Unit 8 Mechanical Waves
1/428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
429 Terms
One wavelength =
Peak to peak
Trough to Trough
Anti-node to anti-node
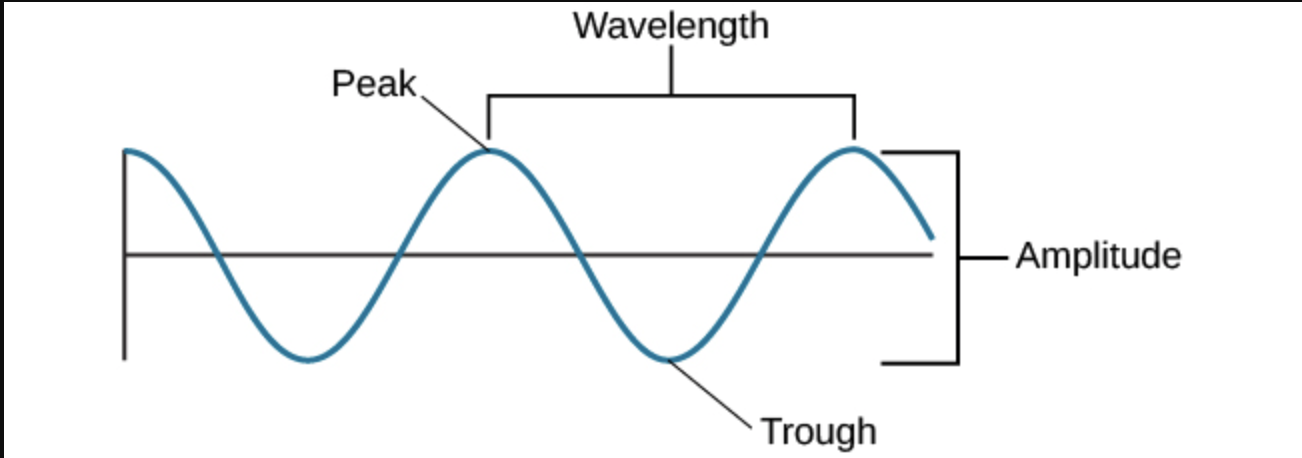
How do you measure a wavelength?
By using any starting point on a wave and measuring to the next point on the wave. It’s always a fixed distance.
What does a short wavelength represent?
High frequency, high energy, and high temperature.
What does a long wavelength represent?
Low frequency, low energy, and low temperature.
In scientific notation, moving the decimal point to the left _____ the exponent.
Increases (LP)
In scientific notation, moving the decimal point to the right _____ the exponent.
Decreases (RN)
When light moves from one medium to another, it can be either _______, _________, or ___________.
Reflected, absorbed, or transmitted,
What is reflection?
When light bounces off the surface
What is absorption?
When light is converted to another form of energy (light disappears as it enters another medium)
What is transmission?
Granted safe passage through the medium itself (goes through the medium)
As light is reflected, the angle it comes at is known as the ________________.
Angle of incidence
The angle of incidence is always equal to the _____________.
Angle of reflection
Absorption is generally converted into __________.
Heat (thermal) energy.
The color the object appears to be is the ______ light.
Reflected
Colors that do not show through the object are typically the ______ light.
Absorbed
What is an example of reflection?
A ball bouncing (light bounces off surfaces similar to how a ball does)
Does light have to travel through a medium?
No, light is the only type of wave that does not have to travel through a medium. However, it can travel through air, water, and other substances such as gummy bears.
What is a medium?
A substance that waves can move through.
Is there a medium in space?
No, since there is no air and no water.
Space is similar to a ______.
Vacuum
What types of waves can go through space with no medium?
Electromagnetic waves
What do you call an angle that is created with the surface and the sun?
The angle of insulation or the angle of incidence
What is an example of refraction?
When light travels through a prism or water droplet.
What do you call it when all the colors from the light of the sun is being refracted?
A rainbow
What is frequnecy?
How many waves go by (complete one cycle) in a second.
What does it mean if something is absorbed?
It means it’s energy was turned into heat
What is special about the color white?
It reflects all the colors of light.
Why is black a shade and not a color?
Since it absorbs all the colors of light
All the colors of the objects we see are _______.
Reflected
We don’t see colors that are _________ by the object.
Absorbed
What are the two types of waves?
Electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves.
What are the two subcategories that form mechanical waves?
Transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
What must there be for a wave to be created?
An energy input
What is an example of a wave?
Ripples in the water after a stone in thrown into a lake
What do you call an input of energy?
A disturbance
What is an example of a disturbnace?
Wind is a disturbing force that creates waves in the ocean. The energy source is the wind.
A wavelength is when a wave goes __________________.
Up and down
What is the definition of a wave?
A disturbance in a medium that carries energy away from the source
What is the only unique wave?
Light waves because they do not require a medium to travel, unlike all other waves.
As water moves further away, waves get _____________.
Less intense
What are some examples of mechanical waves?
Sound waves, which travel through the medium of air
Water waves, which travel through the medium of water
Waves on a string, which travels through the medium of the string
What is the only type of wave that can go through space?
Light is the only type of wave that can travel through space, which can also go through mediums
A wave is in the ____________ direction as the disturbance.
Opposite
The transverse is _______________ to the direction of the waves travel.
Perpendicular (forms a right angle)
A disturbance goes _____________.
Up and down
Frequency is _______________________.
The number of cycles of a wave per second.
What is the definition of a wave period?
The time it takes for a wave to complete one full oscillation.
What is the definition of frequency?
The number of oscillations that a wave makes in one second.
What is color?
The frequency of the light that our eyes detect. It’s also the measure of how quickly the light waves are “waving”.
What makes the visible light spectrum?
All the frequencies of light form a band of colors, called the visible light spectrum.
What colors does the sun emit?
The sun emits all colors of light.
Why do people feel hot when they wear black T-shirts on a sunny day?
The shirt absorbs all the light frequency from the sun and the energy from those light waves transforms into heat.
Wavelengths are a measure of __________.
Distance
What is the unit for wavelengths?
Meters
What is the symbol for wavelengths?
λ.
What is the wave period a measure in?
“Seconds per cycle”
What is the unit for a wave period?
Seconds
What is the symbol for the wave period?
T
What is the frequency a measure in?
“Cycles per second”
What is the unit for frequency?
1/s, which is referred to in hertz (Hz)
What is the symbol for frequency?
f
What is the amplitude of a wave equal to?
The maximum distance that the wave travels from its equilibrium position (node).
Amplitude is a measure of __________.
Distance
What is the unit for amplitude?
Meters
What is the symbol for amplitude?
A
What is the wave speed?
The speed at which the wave spreads through space
What is the unit for wave speed?
Meters per second (m/s)
What is the symbol for wave speed?
v
What does the speed a wave travel depend on?
The nature of the medium it is passing through
All mechanical waves require ___________ for their transmission.
Matter
What moves outwards with the wave?
The energy of the disturbance that is carried by the waves.
What are the two basic types of waves energy is transported by?
Transverse and longitundial.
In longitudinal waves, the disturbance is _______________ to the direction of the wave’s travel.
Parallel
What is a wavelength?
The distance of one complete wave.
What is amplitude?
The maximum different of the disturbance (wave height)
What is velocity?
The relationship between the wavelength and the frequency.
What is the velocity equation?
Velocity = wavelength x frequency
What is the velocity of a wave limited by?
The properties of the medium it travels through
What are common to all waves?
Wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and velocity.
All waves are ___________________________________.
Traveling disturbances that carry energy from place to place.
What axis is the disturbance on?
The y-axis
What is propagation?
The movement of a wave
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves?
Transversal waves
Are mechanical ways transversal?
Some mechanical waves are transversal
What is an example of a node?
The point when the slinky remains still when being slung.
What are longitudinal waves?
Waves that travel in the same direction as the disturbance
Definition of a wave
Energy from a disturbance that propagates in a certain direction
What is an example of longitudinal wave?
Beating a drum
Definition of a wavelength?
The distance of a complete wave from any of the two same points on a wave
Definition of wave frequency?
Number of cycles a wave completes in a second
What is a cycle also known as?
An oscillation
What does one cycle of a wave mean?
A wavelength going past a particular point
What is the definition of amplitude?
The distance between the equilibrium state and the high crest, or lowest trough
What is the distance of the peak to equilibrium point equal to?
The distance from the equilibrium point to the trough
What is the equilibrium?
The resting point (or straight line) a wave travels around
What is the wave height?
The crest to the trough
How do you calculate the amplitude of a wave?
By taking half the wave height
Velocity is the _________________ of a wave.
Speed (how fast the wave is propagating)
Propagation is the movement of a wave _____________________.
Away from the disturbance
Does sound travel faster in air or water?
Sound waves travel faster in denser mediums like water.