g. 2nd/3rd Tri Path P3
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
asymmetric IUGR is most commonly caused by
.
symmetric IUGR is most commonly caused by
.
a) gestational diabetes, diabetes mellitus
b) paravovirus, gestational diabetes
c) placental insufficiency, chromosomal anomalies
d) maternal smoking, maternal alcoholism
c) placental insufficiency, chromosomal anomalies

what cardiac defect is most common in ellis van creveld syndrome
a) VSD
b) transposition of great arteries
c) ASD
d) truncus arteriosus
c) ASD

polyhydramnios is an expected finding w/
.
causes a narrowed fetal thoracic cage —> impairs fetal swallowing —> reduces amniotic fluid absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
.
a) skeletal dysplasia
b) premature rupture of membranes
c) IUGR
d) potter syndrome
a) skeletal dysplasia

a cisterna magna that measures greater than 10mm is a common finding w/
a) renal agenesis + omphalocele
b) spina bifida + anencephaly
c) cerebellar agenesis + dandy walker malformation
d) acrania + anencephaly
c) cerebellar agenesis + dandy walker malformation

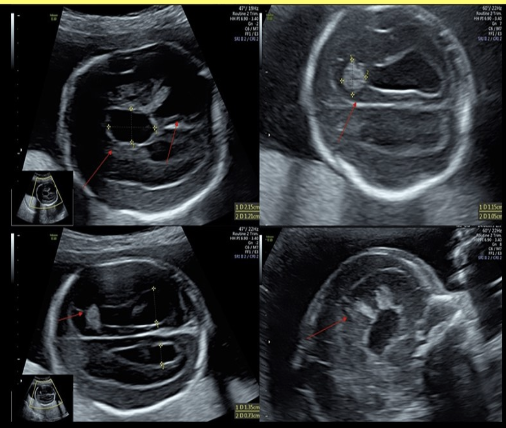
which describes the early appearance of intracranial hemorrhage in a fetus?
.
blood first appears as
.
a) anechoic fluid
b) hypoechoic fluid
c) hyperechoic fluid
d) complex cystic area of fluid
c) hyperechoic fluid
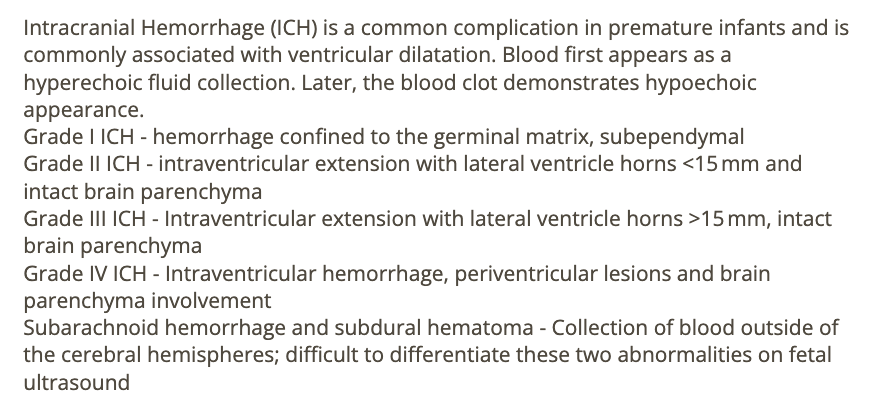
in the 2nd trimester, a nuchal skinfold >6mm and absent/hypoplastic nasal bone are the sono markers most specifically assoc w/
a) triploidy
b) trisomy 13
c) trisomy 18
d) trisomy 21
d) trisomy 21
a dilated 3rd ventricle, colpocephaly + sunburst sign in cerebral tissue are findings of
.
a) dandy walker cyst
b) schizencephaly
c) agenesis of cerebellar vermis
d) agenesis of corpus callosum
d) agenesis of corpus callosum

which skeletal dysplasia only affect one side of the body
a) asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia
b) cleidocranial dysplasia
c) CHILD syndrome [Congenital Hemidysplasia with Ichthyosiform Erythroderma and limb defect]
d) achondroplasia
c) CHILD syndrome

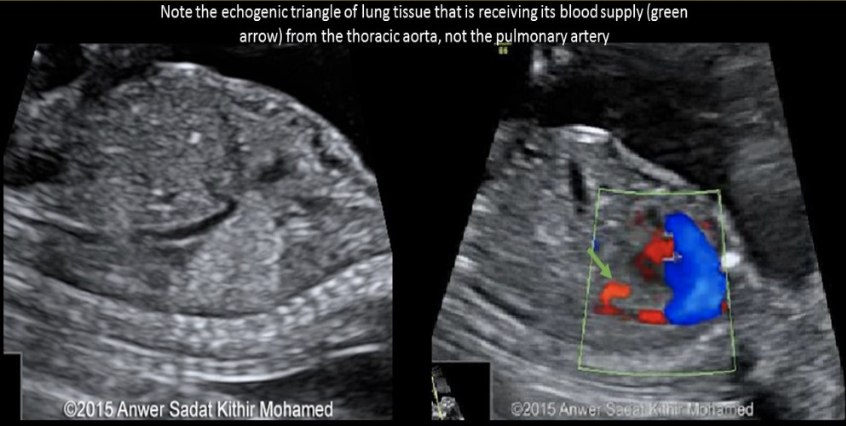
how is pulmonary sequestration differentiated from other chest masses
a) the only hyperechoic fetal chest mass
b) the only hypoechoic fetal chest mass
c) use color doppler to confirm there is no blood supply to the mass
d) use color doppler to identify the feeding artery from the AO
d) use color doppler to identify the feeding artery from the AO
all are sono signs that fetal demise occurred more than 1w ago except
a) cullen sign [ruptured ectopic]
b) spalding sign [suture overlap on skull]
c) robert sign [air in circulatory]
d) deuel sign [scalp edema]
a) cullen sign

renal agenesis can be ruled out w/
a) linear adrenal glands adjacent to the spine
b) pulmonary hypoplasia
c) urinary bladder that fills + empties every 30-45 minutes
d) small fetal stomach
c) urinary bladder that fills + empties every 30-45 minutes

all are potential adverse complications of an intrauterine device except
a) perforation of the myometrium
b) ecoptic pregnancy
c) PID
d) infertility
d) infertility
absent cavum septum pellucidum + septop-optic dysplasia are common findings in
.
a) dandy walker malformation + lissencephaly
b) cerebellar agenesis + dandy walker malformation
c) holoprosencephaly + schizencephaly
d) holoprosencephaly + dandy walker malformation
.
septo-optic dysplasia = mild form of lobar holoprosencephaly
* absent cavum septum pellucidum + optic nerve hypoplasia
c) holoprosencephaly + schizencephaly
which is a complication of severe hematometrocolpos
a) endometritis
b) hydronephrosis
c) menometrorrhagia
d) cervical stenosis
b) hydronephrosis

the US for a 20w fetus shows an
absent nasal bone
shortened femur + humerus
hypoplasia of middle phalanx of 5th digit
frontal bossing.
.
this shows trisomy
.
a) 9
b) 18
c) 21
d) 13
c) 21

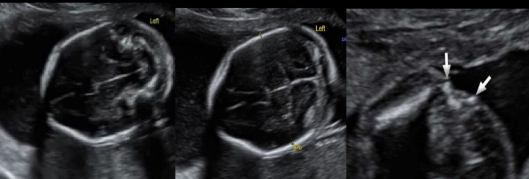
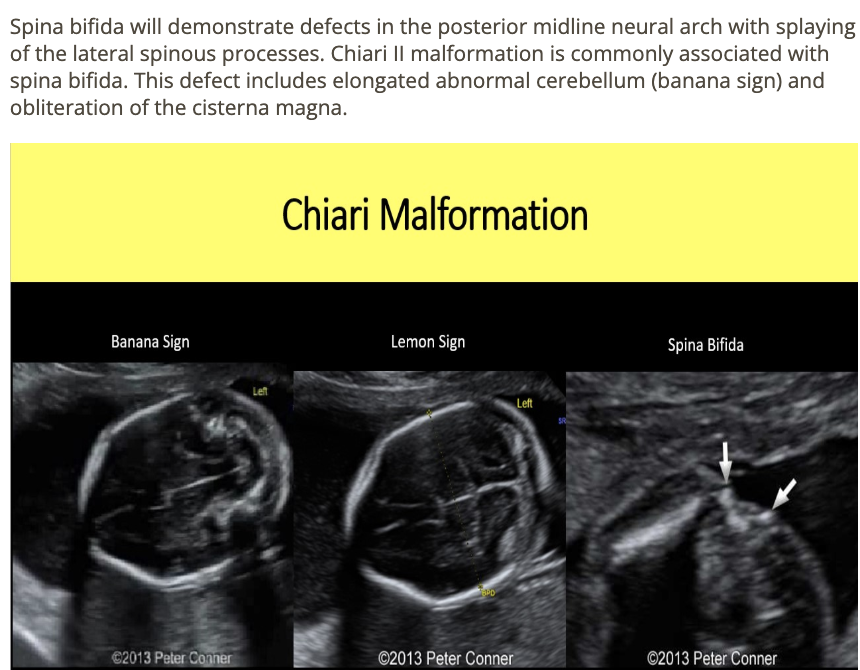
splaying of lateral spinous process + abn cerebellum indicates
a) holoprosencephaly
b) spina bifida
c) ellis van creveld syndrome
d) thanatophoric dysplasia
b) spina bifida
a cephalic index of 70% in a 28w fetus indicates
a) dolichocephaly
b) brachycephaly
c) micrognathia
d) macroglossia
a) dolichocephaly

all are related to premature ossification of the cranial sutures except
a) osteogenesis imperfecta
b) clover leaf skull
c) craniosynostosis
d) strawberry skull
a) osteogenesis imperfecta

which is not a teratogen
. drug, chemical, or physical agent causing birth defects in a developing fetus
.
a) maternal use of folic acid
b) diabetes
c) maternal use of ibuprofen
d) toxoplasmosis
a) maternal use of folic acid

fetal erythroblastosis is commonly treated by
a) fetal blood transfusion
b) antibiotics
c) periumbilical blood sampling
d) methotrexate
a) fetal blood transfusion
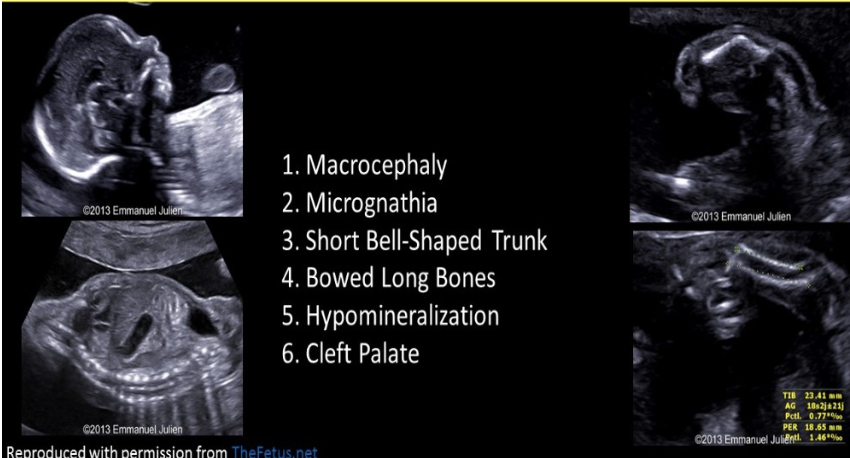
bowing of the long bones, especially the bones of the lower leg, is indicative of
.
. lethal short-limbed dwafism
.
a) ellis van creveld syndrome
b) radial ray anomalies
c) campomelic dysplasia
d) holt oram syndrome
c) campomelic dysplasia

using the 4 quadrant method, which AFI values would most likely be assoc w/spina bifida in a 27w gestation
a) 12cm
b) 8cm
c) 26cm
d) 4cm
c) 26cm

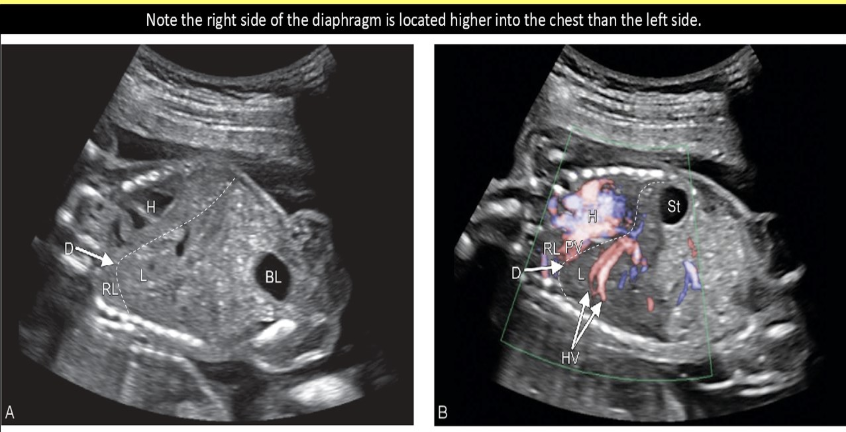
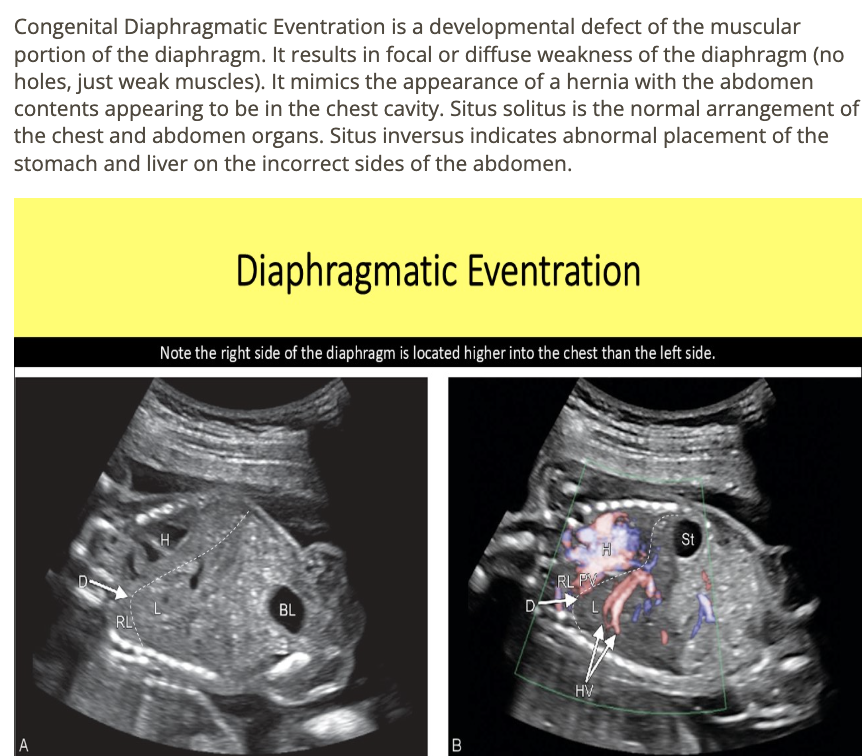
muscle weakness of the fetal diaphragm that mimic the appearance of a hernia is called
a) diaphragmatic eventration
b) hydrothorax
c) chylothorax
d) diaphragmatic
a) diaphragmatic eventration

the most common chromosomal anomaly assoc w/abn thickened nuchal fold is trisomy
a) 9
b) 13
c) 18
d) 21
d) 21
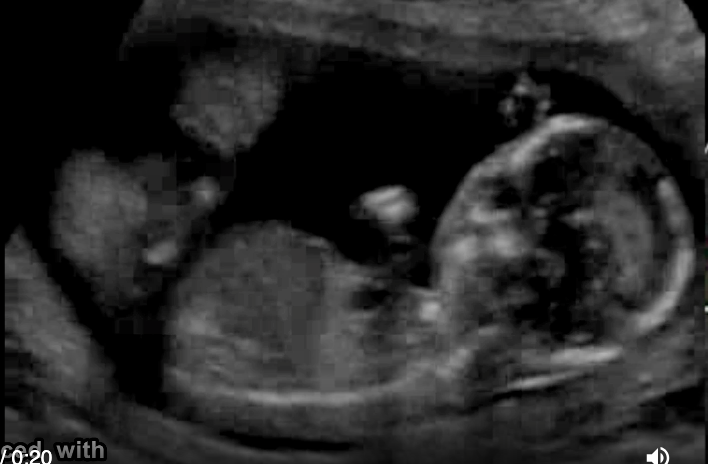
a pt has recent acute onset HTN, nausea, vomit. she has no pain, cramping, or vaginal bleeding. a prior US at 6w indicates the pregnancy should now be 17w6d GA. the image shows strong suspicion of
.
video is of trophoblastic gestation/molar - most fetuses have asymmetrical large head + small body
.
a) trisomy 21
b) triploidy
c) trisomy 13
d) trisomy 18
b) triploidy

if the calvarium is not seen in a 16w fetus, ____ should be suspected
a) noonan syndrome
b) osteogenesis imperfecta
c) thanatophoric dysplasia
d) acrania
d) acrania

![<p>which fetal abn <strong>mimics</strong> the sono appearance of <strong>diaphragmatic hernia</strong></p><p>.</p><p>a) situs inversus</p><p>b) situs solitus</p><p>c) duodenal atresia</p><p>d) [diaphragmatic] eventration</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fb09b330-9246-4c19-aca1-23f15e204620.png)
which fetal abn mimics the sono appearance of diaphragmatic hernia
.
a) situs inversus
b) situs solitus
c) duodenal atresia
d) [diaphragmatic] eventration
d) eventration
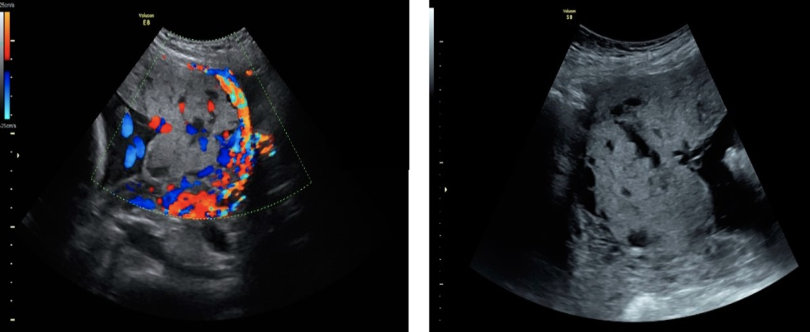
![<p>the most common <strong>cause</strong> of <strong>pleural effusion </strong>in a fetus is</p><p>.</p><p>a) <strong>chylothorax</strong> [fluid accumulation in the fetal chest (pleural effusion) that compresses the lungs]</p><p>b) fetal heart failure</p><p>c) polyhydramnios</p><p>d) maternal heart failure</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b07ad15e-439c-4726-a186-bdecc93d2389.png)
the most common cause of pleural effusion in a fetus is
.
a) chylothorax [fluid accumulation in the fetal chest (pleural effusion) that compresses the lungs]
b) fetal heart failure
c) polyhydramnios
d) maternal heart failure
a) chylothorax
which shows as hypoechoic areas within the placenta that display turbulent flow on color doppler
.
a) infarction
b) placenta accreta
c) fibrin deposition
d) venous lake
b) placenta accreta

which is considered a normal cervix
a) membranes bulging into the cervical canal
b) 3cm dilation at 28w
c) 2cm length at 28w
d) pt w/cerclage in place
d) pt w/cerclage in place

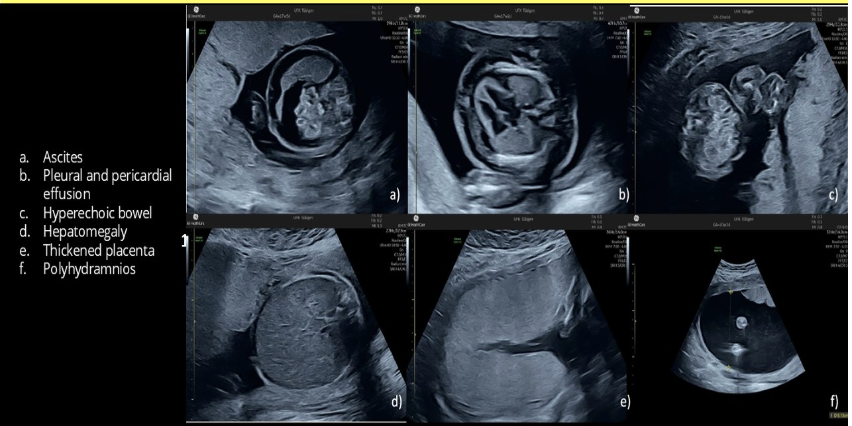
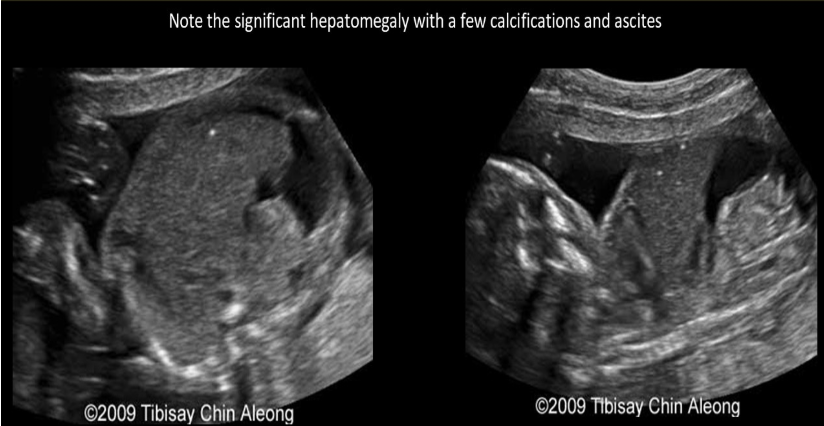
which is most likely to cause polyhydramnios, fetal ascites, and hepatomegaly
.
a) parvovirus infection
b) IUGR
c) potter syndrome
d) autosomal recessive PKD
a) parvovirus infection

lethal skeletal dysplasia typically has a FL/AC ratio
a) >0.50
b) <0.50
c) <0.16
d) <0.77
c) <0.16
![<p>there are several cysts in the left lung that measure <strong>2-4 cm</strong>. this is</p><p>.</p><p>macrocystic = 1</p><p>medium cystic</p><p>microcystic = 3 [<0.5cm]</p><p>.</p><p>a) type 2 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation</p><p>b) bronchogenic cyst</p><p>c) type 1 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation</p><p>d) type 3 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/87b3c7ec-be37-4060-a91c-504c6868bc58.png)
there are several cysts in the left lung that measure 2-4 cm. this is
.
macrocystic = 1
medium cystic
microcystic = 3 [<0.5cm]
.
a) type 2 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
b) bronchogenic cyst
c) type 1 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
d) type 3 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
c) type 1 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation

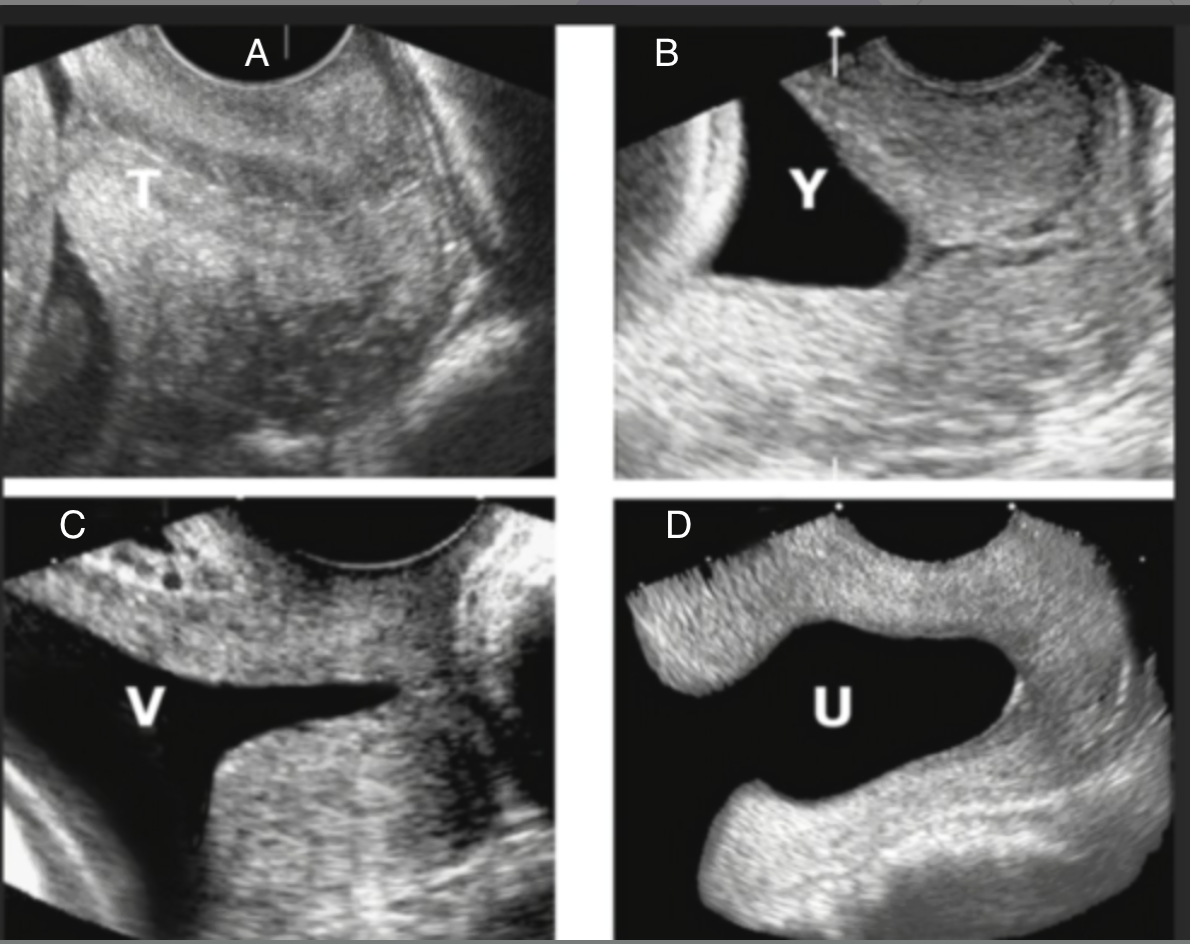
which shows funneling of the cervix
a) C + D
b) A + B
c) D only
d) B, C, D
d) B, C, D

oligohydramnios is commonly seen w/
a) pulmonary hypoplasia
b) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
c) cystic hygroma
d) holoprosencephaly
a) pulmonary hypoplasia

macrocephaly is seen w/
a) BPD + HC are 2+ standard deviations above average for GA
b) cranial volume greater than 95th percentile
c) cranial volume greater than 90th percentile
d) BPD + HC are 3+ standard deviations above average for GA
a) BPD + HC are 2+ standard deviations above average for GA
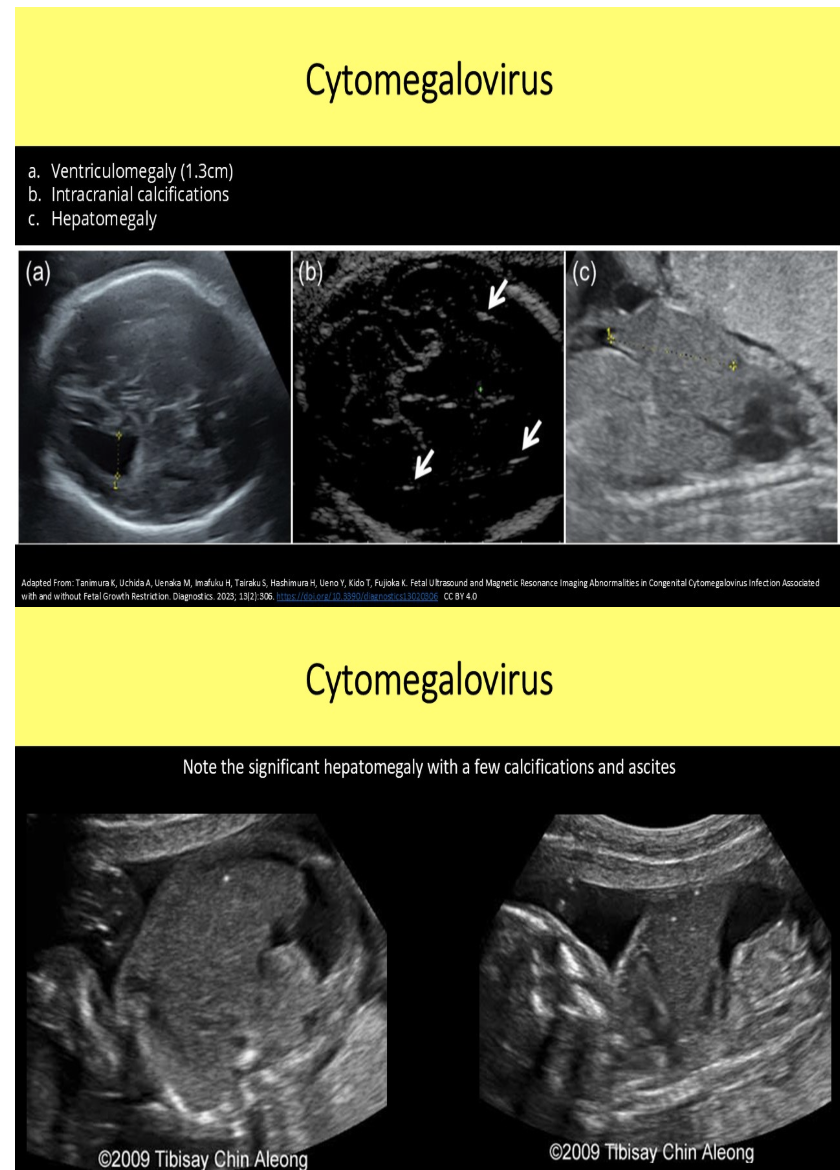
multiple small calcifications are seen in the fetal liver + brain. mild ventriculomegaly is also noted. which is the most likely cause
a) air in the fetal vessel
b) trisomy 13
c) cytomegalovirus infection
d) atherosclerosis in the fetal vessels
c) cytomegalovirus infection
IUGR identified in early 2nd trimester is typically assoc w/
.
IUGR identified in the 3rd trimester is typically assoc w/
.
a) chromosomal abn, maternal factors
b) maternal factors, chromosomal abn
c) maternal alcohol abuse, maternal diabetes
d) maternal smoking, maternal diabetes
a) chromosomal abn, maternal factors

a pt has a 9 cm fibroid that is causing compression of UT cavity that could lead to fetal growth issues. if surgical intervention is performed to remove the fibroid, at what point in the pregnancy is it recommended for the best outcome
a) <12w
b) 12-14w
c) 16-20w
d) >25w
c) 16-20w
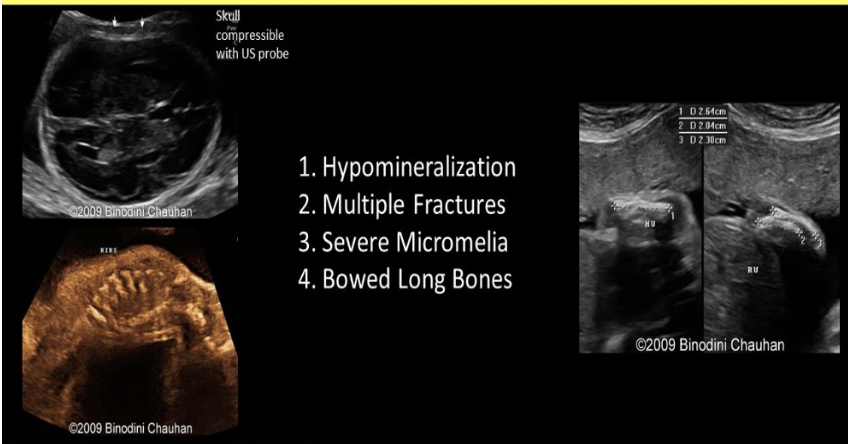
which refers to hypophosphatasia
.
a) congenital bowel defect that causes abn filtration of phosphates + polyhydramnios
b) congenital kidney defect that causes abn filtration of phosphates + polyhydramnios
c) increased echogenicity w/excessive posterior shadowing from skull + long bones
d) poor skull ossification leads to increased echogenicity of the falx cerebri
d) poor skull ossification leads to increased echogenicity of the falx cerebri

in most cases, unilateral renal agenesis will show
a) normal AFI + fetal bladder
b) oligohydramnios + fetal bladder
c) polyhydramnios + no fetal bladder
d) oligohydramnios + no fetal bladder
a) normal AFI + fetal bladder

what is the most common cerebral finding w/cytomegalovirus
a) macrocephaly
b) cerebellar hyperplasia
c) exaggerated clefting of the cerebral tissue
d) hyperechoic periventricular halo + septations within occipital horns
d) hyperechoic periventricular halo + septations within occipital horns

it is most important to establish fetal gender when evaluating a fetus for suspected
a) spinal defects
b) urinary tract defects
c) cardiac defects
d) digestive system defects
b) urinary tract defects

how can you differentiate a ureterocele from obstruction of the ureteropelvic junction of the kidney
a) the ureter will be dilated w/UPJ obstruction but not with a ureterocele
b) the ureter will be dilated w/a ureterocele but not with a UPJ obstruction
c) a ureterocele causes hydronephrosis of the upper pole of the kidney while hydronephrosis of the lower pole is identified w/UPJ obstruction
d) severe hydronephrosis occurs w/ureterocele but only mild hydronephrosis occurs w/UPJ obstruction
b) the ureter will be dilated w/a ureterocele but not with a UPJ obstruction

when evaluating a fetus w/alobar holoprosencephaly,
.
you identify a proboscis + a single midly enlarged, anechoic orbital cavity. what is the term for the ocular abn
.
a) cyclopia
b) epignathus
c) encephalocele
d) arhinia
a) cyclopia

a pt has a 3rd trimester scan following a recent shirodkar procedure. which describes the findings if the procedure was a success
a) fetus is now in the vertex position after a recent scan showed a footling breech presentation
b) reduced amniotic fluid volume
c) echogenic linear reflection at the cervix preventing funneling of membranes
d) fetus is now in the vertex position after a recent scan showed a frank breech presentation
c) echogenic linear reflection at the cervix preventing funneling of membranes

![<p><strong>cleidocranial dysplasia</strong> is an autosomal <strong>dominant</strong> condition characterized by</p><p>a) lack of formation of the ribs + vertebral processes</p><p>b) lack of formation of the long bones</p><p>c) clavicular aplasia or hypoplasia [short, straight]</p><p>d) cloverleaf skull + cleft palate</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/610e671e-7a55-454f-95c0-57a3e1127b7a.png)
cleidocranial dysplasia is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by
a) lack of formation of the ribs + vertebral processes
b) lack of formation of the long bones
c) clavicular aplasia or hypoplasia [short, straight]
d) cloverleaf skull + cleft palate
c) clavicular aplasia or hypoplasia
_____ refers to the absence of the hands while ____ refers to absence of the feet
a) acheria, apodia
b) apodia, acheiropodia
c) hemimelia, amelia
d) acheiropodia, acheira
a) acheria, apodia

a single large vessel in the heart that receives blood from the right + left ventricles is
a) truncus arteriosus
b) total anomalous pulmonary venous return
c) normal anatomy
d) transposition of great arteries
a) truncus arteriosus

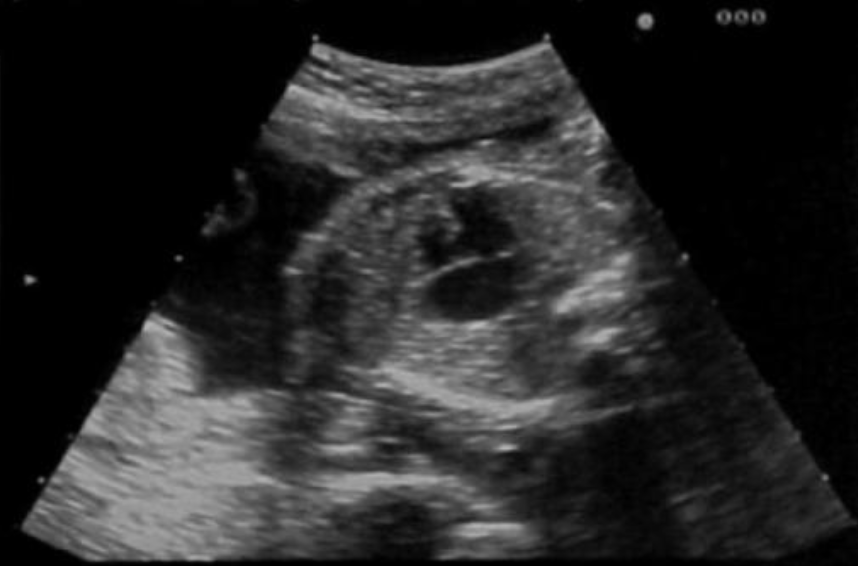
a) noonan syndrome
b) potter syndrome
c) trisomy 18
d) trisomy 21
d) trisomy 21

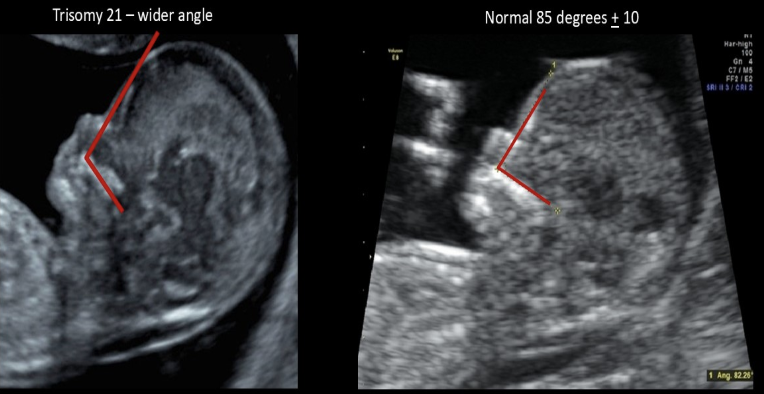
fetal frontomaxillary facial (FMF) angle
a) is larger in normal fetuses than those w/aneuploidy
b) is measured in fetuses w/suspected trisomy 21
c) is measured after birth to see the true age of the fetus
d) should be measured on a fetus w/suspected cleft palate
b) is measured in fetuses w/suspected trisomy 21

which has the highest risk of acute neonatal respiratory distress
a) retrognathia
b) microphthalmia
c) cleft lip
d) philtrum defects [mustache area]
a) retrognathia

what is the lab values of a mother w/preeclampsia
. HELLP syndrome
.
a) high platelet + decreased LFTs
b) high platelet + increased LFTs
c) low platelet + increased LFTs
d) low platelet + decreased LFTs
c) low platelet + increased LFTs

which is not an expected finding in cases of unilateral ureterocele formation
a) unilateral ureterovesicular junction obstruction
b) nonvis of the bladder
c) unilateral hydronephrosis
d) normal fetal bladder
b) nonvis of the bladder

a fetus w/ xxx is most likely
midline facial clefting
ocular abn
echogenic kidneys
microcephaly
.
a) trisomy 18
b) triploidy
c) trisomy 21
d) trisomy 13
d) trisomy 13

which is most consistent w/fetal Hirschsprung disease
a) multiple dilated bowel loops + colon segments
b) pleural + pericardial effusion
c) IUGR + calcified placenta
d) ventriculomegaly + dangling choroid plexus
a) multiple dilated bowel loops + colon segments

fetal measurements from 23w GA exam
HC 23w2d
BPD 23w
AC 26w1d
FL 23w5d
what would be the most likely cause
a) macrosomia
b) maternal syphillis
c) hydrops
d) head sparing w/asymmetric IUGR
b) maternal syphillis
which is usually assoc w/oligohydramnios
a) spina bifida
b) autosomal recessive PKD
c) thanatophoric dwarfism
d) cleft lip
b) autosomal recessive PKD


trisomy 13 is suspected
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
c) C

which is a form of dwarfism w/congenital heart defects that is considered the male version of turner syndrome
.
a) trisomy 9
b) monosomy x
c) noonan syndrome
d) shone complex
c) noonan syndrome

which is an autosomal dominant disorder strongly assoc w/defects of the mandible + palate
.
a) apert syndrome
b) holt oram syndrome
c) treacher collins syndrome
d) turner syndrome
c) treacher collins syndrome

which is commonly seen w/spina bifida occulta
a) normal AFP levels
b) open vertebral defect
c) normal vertebral bodies
d) banana sign
a) normal AFP levels

cystic dilation of the 4th ventricle, 12mm cisterna magna, and absent cerebellar vermis are most suggestive of
.
a) dandy walker malformation
b) hydranacephaly
c) lissencephaly
d) agenesis of corpus callosum
a) dandy walker malformation

a pt w/previous infant w/arthrogryposis [loss of movement in multiple joints] has a new 20w pregnancy for a level 2 evaluation
.
which describes the expected findings on today’s exam if this child also has the disorder
.
a) craniosynostosis + dysostosis
b) congestive heart failure + hydrops
c) bilateral talipes, deformed elbows, wrists, ankles, knees, and hips
d) abn curvature of the long bones
c) bilateral talipes, deformed elbows, wrists, ankles, knees, and hips
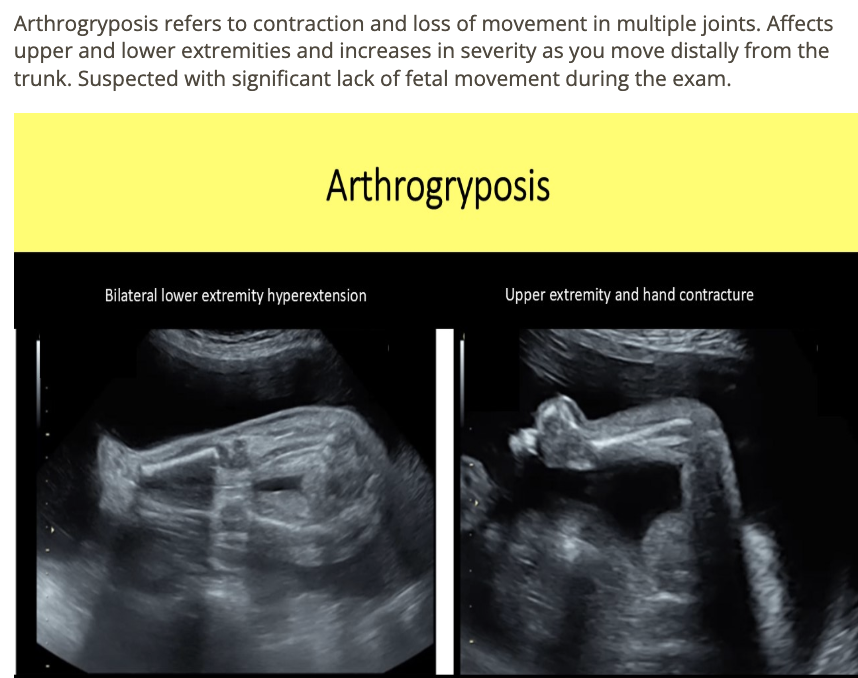
which describes an autosomal recessive disorder
a) usually skips generations
b) 1 parent has the disorder
c) if 1 parent has the disorder, there is a 50% chance of having a normal fetus
d) if 1 parent is normal, there is a 50% chance of a normal fetus
a) usually skips generations

amniocentesis screens for all except ___ levels
a) sphingomyelin
b) lecithin
c) MSAFP
d) AFAFP
c) MSAFP

if there is a normal AFI, but nonvisualization of the bladder after 30 minutes, ___ should be suspected
a) trisomy 21
b) omphalocele - extrophy - imperforate anus - spinal defect complex (OEIS)
c) bladder extrophy - epispadias complex
d) trisomy 18
c) bladder extrophy - epispadias complex

![<p><strong>colpocephaly</strong> [dilation of posterior horns of lateral ventricle] is commonly assoc w/</p><p>.</p><p>a) hydranencephaly</p><p>b) alobar holoprosencephaly</p><p>c) agenesis of corpus callosum</p><p>d) acrania</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/81b845e6-0406-410b-9a3a-3a13021f6ca5.png)
colpocephaly [dilation of posterior horns of lateral ventricle] is commonly assoc w/
.
a) hydranencephaly
b) alobar holoprosencephaly
c) agenesis of corpus callosum
d) acrania
c) agenesis of corpus callosum

oligohydramnios is commonly seen w/
a) IUGR
b) thanatophoric dysplasia
c) holoprosencephaly
d) anencephaly
a) IUGR

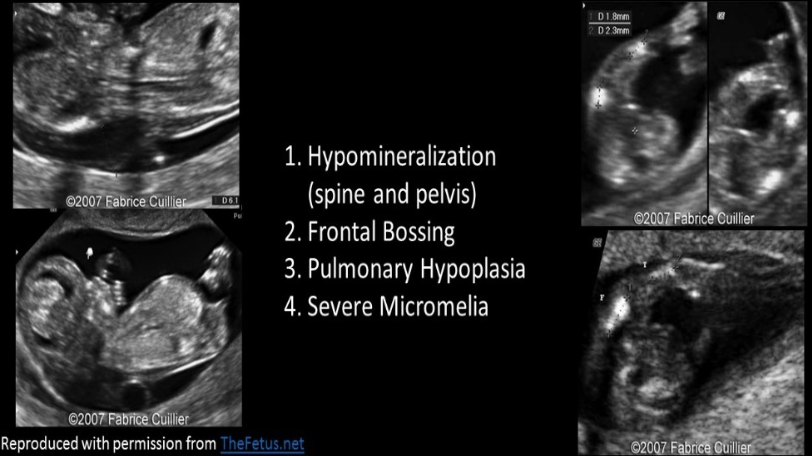
which is not expected finding in a fetus w/achondrogenesis
a) poor vertebral ossification
b) macrocrania
c) severe micromelia
d) oligohydramnios
d) oligohydramnios

placenta previa should not be dx before ___ weeks
a) 12
b) 16
c) 18
d) 14
b) 16

all describe post-partum hemorrhage except
a) defined as >1,000 mL blood loss w/c-section delivery
b) pt lab testing will show excessively high hematocrit levels
c) pt may exhibit signs of shock
d) defined as >500 mL blood bloss w/vaginal delivery
b) pt lab testing will show excessively high hematocrit levels

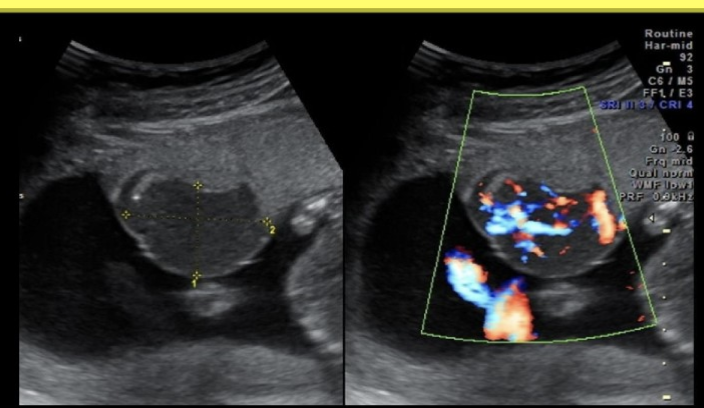
which describes a chorioangioma
.
a) mass of hypervascular placental tissue that forms separate from the placenta
b) benign ovarian mass that causes hypersecretion of testosterone
c) benign hypervascular placental mass that leads to polyhydramnios
d) triangular shaped anechoic area within the placenta
c) benign hypervascular placental mass that leads to polyhydramnios

absence of aortic valve opening is called
a) truncus arteriosus
b) aortopulmonary window
c) aortic coarctation
d) aortic atresia
d) aortic atresia

which indicates abn fetal growth in twins
.
a) 28% difference in EFW between fetuses
b) 2.4mm difference in CRL in 1st trimester
c) 400g difference in EFW between fetuses
d) EFW at the 28th percentile on singleton growth curve
a) 28% difference in EFW between fetuses

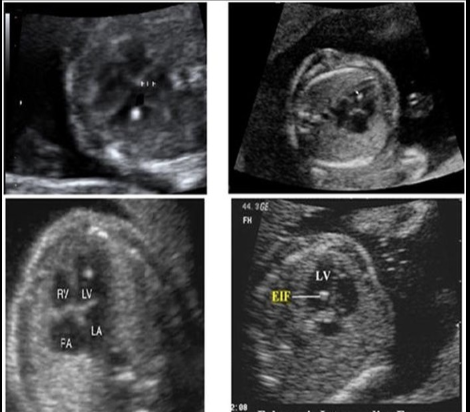
while scanning the fetal heart in the 4 chamber view,
.
.you identify an echogenic focus near the apex of the left ventricle + two more along the ventricular septum.
.
these would cause the greatest increase in suspicion for what fetal syndrome
.
a) trisomy 21
b) trisomy 18
c) trisomy 13
d) turner syndrome
a) trisomy 21

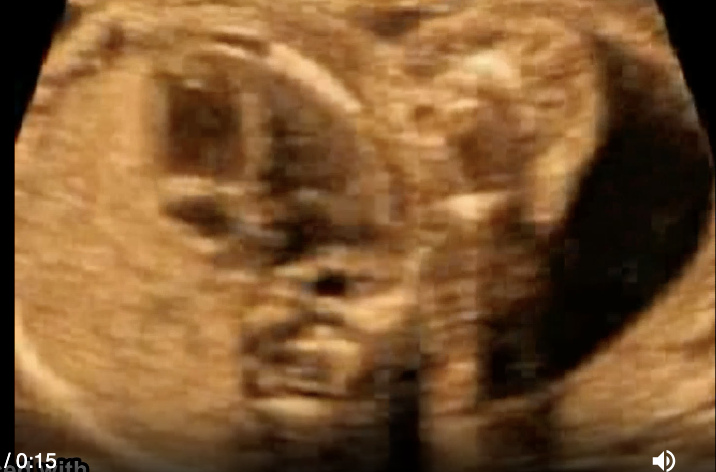
a) type 1 congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
b) diaphragmatic hernia left side
c) diaphragmatic hernia right side
d) left lung agenesis
d) left lung agenesis
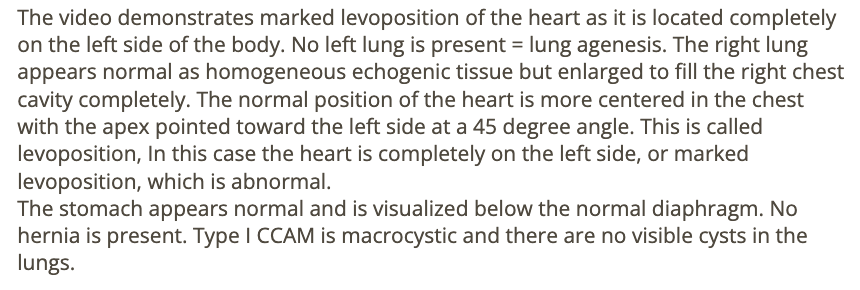
an isolated finding of cavum vergae is considered
.
. prominent posterior continuation of CSP
.
a) a sign of potential mental deficit in the fetus
b) a normal variant
c) a soft marker for trisomy 21
d) a hard marker for trisomy 21
b) a normal variant

which has the greatest potential to cause maternal hydronephrosis
a) posterior urethral valves
b) cervical stenosis
c) 9cm leiomyoma
d) oligohydramnios
c) 9cm leiomyoma

while scanning a 26w fetus, you can only identify a single thick femur positioned midline below a misshapen pelvic bone. no fetal kidneys can be identified + oligohydramnios is present
.
a) spina bifida
b) sirenomelia
c) thanatophoric dysplasia
d) heterozygous achondroplasia
b) sirenomelia

which describes the difference between porencephalic + arachnoid cyst
.
a) arachnoid cysts are in the brain tissue + communicate w/ventricular system; porencephalic cysts form between brain tissue + calvarium
b) porencephalic cysts are filled w/serous fluid; arachnoid cysts are filled w/mucous
c) arachnoid cysts only form postnatally; porencephalic cysts only form in utero
d) porencephalic cysts are in the brain tissue + communicate w/ventricular system; arachnoid cysts form between brain tissue + calvarium
d) porencephalic cysts are in the brain tissue + communicate w/ventricular system; arachnoid cysts form between brain tissue + calvarium
which describes an autosomal dominant disorder
a) 2 copies of abn non-sex chromosome must be present for the trait to develop
b) if 1 parent carry an autosomal dominant mutation, the fetus has a 50% chance of getting the malfunctioning genes from the parent + developing trait
c) commonly skips generations
d) parent does not show disorder
b) if 1 parent carry an autosomal dominant mutation, the fetus has a 50% chance of getting the malfunctioning genes from the parent + developing trait

if fractures of the femur + humerus are seen on a 23w scan, _____ should be suspected
a) arthrogryposis
b) holt oram syndrome
c) osteogenesis imperfecta
d) ellis van creveld syndrome
c) osteogenesis imperfecta

![<p>an abnormally <strong>shor</strong>t fetal <strong>neck </strong>w/<strong>fixed posterior flexion</strong> is called</p><p>.</p><p>a) lissencephaly [smooth cerebral tissue - no sulci or gyri] </p><p>b) scoliosis</p><p>c) schizencephaly [abn clefting of cerebral tissue]</p><p>d) iniencephaly</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/33d27dea-43b7-4691-ac33-45d6fb9db68c.png)
an abnormally short fetal neck w/fixed posterior flexion is called
.
a) lissencephaly [smooth cerebral tissue - no sulci or gyri]
b) scoliosis
c) schizencephaly [abn clefting of cerebral tissue]
d) iniencephaly
d) iniencephaly

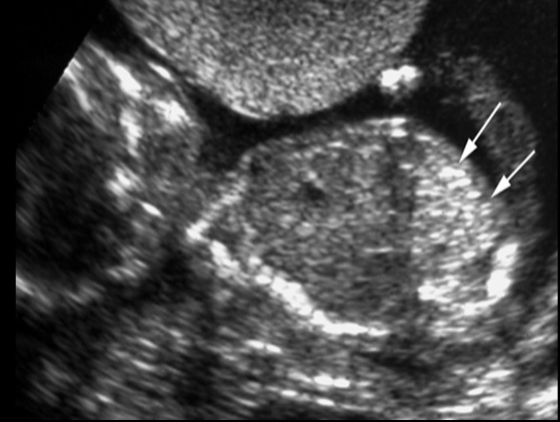
all describes echogenic bowel except
a) can be a normal variant
b) echogenic bowel causes posterior shadowing
c) bowel is increased in echogenicity similar to bone
d) unable to dx until late 2nd trimester
b) echogenic bowel causes posterior shadowing

findings of xxxx are most suggestive of
echogenic bowel
meconium peritonitis
meconium ileus
absent GB
.
a) esophageal atresia
b) cystic fibrosis
c) hirschsprung disease
d) anal atresia
b) cystic fibrosis

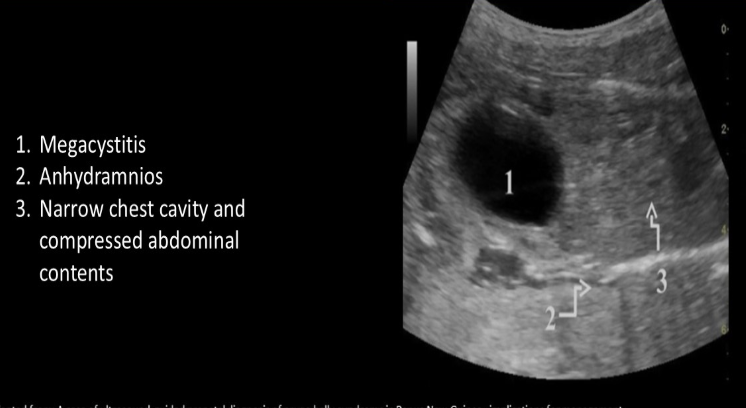
nonvisualization of fetal abd muscles, urinary tract abn, and undescended testes are classic triad of signs of ___ syndrome
a) prune belly
b) turner
c) meckel gruber
d) cornelia de lange
a) prune belly


chiari 2 malformation is strongly assoc w/
a) megacisterna magna
b) clover leaf skull
c) open spina bifida
d) closed spina bifida
c) open spina bifida
occurence of cleft palate w/normal lip is commonly assoc w/
.
a) trisomy 18
b) trisomy 13
c) pierre robin sequence
d) cornelia de lange syndrome
c) pierre robin sequence

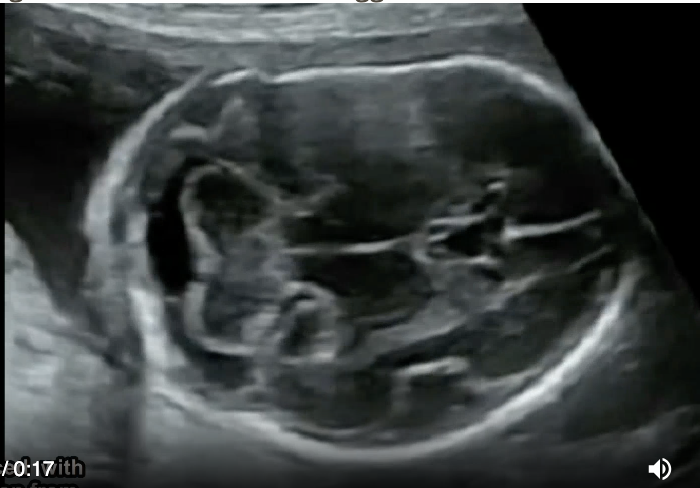
a) osteogenesis imperfecta
b) arthrogryposis
c) thanatophoric dysplasia
d) ellis van creveld syndrome
a) osteogenesis imperfecta

which fetal syndrome is always lethal to the fetus
a) turner syndrome
b) trisomy 21
c) holt oram syndrome
d) potter syndrome
d) potter syndrome

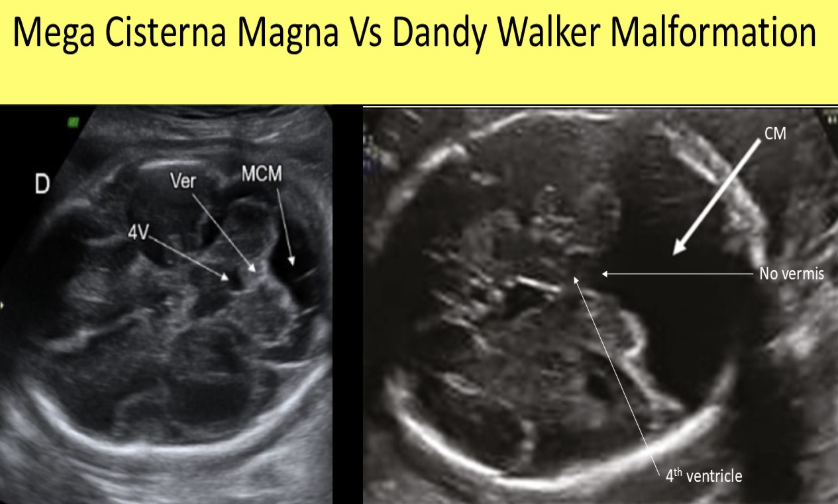
which describe how to differentiate mega cisterna magna from dandy walker malformation
a) neurosonology exam done post-partum
b) a normal cerebellar vermis is usually seen w/DWM but not w/mega cisterna magna
c) a normal cerebellar vermis is usually seen w/mega cisterna magna but not w/DWM
d) fetal MRI
c) a normal cerebellar vermis is usually seen w/mega cisterna magna but not w/DWM
which can still have a normal vaginal delivery
a) maternal herpes
b) placenta previa after 37w
c) signs of fetal distress during labor
d) breech presentation
d) breech presentation

![<p>what is the <strong>most severe form </strong>of<strong><u> spina bifida</u></strong> that causes a <strong>cleft through the entire spine</strong> + <strong>all vertebrae</strong> are <strong>splayed</strong></p><p>.</p><p>a) myelomeningocele</p><p>b) holoprosencephaly</p><p>c) rachischisis [failure of neurulation]</p><p>d) spina bifida occulta</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9cf85d10-ca28-44fe-b6d9-46dfffdbf185.png)
what is the most severe form of spina bifida that causes a cleft through the entire spine + all vertebrae are splayed
.
a) myelomeningocele
b) holoprosencephaly
c) rachischisis [failure of neurulation]
d) spina bifida occulta
c) rachischisis

an opening between the right + left atrium is called
.
an opening between left + right ventricle is called
.
a) atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
b) atrioventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
c) ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
d) atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect
a) atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect

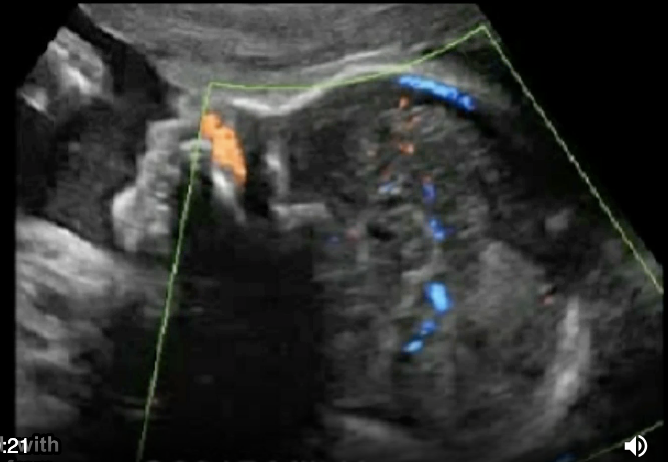
the color doppler portion shows
a) no pericallosal artery
b) thrombus of vein of galen
c) normal fetal anatomy
d) no circle of willis
a) no pericallosal artery

the most significant clinical difference between thanatophoric dysplasia + heterozygous achondroplasia is
.
a) thanatophoric dysplasia is rarely lethal
b) cloverleaf skull only seen in heterozygous achondroplasia
c) multiple fractures only seen w/heterozygous achondroplasia
d) severe shortening of the ribs seen only w/thanatophoric dysplasia
d) severe shortening of the ribs seen only w/thanatophoric dysplasia

a normal AFI level in the 2nd half of pregnancy indicates
a) a normal intrauterine pregnancy
b) no urinary tract anomalies
c) low risk of aneuploidy
d) at least 1 functional kidney
d) at least 1 functional kidney

which is NOT an expected symptom of retained products of conception
.
a) anemia
b) fatigue
c) elevated hemoglobin
d) fever
c) elevated hemoglobin

pulmonary hypoplasia is commonly caused by
.
a) polyhydramnios, maternal use of folic acid
b) oligohydramnios + diaphragmatic hernia
c) maternal use of sucralose or folic acid
d) pulmonary sequestration + macrosomia
b) oligohydramnios + diaphragmatic hernia
