3 - REPRODUCTION
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
yayyy reproduction yayyy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
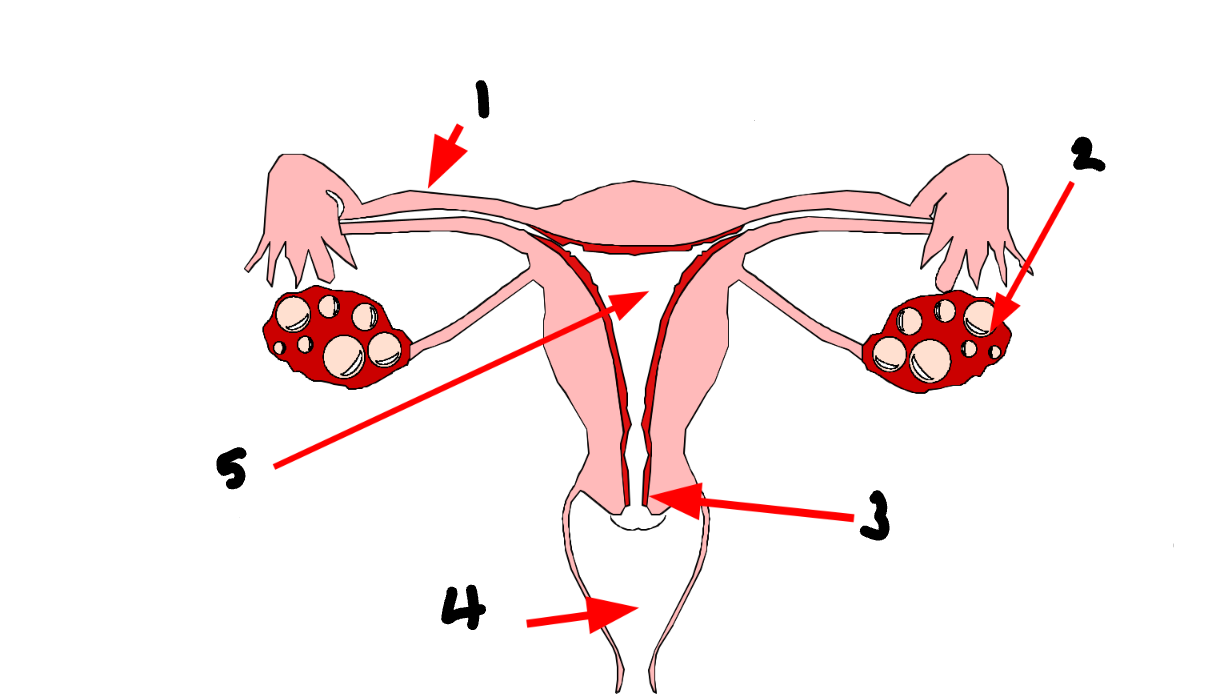
What part of the female reproductive system is 1?
fallopian tube/oviduct
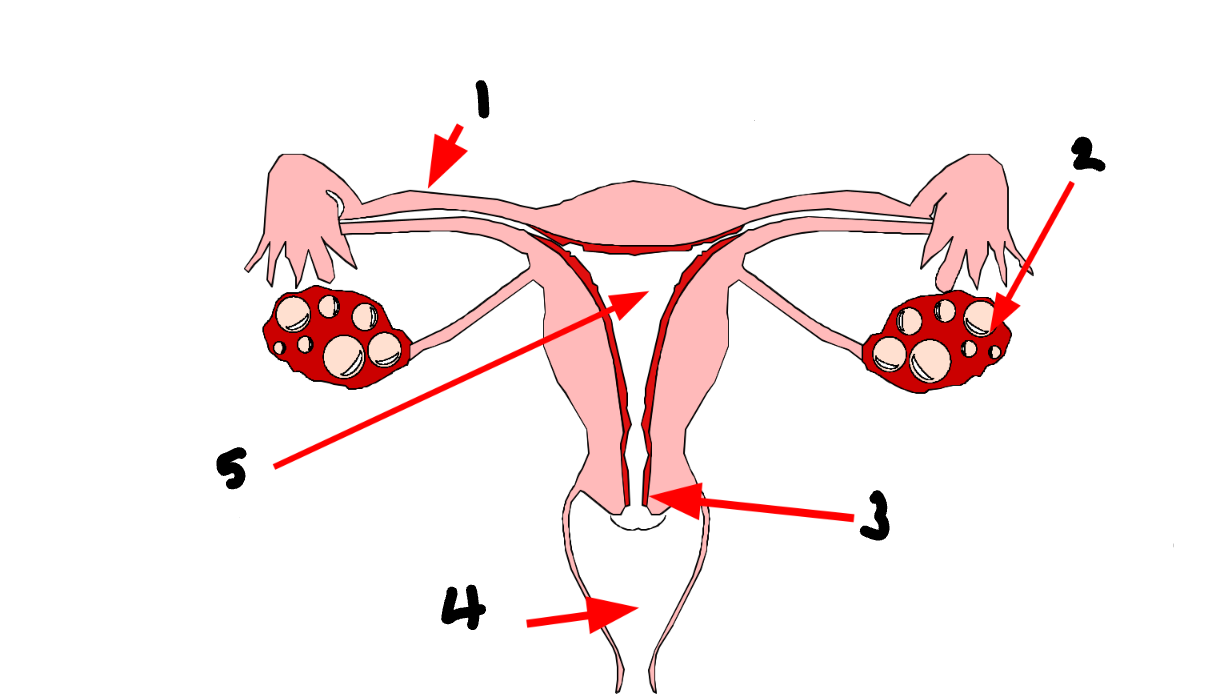
What part of the female reproductive system is 2?
ovary
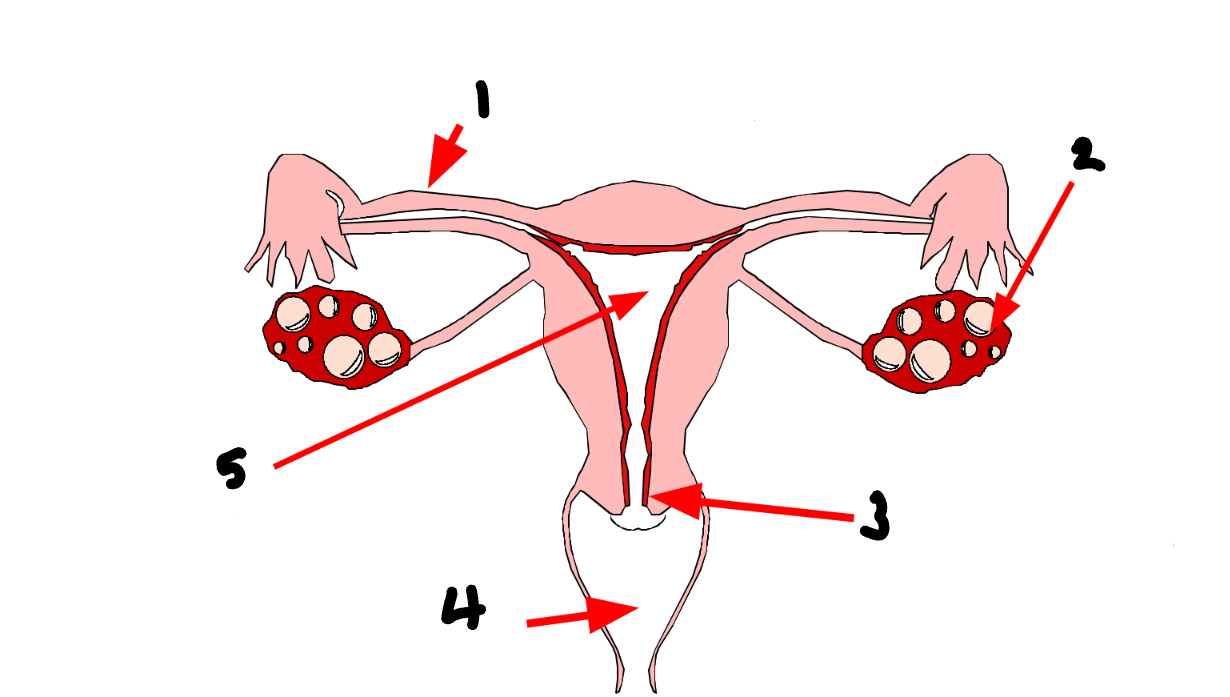
What part of the female reproductive system is 3?
cervix
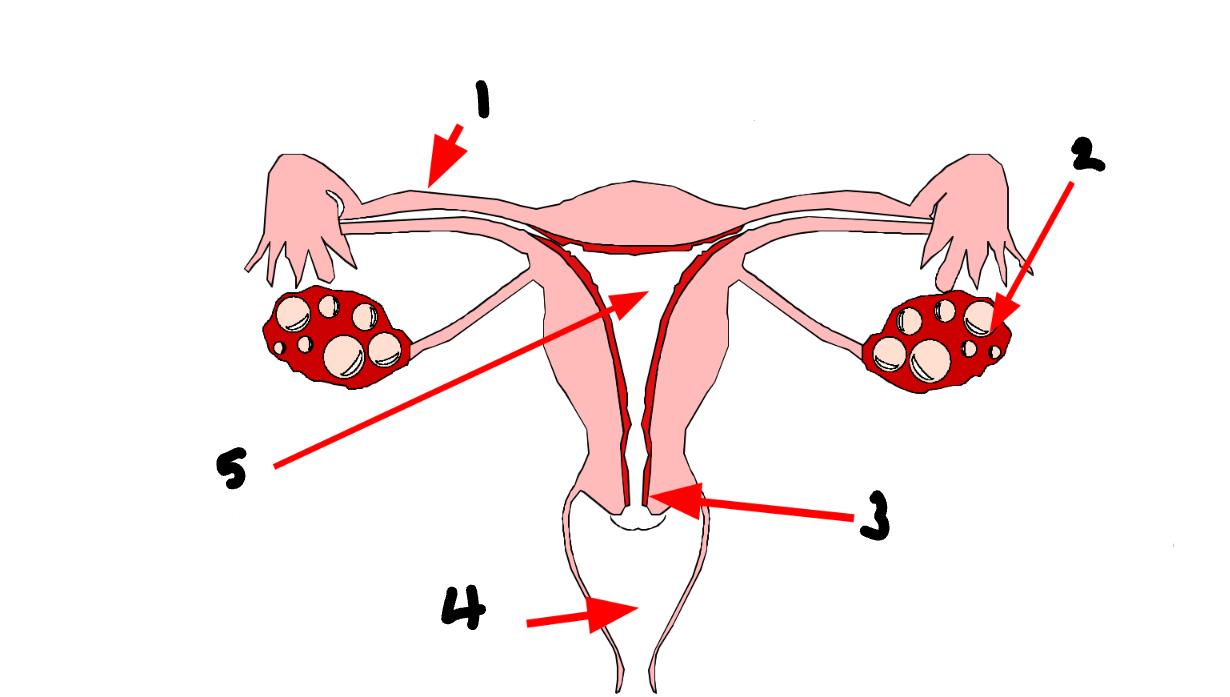
What part of the female reproductive system is 4?
vagina
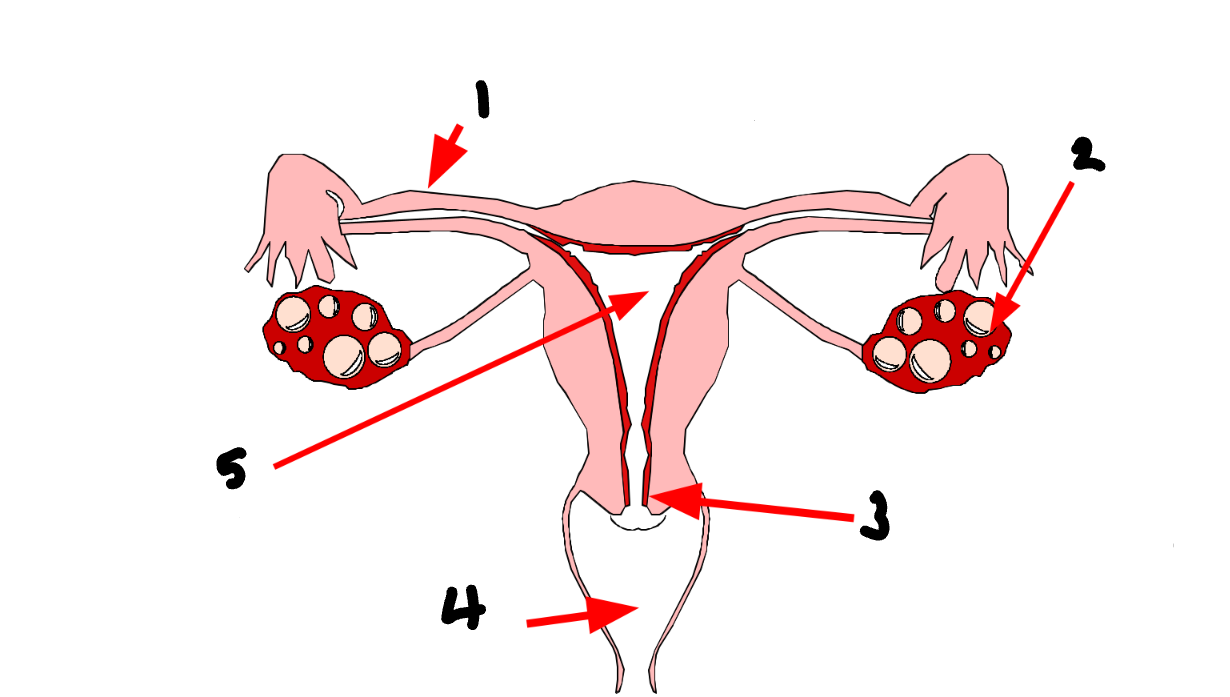
What part of the female reproductive system is 5?
uterus
What does the fallopian tube/oviduct do?
Carries the egg cell to the uterus
fertilisation usually takes place in the oviduct
What does the ovary do?
where eggs mature
What does the cervix do?
entrance to the uterus
What does the vagina do?
where sperm are depositied
What does the uterus do?
where a fertilised egg develops into a foetus
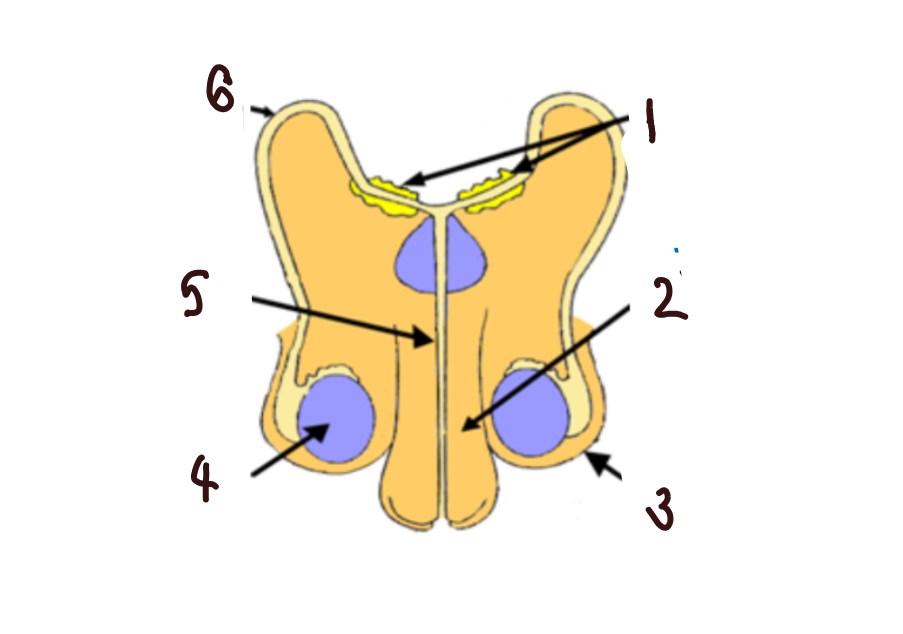
What part of the male reproductive system is 1?
glands
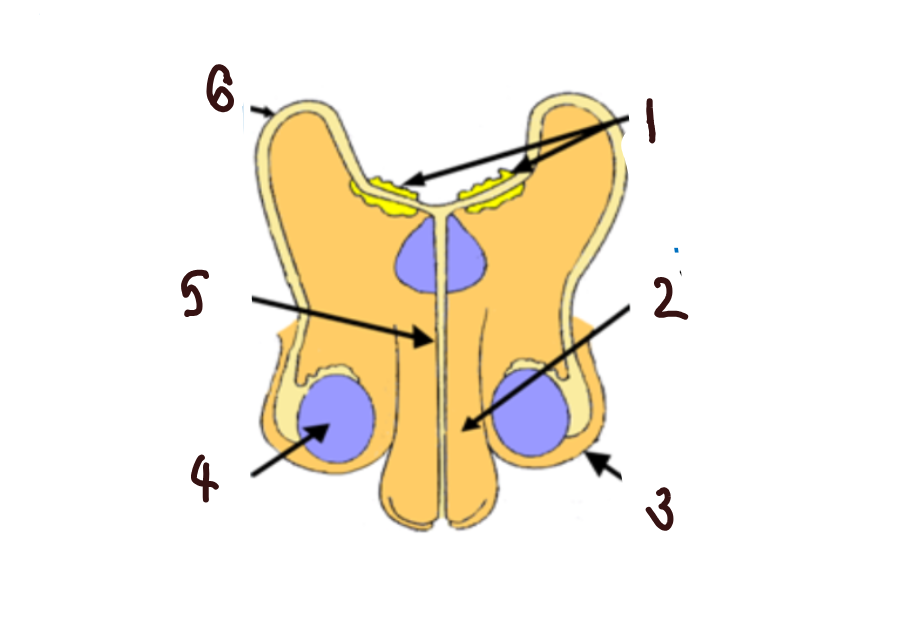
What part of the male reproductive system is 2?
penis
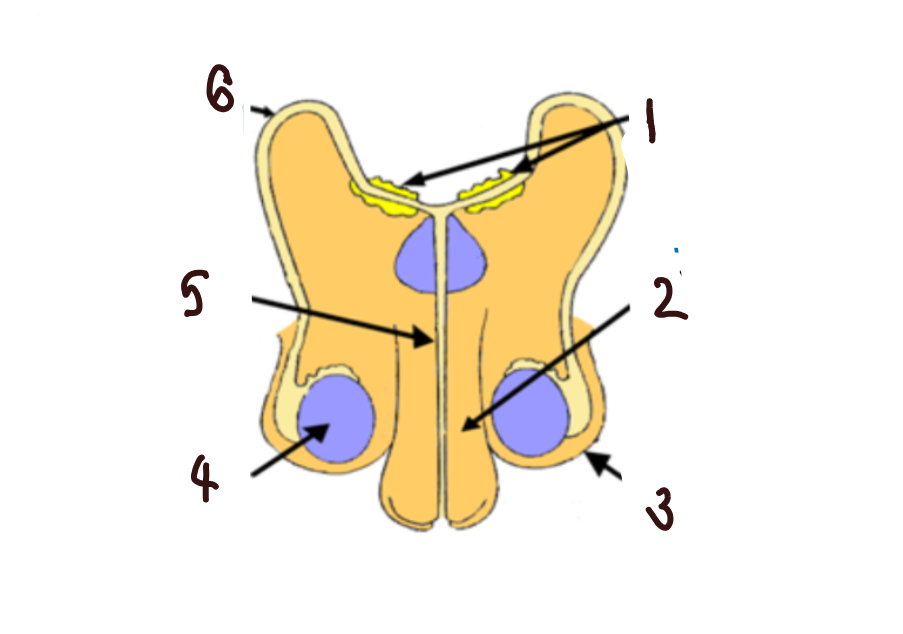
What part of the male reproductive system is 3?
scrotum
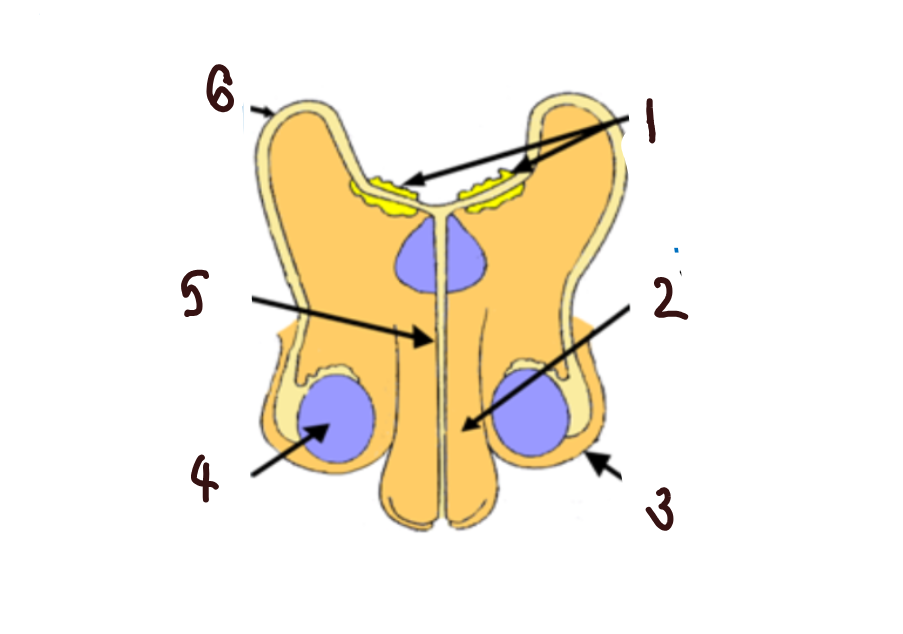
What part of the male reproductive system is 4?
makes sperm
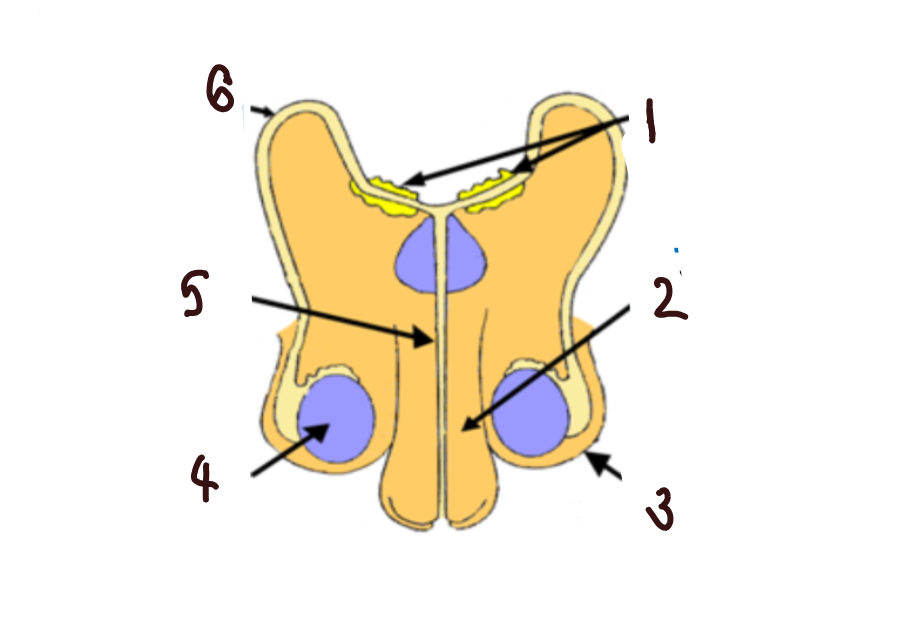
What part of the male reproductive system is 5?
urethra
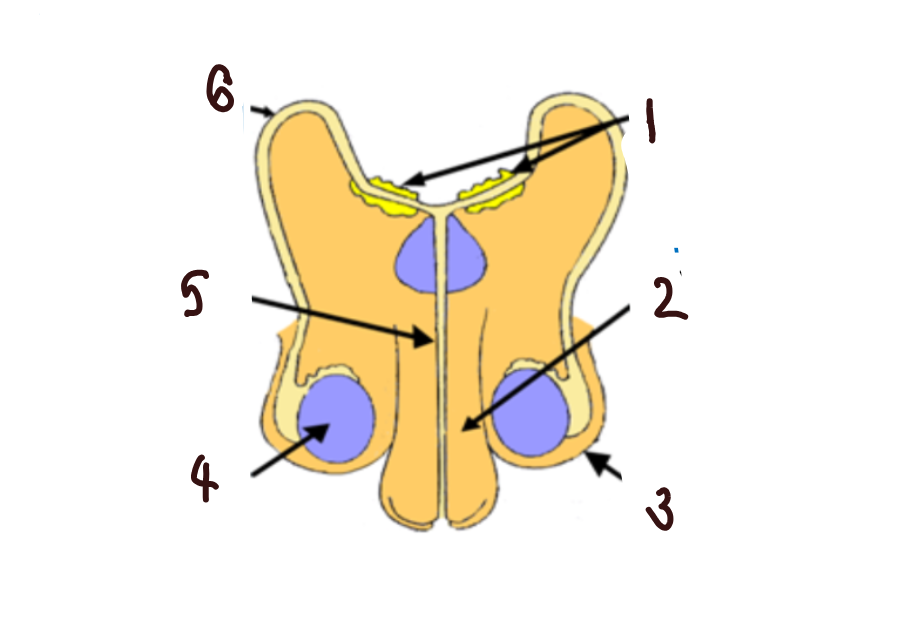
What part of the male reproductive system is 6?
sperm duct
What do the glands do?
adds a liquid to sperm
What does the penis do?
carries sperm out of the body (into the vagina)
What does the scrotum do?
holds testis
What do the testis do?
makes sperm
What do the urethra do?
connects the bladder and testis to the penis
What does the sperm duct do?
carries sperm from the testis to the urethra
Wha happens during puberty?
reproductive organs become active
What do reproductive organs do?
they produce sex hormones and gametes
What do reproductive hormones do?
causes secondary sex characteristics to develop
What is the main female reproductive hormone?
oestrogen
Where is oestrogen produced?
in the ovary
What is a major function of oestrogen?
to trigger the development of secondary sexual characteristics in females
What is the main male reproductive hormone?
testosterone
Where is testerone produced?
produced by testes
What is a major function of testosterone?
stimulating sperm production
triggers development of secondary sexual characteristics
What are changes that happen to both genders during puberty?
growth spurt
brain maturing
body hair
external genetalia growth
skin darkens
What are changes that happen to females during puberty?
breasts development
menstration starts
urerus grows and becomes active
female pattern of fat deposited on hips, buttocks and thights
What are changes that happen to males during puberty?
larynx gets bigger and voice breaks
sperm produced
What hormones involved in the menstrual cycle are secreted by the pituitary gland?
FSH, LH
What hormones involved in the menstrual cycle are secreted by the ovaries?
oestrogen, progestrone
What does the FSH do?
causes eggs to mature
stimulates ovaries to produce ovaries
What does LH do?
causes egg to be released from the ovary
What does oestrogen do?
stimulates growth of uterus lining
stops FSH being produced to ensure that only one egg matures in a cycle
stimulates the pituatary gland to release LH
What does progestrone do?
inhibits both FSH and LH production to keep the body ready for pregnancy until it is clear the egg is not fertilised
maintains uterus lining during middle part of menstrual cucle and during pregnancy
What are contraceptive methods?
prevents eggs and sperm meeting or prevents a fertilised egg from implanting in the uterus wall
What are the different kinds of contraception?
hormone based contraceptives
chemical methods
barrier methods
abstinence
surgical method
What are different kinds of hormone based contraceptives?
oral contraceptives (eg. contraceptive pill)
contraceptive implant
contraceptive injections
contraceptive patch
How do oral contraceptives work?
they contain low dosages of estrogen and progesterone which inhibits FSH which prevents the egg from maturing
it also stops the uterus lining from developing chich prevents implantation of a fertilised egg
it also makes the mucus in the cervix thich to provent sperm entering
What is different about some contraceptive pills?
they contain only progesterone
What is the benefit of a progesterone only pill?
it has fewer side effects from the mixed pill
Why does the progestrone only pill need to be taken regularly?
if you forget progesterone levels decrease which causes FSH/LH to increase as they are no longer inhibited, which causes the egg to mature and be released
What are the advantages of oral only contraceptives?
they are effective and easily reversible
What is a contraceptive implant?
a tiny tube inserted under the skin that slowly releases progesterone to prevent an egg maturing
What are the advantages of a contraceptive implant?
it lasts up to 3 years and is 99.5% effective (because the hormone level in the blood is more constant)
What are the disadvantages of contraceptive implants?
may be bruising/tenderness/swelling at first and can be difficult to remove
What are contraceptive injections?
injections that slowly release progesterone
What are the advantages of progesterone?
99% effective
What are the disadvantages of contraceptive injections?
they only last 12 weeks
What is a contraceptive patch?
a patch that contains estrogen and progestrone and prevents egg maturing/being released
How are the hormones absorbed in a contraceptive patch?
they are absorbed directly into the blood
What are the advantages of contraceptive patches?
they are more than 99% effective and may prevent against ovarian/uterus/colon cancer
What is the main kind of chemical method?
spermicides
What do spermicides do?
kill or disable sperm
What are the disadvantages of spermicides?
they’re not very effective on their own
How are spermicides often used?
with barrier methods
What are different kinds of barrier methods?
condoms
diaphragm/cap
intrauterine devices (IUD)
What do barrier methods do?
they prevent the sperm from reaching the egg
What do condoms do?
collects sperm and prevents them reaching the egg
What are the advantages of condoms?
no side effects
protection against some sexually transmitted infections
What are disadvantages of condoms?
easily damaged
What do diaphragm/caps do?
placed over cervix before sex to prevent spern entry
What are the advantages of a diaphragm/cap?
no side effects
What are the disadvantages of a diaphragm/cap?
needs to be fitted initially by a doctor, needs to be positioned correctly
What does is an IUD?
small structures inserted into the uterus by a doctor
What are the two types of IUD?
copper and progesterone
How do copper IUDs work?
they prevent early embryos from implanting in the uterus wall and thickens mucus around the cervix to prevent sperm from entering
What are the ethical problems with copper IUDs?
involves death of a fertilised egg
How do progestrone IUDs work?
they prevent ovulation
they prevent the uterus wall from thickening
thickens mucus around cervix (prevents sperm entering)
What are the advantages of an IUD?
effective, lasts 3-5 years
What are the disadvantages of an IUD?
very painful to insert
What is abstinence?
not having sexual intercourse specifically around ovulation (rhythm method)
What are the disadvantages of abstinence?
unreliable
What is the main kind of surgical method?
vasectomy
What is a vasectomy for males?
sperm ducts can be cut and tied
What is a vasectomy for females?
oviducts can be cut or tied
What does a vasectomy do?
prevents sperm from getting into semen
What are the advantages of a vasectomy?
effective and usually permanent
Can a vasectomy be reversed?
yes, but its difficult
What are the disadvantages of a vasectomy?
surgery has slight risk of infection, difficult to reverse operation
What are some causes of infertility?
lack of female hormones
damage to oviducts
lack of sperm in semen
increasing age
obesity
eating disorders
What are fertility drugs?
drugs that contain a mixture of FSH and LH taken over a series of days
What does IVF stand for?
in vitro fertilisation
How does IVF work?
Mother given FSH and LH to stimulate several eggs to mature
Eggs collected from the mother’s ovaries
The eggs are then fertilised with sperm outside the body in the laboratory
Fertilised eggs will divide by mitosis and develop into embryos
1 or 2 embryos are inserted back into the mother’s uterus
When is IVF used?
If the oviduct is damaged or blocked by infection
The donor egg has to be used
Very few sperm produced
No obvious cause of infertility
What are the disadvantages of IVF?
emotionally and physically stressful
chance of multiple births
success rates are not high (under 30%)
expensive for society and individuals (available free on NHS)
ethical issues
What are the dangers of multiple births?
often result in babies born prematurely or with lower birth rates than normal
increased chance of miscarriages
possible harm to mother and babies
What are the ethical issues of IVF?
discarded embryos