"AP BIO UNIT 6
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
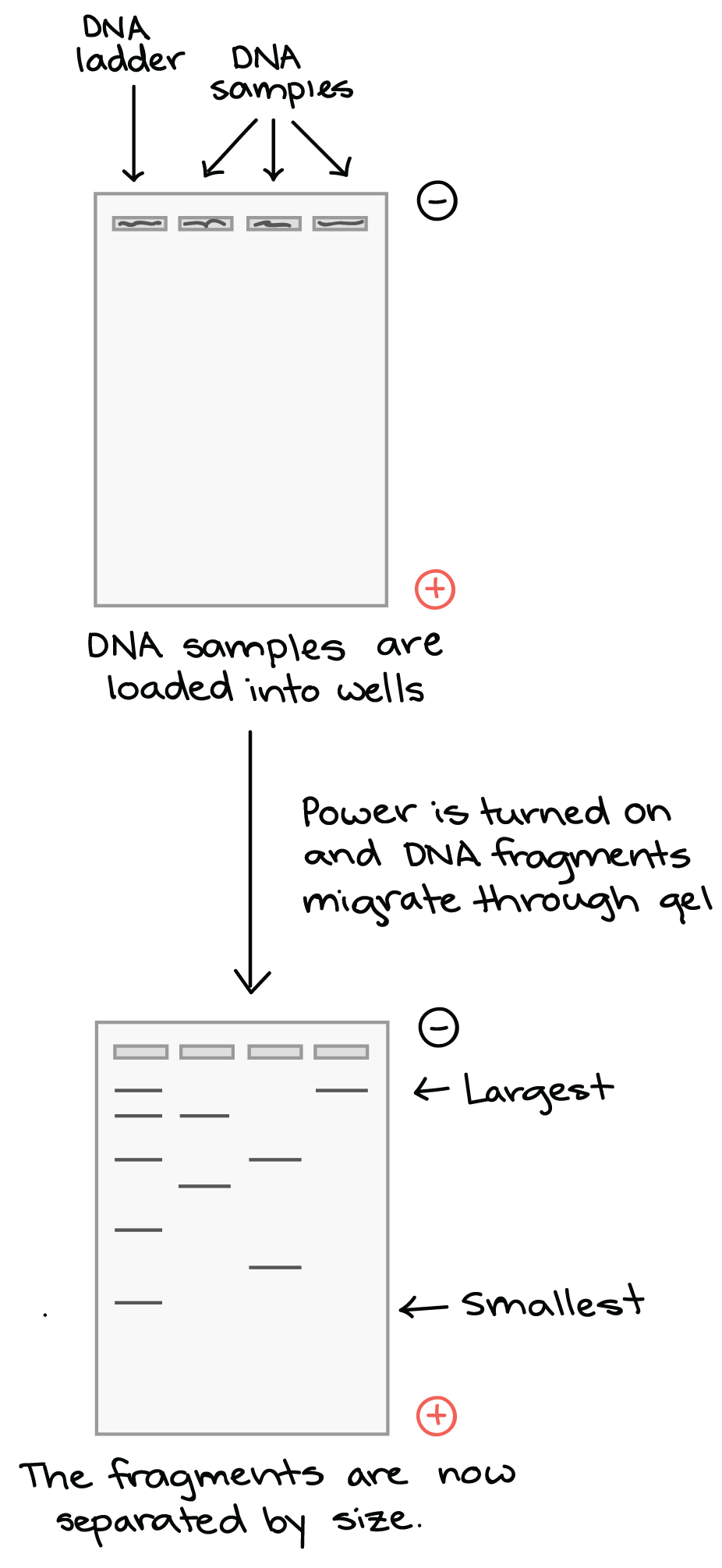
Gel Electrophoresis
Flashcard: Gel Electrophoresis - A technique separating DNA, RNA, or proteins based on size and charge using an electric field in a gel matrix.
dimers
Dimers found in DNA chains damaged by ULTRAVIOLET RAYS. They consist of two adjacent PYRIMIDINE NUCLEOTIDES, usually THYMINE nucleotides, in which the pyrimidine residues are covalently joined by a cyclobutane ring. These dimers block DNA REPLICATION.
topoisomerase (and single strand binding protein)
relieves tension in the overwound DNA in front of a replication fork.
relieves supercoiling
DNA ligase
joins together the DNA fragments at a replication fork to form continuous strands.
DNA primase
catalyzes the synthesis of RNA primers on the lagging strand of a replication fork.
DNA polymerase
synthesizes new DNA by using the leading and lagging strands of a replication fork as templates.
DNA helicase
Enzyme that unzips DNA strands during replication by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs.
rRNA
Flashcard: rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is a type of RNA that combines with proteins to form ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis. does not get translated into protein
direction of synthesis
Direction of synthesis is the order in which nucleotides are added to a growing DNA strand during replication or RNA during transcription. 5' to 3' direction, adding each new nucleotide to the 3' end of the strand.
reading frame
Reading frame: The way a cell's machinery reads a sequence of nucleotides in mRNA during translation, starting from a specific point and grouping them into codons.
DNA polymerase I
A type of enzyme called a polymerase that replaces RNA primers with DNA nucleotides during DNA replication.
DNA polymerase III
DNA Polymerase III is an enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a pre-existing or newly synthesized DNA strand
RNA Primer
The RNA primer is a short sequence of RNA nucleotides synthesized by RNA primase. It provides a 3' end onto which DNA polymerases can add nucleotides to synthesize a new strand of DNA
telomeres
Telomeres are the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent them from deteriorating or fusing with neighboring chromosomes. They play a key role in cellular aging and cancer
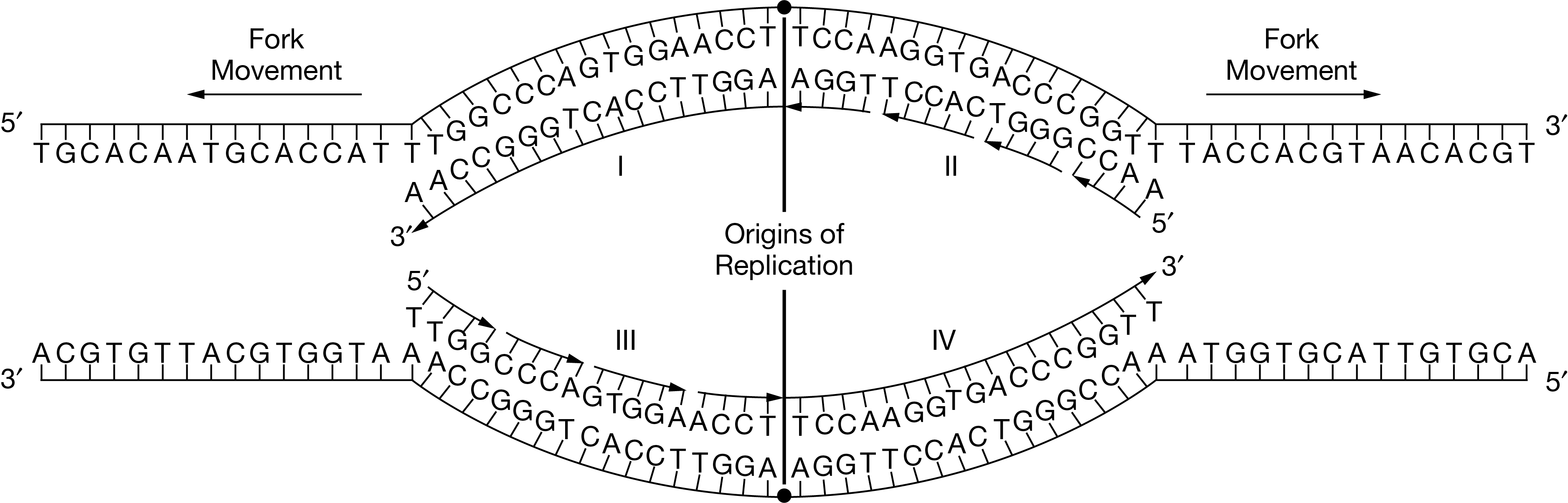
DNA replication
is done through essentially unwinding DNA and then using the existing strand as a template. The proteins involved do their part in replicating. The helicase acts as "scissors" of the DNA and cuts the DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides. The topoisomerase and single-strand binding proteins then keep the DNA from recoiling and messing things up. DNA polymerase III (highly inefficient, needs a lot of conditions satisfied before actually working) is the copier and adds the corresponding nucleotides. But remember! It can't start without a RNA primer, so the RNA primase has to go and add a primer consisting of RNA nucleotides. Then, DNA polymerase III can do its job. But since it makes a lot of mistakes, the DNA polymerase I goes back and edits any mistakes and replaces the RNA primer with actual DNA nucleotides. Lastly, the ligase is the glue!
tRNA
tRNA molecules, also known as transfer , are small molecules that function in protein synthesis. They have specific binding sites for specific amino acids, as well as an anticodon sequence that base pairs with the codon sequence of the mRNA.
mRNA
Messenger RNA - This is like the written copy of the recipe. It carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm where proteins are made.
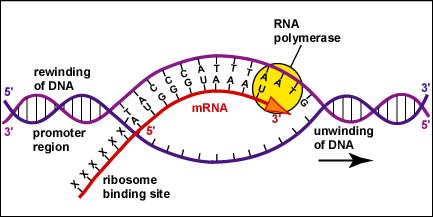
RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes the formation of RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
transcription
5’ to 3’ direction
processing mRNA
add poly a tail 3’ end. protects mRNA from degredation and aids transport
add gtp cap 5’ end cap protect mRNA from degredation mRNA recognition ID
exision of introns splicing/retention of exons
alternate splicing may occur
alternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a regulated process during gene expression that results in a single gene coding for multiple proteins. In this process, certain exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene.
translation
prokaryotes; occurs instantly from DNA to transcription to translation. all in cytoplasm.
eukaryotes transcription in nucleus then to ribosomes in cytoplasm
initiation: ribosome interacts with mRNA at start codon (binding of usually AUG tRNA start codon, kind of key
elongation: tRNA files in and out matching the reading frame and codons
termination: three stop codons read to terminate protein. UAG UGA or UAA
Co-transcriptional Translation
Co-transcriptional translation refers to simultaneous processes of transcription and translation within prokaryotic cells, where the mRNA is being synthesized and read to make proteins at the same time.
Retroviruses
Retroviruses are a unique class of viruses that possess the ability to reverse the flow of genetic information. Unlike other viruses, which use DNA as the genetic material and replicate through transcription and , retroviruses use RNA as the genetic material and replicate through a process called reverse transcription. This process is catalyzed by an enzyme called , which converts the into DNA.
promoter
Where DNA polymerase mounts
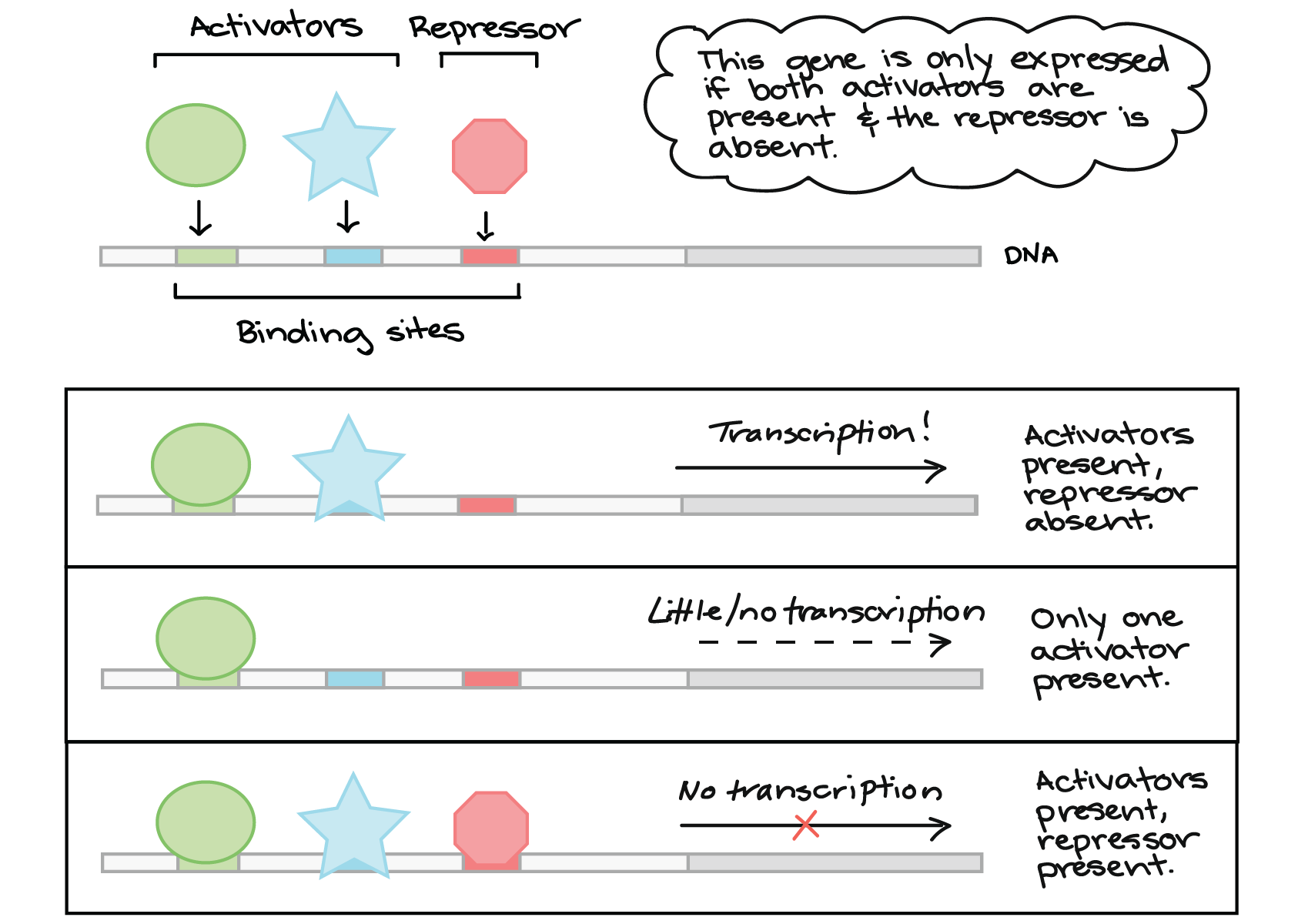
Regulatory sequences
sections of DNA that regulate gene expression turning on or off, located near or within promoter region of genes usually. interact with regulatory proteins to turn gene on or off
regulatory proteins
Regulatory proteins are proteins involved in the expression of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. They can either enhance or inhibit the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA, controlling the rate of transcription.
enhancers and silencers
sequences that either increase or decrease level of transcription of gene
terminators
signal end of transcription
Epigenetic changes
Epigenetic changes refer to modifications in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. These can include things like methylation or histone modification.
plasmids
prokaryotes eukaryotes have it. small extrachromosal double stranded circular DNA molecules
reverse transcriptase
copies viral RNA to DNA
reversible modifications of DNA or histones
operons
"Operons are genetic units in prokaryotes that consist of a promoter, operator, and genes controlled by a single regulatory region. They regulate gene expression by coordinating the transcription of multiple genes together." prokaryotes
gropsps of genes
eukaryotes influenced by same transcription factors
promoters
DNA sequences upstream where RNA polymerase bninds and starts to intiate transcription
negative regulatory molecules
inihbit gene expression
DNA mutations
positive negative or neutral based on type
types of DNA transmission (mainly bacteria)
transformation uptake of naked DNA, transduction virus transmition oc genetic transposition DNA segments exchanged between DNA
viruses pair and recombine when infecting same host cell
reproduction processes inc genetic variation evolutionary shared
polymerase chain reaction
Flashcard: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique to amplify DNA in vitro. It involves cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension using a DNA polymerase enzyme.
bacterial transformation
introduce DNA into bacteria cells
DNA sequencing
template strand
non coding strand
coding strand
it codes
muitation
insertion deletion inversion (portion of DNA get on inverted/backwards) translocation
point mutation silent (same codon) missense amino acid substitute nonsense stop codon,
frameshift mutation insertion or deletion shifts the reading frame or insertion of stop codon.
prokaryotic gene regulation
operons lac operon trp operon. induceable normally off repressable normally on.
eukaryotic gene regulation0
transcription factors activators and repressors
chromatin structiure modify histone protein and DNA to influence gene expresion.
Euchromatin loose
hetero chromatin tightly packed
mRNA degredation a tail gets eaten away
micro RNA non coding segments DNA that bids to mrNA and blopck translation at ribosomes
acetylation
unwinds histones transcription increrases
methylation
winds histones decreases transcription meth makes everything decrease
enhancers silencers
Flashcard: Enhancers are DNA sequences that increase gene expression by binding transcription factors, promoting transcription. They are distant from the gene they regulate.
binding sites for activators and repressors
nucleosome
histone wrapped thingy