structure of brain - phys
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
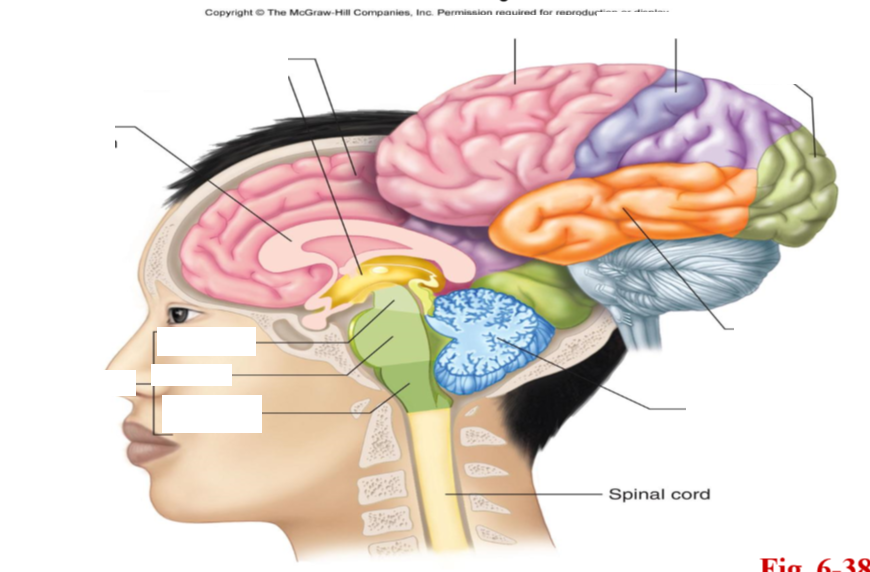
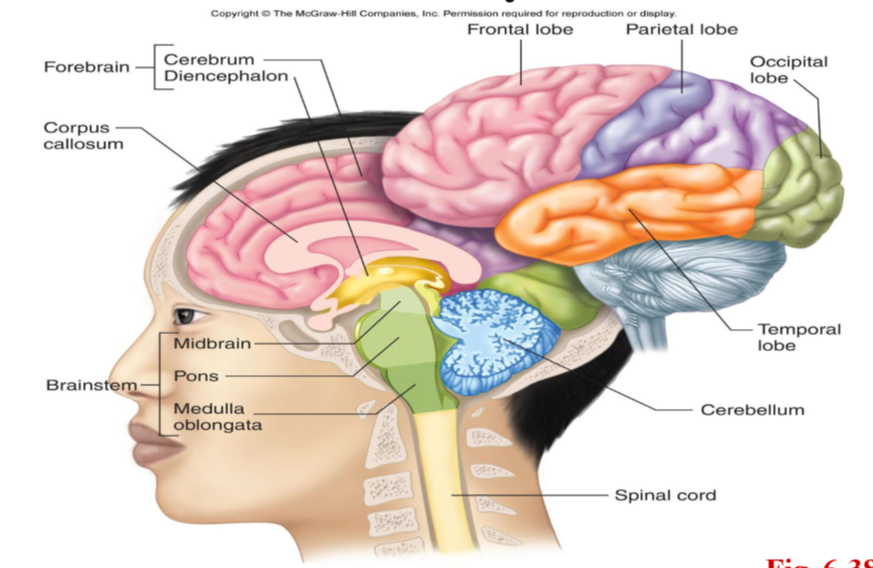
identify structures of the brain
cerebral cortex
covers the cerebrum, which is part of the forebrain
divided into 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
3mm thick, gray matter
integrating center: connects and processes input and controls skeletal muscle movement
cerebrum
part of forebrain
divided into left and right hemispheres, connected by corpus callosum
surrounded by cerebral cortex
thalamus
in the diencephalon (forebrain)
serves as a synaptic relay point
integrates incoming information
plays a key role in general arousal, focusing attention (filter out extraneous info)
hypothalamus
in the diencephalon (forebrain)
lies below the thalamus and above the pituitary gland
functions: homeostatic regulation, preservation of the individual (eat/drink) and species (reproduction)
epithalamus
part of diencephalon (forebrain)
small mass of tissue that includes the pineal gland
pineal gland helps control circadian rhythms by releasing melatonin
connection between limbic system and rest of brain
limbic system (components and functions)
components: thalamus, hypothalamus, part of frontal and temporal lobe cortexes, hippocampus and connections to other parts of CNS
gray matter
function: Learning, Emotional experience and behavior, Endocrine and Visceral functions
cerebellum
part of hind brain
coordinates movements and controls posture and balance (does not initiate movement)
receives info from muscles, joints, skin, eyes, ears, viscera, other parts of brain involved in control of movement
mostly motor functions but also implicated in some forms of learning
brainstem
made of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
all nerve fibers between spinal cord and brain pass through here
reticular formation (in brainstem): receives and integrates info from all region of CNS
involved in motor functions, cardiovascular and respiratory control, regulation of sleep, consciousness, focus of attention
part of spinal cord associated with sympathetic NS
T1-L2 vertebrae
part of spinal cord associated with parasympathetic NS
cranial nerves 3, 7, 9, 10
sacral vertebrae
where is CSF secreted?
by ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain
flow of CSF
from ependymal cells → throughout brain and spinal cord → valves in the top of the brain → large veins via venous sinuses (becomes a part of venous blood)
completely replaced ~3x per day