Ch 6: The Respiratory System (3%)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Lungs
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
overall where gas exchange occurs
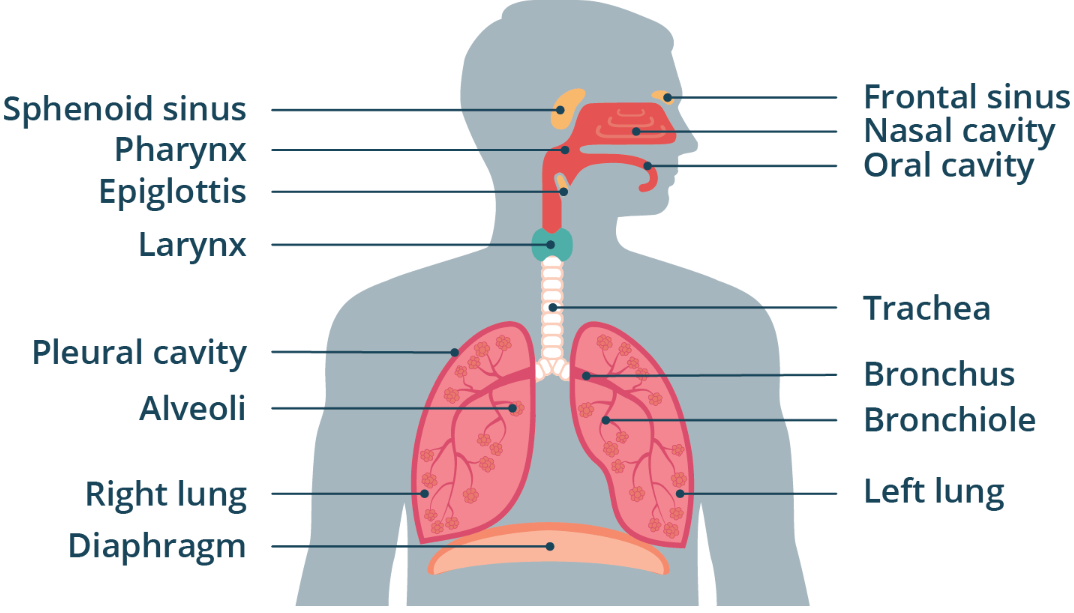
Pharynx
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
Resides behind the nasal cavity and at the back of the mouth
It is a common pathway for both air destined for the lungs and food destined for the esophagus.
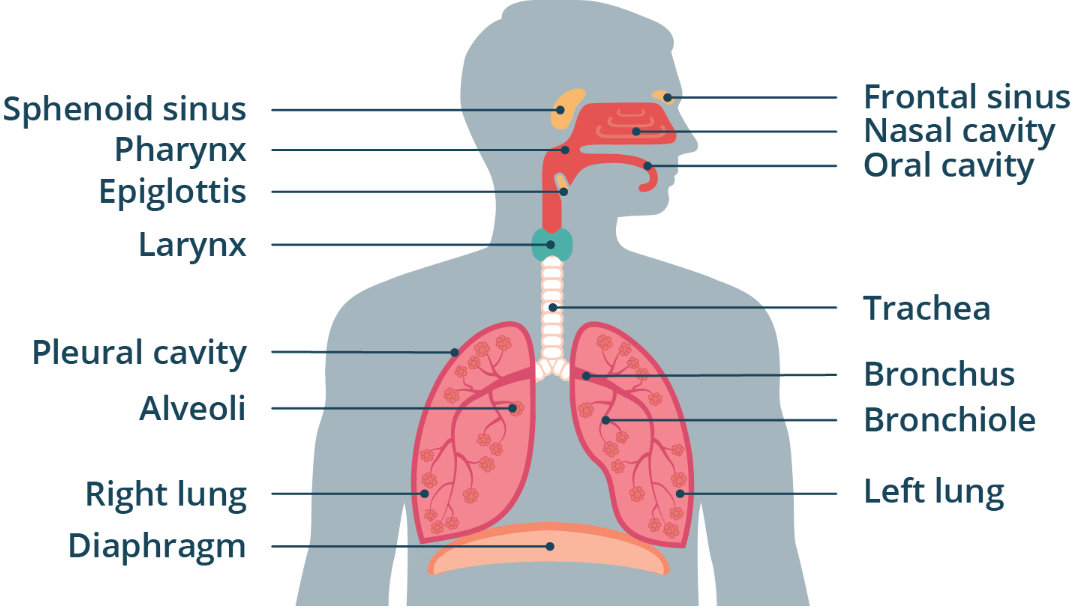
Larynx
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
Also known as the glottis
Lies below the pharynx
Only a pathway for air
Contains two vocal cords.
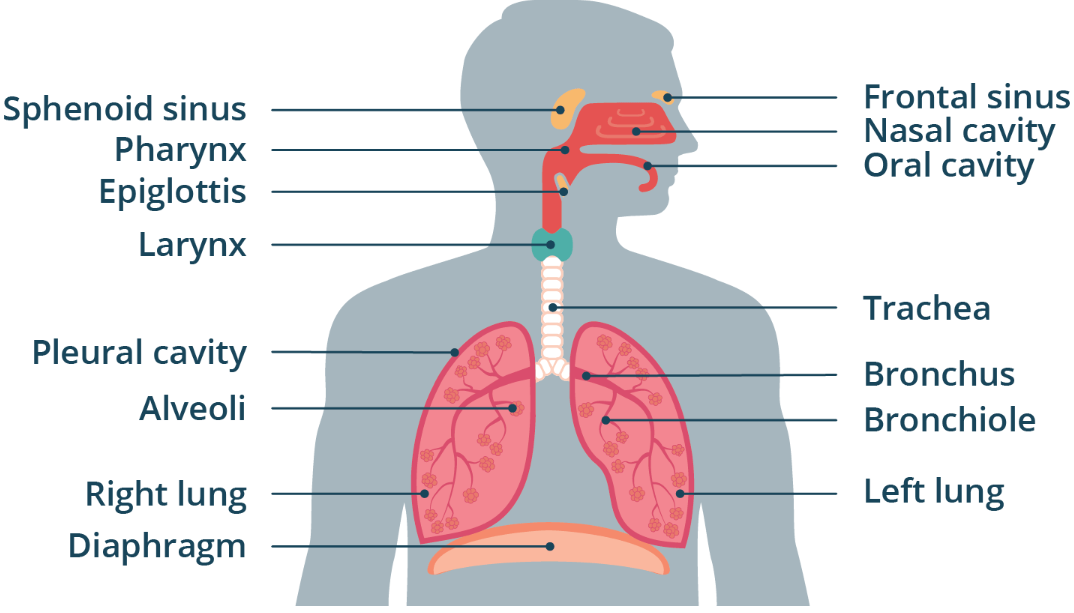
Epiglottis
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
The opening of the larynx is covered by THIS to prevent food from entering the respiratory tract during swallowing.
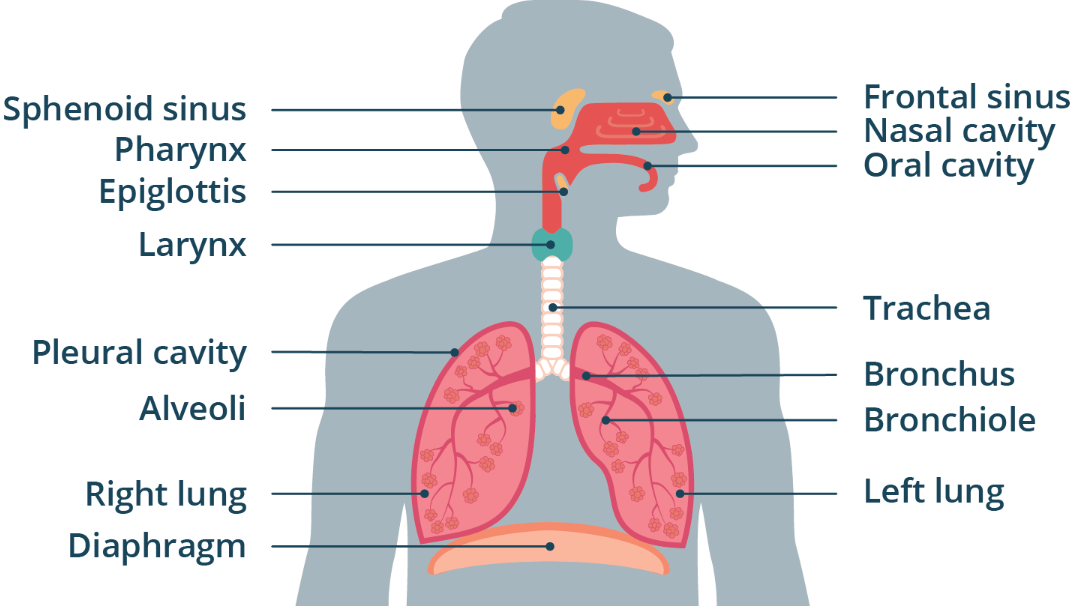
Trachea
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
Air passes into THIS cartilaginous membrane after the larynx.
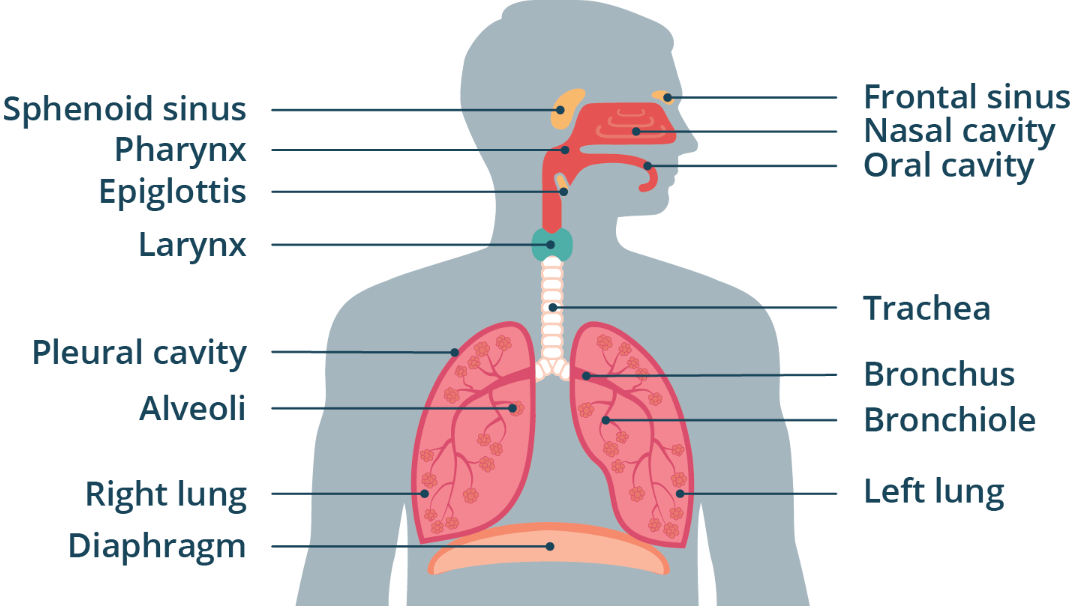
Bronchi
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
Air passes into THESE after the trachea.
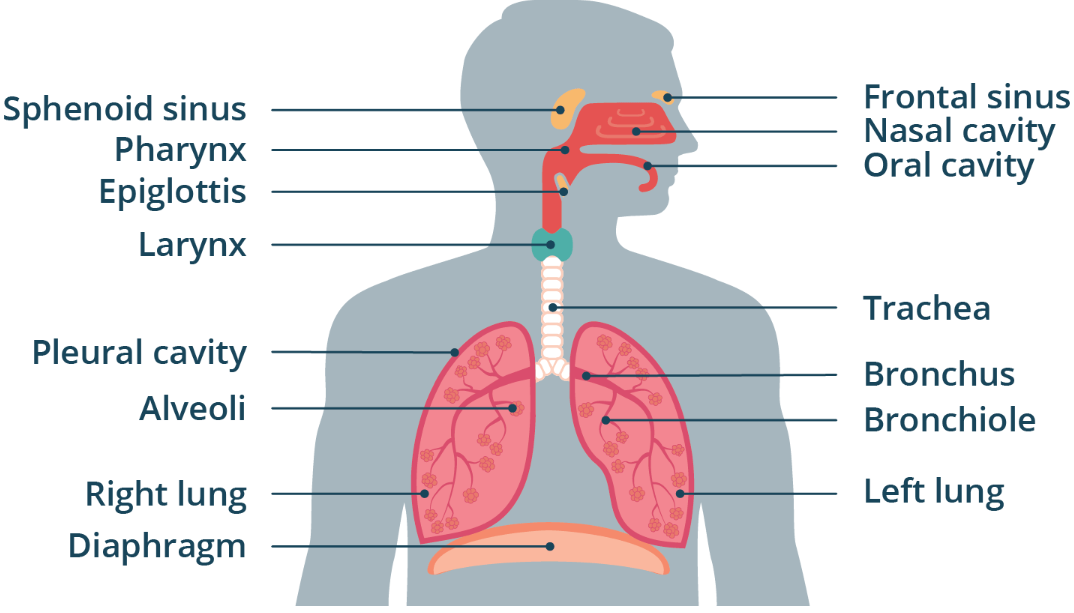
bronchioles, alveoli
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
In the lungs, the bronchi divides into smaller structures which divide into even smaller structures (2 total)
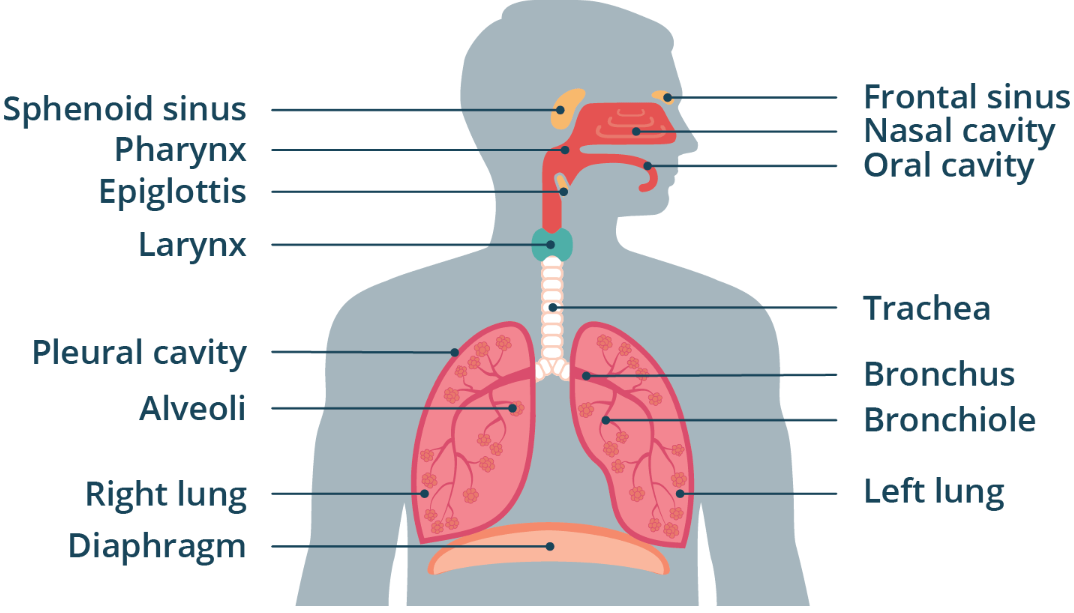
Alveoli
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
Balloon structures that are derived from the bronchioles
Where gas exchange occurs due to the surrounding network of capillaries.
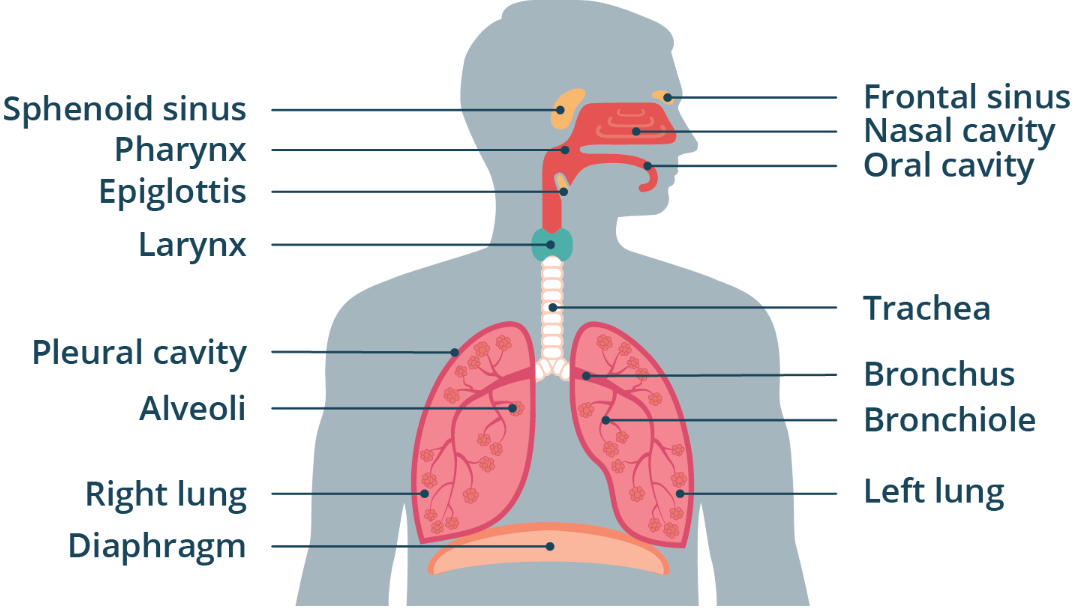
Surfactant
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
A detergent substance coating each alveolus
Decreases surface tension at the liquid-gas interface
Prevents alveolar collapse.
Left
Anatomy - Right vs. Left
THIS side lung is slightly smaller than the other in order to make room for the heart in the thoracic cavity
Pleurae
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
Membranes that surround each lung
Forms a closed sac against which the lung expands
Visceral Pleura
Anatomy - Visceral vs. Parietal Pleura
The inner membrane adjacent to the lung
Parietal Pleura
Anatomy - Visceral vs. Parietal Pleura
The outer membrane that touches the chest wall
Intrapleural Space
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
The space between the two pleurae
Contains a thin layer of fluid that lubricates the two pleural surfaces
An example of a potential space (a space that is normally empty or collapsed)
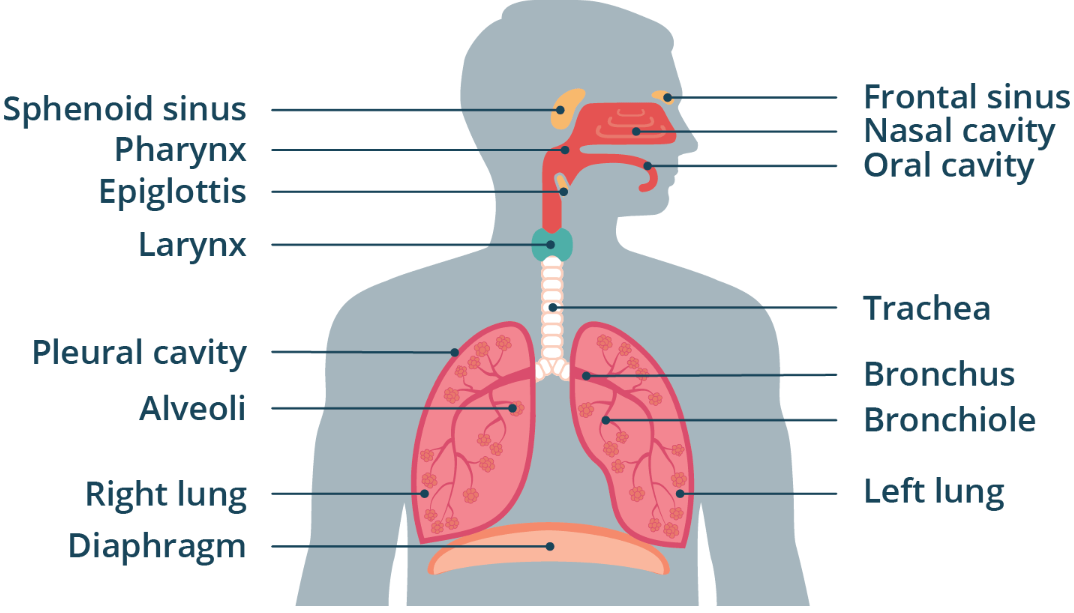
Diaphragm
Anatomy
WORD BANK: Lungs, Epiglottis, Larynx, Trachea, Pharynx, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Pleurae, Surfactant, Intrapleural Space, Diaphragm
——
The thin skeletal muscular structure that divides the chest from the abdomen
Helps create the pressure differential required for breathing
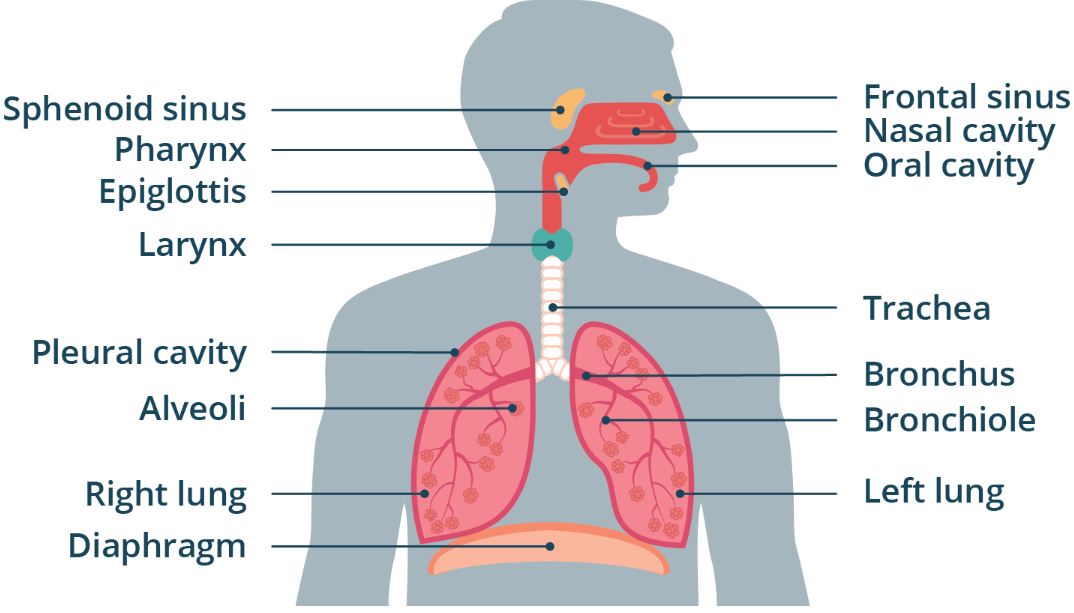
somatic, autonomic
Autonomic vs. Somatic
The diaphragm is under _________ control even though breathing itself is under ____________ control
active, external, expand, increasing, decreases, expands, dropping, drawing, negative-pressure
Inhalation
Inhalation is an _________ process.
The diaphragm and __________ intercostal muscles _________ the thoracic cavity, _____________ the volume of the intrapleural space.
This ____________ the intrapleural pressure.
This pressure differential ultimately ________ the lungs, __________ the pressure within and _________ in air from the environment.
This mechanism is termed __________-__________ breathing.
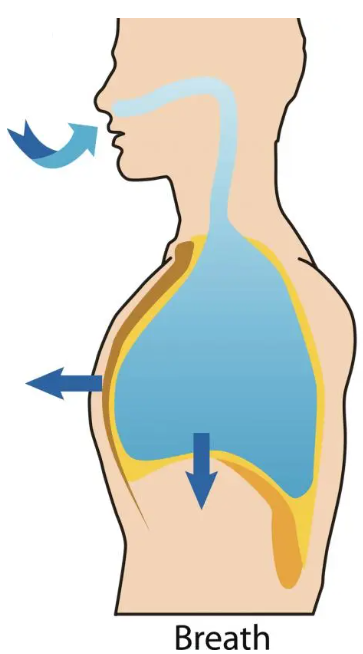
passive, active, passive, external, decreases, higher, pushed, active, internal, abdominal, decrease, pushing
Exhalation
Exhalation is usually a ________ process, but can also be ________.
In ________ exhalation, as the diaphragm and __________ intercostal muscles relax, the chest cavity ___________ in volume.
Now pressure in the intrapleural space is ________ than in the lungs, causing air to be _______ out.
In ________ exhalation, the _________ intercostal muscles and ____________ muscles can be used to forcibly _________ the volume of the thoracic cavity, _________ air out.
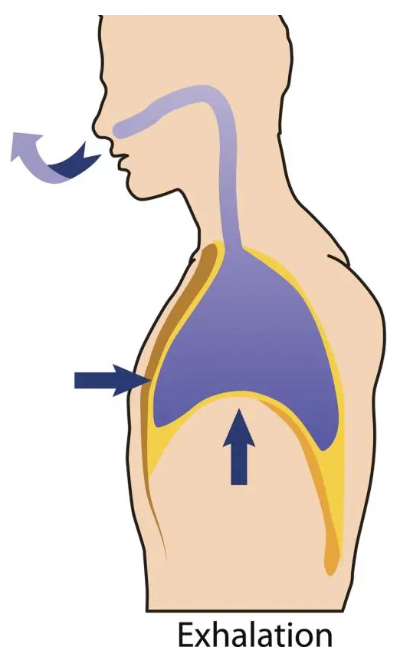
inhalation
Inhalation vs. Exhalation
The diaphragm contracts (pulls down)
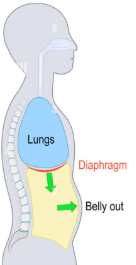
exhalation
Inhalation vs. Exhalation
The diaphragm relaxes (springs upwards)
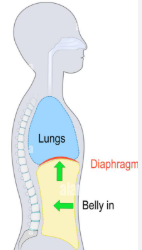
inhalation
Inhalation vs. Exhalation
Normally an active process
exhalation
Inhalation vs. Exhalation
Normally a passive process
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
WORD BANK: Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), Total Lung Capacity (TLC), Vital Capacity (VC), Tidal Volume (TV), Residual Volume (RV)
——
the maximum volume of air in the lungs when one inhales completely
Residual Volume (RV)
WORD BANK: Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), Total Lung Capacity (TLC), Vital Capacity (VC), Tidal Volume (TV), Residual Volume (RV)
——
the volume of air remaining in the lungs when one exhales completely
Vital Capacity (VC)
WORD BANK: Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), Total Lung Capacity (TLC), Vital Capacity (VC), Tidal Volume (TV), Residual Volume (RV)
——
the difference between the minimum and maximum volume of air in the lungs (TLC - RV)
Tidal Volume (TV)
WORD BANK: Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), Total Lung Capacity (TLC), Vital Capacity (VC), Tidal Volume (TV), Residual Volume (RV)
——
the volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a normal breath
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
WORD BANK: Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), Total Lung Capacity (TLC), Vital Capacity (VC), Tidal Volume (TV), Residual Volume (RV)
——
the volume of additional air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal exhalation
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
WORD BANK: Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), Total Lung Capacity (TLC), Vital Capacity (VC), Tidal Volume (TV), Residual Volume (RV)
——
the volume of additional air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal inhalation
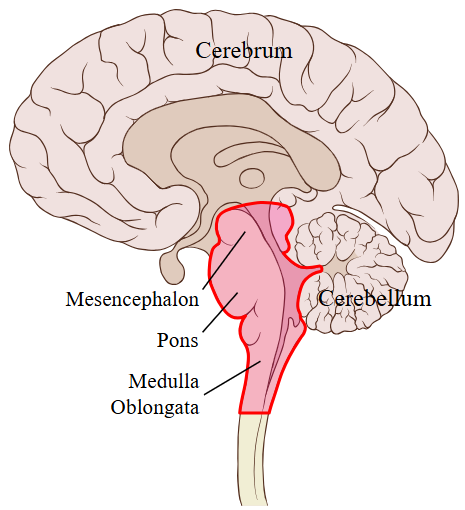
ventilation center, medulla oblongata, chemoreceptors, increasing, ventilation center, increasing, cerebrum, medulla oblongata
Ventilation is regulated by the ___________ _______, a collection of neurons in the ___________ ___________.
__________________ respond to carbon dioxide concentrations, ____________ the respiratory rate when there is a high concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood.
The ___________ ________ can also respond to low oxygen concentrations in the blood by ____________ ventilation rate.
Ventilation can also be controlled consciously through the __________, though the __________ __________ will override it during extended periods of hypo- or hyperventilation.
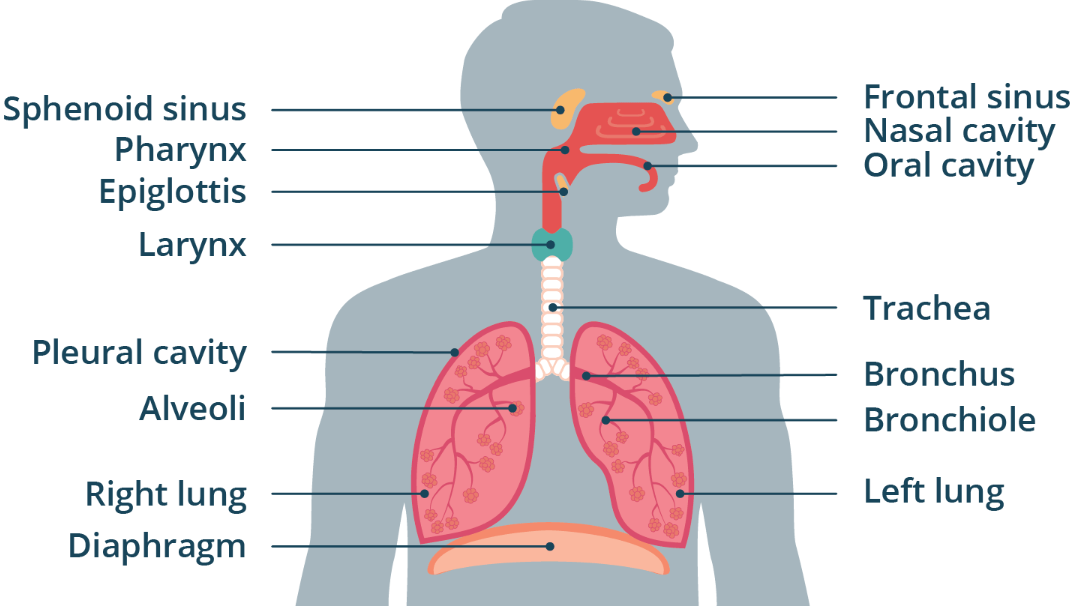
gas exchange, diffusion, concentration gradients
The lungs perform ____ ________ with the blood through simple ___________ across _____________ __________
enter, pulmonary arteries
(*** the CO2 is moving AWAY from the heart to the lungs to be expelled)
Does deoxygenated blood with a high carbon dioxide concentration ENTER the lungs or EXIT the lungs?
Is it transported by PULMONARY ARTERIES or PULMONARY VEINS?
exit, pulmonary veins
(** the oxygenated blood VISITS the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body)
Does oxygenated blood with a low carbon dioxide concentration ENTER the lungs or EXIT the lungs?
Is it transported by PULMONARY ARTERIES or PULMONARY VEINS?
surface area, vasodilation, vasoconstriction
The large _________ ______ of interaction between the alveoli and capillaries allows the respiratory system to assist in thermoregulation through _____________ and ________________ of the capillary beds.
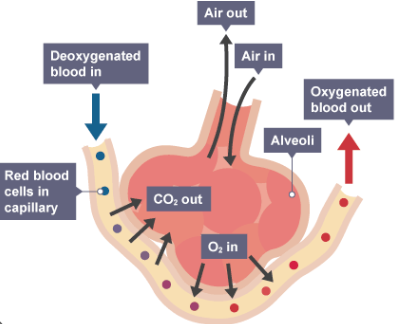
decrease
Does vasodilation of the capillary beds in the respiratory tract lead to a DECREASE in body temperature or an INCREASE?
increase
Does vasoconstriction of the capillary beds in the respiratory tract lead to a DECREASE in body temperature or an INCREASE?
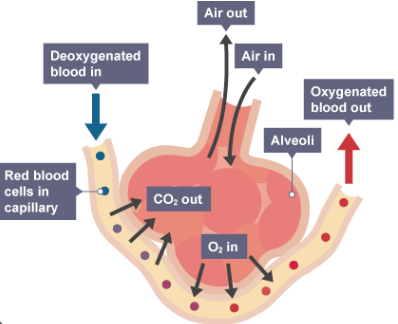
alveoli, capillaries, hemoglobin, capillaries, alveoli, expiration
O2 in the lungs flows down its pressure gradient from the _________ to the _____________ where it can bind to _______________ for transport.
Meanwhile, CO2 flows down its partial pressure gradient from the ____________ into the _________ for ______________.
lysozyme
Which enzyme, found in the nasal cavity and saliva, is able to attack the peptidoglycan walls of gram-positive bacteria in order to protect the lungs from pathogens?
mucus, cilia, mucus, oral, mucociliary escalator
The internal airways are lined with ________, which traps particulate matter and larger invaders.
Underlying _____ then propel the ________ up the respiratory tract to the ______ cavity, where it can be expelled or swallowed.
This mechanism is called the ___________ __________.
mucus membranes, mucociliary escalator, vibrissae (small hairs in the nasal cavity)
name the 3 main mechanisms used by the respiratory tract to filter the incoming air and trap particulate matter to protect it from pathogens
macrophages
immune cells that engulf and digest pathogens and signal to the rest of the immune system that there is an invader
IgA antibodies
mucosal surfaces are covered in THESE to help protect against pathogens that contact the mucus membranes
mast cells
Immune cells with antibodies on their surface that, when triggered, can promote the release of inflammatory chemicals
Often involved in allergic reactions
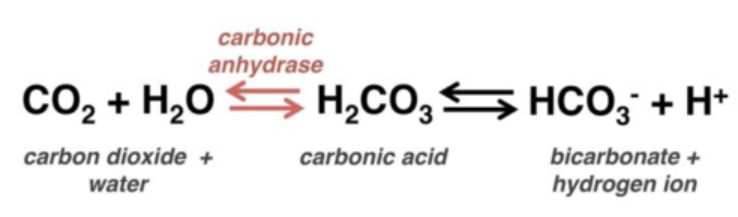
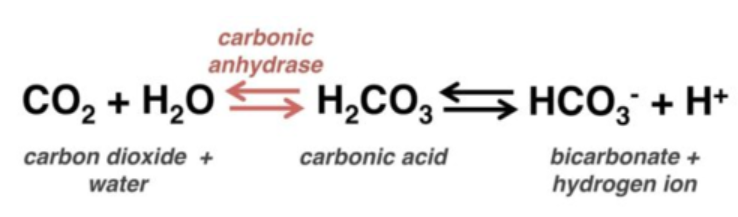
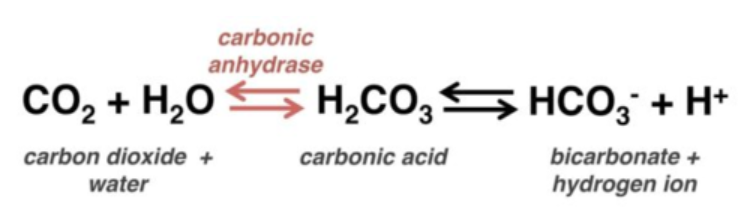
bicarbonate buffer system
the respiratory system uses THIS to maintain pH balance
CO2 (g) + H2O (l) ⇌ H2CO3 (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
write out the chemical formula for the bicarbonate buffer system
acidic, increases, carbon dioxide, left, decreasing
According to the bicarbonate buffer system, when blood pH decreases (gets more _______), respiration rate __________ to compensate by blowing off _________ _________.
This causes a ______ shift in the buffer equation, ____________ hydrogen ion concentration.
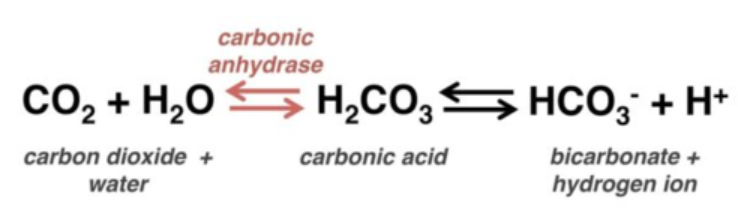
basic, decreases, carbon dioxide, right, increasing
According to the bicarbonate buffer system, when blood pH increases (gets more _______), respiration rate __________ to compensate by trapping _________ _________.
This causes a ______ shift in the buffer equation, ____________ hydrogen ion concentration.
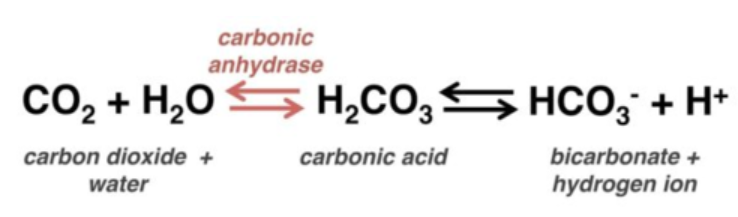
increase
If the blood pH is too acidic (acidemia), does the respiratory rate INCREASE or DECREASE?
decrease
If the blood pH is too basic (alkalemia), does the respiratory rate INCREASE or DECREASE?
expel
If the blood pH is too acidic, do we want to RETAIN carbon dioxide or EXPEL it?
retain
If the blood pH is too basic, do we want to RETAIN carbon dioxide or EXPEL it?