BIOL 319 Lab Practical 2
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
what prefixes refer to muscle?
myo, mys, sarco
excitability
ability to respond to stimuli, all muscle cells are this
contractibility
ability to shorten, all muscle cells
extensibility
all muscle cells can be stretched
elasticity
all muscle cells, can go back to their normal size after being stretched
what is in skeletal muscle with the muscle fibers
nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues
epimysium, perimysium, endomysium
3 connective layers that make up muscle, the epimysium is around the muscle, the perimysium is around the muscle fascicle, and the endomysium is around the muscle cell/fiber
is skeletal muscle autorhythmic?
no
tendons
attach muscle to bone
what determines the insertion of a muscle?
the insertion is the muscle is the bone or structure that is being moved by the muscle
what determines the origin of a muscle?
the origin of the muscle is the structure or bone that mostly doesn't move
thick filament anatomy
-made of myosin
-runs the length of the A band
-golf club shaped, stacked on top of each other in alternating directions, each is two golf clubs that form a double helix and the two heads join together
-connected by the M-line
-each thick filament contains over 300 myosin molecules
thin filament anatomy
-made of actin
-connect at the Z-line
-have a helix of two actin chains
-also have tropomyosin and troponin
-the troponin has 3 globular polypeptides
-one binds actin, one binds tropomyosin, and the other binds calcium ions
what is z-line made of mostly
alpha-actinin
cross section anatomy
3 thick filaments surround each thin filament, and six thin filaments surround each thick filament
T tubules
Also called transverse tubules, these are deep invaginations of the plasma membrane found in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. These invaginations allow depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate to the interior of the cell.
-when a muscle contracts the nerve travels down the T tubule to penetrate deep in the muscle
sliding filament model
when sarcomeres shorten, thick and thin filaments slide past one another
- H zones and I bands narrow
- Z lines move closer together
A-band
where thin and thick filaments overlap in a relaxed muscle
-dark band on sarcomere
-these never change size in muscle contractions, they become closer together
muscle contraction steps
a motor nerve will stimulate a electrical action potential that will go to the sarcolemma. this will briefly allow calcium to be released in the cell, resulting in excitation-contraction coupling. somatic (voluntary) motor neurons activate skeletal muscles.
where are somatic (voluntary) motor neurons?
in the brain and spinal cords. the axons are bundled together and form a nerve that then runs to the muscle they innervate.
what happens to a nerve once it enters the muslce?
the axon enters the muscle, it divides into several axon branches which serve muscle fibers (cells)
How many neuromuscular junctions (motor end plate) does each muscle fiber have?
only one, it is used to communicate with the muscle
space between end of axon and the axon and the muscle fiber
the end of the axon is the synaptic cleft, and the space between that and the muscle fiber is called the synaptic cleft and it is filled with extracellular fluid with collagen fibers and glycoproteins. there are "mounds" called the axon terminals have ACh (acetylcholine). there are folds to increase surface space for more ACh receptors.
muscle contraction explained
motor neurons release action potentials to the muscle fibers. when the action potential go through the cell it causes calcium/sodium? to temporarily be released. this then causes ACh to be released and the chemicals diffuse across the membrane and out of the NaK channels. it is then depolarized and stoped by acetylcholinervse at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
Myasthenia gravis
immune system attacks the ACh receptors causing the muscles to not be able to contract. symptoms are difficulty swallowing, drooping eyelids, and generalized muscle weakness
initiation and propagation of a muscle action potential
1. acetylcholine binds to its receptors opening the chemical ligand-gated ion channels for sodium and potassium. sodium enters the cell due to diffusion and having a higher concentration outside of the cell. this makes the inner surface of the sarcolemma less negative, aka depolarized. this is called the end plate potential
2. voltage-gated sodium channels on the surrounding sarcolemma respond to the charge change and open to allow positive charged sodium to enter. once threshold is met, then it can spread and open more channels called a muscle action potential
3. once the voltage becomes sufficiently less negative , the voltage-gated sodium channels close and the voltage-gated potassium channels open. potassium exits the cell and it is polar again. these channels close once it is negative enough
what happens when a muscle contraction starts before the other is finished?
the second contraction will be stronger and/or more sustained due to intracellular calcium still being present in the cell from the first contraction
what is a motor unit?
a motor unit is the motor neuron with all the individual muscle fibers it innervates
-they vary in size, a small motor unit only has a few muscle fibers, where a large motor unit has thousands of muscle fibers
-each only contains one motor neuron regardless of size
-not in bundles in the muscle fiber, are spread out to have control of whole muscle and not just little parts of it
-small motor units may only go in a few fibers, while large motor units go to more fibers
small motor unit
for fine motor control (hand, fingers, eye)
large motor unit
occur in weight-bearing muscles, limb muscles
isometric contraction
muscles contract but joints do not move and muscle fibers maintain a constant length
-muscle tension increases but muscle length remains constant
-performed against a immovable constant
-help maintain posture and stabilize joints
isotonic contraction
body part is moved and the muscle fibers shorten and lengthen. muscle tension remains constant and muscle length changes
-concentric= muscle length decreases, bicep curl
-eccentric= muscle length increases, calf mucles when walking
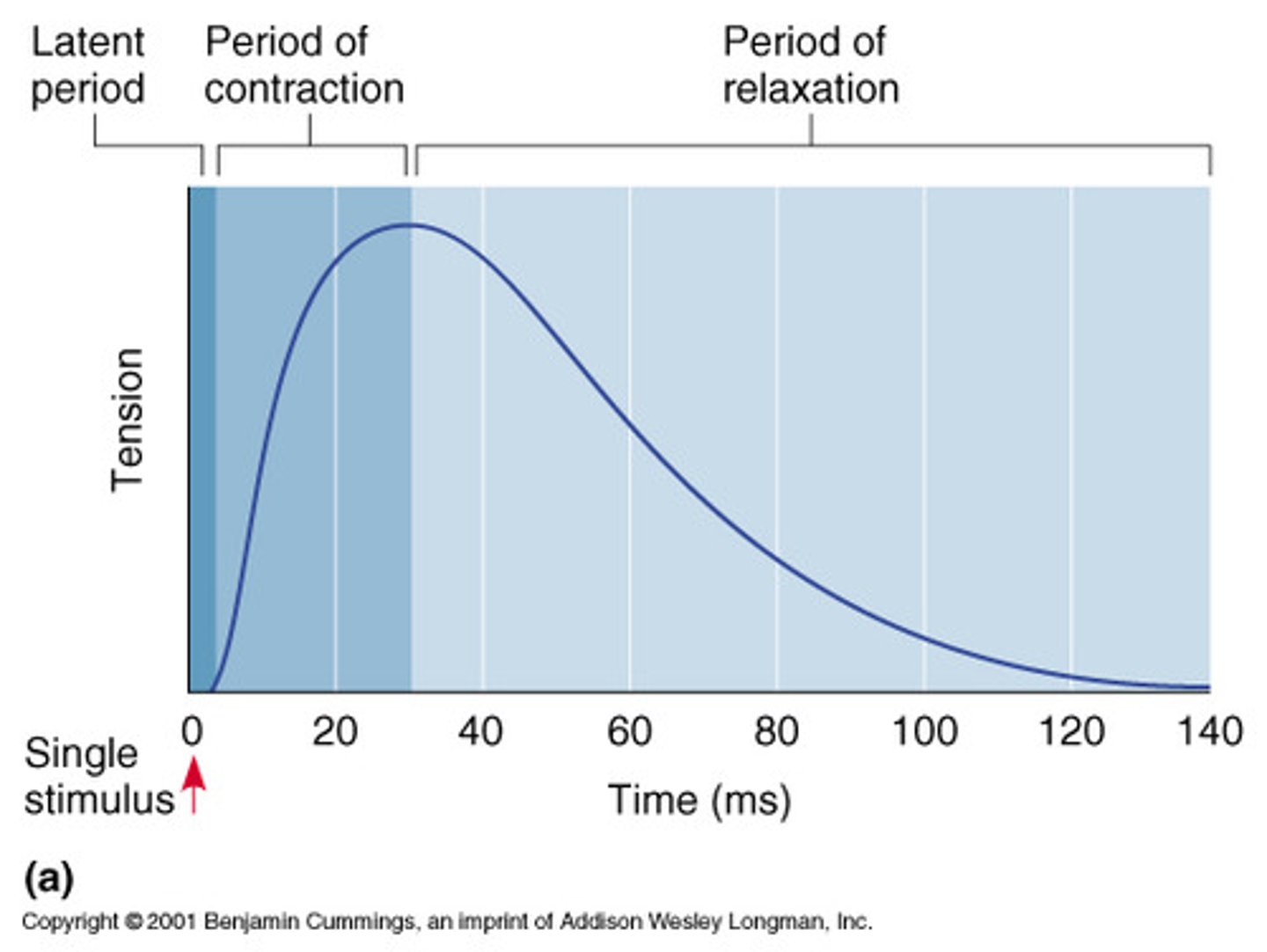
isometric twitch graph
latent period, period of contraction, period of relaxation
hoe many motor axons control a whole muscle?
up to hundreds, use recruitment (adjusting the number of motor axons firing to control the number of twitching muscle fibers
when does a threshold stimulus occur?
when the stimulus is just strong enough to generate an observable contraction
the strenth of the stimulus...
affects the strength of the muscle contraction
-low threshold, easily excitable motor neurons control small motor units
-high threshold, least excitable motor neurons control large motor units
summation
when stimulation levels between 200 and 75ms are still active when another contraction starts. the next contraction will be stronger than normal
tetanic contraction
continuous, forceful muscular contraction without relaxation
complete tetanic contraction
when the resulting forceful, sustained contraction lacks even partial relaxation
antagonistically
two or more muscles where contraction of one muscle stretches/elongates the other
Electromyography (EMG)
recording the strength of muscle contraction as a result of electrical stimulation
-provides depiction of the timing and pattern of muscle activity during complex movements
co-activation of muscles
when a contraction of one muscle leads to some minor contractile activity in the antagonist muscle
-helps stabilize joints and generate smooth contractions and relaxations against the load on the muscle
learned reflexes result from
repetition
an inborn reflex is
a rapid, predictable, involuntary, and unlearned reflex as a result of a stimulus
visceral reflex
regulated my more primitive regions of the central nervous system, pupil
myotatic reflex
A fundamental spinal reflex that is generated by the motor response to afferent sensory information arising from muscle spindles. The knee jerk reaction is a common example. Also called a "stretch" or "deep tendon" reflex.
5 parts of reflex arc
1. receptor- senses the stimulus, initiates signal
2. sensory neuron- carries afferent nerve impulses to the CNS
3. integration center- where signal is processed, mostly in the CNS
-one single synapse between a motor and sensory neuron is this in simple monosynaptic
-polysynaptic reflexes have a few synapses and interneurons
4. motor neuron- carries efferent signals to effector from integration center
5. effector- muscle or gland where the response to the signal is generated
somatic reflex
contraction of skeletal muscles
autonomic reflex
regulate the activity of smooth muscles, the heart, and glands
what do the muscle spindles do in skeletal muscle?
convey information about muscle length or the amount of stretch
what do the golgi tendon organs do?
the golgi tendon organs convey information about tendon tension to inform the central nervous system for the regulation of these reflexes
-proprioceptive feedback
muscle spindles
made up of 3-10 modified skeletal small muscle fibers called intrafusal muscle fibers
what makes a fiber contractable?
presence of myofilaments
anulospiral endings
endings of large axons that wrap around the spindle center, stimulated by both rate and degree of stretch
flower spray endings
smaller axons, supply the ends of the muscle spindles and are the only stimulated in response to amount of stretch
gamma efferent fibers
-from small motor neurons of the spinal cord ventral horn, stimulates the contraction of intrafusal fibers when rest of muscle contracts.
what maintains tension in the intrafusal fibers and why?
the gamma efferent fibers, makes sure they do not slack as the muscle contracts to not loose sensitivity.
Alpha efferent fibers
Stimulate the extrafusal muscle fibers to contract
alpha-gamma coactivation
When the muscle is stimulated to contract by the alpha motor neuron, the gamma motor neuron is simultaneously stimulated
why does the brain stimulate gamma neurons?
to cause the spindle to stretch and become more sensitive or to make them loose and insensitive. increases sensitivity during difficult or fast movements
Ipsilateral
involve motor activity on the same side of the body
all stretch reflexes are
ipsilateral and monosynaptic
-on one side of the body and one synapse
-includes the myostatic reflex (knee cap hit)
the total stretch reflex arc is
polysynaptic
a absent reflex could indicate
damage of peripheral nerves such as from neurosyphilis or chronic diabetes mellitus
what prevents tendons and muscles from tearing?
the stretch reflex stimulates a contraction when the muscle is stretched but the tendon reflex has the opposite response
reciprocal activation
contracting muscle relaxes, antagonist contracts
-relieves tension on the tendon
what causes a longer delay between stimulus reception in more complicated reflexes?
they have interneurons and more than one population of motor neurons
-pupillary reflex is an example
consensual light reflex
shining a light into one eye causes the pupil of the other eye to contract
Miosis
constricted pupils
mydriasis
dilation of the pupil
flexion reflex
A polysynaptic spinal reflex that produces withdrawal of a limb from a painful stimulus
-ipsilateral
nociceptive pain
pain from a normal process that results in noxious stimuli being perceived as painful
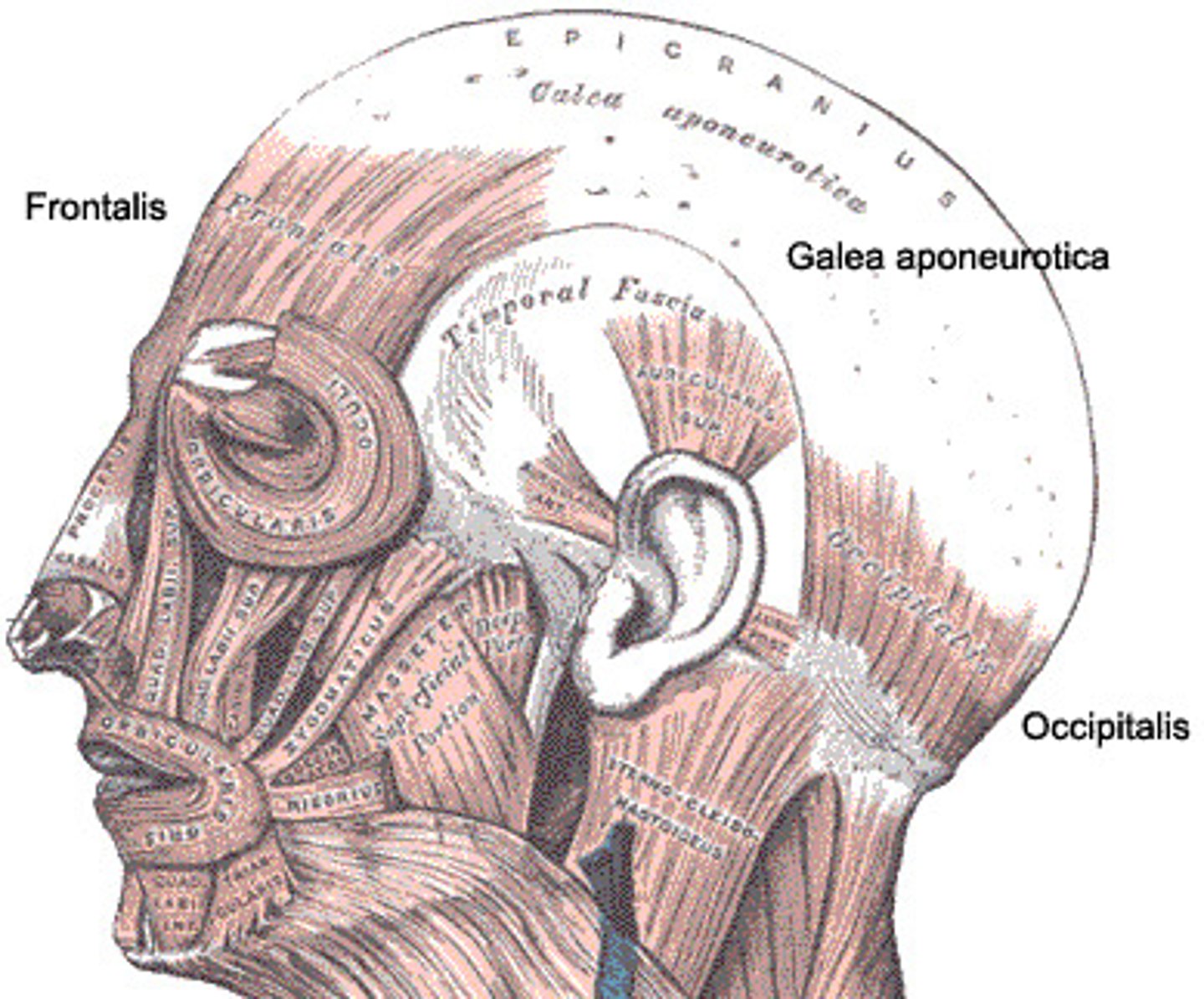
frontalis action
elevates eyebrows, creases skin of forehead, move scalp forward
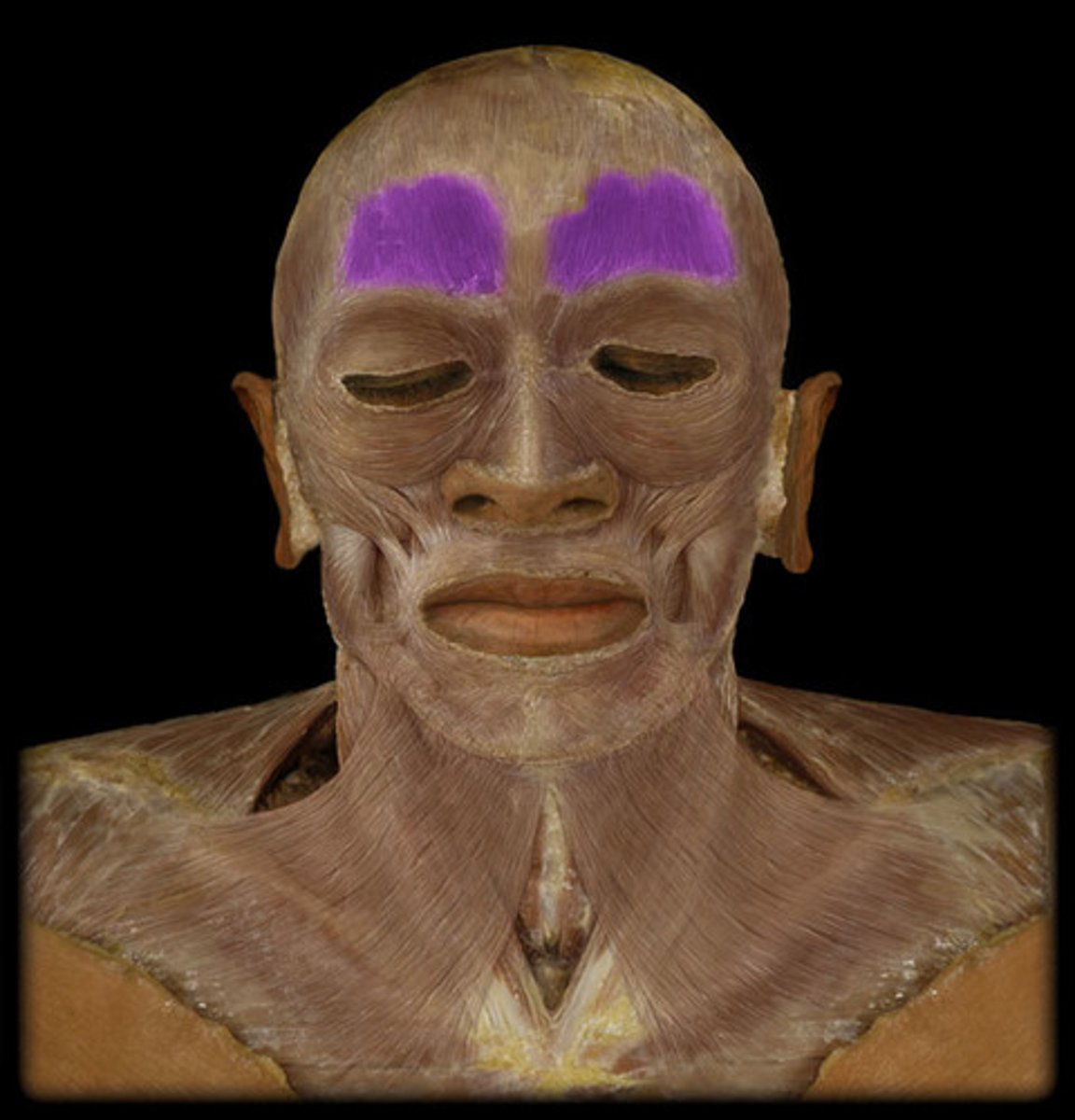
frontalis origin
epicranial aponeurosis
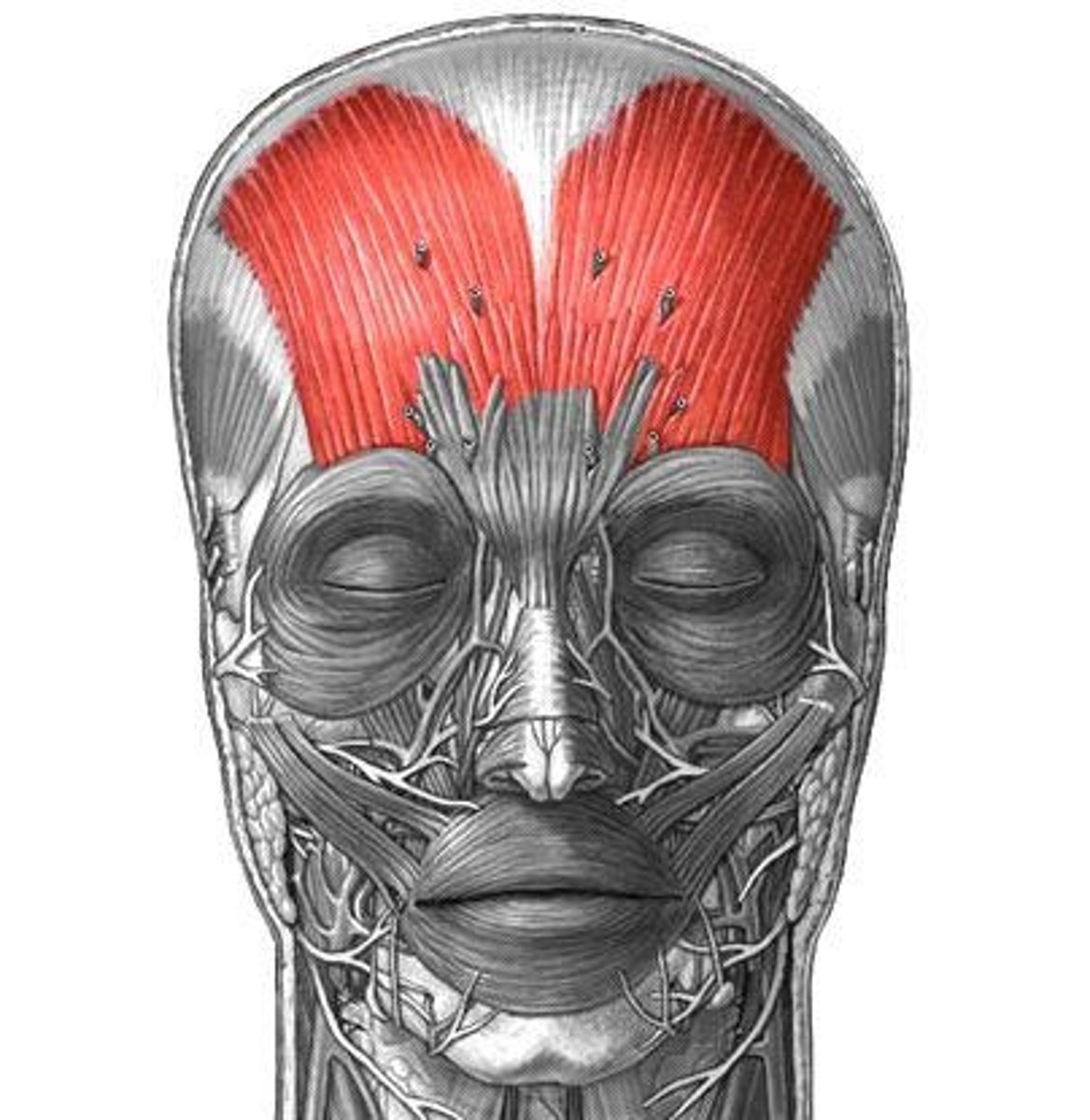
Frontalis Insertion
skin of eyebrows and forehead
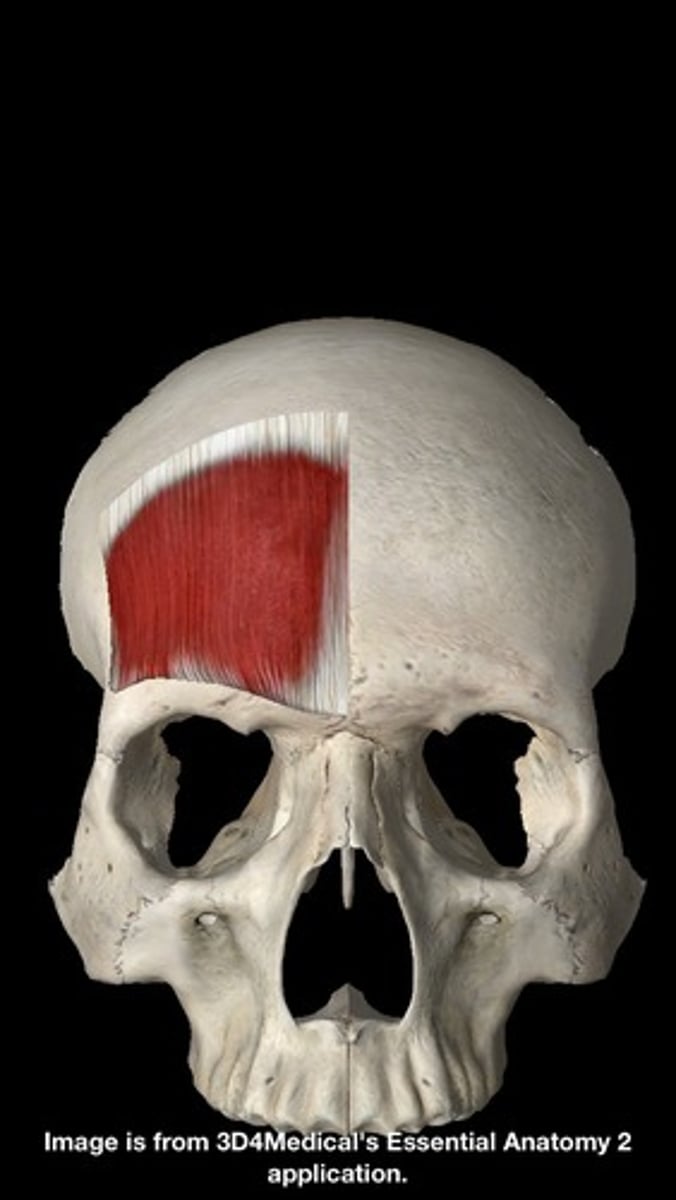
occipitalis action
moves scalp backwards (as part of epicranius muscle-elevation of eyebrows, creases forehead)
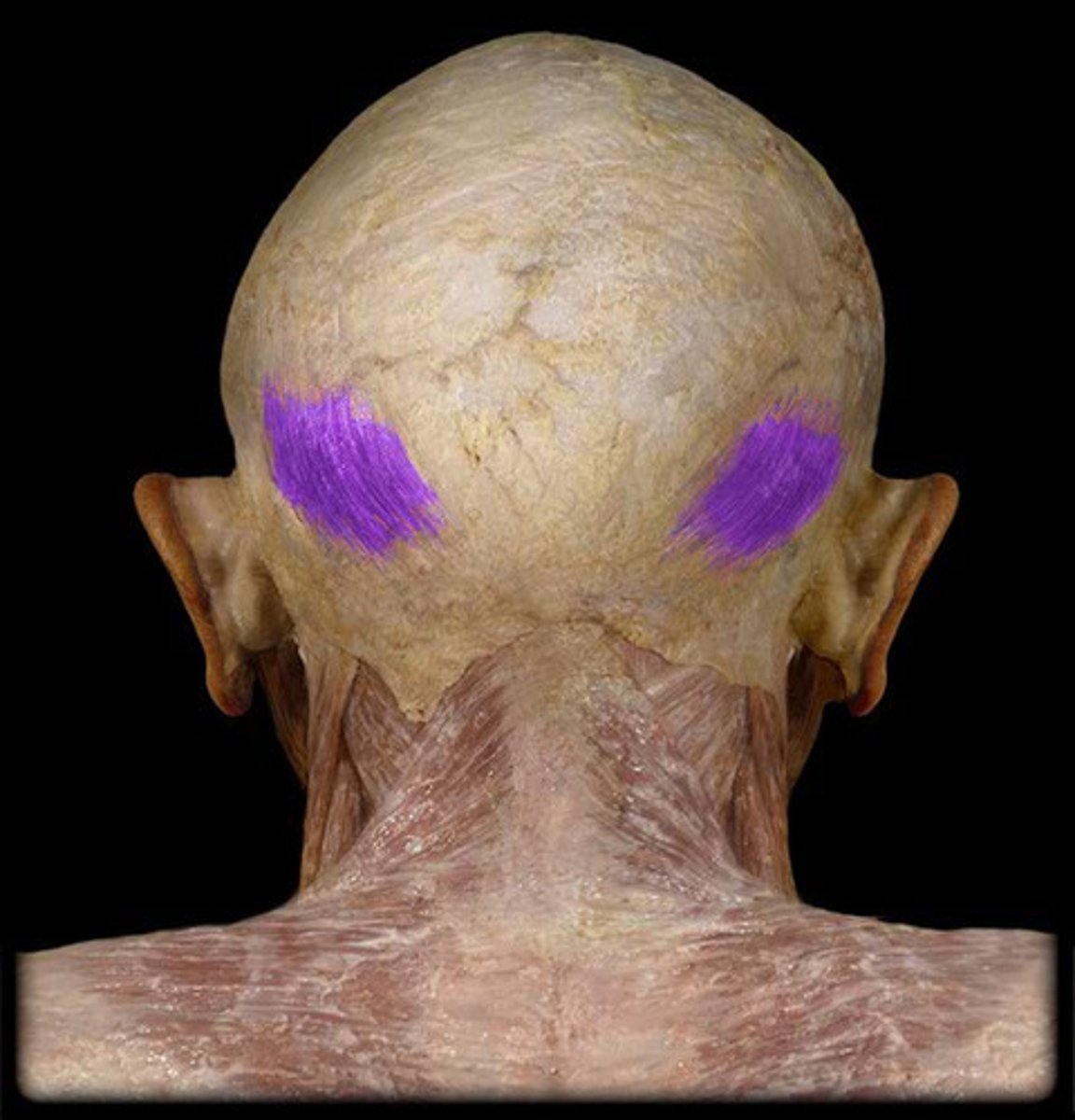
occipitalis origin
occipital bone (superior nuchal line)
occipitalis insertion
epicranial aponeurosis
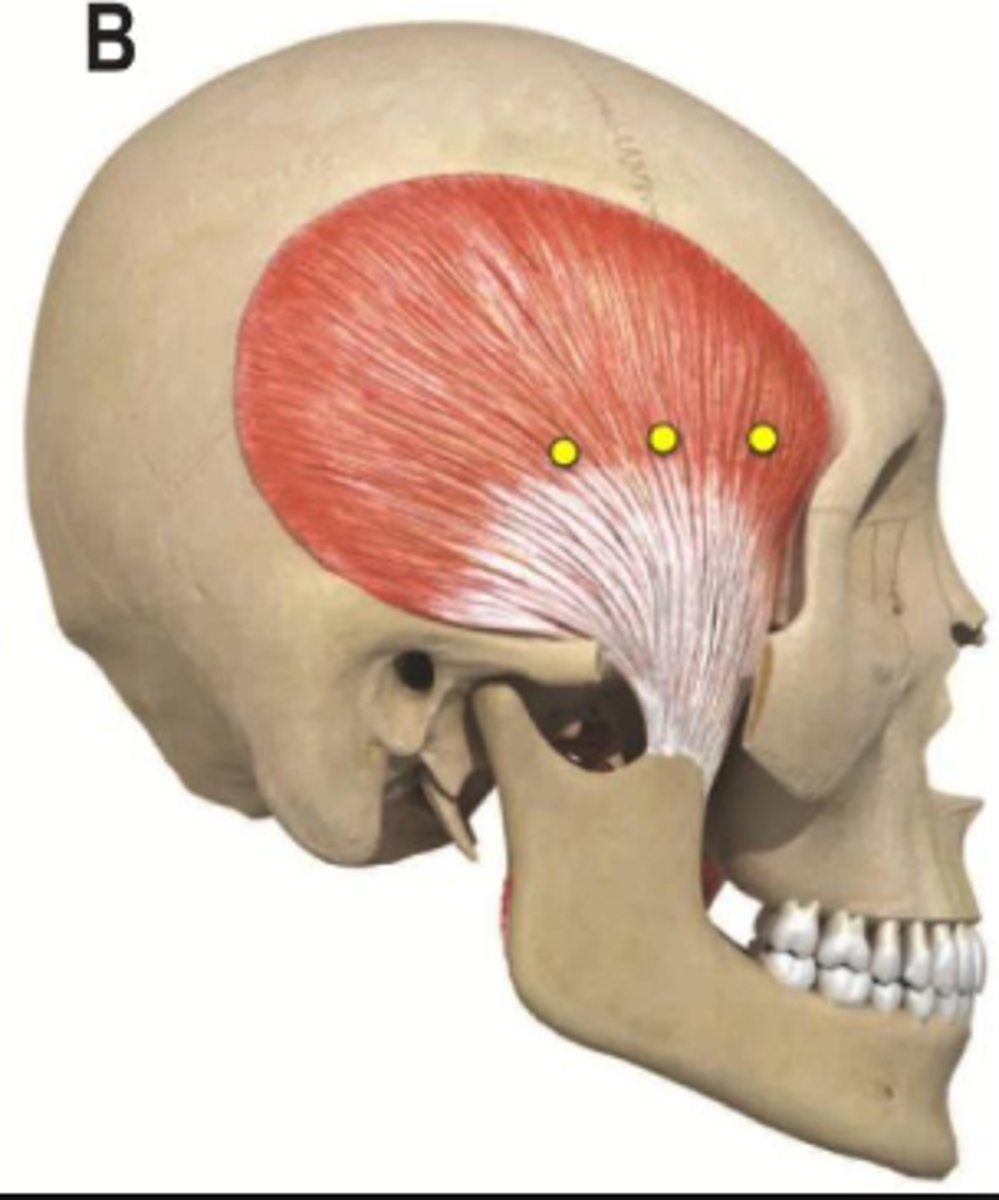
temporalis action
elevation and retraction of mandible
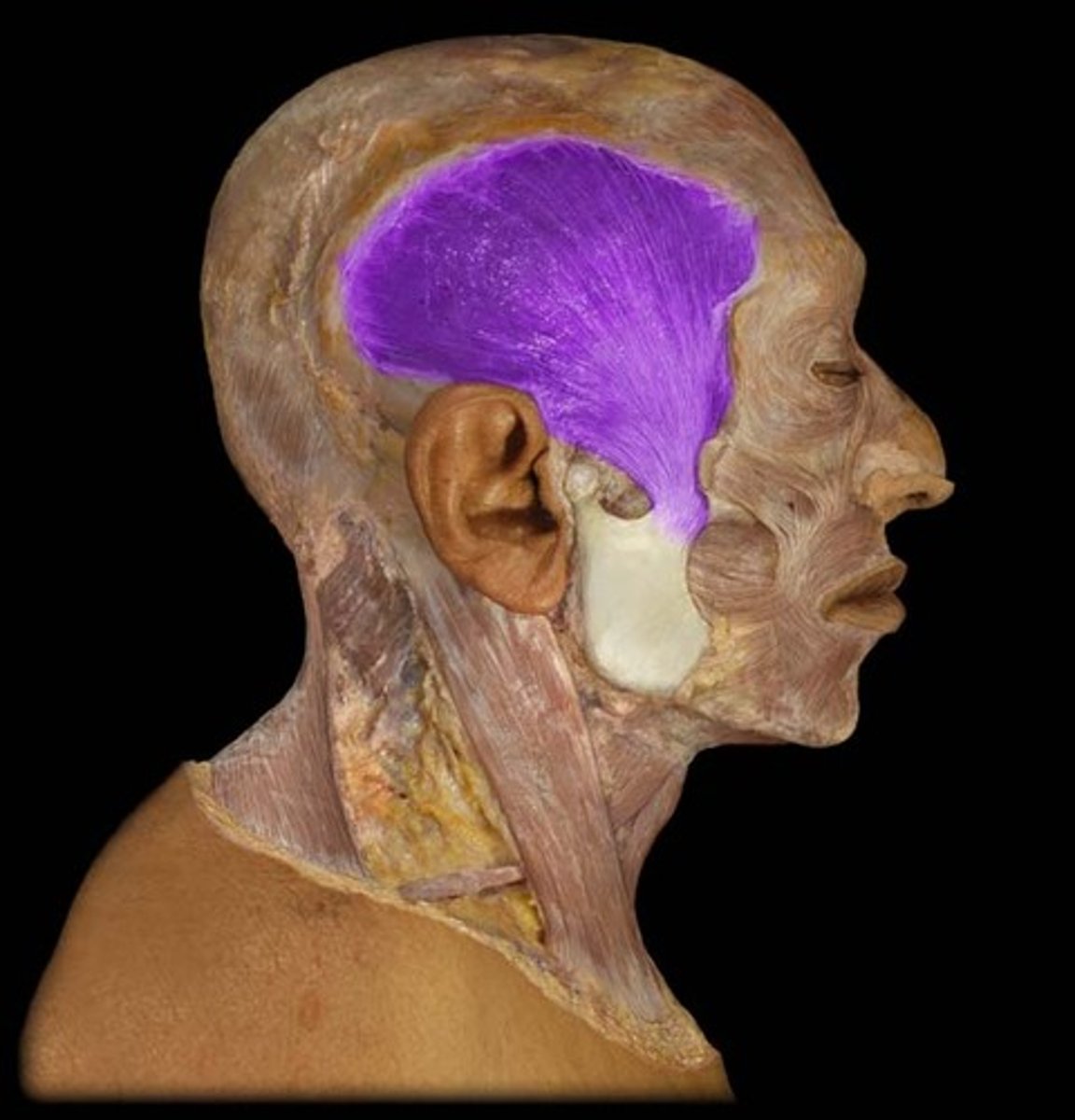
temporalis origin
temporal fossa
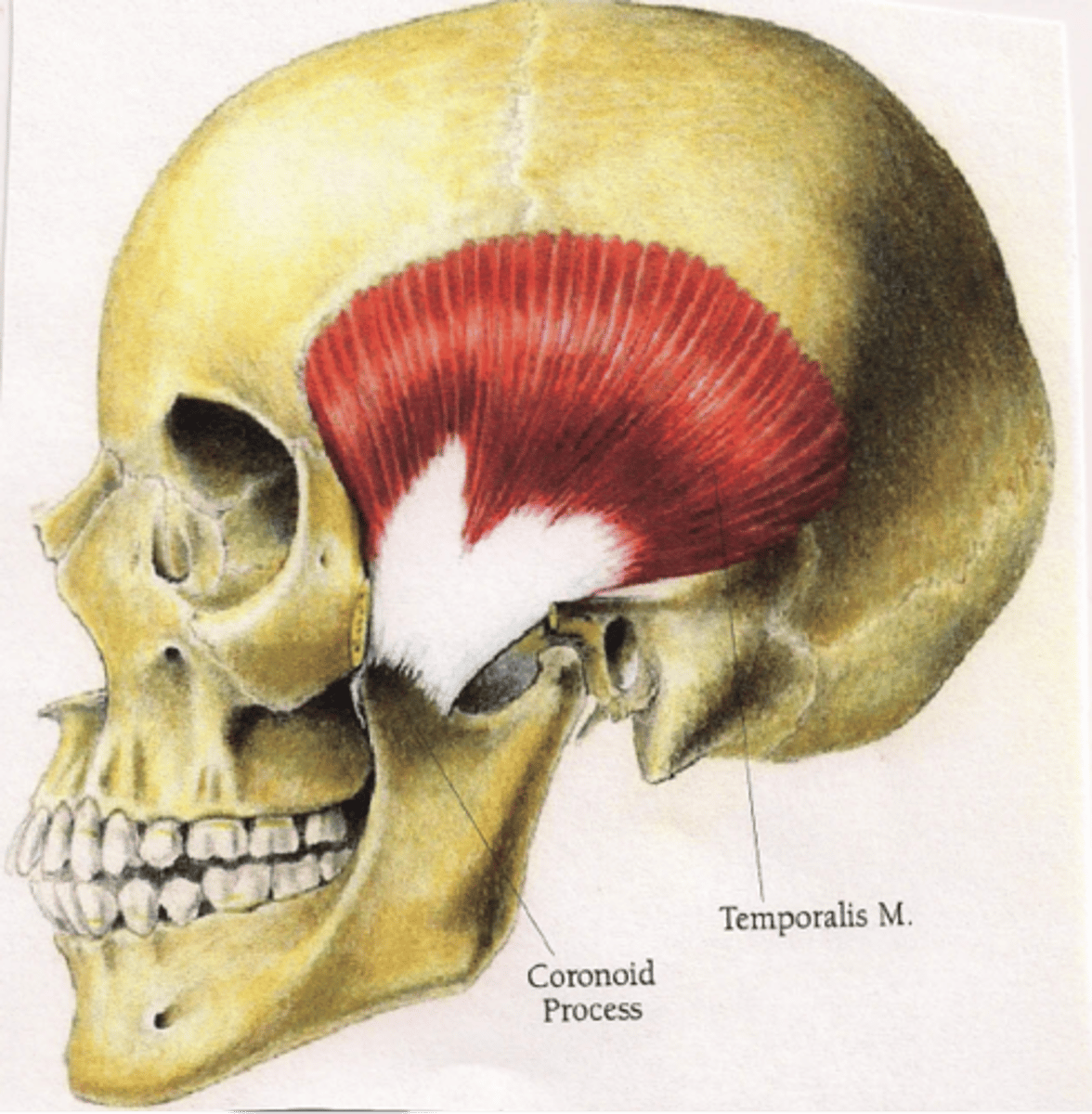
temporalis insertion
coronoid process and ramus of mandible
masseter action
elevation and protraction of mandible
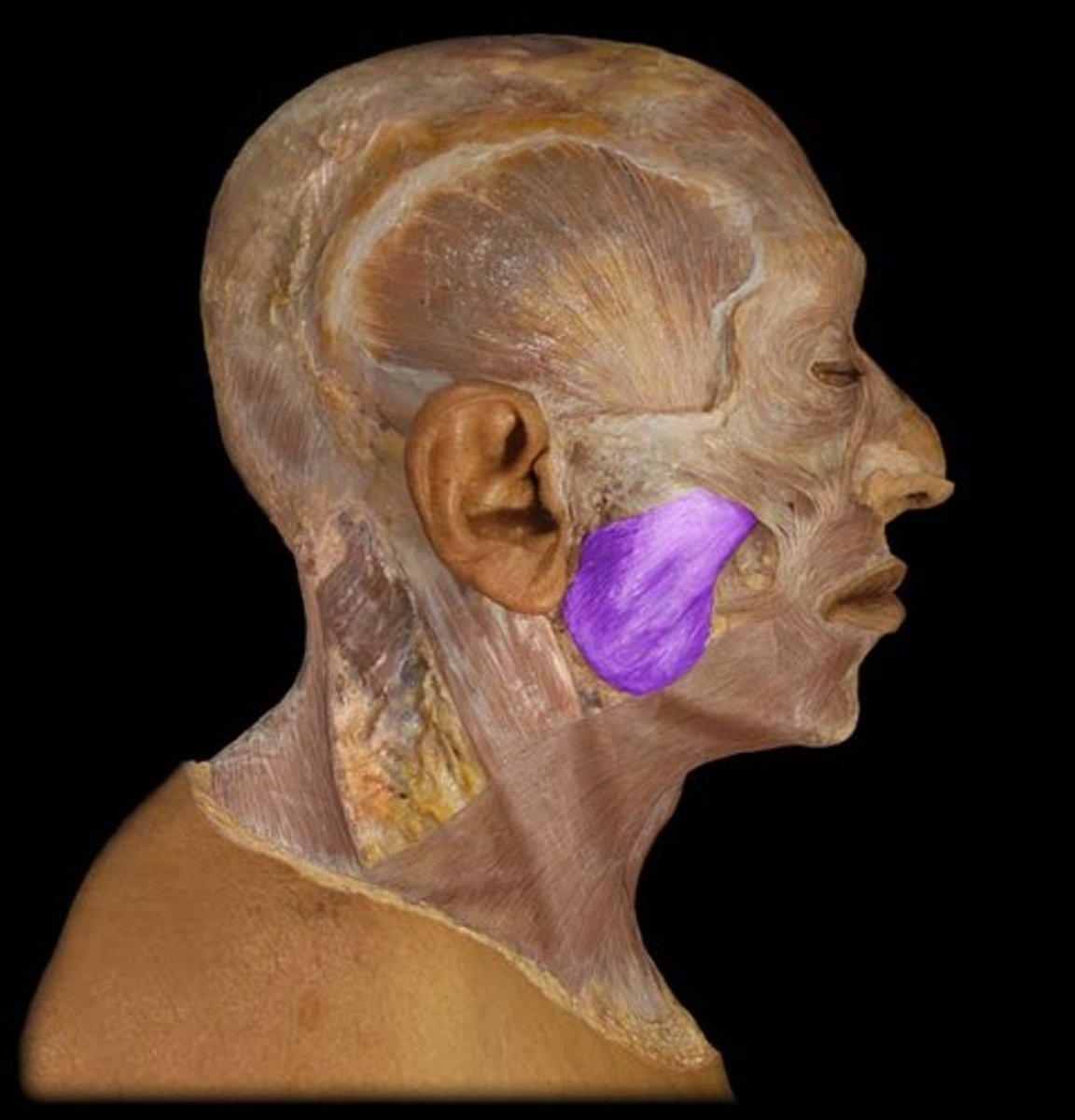
masseter origin
zygomatic arch
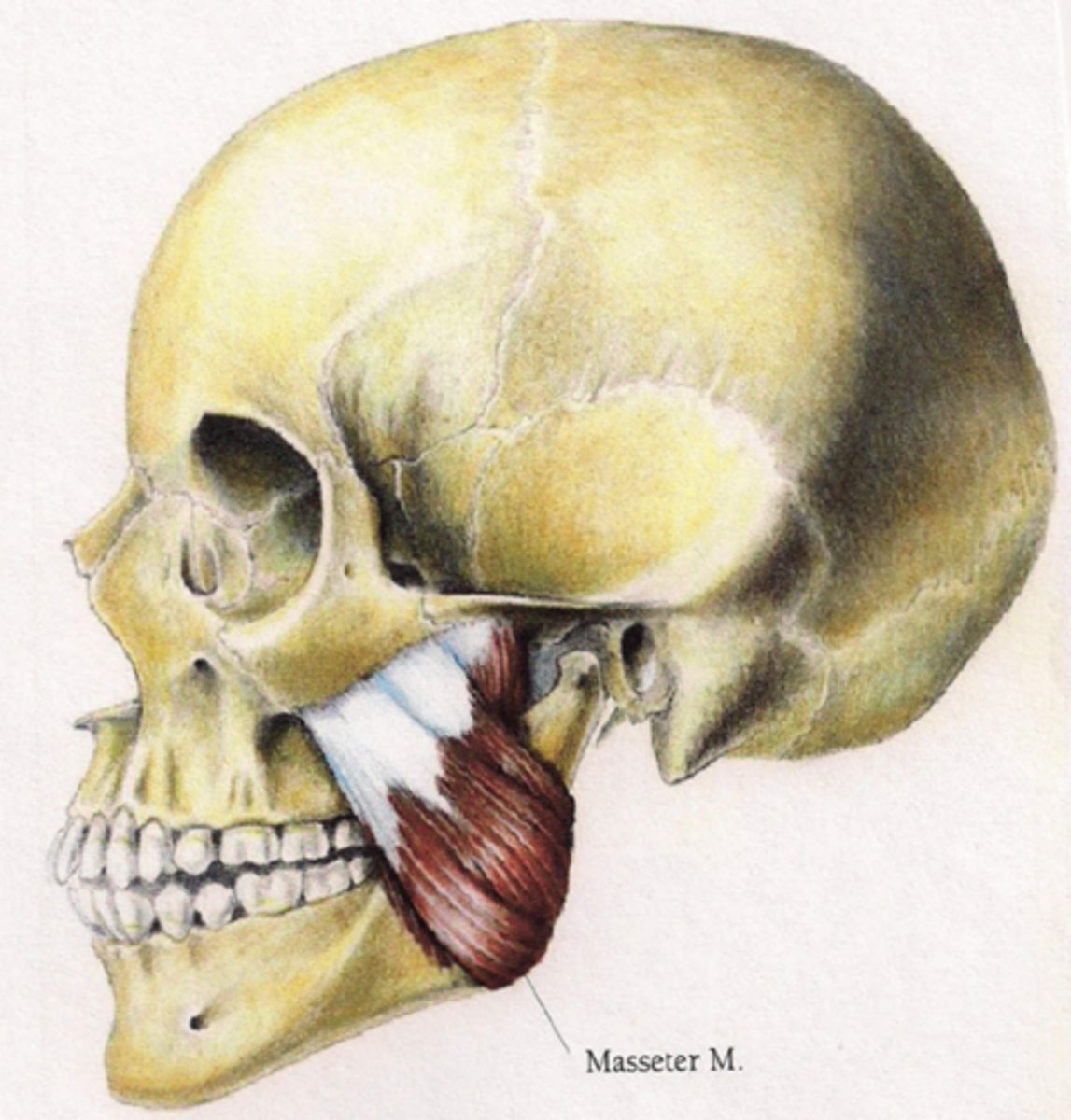
masseter insertion
mandible (external surface of angle and ramus)
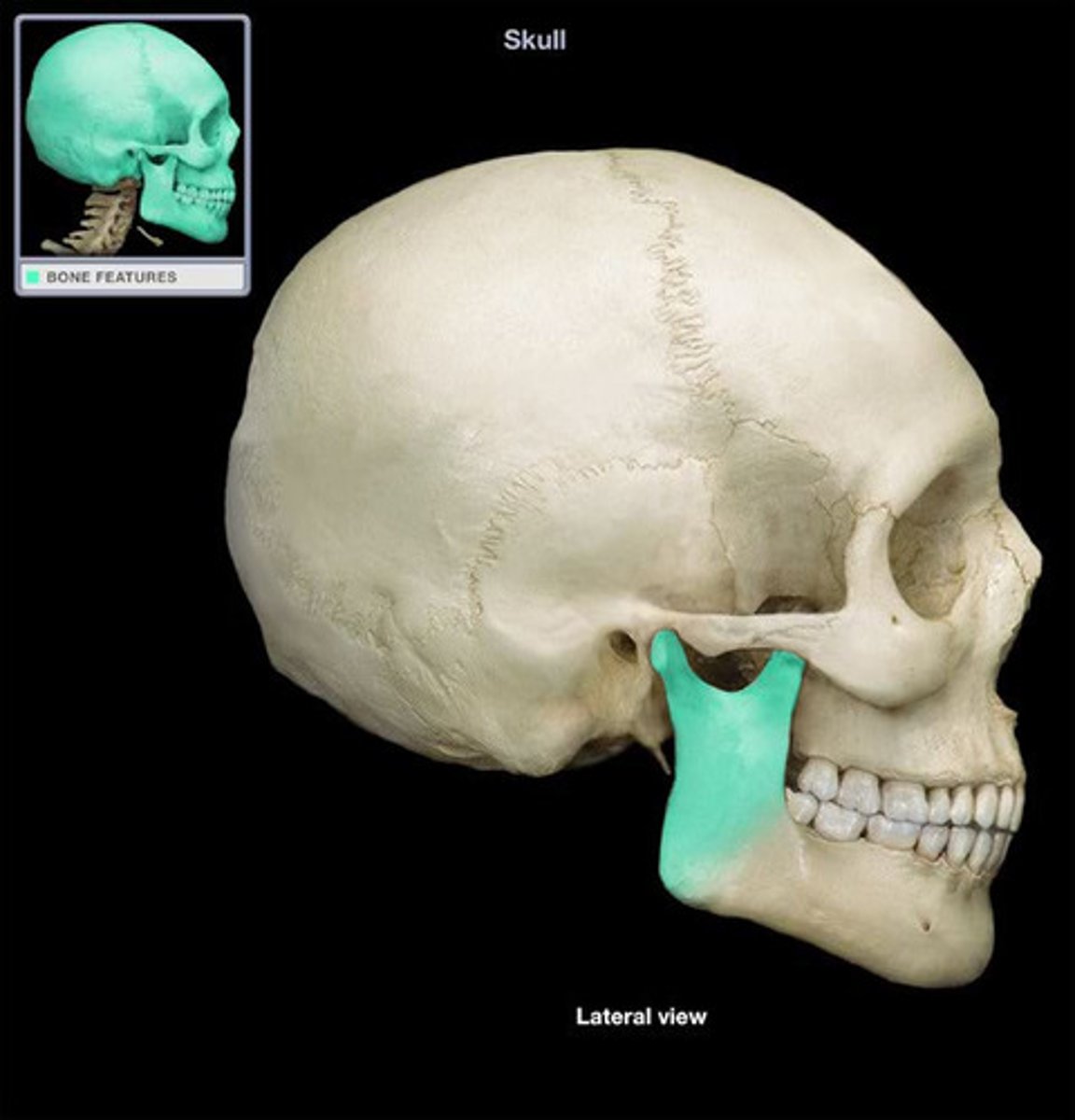
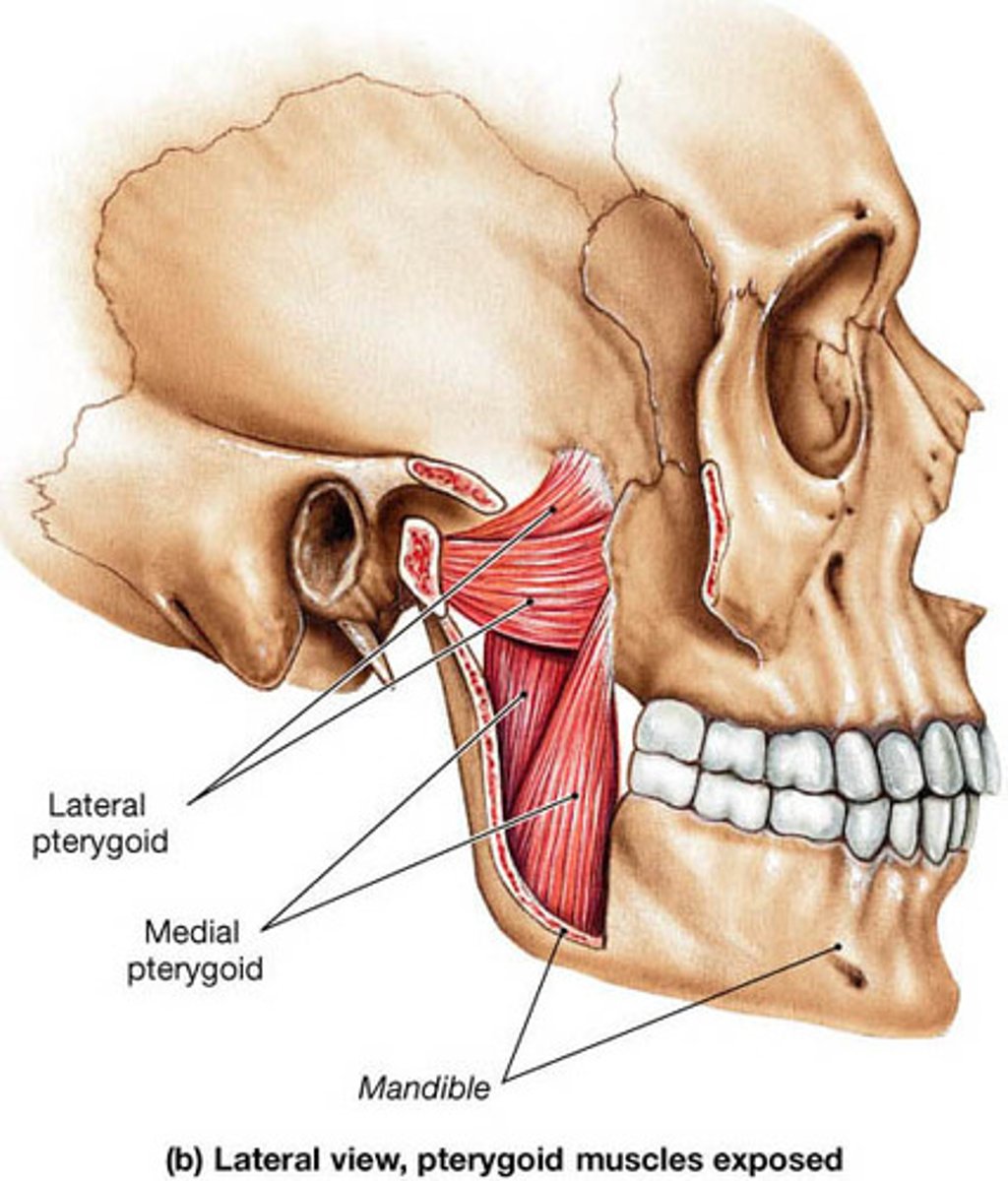
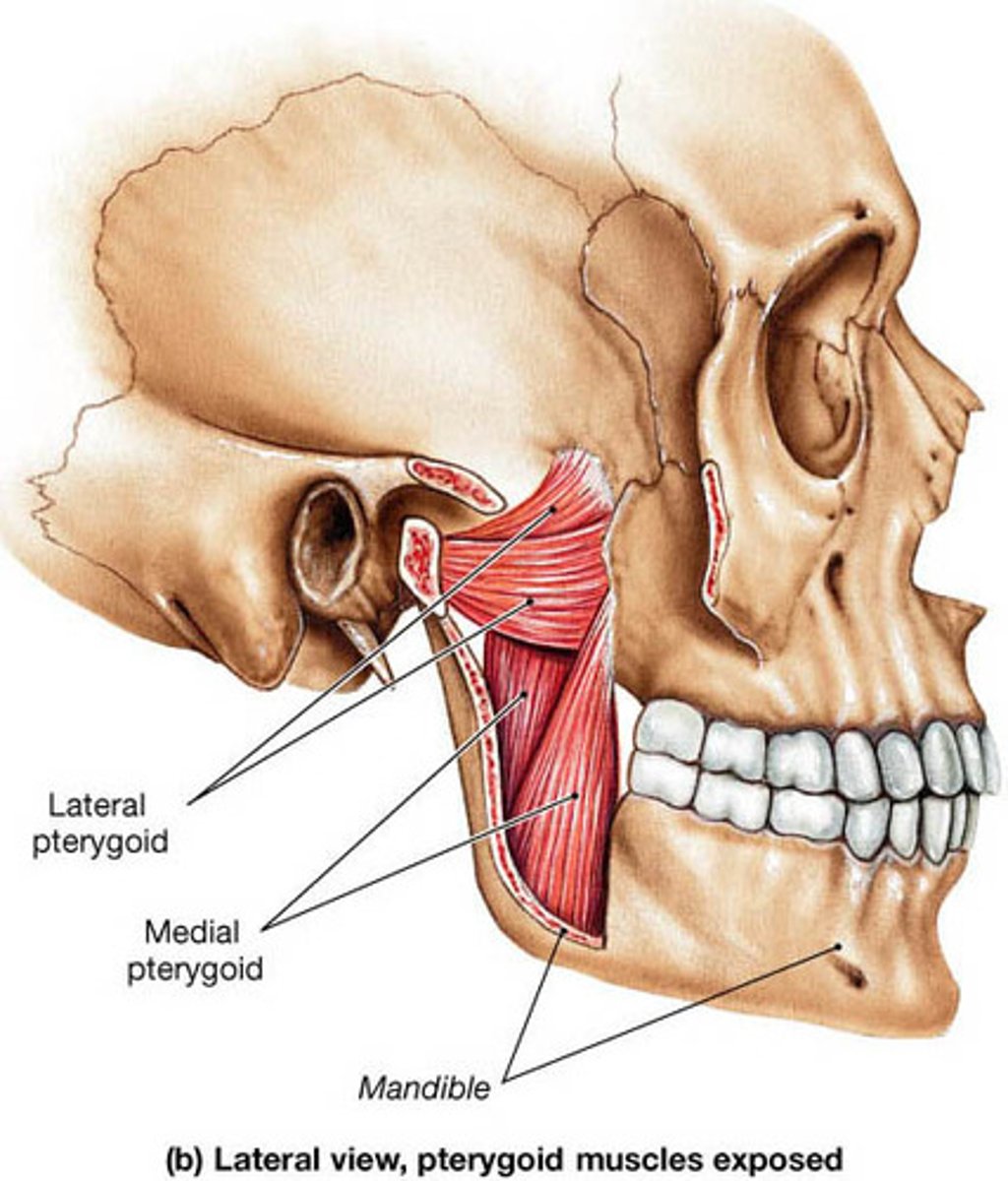
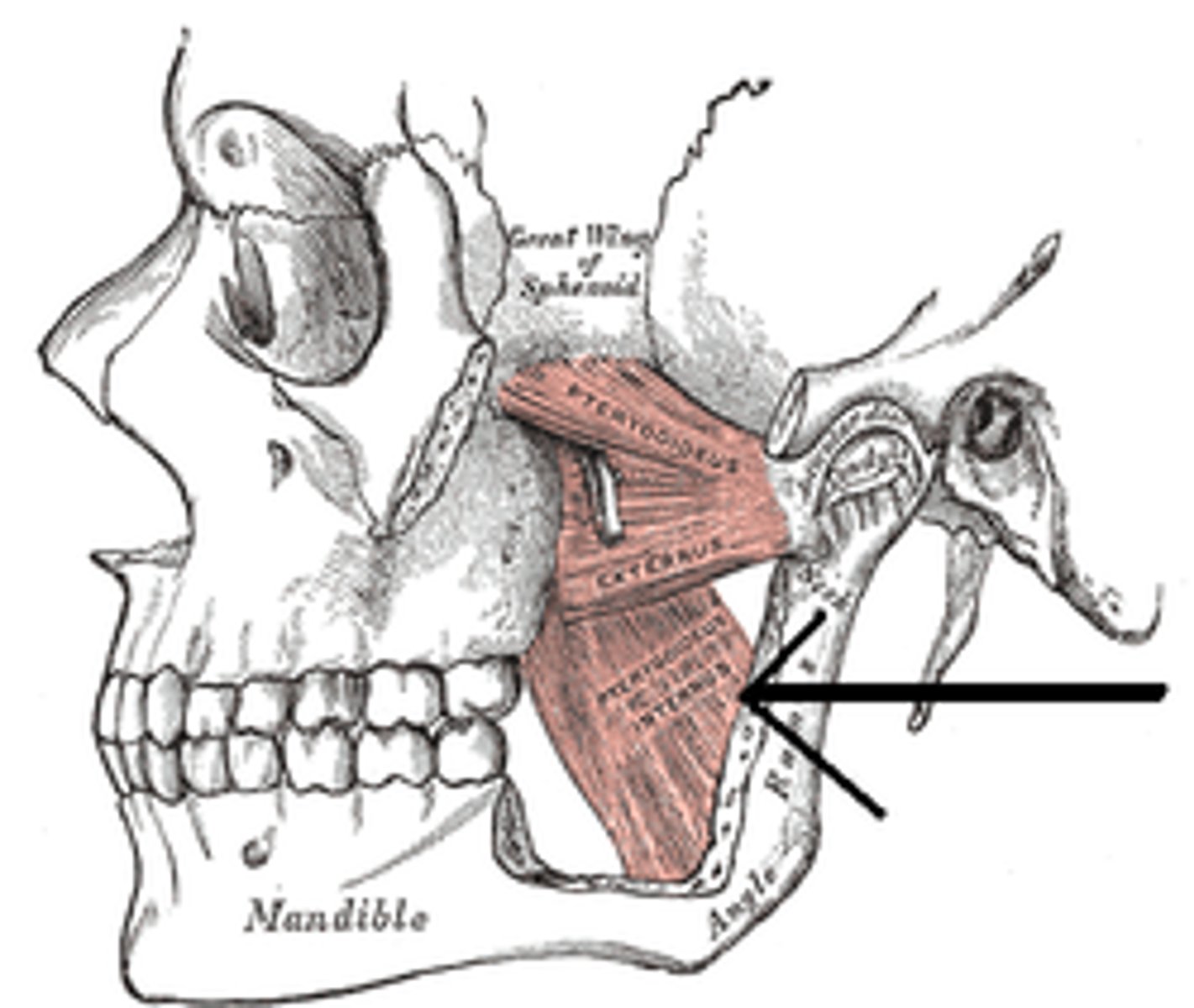
medial pterygoid action
elevation, protrusion and side-to-side movement of mandible
medial pterygoid origin
sphenoid bone (pterygoid process)
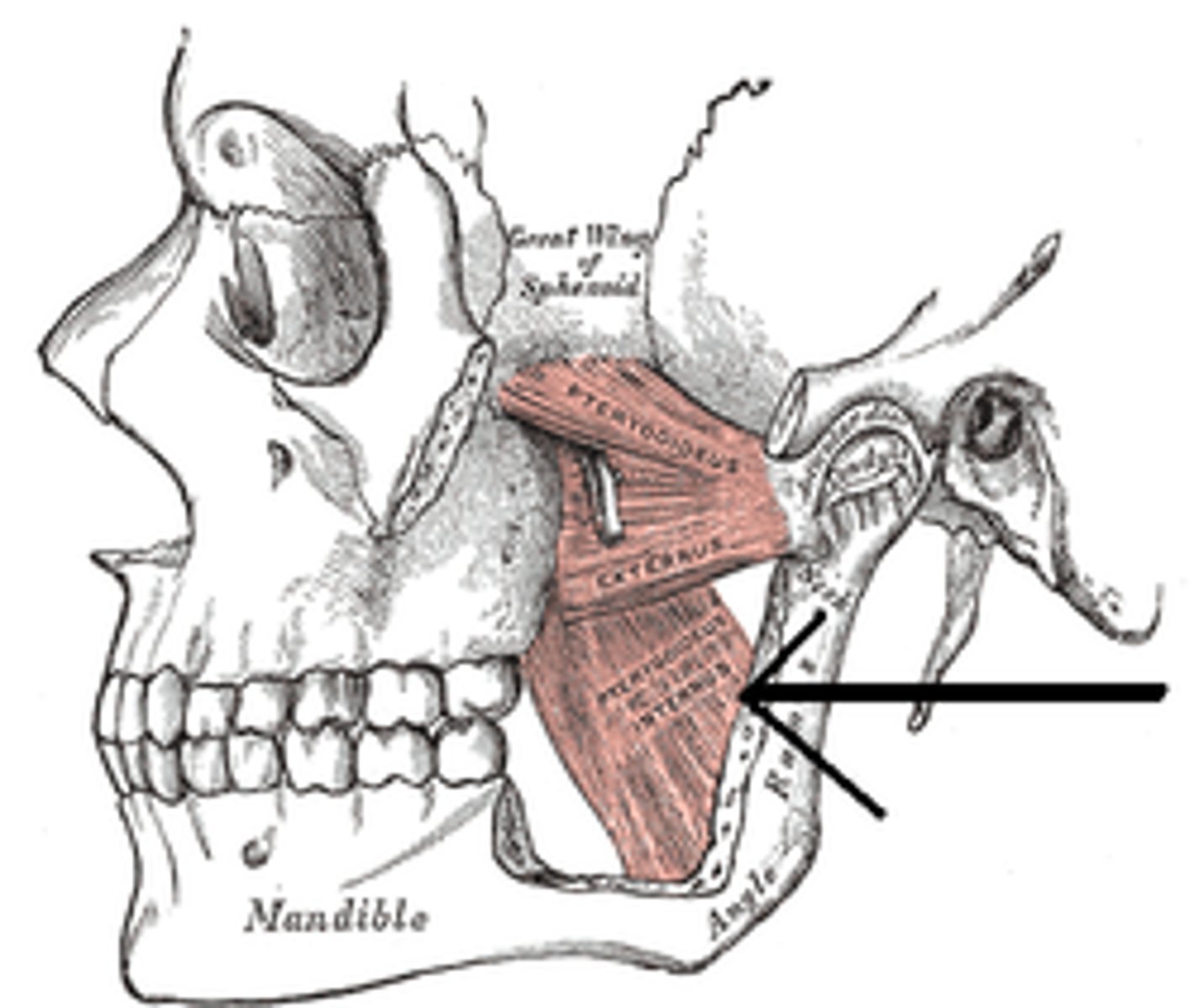
medial pterygoid insertion
mandible (medial surface of angle and ramus)
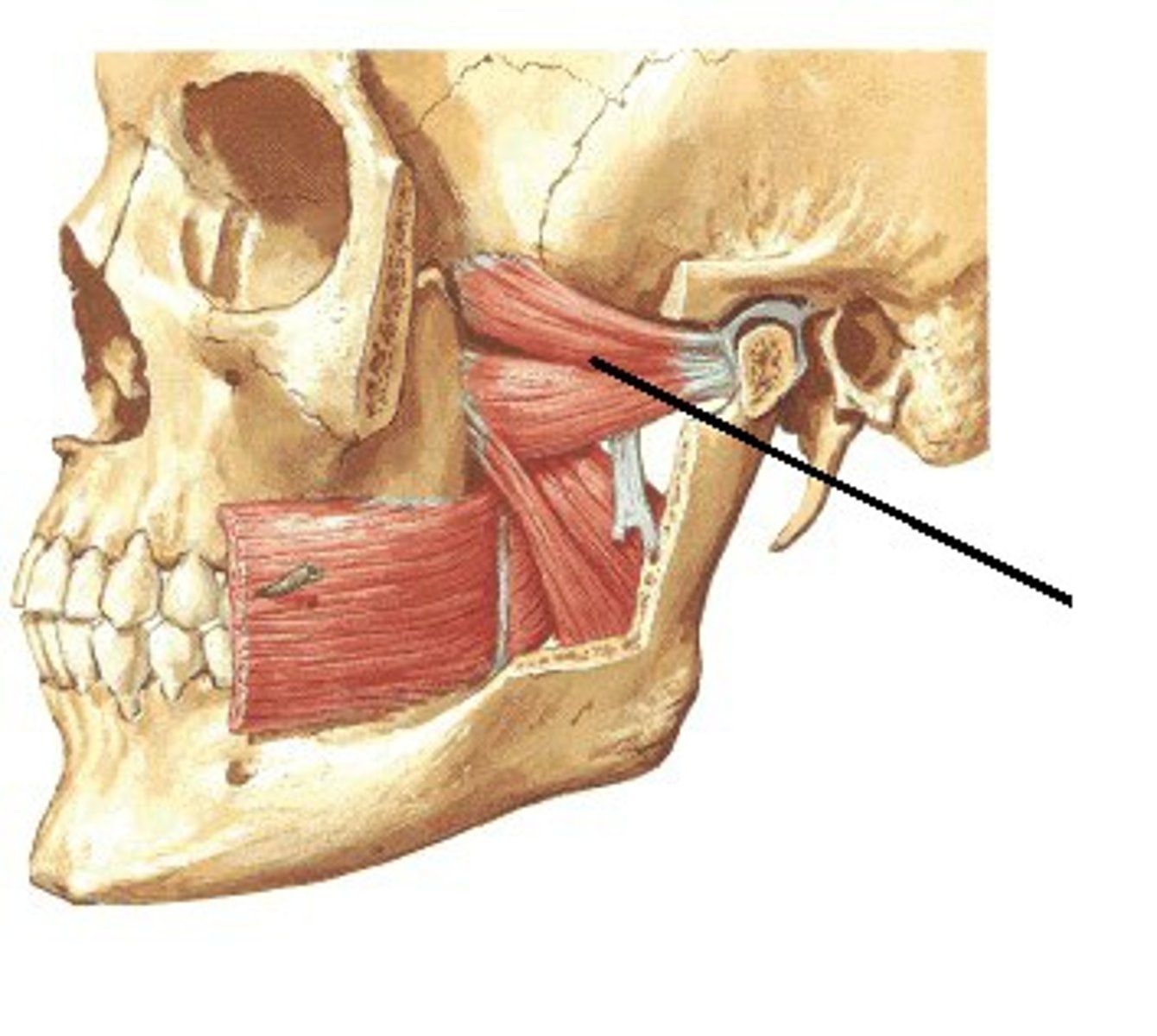
lateral pterygoid action
protraction and side-to-side movement of mandible
lateral pterygoid origin
sphenoid bone (greater wing and lateral pterygoid process)
lateral pterygoid insertion
mandible (neck); articular disk of temporomandibular (TM) joint
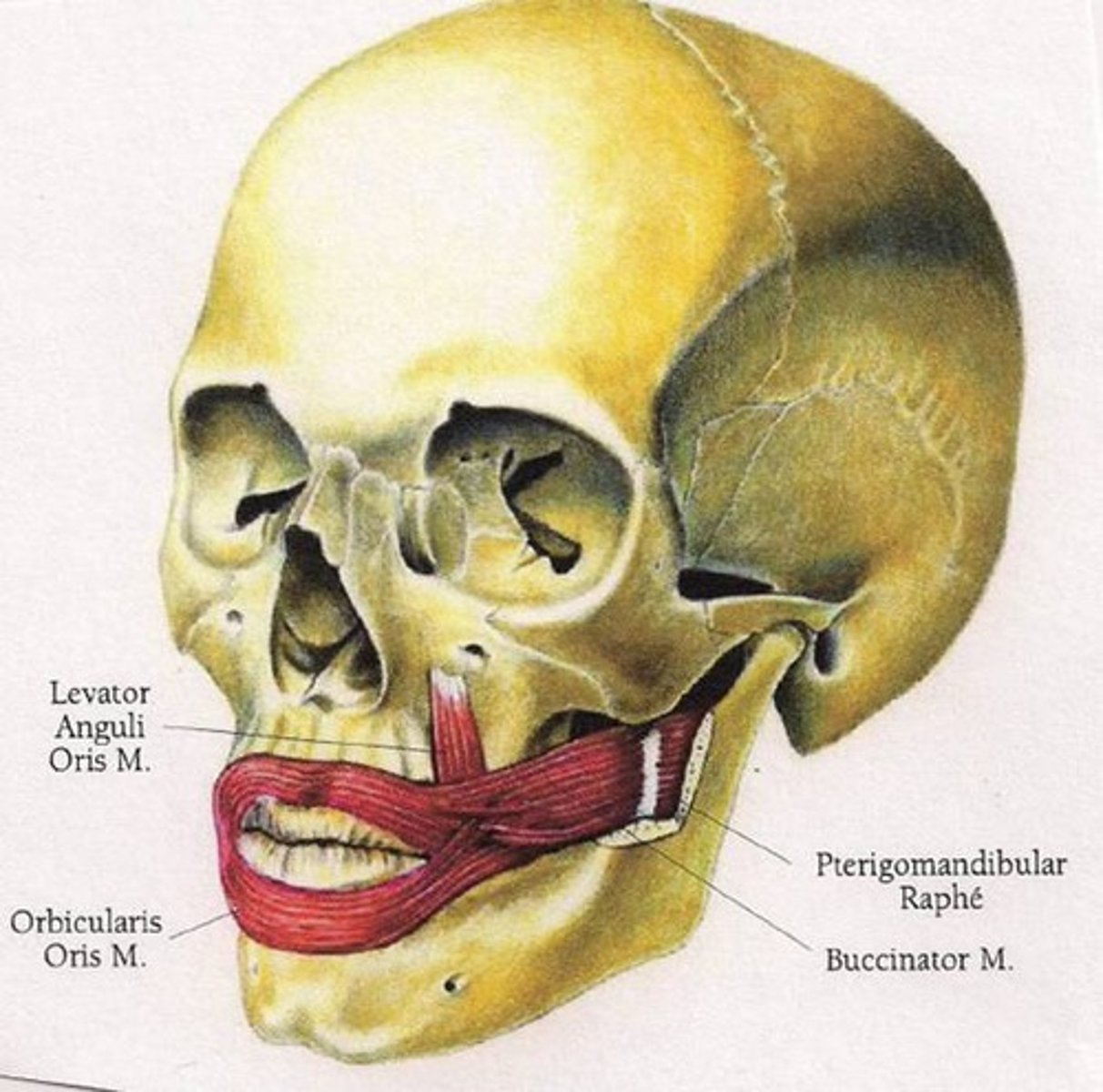
zygomaticus action
elevation of corner of mouth and upper lip
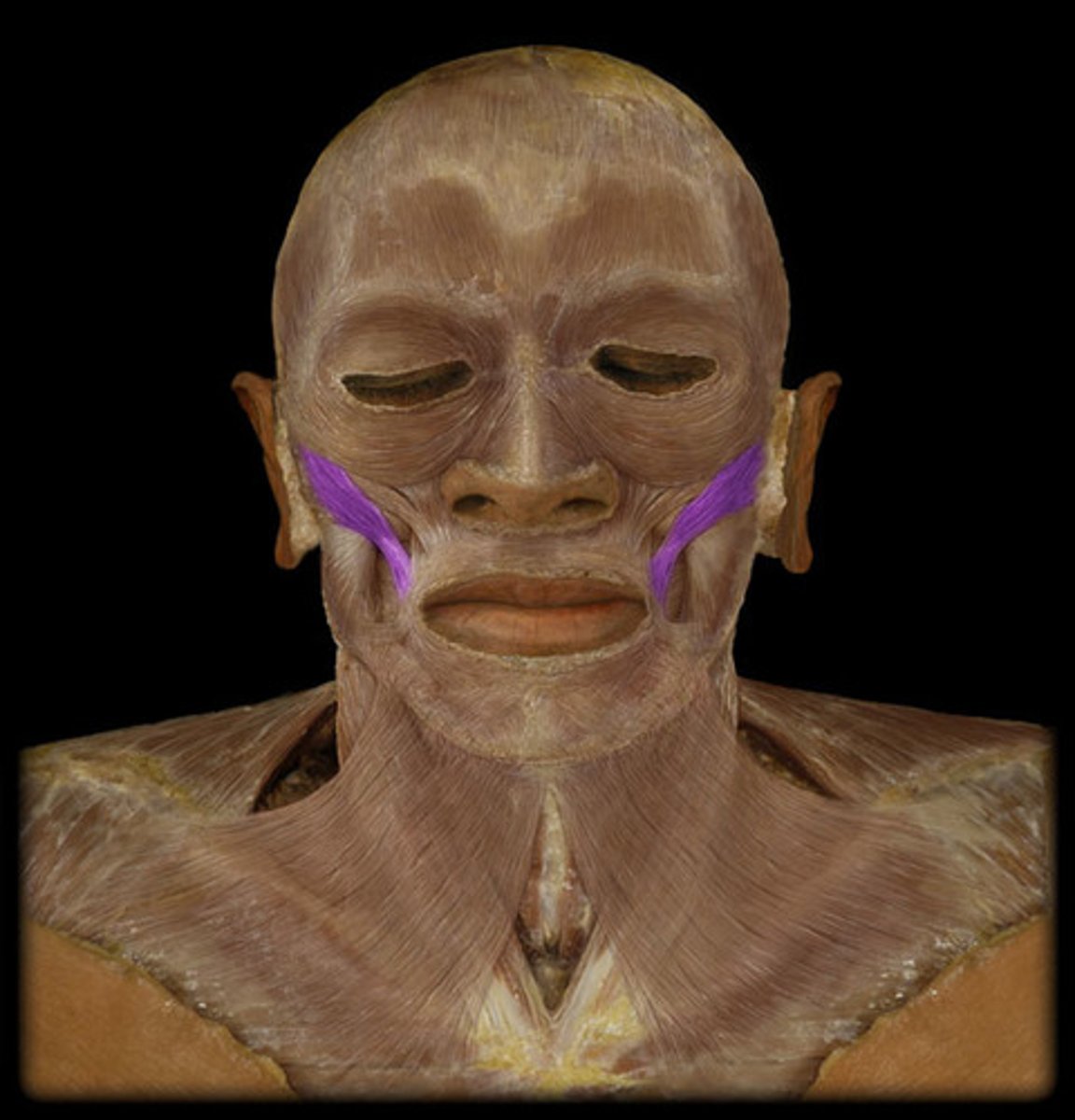
zygomaticus origin
zygomatic bone
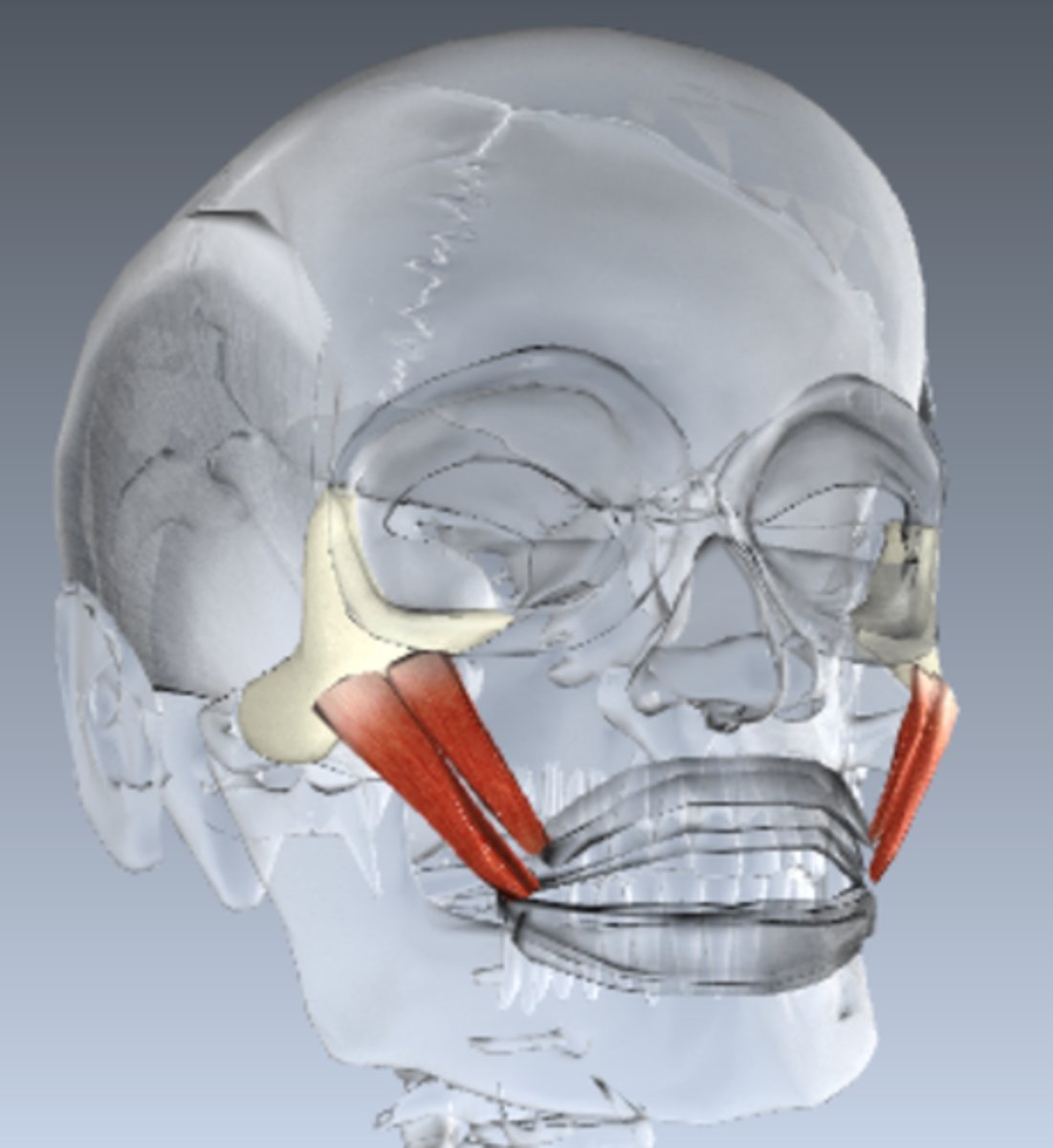
zygomaticus insertion
muscle at angle of mouth and orbicularis oris muscle
buccinator action
compresses cheek
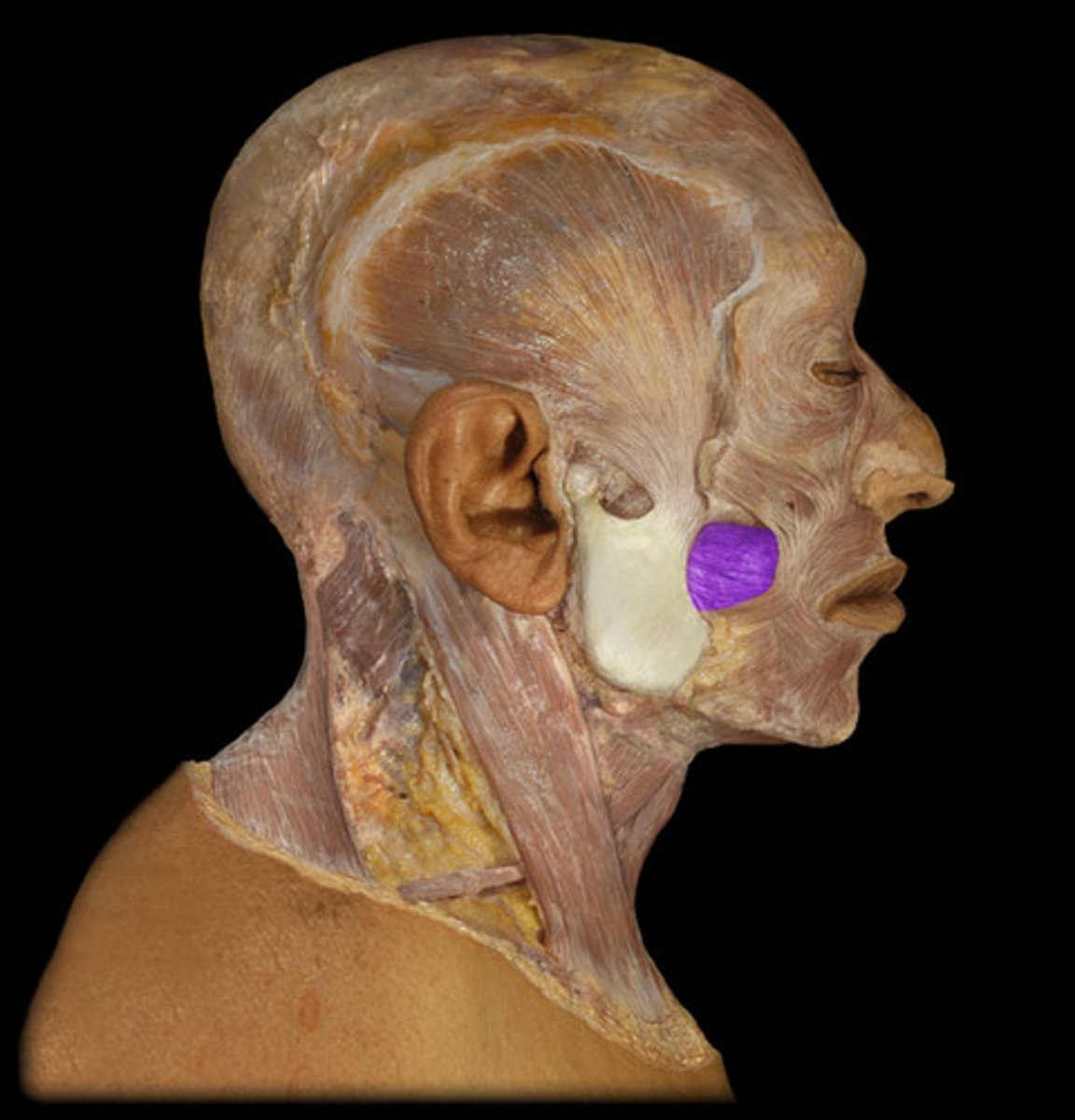
buccinator origin
pterygoidmandibular raphe, maxilla (lateral), mandible (lateral body)
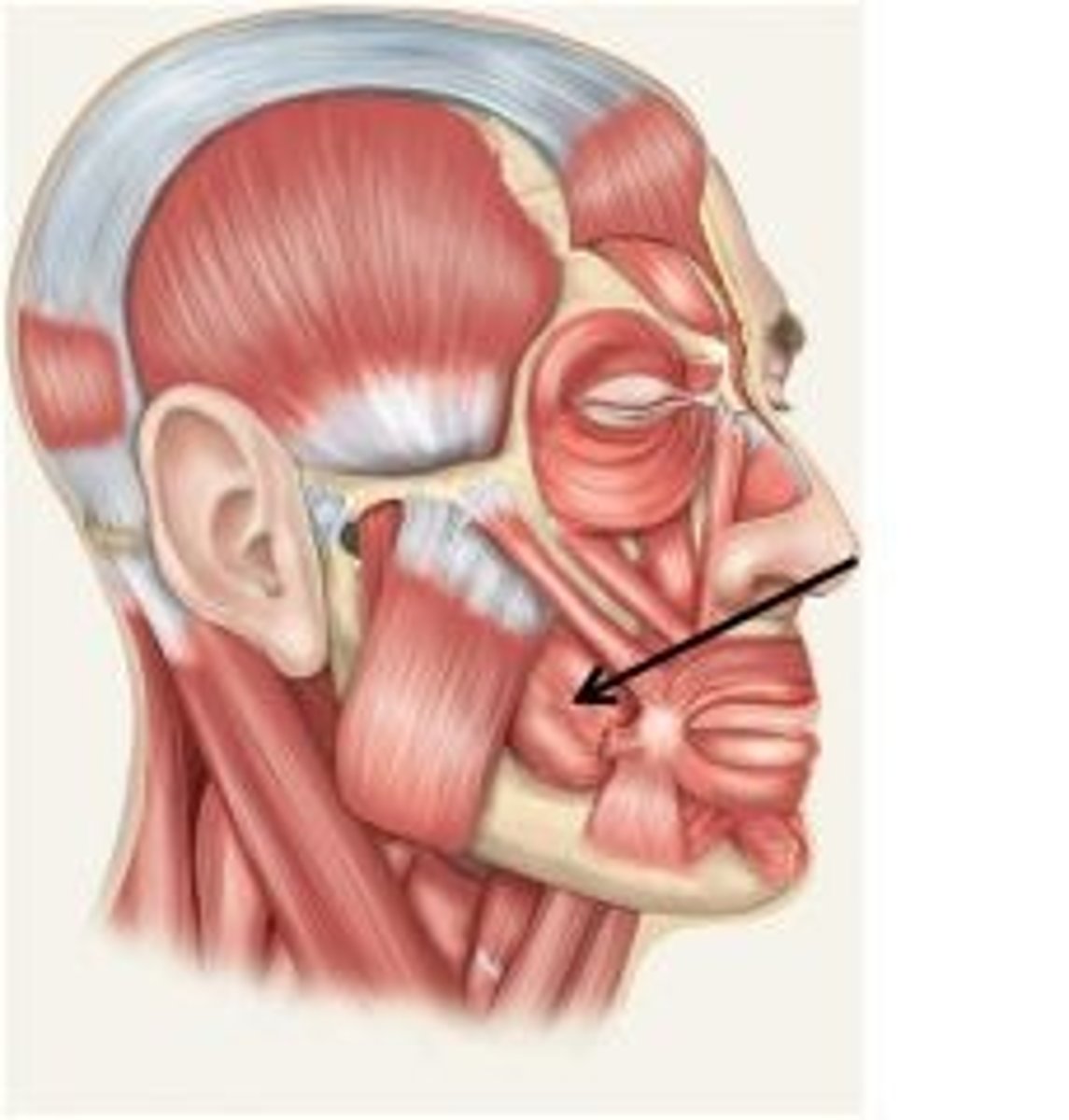
buccinator insertion
muscles at angle of mouth
platysma action
elevates and creases skin of neck; depression of lower lip and angle of mouth
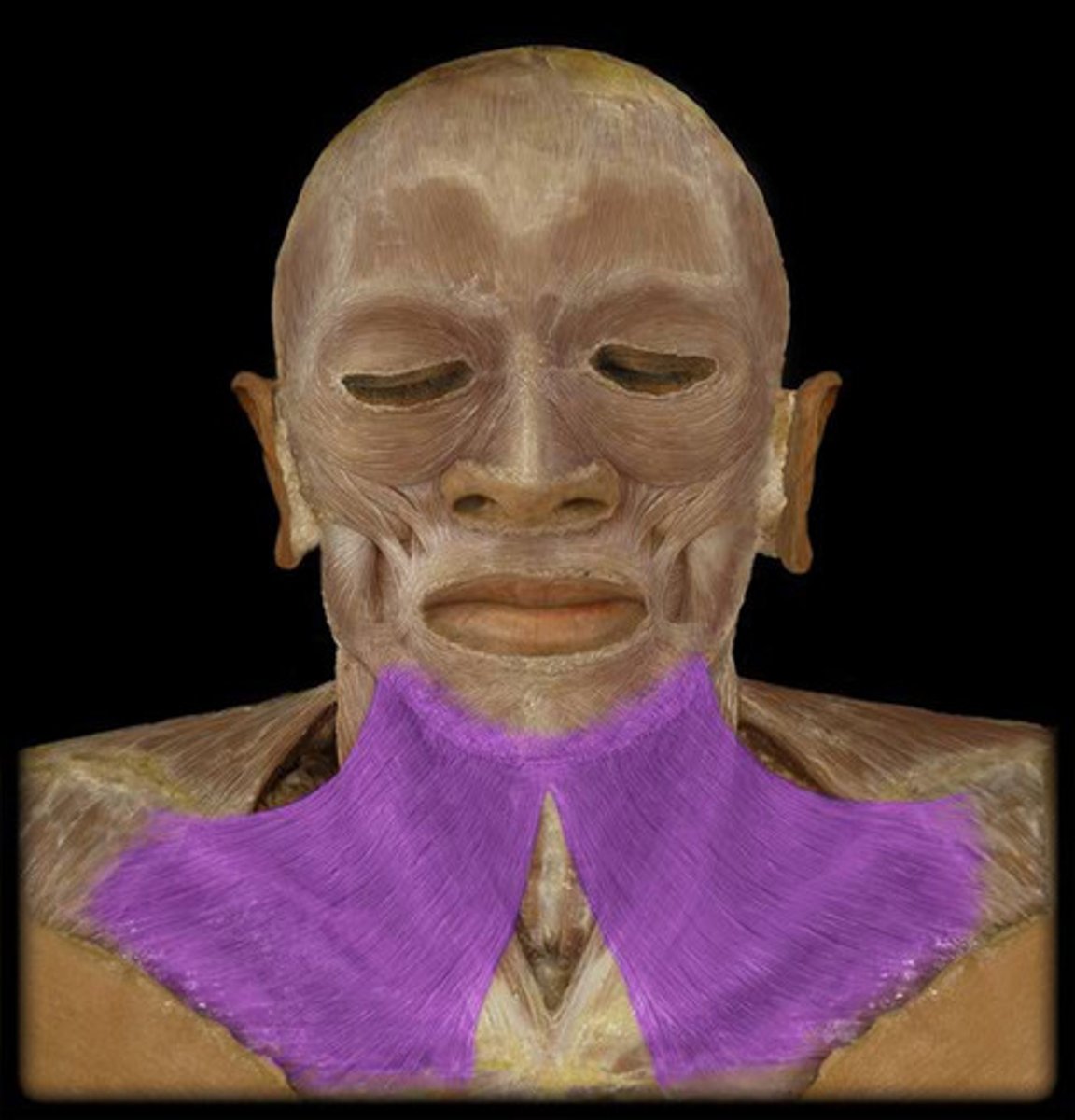
platysma origin
fascia of upper thorax and lower neck
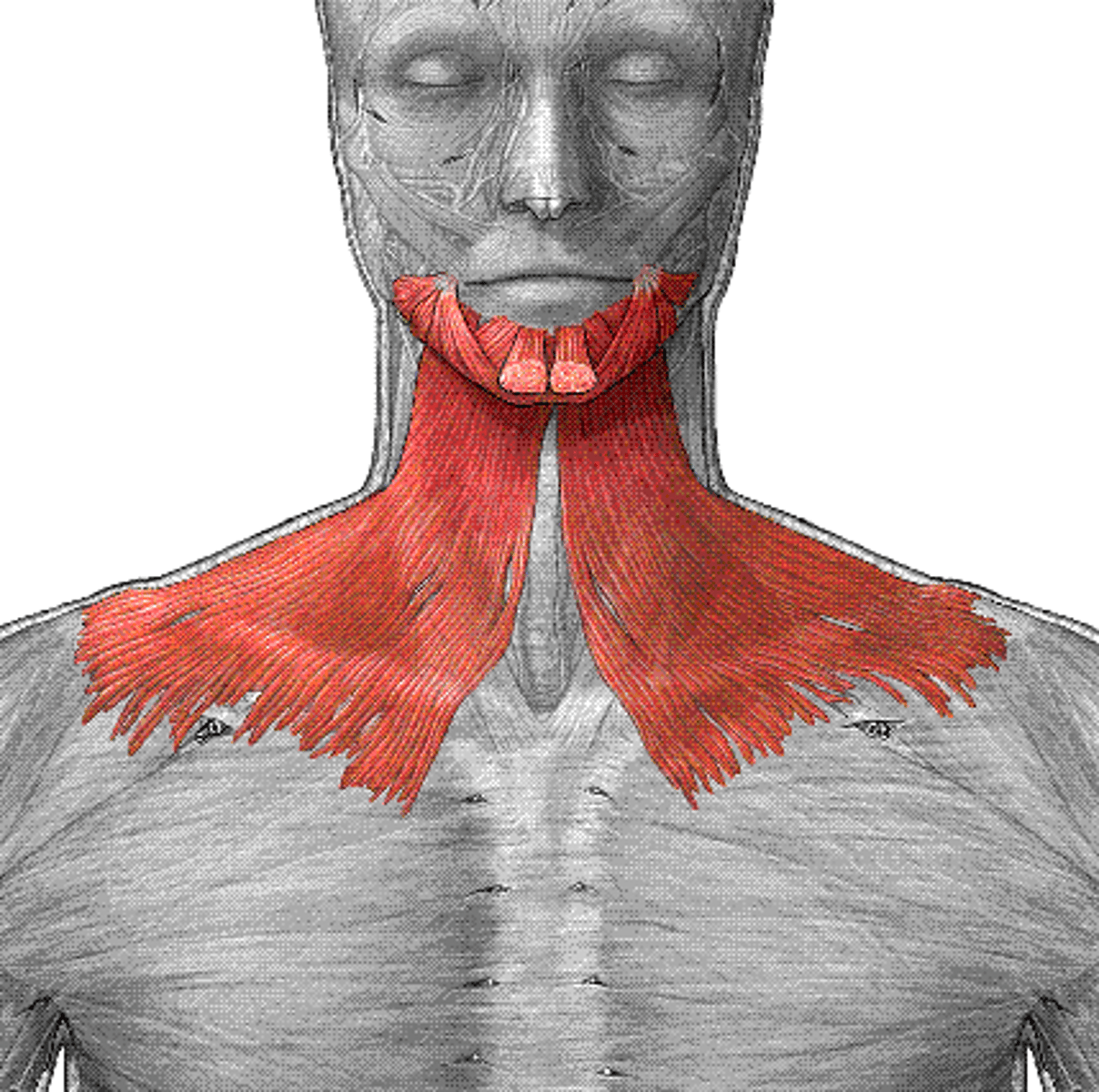
platysma insertion
mandible (lower border); skin and fascia of lower face; muscles of lower lip and angle of mouth
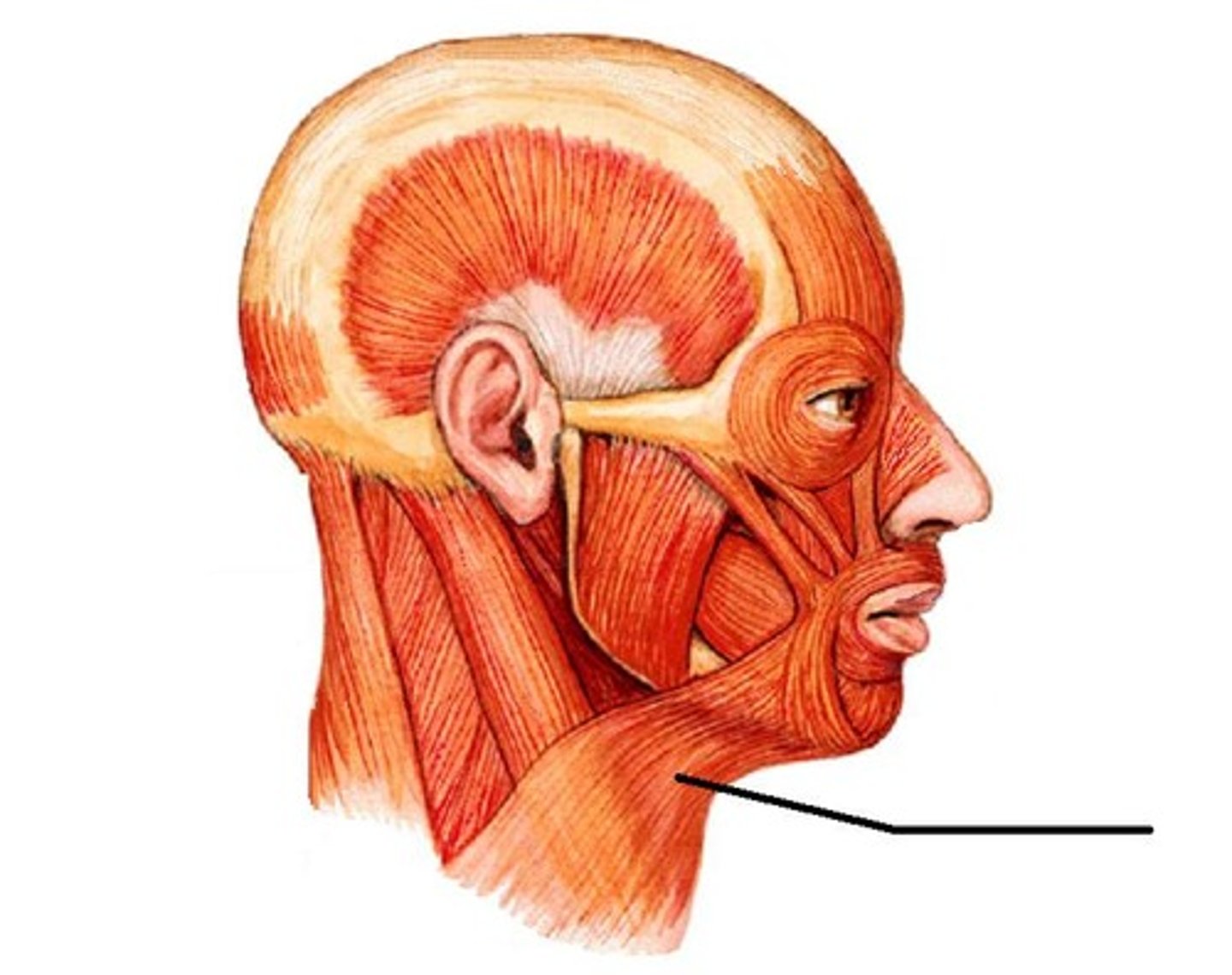
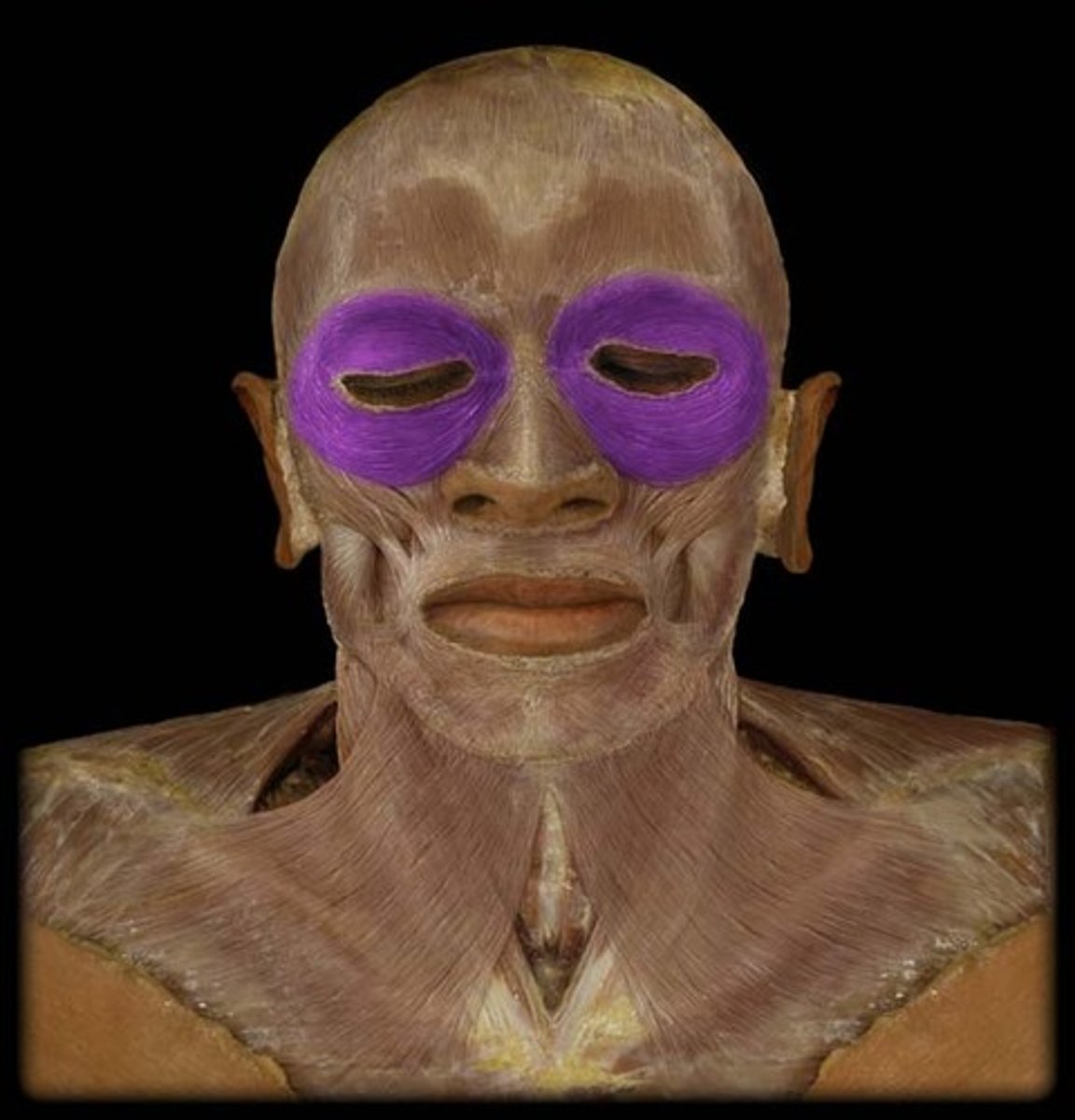
orbicularis oculi action
closes eyelids