Unit 1- Chemistry- [A1] Structure an bonding in applications in c
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is specifically for the BTEC foundation diploma Pearson edexcel course however, you can use this for A-level chemistry as it is the same content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What does the nucleus include?
protons, neutrons and electrons
What is the relative mass of a proton?
1
What is the relative mass of an electron?
1
What is the relative mass of a neutron?
0
What are the electrons in around the nucleus?
shells
Where are protons and neutrons found in an atom?
in the centre
How many electrons can the first shell hold?
2
How many electrons can the second shell hold?
8
How many electrons can the third shell hold?
18
How many electrons can the fourth shell hold?
32
What are orbitals?
regions where there is a 95% probability of locating an electron
How many electrons can an orbital hold?
2
What are the names of the different orbitals?
s,p,d and f
Do all the orbitals have the same energy?
no, they have different energy states
What are cations?
positively charges ions
What are anions?
negatively charged ions
What is Aufbau principle?
the electrons fill the orbitals with the lowest available energy state in relation to the proximity to the nucleus before filling orbitals with higher energy states.
what does the Aufbau principle do ?
gives the most stable electron configuration
What is the meaning of electron configuration?
the distribution of electrons in an atom or molecule
What is the meaning of spin?
in an orbital, each electron will be a different spin state
What can the first shell hold in written notation?
2 electrons
What type of orbital is in the first shell?
s orbital
What type of orbital is at the second shell?
s and p orbitals
What do the half arrows represent?
the spin of different electrons
What is ionic bonding?
electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions
What do you use to represent ionic bonding?
dot and cross diagram
What is electrostatic attraction?
the force experienced by oppositely charged particles
What is a giant ionic lattice?
a regular arrangement of positive ions and negative ions
What is an example of a giant ionic lattice?
sodium chloride
What does the strength of the ionic bond dependent on?
the ionic charge and the ionic radii of ions
What would happen if the the ionic compound had more positive ions?
the more shells it would have
If the ionic charge is higher…
the electrostatic force is stronger
What does ionic bonding occur between?
non-metal and metal
What is Bohr theory?
plum pudding model
What is covalent bonding?
when an electron is shared between the atoms
What does a covalent bond usually occur between?
non-metal and non-metal
What is it called when both sharing electrons come from one atom?
dative covalent bond
What is dative bonding also known as?
Coordinate bonding
What is it called if three pairs of electrons are shared?
a triple covalent bond
The shorter the length of the bond….
the stronger the bond is
True or false, single bonds have a greater length than double bonds ?
true
Do double bonds have a greater length than triple bonds?
yes
Are triple bonds stronger than double bond and single bonds?
yes
How does ammonia form a dative bond with hydrochloric acid?
when ammonia reacts with HCL, a hydrogen ion from the acid transfers to the ammonia molecule. a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom forms a dative bond with the hydrogen ion.
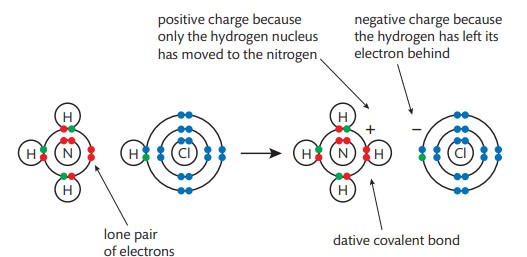
What does lone pair of electrons mean?
a non-binding pair of electrons
What is an organic compound?
a compound that contains one or more carbons in a carbon chain
What does having four bonds mean?
it has a tetrahedral shape
What is the bond molecule angle?
109.5
What is metallic bonding?
the highest level of a metal atom has the ability to become delocalised
What is the meaning of electronegativity?
the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electron
What is the meaning of when a molecule is non-polar?
a molecule where the electrons are distributed evenly throughout the molecule
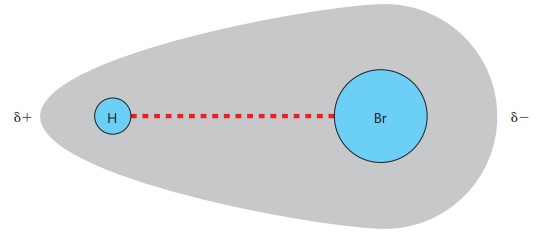
What is the meaning of a polar molecule?
a molecule with partial positive charge in one part of the molecule and similar negative charge in another part due to an uneven electron distribution
What are intermolecular forces?
the attraction or repulsion between neighbouring molecules
What is the meaning of dipole?
separation of charges within a covalent molecule
What are the two types of dipole forces?
temporary dipole and induced dipole are the weak forces present in non-polar covalent molecules

What is A on the picture?
more electrons

What is B on the picture?
more movement

What is C on the picture?
bigger dipoles

What is D on the picture?
stronger attraction
What are the only types of forces that exist between noble gases and non-polar molecules?
London dispersion forces
What is the meaning of Van der waals forces?
all intermolecular attractions are an der waals forces
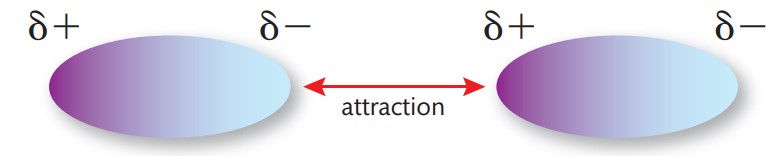
What are dipole-dipole forces?
permanent forces between polar molecules
What do polar molecules have?
a permanent negative and permanent positive end
What do these oppositely charged ends do?
attract each other
Are dipole-dipole forces stronger or weaker than London dispersion forces?
slightly stronger but are still weak in comparison to a covalent bond
What are some examples of molecules that have a permanent dipole-dipole forces?
hydrogen chloride, iodine monochloride
What is the strongest form of intermolecular force?
hydrogen bond
What is a hydrogen bond?
a special type of dipole-dipole bond and are forces that are 10% of the strength of a covalent bond
When do hydrogen bonds form?
when compounds have hydrogen directly bonded to fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen
Why is it that a hydrogen bond forms only when it is directly bonded to some elements?
there is a large difference in electronegativity between hydrogen and the three atoms. This difference means that very polar bonds are formed so the molecules have permanent dipoles. When two of these molecules are close together, there will be an attraction between the positive end and the lone pair. This is the hydrogen bond
What is the formula for moles?
moles=mass /Mr
What is the empirical formula?
the ration between elements in a chemical compound
What is a titration?
a method of volumetric analysis used to calculate the concentration of a solution
What is a solution?
a liquid mixture where a solute is dissolved in a solvent
What is a standard solution?
a solution of a known concentration used in volumetric analysis
What is a solute?
the substance dissolved in a solvent to form a solution
What is a solvent?
a liquid that dissolves another substance
What is theoretical mass?
the expected amount of product from a reaction calculated from the balanced equation
What is the percentage yield?
the actual amount of mass worked out as a percentage of the theoretical mass
What is the formula for percentage yield?
