Lecture 7 - Humanistic Approach and Positive Psychology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Explain the key elements of Humanistic Psychology?
Humanistic (studies humans)
Holistic (it encompasses the human system, not just its individual parts)
Historic (it looks at people from birth to death, not just singular moments in their life)
Phenomenological (focuses on the interior, experiential and existential aspects of personality)
Real Life (looks at people in the real world vs. the lab where things are arguably confined)
Positivity (looks at how we promote joy in our lives)
Will (looks at how we choose to live our life and make decisions)
Value (looks at what a meaningful life means for people)
Explain Carl Roger’s thinking in terms of how people perceive reality.
Carl Rogers felt that people’s perception of reality is their true reality because people have the choice to decide how to perceive things.
*However, he still agreed that there is an objective reality and that we can’t just rely on our personal perceptions
Explain the method Carl Roger’s liked to use with his patients. Why?
Carl Rogers liked to make his patient’s think about how their patterns of thinking in the past has caused issues, instead of directly telling them about any ‘problems’ they have.
This is because Rogers felt that the idea of the ‘self’ was very important and he did not want to hurt people’s self-worth, self-image and ideal-self.
According to Carl Roger’s what is our self-worth shaped by?
Roger’s felt that our self-worth is shaped by our early childhood experiences. Therefore, making us develop a sense of:
unconditional positive regard
OR
conditional positive regard
Define unconditional positive regard.
When parents and significant others accept and love the child for who they are—no matter the circumstance.
Define conditional positive regard.
When parents and significant others only show positive regard to the child when the child behaves in a particular way.
What does it mean to have a self-image that is congruent with your ideal self?
This means that who you are matches with who you want to be.
What does it mean to have a self-image that is incongruent with your ideal self?
This means that who you are does not match with who you want to be.
Explain Carl Roger’s Person-Centered Therapy technique.
Roger’s thought that if a patient was in a state of incongruence (ie. anxiety) the therapist should:
Treat the patient like someone they genuinely care about by validating their feelings and listening to them without judgement
thus, treating them with unconditional positive regard
and empathy
Explain Abraham Maslow’s way of thinking.
Abraham Maslow felt that “health means more than simply the absence of disease,” meaning our mental health and the way we view ourselves is equally important for our overall well-being.
Therefore, Maslow was interested in how we cultivate meaningful lives, instead of how do we ‘get rid’ of conditions (ie. depression and anxiety).
From that, he created Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
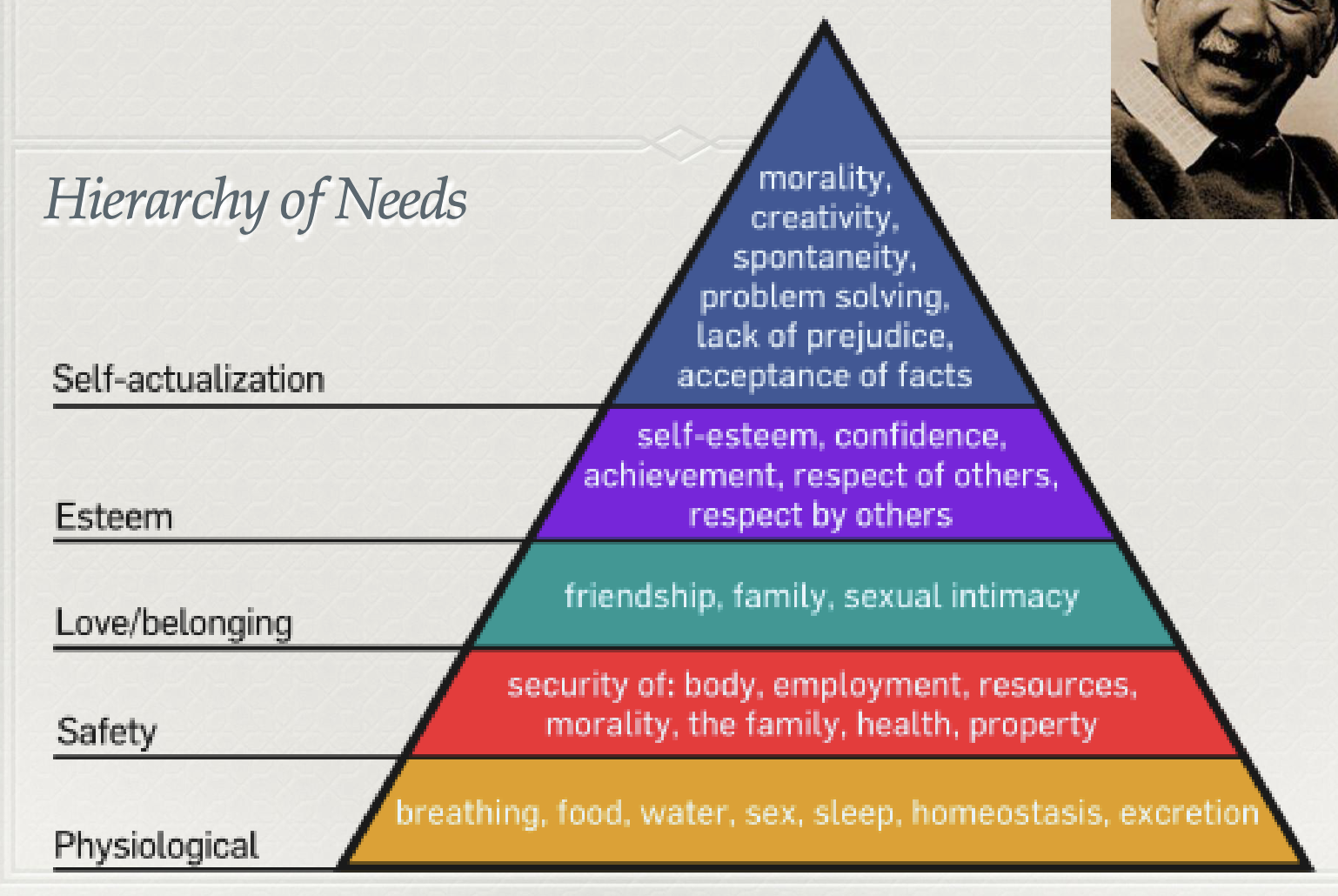
Explain Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Maslow felt that there are 5 hierarchy’s:
Physiological (breathing, food, water, sleep)
Safety (shelter, health, employment)
Love/belonging (friendship, family, sexual intimacy)
Esteem (self-esteem, respect for and from others)
Self-actualisation (morals, lack of prejudice, creativity)
He felt that people had to first be satisfied in the lowest tier in order to be able to progress into higher tiers. Hence, level 5 is not better than level 1, level 1 is just a basis for higher levels. This is because, if someone is living in poverty, their number 1 goal is usually not about becoming more creative, but finding a way out of poverty and so on and so forth.
Therefore, he felt that what is meaningful to one’s life is dependent on what stage of the hierarchy they are experiencing at the moment.
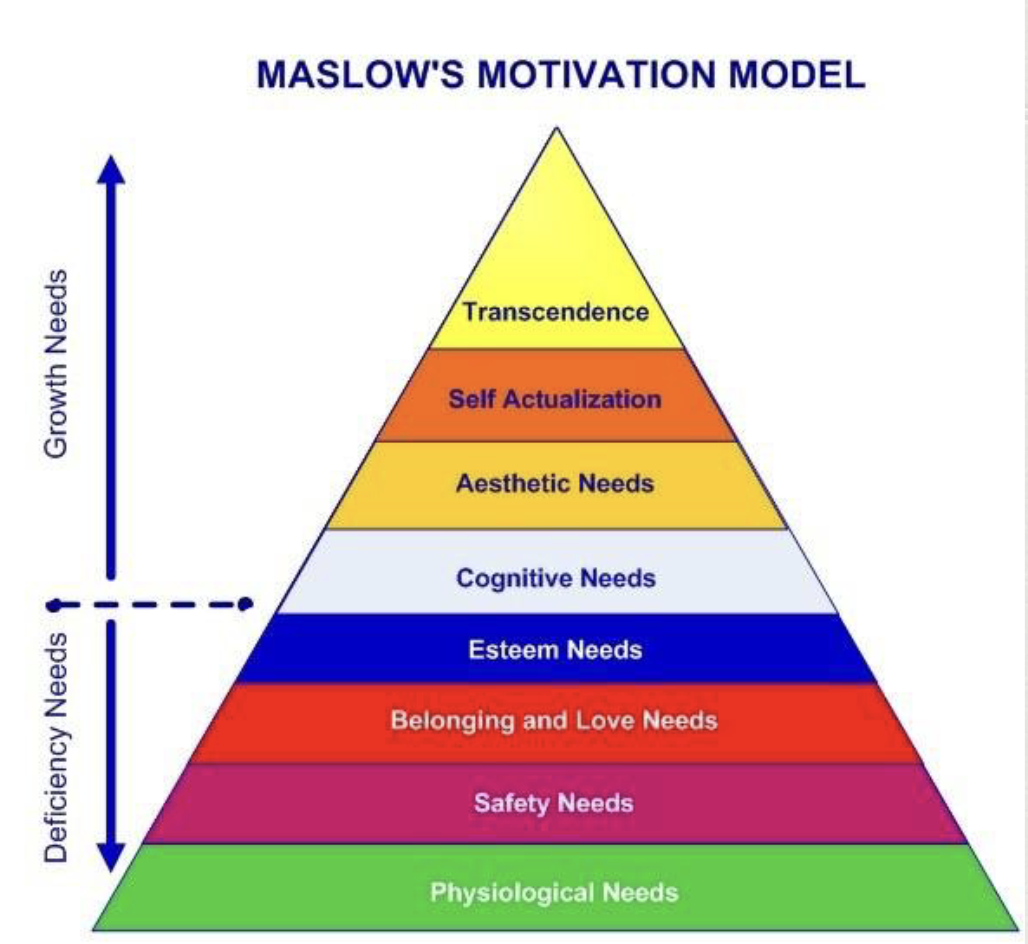
Explain Maslow’s updated version of his Hierarchy of Needs model.
Maslow created a new model that was split into deficiency needs and growth needs. Deficiency needs being goals that, once attained, we don’t feel the need to have more of (ie. got food, now full, no need more food). Whereas, growth needs being goals that we always want to improve on (ie. learned about psych topic you like, desire to learn more and more).
He also extended the 5th stage (self-actualisation) and added 4 more sections:
cognitive needs (our desire to learn more)
aesthetic needs (things that are pleasing to the eye)
self-actualisation (the realisation of one's full potential and the desire to become everything one is capable of being)
transcendence (understanding that there is something beyond you)
Explain the main elements of Positive Psychology.
Psychology should be just as concerned about the strengths of people, and not just their weaknesses
Psychology should be just as concerned about building the best life for someone, compared to just fixing the worst parts of it
Psychology should be just as concerned about making the lives of normal people fulfilling, and not just focus on helping people with pathological issues
What is Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi best known for?
He is a positivist psychologist who is best known for his theory on Optimal Experience and Flow.
Define flow.
A state of "optimal experience" where a person is completely immersed in an autotelic activity for its own sake, leading to a feeling of full involvement and enjoyment.
Define autotelic activities.
Tasks that someone finds challenging but still does because the task itself is enjoyable to them.
What do you need in order to get into a flow state?
the task must be challenging
you must feel capable to complete the task
Why must the activity be challenging in order for people to reach a flow state?
If the activity is not challenging enough, people may get bored, preventing them from getting fully immersed in the activity and getting into a flow state.
Why must the person feel like they are capable to do the activity in order for them to reach a flow state?
If people do not feel like they are capable to complete the task, it might create too much stress, therefore hindering the person from reaching a flow state.
What is an example of being in a flow state?
Running
When someone runs they can get fully immersed in the activity because they genuinely enjoy running, even though it is challenging (making it an autotelic activity).
Therefore, time passes by effortlessly and people feel a sense of accomplishment and enjoyment afterwards.
What do you feel when you are in a flow state?
deep concentration of the task at hand
sense of control
loss of self-consciousness
transformation of time (time passes effortlessly)
clarity of goals
What type of psychologists was Martin Seligman?
Positivist Psychology.
Explain Martin Seligman’s way of thinking.
Seligman had 3 main thoughts about positive psychology and felt that they needed to work together in order for people to live their best life:
The Pleasant Life
The Good Life
The Meaningful Life
Define The Pleasant Life.
When we appreciate the basic pleasures of life.
According to Seligman, why is focusing too much on the basic pleasures of life a bad thing?
Focusing too much on the basic pleasures of life can detract from the meaningful things in our life and skew our priorities.
Define The Good Life.
When we discover our own strengths and virtues in order to enhance our lives.
Define The Meaningful Life.
When we use our unique strengths for something greater than ourselves.
Explain the study by Schueller and Seligman (2010) that was asking about ‘what makes an ideal life?’
Participants were told to complete a measure of orientation toward pleasure, engagement and meaning as pathways to happiness.
the researchers analysed subjective measures of wellbeing based on statements like ‘overall I am satisfied with my life’
and objective measures of wellbeing like educational an occupational attainments
The results were that pleasure, engagement and meaning were good predictors for subjective well-being, especially engagement and meaning. Also, only engagement and meaning was a good predictor for objective well-being (makes sense since objective measures were about educational and occupational achievements).
Within the view of positive psychology, how do we foster meaningful relationships?
We must go through a process of self-disclosure with others, meaning we share something about our identity to someone else, and then the other person does the same.
Explain what self-disclosure is.
When we reveal intimate aspects about ourselves to someone else.
Within a positive psychology perspective, are social interactions always necessary for happiness?
No, solitude can be very beneficial for our happiness and sometimes people actually prefer being alone.
What are the benefits of solitude?
Solitude for short periods of time
during this time people can emotionally renew themselves
Solitude for long periods of time
during this time people can work through personal problems and make important decisions
Solitude for extended periods of time
this time can give people the opportunity to develop one’s spirituality, intellect and creativity
Explain a study that examined people who prefer solitude. What were the results and what was the conclusion?
In the study, the extent to which different people enjoy solitude was measured. To do so, researchers got the participants to do a Daily Diary entry for 7 days;
They had to report when they were alone or with others
and how much they enjoyed each occasion
The results showed that overall, regardless of one’s preference for solitude, everyone spends a lot of time with people. Similarly, both groups found their time with others to be pleasant (almost equal). However, the time alone that was considered pleasant was much higher for those with a preference for solitude, and much lower for those who have a low preference for solitude.
Therefore, indicating that people’s tolerance for being alone is different.
What are the virtues identified with positive psychology?

Why is gratitude a pro-social emotion?
It can strengthen our social bonds and inspire further generosity.
This is because if you’re feeling grateful, you are more likely to want to be nice to others.
How does systematic underestimation affect gratitude?
People tend to undervalue the impact of their kindness on the recipient and on themselves. For example, givers tend to assume that the gestures are too small or are awkward, but the recipients usually feel happier and less awkward than one would expect.
Why do people underestimate the impact of gratitude towards others?
This can be explained by egocentric biases in social judgements; the idea that we focus on how we think others will see us rather than how they will actually see us.
What can mindfulness lead to?
Attention and acceptance.
What are the trait characteristics of mindfulness?
being non-reactive to inner experiences
being attentive to your feelings and surroundings
being able to describe how you feel with words
when you can forgive yourself and not shame yourself