Humanities unit 2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
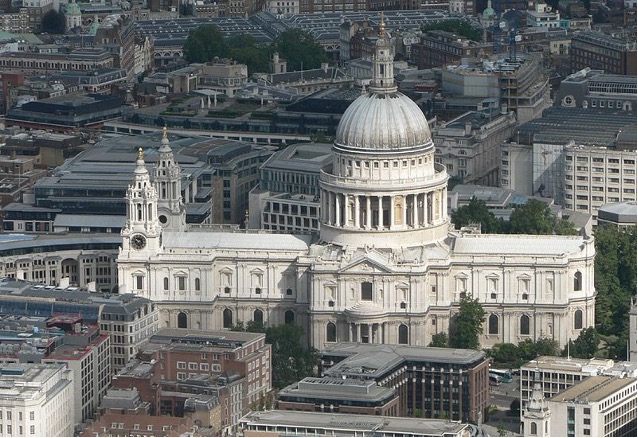
St pauls cathedral, London
Christopher Wren designed this late-17th century building that features a dome within a dome.

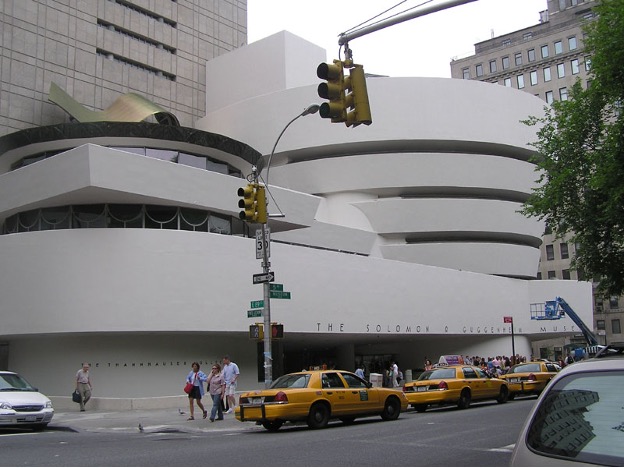
The Guggenheim Museum, New York
Frank Lloyd Wright designed this spiral-shaped building that resembles a parking garage design.

The Walt Disney Concert Hall, Los Angeles
Architect Frank Gehry designed this building that was completed in 2003 that is an example of his sculptural approach to modern architecture.

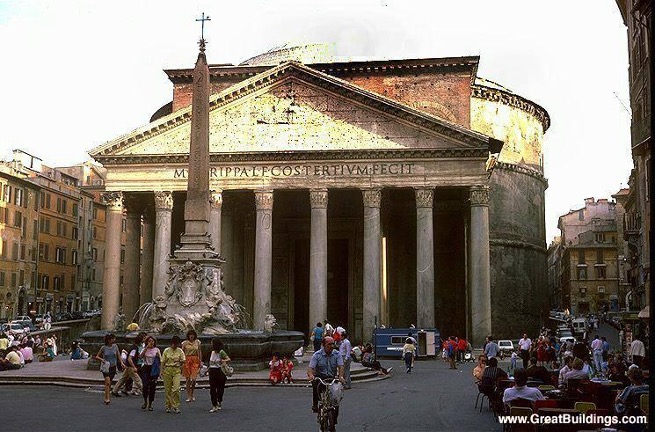
The Pantheon
This Roman masterpiece was built in the 2nd century A.D., featuring a concrete dome with an oculus.

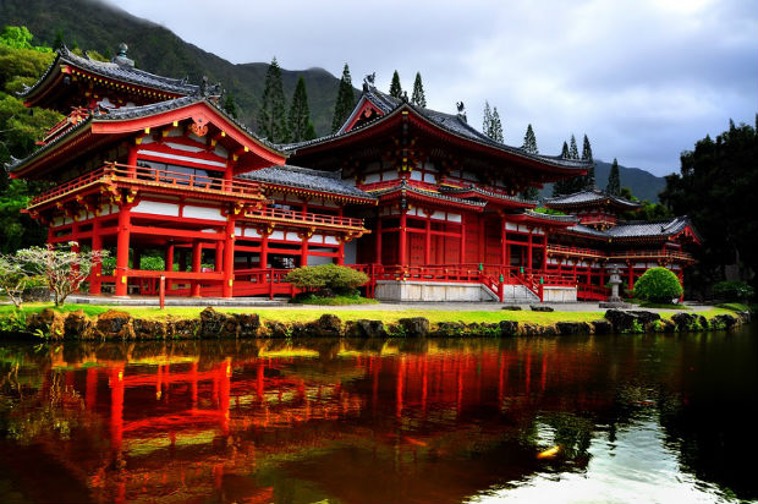
Byodo-in, Uji,
Kyoto prefecture, Japan
This Buddhist temple is 1000 years old and is an excellent example of traditional Japanese design.

The U.S. Capitol Building
This Neoclassical American landmark built in the first part of the 19th century features a massive dome.

Fallingwater
This Frank Lloyd Wright masterpiece was a private residence built atop a waterfall in western Pennsylvania in the
1930s.

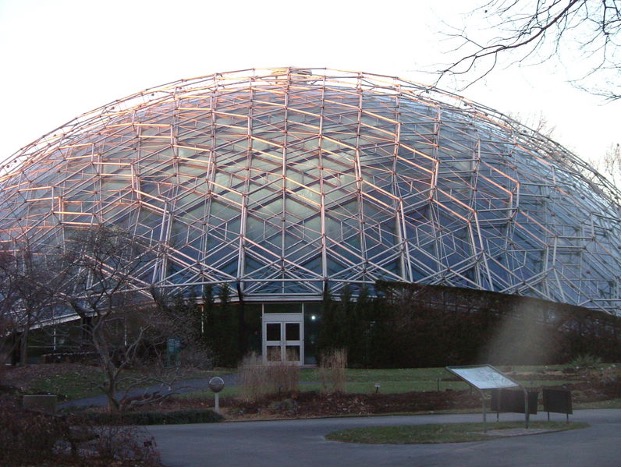
The Geodesic Dome
This provocative 1950s architectural design by R. Buckminster Fuller featured an exterior framework of metal rods and six-sided plates.

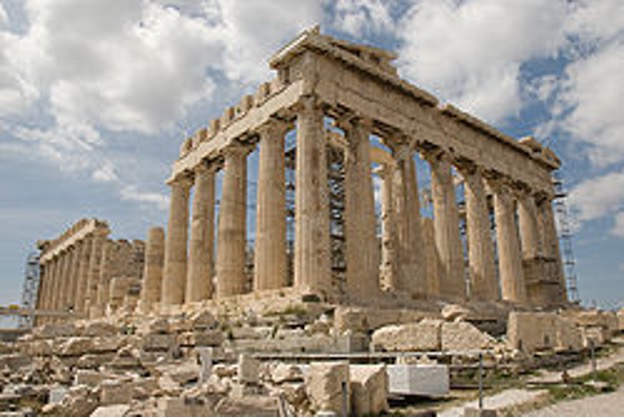
The Parthenon
This ancient Greek temple built in the 5th century B.C. is a refined example of post-and-lintel construction.

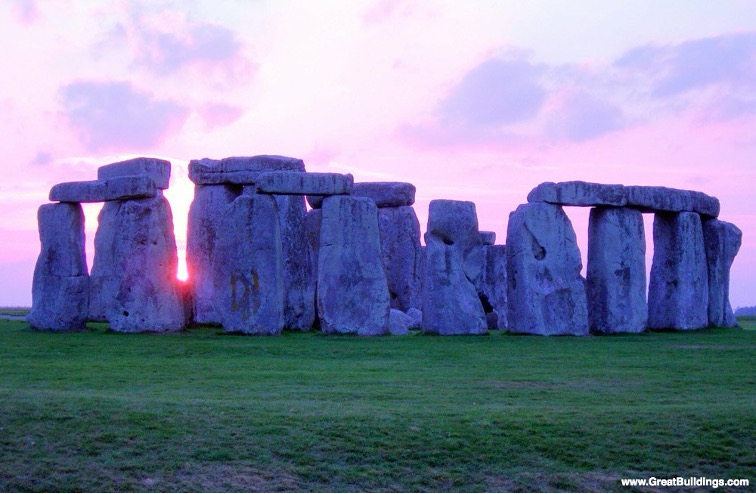
Stonehenge
This ancient and mysterious configuration of giant stones in England reflects the ancients’ awareness of celestial bodies.

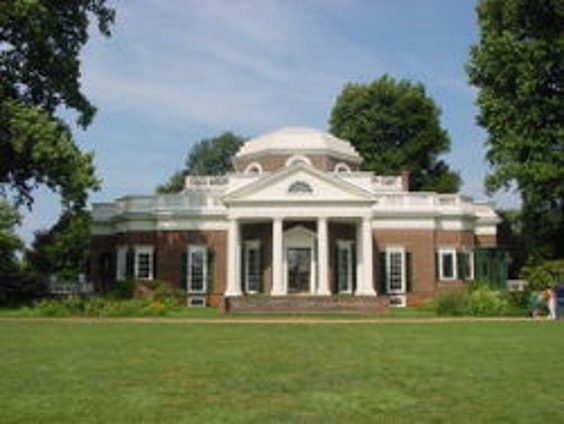
Monticello
Tho as Jefferson designed this neoclassical style home in Virginia in the late 18th century

Burn khalifa
Completed in 2010, this middle eastern skycraper is the tallest building in the world

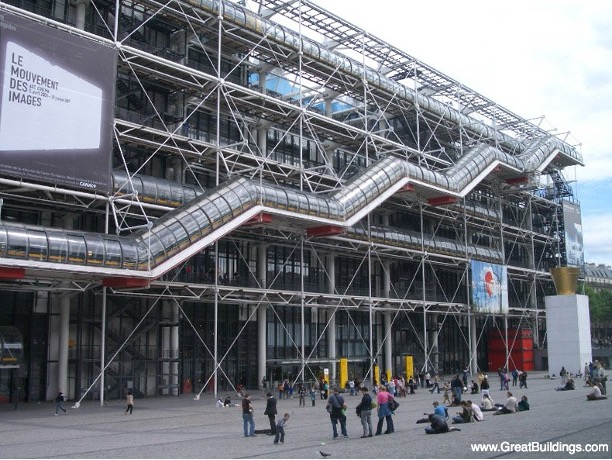
The Pompidou center
This parisan modern are museum built in the 1970s features a controversial “inside out” design

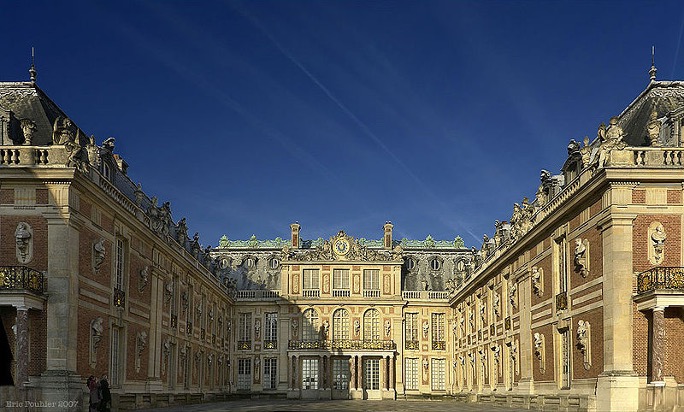
The palace at Versailles
King Louis XIV started the building of the extraordinarily magnificent French summer palace in the 1660s

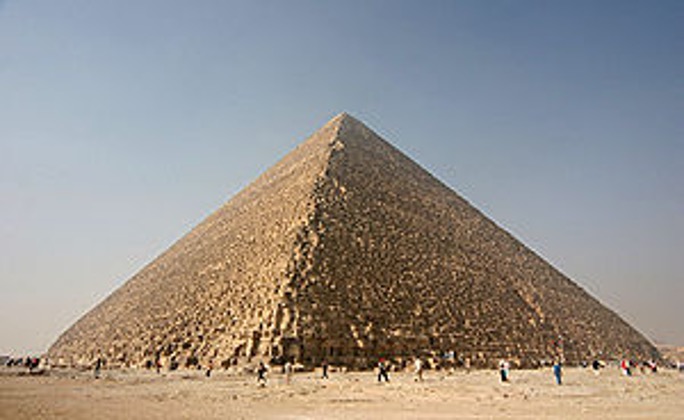
The great pyramid of Cheops
This extraordinary architectural work was completed about 4500 years ago as a burial chamber for the Egyptian pharaoh and his family

Romanesque
This architectural style period of the early Middle Ages (1000-1150 A.D.) featured rounded arches, thick walls and pillars, and small windows.
The International Style
This style of architecture dominates the skylines of most of the world’s cities today. It is seen in the glass-and-steel box forms of modern skyscrapers.
Neoclassical
This style period of architecture (1750-1825 A.D.) featured an ongoing influence from archaeological discoveries of the ancient Greeks and incorporated elements of those ancient styles, displayed an eclectic approach by combining elements from various styles, and expressed an attitude of modernism (that artistic design could uniquely express itself anew in the modern era).
Gothic
This architectural style period (1150-1400 A.D.) featured the pointed arch and is best illustrated by its cathedrals.
Romantic
This style period of architecture (1825-1900 A.D.) borrowed greatly from other historic styles, including the Gothic and Oriental styles. Exterior walls tended to function as a screen, disguising the structure, interior design and usage of a building. There were frequently strong contrasts of forms and asymmetrical balance. Experimentation and the use of new materials also characterized the period.
Renaissance
This style period of architecture (1400-1600 A.D.) featured a revival of Classic Roman style that included copying the size and proportions of Roman ruins, the addition of decorative detail to the façades of buildings, and a development of external designs that concealed the underlying structures.
Baroque
This style period of architecture (1600-1750 A.D.) was characterized by grandeur, decorative detail, and ostentatious display of wealth. A prime example is the Palace at Versailles.
Organic Architecture
Frank Lloyd Wright’s approach to architectural design which emphasized designs that were in complete aesthetic harmony with their surroundings became known as this.
Louis Sullivan
This late-19th century Chicago architect created an approach to design that emphasized careful consideration of the use of spaces within his designs and then the design of structure to provide those spaces, summarized as “Form follows function.”
Eclecticism
The combining together of aesthetic elements taken from more than one style.
Facade
An exterior face of a building that hides its underlying structure.
Post-and-Lintel Structures
Horizontal beams are supported by vertical posts or columns. These structures were made of stone.
Cantilever
STRUCTURE SUCH AS AN OVERHANGING ROOF of beam that is supported only in one end
Bearing wall structures
These structures use the walls to support the roof, floors, and themselves. Examples are concrete block structures, common in South Florida, and log cabins.
The arch
This stone structural technique was developed by the ancient Romans. It can define large spaces, transferring stresses outward from its center, the keystone, to its legs, and not depending upon the tensile strength of the material.
An arcade
Several arches placed side by side
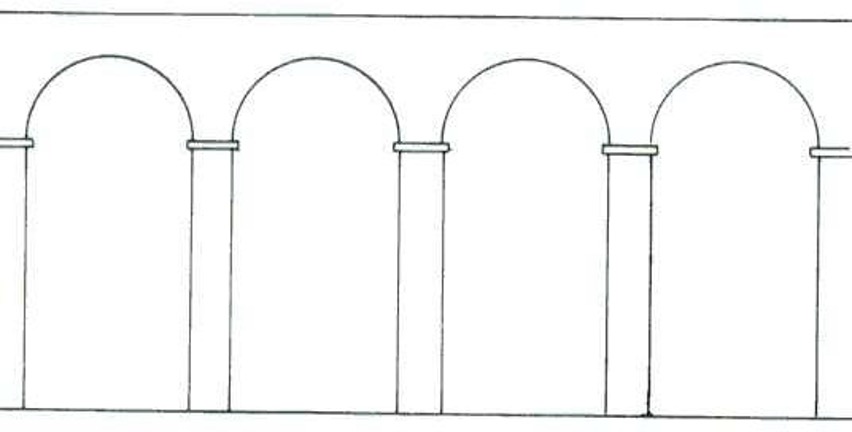
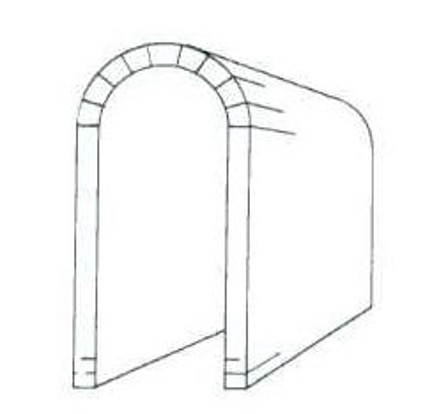
Vaults
The extension of arches to create enclosed spaced
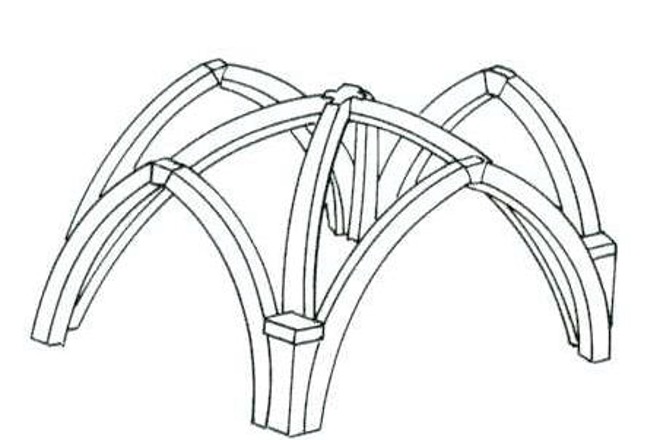
Rib vaulting
Protruding masonry as the diagonal junctures of a vault
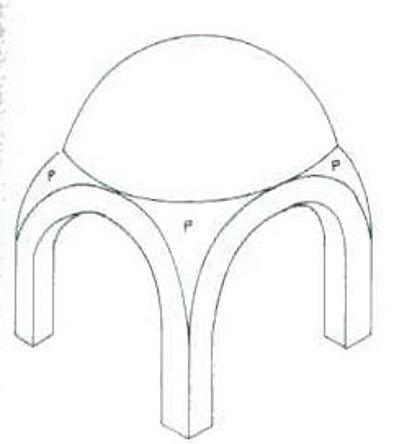
A done
A structure containing arches whose legs form a circle

Pendentives
Triangular transitional structures between the base of a dome and the arches beneath it
Doric
The name of the Ancient Greek column shows below

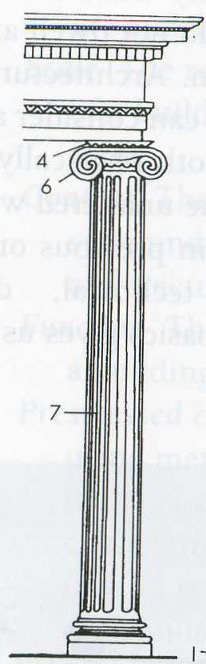
Ionic
The name of the Ancient Greek column shown below
Corinthian
The name of the Ancient Greek column shown below

Capital
The transition between the top of a column and the lintel
Fluting
Vertical ridge a cut in to a column
Structure
The means by which a building support a itself, is roof, its walls and is floors
Tensile strength
The capacity of a material to resist withstand bending forces
Compressive strength
The ability of a material to support weight and resist of withstand crushing
Compressive Strength of the Concrete,
Tensile Strength of the Steel
In modern architecture, concrete and steel are often combined to gain the benefits of each material, the _____ and the _____.
Prototype
A model on which another design is based
Buttress
A projecting structure, generally of stone, built against a a wall to support it
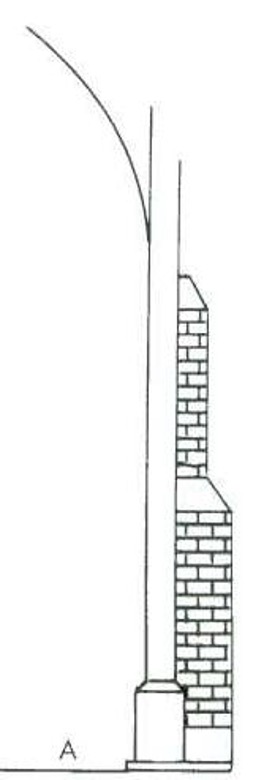
A flying buttress
A semidetached buttress connected by stone arms to the wall in is supporting

Skeleton frame structure
These structures use a framework to support the building. Examples are steel-cage construction that uses a framework of steels beams, and balloon construction that uses a framework of wooden beams
scale
The relationship of the size of a building to the human form
Proportion
The relationship of individual elements to each other in a design
Pitched roofs
In climate a where there is heavy snowfall, houses typically have sloped roofs called this
Pediment
A triangular window casing of architectural element
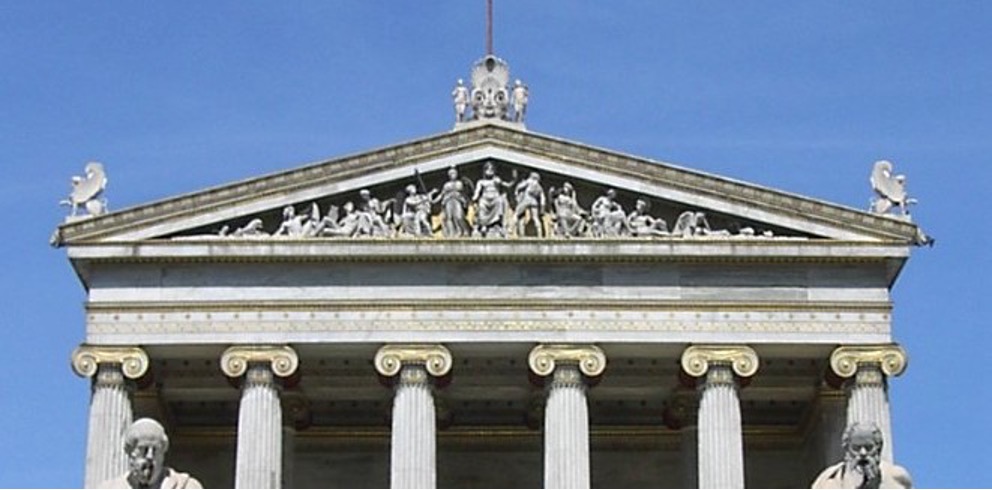

Portico
A porch like structure with a roof supported by columns

The inability to enclose large spaces
The principal limitation of post-and-lintel structure was this
Reflective Glass, Overhangs, Hurricane Shutters, Impact Resistant Glass, etc.
The se are examples of south florid architecture meets the challenges of our climate