Unit 1 Lesson 2: Regulatory Compliance
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary-style flashcards covering regulatory compliance topics from HIPAA basics to PHI identifiers, consent types, EHR incentives, and related laws referenced in the video notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Implied consent
Consent inferred from a patient’s actions or behavior for low-risk or routine procedures, rather than explicit verbal or written confirmation.
Verbal consent
Consent given orally by the patient or their representative, without a written document.
Informed consent
Consent given after the patient is informed about risks, benefits, alternatives, and questions are answered; often documented in writing for high-risk or invasive procedures.
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act; a federal law protecting patient privacy, securing PHI (Patient Health Information), and standardizing electronic health information transactions.
PHI (Protected Health Information)
Identifiable health information created, received, stored, or transmitted by covered entities.
HIPAA Privacy Rule
WHAT you can/can’t do with patient info (all forms)
HIPAA - standardizes electronic transactions
uniform code sets and electronic formats
ICD-10-CM for diagnoses
CPT/HCPCS for procedures and services
standard electronic forms (837 claim form)
Ensures compliance
mishandles PHI or fail follow HIPPA rules can face heavy fines and penalties
HIPPA Security Rule
HOW you must protect patient info in electronic form
Covered entities
organizations or people who must follow HIPAA rules because they handle protected health information (PHI) in connection with healthcare services or payment.
1. Healthcare Providers
2. Health Plans
3. Healthcare Clearinghouses
Healthcare Providers
Doctors, nurses, hospitals, clinics, therapists, pharmacies, etc., who transmit health information electronically (for billing, claims, eligibility checks).
Health Plans
Insurance companies, HMOs, Medicare, Medicaid, employer-sponsored health plans.
Healthcare Clearinghouses
Entities that process non-standard health information into a standard format (or vice versa), such as billing services or repricing companies.
Under HIPAA, there are 18 identifiers that are considered Protected Health Information (PHI)
1. Name
2. Address
3. All elements of dates (except year)
4. Telephone numbers
5. Fax numbers
6. Email addresses
7. Social Security numbers
8. Medical record numbers
9. Health plan beneficiary numbers
10. Account numbers
11. Certificate/license numbers
12. Vehicle identifiers (license plate numbers, serial numbers, etc.)
13. Device identifiers and serial numbers
14. Web URLs
15. IP addresses
16. Biometric identifiers (fingerprints, voice prints, retinal scans, etc.)
17. Full-face photographs and comparable images
18. Any other unique identifying number, code, or characteristic
PHI breaches
Incidents where Protected Health Information is accessed, used, or disclosed without authorization, potentially compromising patient confidentiality and privacy.

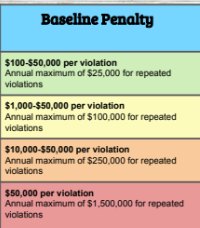


Written Consent
A formal agreement from a patient allowing the use or disclosure of their health information for specific purposes, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Release of Patient Information
information (PHI) can be used and disclosed without a specific authorization to release the information
Treatment
payemnt
operations
law enforcement, public interest and benefit activities
limited data set
Psychotherapy notes
Confidential notes taken by a therapist during or after a therapy session, focusing on the patient's thoughts and feelings. They are protected under HIPAA and have stricter requirements for disclosure compared to general medical records.
HITECH (health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health) ACT
A federal law aimed at promoting the adoption and meaningful use of health information technology while enhancing the privacy and security protections for electronic health information.
*if more than 500 patient records are affected, HITECH requires the media to be notified and offered identity theft protection services*
Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
protect consumers from abusive, unfair, or deceptive collection practices
False Claims Act
federal law that makes it illegal to knowingly submit, or cause someone else to submit, false or fraudulent claims for payment to the U.S. government.
● allows penalties to be placed on anyone who knowingly submits a fraudulent claim to the United States government for money.
Stark Law
A federal law that prohibits physician self-referral, specifically when referring patients to facilities in which they have a financial interest, to prevent conflicts of interest and protect patients from unnecessary procedures.