Honors Biology - Unit 2
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Carbohydrates
the organic compounds made up of sugar molecules used mainly for energy
Total sugars
Monosaccharides aka. simple sugars
Dietary fiber
Polysaccharides aka. complex carbs
Lipids
an organic molecule such as fat or oil used to store energy and form cell membranes
Saturated fat
Mostly come from animal fats and are solid at room temperature
Unsaturated fat
Mostly come from plants and fish and are liquid at room temperature
Trans fat
Type of unsaturated fat that is made when liquid oils turn into solid fats during food processing
Proteins
molecules made up of amino acids that repair muscle tissue, act as an enzyme, transport nutrients, and defend the body
Calorie
A unit of measure that indicates the amount of energy our bodies would obtain with eating or consuming a particular food or drink
Amino acid
organic compounds that serve as the fundamental building blocks of proteins
Cellulose
forms the cell walls in plants, fungi, and bacteria
Chitin
A tough, fibrous structural substance, a type of complex carbohydrate (a polysaccharide) that forms the outer covering of arthropods like insects and crustaceans and is also found in the cell walls of fungi
Cholesterol
a lipid responsible for narrowing the arteries and causing the disease atherosclerosis
Dehydration reaction
when you build macromolecules together, and each time a monomer is added, a water molecule is released. It requires the assistance of an enzyme to speed up the reaction
Denaturation
The process where a protein or nucleus acid loses its natural, 3D folded structure due to external factors like heat, extreme pH, or certain chemicals
Deoxyribose
A simple, five-carbon sugar molecule that forms the backbone of DNA, the genetic material in living organisms
Disaccharide
formed when two monosaccharides bond together, also used for energy
fatty acid
A molecule that has a long chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms (a hydrocarbon chain) with a special group called a carbonyl group at one end
glucose
a monomer or “building block” of carbs (example a monosaccharide) used for energy by cells
Glycerol
A sweet, colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is a simple alcohol with three carbon atoms and three hydroxyl groups
Glycogen
how animals store energy
Hydrocarbon
A simple organic compound made up only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms
Hydrolysis reaction
Breaking down a macromolecule where each time water is added to a polymer, it breaks down monomers. It requires the assistance of an enzyme to help speed up the reaction
Hydrophilic
water-loving and easily soluble in water
Hydrophobic
Water-fearing, describing a substance that repels or does not mix with water, such as oil or fat, because it is nonpolar
Inorganic molecule
Molecules that don’t contain carbon, and are not carbon-based.
Insoluble
Something that cannot be dissolved in a liquid, like sand in water
fats
a type of lipid that’s an organic compound composed of a 3-carbon backbone (glycerol) and three fatty acids containing long hydrocarbon chains
Macromolecule
A molecule that’s found in living cells that are so large that you can distinctly separate them from other molecules in the body.
Monomer
smaller units that are building blocks of larger molecules
Monosaccharide
a simple sugar used for energy, the monomer of carbs
Nitrogenous base
A molecule containing nitrogen that functions as a building block for DNA and RNA, storing genetic information through specific pairing patterns
Nonpolar
A molecule with an even distribution of electrical charge, meaning it doesn’t have a distinct positive and negative “poles”
Nucleotide
The basic unit that links together to form DNA and RNA
Organic molecule
carbon-based molecules that have a bond between carbon and another atom or molecule
Phosphate group
A chemical unit of one phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms
Phospholipid
the major components of cell membranes
Polar
A molecule that has one side that is slightly positive, and another side that is slightly negative, like a battery
Polypeptide
A long chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds, serving as the fundamental building block for proteins
Polysaccharide
Complex carbohydrate where simple sugars form a chain. The polymer of carbs, stores energy and forms structures
Primary structure
The specific, linear sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain, linked together by peptide bonds
Ribose
A simple sugar with a five-carbon ring structure that is vital component of RNA, DNA, and ATP, the main energy-carrying molecule in cells
Saturated fatty acid
A fat molecule whose carbon chain contains only single bonds between carbon atoms
Soluble
A substance that is capable of being dissolved in a liquid
Triglyceride
The main form of stored energy in animals
Starch
how plants store energy
Cellular respiration
A process that breaks down food (in presence of oxygen) and converts chemical energy to ATP
ATP
The molecule cells depend on to perform day to day activities
Chemical energy
The energy that builds, rearranges, and breaks apart substances
Mechanical energy
The energy in charge of the movement of flagella and cilia, cell structures, and parts of our whole body
Electrochemical energy
The energy in charge of moving substances across the cell membrane via active transport
Vitamins
Contain necessary nutrients our body is unable to make, helps enzymes perform their jobs, essential components in skin/muscle/bones, help your body fight infections
Valence electrons
Electrons found in the outermost shell of an atom that take part in chemical bonding.
Functional group
A group of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecules in chemical reactions. They’re polar molecules because the O or N molecules are highly electronegative, and exert a strong pull on shared electrons
Polymer
Long chains of molecules formed by linking monomers together
Organic chemistry
? = the study of molecules that contain carbon
4
How many bonds is carbon capable of making?
Monomers make up polymers
How are the terms monomer and polymer related?
Carbohydrates
The picture represents the monomer for which macro-molecule?
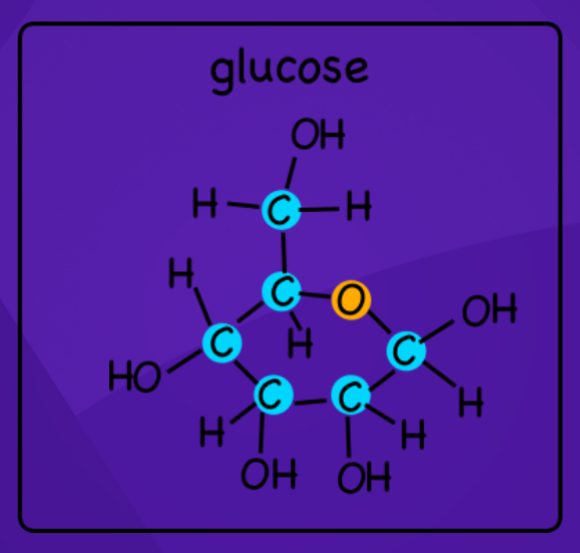
Lipids
The picture represents the monomer for which macro-molecule?
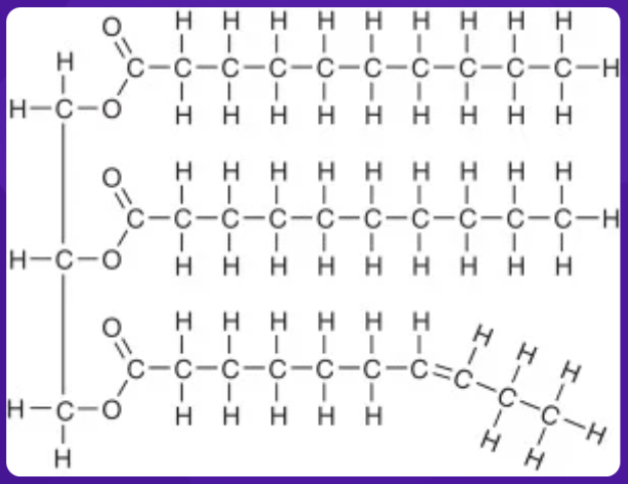
Hydrophilic
? = water loving
Hydrophobic
? = water fearing
Dehydration
What type of process occurs when water is removed to combine two monomers?
Hydrolysis
What type of process occurs when water is used to break bonds between monomers?
Carbohydrates
Which type of biomolecule is used as an energy source and for structural support?
Lipids
Which type of biomolecule is used to store energy and also to build biological membranes?
Carbohydrates
Which of the following biomolecules do plants use as “building materials”?
Polysaccharide
What is the name for a complex sugar?
Monosaccharide
What is the name for a simple sugar?
c. Glucose
Which of the following is NOT an example of a polysaccharide?
a. Starch
b. Cellulose
c. Glucose
d. glycogen
Monosaccharide
Which of the following structures is known as the monomer for carbs?
b. Glycogen
Which of the following polysaccharides is only found in animals?
a. Starch
b. Glycogen
c. Cellulose
d. chitin
Starch
Which type of polysaccharide is used by plants to store sugars?
Glycogen
Which type of polysaccharide is used by animals to store sugars?
Cellulose
Which type of polysaccharide is used as structural support by plants?
Chitin
Which type of polysaccharide is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods (insects)?
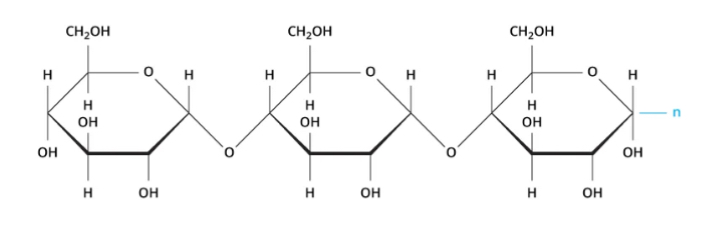
Starch
Which type of polysaccharide is represented by a single chain structure (image)?
Glycogen
Which type of polysaccharide is represented by a branched structure (image)?

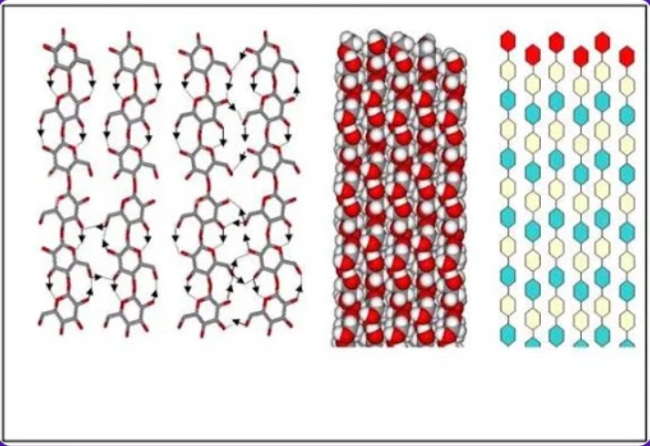
Cellulose
Which type of polysaccharide is represented by a multi-chained structure (image)?
b. Transporting materials
Which of the following is not a function of lipids?
a. Energy storage
b. Transporting materials
c. Waterproof coverings
d. Components of biological membranes
Trans fat
Which type of fat is most often linked to health issues?
Glycerol + fatty acids
What is the building block of lipids?
Saturated fat
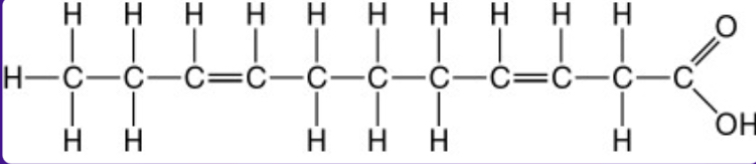
Saturated or unsaturated fat?
Unsaturated fat
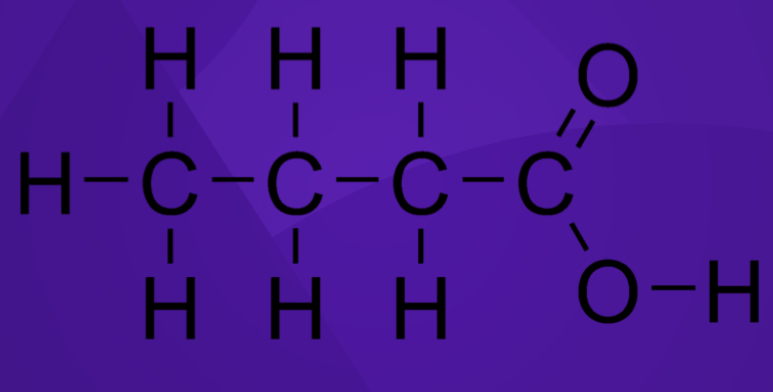
Saturated or unsaturated fat?
Saturated fat
Which type of fat is a solid at room temperature?
Unsaturated fat
Which type of fat is a liquid at room temperature?
Phospholipid
Which lipid is an important component of cell membranes?
Why do we eat
To obtain energy, to obtain essential building blocks to help us grow, to obtain essential building blocks to help repair our body, for fun
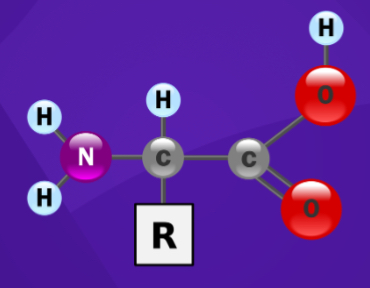
Proteins
The picture represents the monomer for which macro-molecule?
Dehydration reaction
What type of process occurs to allow amino acids to join together to create a polypeptide chain?
Hydrolysis reaction
What type of process occurs to break down a polypeptide chain apart into individual amino acids?
Protein
Which type of macromolecule aids in cell transport and receives/sends signals?
Denature
? = occurs when a protein loses its shape due to heat
R group
Which part of an amino acid is unique to all amino acids?
c. Phosphorous
Which of the following elements is not found in proteins?
a. Carbon
b. Nitrogen
c. Phosphorous
d. Oxygen
20
How many different amino acids are commonly found in proteins?
Bond between 2 amino acids
What is a peptide bond?
b. Providing energy for cells
Which of the following is not a function of a protein?
a. Transporting materials into and out of cells
b. Providing energy for cells
c. Sending and receiving signals
d. Speeding up chemical reactions
Shape
What dictates the function of a protein?
Amino acids
Which monomers are used to form enzymes?