Wk 2: USP 797 Standards for Sterile Compounding
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
NECC Tragedy
-New England Compounding Center (NECC)
->in 2012, 20 states received compounded methylprednisolone acetate injection that was contaminated w/ Exserohilum and Aspergillus species
->64 pts died, 753 total cases of infections, 386 cases involved fungal meningitis
-this case caused many regulatory bodies to educate themselves of USP standards and enforce them at compounding facilities
-sterile compounding and clean room are cleaner/more sterile than ORs!
what is USP?
-United States Pharmacopeia: an independent organization that sets best practice standards across compounding practices
-there are many chapters published by USP: any that have number designation until 1000 chapters become part of FDCA
->enforceable by FDA, JC, CMS
USP standards important to pharmacy practice
-USP 797: sterile compounding (est 2004, newer version published Nov 2022 w/ enforcement Nov 2023)
-USP 795: nonsterile compounding (separate chapter established 2014, newer version in Nov 2022 w/ enforcement in Nov 2023)
-USP 800: sterile and nonsterile hazardous compounding (published 2016, effective Dec 2019)
USP 797
-purpose: establish standards to prevent harm, including death to human and animal patients that could result from
1. contamination
2. excessive bacterial endotoxins
3. variability from intended strength or correct ingredients
4. use of ingredients if inappropriate quality
->touch contamination is the greatest risk to compromising sterile compounded products
-goal of chapter is to control 3 things: people, places, processes/procedures
-maintaining sterility is the highest priority and focus of USP 797
USP 797 and CSPs
-Compounded sterile preparations (CSPs) must be sterile bc they bypass the body's defense mechs and incl:
->injections, incl infusions
->aqueous bronchial inhalations
->baths and soaks for live organs and tissues
->irrigations for internal body cavities (any sapce that does not freely communicate w/ environment outside of the body)
->ophthalmic dosage forms
->implants
USP 797: where and whom does it apply?
-all ppl who prepare CSPs
-all places where CSPs are prepared
->hospitals and other institutions, medical and surgical pt treatment sites, infusion facilities, pharmacies, physician or vet practice sites
-all employees are responsible for ensuring standards are applied and for identifying and remediating problems
-the regulations outlines are the minimum standard that sterile compounders and facilities are expected to abide by
organizations of 2022 USP 797 chapter
-personnel training and evaluation
-personal hygiene and garbing
-facilities and engineering controls
-certification and recertification
-microbiological air and surface monitoring
-cleaning, disinfecting, and applying sporicidal disinfectants and sterile 70% IPA
-introducing items into the SEC and PEC
-equipment, supplies, components
-sterilization and depyrogenation
-master formulation and compounding records
-release inspections and testing
-labeling
-establishing beyond-use dates
-use of conventionally manufactured products as components
-used of CSPs as components
-SOPs
-quality assurance and quality control
-CSP handling, storage, packaging, shipping, transport
-documentation
-compounding allergenic extracts
abbreviations to know
-CSP: compounded sterile preparations
-PEC: primary engineering control
-LAFW: laminar airflow workbench
-BSC: biological safety cabinet
-CAI: compounding aseptic isolator
-CACI: compounding aspetic containment isolator
-SEC: secondary engineering control
-ISO: international org for standardization
-LOD: line of demarcation
-HEPA: high efficiency particulate air
-BUD: beyond use date
-IPA: isopropyl alcohol
-DCA: direction compounding area
clean room suite
-PEC: a device or zone that provides an ISO Class 5 air quality environment for sterile compounding
->LAFWs, BSCs (safe for hazardous compounding), CAIs, CACIs
-SEC: area where PEC is placed (ex cleanroom suite or an SCA); it incorporates sepcific design and operational parameters required to minimize the risk of contamination within the compounding areas
-Anteroom: ISO class 8 or cleaner room w/ fixed walls and doors where personnel hand hygiene, garbing procedures, and other activities that generate high particulate levels may be performed
->transition room btwn unclassified area of the facility and the buffer room
->room must be ISO 7 class if adjacent to hazardous buffer room
-Buffer room:
->ISO class 7 cleaner room w/ fixed walls and doors where PECs that generate an maintain an ISO class 5 environment are physically located
->buffer room may only be accessed thru anteroom or another buffer room
-pharmacy -> ante room -> buffer room -> hood
clean room suite classified area
-area that maintains an air quality classification based on the ISO standards req in USP 79
ISO
-International organization for standardization
-ISO Class: air-quality classification
->compounding hood is ISO class 5
->buffer room is class 7
->anteroom is class 8 (most are class 7)
line of demarcation
-visiable line on floor that separates clean and dirty sides of anteroom
designated person
-each facility must designate a person(s) who are responsible for enforcing and ensuring compliance w/ USP 797
-new USP chapter uses the terms SOP (standard operating procedure) 47 times
personnel training and evaluation
-compounding personnel are required to undergo mandatory training both before compounding for patients but also ongoing
->demonstrating knowledge and competency of core skills
->demonstrating competency in garbing and hand hygiene
->competency testing in aseptic manipulation
demonstrating knowledge and competency of core skills
-training, demonstrating, and competency are all separate actions
-Core competencies:
->hand hygiene, garbing, cleaning and disinfection
->calculations, measuring, mixing
->aseptic technique
->achieving and/or maintaining sterility (and apyrogenicity if compounding w/ nonsterile components)
->use of equipment
->documentation of the compounding processes (ex master formulation and compounding records)
->principles of high-efficacy particulate air (HEPA)-filtered unidirectional airflow within the ISO class 5 area
->proper use of PECs
->principles of movement of materials and personnel within the compounding area
demonstrating competency in garbing and hand hygiene
-tests that you properly complete: hand hygiene, garbing, donning of sterile gloves
-gloved fingertip testing: evaluates that you can complete hand washing, garbing, and donning of sterile gloves w/o contaminating them
-test is completed by using agar plates to test the gloves once all steps are completed:
->gloves are sterile so there is no growth on them, if hand washing and garbing is not performed properly, growth will appear on the gloves and therefore, on the plate
->plates are incubated at a certain temperature and duration to check for bacterial or fungal growth
-for new employees, must be completed three separate tests done in succession -> failure of one requires repeated the entire test
-this is then completed once every 6 months
competency testing in aseptic manipulation
-tests that you properly complete: proper intro of materials into PEC, able to perform aseptic manipulation w/o contamination
-media fill test: a complex manipulation that has a growth media to identify if product is contaminated (turns turbid)
-glove fingertip test: after the media fill test, gloves are tested to ensure sterility of gloves was maintained
-DCA surface test: after the media fill test, the surface of the compounding hood is tested to ensure hood was not contaminated
-plates are incubated at a certain temp and duration to check for bacterial or fungal growth
-this is completed for new employees: failure of any component req repeating the entire test
-this is then completed once every 6 months
establishing BUD
-BUD: the date/hr after which a CSP must NOT be used / how long it can be stored
-BUD is determined from the date and time of the preparation of a CSP
-expiration date is NOT the same as BUD
-expiration data: date that a manufacturer applies to a conventionally manufactured product
-compounders do not assign expiration dates: they assign BUDs
-BUDs cannot exceed the manufacturer's expiration date and often may be much shorter
-BUD stops at admin
-BUD is labeled on the bag as "USE BY"
sterility vs stability
-BUD is determined by many different factors
-Sterility: how long the CSP remains free from microbial growth
->where it is made, where it is stored, how many are made (more manipulations = inc risk contamination), determined by USP 797
-Stability: how long CSP is chemically active
->does the medication precipitate in the refrigerator, does the med leech into plastic, does it maintain effectiveness after 24 hrs, is it compatible w/ a diluent, determined by manufacturer and references
-once you determine the sterility and the stability, you can assign the BUD that is SHORTER
-if there is no stability data in the manufacturer info or Trissel's, cam default to UDP dating as long as the med is stable in the storage condition that the BUD is being applied
2022 USP 797: BUD = environment
-outside of a compounding hood (PEC):
->ex: making a drip for a code or a cocktail for the OR
->immediate use
-> BUD = 4 hrs
-segregated compounding area (hood outside of clean room (PEC)):
->ex: a compounding hood (PEC) -> laminar airflow or isolator in an unclassified area
->category 1
->12 hrs room temp, 24 hrs refrigeration
-Clean room suite:
->ex: iso-classified rooms w/ compounding hoods inside
->category 2 or 3
-difference btwn different category 2 dates is using non-sterile or sterile items
-differences btwn category 2 and 3 is sterility testing and many more requirements for longer BUDs
BUD limits for category 1 CSPs
-controlled room temp: < 12 hrs
-refrigerator: <24hrs
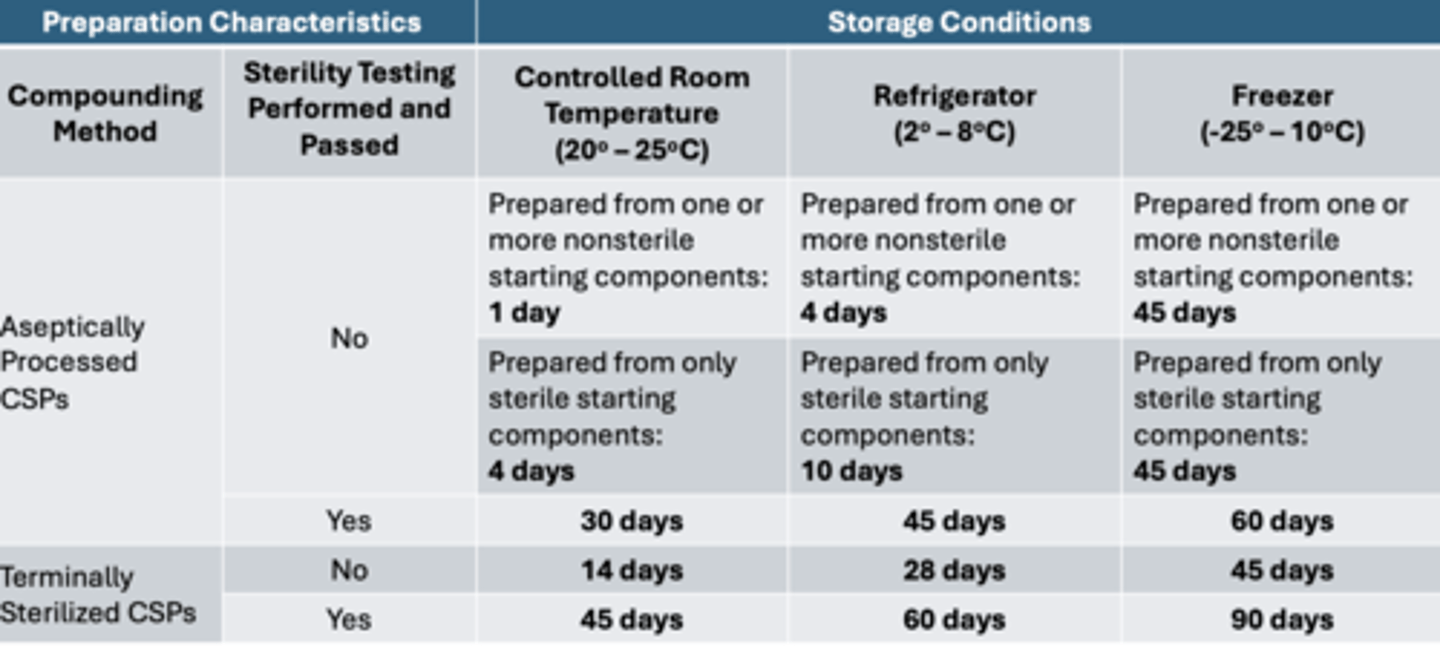
BUD limits category 2 CSPs
-aseptically processed
->room temp = 4 days
->fridge = 10 days
->freezer = 45 days