TAGs & beta-oxidation
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L20 fat metabolism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
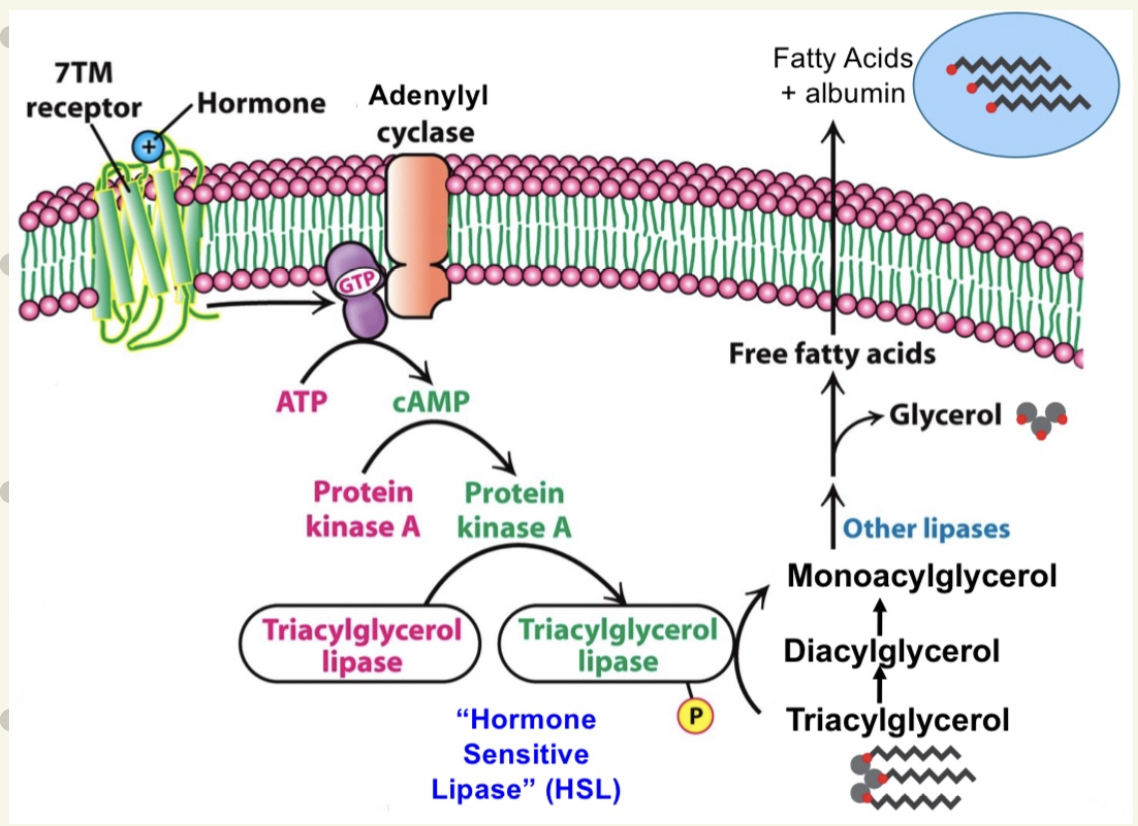
How does hormone signals fatty acid chain release?
epinephrine & glucose signal via GPCRs on adipose cells
involves: Ga-ATP release → adenylyl cyclase activation → cAMP production → PKA activation → phosphorylates & activates triacylglycerol lipase → hydeolyzes ester bonds to produce free fatty acids & glycerols
FFAs are transported in blood via albumin for cellular use
acyl-CoA vs. acetyl-CoA?
Acyl-CoA:
broad term, any FA conjugated to CoA via thioester linkage
Acetyl-CoA:
2C acyl CoA

How does fatty acid activation occur in cytoplasm? what’s needed?
after entering cells from bloodstream, acyl chains are trapped to prevent diffusion back out by forming covalent thioester bond with CoA
catalyzed by Acyl CoA Synthetase
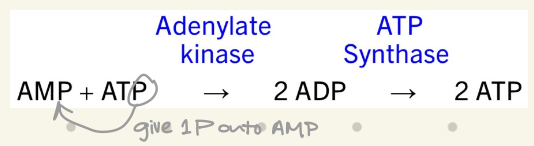
reversible reaction, uses ATP → AMP + PPi
PPi hydrolysis makes this reaction favorable
to use AMP, it must be converted to ADP by sacrificing a 2nd ATP
→ Fatty acid activation by CoA requires 2ATP (1 for activation, 1 for ADP production) & 1H2O to hydrolyze PPi
where does acyl-CoA & β-oxidation occur?
acyl-CoA = cytoplasm
β-oxidation = matrix
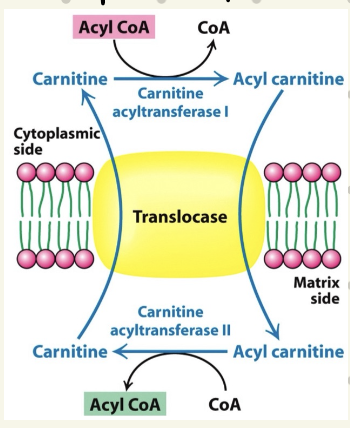
How is acyl-CoA transported into matrix?
via Carnitine Shuttle (CoA is hydrophilic)
temporarily transfers acyl group to carnitine (can cross membrane)
shuttle has 3 components:
carnitine acyltransferase I (CAT1)
translocase (antiporter)
carnitine acyltransferase II (CATII)
CATI moves acyl chain onto carnitine from CoA
translocase moves acyl-carnitine in, free carnitine out
CATII moves acyl chain back onto CoA
acyl-CoA can then be catabolized in β-oxidation
how to calculate the number of rounds needed in β-oxidation?
#of rounds = (number of carbon/2) - 1
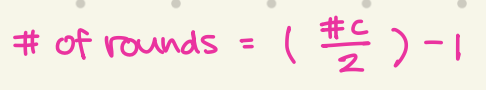
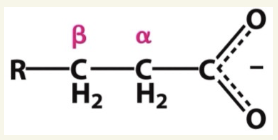
which carbon does fatty acid oxidation occur on?
β-carbon (3rd C)
TCA is dependent on the amount of ___ present
oxaloacetate
how many enzymes are needed in beta-oxidation?
4