Spectrophotometers
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Which analytical method is useful when studying analytes dissolved in complex mixes (with matrix effects) by absorbance and luminescence techniques?
standard addition
Emission spectra are obtained showing phoshoresence and fluorescence. Which of the following are/is true?
A
Phosphorescence occurs at higher energy than fluorescence.
B.
Fluorescence occurs at longer wavelengths than phosphorescence.
C.
Fluorescence occurs at shorter wavenumbers than phosphorescence.
D.
None of the Above
none of the above
The basic single-beam absorbance spectrophotometer is composed of four components. Which component listed below is NOT one of the four?
A. light source
B. beam splitter
C. monochromator
D. sample
E. light detector
beam splitter
Which of the following processes could be described as a radiationless process?
A.
internal conversion
B.
absorbance
C.
fluorescence
D.
phosphorescence
E. chemiluminescence
internal conversion
A triplet excited state is:
an electronic excited state in which the electron spin is no longer paired with the electron remaining in the ground state.
When an electron is excited from So to S1 in an atom during a molecular absorbance, what accounts for the broadness of the peaks (bands) in the absorbance spectrum?
the presence of vibrationally excited energy states and
the presence of rotationally excited energy states
Very small amounts of stray light can cause the greatest relative errors in...
high absorbance measurements and .
low intensity fluorescence measurements
A solution was found to have a 15.6 % transmittance at 500 nm, its wavelength of maximum absorption, using a cell with a path length of 5.00 cm. Calculate the absorbance of the solution in a 1.00 cm cell at 500 nm.
answer: .161
The first excited state of Ca is reached by absorption of 432.7 nm light. Find the energy difference (kJ/mol) between the ground and first excited state.
276
A molecule emits light at a wavelength of 3.10 x 104 nm. Calculate the wavenumber in cm-1.
323
A _______________ disperses light into its component wavelengths and selects a narrow band of wavelengths to pass on to the sample or detector.
monochromator
A compound with a molecular weight of 229.61 g/mol was dissolved in 50.0 mL of water. 1.00 mL of this solution was placed in a 10.0 mL flask and diluted to the mark. The absorbance of this diluted solution at 510 nm was 0.472 in a 1.000 cm cuvet. The molar absorptivity of the compound, at 510 nm, is 6,310 M-1 cm-1. Calculate the concentration of the compound in the initial 50.0 mL solution.
7.48 x 10-4 M
What wavelength of light carries 3.74 x 10-19 J of energy per photon?
.
532 nm
The lifetime of fluorescence is longer than the lifetime of phosphorescence.
false
If a molecular species absorbs a photon of light in the in the frequency range of 1014 Hz to 1010 Hz, which of the following transitions will occur? (use your notes to best estimate)
. vibrational and rotational
Which of the selections below is most correct?
Infrared absorption à molecular vibration transition
UV absorption à valence electron transition
X-ray absorption à core electron transition
Microwave absorption à molecular rotation transition
Which property of laser light is NOT correctly defined/described?
A. coherent: all waves in phase
B. monochromatic: emits one wavelength of light
C. collimated: parallel rays of light
D. extremely bright: high power at one wavelength
E. polarized: electric field oscillates between two perpendicular planes
polarized: electric field oscillates between two perpendicular planes
The following data were obtained for a complex of nickel at 575 nm in a 1.00 cm cell. Construct a calibration plot and accurately calculate the molar absorptivity for the nickel-complex at 575 nm.
.
5.425 M-1cm-1
Emission spectra are obtained showing phosphorescence and fluorescence. Which of the following is or are true? Read through all before making your one selection.
A.
Phosphorescence occurs at higher energy than fluorescence
B.
Fluorescence occurs at longer wavelengths than phosphorescence.
C.
Fluorescence occurs at shorter wavenumbers than phosphorescence.
none of the above
What is the relationship between S/N (signal-to-noise ratio) and light throughput in a spectroscopic instrument?
.
S/N increases with light throughput
For the spectrophotometric titration curve shown below,
X + T --> P, what set of molar absorptivities best fits the data? (X = analyte; T = titrant; P = product
.
εx = 0 M-1cm-1 εT = 1000 εP = 2000
In a standard additions method workup what information from the linear regression is most closely related to the unknown concentration? (used to determine it)
the x-intercept of the std. addn. line
To best view the ABS spectrum with average peak widths of approximately 15 nm, what ideal slit width would you use in your monochromator (from the choices) if building your own?
3 nm
Which statement is true regarding the resolution of a grating?
.
resolution increases with slit width
B.
resolution decreases with number of grooves per mm
C.
resolution increases with wavelength
D.
resolution increases with number of grooves per mm
E. resolution is not determined by the monochromator
resolution increases with number of grooves per mm
A "lock in" amplifier is often used in modern spectroscopy to help reduce sources of noise. What types of noise can best be reduced using this type of instrumentation?
.
1/f noise and
line noise
What property of noise does signal averaging exploit to improve the S/N ratio?
noise is random and both positive and negative relative to baseline
In modern FT spectroscopic techniques, the EM radiation data collected immediately after it passes through the sample is in what form before it is mathematically worked up and interpreted?
interferogram
Given the block diagram of the Czerny-Turner monochromator shown below, which of the following are the correct labels for components M1, C1, and M2, in this order.
collimating mirror, diffraction grating, focusing mirror
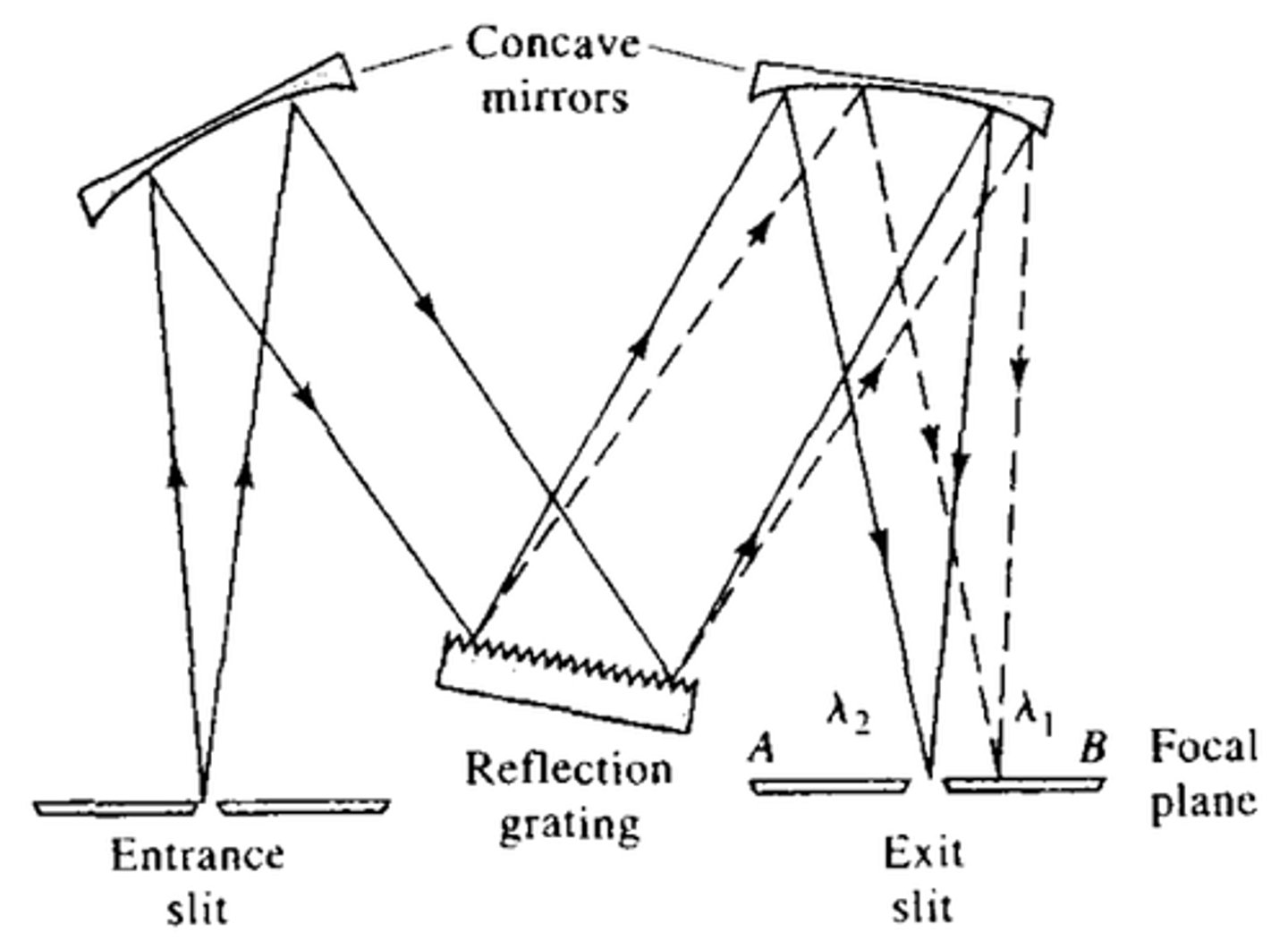
What number of scans should be signal-averaged in FTIR spectroscopy to increase the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of at least 7?
50
Which of the following types of electromagnetic radiation is represented if the wavelength () is equal to 1000 nm?
infrared
Electronic excitations are most likely to occur in a molecule when it is irradiated with which region of the EM spectrum (NOTE: in a spectroscopically useful manner)?
UV
Which term is measure of the ability of a monochromator to separate or spread out the wavelengths of light passing through it across some angle?
dispersion
Which of the following is the best method of atomization for a small, wet sample in atomic spectroscopy?
graphite furnace
What number of scans should be signal-averaged in FTIR spectroscopy to increase the signal-to- noise ratio by a factor of at least 7?
50
Which of the following sources of noise is not able to be reduced by carefully choosing the beam chopper frequency in spectroscopy?
white noise
What is the preferred source lamp in atomic absorption spectroscopy to help alleviate the linewidth problem?
hollow cathode lamp
At what Absorbance value is the transmittance approximately equal to the absorbance? to one decimal place)
0.40
Which of the following wavelengths cannot feasibly be studied in absorbance spectrophotometry
using a glass sample cuvet?
200 nm
Which source lamp is the best to use if the desired wavelengths are in the UV region of the EM spectrum?
deuterium
In which of the following quantitative methods of spectroscopy is the concentration of the unknown determined by adding a known concentration of another analyte?
internal standard
Which of the following is the most sensitive method of atomic spectroscopy?
atomic fluorescence
What point on an absorbance spectrum for a compound should be used for quantitative work involving Beer's Law calculations?
point of maximum absorbance
Beer's Law for a solution of dissolved analyte is most closely obeyed if the concentration is.....
between .4 and .9
When an electronic excitation occurs in an atom and the spin of the electron flips during the process, the excited state is known as a.....
triplet excited state
Which of the following processes has the LONGEST lifetime?
phosphorescence
Which of the following is NOT commonly used as a detector in IR spectrophotometry?
Photodiode array
When the standard addition technique is used for spectrophotometric quantitation with a series of additions, the concentration of the unknown can be determined from the graph of signal plotted vs. conc. of added standard because it is equal to....
the x intercept
The bandwidth of the monochromator used in absorption spectrophotometry should have what relationship to the absorption band being studied? Monochromator should have....
smaller bandwidth
Which of the following is the best reason for the mirror image often given by the emission spectrum for a given absorption spectrum?
radiationless relaxation process
Doubling the intensity of the incident radiation in a spectrophotometric instrument has NO effect on....
absorbance
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of fluorescence techniques over absorbance techniques?
universal detection
In 10 words or less, describe the main difference between the instrumental setup of atomic absorption and atomic fluorescence spectroscopy.
Jablonski Diagram
An energy diagram that illustrates the electronic states of a molecule and the transitions between them; the states are arranged vertically by increasing energy and grouped horizontally by spin multiplicity.
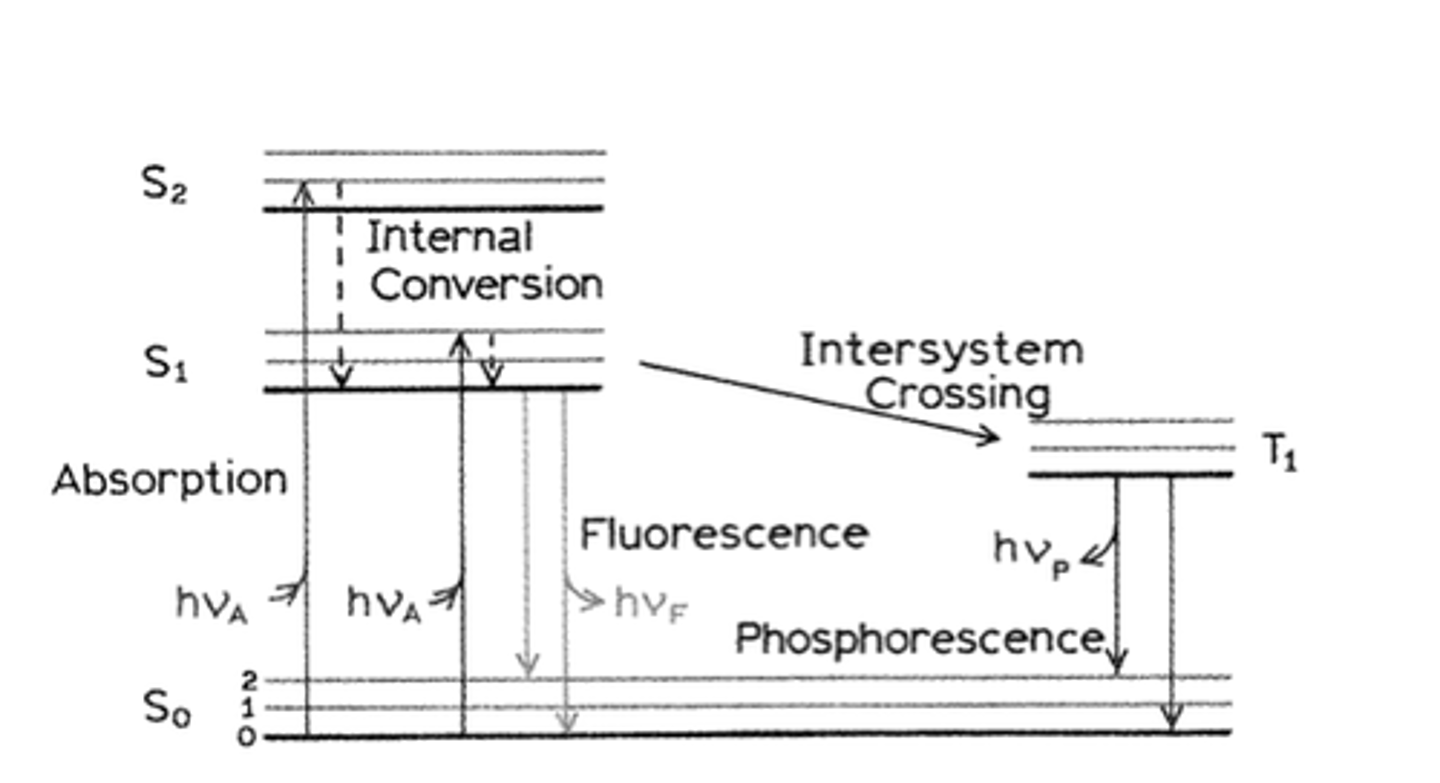
Why is fluorescence intensity doubled when the source intensity is doubled? Why is the same not true for absorbance?
fluorescence intensity is directly correlated to source intensity. this is not true for absorbance
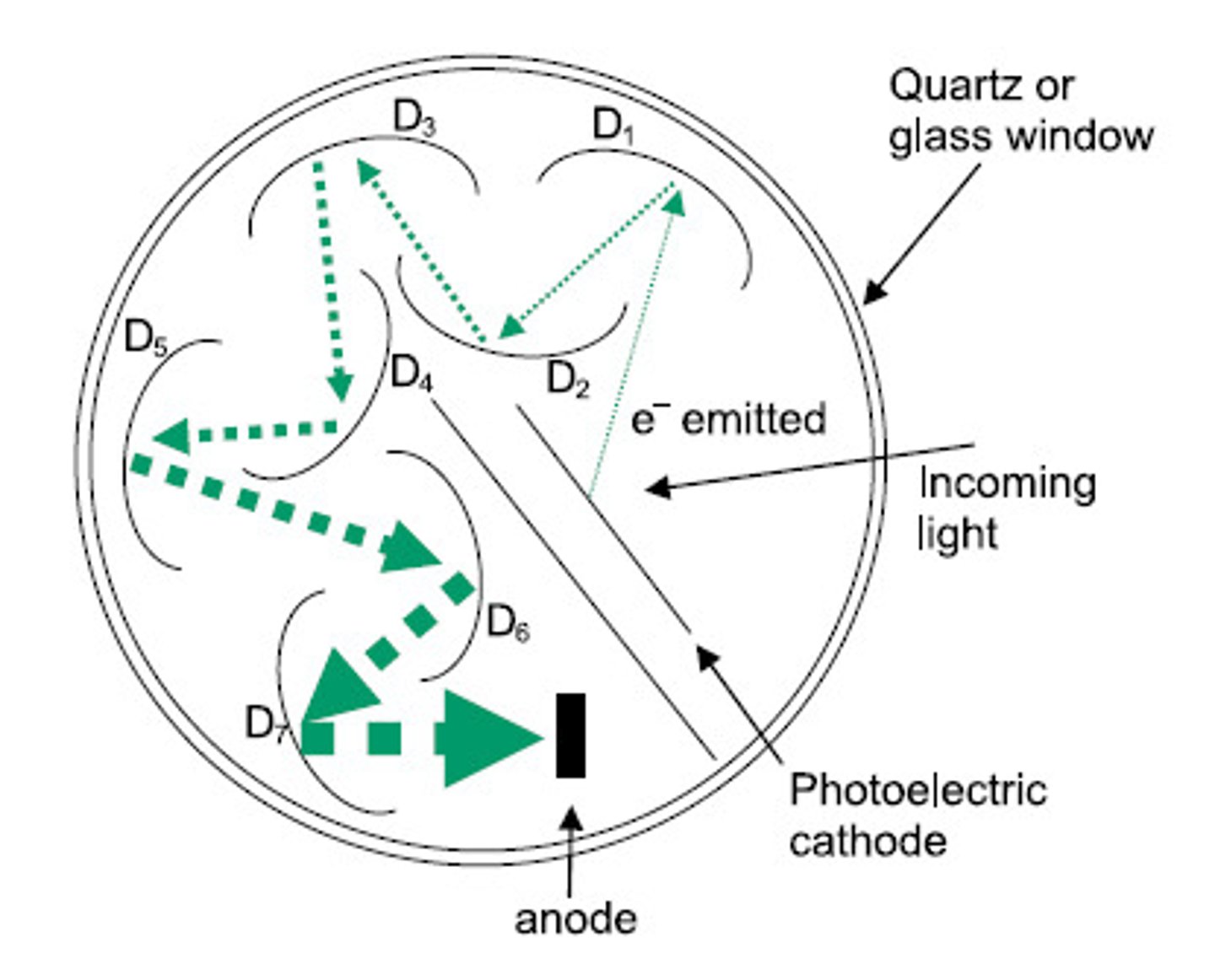
photomultiplier tube
An apparatus that converts a photon of visible light into an electrical pulse, for example as part of a gamma camera.
cathode, anode, dynode
dynode: u shaped things
anode: at the end
cathode: beginning
What is the advantage of decreasing monochromator slit width in spectroscopic techniques? What is the disadvantage?
The advantage is higher resolution (better instrument selectivity and smaller Beer's law deviations). The disadvantage is less light through (this would, for example, decrease sensitivity in a fluorescent spectrometer).
Adv: increased ability to resolve closely spaced peaks
Dis: more noise because less light reaches the detector