Japan, Abbasid, Ottoman, Ming
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Decentralized power
The authority and responsibility of governing is spread throughout different levels of government. For example, local leaders may hold more power.
Feudalism
A political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land
Edo Period
The period in Japanese history between 1600 and 1853; also known as the Tokugawa period during the beginning of the early modern period of Japan.
Centralized feudalism
Japan kept the outward form of feudal society but imposed central government control. The Shogun held most of the power.
Emperor
Held highest rank in society but had no political power.
Shogun
Military ruler who held most of the actual power in Japan. The shogunate maintained control by enforcing a strict social hierarchy and concentrating land ownership in the hands of about three hundred daimyo.

Daimyo
A Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai and owned large estates (land).
Samurai
Class of warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a daimyo in return for land.
Peasants, merchants, and artisans
Made up majority of the population. Had low status but gradually gained influence.
Bushido
The Feudal Japanese code of honor among the warrior class. Similar to the code of chivalry that knights followed in Europe.
The Three Unifiers
-Oda Nobunaga
-Toyotomi Hideyoshi
-Tokugawa Ieyasu
They unified Japan under a single government and set up a system of centralized feudalism.
Neo-Confucianism
A unification of Daoism or Buddhism with Confucianism. Dominated Japan during the Tokugawa Period.
Archipelago
Chain of islands
Shinto Religion
Believed that ancestors lived in the air around them. Believed all objects and things had a spirit inside. No single god, and the emperor was viewed as a god.
Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258)
Considered the Golden Age of Islam because it was a long period of stability in which centers of trade became wealthy centers of learning and innovation.
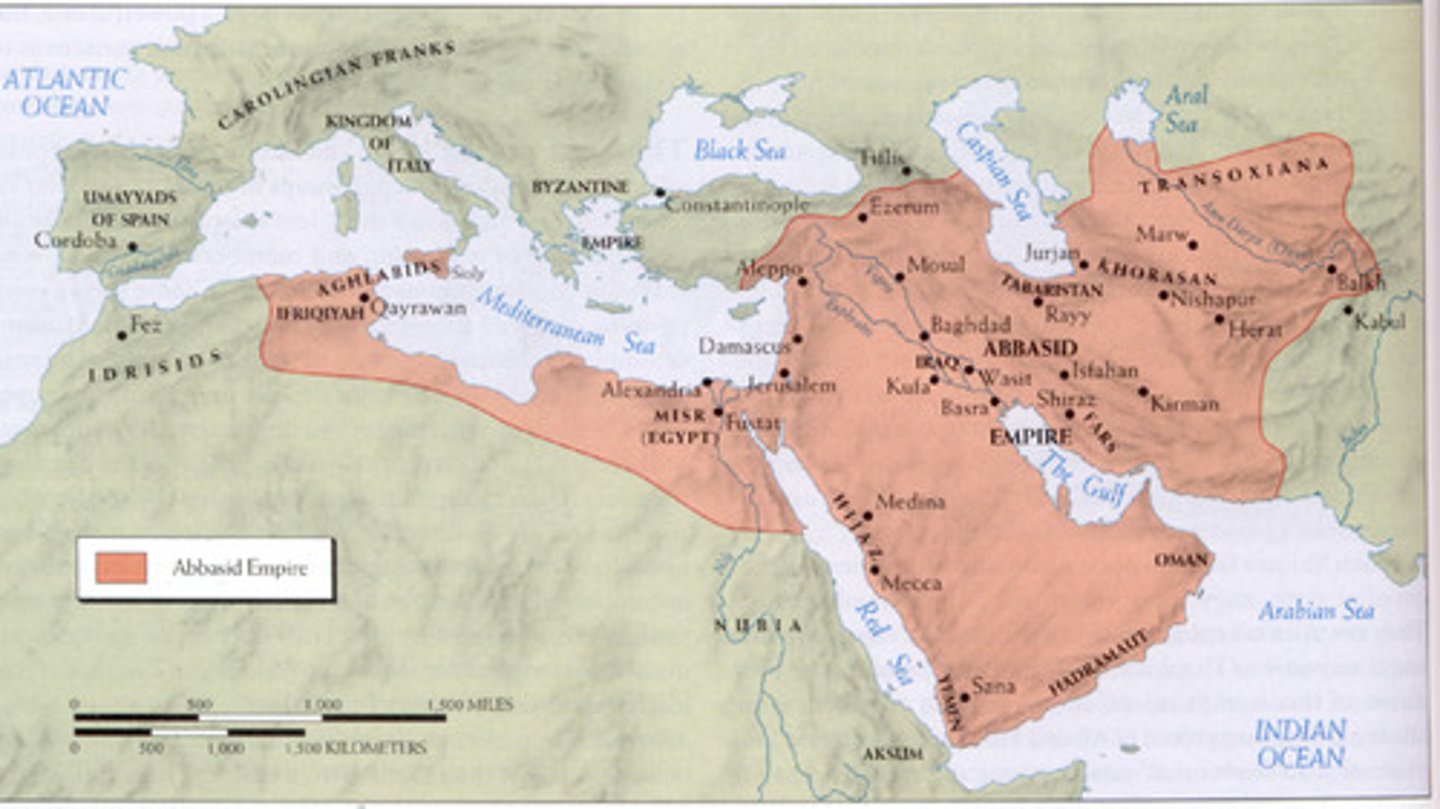
Baghdad
Capital of Abbasid dynasty located in present-day Iraq. As a result of its location at a crossroads of trade between Europe, Asia, and North Africa, the city attracted merchants and scholars.
Mecca
the holiest city of Islam; Muhammad's birthplace
Hajj
A pilgrimage to Mecca, performed as a duty by Muslims
Islamic scientists of the Abbasid
Made achievements in algebra and trigonometry, engineering and astronomy that are influential today.
Caliph
A supreme political and religious leader in a Muslim government. A Caliphate is an empire that was ruled by a caliph.
Umayyad Caliphate (661-750)
The Umayyad family took control of the Islamic Empire, founding the Umayyad Dynasty and ruling from Damascus. They expanded by invading Spain in the west and India in the east.
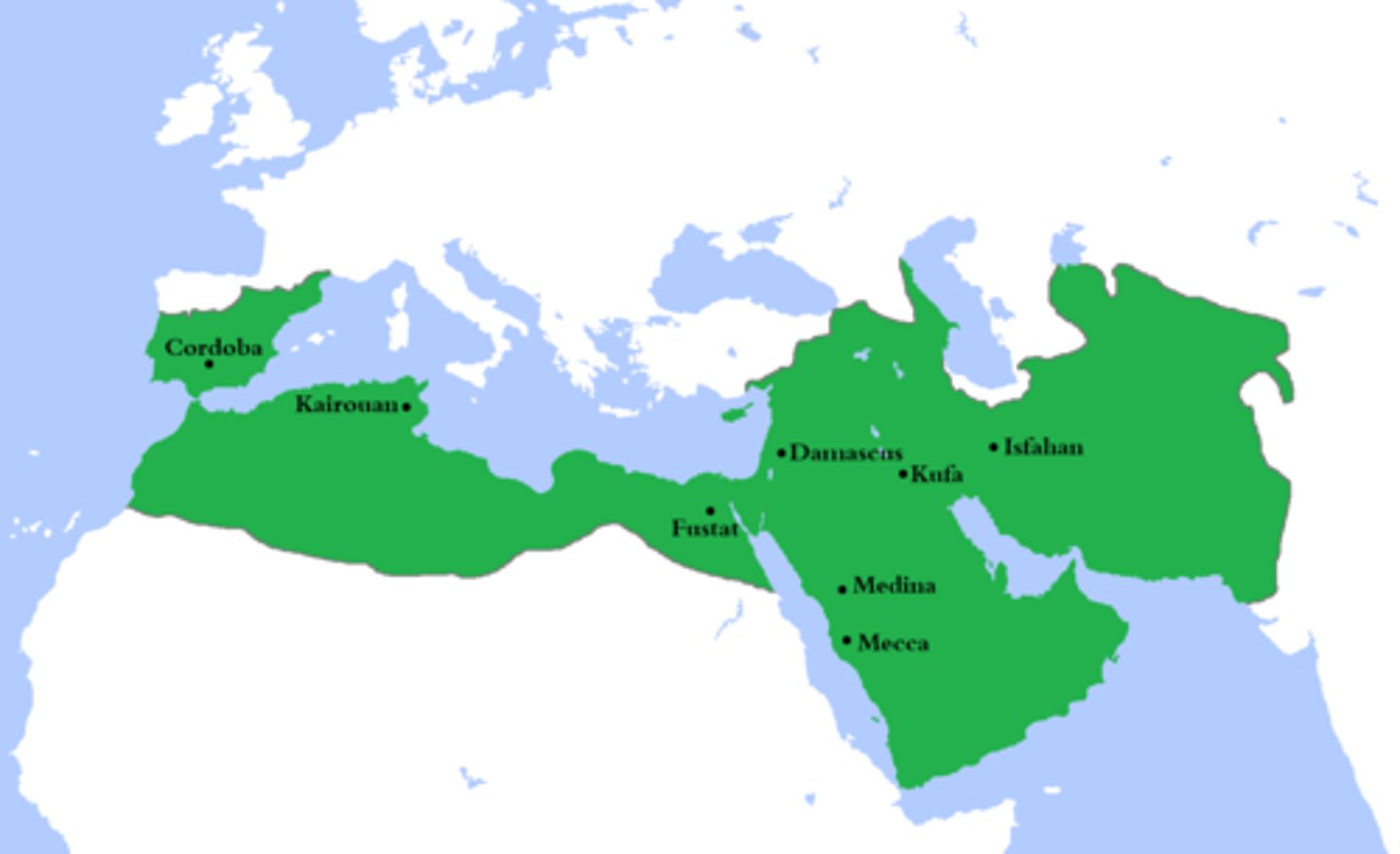
Tariq ibn Ziyad
was a Muslim commander during the Umayyad Dynasty who led the armies that conquered most of Spain from 711 to 718 CE.
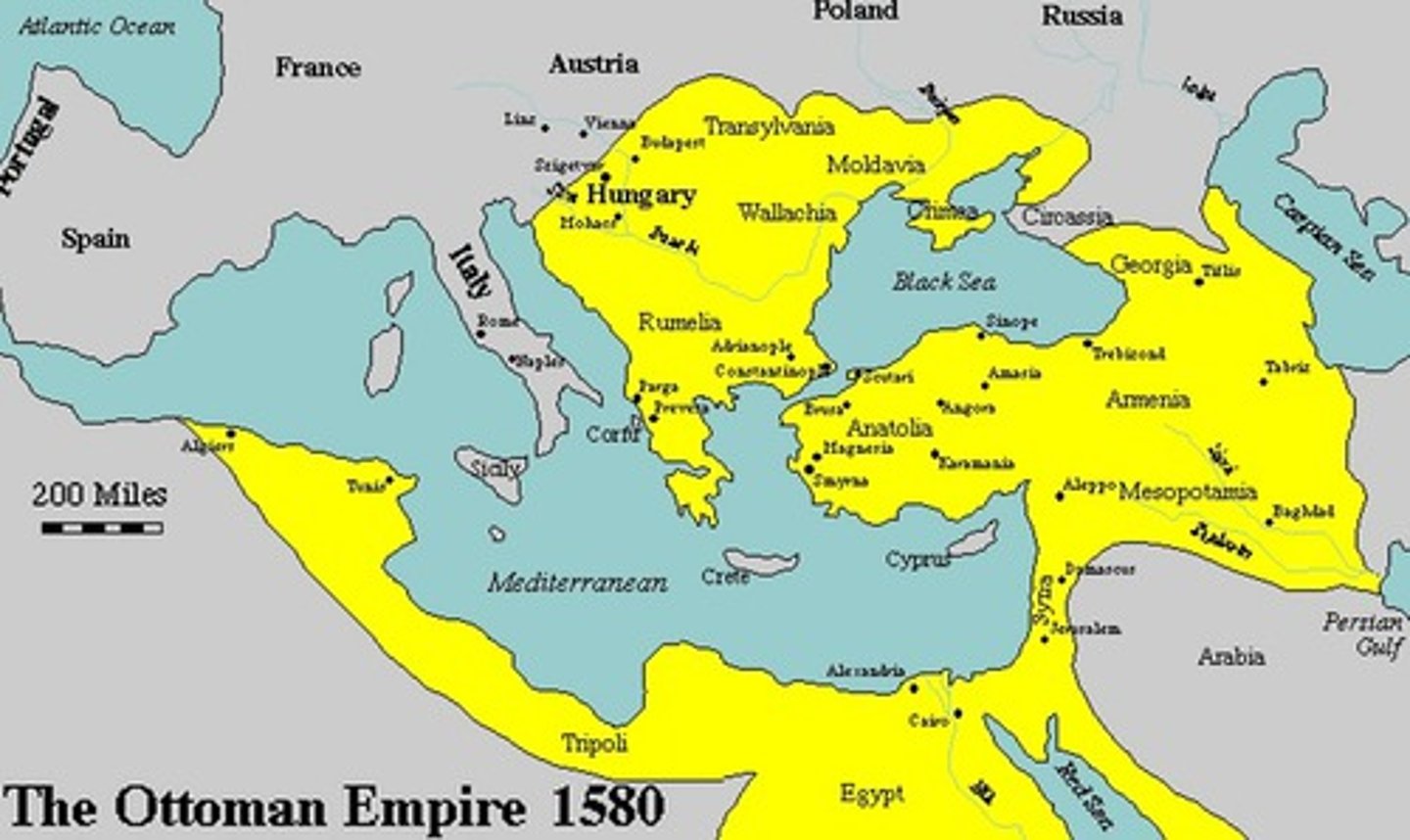
The Ottomans
Were a Muslim Turkish-speaking nomadic people who migrated from Central Asia in northwestern Asia Minor. They quickly conquered other societies and expanded their empire.
Ottoman Empire
A Muslim empire based in present-day Turkey (Asia Minor) that lasted from the 1300's to 1922. It expanded throughout the Middle East.
The Crusades
A series of holy wars from 1096-1270 AD undertaken by European Christians to free the Holy Land from Muslim rule.

Osman
Most successful warrior and "founder" of Ottomans. His army took over areas of Asia Minor and the Balkan Peninsula in Eastern Europe near the Byzantine Empire.
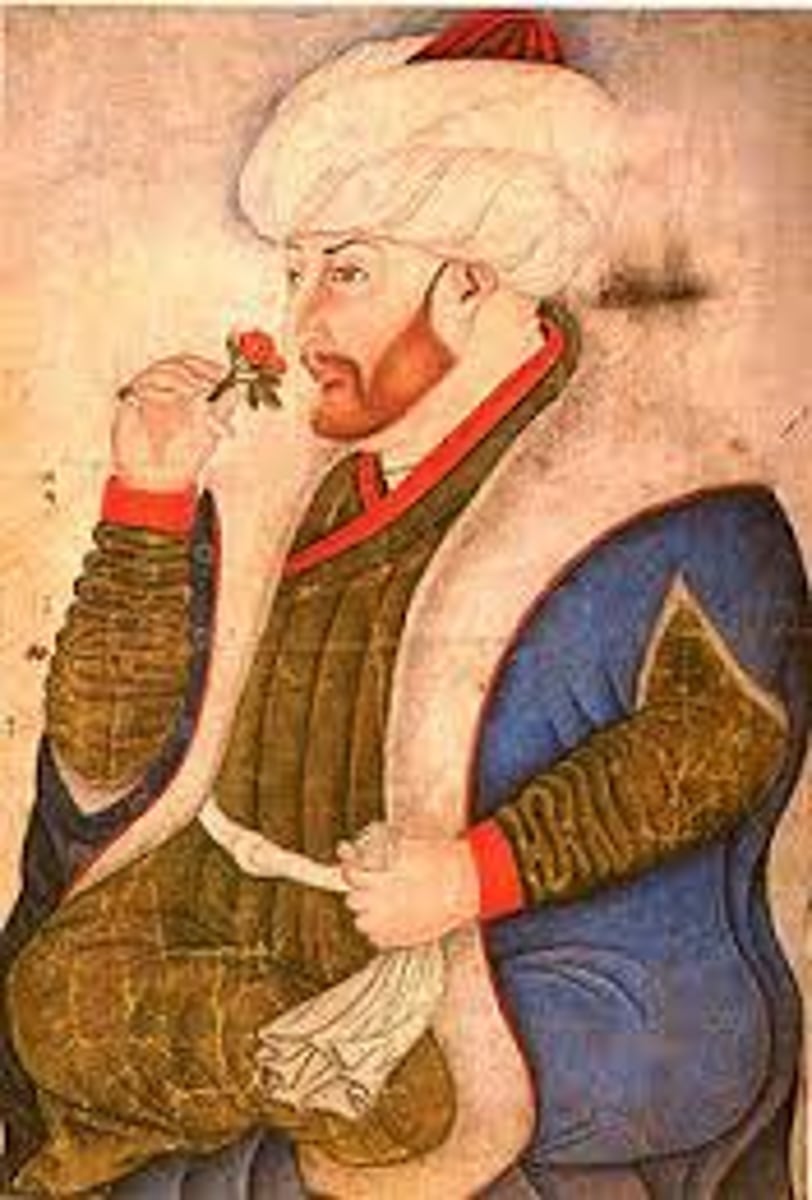

Mehmet II
Under this leader, the Ottomans continued to expand and they captured the capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople, after a 54-day siege. Constantinople was renamed Istanbul and became the new capital of the Ottoman Empire.

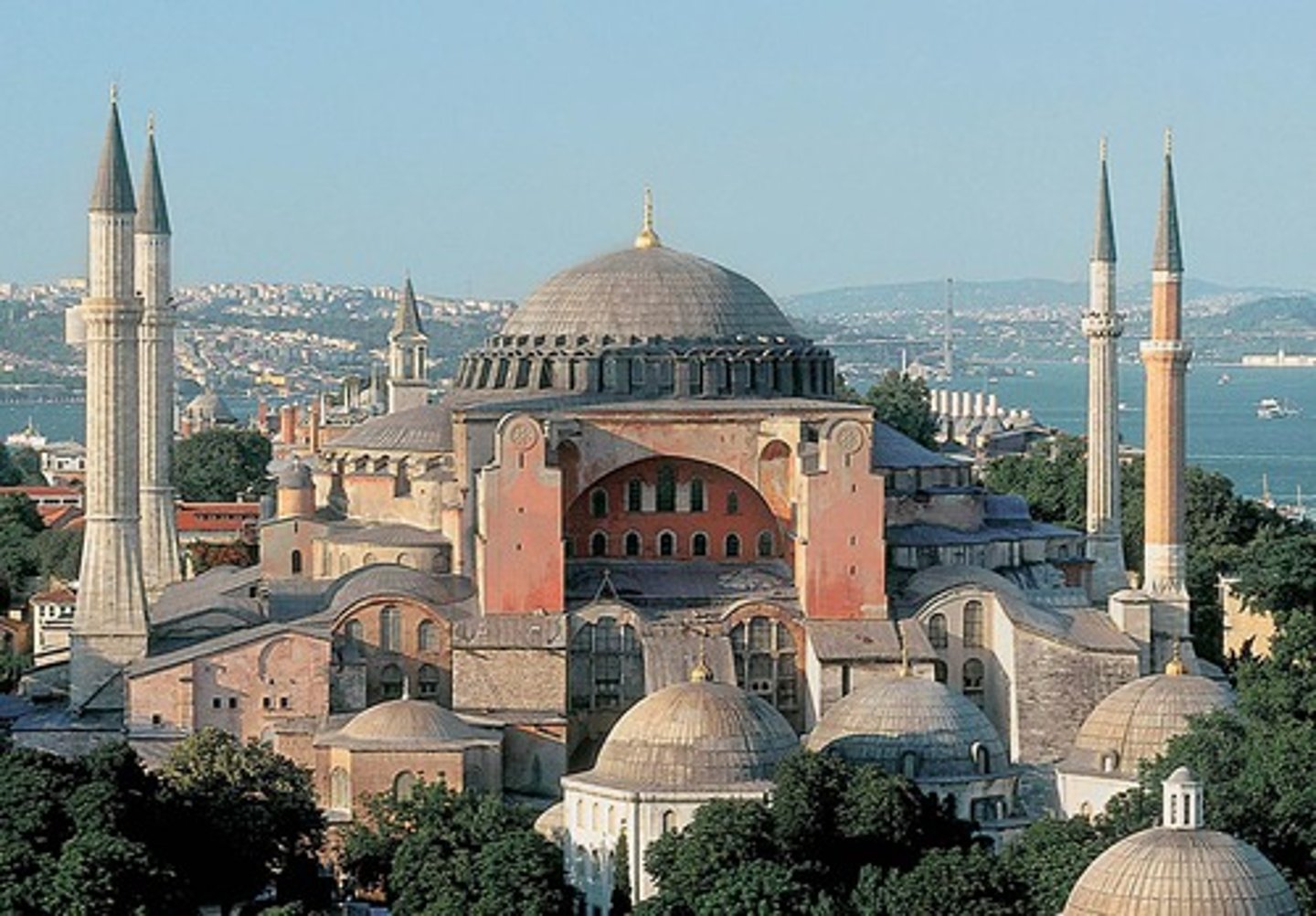
Hagia Sophia
New church constructed in Constantinople during reign of Justinian in the Byzantine Empire. It was turned into a mosque when the Ottomans captured the city.

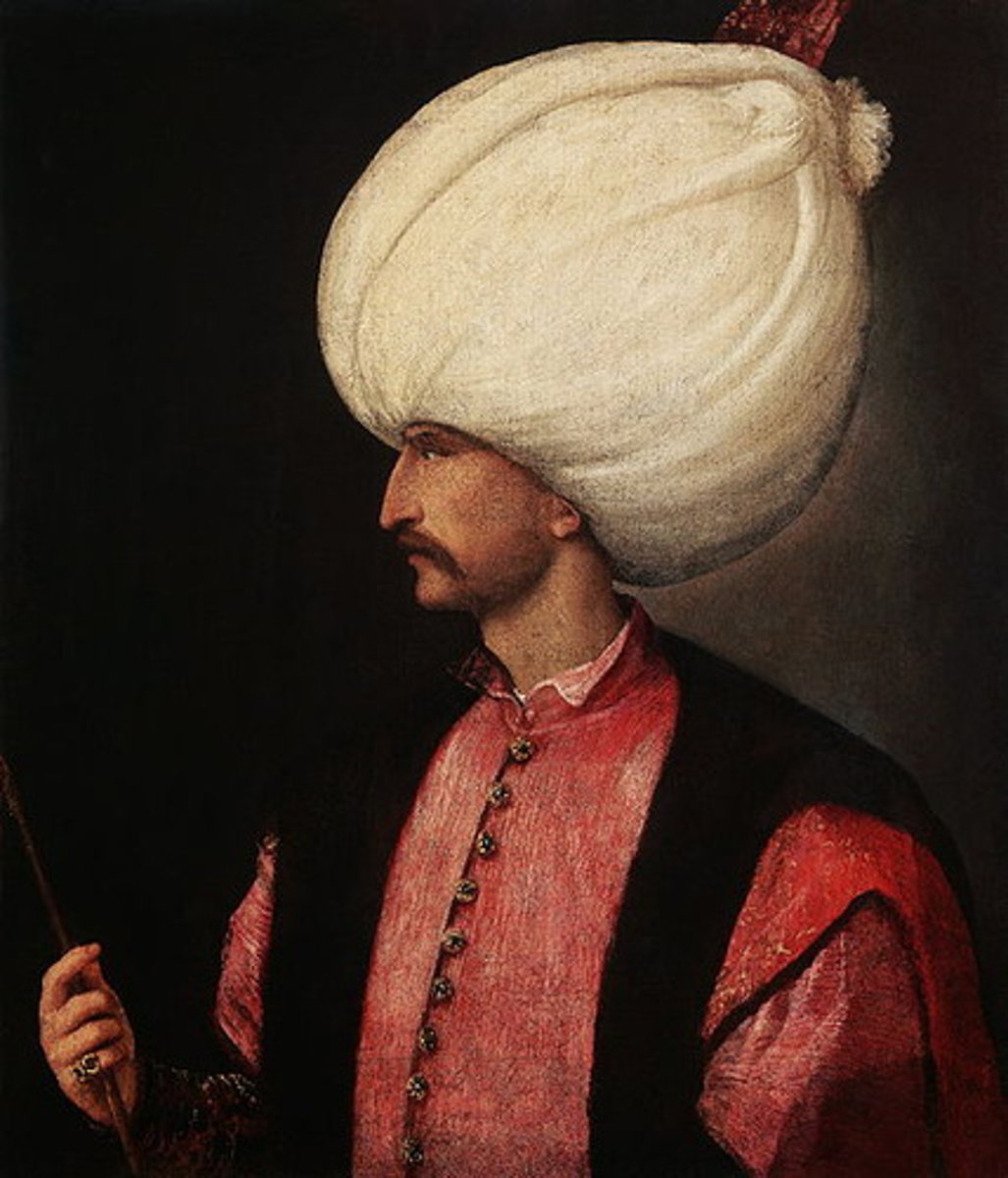
Suleiman
The Ottoman Empire had a golden age under the sultan Suleiman.
-Took on military campaigns that increased the territory controlled by the Ottomans.
-Increased naval strength.
-oversaw achievements in the fields of law, literature, art, and architecture.
-Built strong fortresses.
-improved cities by building mosques, bridges, and aqueducts.

Mughal Empire
Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
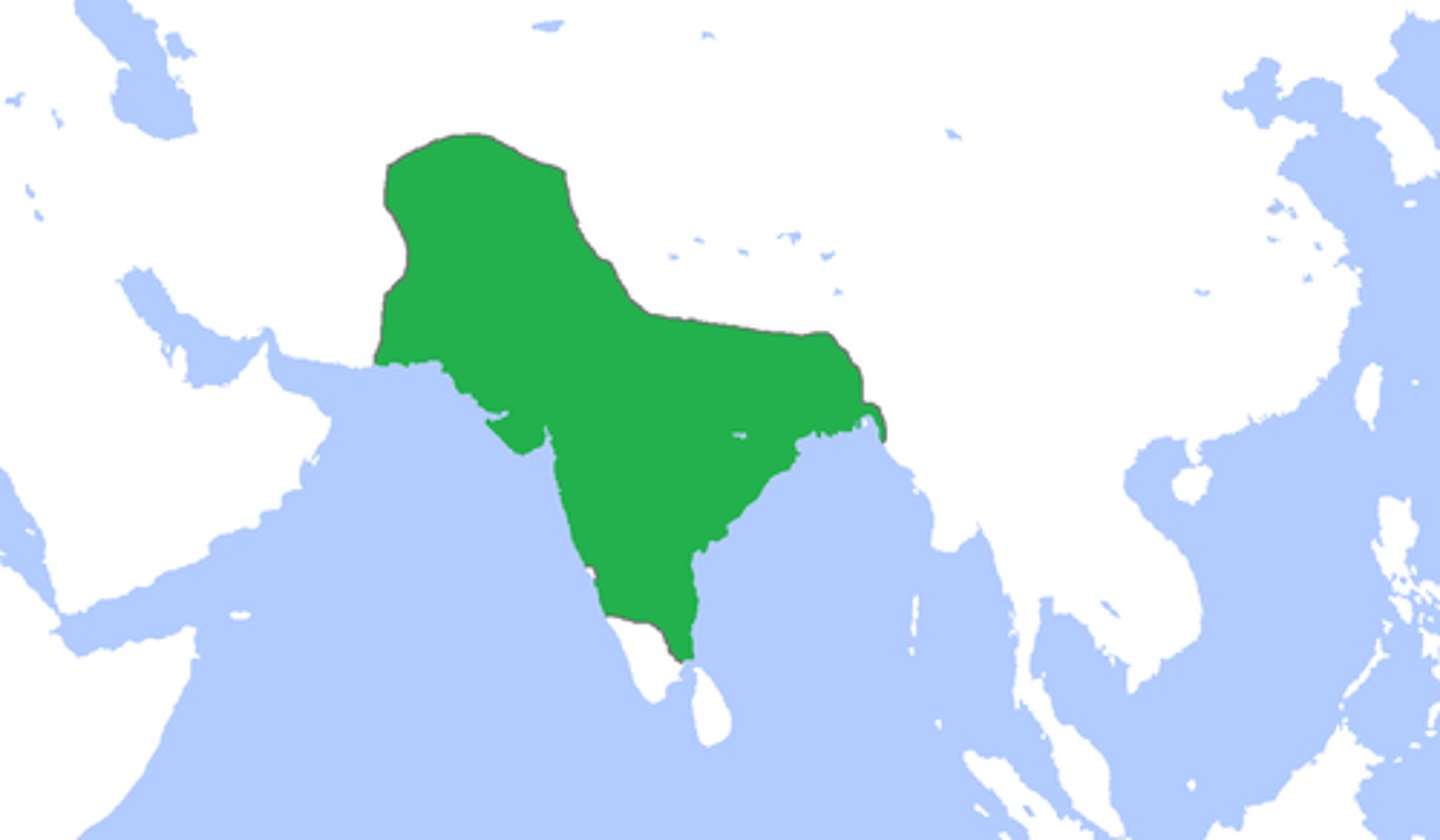
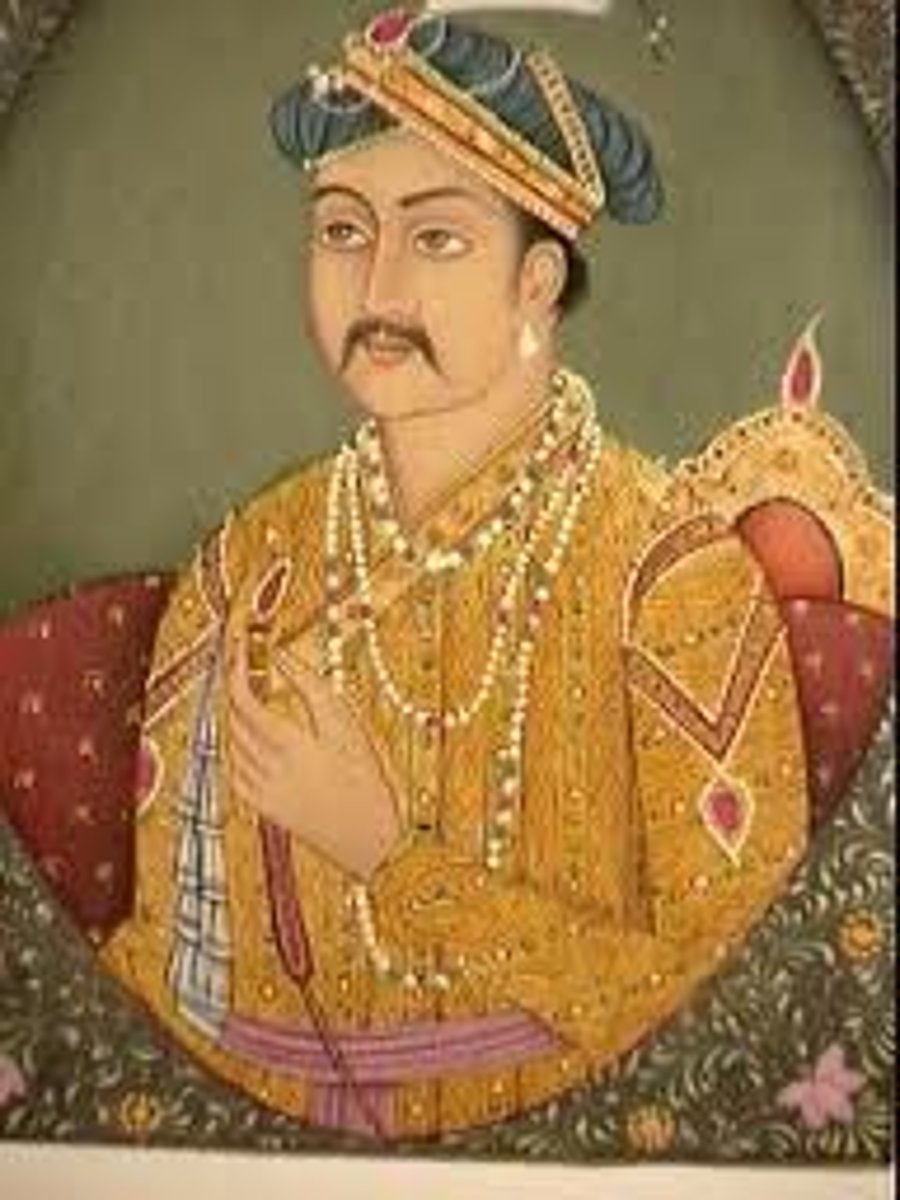
Babur
First sultan of the Mughal Empire (1526-1530); took lots of land in India. When Babur first founded the empire, he did not emphasize his religion, but rather his Mongol heritage. Hinduism was tolerated and new Hindu temples were built with his permission.
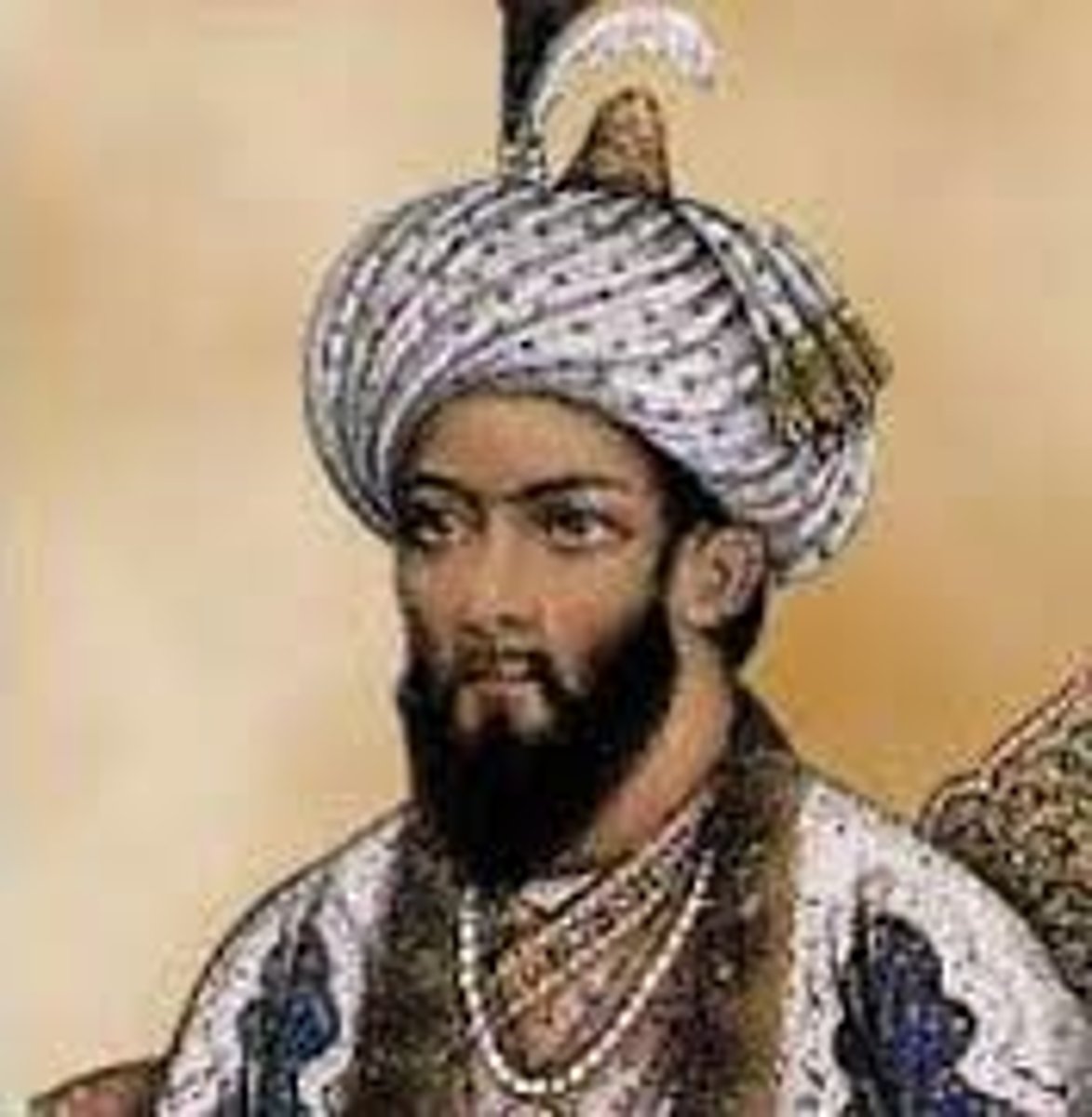

Akbar the Great
The most famous Mughal leader (1556-1605), known for religious tolerance and building the Taj Mahal. He abolished the jizya, a tax paid by non-Muslims in return for religious liberty. Akbar's government included many Hindus who were allowed to reach senior government or military positions of responsibility.

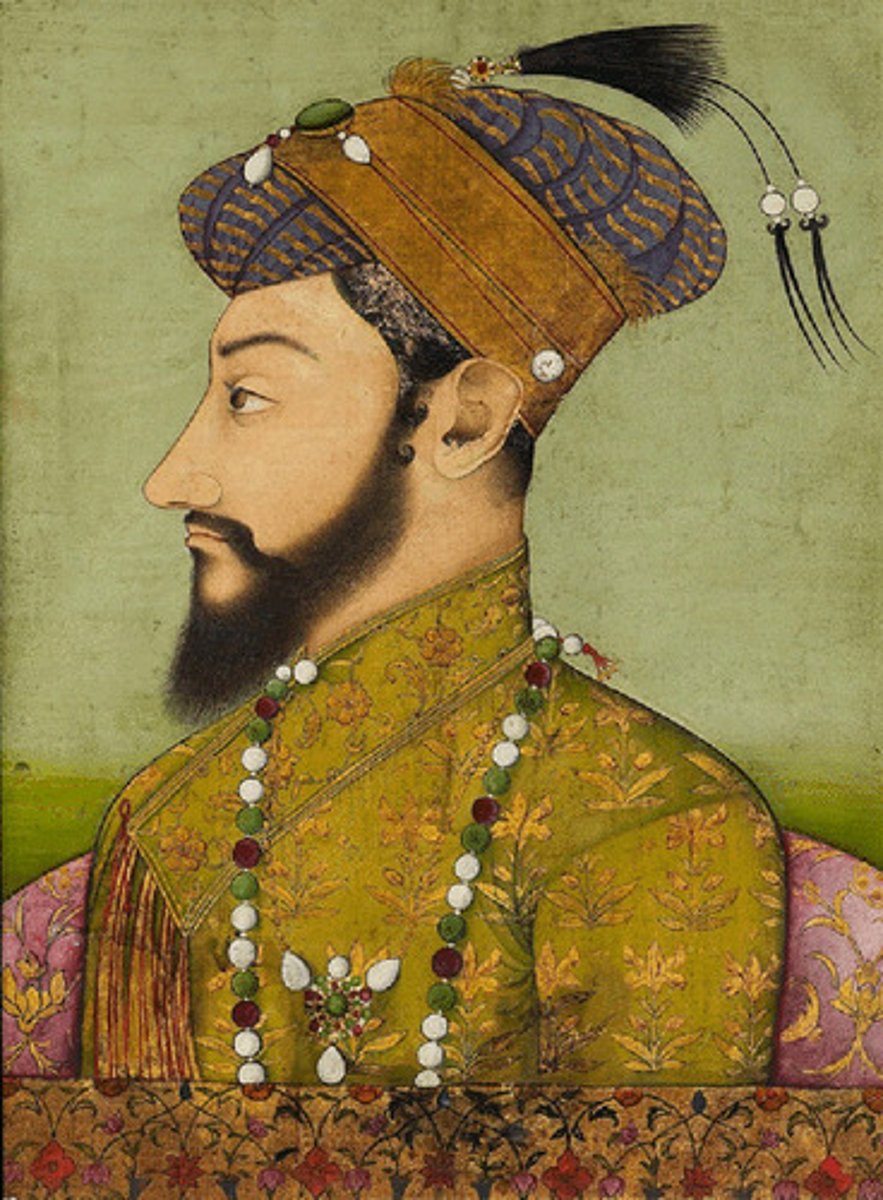
Aurangzeb
Mughal emperor in India and great-grandson of Akbar 'the Great'. He reversed previous policies of religious tolerance, tore down Hindu temples and shrines, and reinstated the jizya tax. Aurangzeb imposed Islamic law over the whole empire. Incessant warfare depleted the empire's resources and it collapsed after Aurangzeb's death.

Mansabdar
A system to generate land revenue and control the empire. The emperor would give the mansabdar (a military officer) the right to tax the people in the area they managed in exchange for promises of soldiers in wartime. The greater the size of the land the emperor granted, the greater the number of soldiers the mansabdar had to promise.
Ming Dynasty (1368-1644)
It was perhaps the peak of Chinese civilization with 300 years of peace and prosperity.
-new and harsher law codes and punishments.
-organized taxes
-reformed government
-replaced Mongols in all civil service posts
-Confucianism became the official system with strict civil service exams.
-government repaired the canal system
-trade flourished and led to economic prosperity
-Increased silk production, textiles, tea, porcelain.
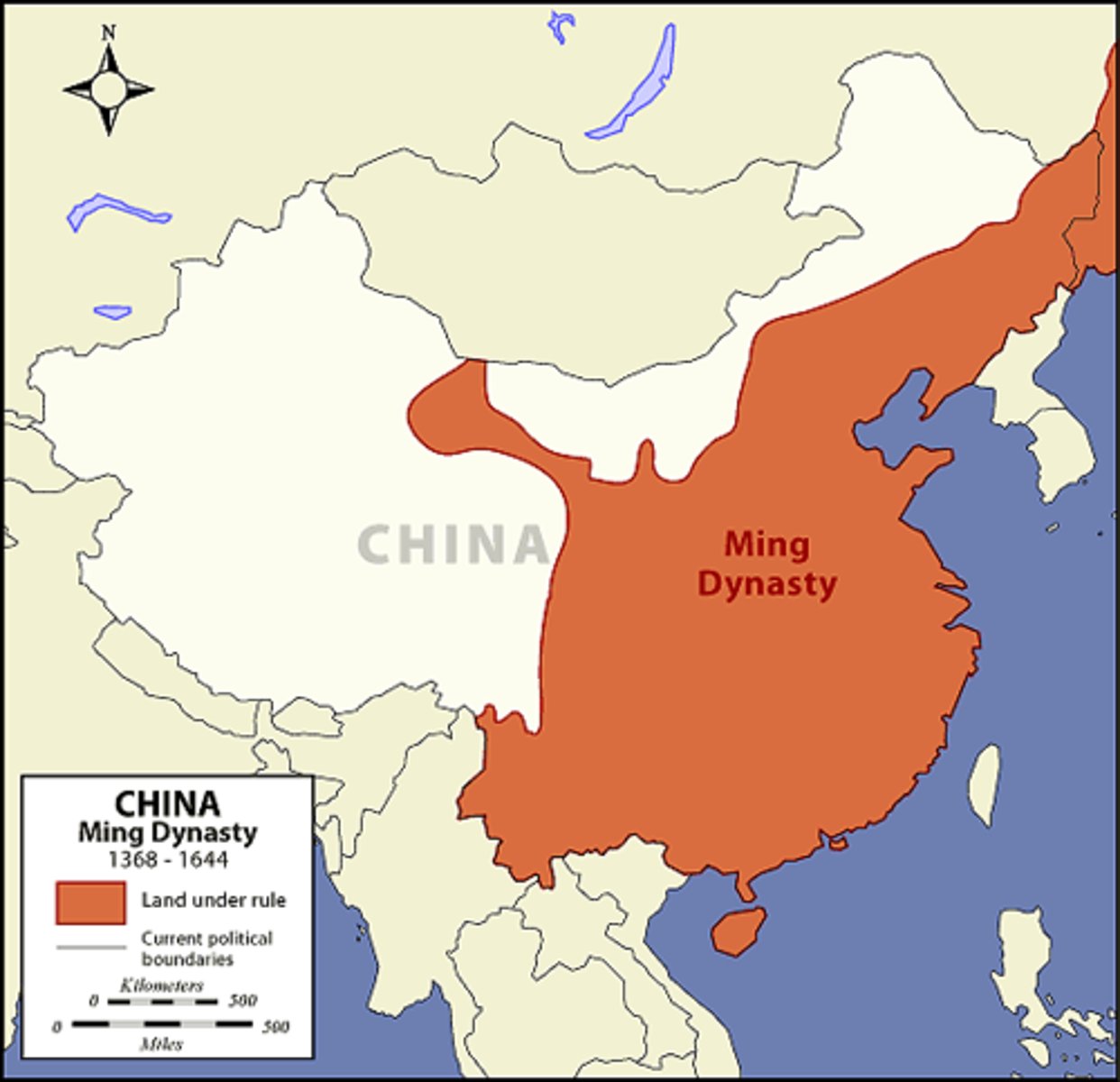
Hong Wu
Came from a peasant family and became emperor of the Ming Dynasty. He established the capital at Nanjing.
Ming Exploration
-Built a navy to sail to foreign ports
-1405-1433- led a series of 7 expeditions took place to show wealth and power
-Brought back goods from many lands.
-Merchants settled in these territories and spread Chinese culture.
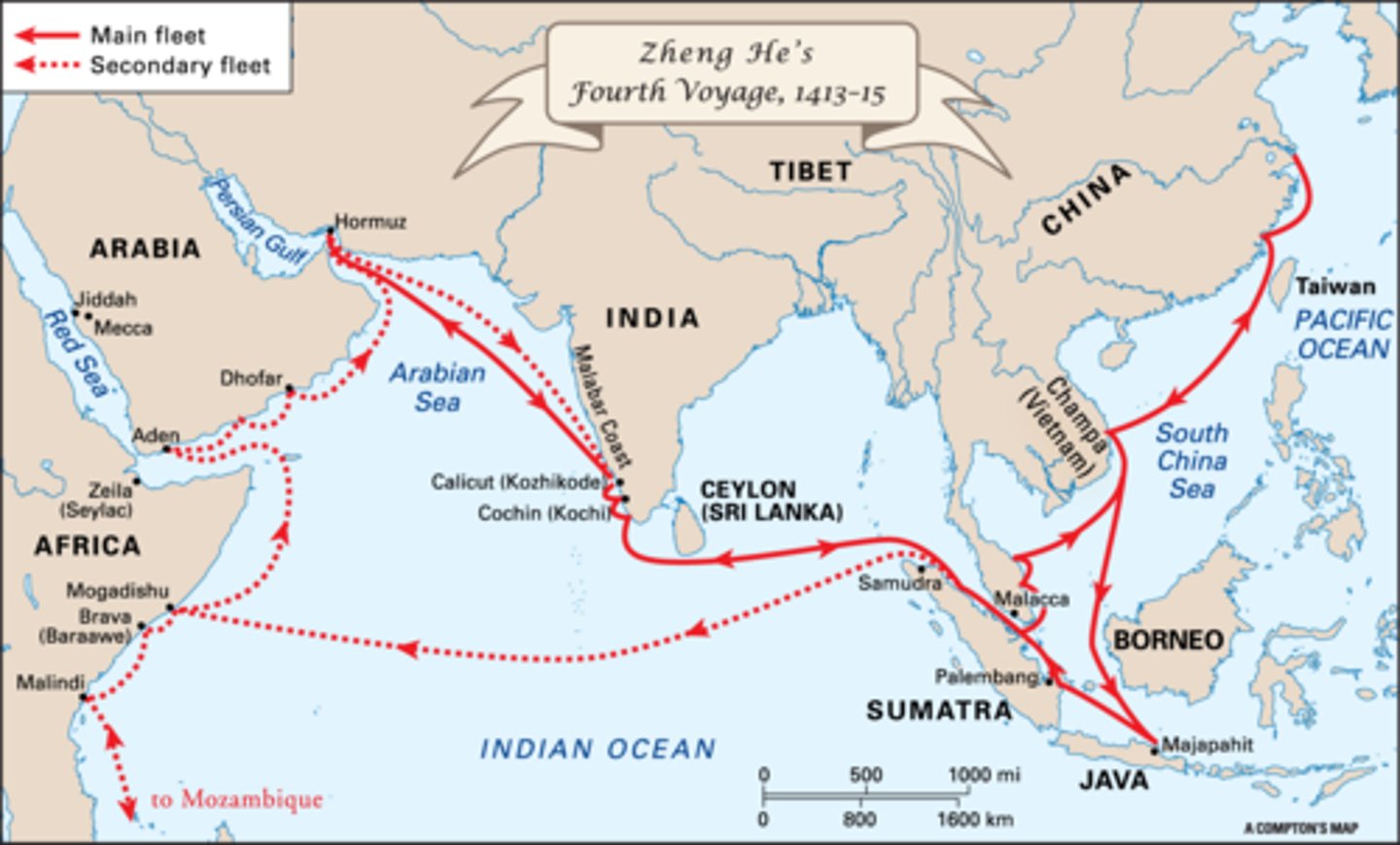
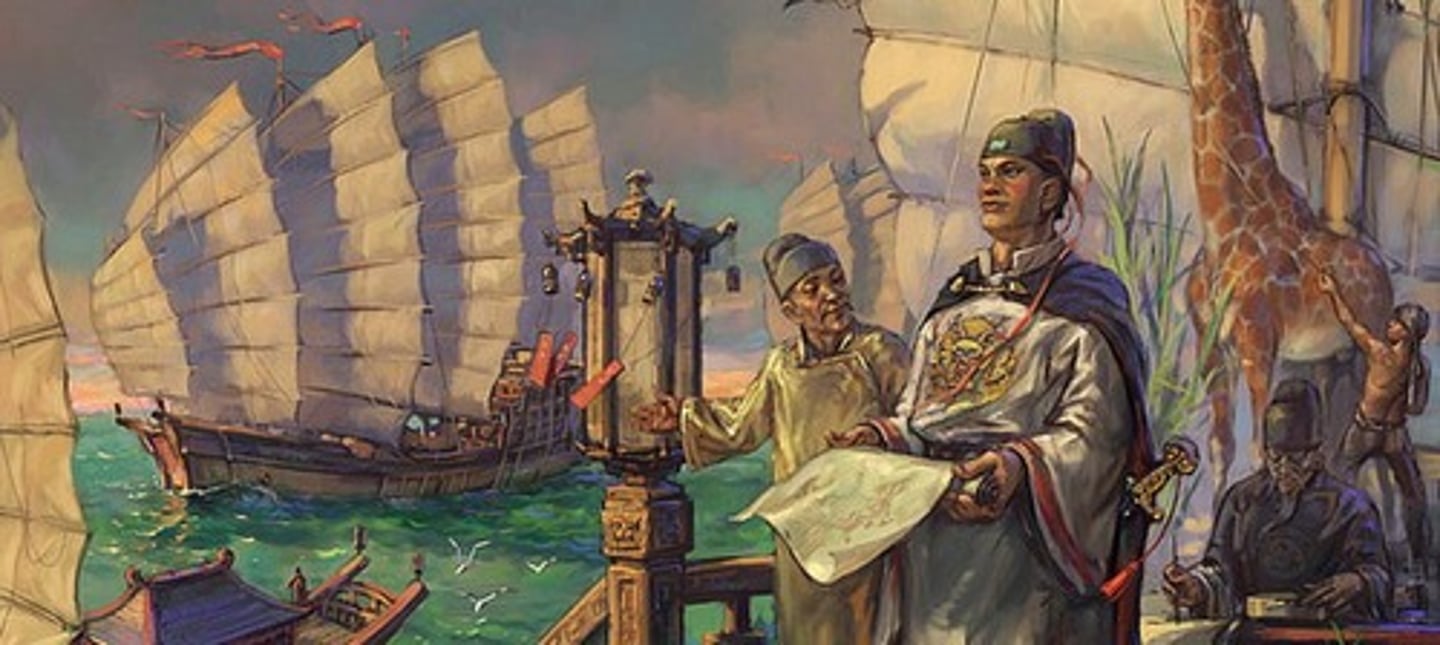
Zheng He
From 1405-1433 he led a series of 7 expeditions to show China's wealth and power.
-1st fleet: went to Southeast Asia
-Later: went to India, Persian Gulf, Arabia, East Africa

Fall of the Ming Dynasty
-Corrupt officials took over
-Law and order collapse
-Manchu invaders from Manchuria attack the north
-Military spending was cut because so much was spent on the emperor
-Manchus conquer China