CMS II: Ortho - Knee
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Common locations of KNEE pain.
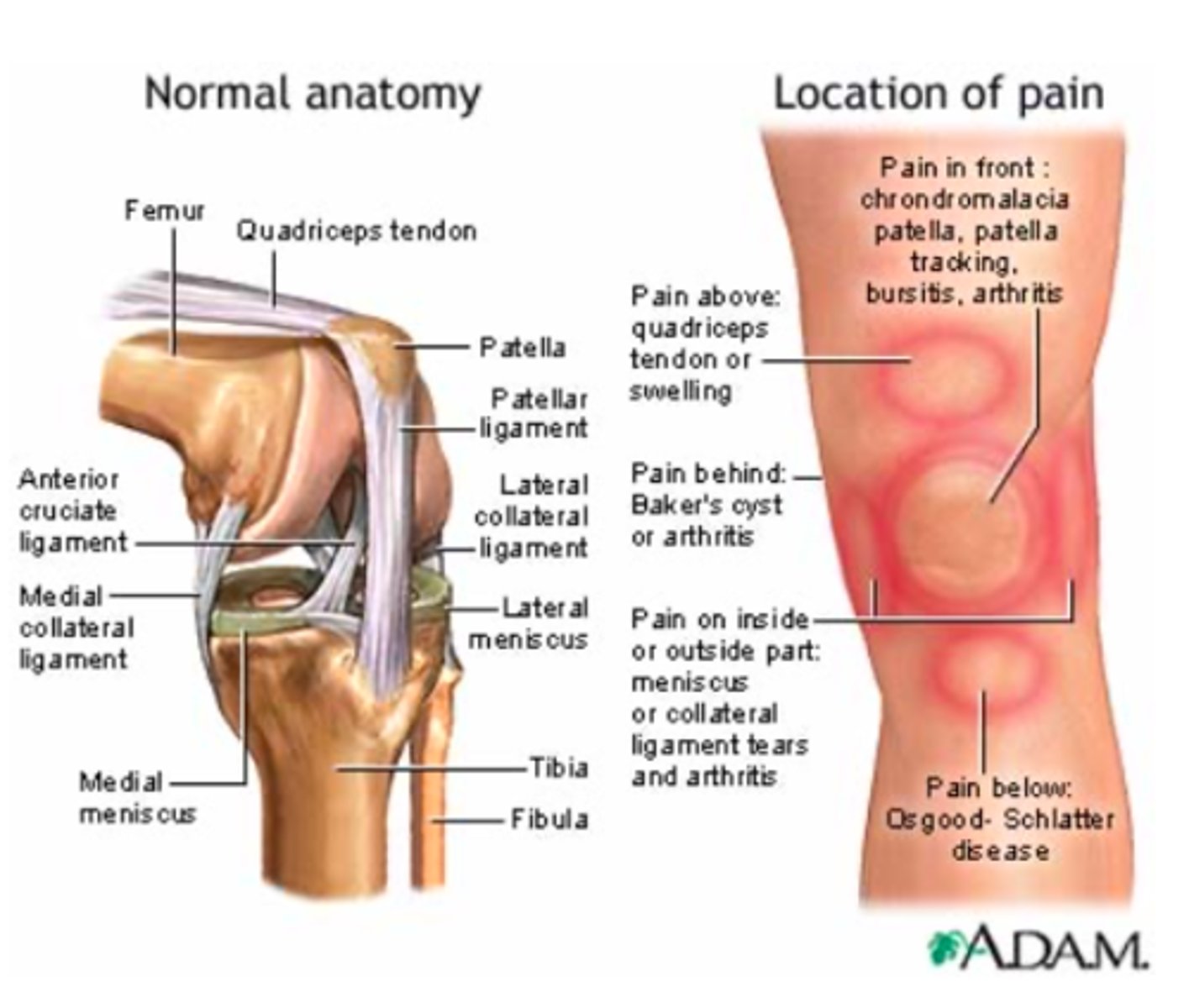
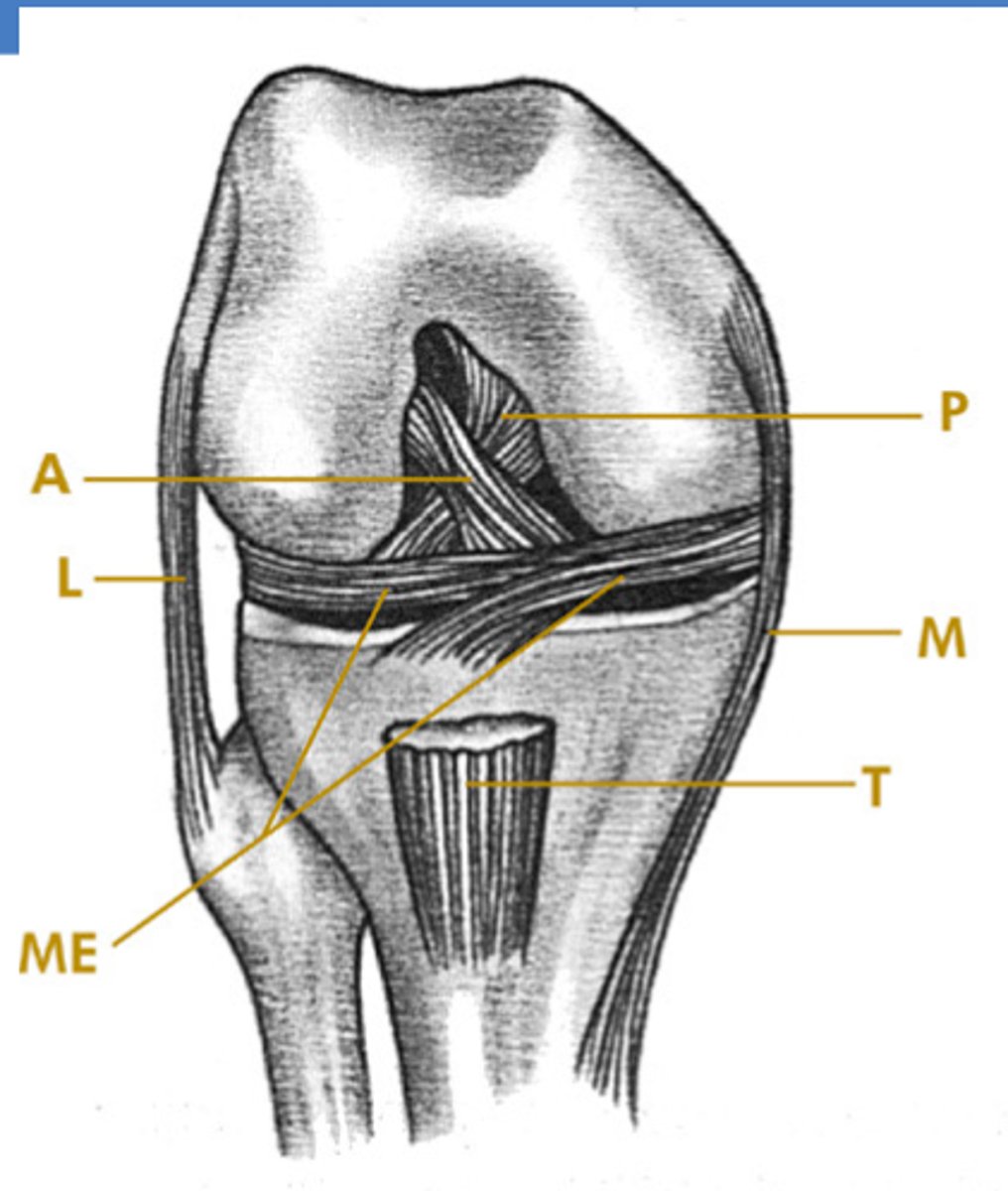
What are the FOUR ligaments of the knee?
A - anterior cruciate ligament
P - posterior cruciate ligament
L - lateral collateral ligament
M - medial collateral ligament
L3 is associated with what knee dermatomal distribution?
anterior MEDIAL knee
L4 + L5 are associated with what knee dermatomal distribution?
anterior LATERAL knee
Turning the leg INWARD is _____ rotation, while turning the leg OUTWARD is ______ rotation.
medial; lateral
What is the difference between valgus and varus deformities?
Valgus → "knocked knee"
Varus → "bowed leg"
**presentation depends on whether it results from a bony injury OR ligament injury!
What TWO tests can be used to assess lateral/medial ligament stability of the knee?
Valgus + Varus Stress Test
A POSITIVE valgus stress test indicates what?
MCL injury
- knee is unstable medially
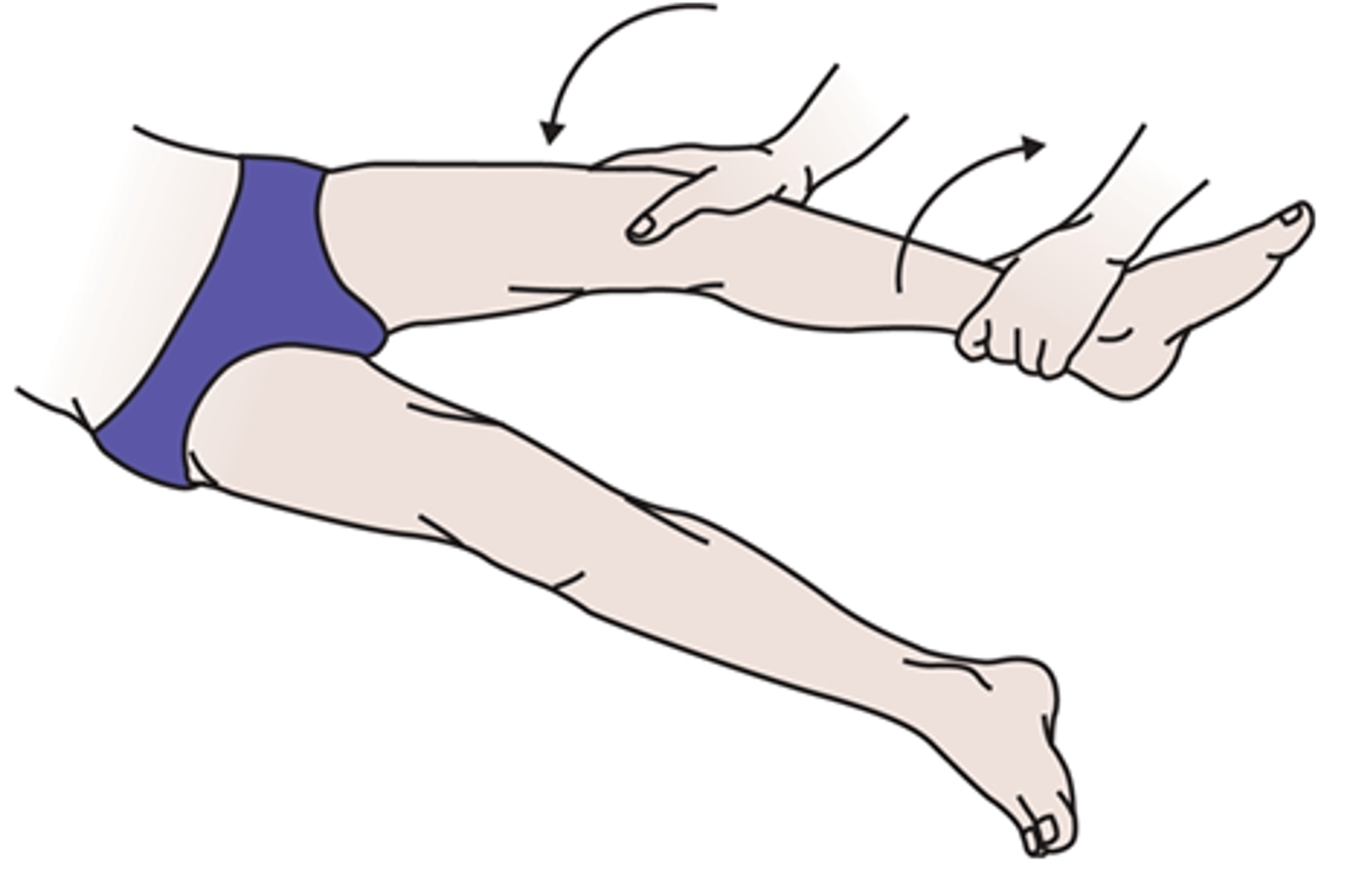
A POSITIVE varus stress test indicates what?
LCL injury
- knee is unstable laterally
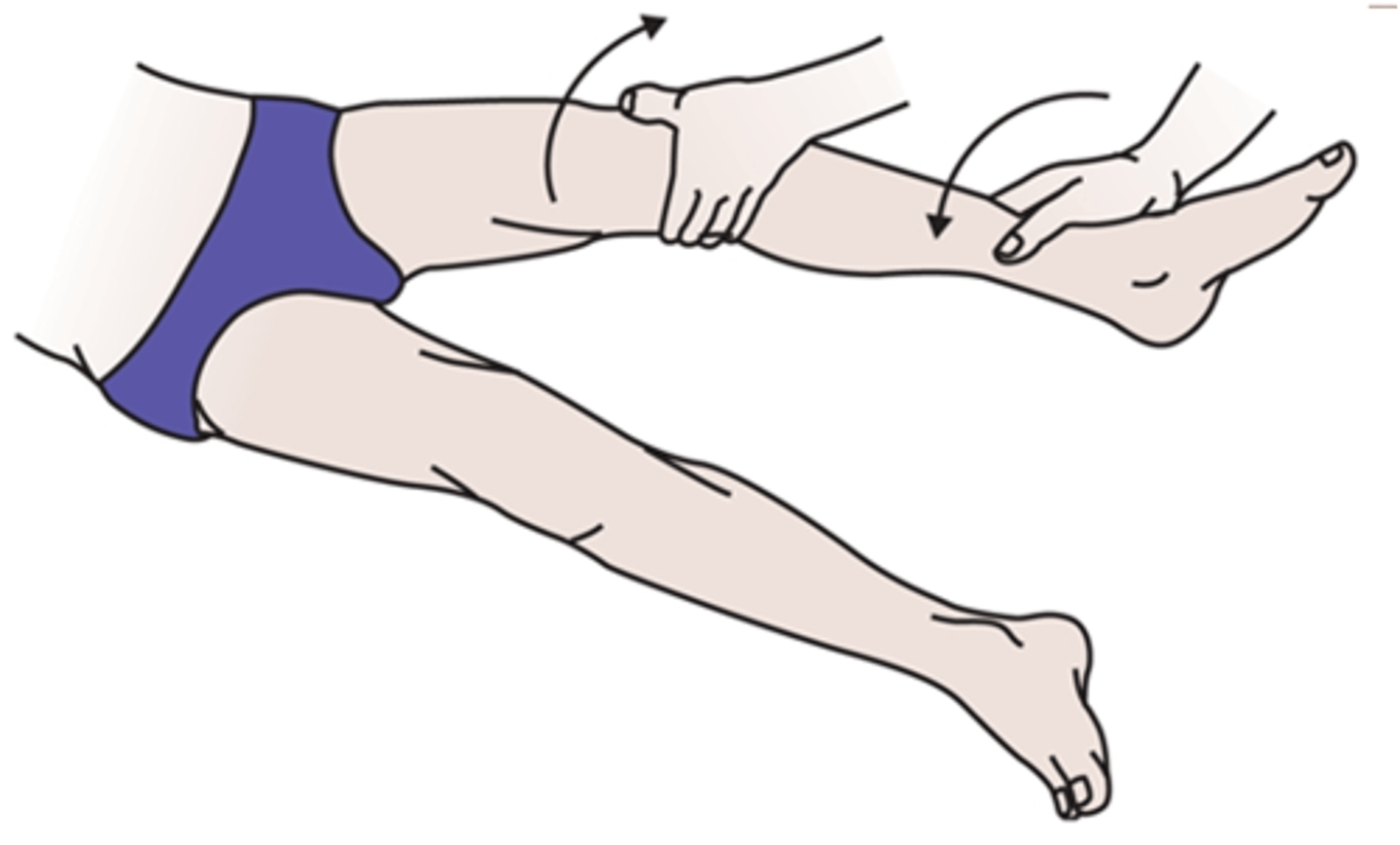
What does a POSITIVE McMurray's test indicate?
If + with medial/internal rotation → lateral meniscus injury
If + with lateral/external rotation → medial meniscus injury
+ = snap/click/pain
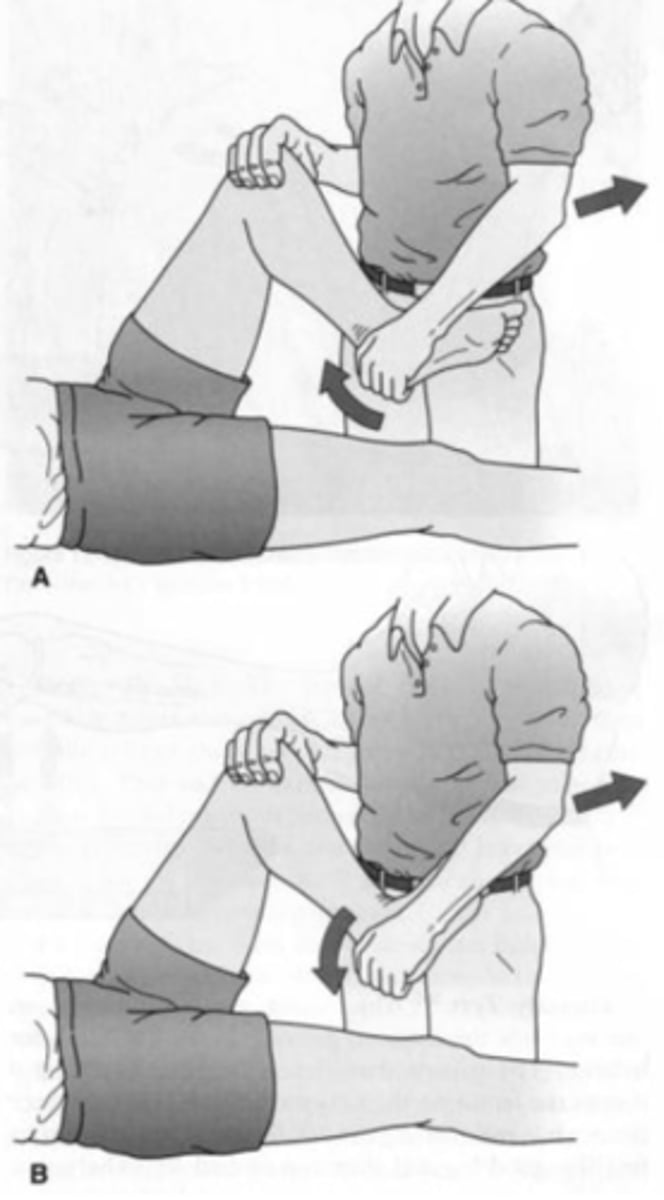
What does a (+) apley's compression/distraction test indicate?
+ medial pain/distraction → medial meniscus injury
+ lateral pain/distraction → lateral meniscus injury
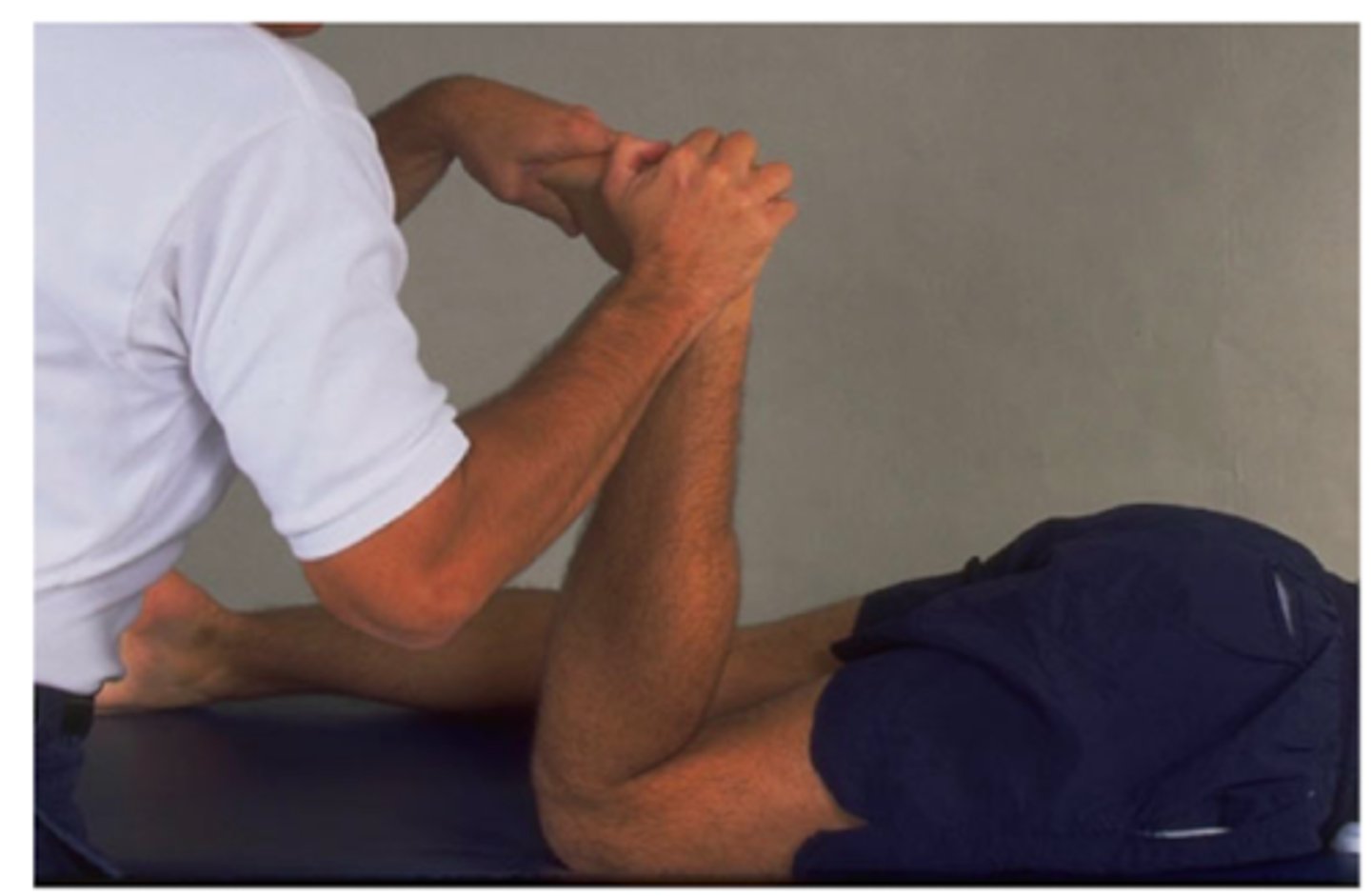
What does a POSITIVE patellar apprehension test indicate?
indicates patient is prone to patellar dislocations
- positive = patient tells you to stop or face grimaces
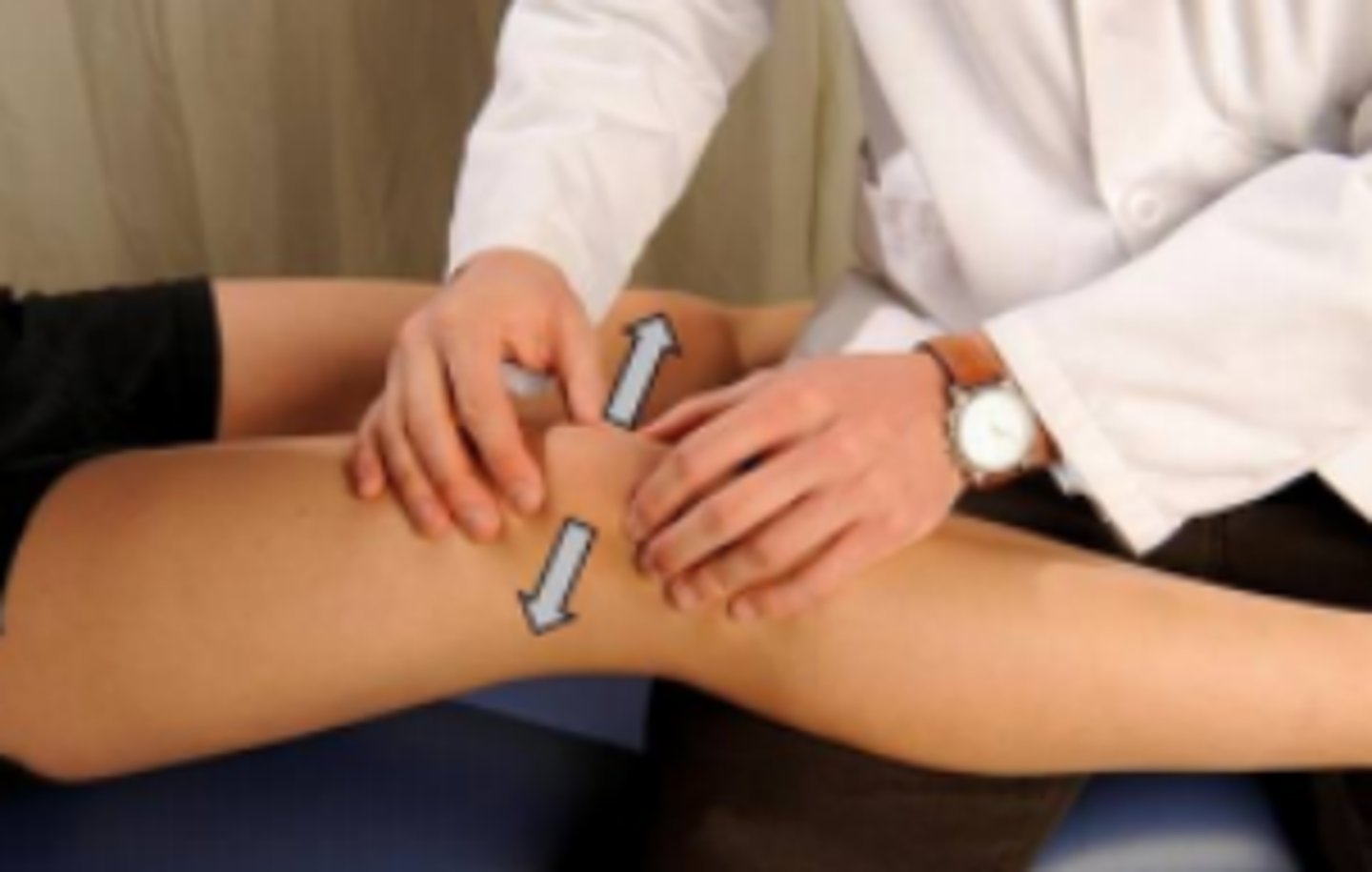
What does a Lachman test evaluate?
ACL tears/injuries
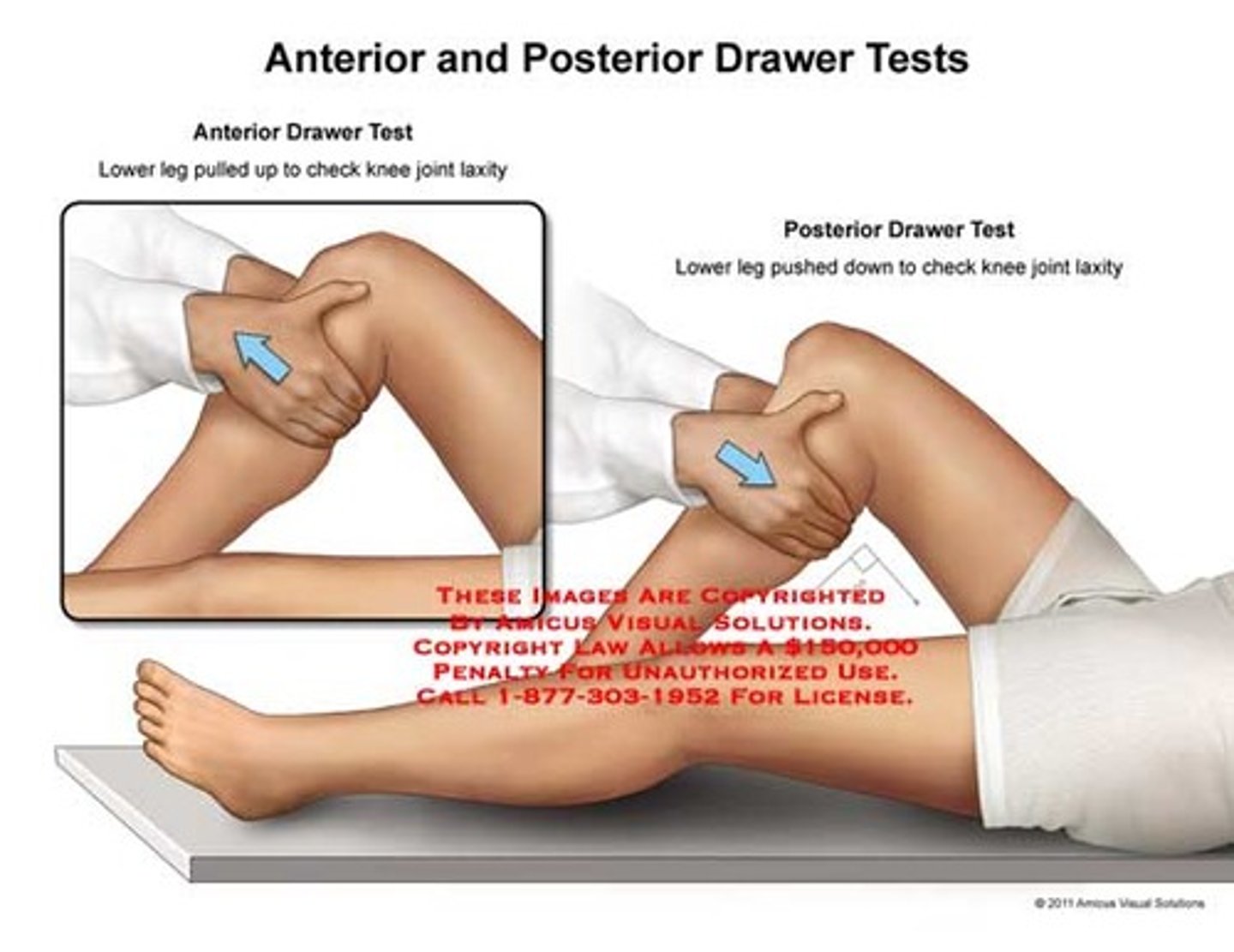
A POSITIVE anterior drawer test indicates what?
torn ACL
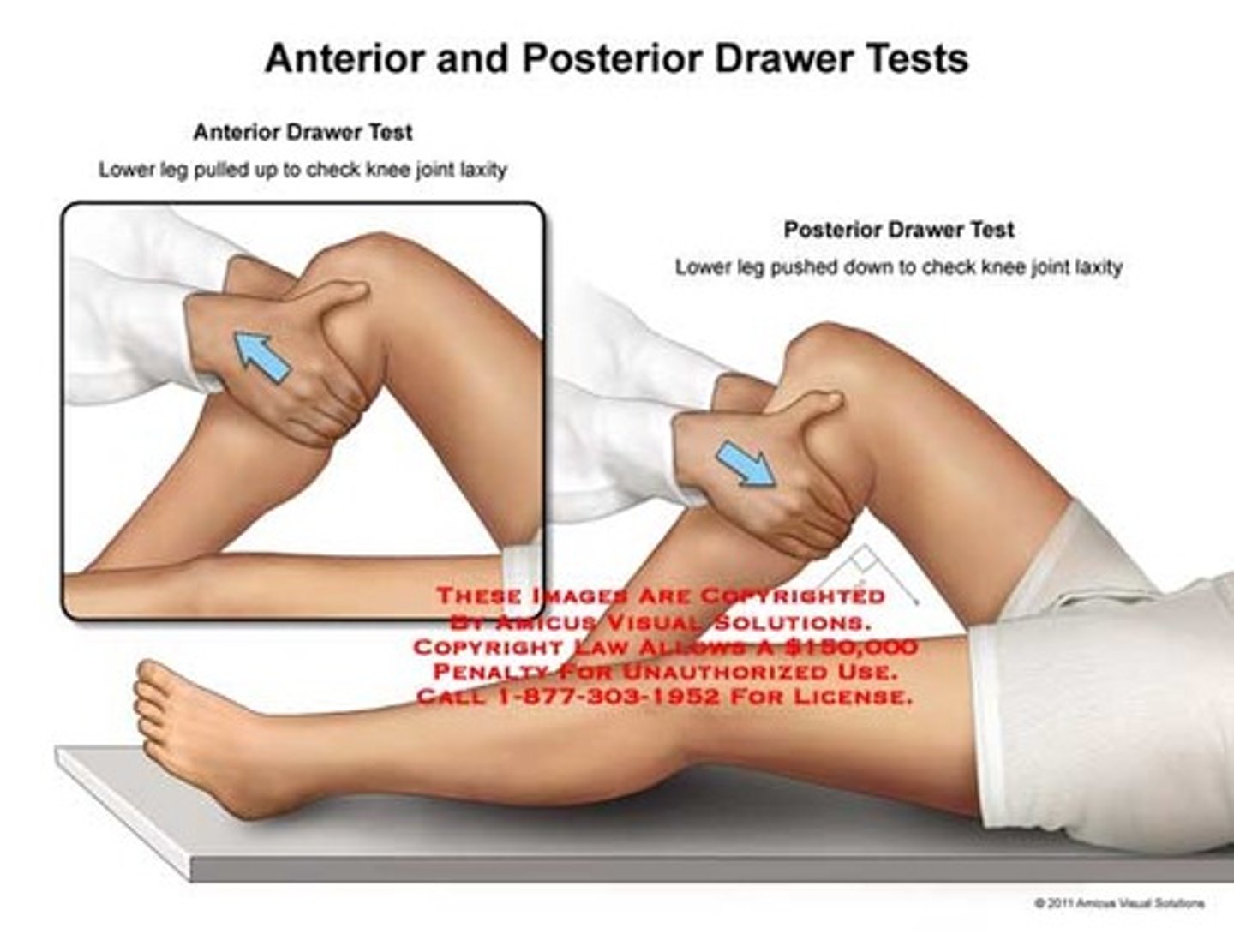
A POSITIVE posterior drawer test indicates what?
torn PCL (Sag sign)
What is the difference between swelling and effusion? What test can help differentiate between them?
Swelling → fluid in the soft tissue
Effusion → fluid in the joint space
Can "milk the knee" to differentiate between them
What does (+) joint line tenderness indicate?
possible meniscus injury
What type of motion can result in a meniscal injury?
occurs with ABRUPT turning/twisting while the LE is planted on the ground
What THREE PE exam findings are consistent with a meniscal injury?
(+) Apley's
(+) McMurray's
(+) joint line tenderness
What diagnostic imaging study can help with diagnosing meniscal injuries?
MRI
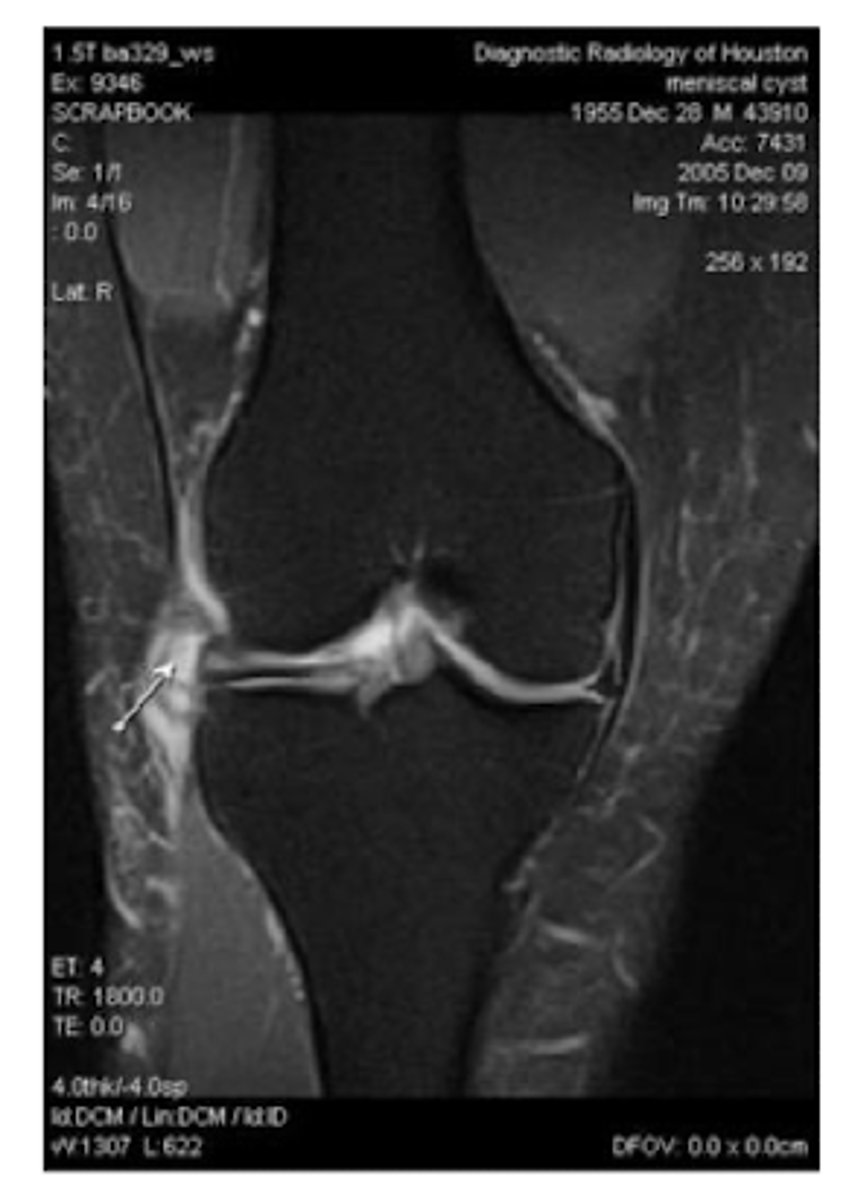
What can form if a meniscal injury results in a tear?
meniscal cysts
- results from extrusion of synovial fluid through the meniscal tear; can accumulate in the joint capsule
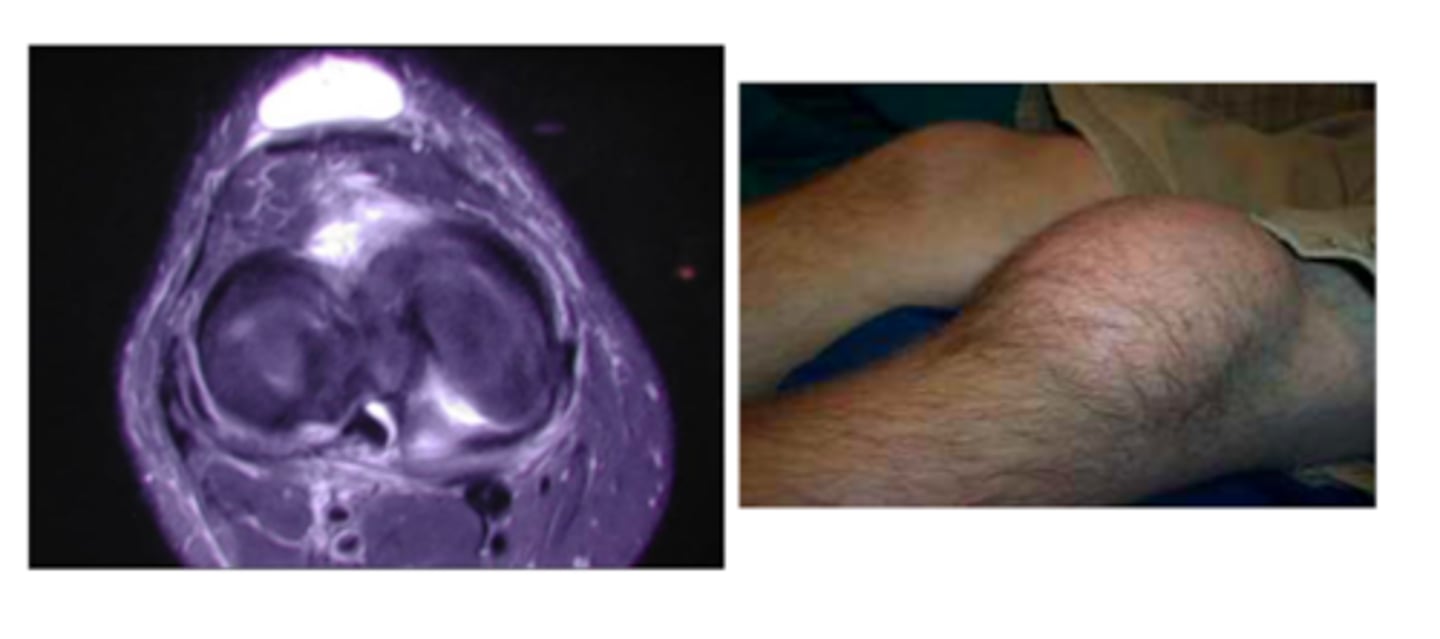
What type of bursitis can occur due to trauma or chronic inflammation from kneeling? How will it present?
pre-patellar bursitis ("housemaid's knee")
- will present with swelling + pain on the anterior aspect of the knee
What type of pain can present with pes anserine bursitis?
medial knee pain
- common in athletes and older patients
Decreased flexion + a "popping" sensation in the posterior thigh can signal towards what type of injury?
hamstring strain
T/F. A popping or snapping sensation with injury can signal towards a ligament injury.
TRUE
Are XR indicated for hamstring strains?
NO
What is involved in the treatment of a hamstring strain?
RICE
Crutches
NSAIDs
PT
What ligament serves as the primary stabilizer of the knee against anterior translation?
ACL
What is the unhappy/terrible triad?
ACL tear (complete>partial)
Meniscal tear
MCL tear
What 2 PE exam findings are consistent with an ACL tear? Which one is most sensitive?
+ Lachman test
+ Anterior drawer test
What is the diagnostic imaging of choice for ACL injury?
MRI
*same for PCL/MCL/LCL
What is involved in the treatment for ACL injury?
RICE
Crutches
Knee immobilizer
Ortho (remove effusion)
ACL reconstruction - to return to sports (best prognosis)
*similar treatment for PCL/MCL/LCL minus surgery
If a patient presents with trauma that displaced their knee posteriorly, what ligament is most likely injured? What special test would confirm it?
PCL injury
- will present with a (+) posterior drawer test
What type of trauma and special test are associated with an MCL injury?
occurs following trauma to the LATERAL knee
- will have a (+) valgus stress test
What type of trauma and special test are associated with an LCL injury?
occurs following trauma to the MEDIAL knee
- will have a (+) varus stress rest
T/F. For ACL tear, if a patient is put on a knee immobilizer, it is recommended they take a BREAK from it every so often to avoid stiffness.
TRUE - educate patients!
What type of fracture can present with thigh pain and inability to wear weight?
femoral shaft fracture
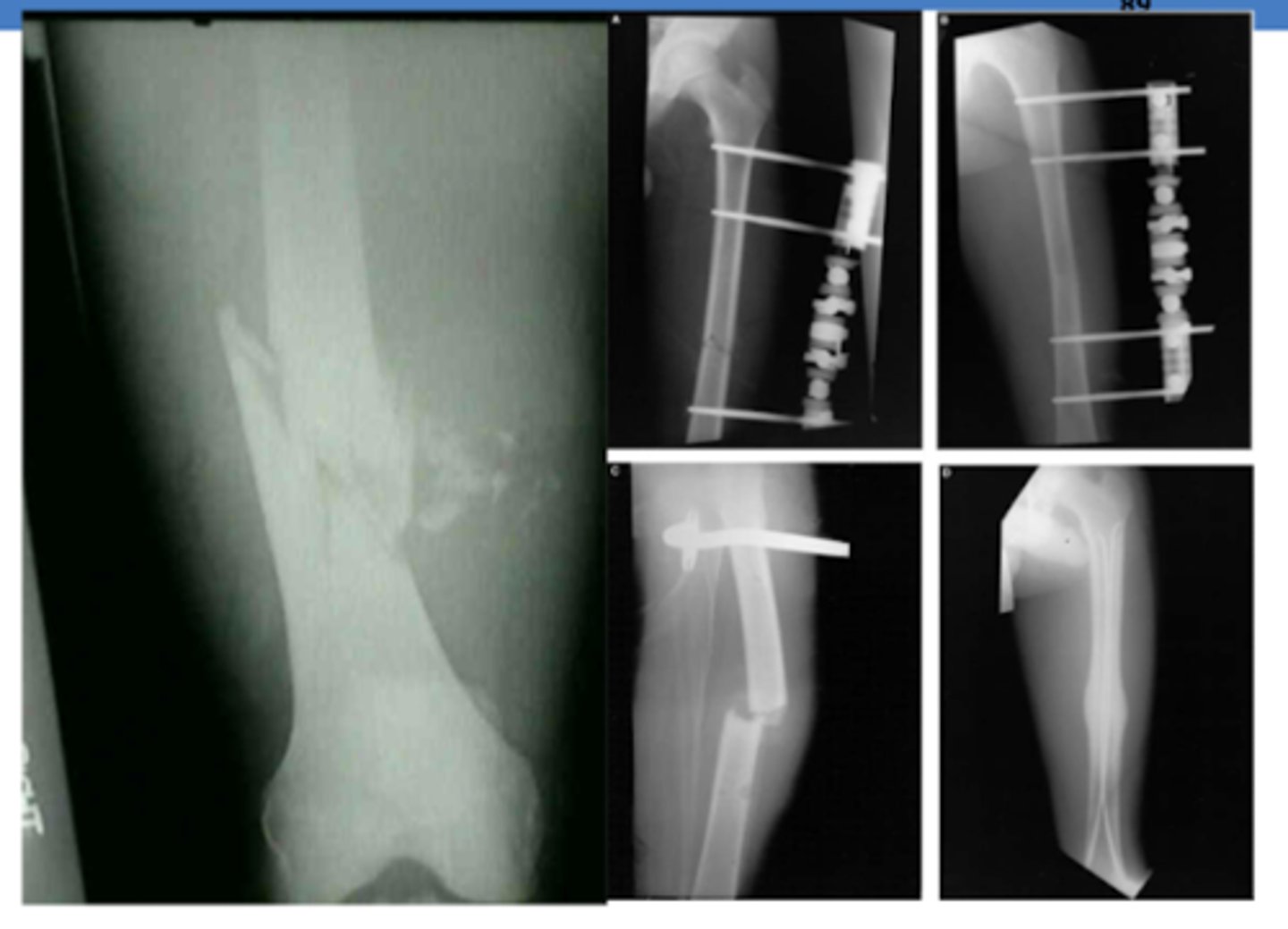
What type of fracture can present with lower leg pain and inability to wear weight?
tibial plateau fracture
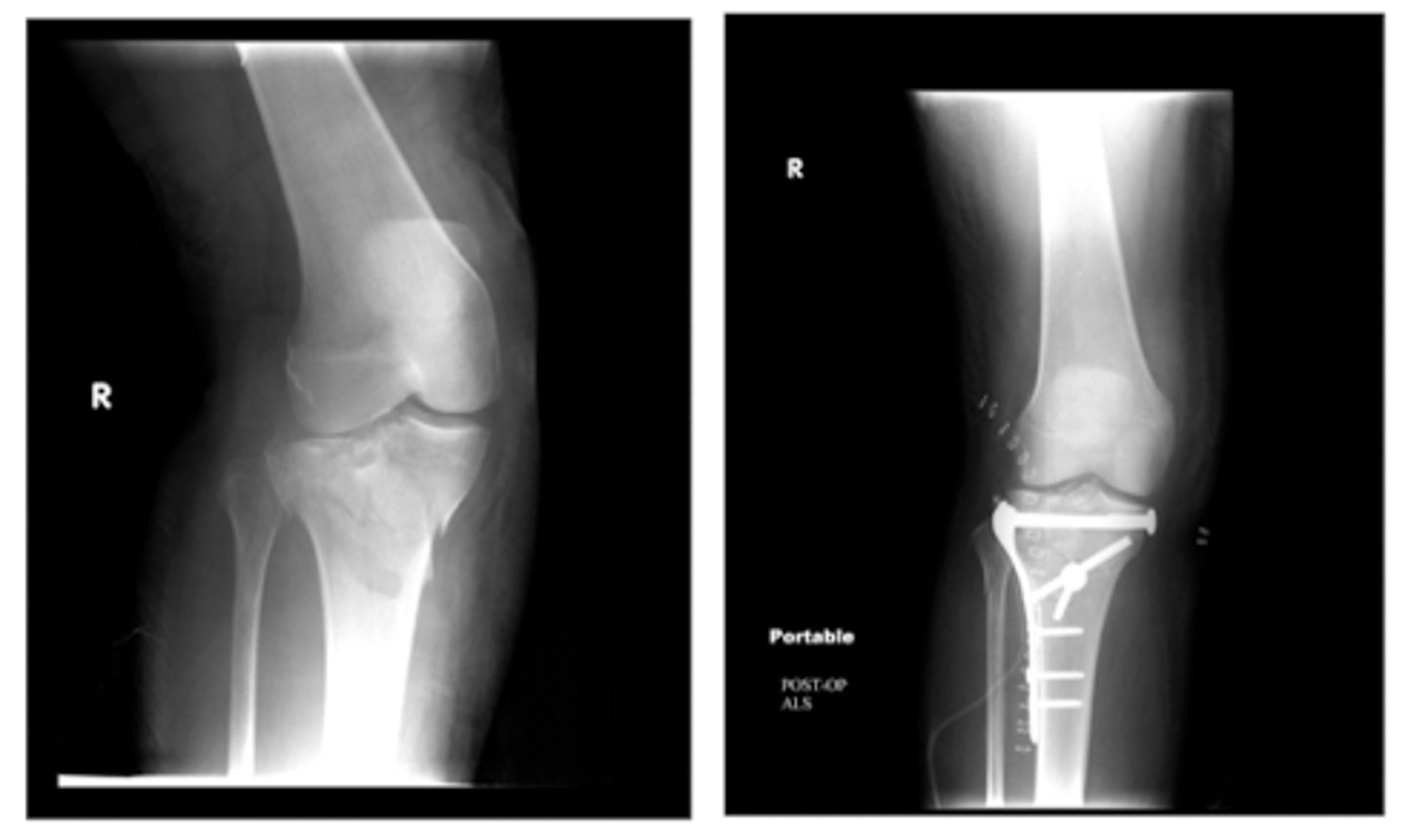
What motion will be restricted with a patellar fracture? What XR view is indicated for evaluation?
inability to extend the knee
- occurs due to trauma
**requires a SUNRISE view for examination
What is patella alta? What does causes it?
occurs when the patella moves up and sits very high following patella tendon rupture
- makes the knee unstable
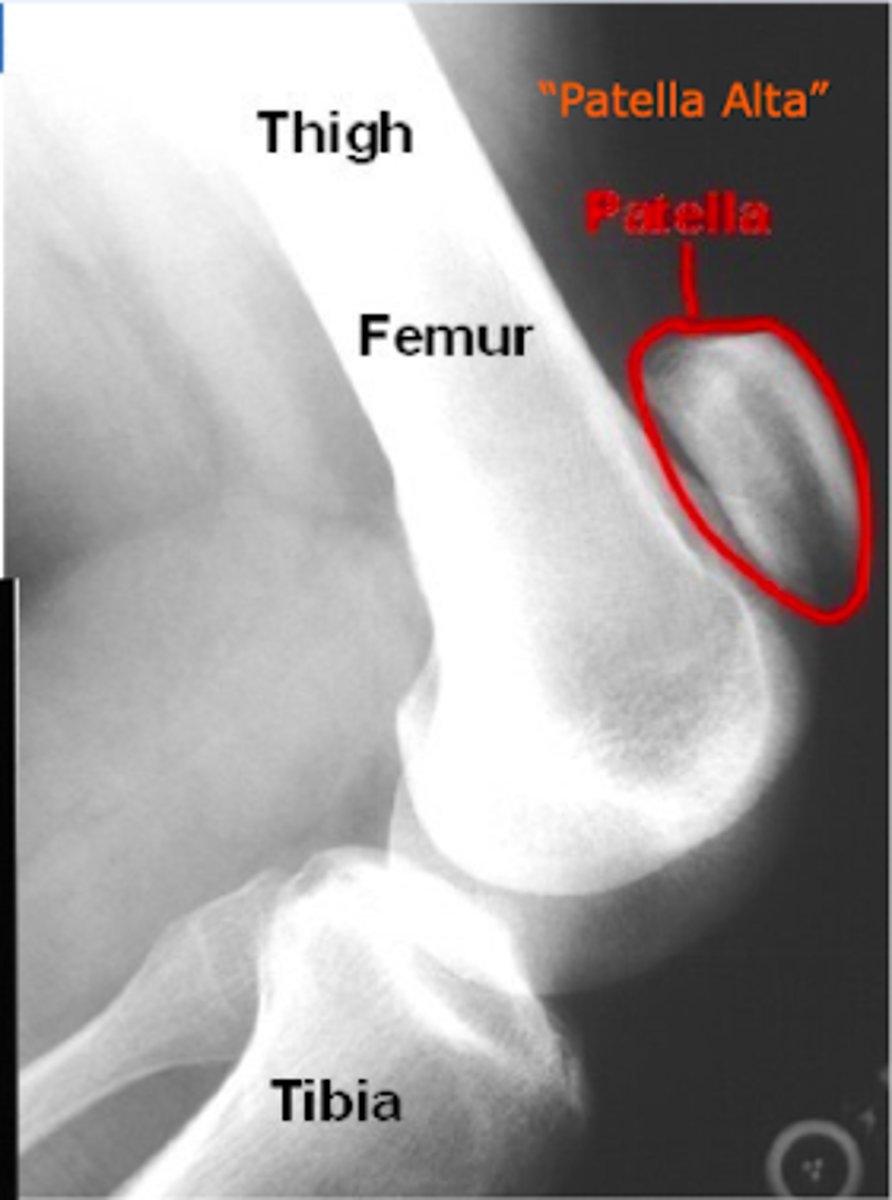
What motion is restricted with a patellar tendon rupture?
extension of the knee
What is the treatment for patella alta?
surgical repair
What is the difference between a subluxation and a dislocation?
Subluxation = moves and can return
Dislocation = moves but does not return
**treated the same
What type of dislocation most commonly occurs at the patella?
lateral dislocation
What PE finding can indicate a patellar dislocation?
+ apprehension test
**can also present with effusion and pain
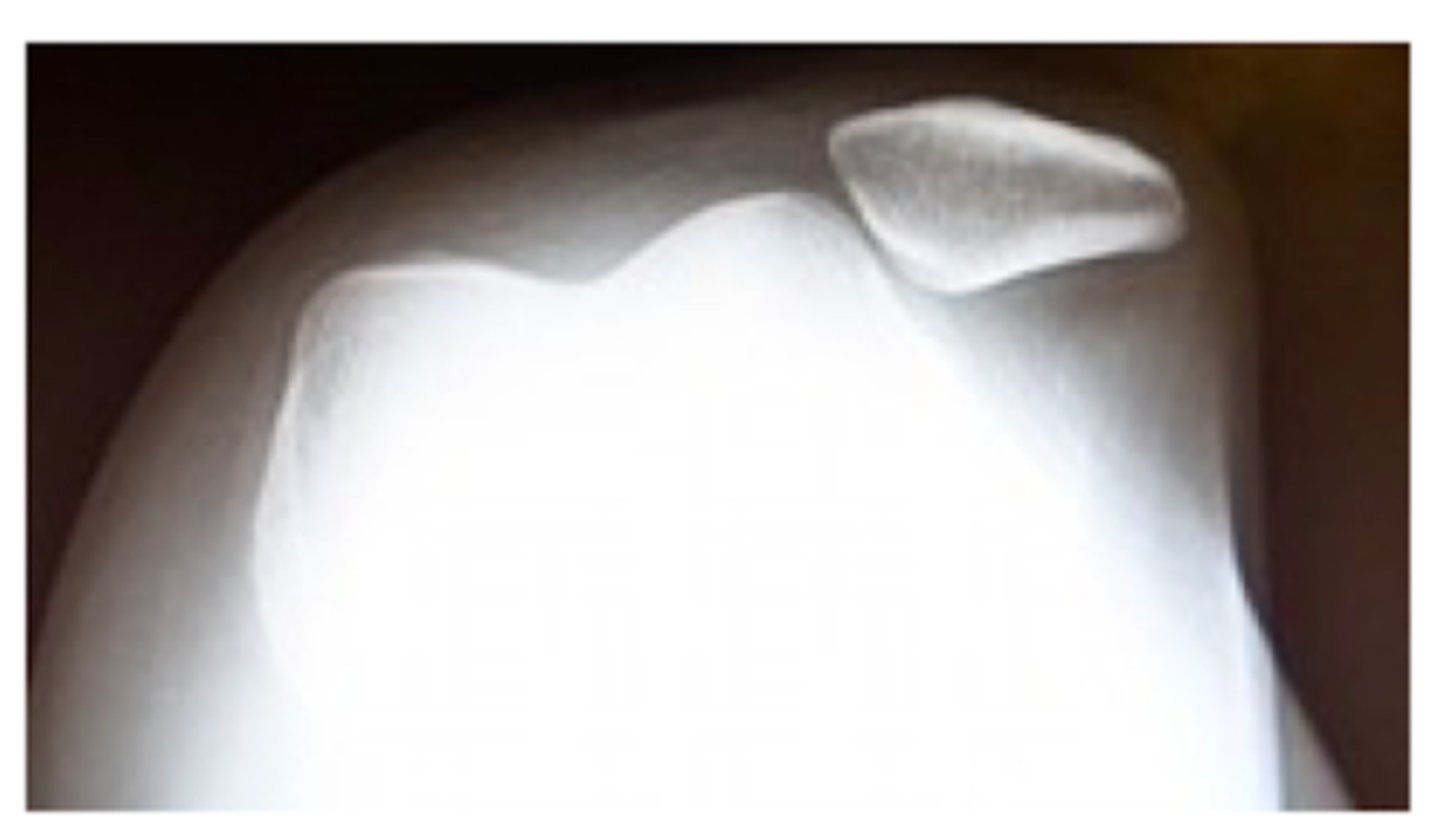
What joints are displaced in a KNEE dislocation?
tibiofemoral joint (femur + tibia)
What must occur immediately following knee dislocation?
IMMEDIATE reduction
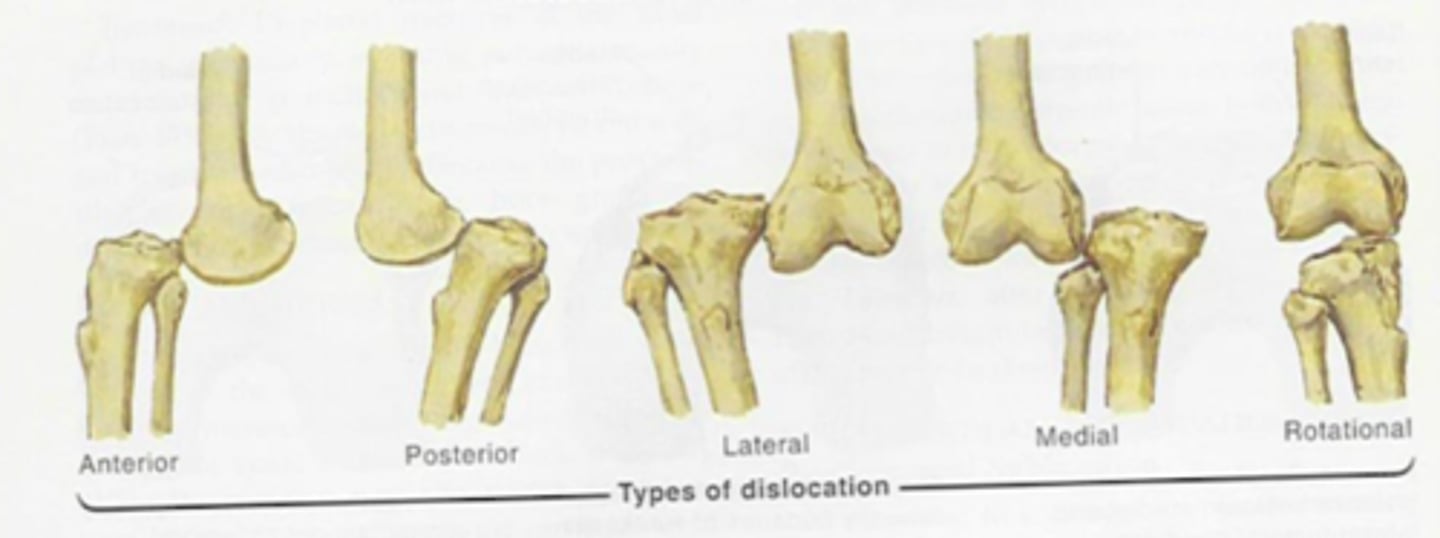
What type of dislocation is NOT reducible?
posterolateral dislocation
What MUST be performed if a patient presents with a knee dislocation?
CHECK PULSES
What is the most dangerous complication following a tibiofemoral dislocation?
popliteal artery injury
*any vascular compromise will need vascular surgery stat
What childhood disorder can present with pain and swelling over the ANTERIOR knee over the tibial tuberosity?
Osgood-Schlatter disease
- will have a painful bump on the anterior knee
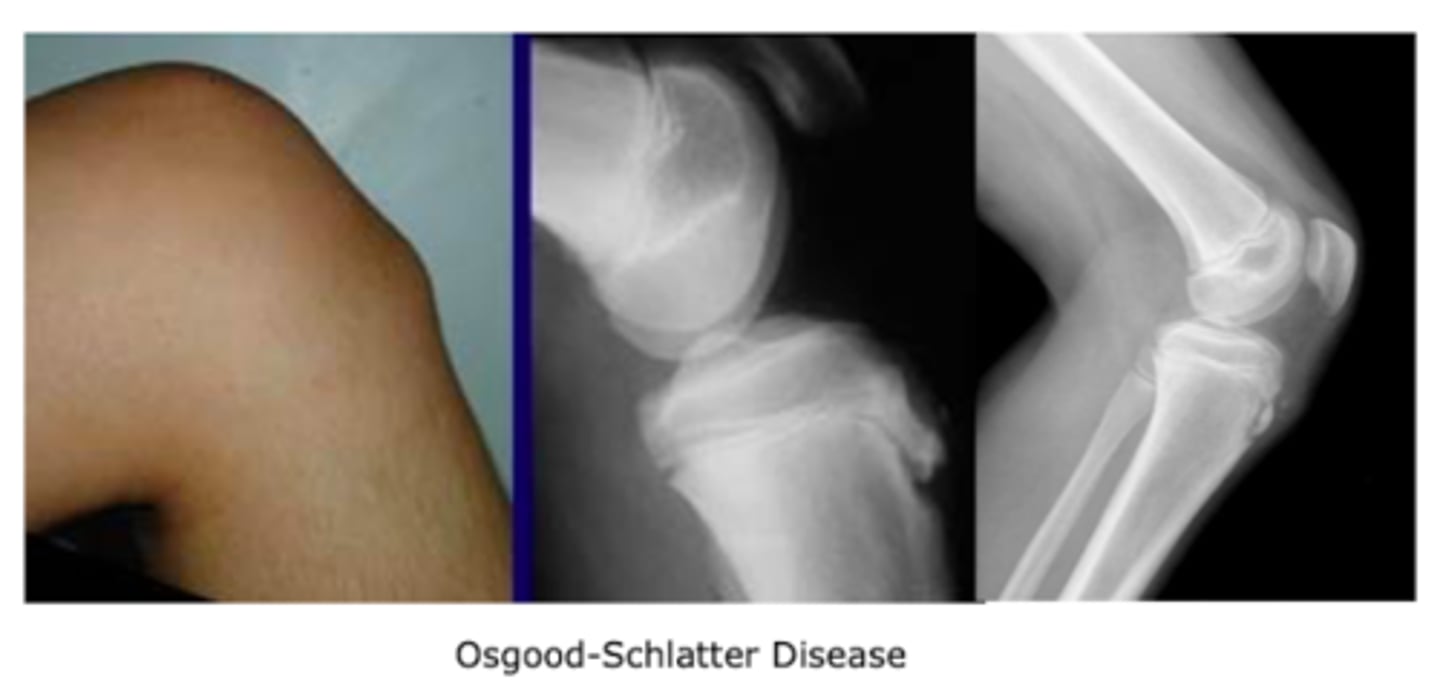
Who is most commonly affected by Osgood-Schlatter disease?
adolescent athletes
M>>F
What joint is most commonly affected by OA? What compartment is most affected?
KNEE - most commonly in the medial compartment
*joint space narrowing
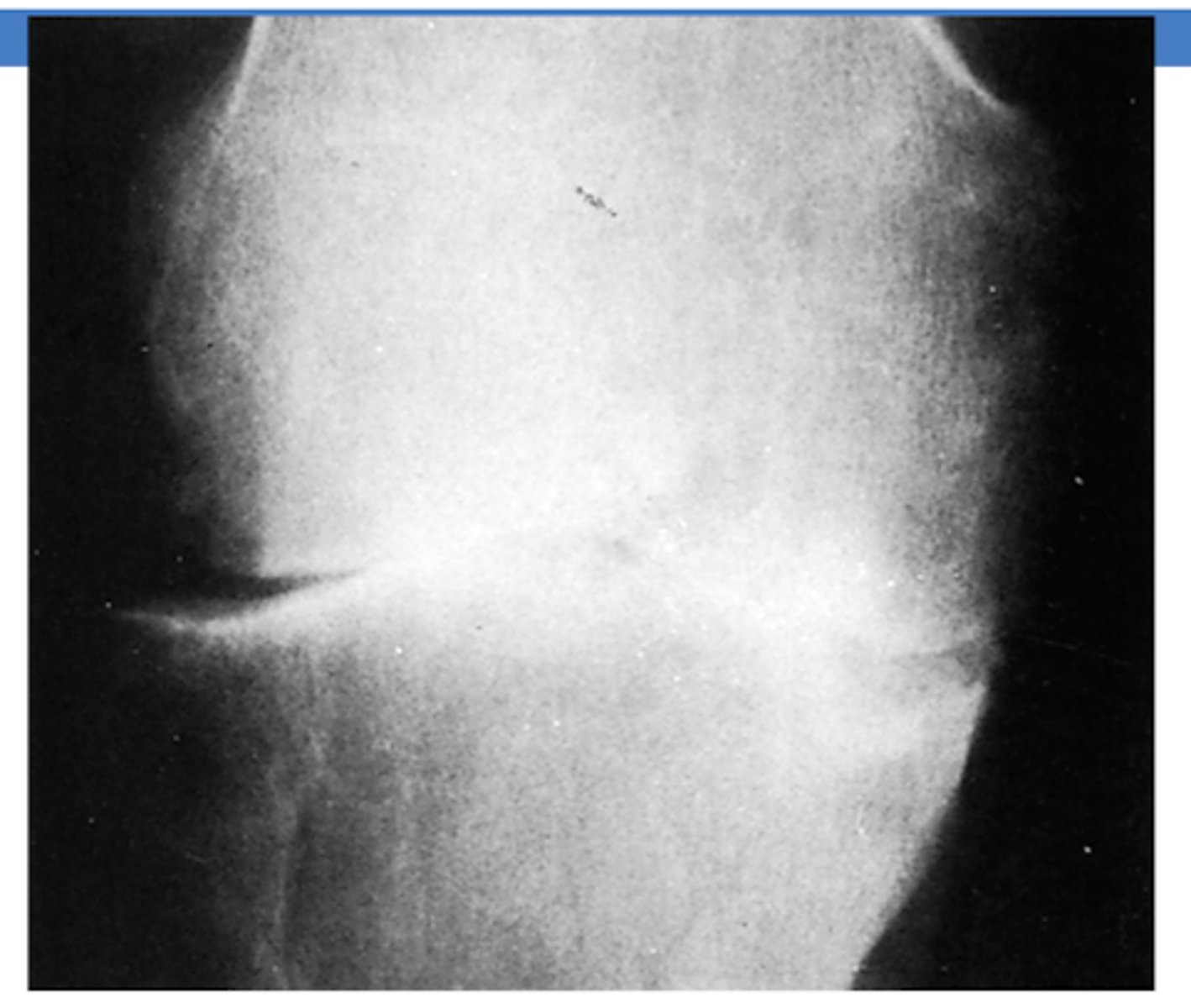
What type of deformity is associated with OA of the MEDIAL knee compartment?
VARUS
What type of deformity is associated with OA of the LATERAL knee compartment?
VALGUS
What is a windswept deformity in OA?
one valgus and one varus knee

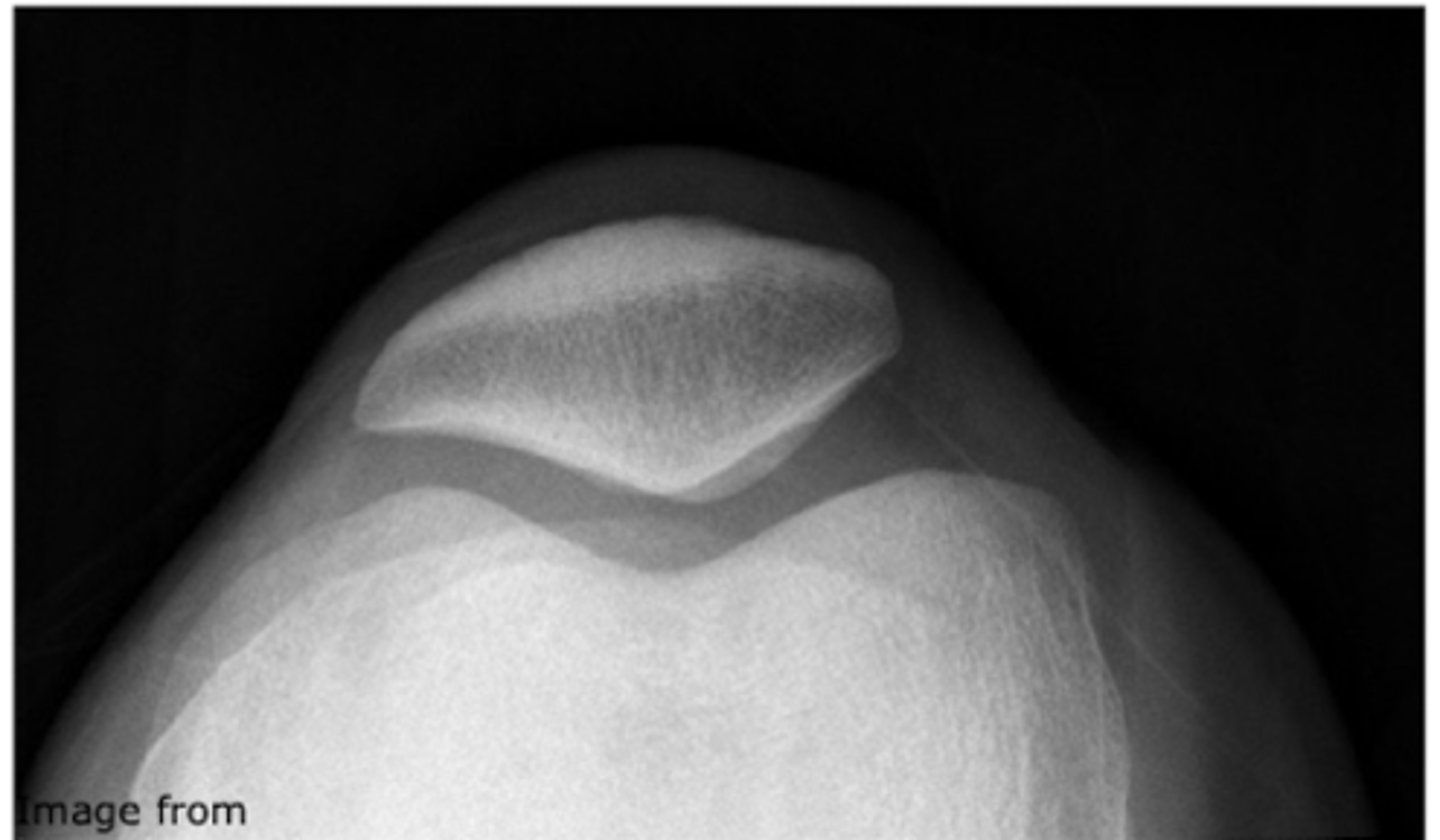
What type of XR view can help evaluate for osteophytes?
tunnel/intercondylar notch view
What condition is also referred to as "runner's knee"?
patellofemoral syndrome (anterior knee pain syndrome)
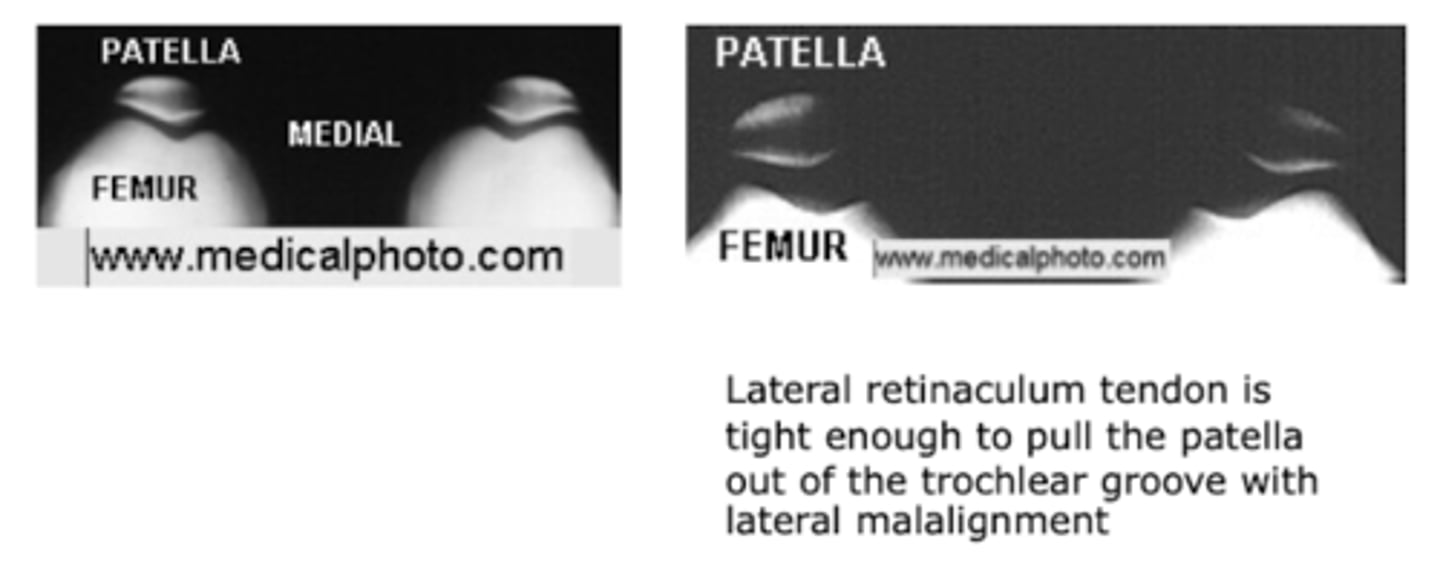
What type of pain can present with patellofemoral syndrome?
dull aching pain in the ANTERIOR knee that is worse with stair climbing/prolonged sitting
What is involved in the treatment for patellofemoral syndrome?
PT
RICE
NSAIDs
Surgery (release tendon)
What is a plica?
band of thick, fibrotic tissue that extends from the synovium of a joint
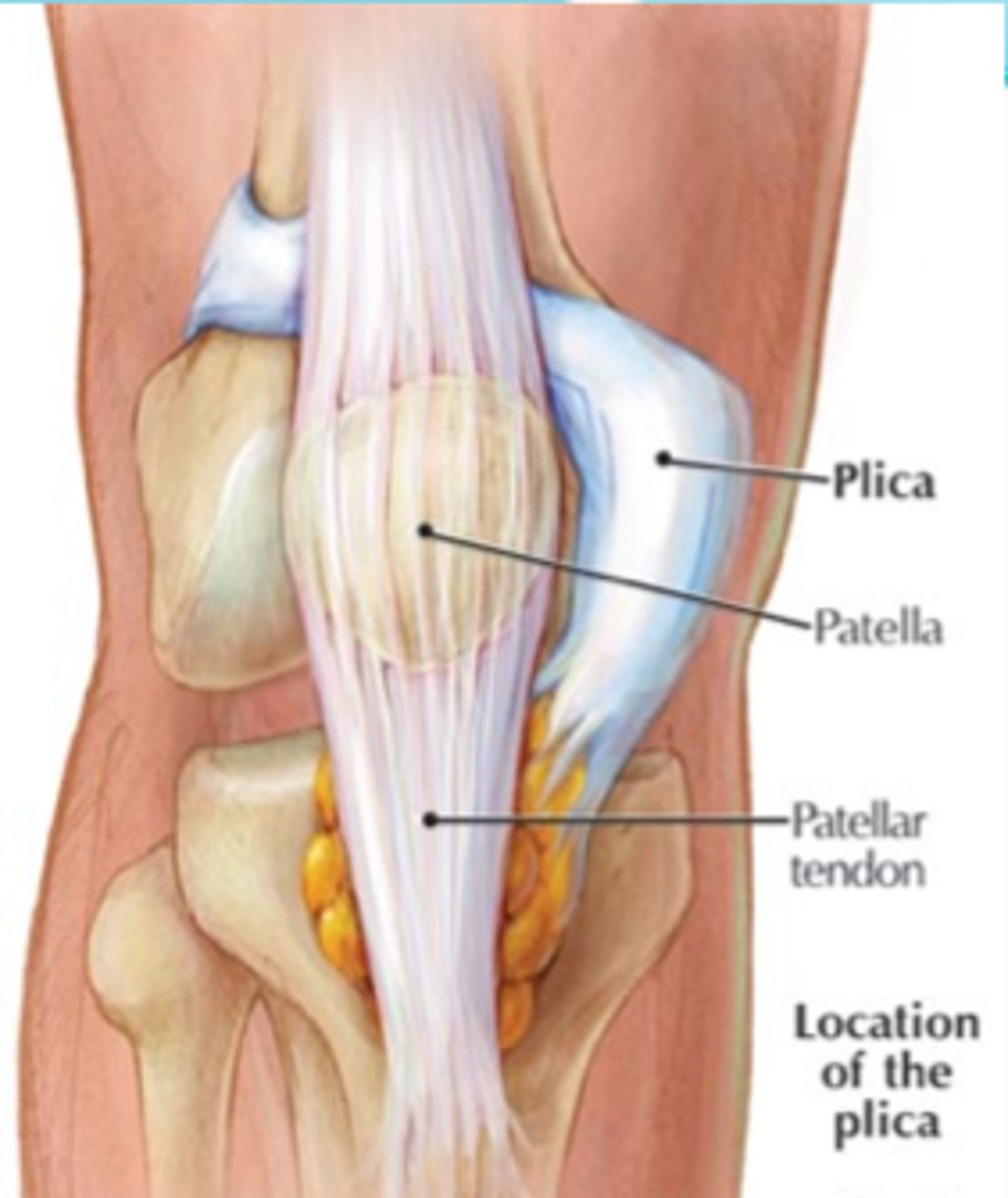
What type of pain is plica syndrome associated with?
anterior knee pain as well as clicking, catching and locking of knee
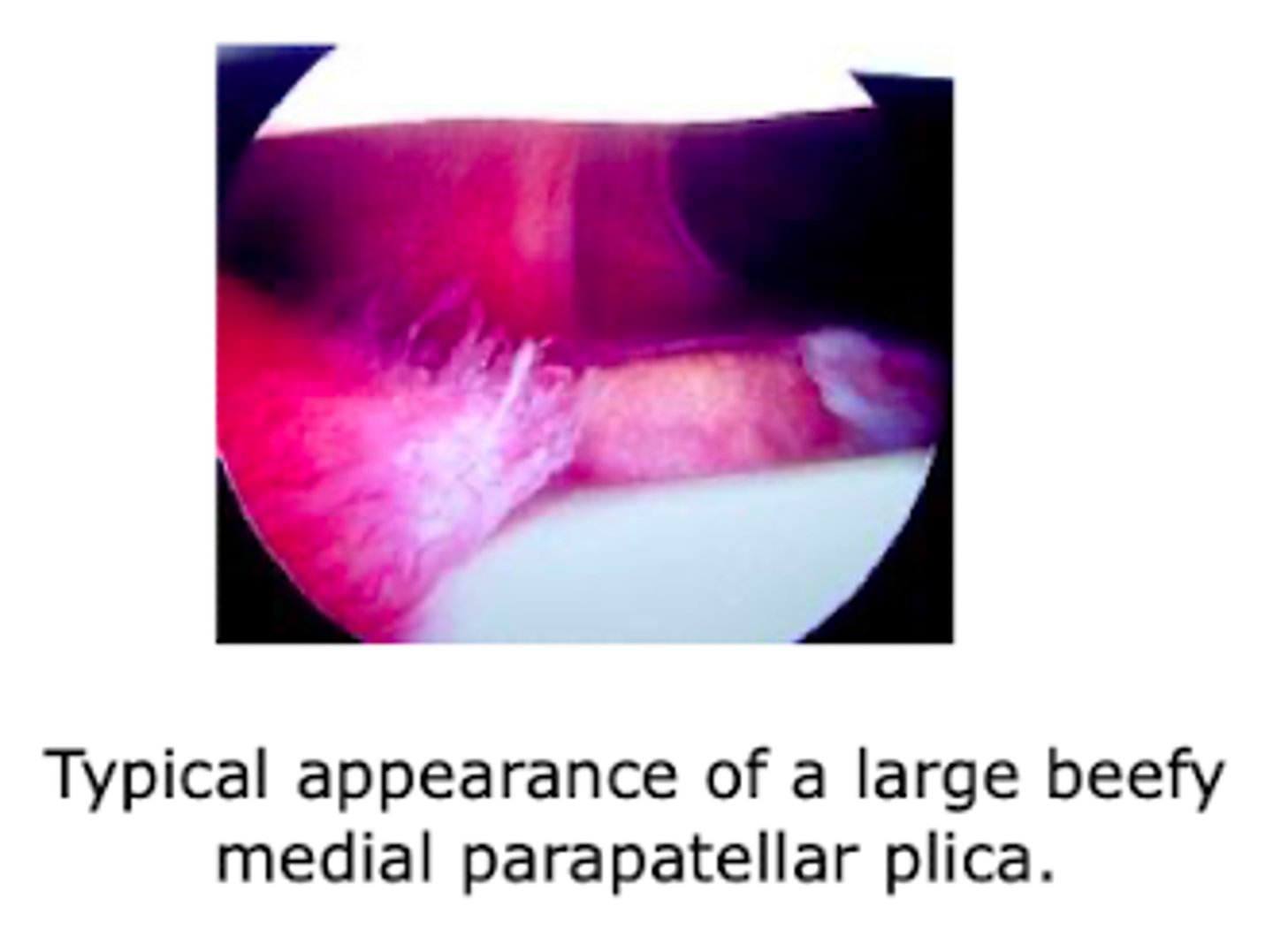
What joint is most commonly affected by septic arthritis?
knee joint
What is the m/c organism causing septic arthritis?
staph aureus
*if SA → N. gonorrhea
What is the diagnostic modality of choice for septic arthritis?
arthrocentesis
- fluid → purulent; opaque; >50,000 WBC count
What is the treatment for septic arthritis?
ABX