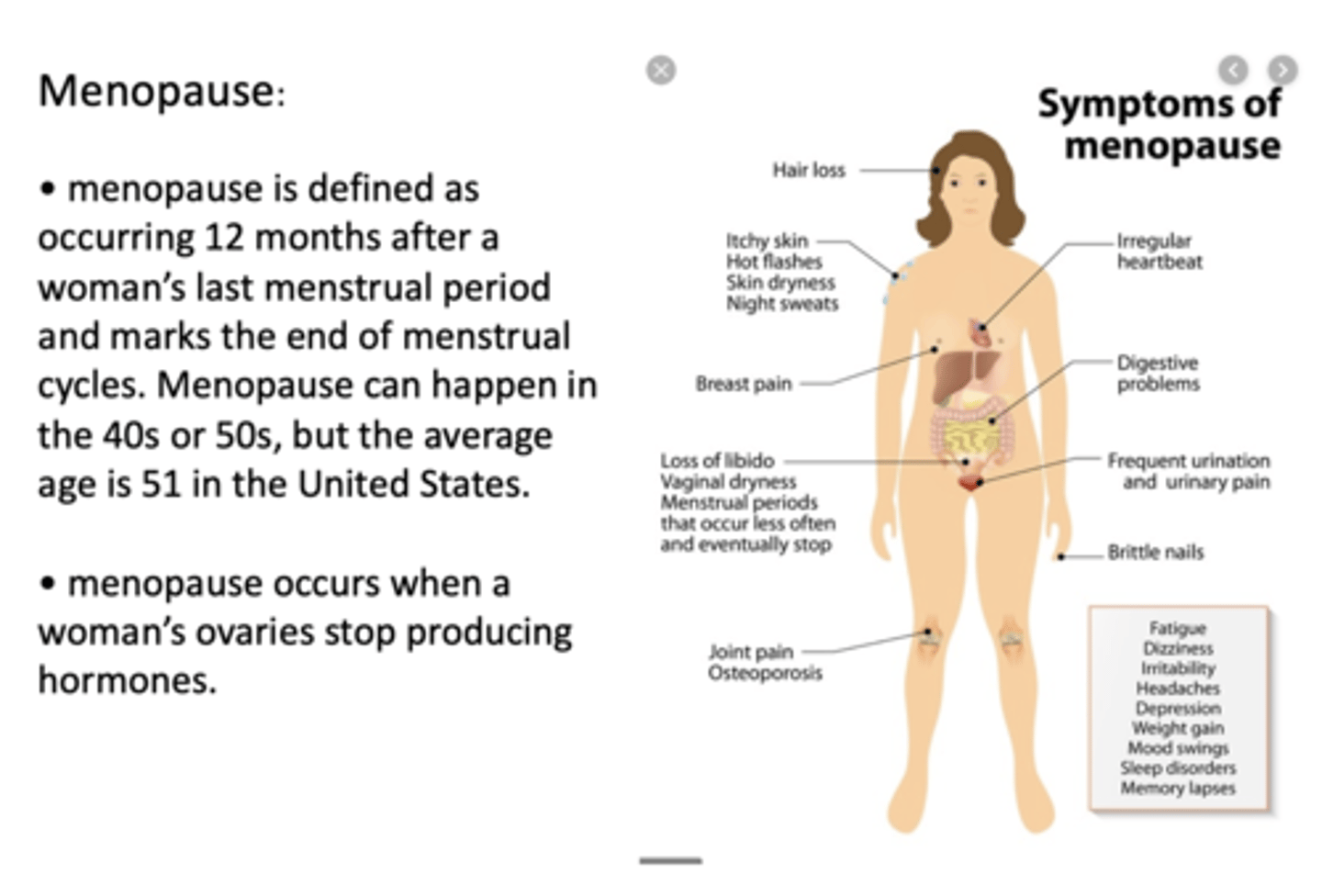
the average age of menopause in the US is ___
51
What is the approximate size of the uterus?
Fist-sized
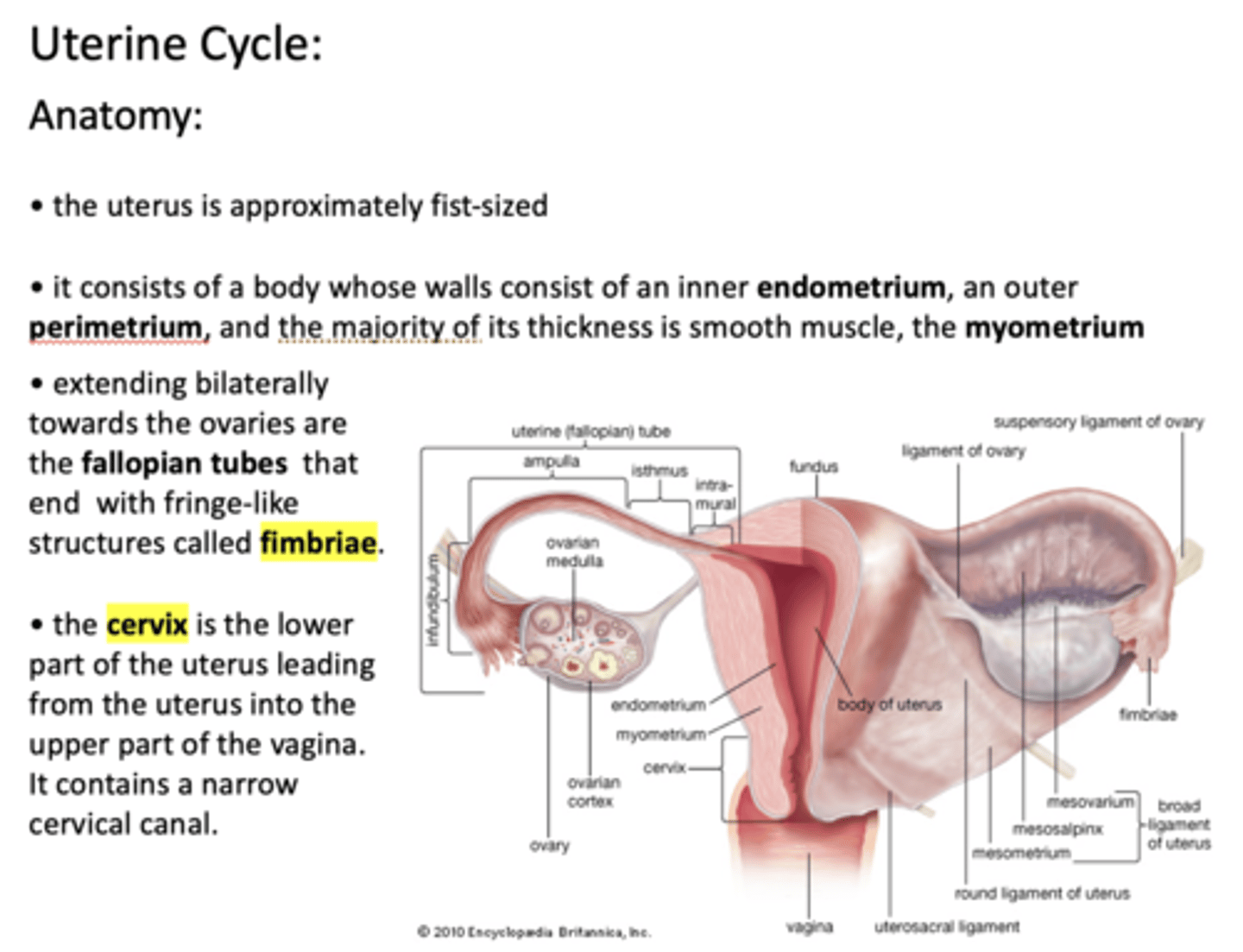
The uterus consists of a body whose walls consist of an inner _____________, an outer _____________, and the majority of its thickness is smooth muscle, the _____________
endometrium, perimetrium, myometrium
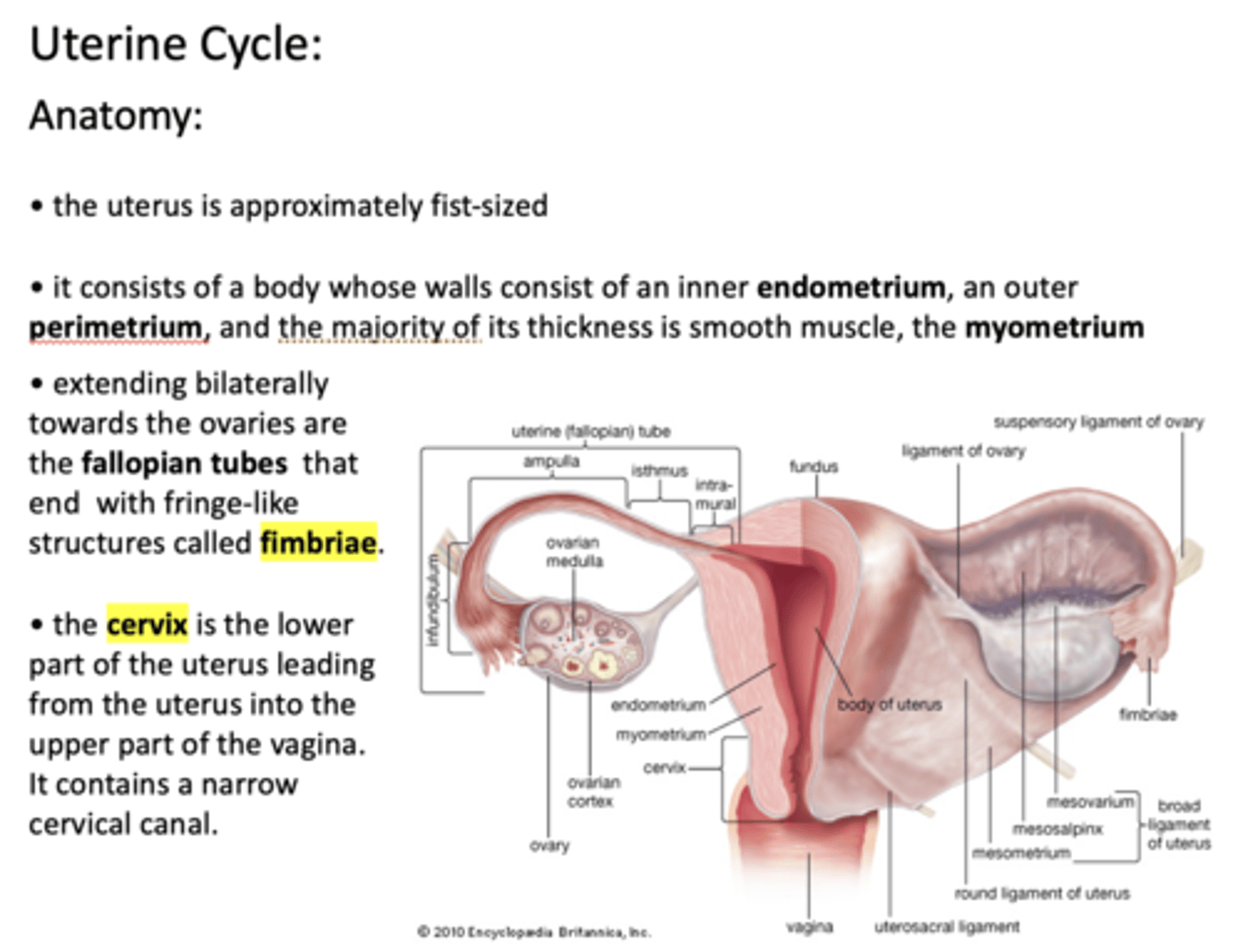
extending bilaterally from the uterus towards the ovaries are the _____________ that end with fringe-like structures called _____________
Fallopian tubes, fimbriae
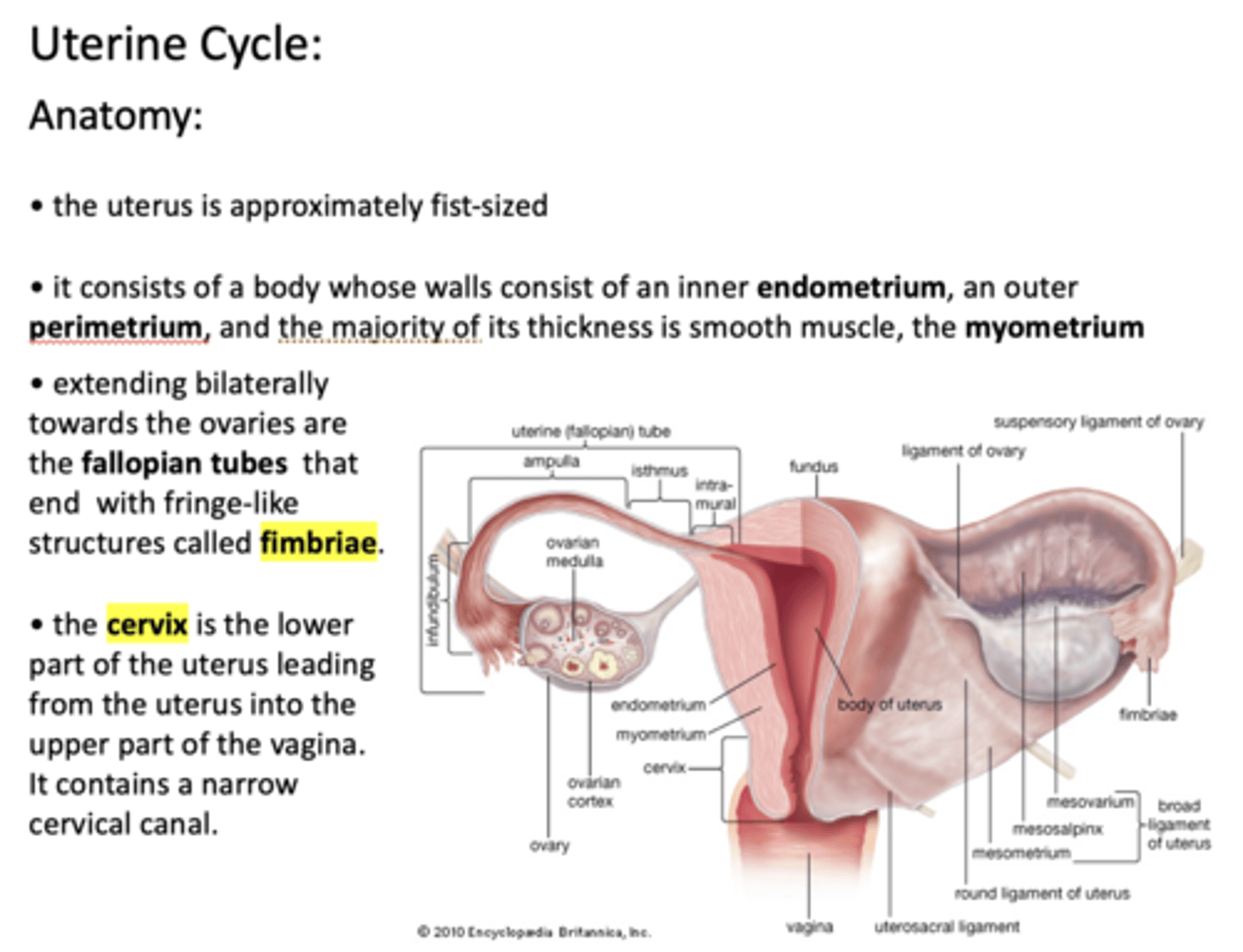
The _____________ is the lower part of the uterus leading from the uterus into the upper part of the vagina. It contains a narrow cervical canal
Cervix
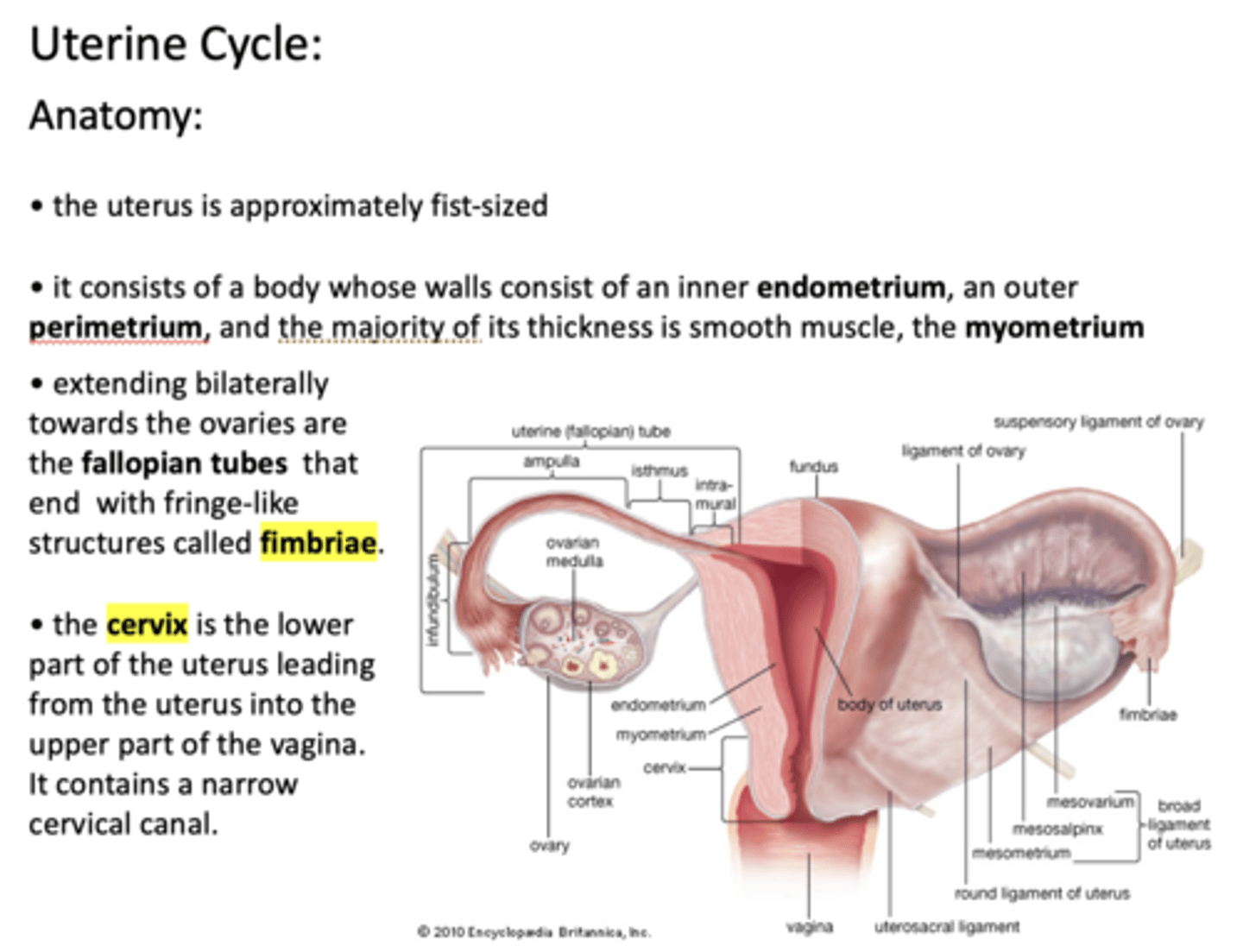
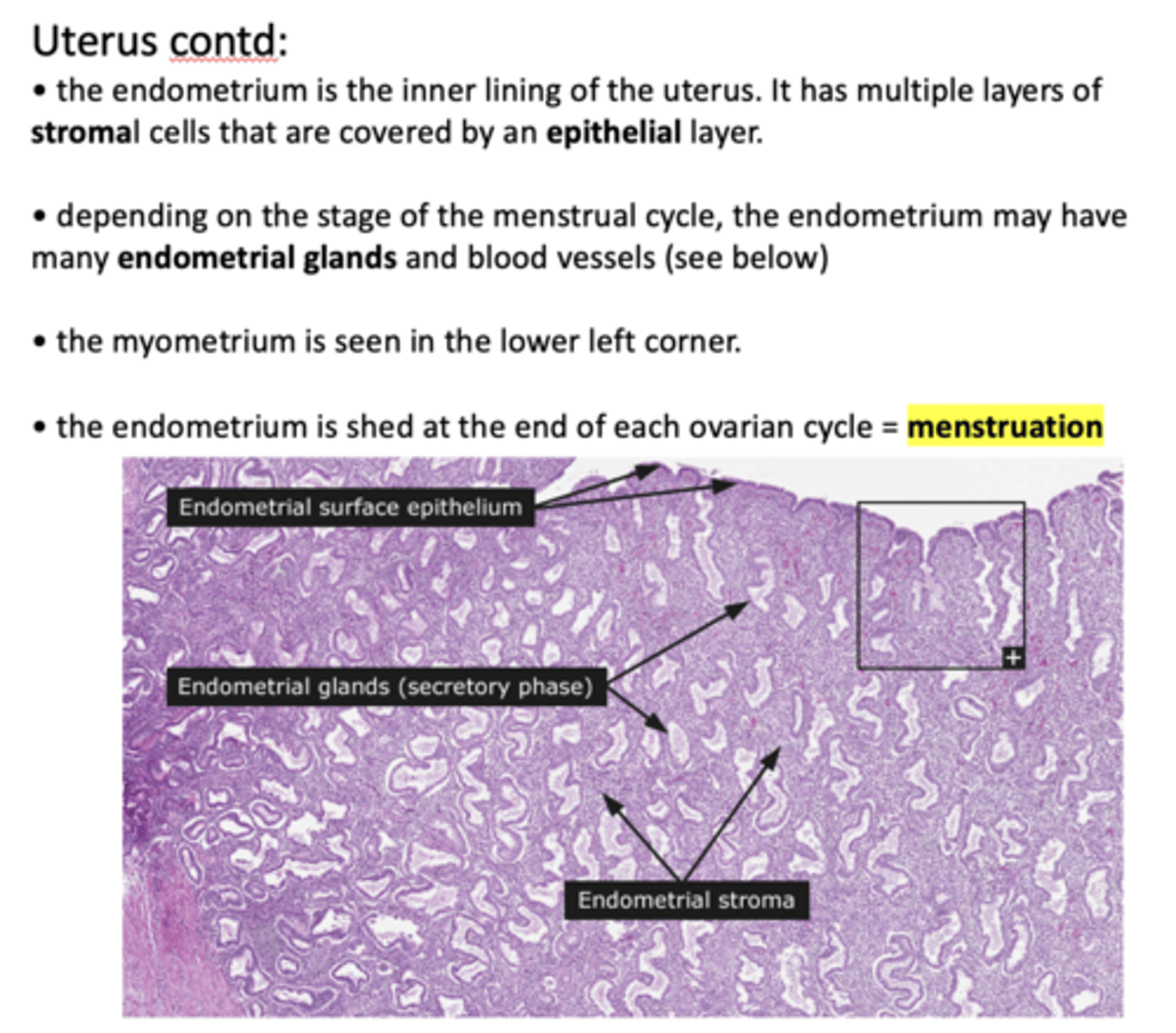
the endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. It has multiple layers of ______ cells that are covered by an epithelial layer.
stromal
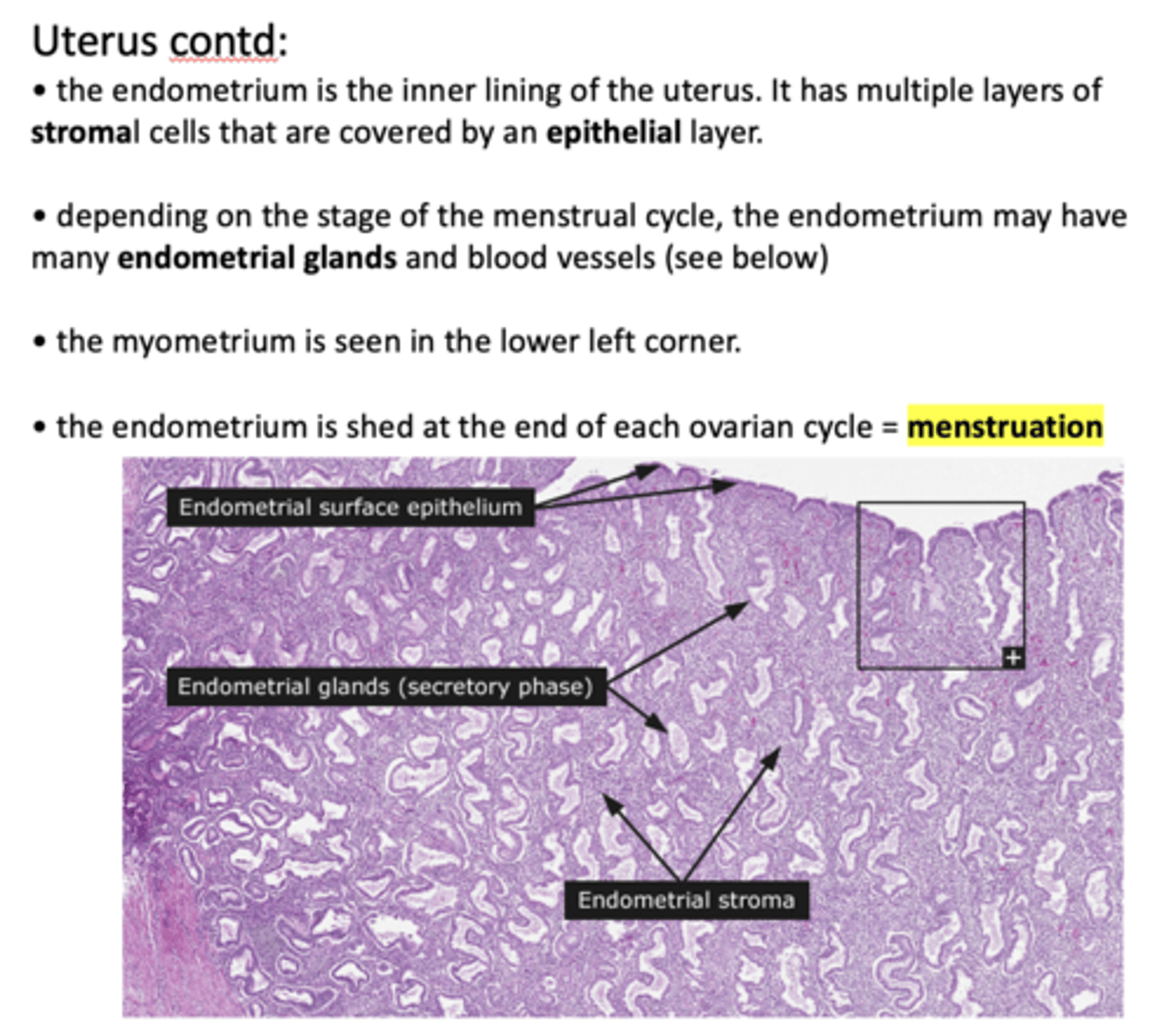
Depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle, the endometrium may have many _____________ and blood vessels
endometrial glands
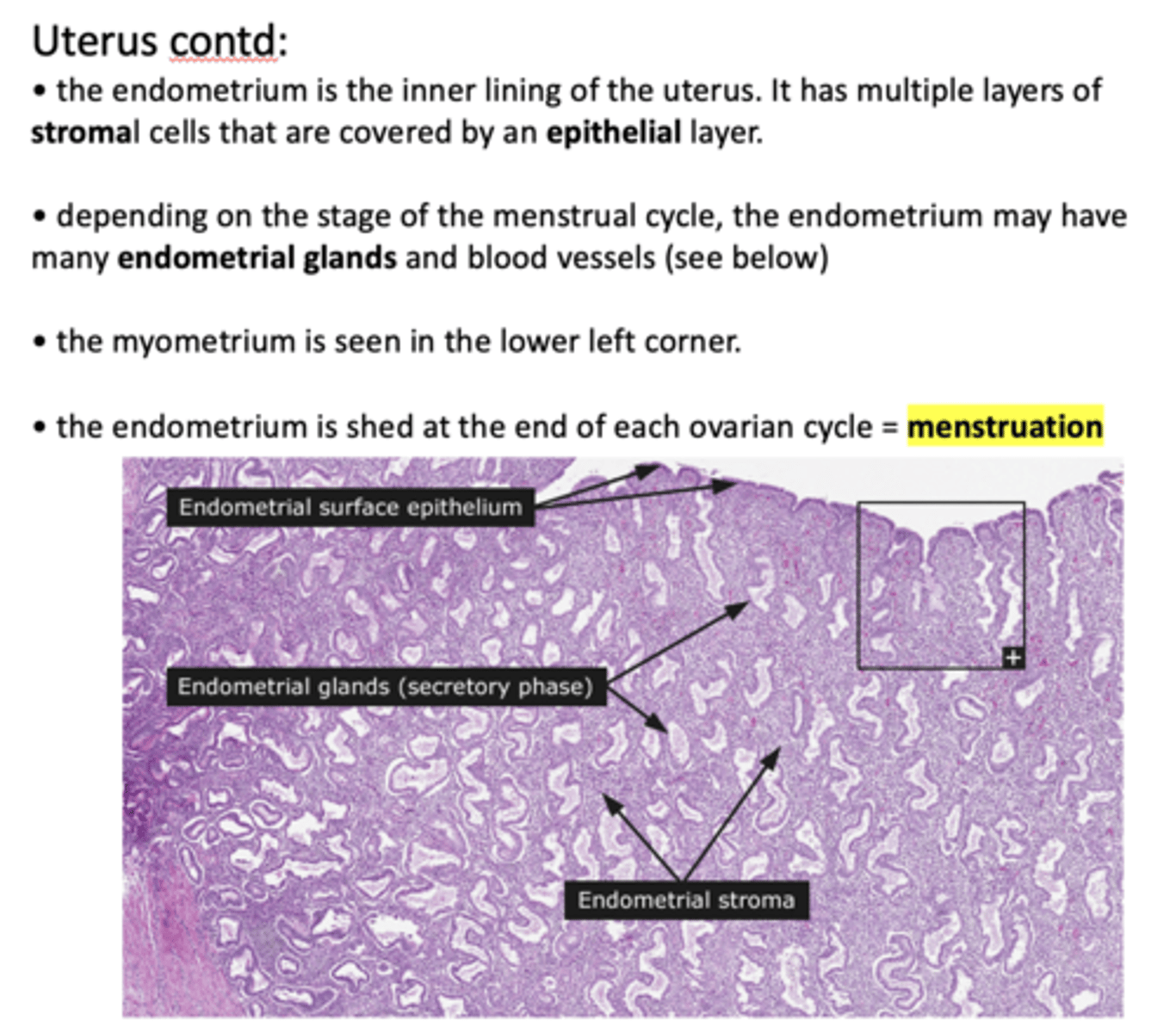
when the endometrium lining is shed at the end of each ovarian cycle, which is known as _____________
menstruation
the secretory phase of the uterus' mensuration cycle matches up with the ______________ phase in the ovaries
luteal phase
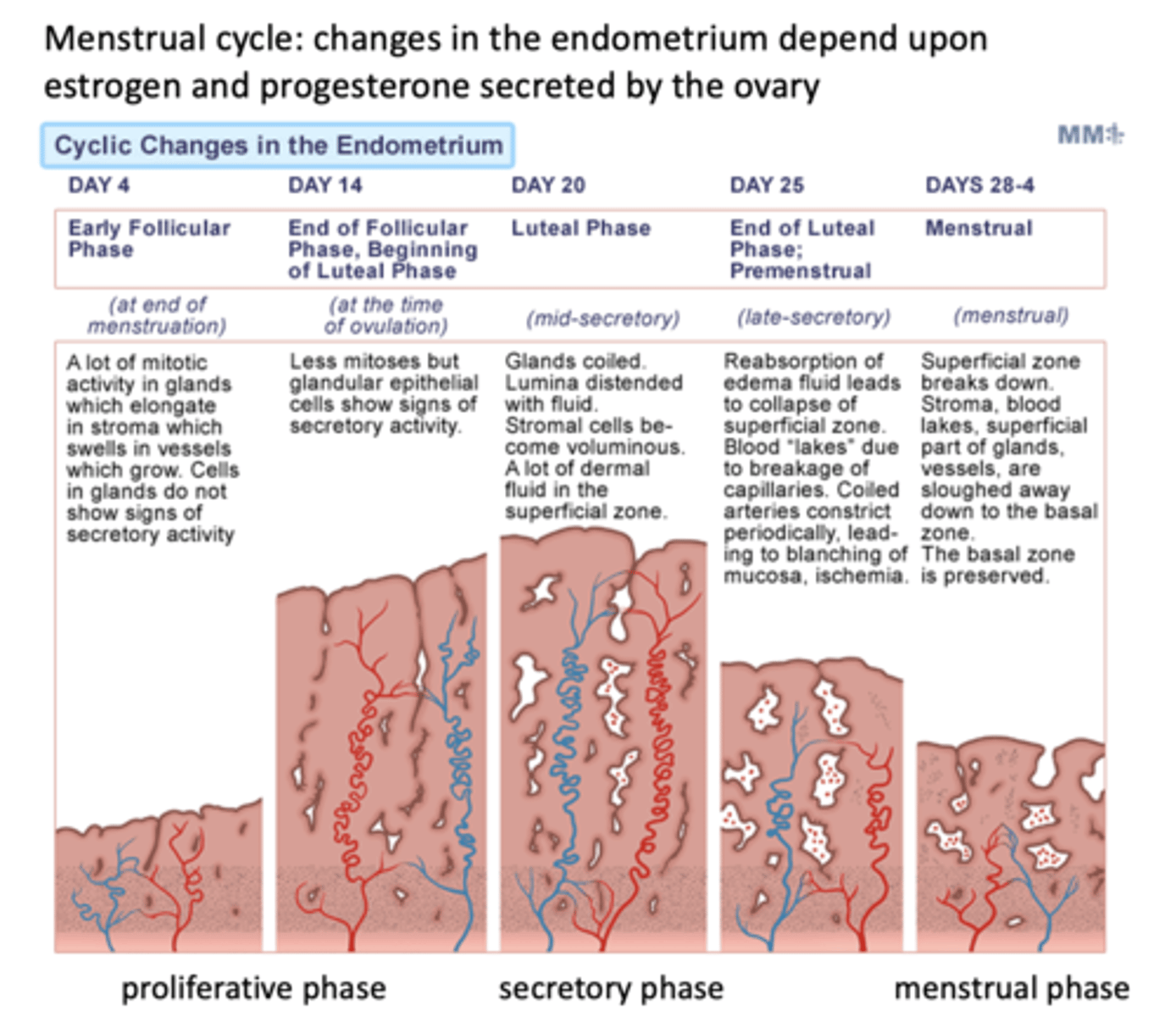
the proliferative phase of the uterus' mensuration cycle matches up with the ______________ phase in the ovaries
follicular phase
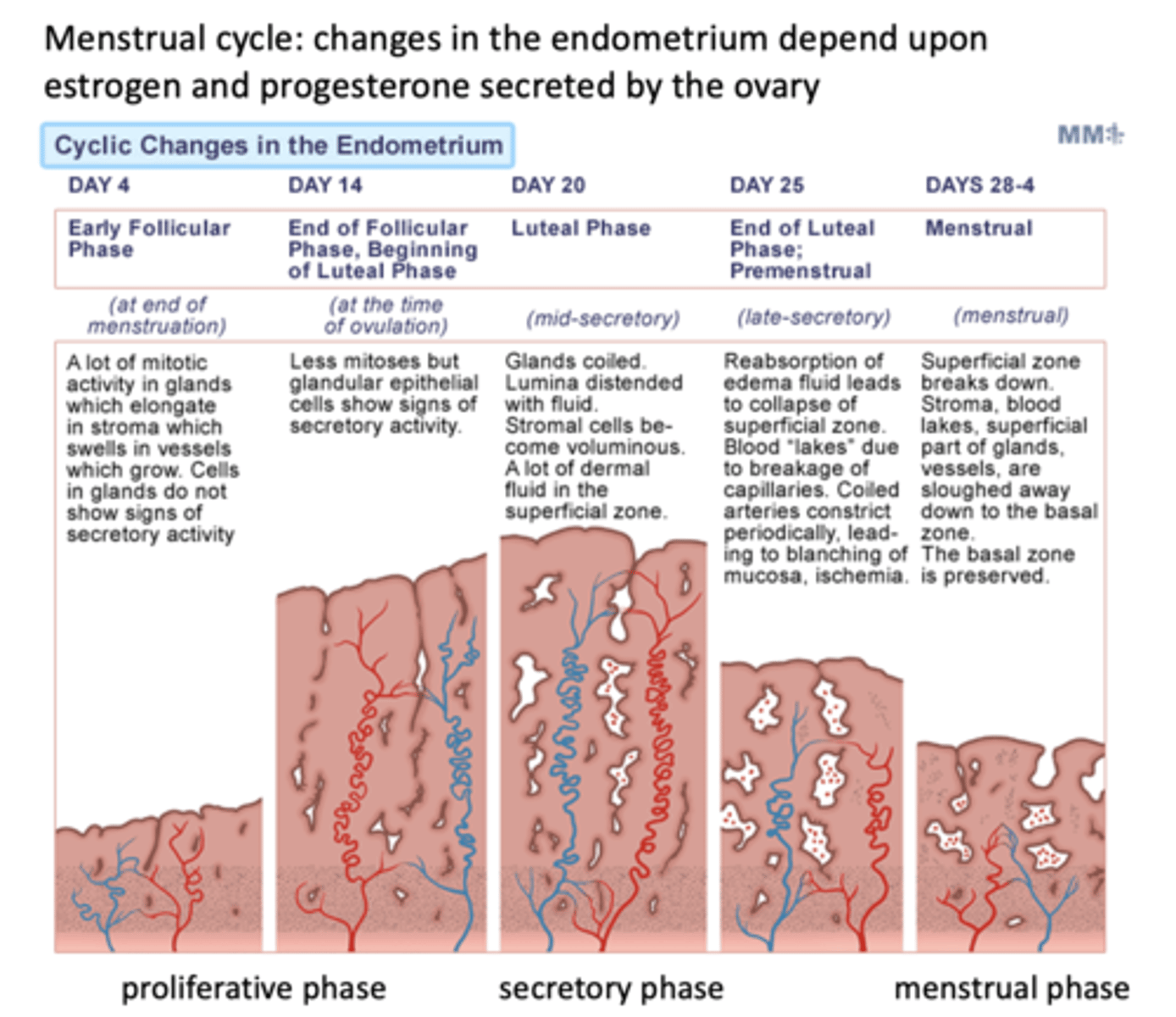
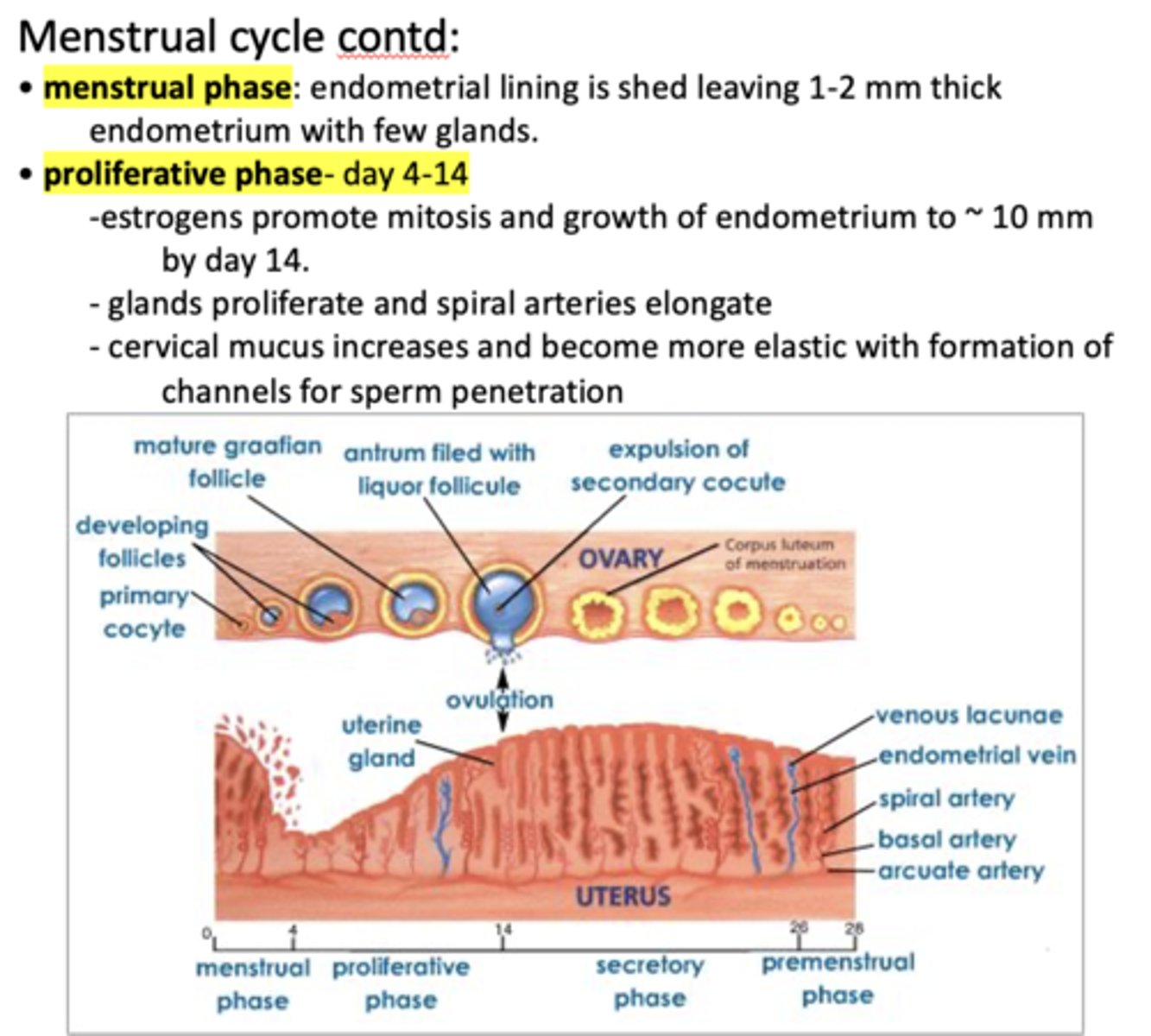
Which phase is the following:
Endometrial lining is shed leaving 1-2 mm thick endometrium with few glands
Menstrual phase
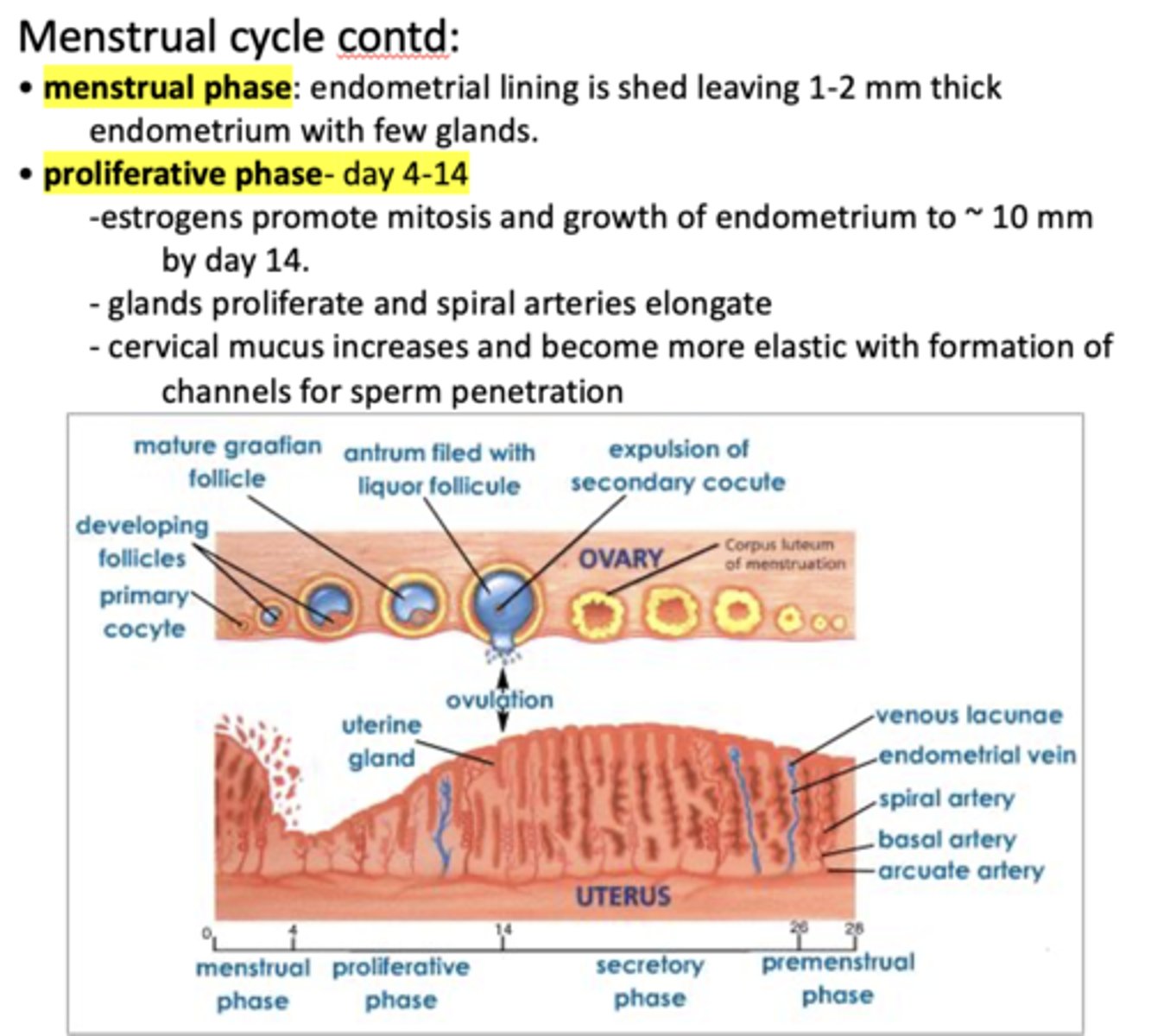
Which phase is the following:
- Day 4-14
- Estrogens promote mitosis and growth of endometrium to ~ 10 mm by day 14.
- Glands proliferate and spiral arteries elongate
- Cervical mucus increases and become more elastic with formation of channels for sperm penetration
Proliferative phase
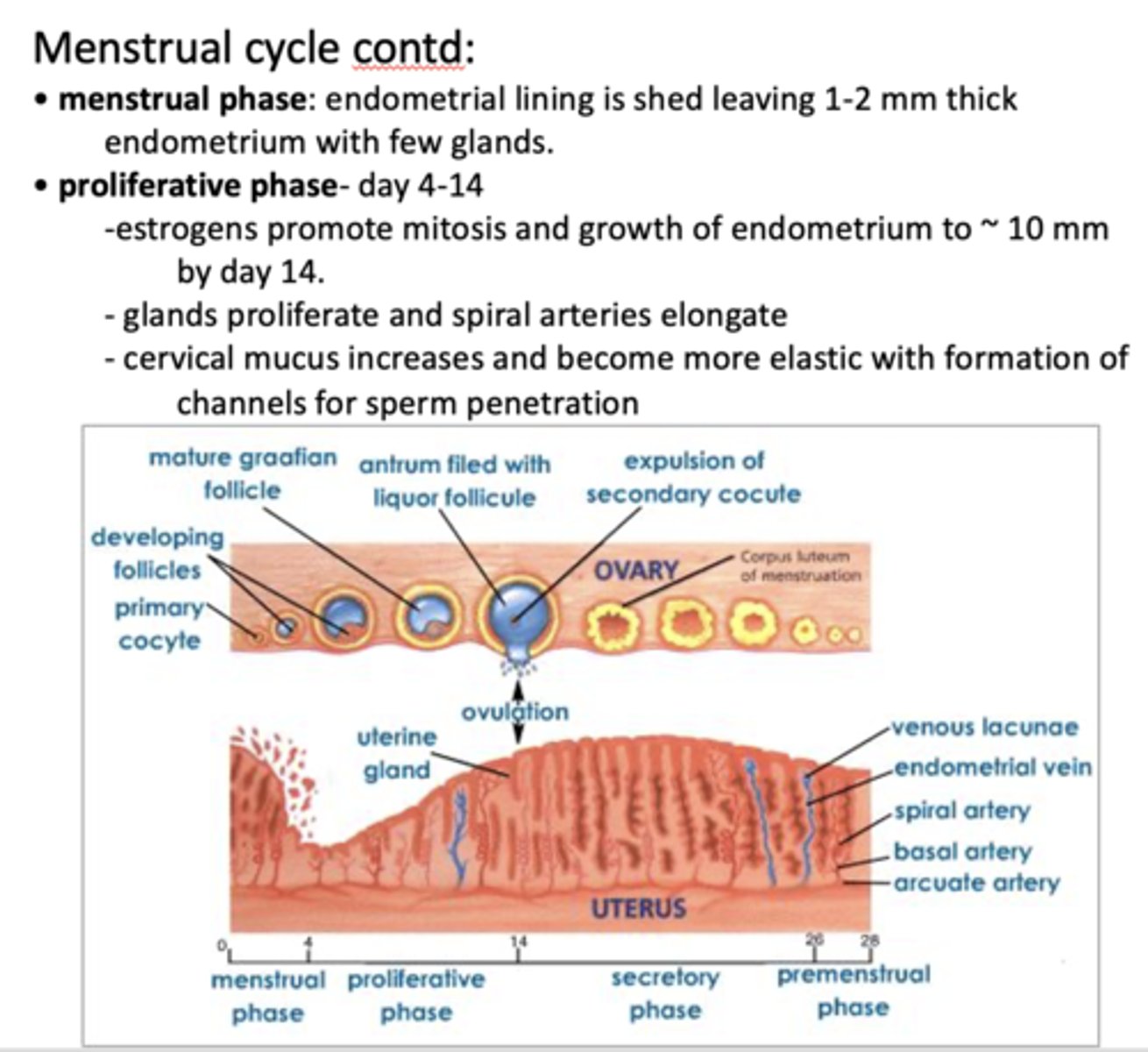
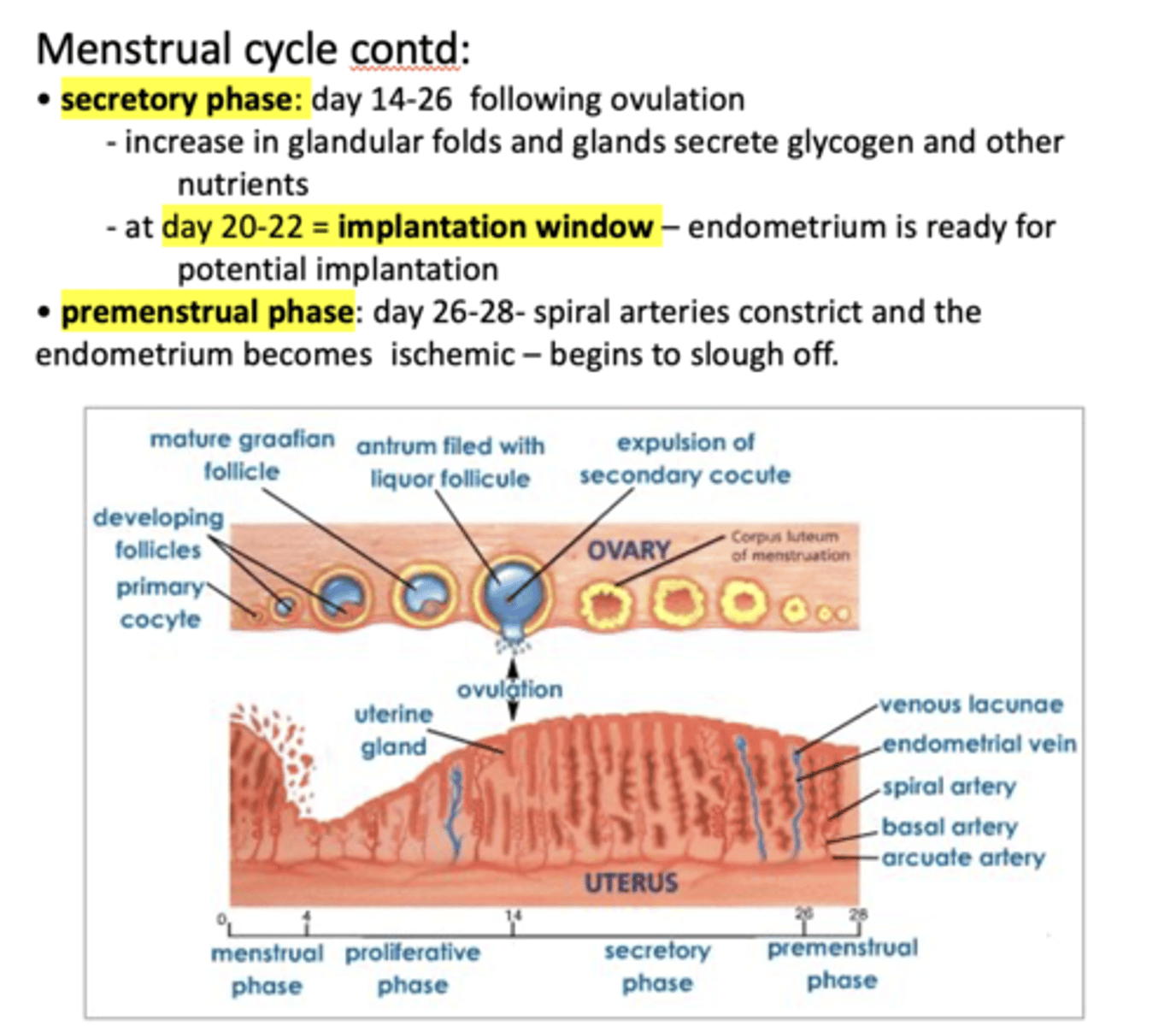
Which phase is the following:
- Day 14-26 following ovulation
- Increase in glandular folds and glands secrete glycogen and other nutrients
- At day 20-22 = implantation window – endometrium is ready for potential implantation
Secretory phase
at day 20-22, endometrium is ready for potential implantation which is known as the ...
Implantation window
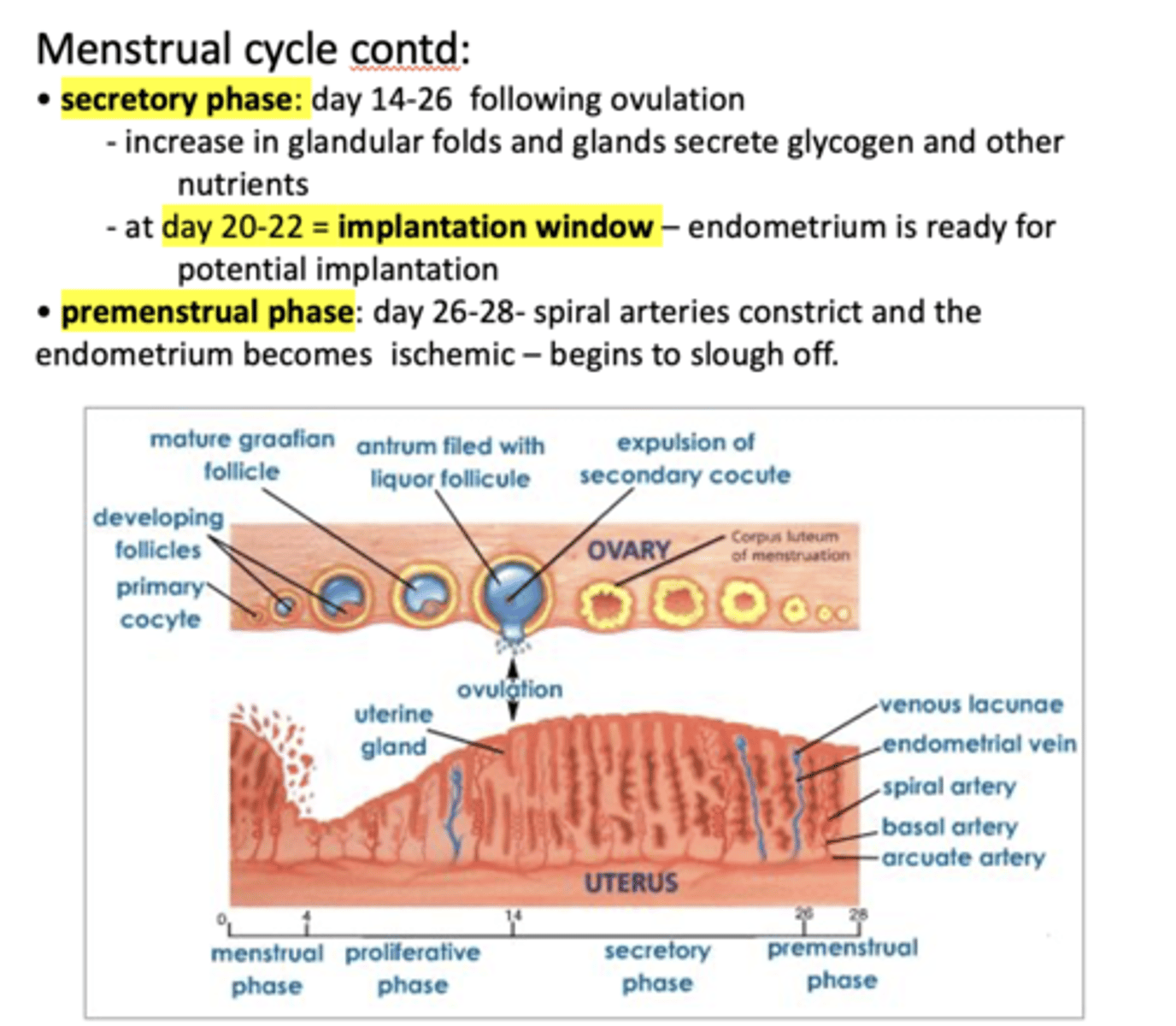
about what day in the 28 day mensural cycle is the implantation window?
20-22
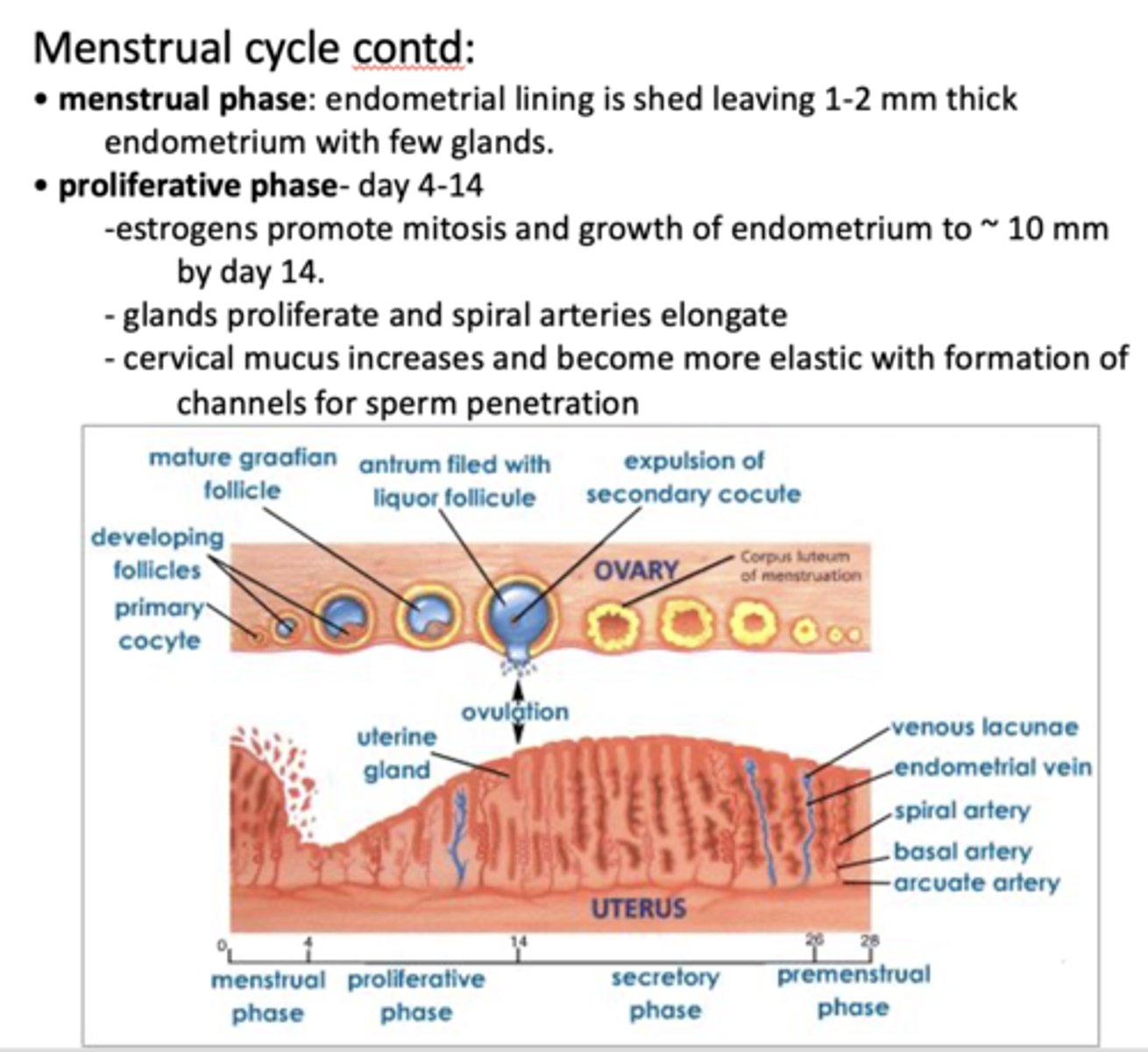
Which phase is the following:
- Day 26-28
- Spiral arteries constrict and the endometrium becomes ischemic - begins to slough off
premenstrual phase
What has the following characteristics:
- The epithelial lining of the tube contains cilia that beat toward the uterus- number and rate of cilia beating is increased by increased estrogens in late follicular phase- can propel fertilized oocyte (zygote) into tube.
- Estrogens increase mucus secretions that provide nutrients to the descending zygote
- At ovulation, tubal contractions and more secretions occur
Fallopian tube

What has the following characteristics:
They increase the thickness of the vaginal lining and induce secretions during follicular phase
steroid hormones on Vagina

What has the following characteristics:
Development at puberty dependent on estrogen- estrogen increases ductile elements and adipose tissue in breast
Breasts
