Bio Exam ch 1-5
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Which of the following is NOT related to the five fundamental characteristics of life?
A) A bacterial cell divides to produce two cells.
B) Sugars are transported on carrier proteins into cells across the plasma membrane.
C) Sugars are broken down inside cells to produce energy.
D) The gene that specifies skin color in frogs is expressed during its development from a tadpole into an adult frog.
E) Giraffes have longer necks so that they can reach food sources unavailable to other animals.
Giraffes have longer necks so that they can reach food sources unavailable to other animals
Pasteur's experiments proved that ________.
A) cells cannot survive in swan-necked flasks
B) in order to grow, cells need to be supplied with oxygen
C) spontaneous generation can only occur if nutrient broth is left open to the environment
D) sterilizing nutrient broth prevents spontaneous generation
E) preexisting cells present in the air can grow in sterilized nutrient broth
preexisting cells present in the air can grow in sterilized nutrient broth
Recall Pasteur's experiment on spontaneous generation. If he had just warmed the nutrient-rich broth, rather than boiled it, what would have been the likely outcome of his experiment? Cells would ________.
A) not have appeared in either flask
B) have appeared in both flasks
C) have appeared in the swan-neck but not the straight-neck flask
D) have appeared in the straight-neck but not the swan-neck flask
have appeared in both flasks
Spontaneous generation ________.
A) was demonstrated to occur under normal laboratory conditions by Pasteur
B) apparently occurred at least once–when life on Earth began
C) occurs every time a new species evolves from a preexisting species
D) addresses the formation of new cells from existing cells
apparently occurred at least once–when life on Earth began
Algae in the genus Caulerpa typically grow to a length of over half a meter and have structures similar to stems, leaves, and roots. Reproduction occurs when adults produce sperm and eggs that fuse to form offspring. Each adult Caulerpa consists of just a single cell, however. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Caulerpa violate the pattern component of the cell theory that all organisms consist of cells.
B) Caulerpa violate the process component of the cell theory that all cells come from preexisting cells.
C) Caulerpa violate both the pattern and process components of the cell theory.
D) The existence of Caulerpa is consistent with the cell theory.
The existence of Caulerpa is consistent with the cell theory.
Cells are ________.
A) only found in pairs, because single cells cannot exist independently
B) limited in size to 200 and 500 micrometers in diameter
C) characteristic of eukaryotic but not prokaryotic organisms
D) characteristic of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
characteristic of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
In comparison to eukaryotes, prokaryotes ________.
A) are more structurally complex
B) use RNA to store genetic information
C) are smaller
D) do not have membranes
E) have chromosomes composed of single-stranded DNA
are smaller
The structure of double helical DNA ________.
A) serves as a template for protein synthesis
B) is used to synthesize messenger RNA
C) contains two identical single strands of DNA
D) must be accurately copied to ensure variation in organisms
is used to synthesize messenger RNA
Which of these provides evidence of the common ancestry of all life?
A) ubiquitous use of catalysts by living systems
B) near universality of the genetic code
C) structure of the nucleus
D) the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein
E) the directionality of protein synthesis
near universality of the genetic code
Protists and bacteria are grouped into different domains because ________.
A) protists eat bacteria
B) bacteria are not made of cells
C) protists have a membrane-bounded nucleus, which bacterial cells lack
D) bacteria decompose protists
E) protists lack the genetic diversity that bacteria have
protists have a membrane-bounded nucleus, which bacterial cells lack
You have isolated and purified a new species of cells from the rain forest and you want to place this new species in the appropriate branch of the tree of life. You sequence the ribosomal RNA genes from these cells and discover that for one particular region of the ribosomal gene (the rRNA) the RNA sequence is AAUGAAGG. You have sequences from the same region of the ribosomal genes (the rRNA) from each of these species: bacteria, eukaryote and archaea, which are listed below.
bacteria AUAGAUGG
eukaryote AAAGAAGG
archaea AAUGGAGU
Based on these sequence results, to which branch of the tree of life should you assign this new species?
A) archaea
B) bacteria
C) eukaryote
D) bacteria and archaea
E) There is not enough information
eukaryote
Louis Pasteur's experiment had a good design because ________.
A) simple equipment was used
B) a major question, spontaneous generation, was tested
C) the possible outcomes led to distinct, unambiguous conclusions
D) the experiment was a success
the possible outcomes led to distinct, unambiguous conclusions
A friend of yours calls to say that his car would not start this morning. He asks for your help. You say that you think the battery must be dead. If so, then jump-starting the car from a good battery will solve the problem. In doing so, you are ________.
A) testing a theory for why the car will not start
B) making observations to inspire a theory for why the car will not start
C) stating a hypothesis and using that hypothesis to make a testable prediction
D) comparing multiple hypotheses for why the car will not start
stating a hypothesis and using that hypothesis to make a testable prediction
Agrobacterium infects plants and causes them to form tumors. You are asked to determine how long a plant must be exposed to these bacteria to become infected. Which of the following experiments will provide the best data to address that question?
A) Measure the number of tumors formed on plants, which are exposed to different concentrations of Agrobacterium for different lengths of time.
B) Measure the number of tumors formed on a plant when exposed to various concentrations of Agrobacterium.
C) Measure the concentration of Agrobacterium in different soil environments where the plants grow.
D) Measure the number of tumors formed on plants, which are exposed to a known concentration of Agrobacterium for different lengths of time
Measure the number of tumors formed on plants, which are exposed to a known concentration of Agrobacterium for different lengths of time
Agrobacterium infects plants and causes them to form tumors. You determine that tumor formation requires a large amount of the plant's energy for tissue formation. How might this change the number of offspring a plant produces, and what is the most likely explanation for this change?
A) The number of offspring should increase, because in general, illness increases the reproductive output of organisms.
B) The number of offspring should increase, because the bacteria will provide energy for the plant.
C) The number of offspring should decrease, because the plant will divert energy from reproduction to tumor formation.
D) There should be no effect of infection on offspring production, because energy for reproduction is independent of infection
The number of offspring should decrease, because the plant will divert energy from reproduction to tumor formation.
In 1668, Francesco Redi performed a series of experiments on spontaneous generation. He began by putting similar pieces of meat into eight identical jars. Four jars were left open to the air, and four were sealed. He then did the same experiment with one variation: Instead of sealing four of the jars completely, he covered them with gauze (the gauze excluded the flies while allowing the meat to be exposed to air). In both experiments, he monitored the jars and recorded whether or not maggots (young flies) appeared in the meat.
What hypothesis was being tested in the initial experiment with open versus sealed jars?
A) Spontaneous generation is more likely during the long days of summer.
B) The type of meat used affects the likelihood of spontaneous generation.
C) Maggots do not arise spontaneously, but from eggs laid by adult flies.
D) Spontaneous generation can occur only if meat is exposed to air
Maggots do not arise spontaneously, but from eggs laid by adult flies.
In 1668, Francesco Redi performed a series of experiments on spontaneous generation. He began by putting similar pieces of meat into eight identical jars. Four jars were left open to the air, and four were sealed. He then did the same experiment with one variation: Instead of sealing four of the jars completely, he covered them with gauze (the gauze excluded the flies while allowing the meat to be exposed to air). In both experiments, he monitored the jars and recorded whether or not maggots (young flies) appeared in the meat.
In both experiments, flies appeared in all of the open jars and only in the open jars. Which one of the following statements is correct?
A) The experiment was inconclusive because Redi used only one kind of meat.
B) The experiment was inconclusive because it did not run long enough.
C) The experiment supports the hypothesis that spontaneous generation occurs in rotting meat.
D) The experiment supports the hypothesis that maggots arise only from eggs laid by adult flies.
The experiment supports the hypothesis that maggots arise only from eggs laid by adult flies.
In the process of science, which of these is NOT used to test a hypothesis?
A) a theory
B) a result
C) an observation
D) a control group
a theory
In presenting data that result from an experiment, a group of students show that most of their measurements fall on a straight diagonal line on their graph. However, two of their data points are "outliers" and fall far to one side of the expected relationship.
What should they do?
A) Change their experiment so that the outlier data points are eliminated.
B) Average several trials, rule out the improbable results, and do not show them in the final work.
C) Show all results obtained and then try to explore the reason(s) for these outliers.
D) Redesign the experiment using a different hypothesis.
E) Change the values on the graph so that only the straight diagonal line is produced
Show all results obtained and then try to explore the reason(s) for these outliers.
Why is a scientific topic best discussed by people of varying points of view, from different subdisciplines, and representing diverse cultures?
A) They can correct each other's approach to make it scientific.
B) Robust and critical discussion between diverse groups improves scientific thinking.
C) Scientists can coordinate with others to conduct experiments in similar ways.
D) This is a way of ensuring that everyone gets the same results.
E) People need to exchange their ideas with other disciplines and cultures because everyone has a right to an opinion in science
Robust and critical discussion between diverse groups improves scientific thinking.
About twenty-five of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which 4 of these 25 elements make up approximately 96 percent of living matter?
A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen
B) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, nitrogen
D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
E) carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
Why is each element unique with respect to its chemical properties? Each element has a distinctive ________.
A) atomic mass
B) number of electrons
C) number of protons
D) number of neutrons
E) radioactive property
number of protons
Knowing the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about which of the following?
A) the number of electrons in the element
B) the number of protons in the element
C) the number of neutrons in the element
D) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element
E) the number of protons plus electrons in the element
the number of protons plus neutrons in the element
From its atomic number of 15, it is possible to predict that the phosphorus atom has ________.
A) 5 neutrons, 5 protons, and 5 electrons
B) 30 neutrons
C) 15 neutrons and 15 protons
D) 8 electrons in its outermost electron shell
E) 15 protons and 15 electrons
15 protons and 15 electrons
A covalent chemical bond is one in which ________.
A) electrons are removed from one atom and transferred to another atom so that the two atoms become oppositely charged
B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms
C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals
D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another atom
E) electrons from the same atom, but opposite spins, are paired
outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals
Nitrogen (N) is more electronegative than hydrogen (H). Which of the following is a correct statement about the atoms in ammonia (NH3)?
A) Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge; the nitrogen atom has a partial negative charge.
B) Ammonia has an overall positive charge.
C) Ammonia has an overall negative charge.
D) The nitrogen atom has a partial positive charge; each hydrogen atom has a partial negative charge.
E) There are covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms and polar bonds between each hydrogen atom and the nitrogen atom
Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge; the nitrogen atom has a partial negative charge.
Bonds between two atoms that are equally electronegative are ________.
A) hydrogen bonds
B) van der Waals interactions
C) polar covalent bonds
D) nonpolar covalent bonds
E) ionic bonds
nonpolar covalent bonds
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when ________.
A) one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom
B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative
C) carbon is one of the two atoms sharing electrons
D) one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom
E) the two atoms sharing electrons are the same elements
one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom
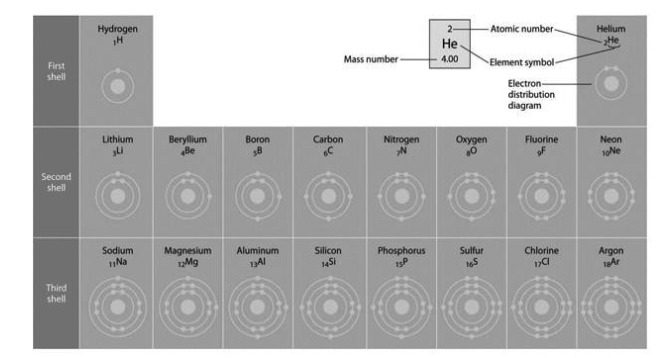
Refer to the following figure to answer the following question
Refer to the figure above (first three rows of the periodic table). What element has
properties most similar to carbon?
A) boron
B) silicon
C) nitrogen
D) aluminum
E) phosphorus
silicon
How many electrons are involved in a single covalent bond?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
two
An atom has four electrons in its valence shell. What types of covalent bonds is it capable of forming?
A) single, double, or triple
B) single and double only
C) single bonds only
D) double bonds only
single, double, or triple
Which of the following is a property of liquid water? Liquid water ________.
A) is less dense than ice
B) has a specific heat that is lower than that for most other substances
C) has a heat of vaporization that is higher than that for most other substances
D) is nonpolar
has a heat of vaporization that is higher than that for most other substances
A solution with a pH of 5 has how many more protons in it than a solution with a pH of 7?
A) 5 times
B) 10 times
C) 100 times
D) 1000 times
100 times
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by ________.
A) hydrogen bonds
B) nonpolar covalent bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) ionic bonds
E) van der Waals interactions
polar covalent bonds
The partial negative charge at one end of a water molecule is attracted to the partial positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called?
A) a covalent bond
B) a hydrogen bond
C) an ionic bond
D) a hydrophilic bond
E) a van der Waals interaction
a hydrogen bond
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because ________.
A) the oxygen atom donates an electron to each of the hydrogen atoms
B) the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus
C) the oxygen atom has two pairs of electrons in its valence shell that are not neutralized by hydrogen atoms
D) the oxygen atom forms hybrid orbitals that distribute electrons unequally around the oxygen nucleus
E) one of the hydrogen atoms donates an electron to the oxygen atom
the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus
Which of the following effects can occur because of the high surface tension of water?
A) Lakes cannot freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B) A raft spider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms can resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Sweat can evaporate from the skin, helping to keep people from overheating.
E) Water can flow upward from roots to the leaves in plants
A raft spider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
Why does ice float in liquid water?
A) The high surface tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top.
B) The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C) Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat.
D) Stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water.
E) The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water
Stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water.
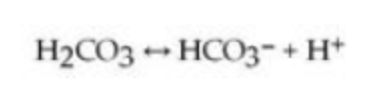
One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is carbonic acid (H2CO3). Carbonic acid is a weak acid that, when placed in an aqueous solution, dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO3−) and a hydrogen ion (H+), as noted below.
If the pH of blood increases, one would expect ________.
A) a decrease in the concentration of H2CO3 and an increase in the concentration of HCO3−
B) an increase in the concentration of H2CO3 and a decrease in the concentration of HCO3−
C) a decrease in the concentration of HCO3− and an increase in the concentration of H+
D) an increase in the concentration of HCO3− and a decrease in the concentration of OH−
E) a decrease in the concentration of HCO3− and an increase in the concentration of H2CO3 and H+
a decrease in the concentration of H2CO3 and an increase in the concentration of HCO3−

Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule depicted here is most likely ________.
A) positively charged
B) negatively charged
C) without charge
D) hydrophobic
E) nonpolar
positively charged
You have two beakers. One contains pure water; the other contains pure methanol (wood alcohol). The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. You pour crystals of table salt (NaCl) into each beaker. Predict what will happen.
A) Equal amounts of NaCl crystals will dissolve in both water and methanol.
B) NaCl crystals will not dissolve in either water or methanol.
C) NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
D) NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in methanol but will not dissolve in water.
E) When the first crystals of NaCl are added to water or to methanol, they will not dissolve; but as more crystals are added, the crystals will begin to dissolve faster and faster
NaCl crystals will dissolve readily in water but will not dissolve in methanol.
Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
A) The majority of their bonds are polar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
B) The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
C) They are hydrophilic.
D) They exhibit considerable molecular complexity and diversity.
E) They are less dense than water
The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
Why do chemical reactions tend to speed up when the concentration of the reactants is increased?
A) The reactants move faster.
B) The reactants collide more often.
C) The reactants have greater energy.
D) All of the listed responses are correct
The reactants collide more often.
The first chemicals that provided potential energy on Earth may have been formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide. While these were produced by sunlight-driven reactions, they also occurred around deep-sea vents. If the first organisms on Earth evolved around these vents, the first life on Earth was ________.
A) photosynthetic, obtaining energy from the Sun
B) chemosynthetic, obtaining energy from chemicals
C) herbivorous, obtaining energy from plants
D) carnivorous, obtaining energy from animals
chemosynthetic, obtaining energy from chemicals
Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments supported the hypothesis that ________.
A) life on Earth arose from simple inorganic molecules
B) organic molecules can be synthesized abiotically under conditions that may have existed on early Earth
C) life on Earth arose from simple organic molecules, with energy from lightning and volcanoes
D) the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the origin of life
E) the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the abiotic synthesis of organic molecules
organic molecules can be synthesized abiotically under conditions that may have existed on early Earth
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other atoms?
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) covalent
D) covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
E) ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds
covalent
Side chains of amino acids ________.
A) are all nonpolar
B) are nonpolar if they contain N or S
C) are all polar
D) may be polar or nonpolar
may be polar or nonpolar
What component of amino acid structure varies among different amino acids?
A) the long carbon-hydrogen tails of the molecule
B) the presence of a central C atom
C) the components of the R-group
D) the glycerol molecule that forms the backbone of the amino acid
the components of the R-group
Suppose you discovered a new amino acid. Its R-group contains only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Predict the behavior of this amino acid.
A) It is hydrophobic.
B) It is hydrophilic.
C) Relative to the amino acids found in organisms, its interactions with water will be intermediate.
D) Relative to the amino acids found in organisms, its interactions with water will be very high
It is hydrophobic.
peptide bond ________.
A) forms between the functional R-groups of different amino acids
B) forms between the central carbon and the amino R-group of a single amino acid
C) forms the primary structure of proteins
D) does not play a role in maintaining the tertiary structure of proteins
forms the primary structure of proteins
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires the ________.
A) release of a water molecule
B) release of a carbon dioxide molecule
C) addition of a carbon dioxide molecule
D) addition of a water molecule
E) addition of a water molecule and a carbon dioxide molecule
release of a water molecule
There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid different from another?
A) different side chains (R-groups) attached to a carboxyl carbon
B) different side chains (R-groups) attached to the amino groups
C) different side chains (R-groups) attached to an α carbon
D) different structural and optical isomers
E) different asymmetric carbons
different side chains (R-groups) attached to an α carbon
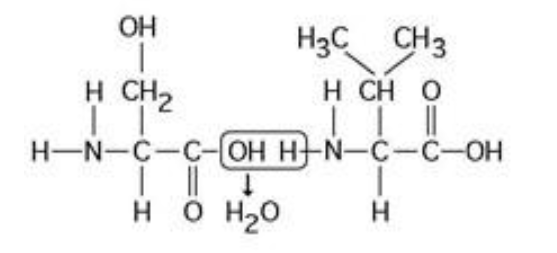
The chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure ________.
A) is a hydrolysis reaction
B) results in a peptide bond
C) joins two fatty acids together
D) links two polymers to form a monomer
E) joins two phospholipids in a bilayer
results in a peptide bond
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
A) ketone and methyl groups
B) carbonyl and amino groups
C) carboxyl and amino groups
D) amino and sulfhydryl groups
E) hydroxyl and carboxyl groups
carboxyl and amino groups
mino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group?
A) amino
B) carbonyl
C) carboxyl
D) phosphate
E) hydroxyl
carboxyl
Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure of a protein?
A) peptide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) disulfide bonds
D) phosphodiester bonds
E) peptide bonds, hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bonds
peptide bonds
Which type of interaction stabilizes the α-helix and the β-pleated sheet structures of proteins?
A) hydrophobic interactions
B) disulfide bonds
C) ionic bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) peptide bonds
hydrogen bonds
You disrupt all hydrogen bonds in a protein. What level of structure will be preserved?
A) primary structure
B) secondary structure
C) tertiary structure
D) quaternary structure
primary structure
Aquaporins are proteins that control the passage of water molecules across a cell membrane. The protein forms a pore, or opening, in the membrane. You isolate what you think are two different molecules of aquaporin and determine that one of the proteins has a larger pore diameter than the second. Which of the following do you conclude?
A) These two forms of aquaporin will have identical sequences of amino acids.
B) These two forms of aquaporin will have different sequences of amino acids.
C) You will have to sequence the proteins to compare their primary structure, because it should have no effect on pore diameter.
D) These two forms of aquaporin have identical primary structure but differ in their tertiary structure
These two forms of aquaporin will have different sequences of amino acids.
How does primary protein structure affect the function of protein enzymes?
A) Substrates interact with R-groups at the enzyme's active site.
B) Substrates interact with R-groups at the enzyme's external surface.
C) Substrates interact with hydrophobic R-groups at any region of the enzyme.
D) Substrates permanently bind to R-groups at the enzyme's active site
Substrates interact with R-groups at the enzyme's active site.
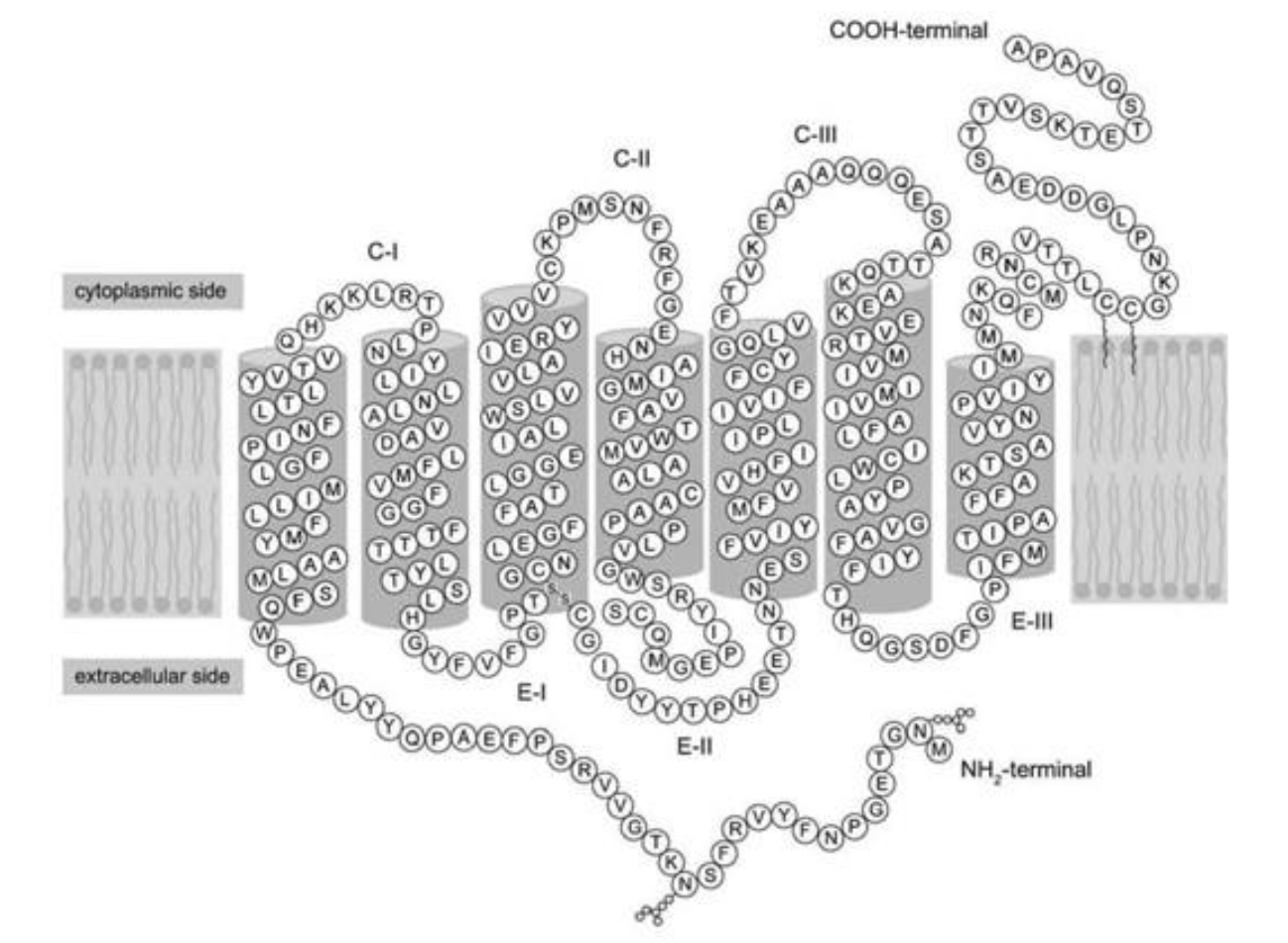
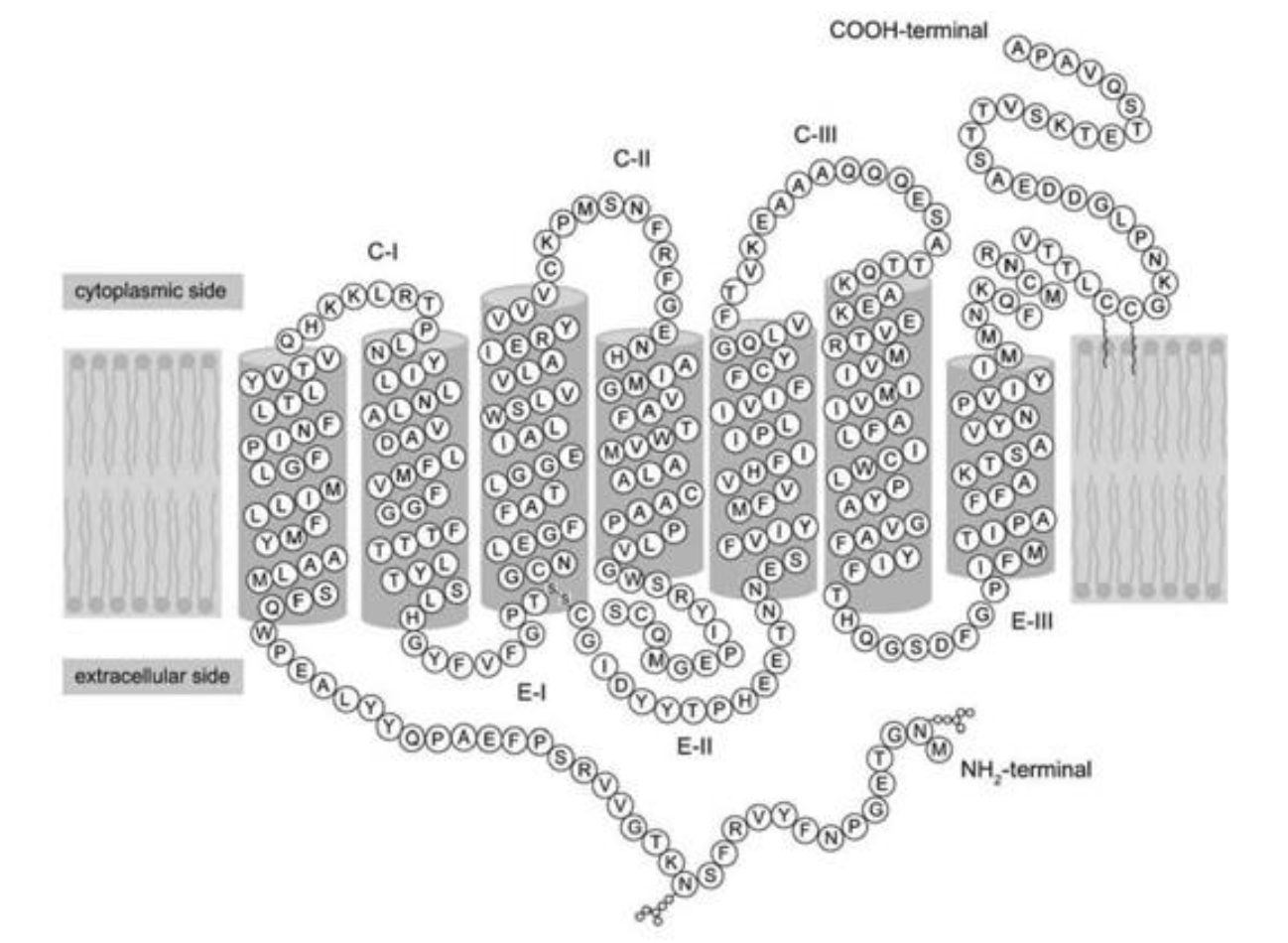
Refer to the following paragraph and accompanying figure to answer the following question(s).
Since structure correlates well with function, look for new ways to probe the complex structure of proteins in order to understand what they do and how they do it. One of the most powerful techniques in existence today is X-ray crystallography. The main difficulty with this technique is getting the protein to crystallize. Once crystallized, the protein is bombarded with X-rays to create a pattern that can be analyzed mathematically to determine the three-dimensional structure of the protein. This analysis has been performed by Palczewski (2000) on the protein rhodopsin, which is a light-sensitive protein found in species ranging from ancient bacteria (archaea) to humans. The structure (schematically shown above, where each letter represents an amino acid) is characterized by a single polypeptide chain with several α-helical segments that loop back and forth across the cell membrane. Another notable feature is the disulfide bond (-S-S-) that can be seen at the bottom of the third transmembrane segment.
If you were reading off the sequence of amino acids in the figure to a biologist friend, what should the first three letters be?
A) M-N-G
B) A-P-A
C) It does not matter, since the protein has no polarity or directionality
M-N-G
Refer to the following paragraph and accompanying figure to answer the following question(s).
Since structure correlates well with function, look for new ways to probe the complex structure of proteins in order to understand what they do and how they do it. One of the most powerful techniques in existence today is X-ray crystallography. The main difficulty with this technique is getting the protein to crystallize. Once crystallized, the protein is bombarded with X-rays to create a pattern that can be analyzed mathematically to determine the three-dimensional structure of the protein. This analysis has been performed by Palczewski (2000) on the protein rhodopsin, which is a light-sensitive protein found in species ranging from ancient bacteria (archaea) to humans. The structure (schematically shown above, where each letter represents an amino acid) is characterized by a single polypeptide chain with several α-helical segments that loop back and forth across the cell membrane. Another notable feature is the disulfide bond (-S-S-) that can be seen at the bottom of the third transmembrane segment.
Identify the location of the disulfide bond in the figure, located at the bottom of the third transmembrane segment. What is the name of the amino acids that are forming this bond?
A) cytosine
B) aspartic acid
C) cysteine
D) glycine
cysteine
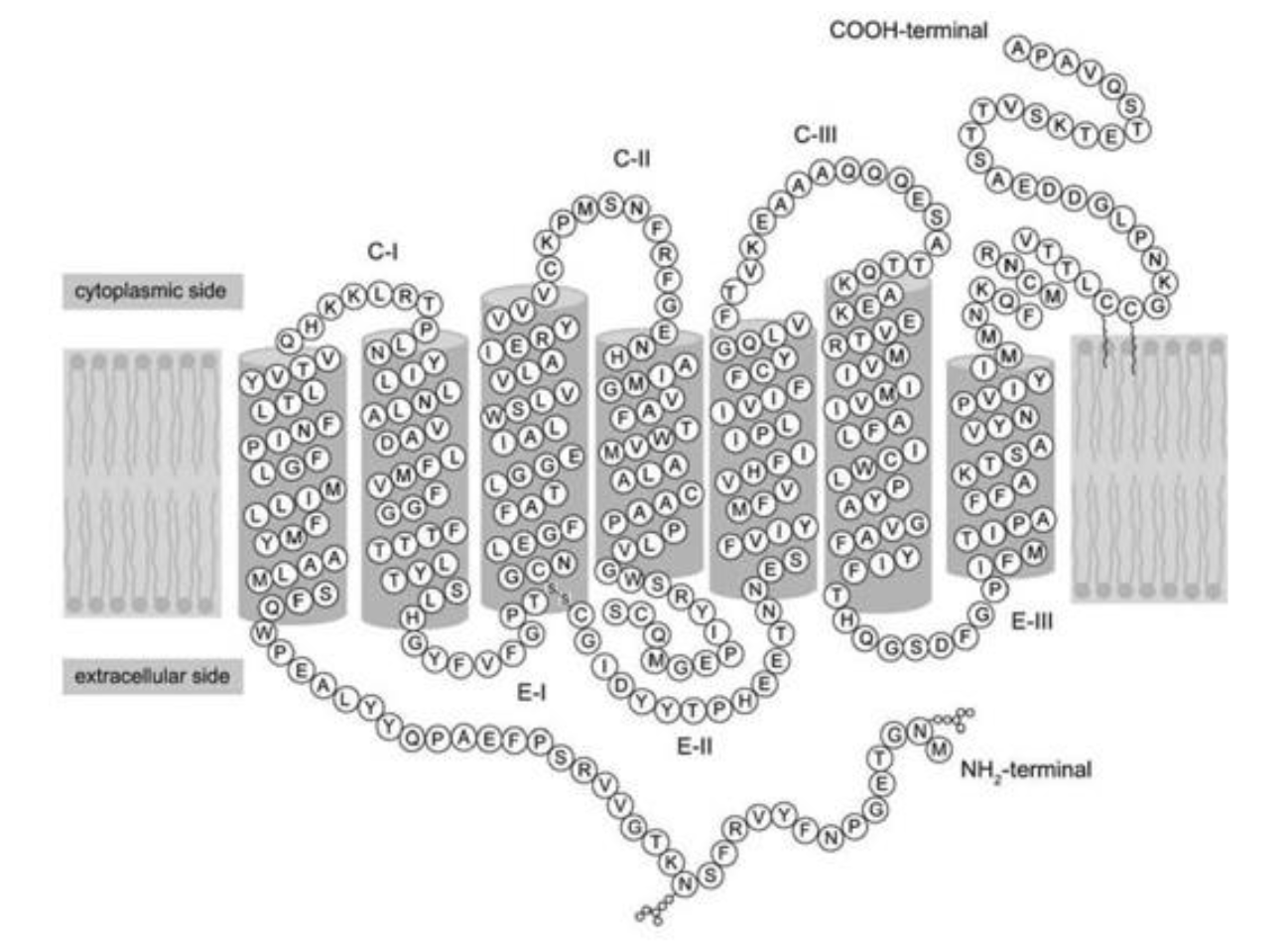
What is the location of the C-terminus of the protein in the figure?
A) extracellular
B) cytoplasm
C) embedded within the membrane
D) nucleus
cytoplasm
The amino acids of the protein keratin are arranged predominantly in an α-helix. This secondary structure is stabilized by ________.
A) covalent bonds
B) peptide bonds
C) ionic bonds
D) polar bonds
E) hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bonds
The tertiary structure of a protein is the ________.
A) bonding together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds
B) order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain
C) unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide
D) organization of a polypeptide chain into an α-helix or β-pleated sheet
E) overall protein structure resulting from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits
unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide
The R-group, or side chain, of the amino acid serine is -CH2-OH. The R-group, or side chain, of the amino acid leucine is -CH2-CH-(CH3)2. Where would you expect to find these amino acids in a globular protein in aqueous solution?
A) Serine would be in the interior, and leucine would be on the exterior of the globular protein.
B) Leucine would be in the interior, and serine would be on the exterior of the globular protein.
C) Serine and leucine would both be in the interior of the globular protein.
D) Serine and leucine would both be on the exterior of the globular protein
Leucine would be in the interior, and serine would be on the exterior of the globular protein.
Changing a single amino acid in a protein consisting of 325 amino acids would ________.
A) alter the primary structure of the protein but not its tertiary structure or function
B) cause the tertiary structure of the protein to unfold
C) always alter the biological activity or function of the protein
D) always alter the secondary structure of the protein and disrupt its biological activity
E) always alter the primary structure of the protein, sometimes alter the tertiary structure of the protein, and sometimes affect its biological activity
always alter the primary structure of the protein, sometimes alter the tertiary structure of the protein, and sometimes affect its biological activity
In a normal cellular protein, where would you expect to find a hydrophobic amino acid like valine?
A) in the interior of the folded protein, away from water
B) on the exterior surface of the protein, interacting with water
C) in the transmembrane portion interacting with lipid fatty-acid chains
D) in the interior of the folded protein, away from water, or in a transmembrane portion interacting with lipid fatty-acid chains
E) anywhere in the protein, with equal probability
in the interior of the folded protein, away from water, or in a transmembrane portion interacting with lipid fatty-acid chains
If cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive 35S, which of these molecules will be labeled?
A) phospholipids
B) nucleic acids
C) proteins
D) amylose
E) proteins and nucleic acids
proteins
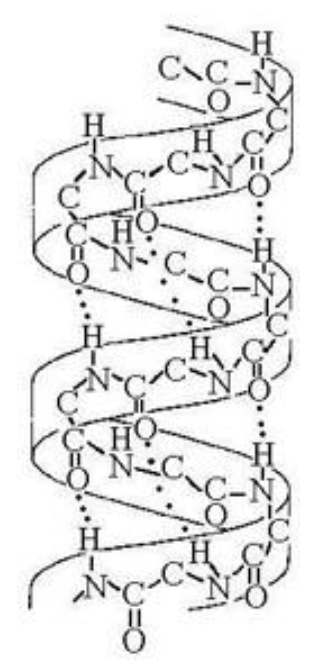
The structure depicted the accompanying figure shows the ________
A) 1-4 linkage of the α-glucose monomers of starch
B) 1-4 linkage of the β-glucose monomers of cellulose
C) double-helical structure of a DNA molecule
D) α-helix secondary structure of a polypeptide
E) β-pleated sheet secondary structure of a polypeptide
α-helix secondary structure of a polypeptide
The structural level of a protein LEAST affected by a disruption in hydrogen bonding is the ________.
A) primary level
B) secondary level
C) tertiary level
D) quaternary level
E) All structural levels are equally affected by a disruption in hydrogen bonding
primary level
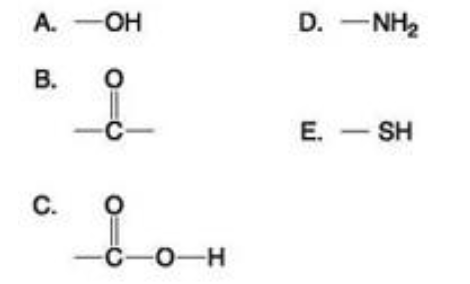
Which of the groups shown above is a functional group that helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
Which level of protein structure do the α-helix and the β-pleated sheet represent?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
secondary
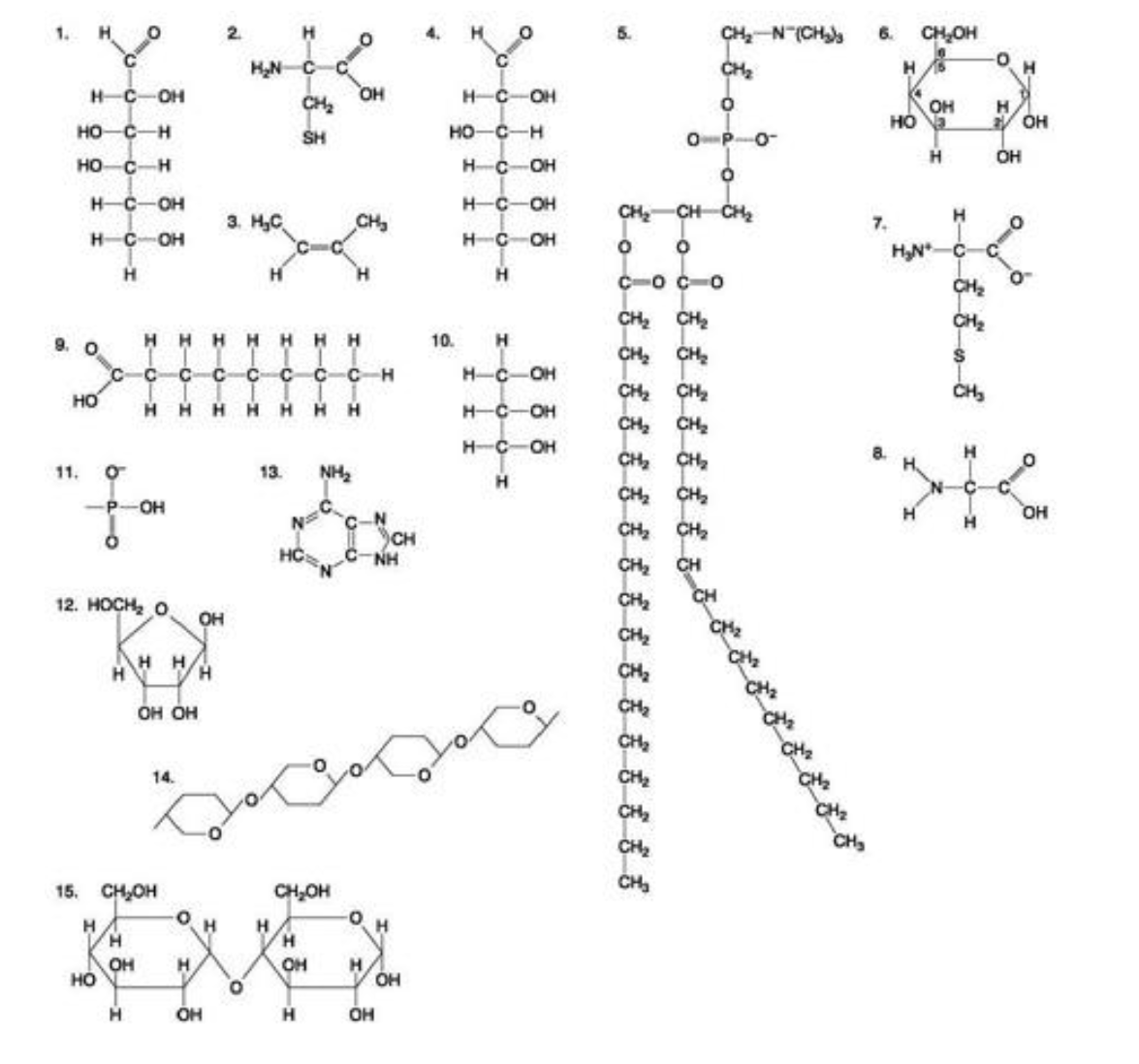
The following question is based on the 15 molecules illustrated below
Which of the following molecules act as building blocks (monomers) of polypeptides?
A) 1, 4, and 6
B) 2, 7, and 8
C) 7, 8, and 13
D) 11, 12, and 13
E) 12, 13, and 15
2, 7, and 8
Which of the following is the strongest evidence that protein structure and function are correlated?
A) Proteins function best at certain temperatures.
B) Proteins have four distinct levels of structure and many functions.
C) Enzymes tend to be globular in shape.
D) Denatured (unfolded) proteins do not function normally
Denatured (unfolded) proteins do not function normally
What are prions?
A) mobile segments of DNA
B) tiny circular molecules of RNA that can infect plants
C) viral DNA that attaches itself to the host genome and causes disease
D) misfolded versions of normal protein that can cause disease
E) viruses that invade bacteria
misfolded versions of normal protein that can cause disease
Proteins in biological systems ________.
A) store genetic information
B) link with other proteins to form bilayers in cell membranes
C) form high-energy intermediates such as ATP
D) catalyze reactions
catalyze reactions
Nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers?
A) nucleotides
B) ribose sugars
C) amino acids
D) nitrogenous bases
E) phosphates
nucleotides
What is the difference between a ribonucleotide and a deoxyribonucleotide?
A) Ribonucleotides contain a phosphate group.
B) Ribonucleotides have a hydroxyl group on the 2 carbon of their sugar subunit.
C) Ribonucleotides contain a sugar with five carbon atoms.
D) Ribonucleotides have a hydrogen atom on the 1 carbon of their sugar subunit
Ribonucleotides have a hydroxyl group on the 2 carbon of their sugar subunit.
What is/are the variable structure(s) of a nucleotide?
A) the phosphate group
B) the sugar
C) the base
D) the sugar and the base
the sugar and the base
Which of the following includes all of the pyrimidines found in RNA and DNA?
A) cytosine and uracil
B) cytosine and thymine
C) cytosine, uracil, and thymine
D) cytosine, uracil, and guanine
cytosine, uracil, and thymine
When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid ________.
A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second
B) a hydrogen bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second
C) covalent bonds form between the bases of two nucleotides
D) hydrogen bonds form between the bases of two nucleotides
a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second
Some viruses consist only of a protein coat surrounding a nucleic acid core. If you wanted to radioactively label the nucleic acids separately from the protein, you would use radioactive ________.
A) sulfur
B) carbon
C) nitrogen
D) phosphorus
phosphorus
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
A) a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group
B) a nitrogenous base and a sugar
C) a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
D) a phosphate group and an adenine or uracil
E) a sugar and a purine or pyrimidine
a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
Which of the following are pyrimidine nitrogenous bases?
A) guanine and adenine
B) cytosine and uracil
C) thymine and guanine
D) ribose and deoxyribose
E) adenine and thymine
cytosine and uracil
Which of the following are purine nitrogenous bases?
A) cytosine and guanine
B) guanine and adenine
C) adenine and thymine
D) thymine and uracil
E) uracil and cytosine
guanine and adenine
The difference between the sugar in DNA and the sugar in RNA is that the sugar in DNA ________.
A) is a six-carbon sugar and the sugar in RNA is a five-carbon sugar
B) can form a double-stranded molecule
C) is an aldehyde sugar and the sugar in RNA is a keto sugar
D) is in the α configuration and the sugar in RNA is in the β configuration
E) contains one less oxygen atom
contains one less oxygen atom
Nucleic acids have a definite polarity, or directionality. Stated another way, one end of the molecule is different from the other end. How are these ends described?
A) One end has a hydroxyl group on the 2 carbon; the other end has a hydrogen atom on the 2 carbon.
B) One end contains a nitrogenous base; the other end lacks it.
C) One end has an unlinked 3' carbon; the other end has an unlinked 5 carbon.
D) One end has one phosphate group; the other end has two phosphate groups
One end has an unlinked 3' carbon; the other end has an unlinked 5 carbon.
If a double-stranded DNA sample were composed of 10 percent thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 80
E) It is impossible to tell from the information given
40
DNA double helices are soluble in water but insoluble in alcohol. How do these physical properties reflect the chemical structure of the DNA molecule?
A) The charged phosphate groups and sugars of DNA are hydrophilic.
B) The purine and pyrimidine bases are hydrophilic.
C) The 5 prime to 3 prime polarity of DNA makes it soluble in water but not in alcohol.
D) The charged R-groups of DNA are hydrophilic.
The charged phosphate groups and sugars of DNA are hydrophilic.
Which of the following best describes DNA's secondary structure?
A) beta-pleated sheet
B) double parallel helical strands
C) turn-loop-turn
D) double antiparallel helical strand
double antiparallel helical strand
Franklin and Wilkins analyzed DNA by bombarding DNA crystals with X-rays. Their analysis yielded two numbers that sparked interest, 3.4 nm and 0.34 nm. What is the significance of these numbers?
A) It turned out to be just a coincidence.
B) DNA molecules are 3.4 nm long and 0.34 nm wide.
C) The width of a DNA molecule is 3.4 nm, whereas the width of a nucleotide monomer is 0.34 m.
D) These numbers demonstrate there are 10 rungs, or steps, on the DNA "ladder" for every turn of the helix.
E) The 10 to 1 ratio signifies that DNA molecules are 10 times longer than they are wide
These numbers demonstrate there are 10 rungs, or steps, on the DNA "ladder" for every turn of the helix.
f one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases 5'ATTGCA3', the other complementary strand would have the sequence ________.
A) 5'TAACGT3'
B) 5'TGCAAT3'
C) 5'UAACGU3'
D) 3'UAACGU5'
E) 5'UGCAAU3'
5'TGCAAT3'
What is the structural feature that allows DNA to replicate?
A) sugar-phosphate backbone
B) complementary pairing of the nitrogenous bases
C) disulfide bonding (bridging) of the two helixes
D) twisting of the molecule to form an α-helix
E) three-component structure of the nucleotides
complementary pairing of the nitrogenous bases
Enzymes that break down DNA catalyze the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. What would happen to DNA molecules treated with these enzymes?
A) The two strands of the double helix would separate.
B) The phosphodiester linkages of the polynucleotide backbone would be broken.
C) The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
D) The pyrimidines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
E) All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars
The phosphodiester linkages of the polynucleotide backbone would be broken.
Which of the following pairs of base sequences could form a short stretch of a normal double helix of DNA?
A) 5'-purine-pyrimidine-purine-pyrimidine-3' with 3'-purine-pyrimidine-purine-pyrimidine-5'
B) 5'-AGCT-3' with 5'-TCGA-3'
C) 5'-GCGC-3' with 5'-TATA-3'
D) 5'-ATGC-3' with 5'-GCAT-3'
E) All of these pairs are correct.
5'-ATGC-3' with 5'-GCAT-3'
Which of the following statements best summarizes the differences between DNA and RNA?
A) DNA encodes hereditary information, whereas RNA does not.
B) The bases in DNA contain sugars, whereas the bases in RNA do not contain sugar.
C) DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides.
D) DNA contains the base uracil, whereas RNA contains the base thymine.
E) The bases in DNA contain sulfur, whereas the bases in RNA do not contain sulfur.
DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides.
RNA and proteins combine in cells to form structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes contain the active site for peptide bond formation. Based on their chemical structures, do you think protein or RNA molecules actually form the active site within the ribosome?
A) protein, because RNA cannot catalyze reactions
B) RNA, because proteins cannot catalyze a reaction that involves another protein
C) proteins, because only proteins can catalyze a reaction that involves another protein
D) It could be either, because both molecules have catalytic properties
It could be either, because both molecules have catalytic properties
Which of the following statements about the 5' end of a polynucleotide strand of RNA is correct?
A) The 5' end has a hydroxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose.
B) The 5' end has a phosphate group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose.
C) The 5' end has phosphate attached to the number 5 carbon of the nitrogenous base.
D) The 5' end has a carboxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose.
E) The 5' end is the fifth position on one of the nitrogenous bases
The 5' end has a phosphate group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose.
One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to ________.
A) transmit genetic information to offspring
B) function in the synthesis of proteins
C) make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity
D) act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA
E) form the genes of higher organisms
function in the synthesis of proteins