Model Standards of Practice for Canadian Pharmacists
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
MSOP
Standards for pharmacy professionals' practices.
Public Perception
How pharmacists are viewed in society.
Pharmacist Portrayals
Representation of pharmacists in films and TV.
Negative Portrayals
63% of pharmacist representations were unfavorable.
Positive Portrayals
Only 13% of portrayals were favorable.
Neutral Portrayals
24% of portrayals had no clear bias.
Demographics
Characteristics of pharmacist characters analyzed.
Retrospective Study
Research analyzing past media portrayals.
Observational Study
Study based on observing pharmacist representations.
Descriptive Study
Study describing characteristics of pharmacist portrayals.
Pharmacist Characters
Unique individuals depicted as pharmacists.
Character Analysis
Evaluation of pharmacist characters' roles in media.
Media Genre
Types of films and shows reviewed.
Algorithm Development
Method to assess portrayal status of pharmacists.
Pharmacy Organizations
Groups providing data on pharmacist portrayals.
Film and Television
Media formats reviewed for pharmacist representation.
Academic Institution
Setting where the study was conducted.
Pharmacy Professionals
Individuals providing insights on portrayals.
Character Demographics
Age, gender, and ethnicity of portrayed pharmacists.
Pharmacist Heroes
Positive representation as protagonists in media.
Pharmacist Villains
Negative representation as antagonists in media.
Pharmacist Victims
Characters depicted as suffering or oppressed.
Negative Media Portrayals
Media representations affecting public perception of pharmacists.
Super Bowl XLIX
Most-watched TV show in U.S. history.
Bryan Cranston's Role
Portrayed a pharmacist in 'Breaking Bad' series.
Brandon Bookstaver
PharmD researching pharmacists' media perceptions.
Standardized Practices
Essential for countering negative stereotypes in pharmacy.
Professional Standards
Guidelines ensuring quality and consistency in pharmacy.
Public Trust
Confidence the public has in pharmacists' professionalism.
Standards of Practice (SOPs)
Minimum performance standards for pharmacists' practice.
Model Standards of Practice (MSOP)
Framework for pharmacists' professional conduct and responsibilities.
Code of Ethics
Aspirational goals based on integrity and respect.
Canadian Health Care System
Publicly-funded healthcare under the Canada Health Act.
Drug-Related Problems (DRPs)
Costing $2-9 billion annually in healthcare.
Aging Population
Increased need for complex medication management.
Expanded Pharmacist Roles
Pharmacists as accessible healthcare providers.
Pharmaceutical Care
Focus on positive patient outcomes and medication management.
Collaborative Practice Model
Team-based approach to healthcare involving pharmacists.
Regulated Pharmacy Technicians
Defined roles enhancing pharmacy practice efficiency.
Healthcare Accountability
Increased responsibility for healthcare professionals.
Scope of Practice
Defines the range of responsibilities for pharmacists.
Public Interest Mandate
Pharmacists' duty to serve and protect the public.
Healthcare Challenges
Issues like doctor shortages and lengthy wait times.
Pharmacy Workforce Optimization
Improving efficiency through clear role definitions.
Professional Boundaries
Clear limits in pharmacist-patient relationships.
Accountability
Responsibility for actions and professional development.
Career-long Development
Ongoing education throughout a pharmacist's career.
Performance Metrics
Quantifiable measures of pharmacy practice effectiveness.
Public Safety Assurance
Commitment to safeguarding patient health and safety.
Evidence-Based Foundation
Reliance on research for pharmacy practice standards.
Continuing Competence Programs
Programs ensuring pharmacists maintain necessary skills.
International Recognition
Global acknowledgment of pharmacy standards and practices.
Quality Assurance Benchmarks
Standards for evaluating pharmacy service quality.
NAPRA
National Association of Pharmacy Regulatory Authorities.
Regulatory Oversight
Supervision of pharmacy practices across Canada.
National Drug Schedules
Classification system for controlled substances in Canada.
Provincial Regulations Alignment
Consistency in pharmacy laws across provinces.
Model Standards of Practice (MSOP)
Minimum practice standards for licensed pharmacists.
Supplemental Standards
Additional guidelines for specific drug schedules.
Medication Safety Program
Mandatory program ensuring safe medication practices.
MSOP Timeline
Key dates for MSOP development and implementation.
Canadian Patient Safety Institute
Organization enhancing patient safety across health professions.
Pharmacist Roles
Categories of responsibilities for practicing pharmacists.
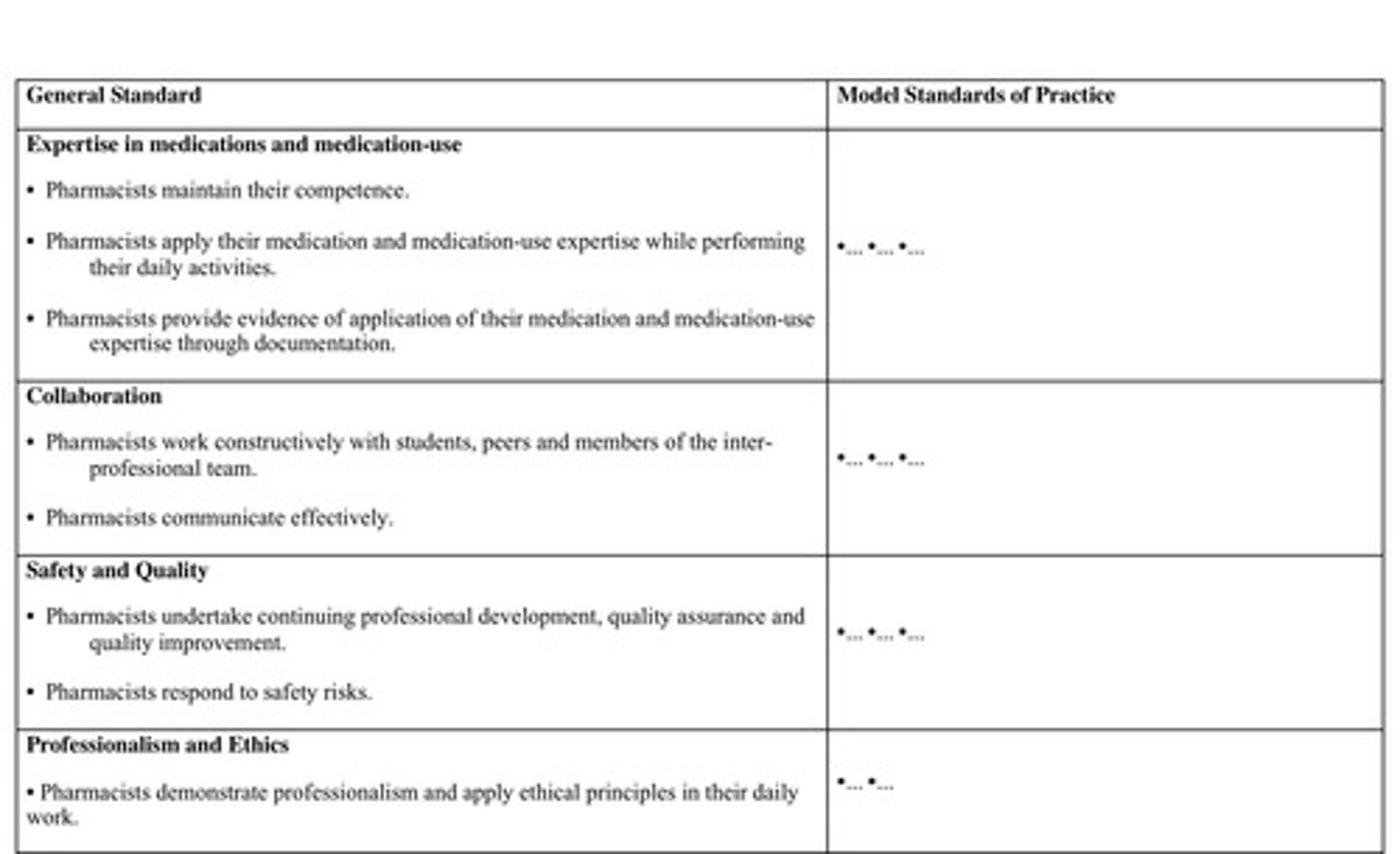
General Standards
Broad guidelines for pharmacist competencies.
Critical Attributes
Essential skills for achieving MSOP compliance.
Competence Maintenance
Pharmacists must continually update their knowledge.
Medication Expertise
Pharmacists apply medication knowledge daily.
Documentation
Evidence of pharmacists' medication expertise.
Life-long Learning
Continuous education for maintaining pharmacist competence.
CE Programs
Continuing Education programs for pharmacists' development.
CPD Activities
Continuing Professional Development for pharmacists.
Patient Assistance
Pharmacists help patients with nonprescription therapies.
Drug Interaction
Significant interactions must be evaluated before therapy.
Contraindications
Conditions that prevent medication use safely.
Patient Characteristics
Factors influencing medication appropriateness for individuals.
Self-Care Measures
Evidence-based strategies for disease management.
Counselling Services
Educating patients on medication benefits and usage.
Inter-Professional Team
Collaboration among healthcare professionals for patient care.
Quality Assurance
Processes ensuring safety and effectiveness in pharmacy.
Professionalism
Demonstrating ethical principles in pharmacist duties.
NAPRA Competencies
Standards for pharmacists' professional competencies.
MSOP
Model Standards of Practice for pharmacists.
Patient Care
Pharmacists' role in providing direct patient services.
Drug Information
Providing accurate medication information to patients.
Drug Distribution
Managing the supply and dispensing of medications.
Pharmacy Management
Overseeing pharmacy operations and staff.
Educating Students
Training pharmacy students and interns effectively.
Safety Risks
Pharmacists must respond to potential medication hazards.
Professional Competencies
Skills required for pharmacists at entry level.
Emerging Scope of Practice
New activities authorized for pharmacists in provinces.
Patient Care
Pharmacists' role in managing medication therapies.
Professionalism
Adherence to ethical standards in pharmacy.
Evidence-Based Practice
Using relevant sources to inform pharmacy activities.
Critical Evaluation
Assessing medication information for accuracy.
Schedule II Drugs
Pharmacy products requiring pharmacist consultation.
Schedule III Drugs
Over-the-counter medications with specific regulations.
Patient Interaction Documentation
Recording pharmacist-patient consultations in profiles.
Confidentiality
Respecting patient privacy in pharmacy practice.
Pharmacy Manager Responsibilities
Ensuring compliance with drug schedule classifications.
Competence Limits
Practicing within one's professional skill boundaries.