Astrophysics
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
mass
the amount of substance or matter that an object contains
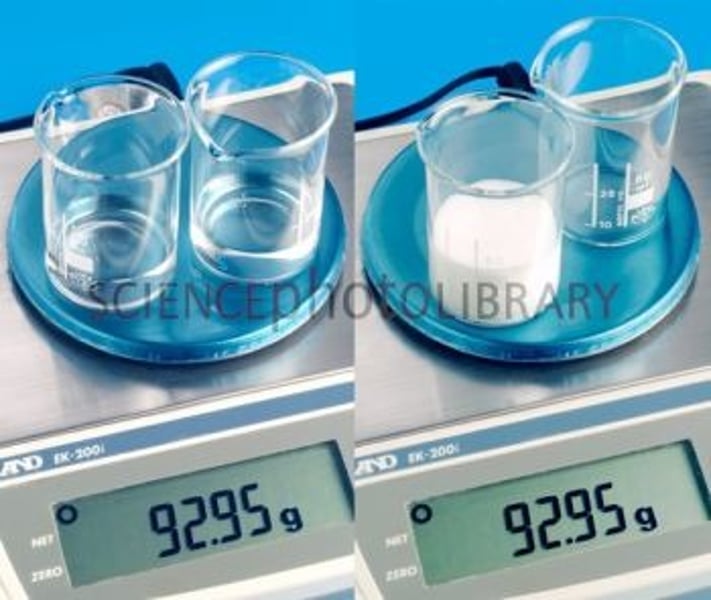

weight
the force of gravity pulling the mass of the object

formula for weight
weight, W (in N) = Mass, m (in kg) * Gravitational Field Strength, g (in N/kg)
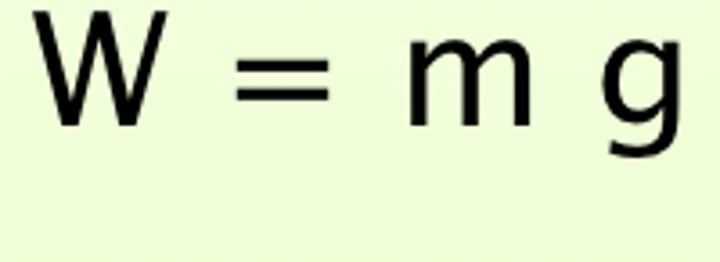
what factors may affect the gravitational field strength?
most significant - the larger the mass of a planet the greater the gravitational field strength
least significant - the larger the radius of a planet the smaller the gravitational field strength at its surface
planets in order from the sun
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
what makes the planets travel in a circular path?
gravitational forces make the planets follow curved paths; a pulling force has to be applied to make the ball travel in a circle
the size of the gravitational force depends on the:
masses of the 2 objects -> the greater the masses of the 2 objects the stronger the attractive forces between them
distance between the masses - if the distance between the masses is increased the forces between them decrease
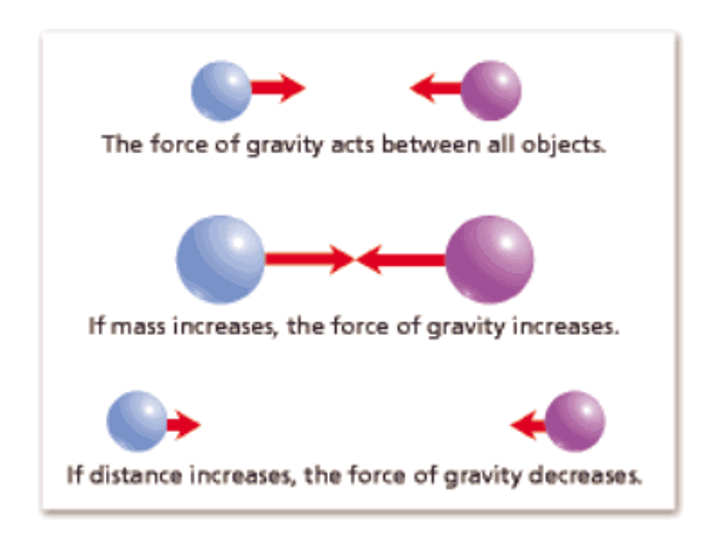
relationship between mass and force formula
m ɑ F, 2m ɑ 2F, 3m ɑ 3F
relationship between distance and force formula
d ɑ 1/F^2, 2d ɑ 1/(2F)^2, 3d ɑ 1/(3F)^2
formula for speed
speed, v (m/s) = distance, s (m)/time, t (s)
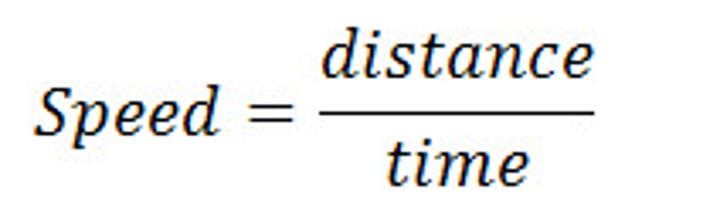
formula for orbital speed
orbital speed, v (m/s) = circumference of a circle, 2πr (m)/time period, T (s)
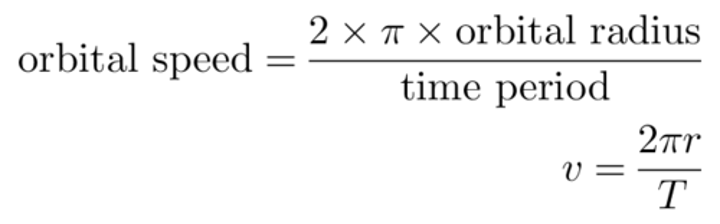
time/orbital period
the time taken for an object to complete 1 orbit
what type of quantity is weight?
vector
what type of quantity is mass?
scalar
the ... of an object never changes
the ... of an object changes by the gravitational field strength in different places
mass, weight
asteroid
a lump of solid rock and metal that orbit the sun

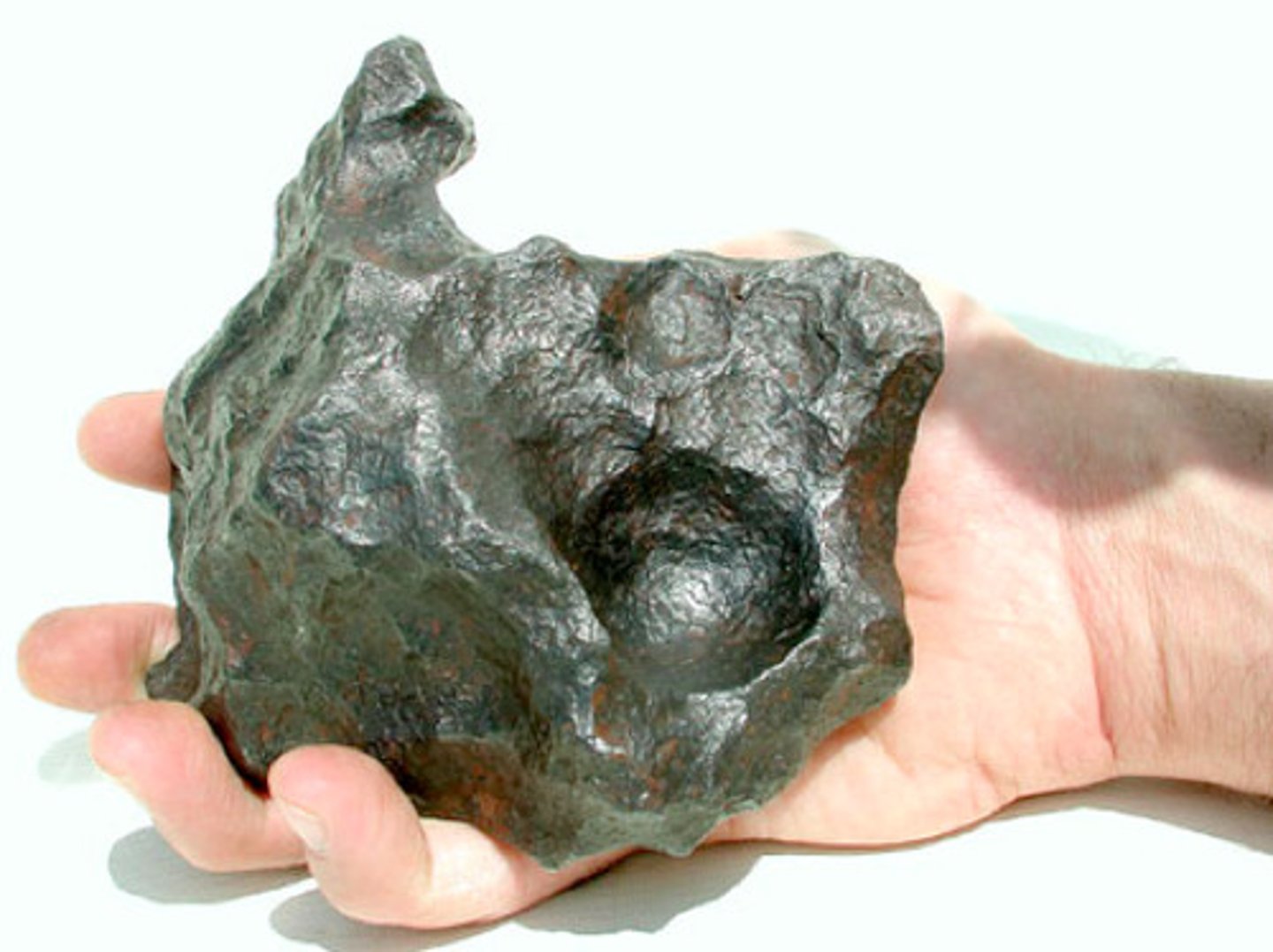
meteorite
when a meteoroid survives a trip through the atmosphere and hits the ground

meteor
when meteoroids enter Earth's atmosphere (or that of another planet, like Mars)
meteoroid
objects in space that range in size from dust grains to small asteroids

shooting star
a small, rapidly moving meteor burning up on entering the earth's atmosphere

comets
balls of dust, rocks and frozen gas

describe the orbit of a comet
highly elliptical
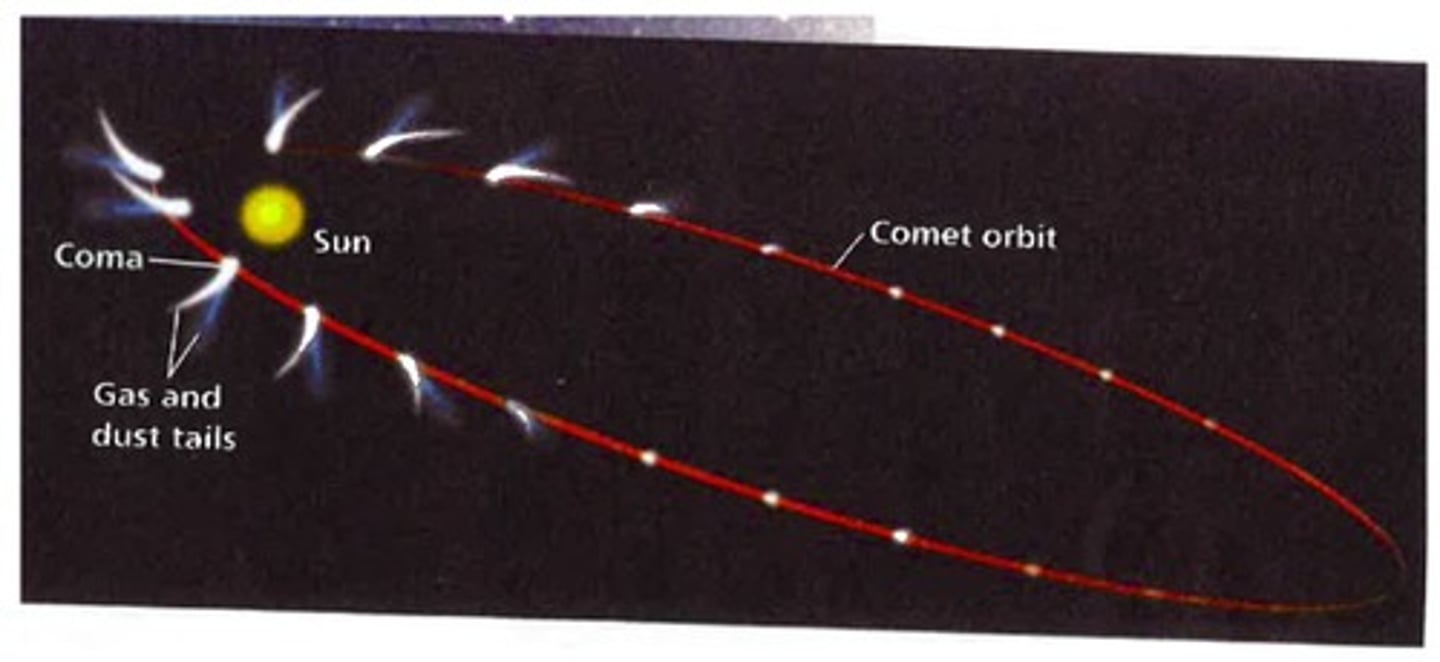
describe the speed of a comet throughout its orbit
fastest closest to the sun & slowest furthest from the sun as strongest gravitational force closes t to the sun & weakest gravitational force furthest from the sun
galaxy
the cluster of billions of stars that all orbit the same point

the milky way galaxy
the name of our galaxy, a spiral galaxy that contains about 200-400 billion stars

what do planets orbit?
sun
what does the moon orbit?
planet
what do comets orbit?
sun
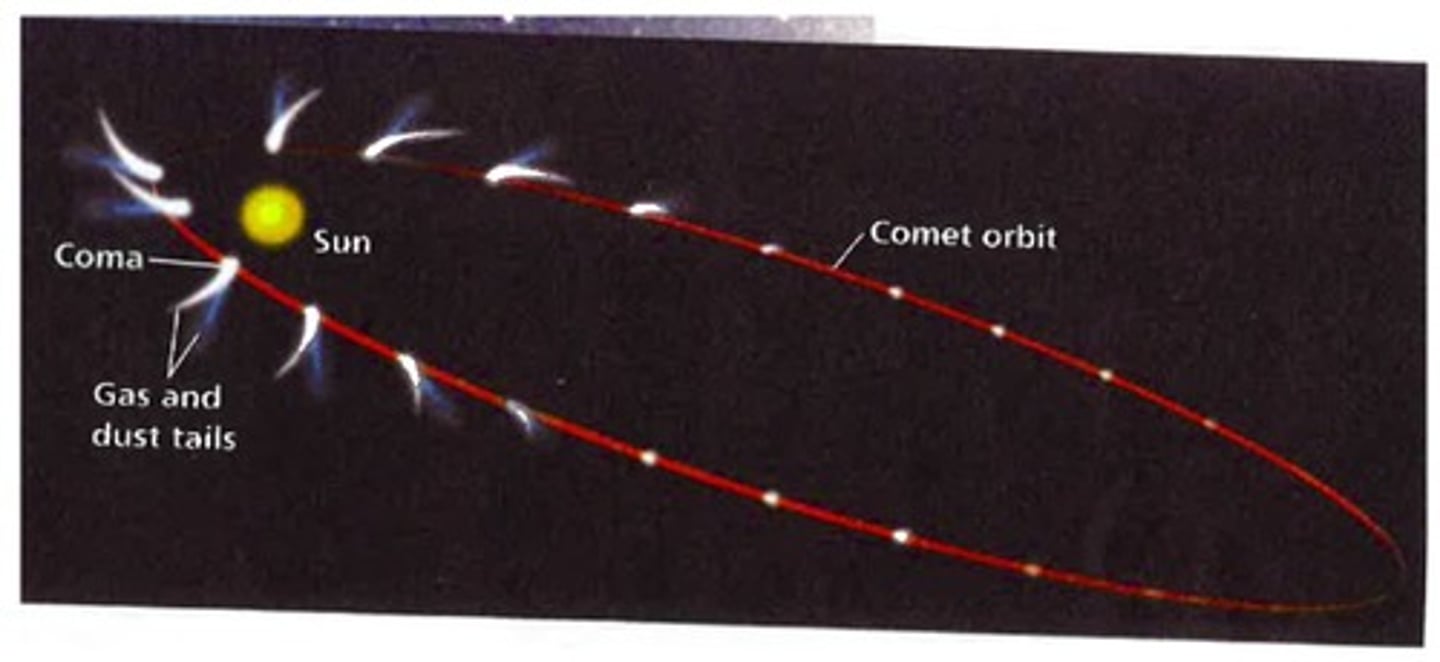
what do asteroids orbit?
sun

what do artificial satellites orbit?
any object/body in solar system
stellar evolution of solar mass stars
stellar nebula -> protostar -> main sequence star -> red giant -> white dwarf -> black dwarf
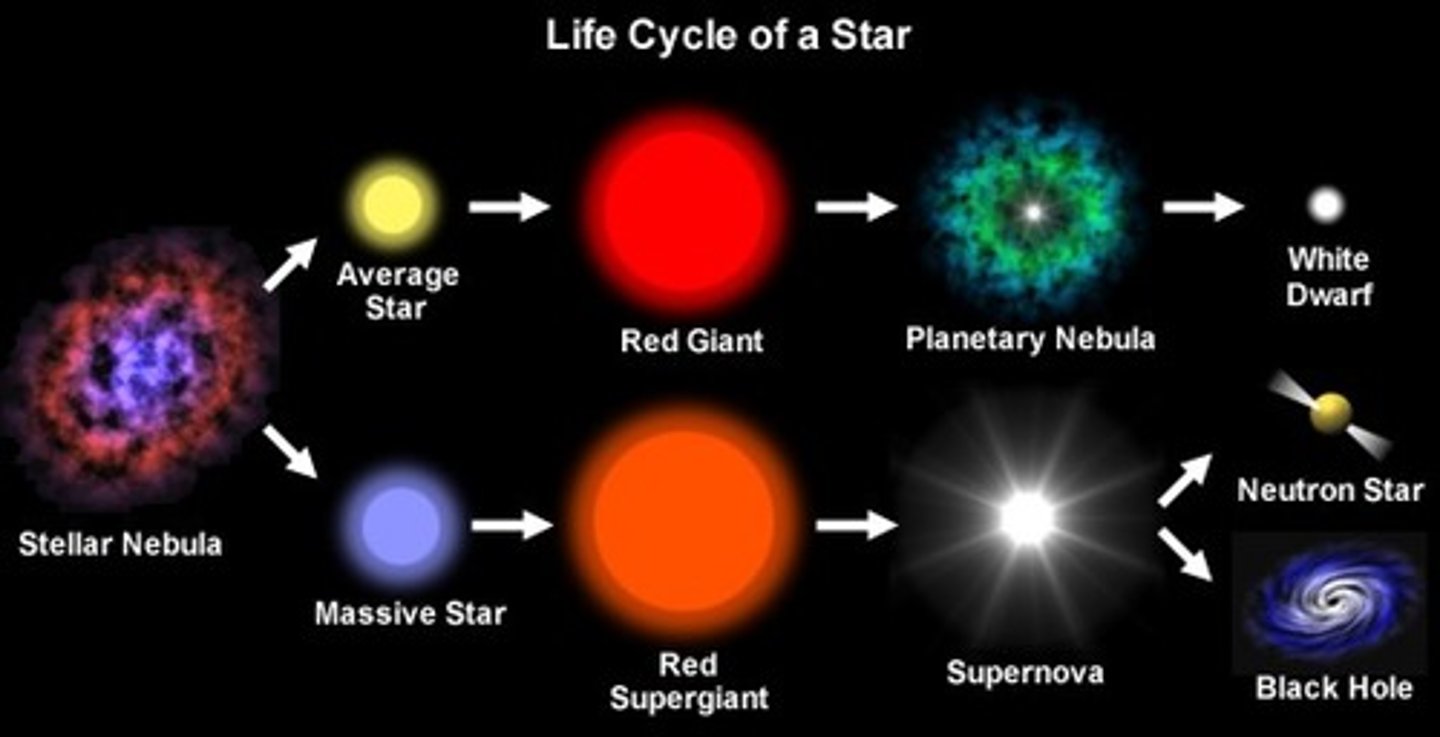
what is a nebula?
cloud of dust and hydrogen gas

what happens in the nebula stage?
1) Cloud of dust & hydrogen gas
2) Gravity pulls it together
3) Core gets denser
4) GPE is changed into thermal energy
5) Temperature and pressure increases

what happens in the protostar stage?
1) More mass is pulled together
2) Core gets even denser
3) Temperature and pressure further increases
4) Nuclear fusion starts - hydrogen fusion
5) Star begins to glow
what happens in the main sequence star stage?
1) Nuclear fusion - hydrogen nuclei fuse together to make helium nuclei
2) Outward energy pressure from heat is balanced with inward pull of gravity
3) Long stable period
what happens in the red giant stage?
1) Hydrogen runs out
2) Core collapses due to unbalance between energy pressure and gravity
3) Core temperature rises again
4) Helium fusion starts
5) Outer layers swell up
what happens in the white dwarf stage?
1) Fusion slowly stops
2) Star ejects outer layer of dust and gas as a planetary nebula
3) Core collapses due to gravity

what happens in the black dwarf stage?
1) Hot dense core left behind
2) No fusion
3) Star cools and fades away
4) Turns into black dwarf

what happens in the red super giant stage?
1) Hydrogen runs out
2) Core collapses due to unbalance between pressure and gravity
3) Outer layers swell up and cool
4) Helium fusion starts
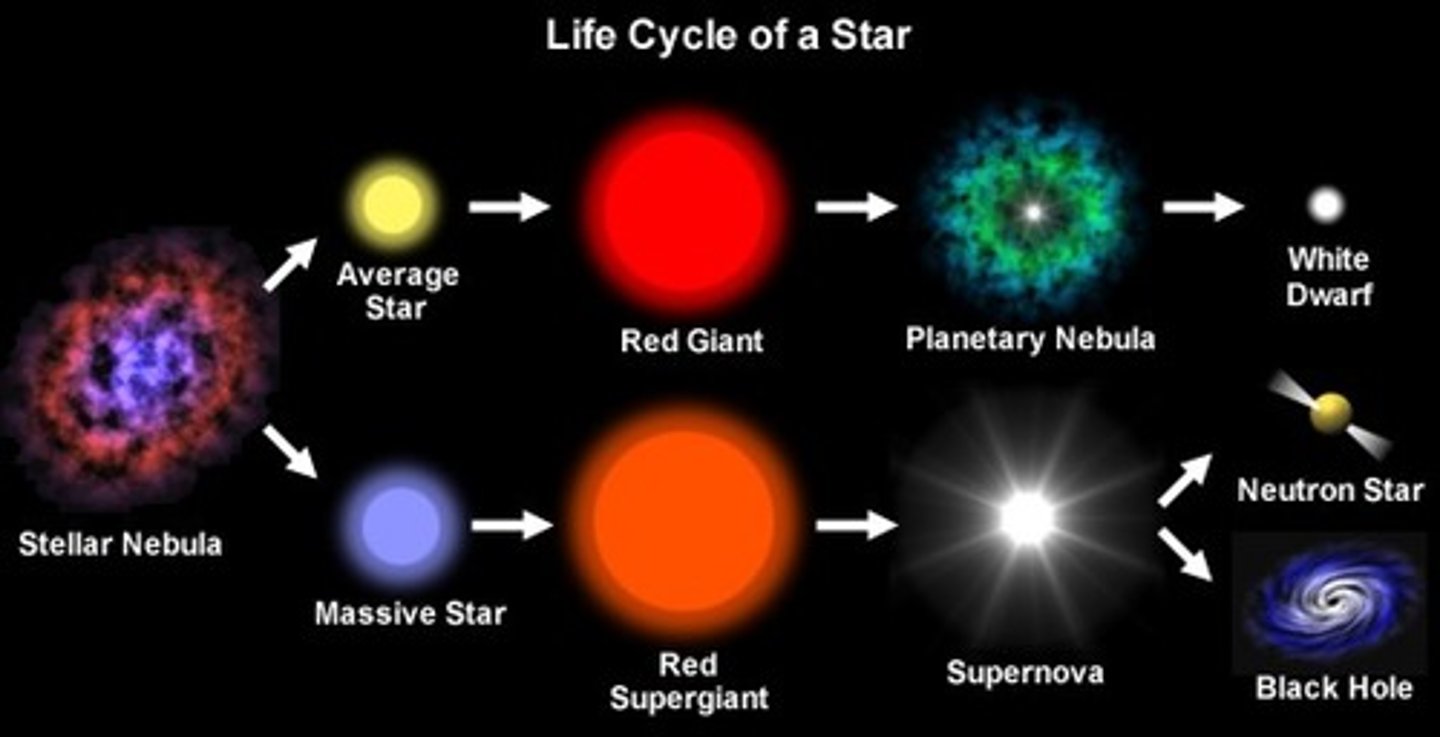
what happens in the supernova stage?
1) Expands and contracts several times
2) Heavier elements form
3) Star explodes
4) Ejects outer layer of dust and gas into space
what happens in the black hole stage?
1) If the core massive enough x4 of our sun
2) Gravity collapses it into a black hole
3) No wave or matter escapes from its gravity
elements in red super giant from outermost to innermost
hydrogen -> helium -> carbon, oxygen -> Si, S -> iron
colour of stars relative to surface temperature
-a v. hot star emits more blue in its spectrum and therefore looks blue
-a medium star like our Sun looks yellow
-cooler stars appear red
what are the different classes of stars from hottest to coolest
Oh, Be, A, Fine, Girl/guy, Kiss, Me
astronomical objects cool as they ... and heat up as they ...
expand, contract
the brightness of a star depends on
1. the distance the star is from earth
2. what the star is made from and the kinds of nuclear reactions that are taking place / how much light the star emits

what are the 3 different ways in which astronomers describe the brightness of a star
-the apparent brightness/magnitude of a star
-the absolute brightness/magnitude
-the luminosity of a star
the luminosity of a star
a measure of how much energy in the form of light is emitted from a star's surface every second
the absolute brightness/magnitude
a measure of how bright stars would appear if they were placed at the same distance away from the Earth (standard distance = 10 parsecs or 32.6 light years or 3.04*10^14 km)
the apparent brightness/magnitude of a star
a measure of how bright a star is seen from earth

absolute magnitude scale
runs back to front:
-the brighter the star, the smaller the magnitude
-the dimmer the star, the larger the magnitude
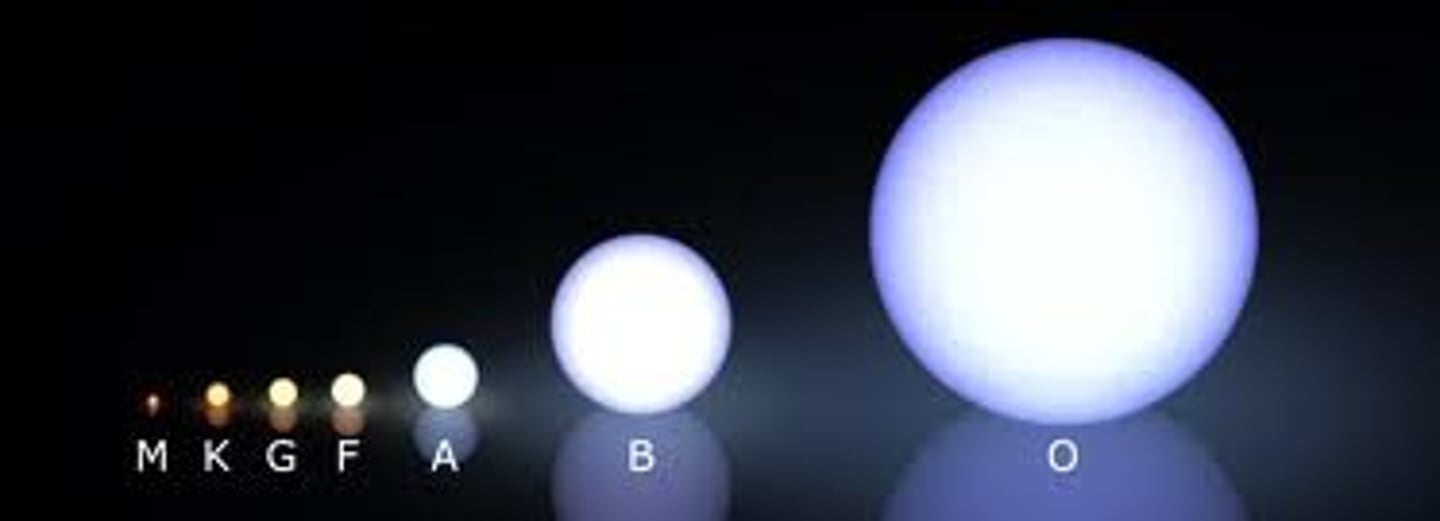

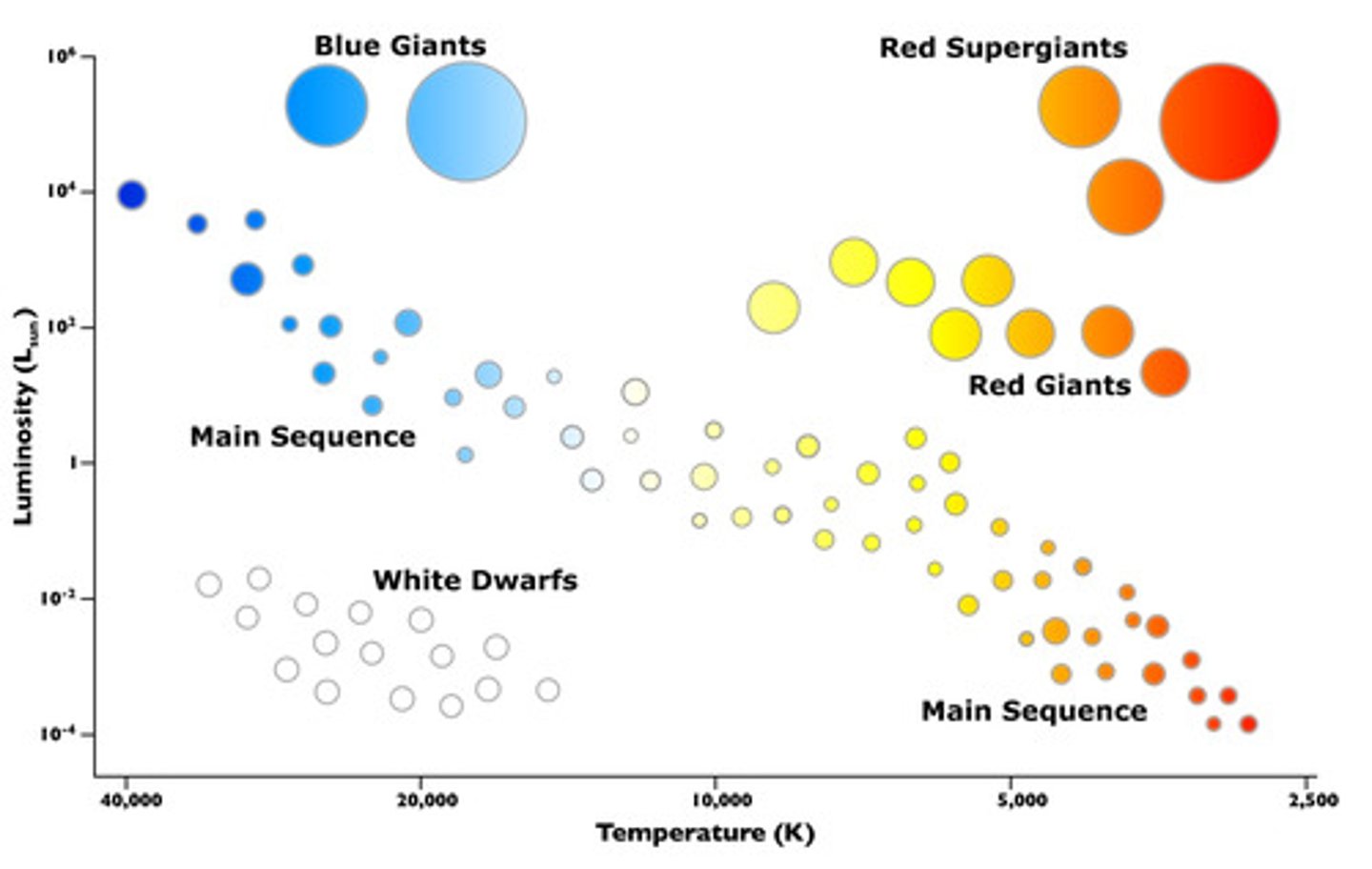
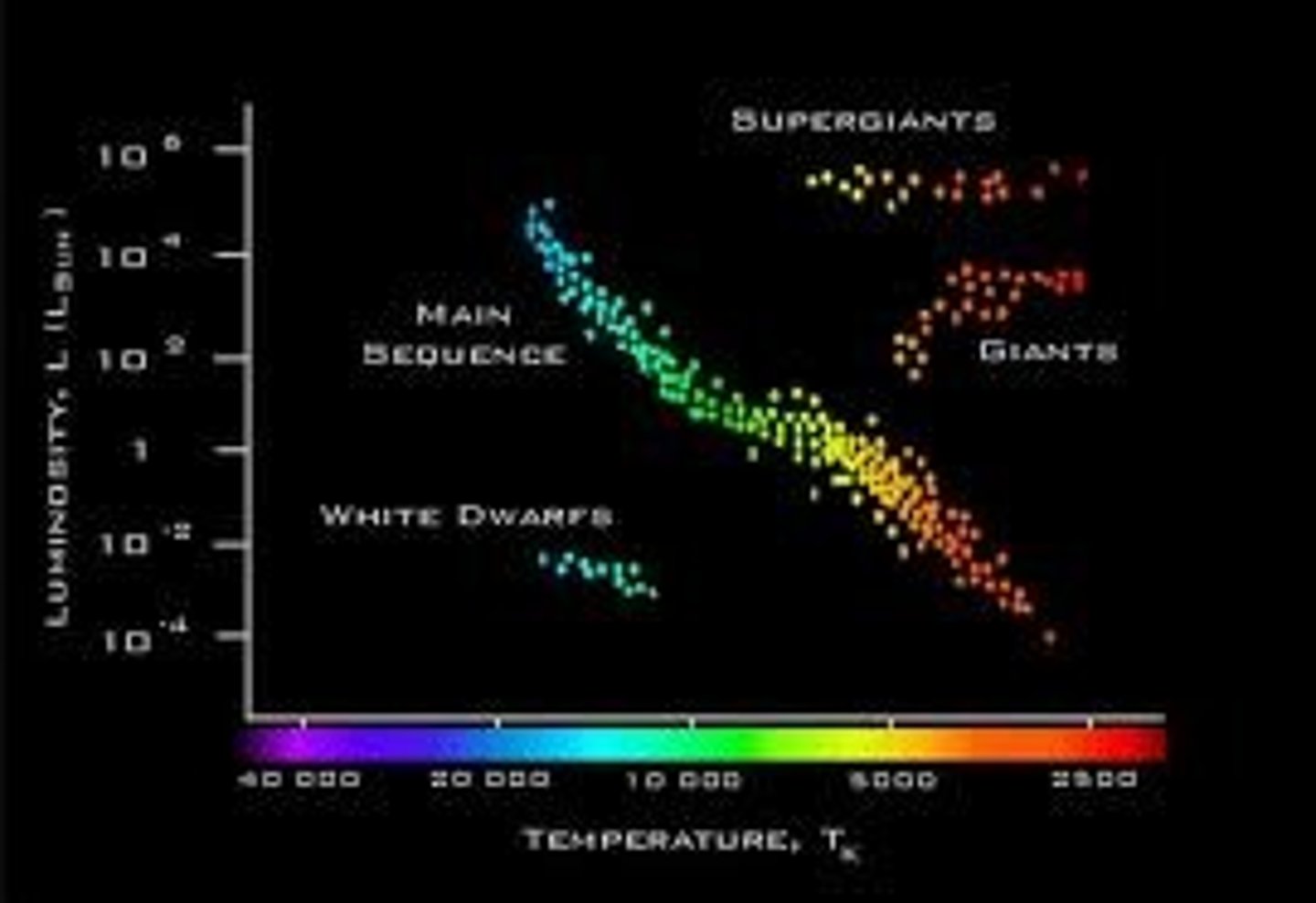
the hertzsprung-russel diagram
relationship between the brightness, and temperature of a star
spectrometry
splitting the light into its spectrum
spectrometer
a device that contains something that can split up the different wavelengths
heated filament or candle produces a ... emission spectrum
continuous
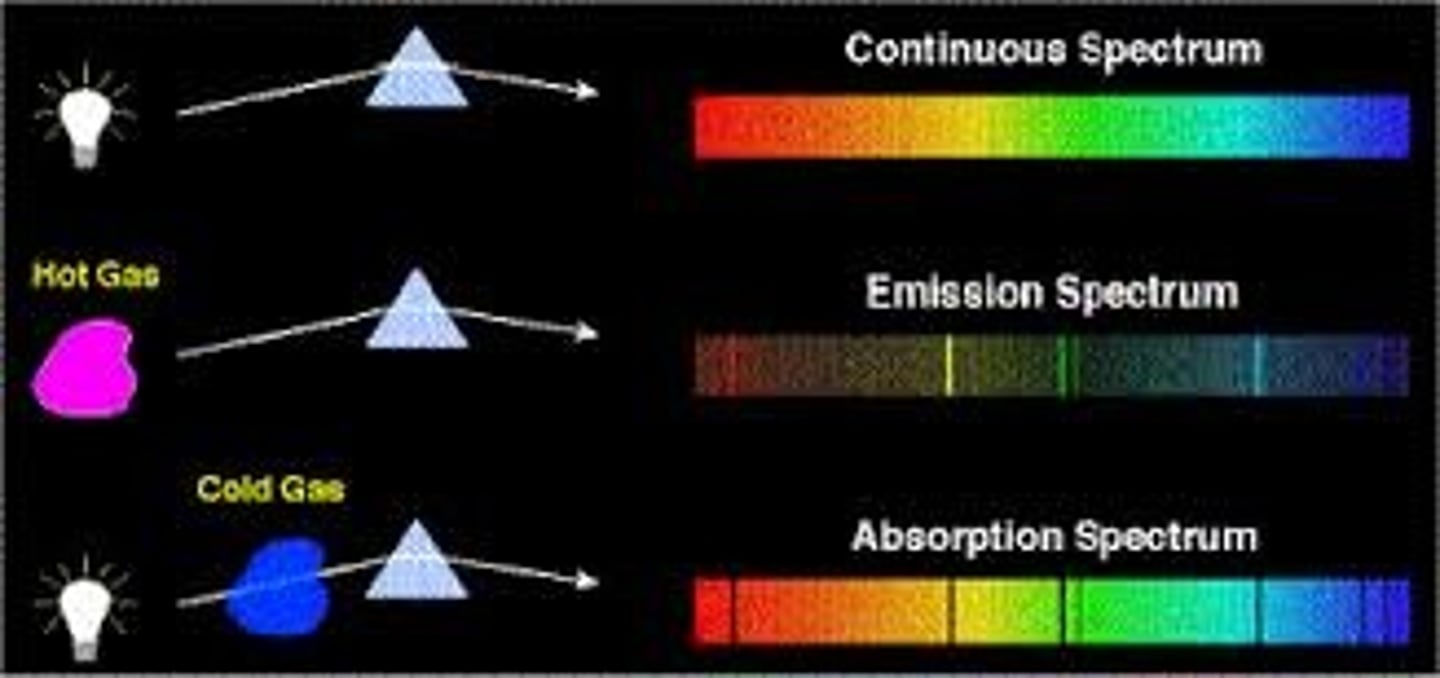
heated element/gases e.g heated hydrogen gas produce a ... emission spectrum
line

if you observe the heated filament or candle through a cool element/gas you see a ... ... spectrum
line absorption
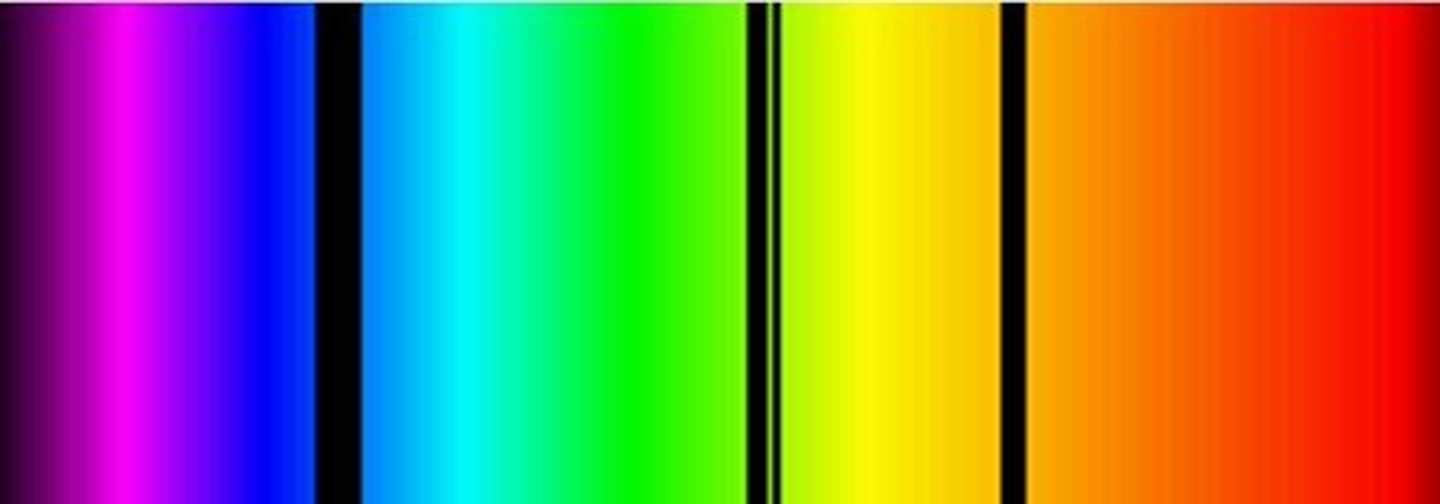
what are the dark bands?
absorption lines and are missing wavelengths (frequencies)
red shift
-the dark bands are absorption lines and are missing wavelengths
-the dark bands are shifted
-the dark bands are shifted to the red end of the spectrum
-the red end of the spectrum is the low frequency, long wavelength end
the doppler effect
the apparent change in the frequency of a sound caused by the motion of either the listener or the source of the sound
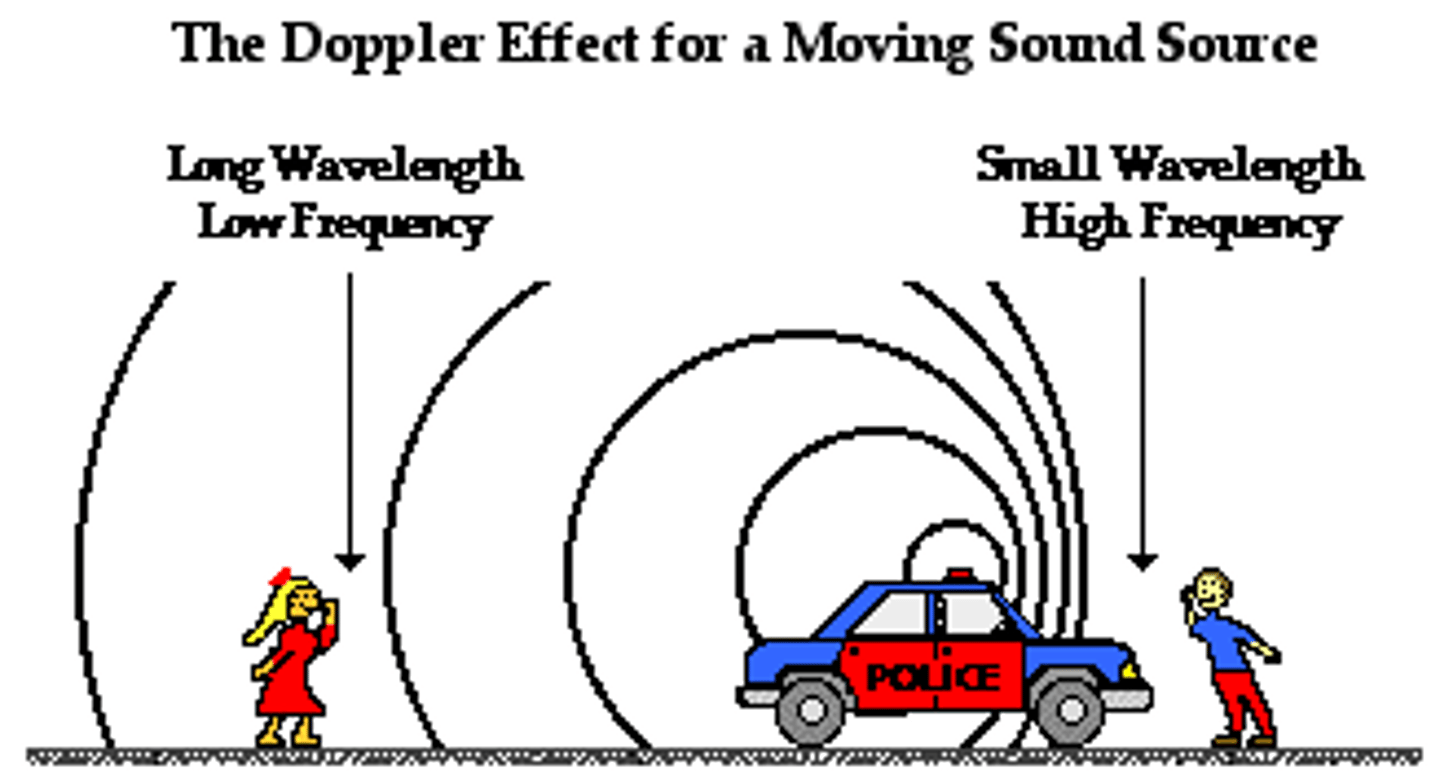
what does the red shift mean in terms of movement?
-if the dark bands are shifted to the red end of the spectrum
-which is the low frequency, long wavelength end of the spectrum
-those stars in the galaxy must be moving away from earth
the doppler equation
change in wavelength/reference wavelength = velocity of galaxy, v/speed of light, c
big bang theory
universe started 13.5 billion years ago from a single point of high density and pressure

what is the evidence of the bing bang theory?
red shift & CMBR
what is an orbit?
curved path of one celestial object/spacecraft around another celestial object
how long does a main sequence star last?
until all of the hydrogen is used up which could be millions/billions of years

what 2 things could form after a supernova? what determines which is formed?
if the star was large, it would condense to a neutron star
if the star was very large it would collapse to form a black hole
what is a natural satellite? give an example
a satellite that is not man-made e.g the moon

are objects in orbit accelerating? explain
objects are accelerating as their direction is constantly changing which means their velocity is changing
any change in velocity is considered acceleration
which elements undergo nuclear fusion in a main sequence star?
hydrogen nuclei fuse to make helium nuclei
which 2 forces are in balance in a main sequence star?
outward energy pressure from heat released from nuclear fusion is balanced with inward pull of gravity
what do we call a protostar was nuclear fusion starts?
a main sequence star
what 2 things could a main sequence star become once it runs out of hydrogen? what determines what it becomes?
if it is relatively small, it will become a red giant
if it is relatively large, it will become a red supergiant
are galaxies moving away from each other through space or is space itself stretching?
space & the universe itself is expanding and this makes galaxies futher apart
for a red super giant, what happens next in the star's lifecycle?
it will explode in a supernova
what happens when a nebula becomes very large?
gravity pulls the particles of dust and gas together to form a protostar
how does red shift support the big bang theory?
shows that the universe is expanding as distant galaxies show a greater red shift so all galaxies are moving away from each other
what is a neutron star?
extremely dense mass of neutrons
what is a black hole?
a region where gravity is so strong that nothing can escape
what must happen to an orbiting object's speed if the radius of its orbit decreases?
if the radius of the orbit decreases, the orbital speed must decrease for it to maintain a stable orbit
what is the solar system?
consists of the sun and the objects that orbit it
for a red giant, what happens next in the star's lifecycle?
the red giant will become a white dwarf, which will then become a black dwarf as it cools
why does your weight vary across planets?
-your weight is dependant on g, since weight = mass x g
-the gravitational field strength (g) of a planet varies depending on the size of the planet
-this means that your weight will also vary
which stage is the sun currently in?
main sequence
formula for wave speed
wavelength x frequency
blue shift
when an objects is travelling towards the earth, wavelength of the light emitted by the object decreases therefore it shifts towards the blue end of the visible light spectrum
describe red shift
when an objects is travelling away from the earth, wavelength of the light emitted by the object increases therefore it shifts towards the red end of the visible light spectrum
how does CMBR support the Big Bang theory?
CMBR that comes from all directions in space. it is the leftover thermal energy from the big bang
stars can be classified in HR diagram. what do the axes of the HR diagrams represent?
x axis: decreasing temp.
y axis: absolute magnitude/luminousity