Echinoderms 2025
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Phylum Echinodermata
Marine animals with calcareous endoskeleton, a complete digestive system, radial symmetry in adults and bilateral larvae

Ossicles
Calcium carbonate pieces of the endoskeleton, each piece is made inside a cell and secreted

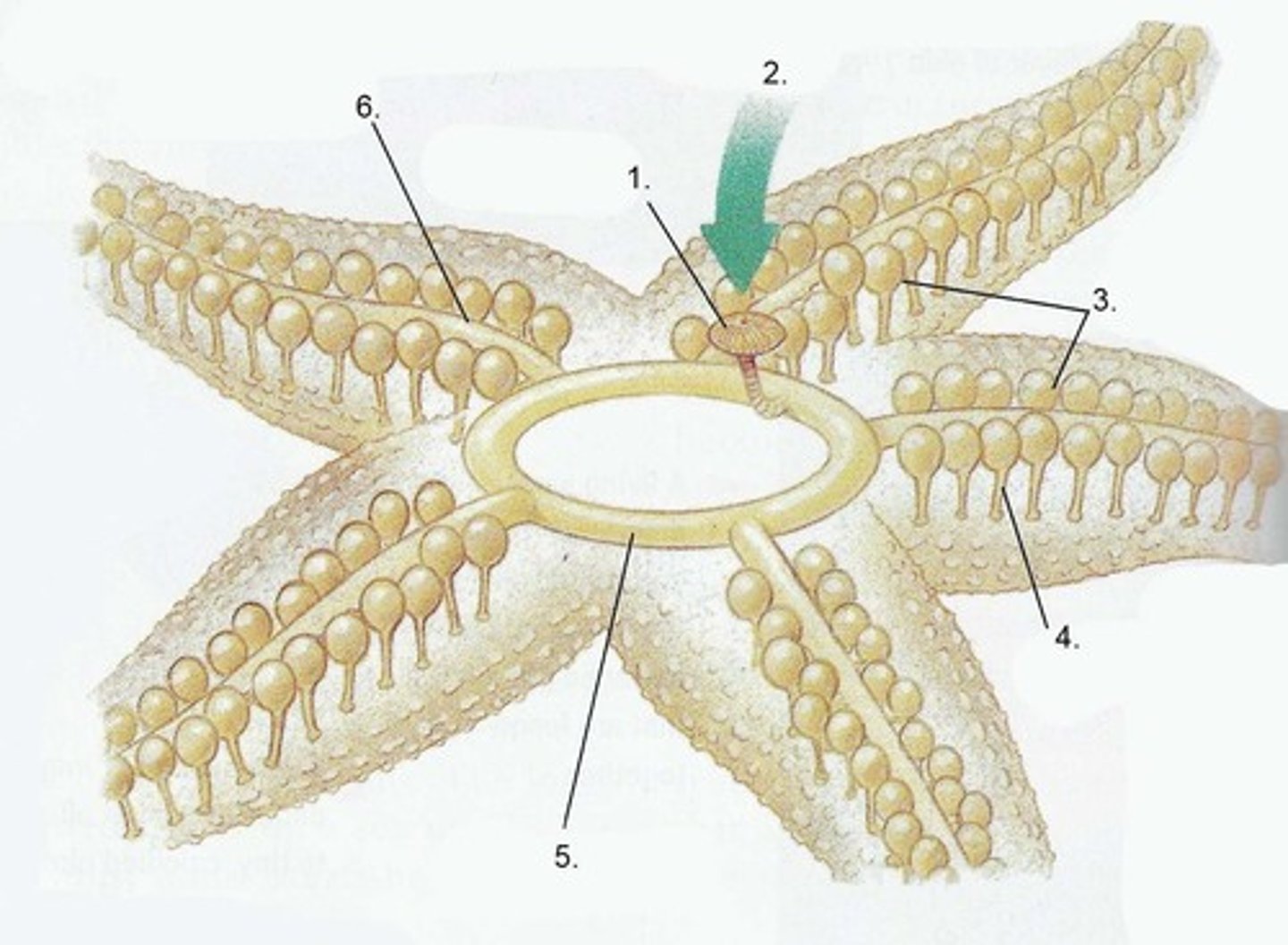
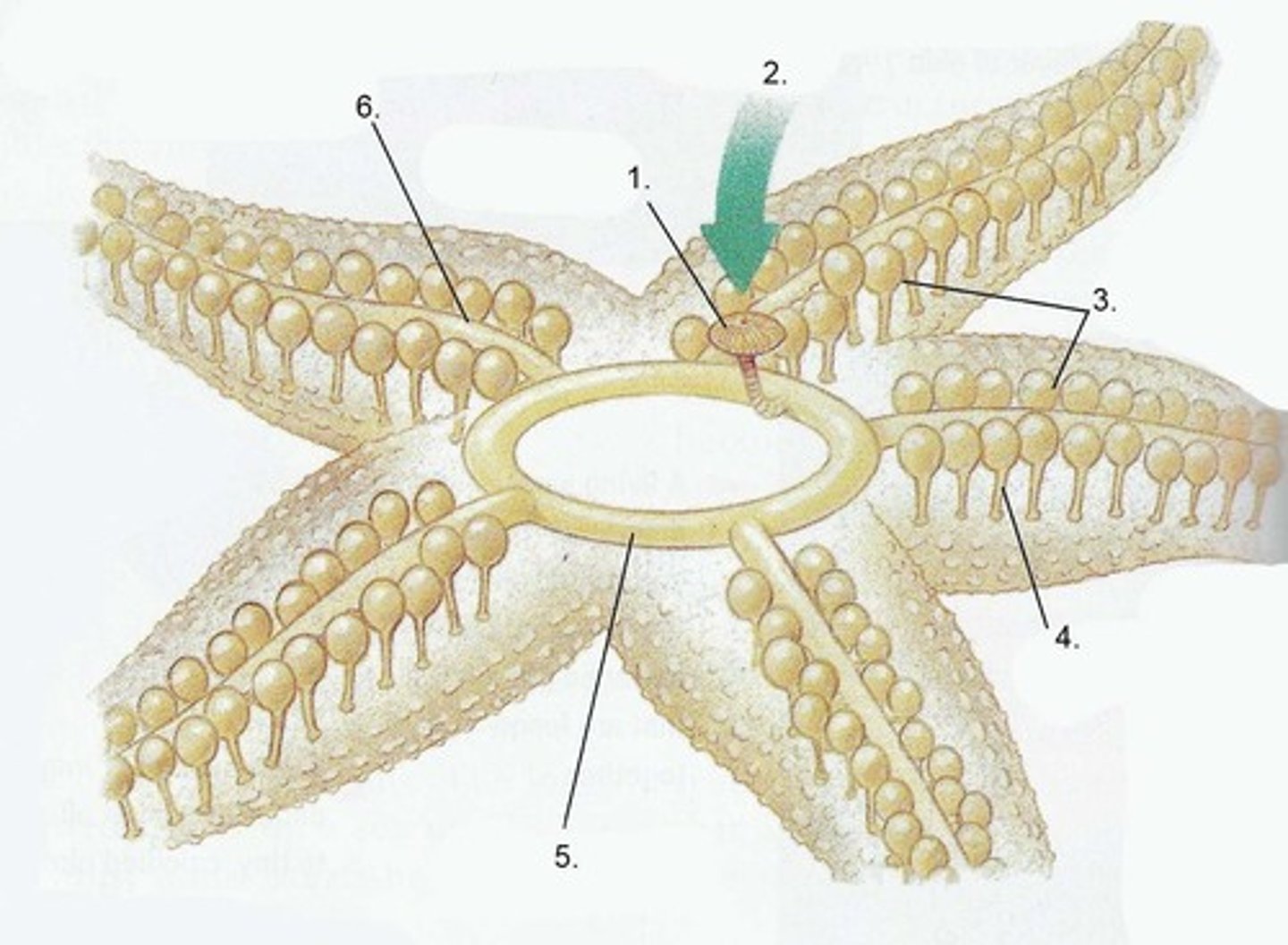
Water Vascular System
water-filled canals used for locomotion, attachment, and/or feeding
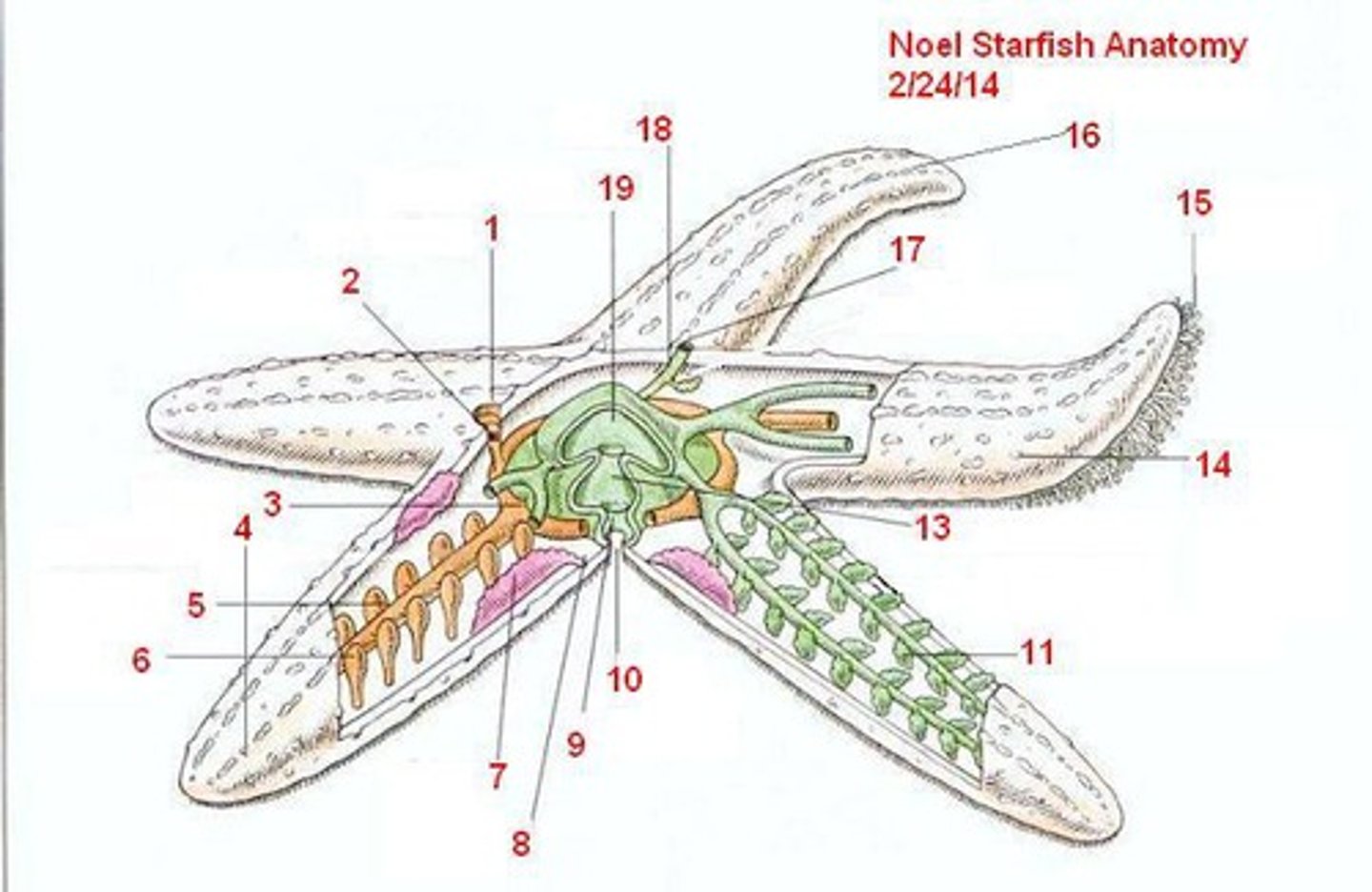
Parts of water vascular system
Madreporite (sieve), ring canal, radial canals, tube feet
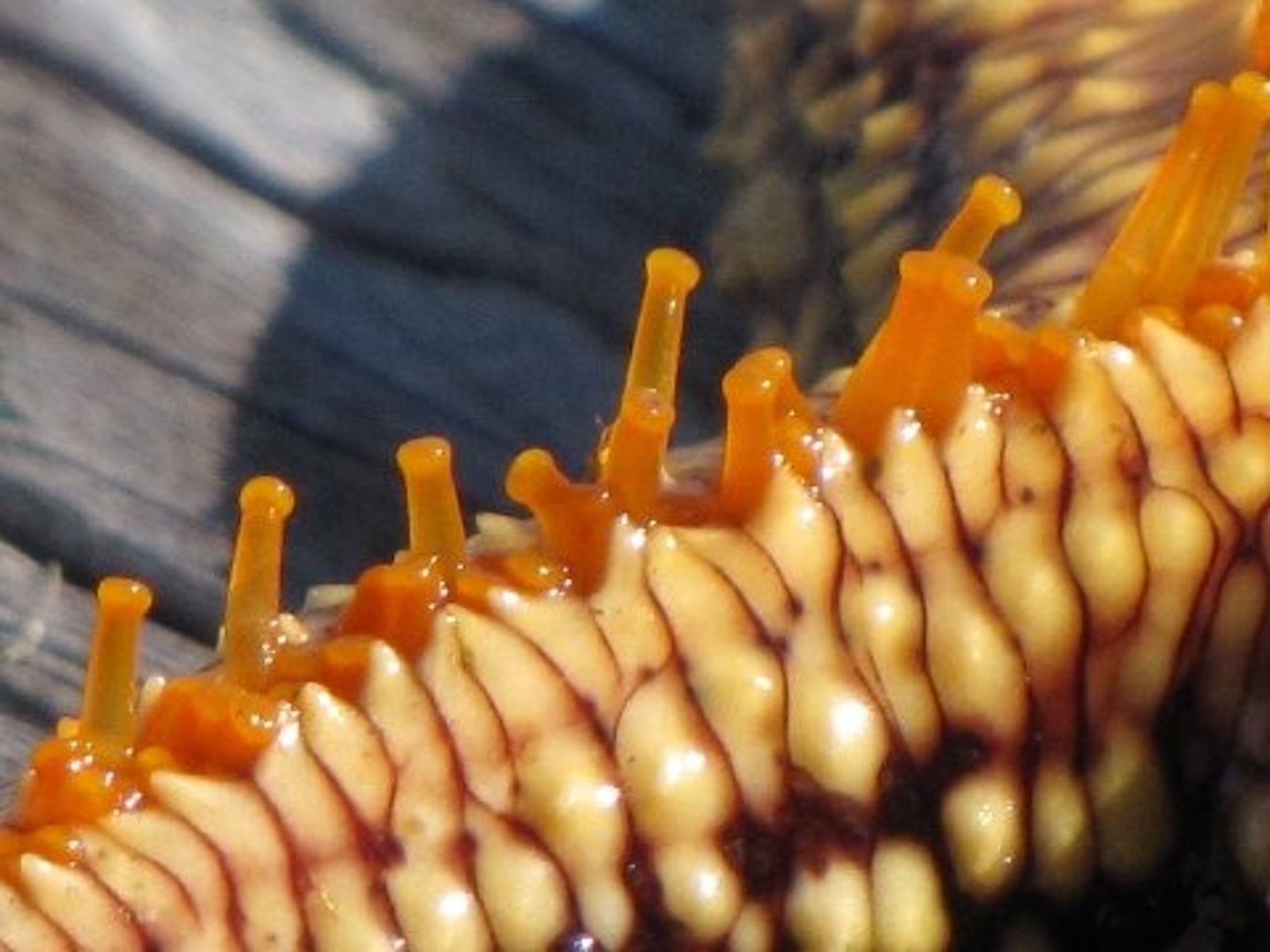
Tube Feet
at the end of the radial canals, often with suction cups, one animal may have 1000s

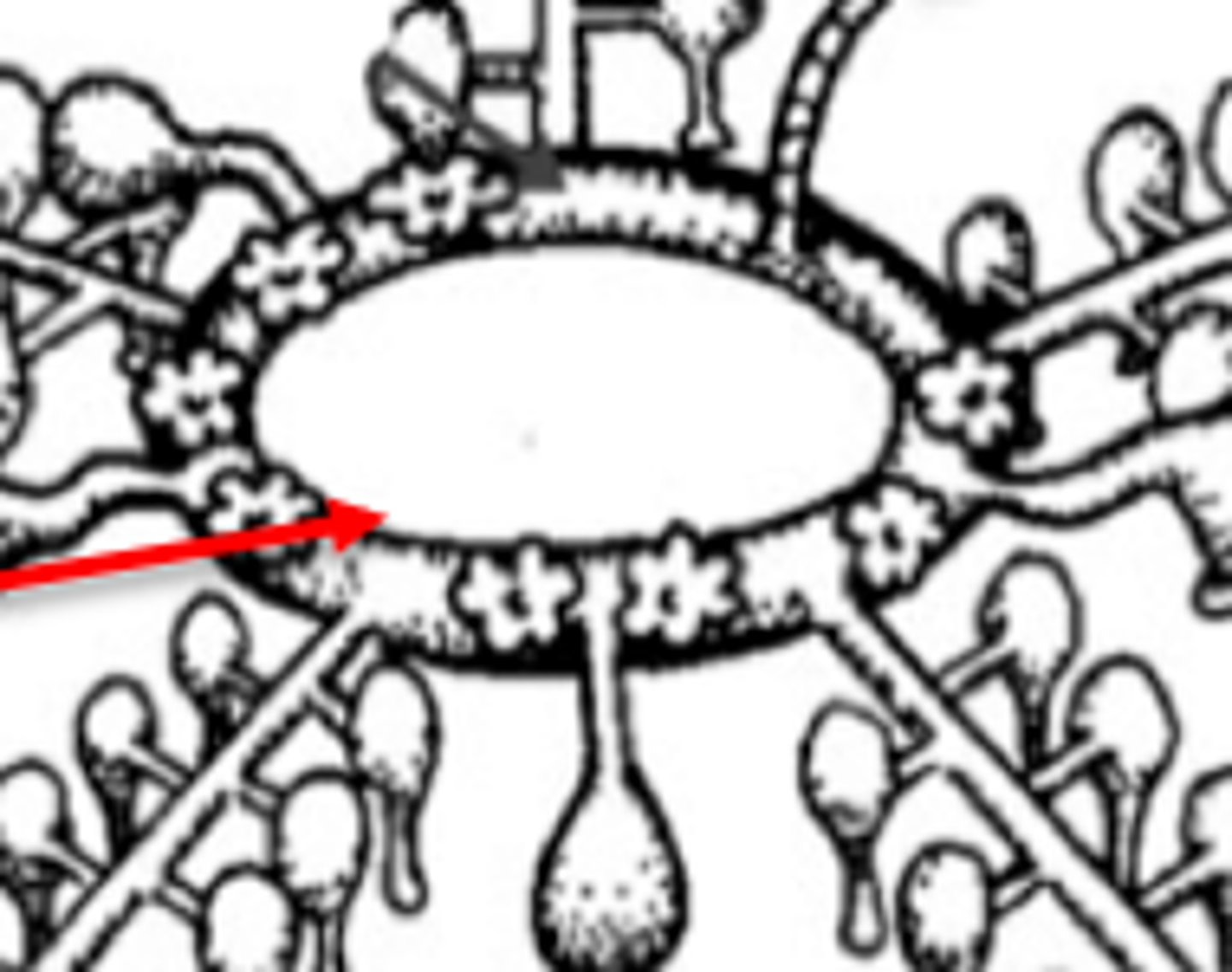
Madreporite
sieve-like opening into the water-vascular system; "sifts" and "strains" the water as it enters the system
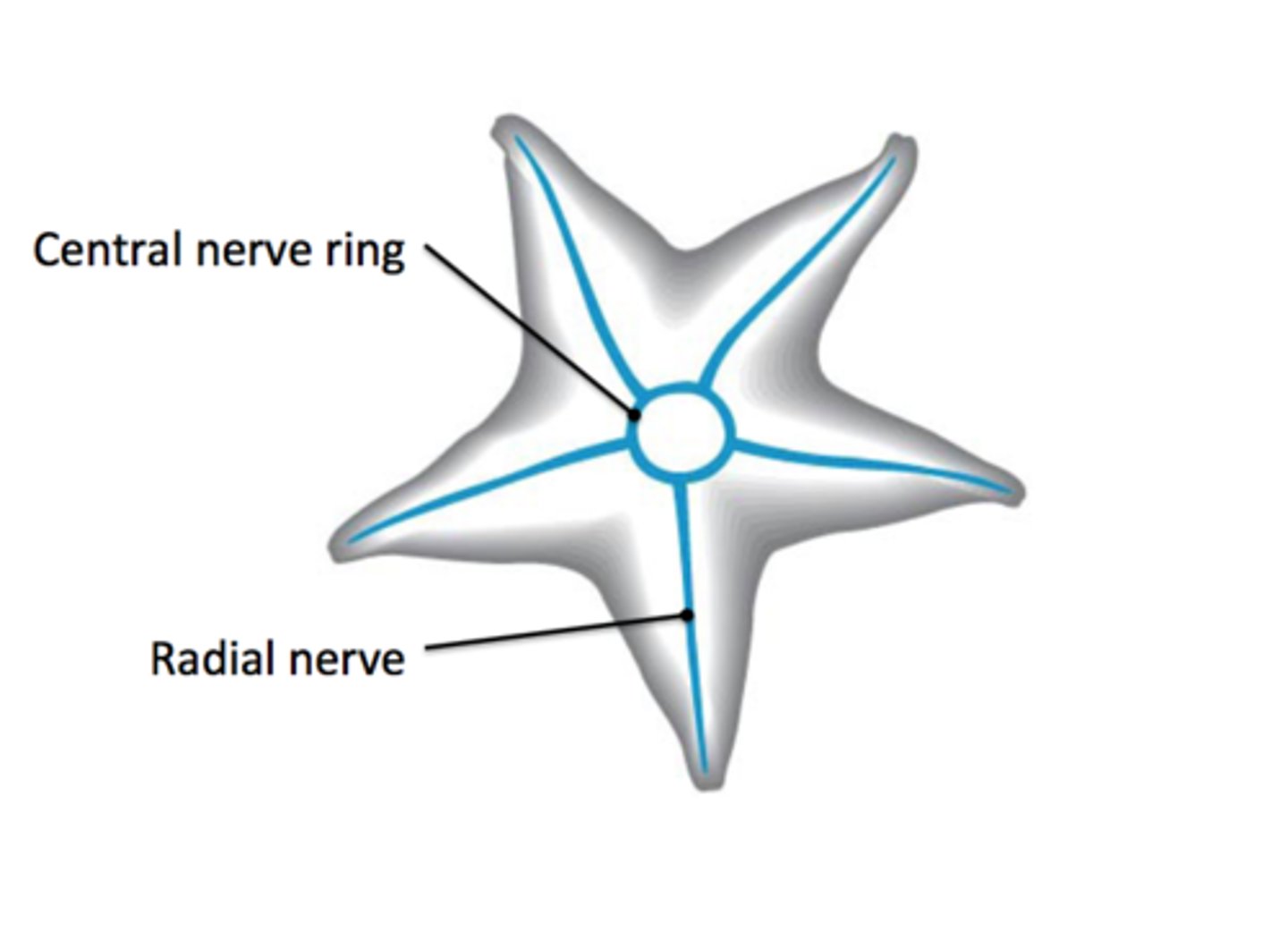
Nervous System of Echinoderms
includes a nerve net and nerve ring; sensory receptors (light, chemical, and mechanical) on body surface and tube feet
Excretory System of Echinoderms
gases, nutrients, and metabolic wastes diffuse across tube feet and other structures (mostly ammonia)
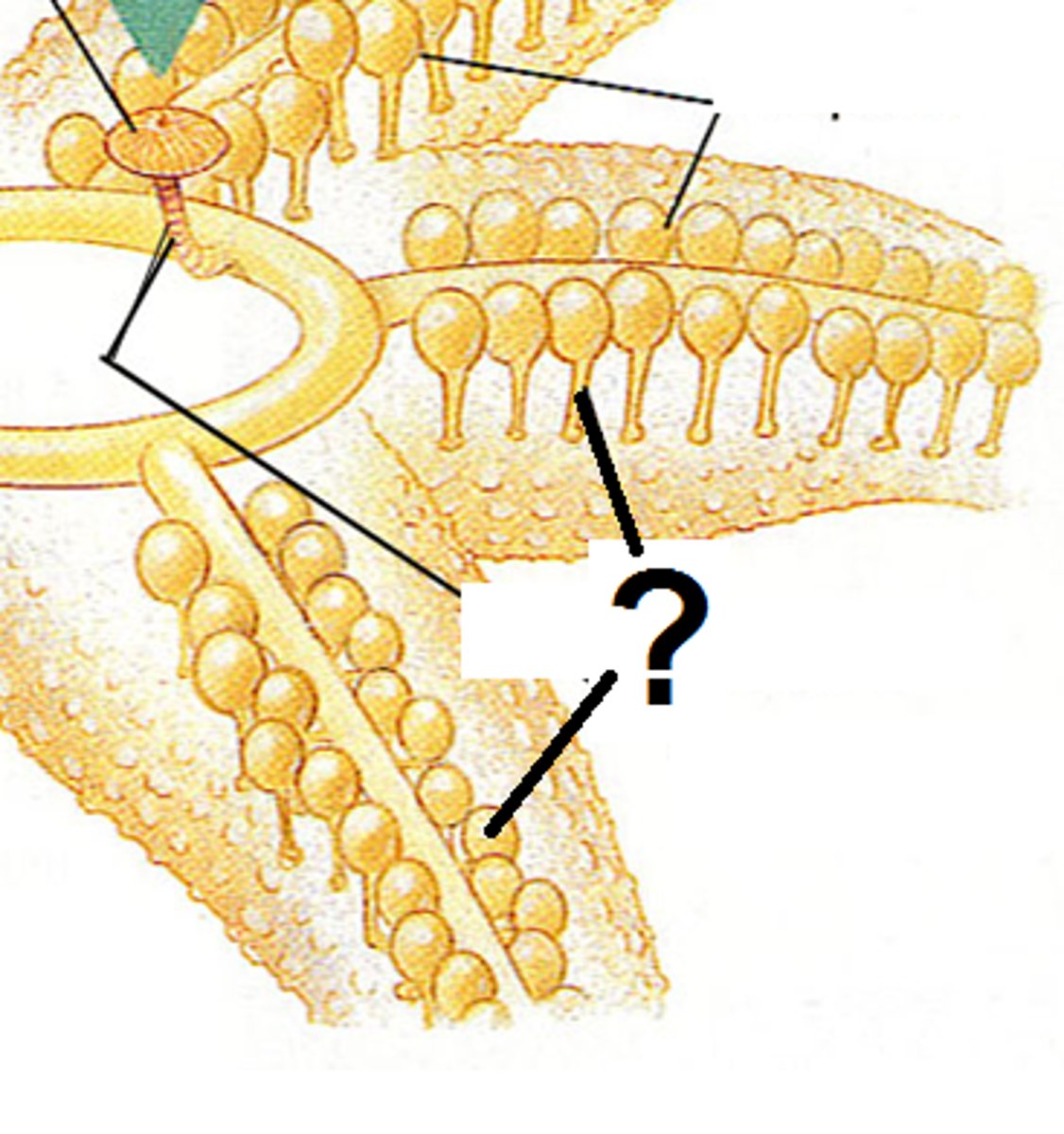
Pedicellaria
pincer-like, claw shaped structures on the outside of the body wall used for cleaning and protection
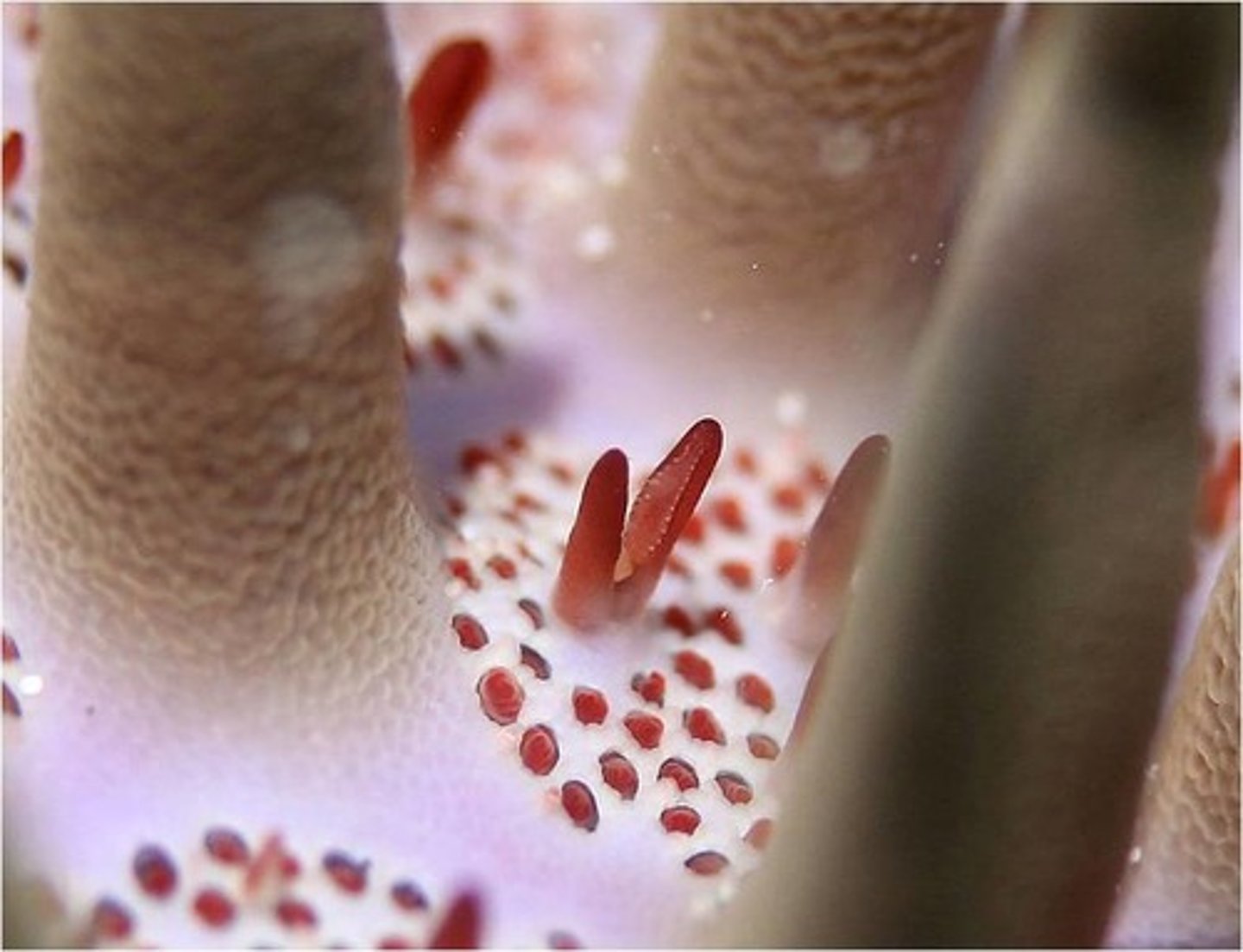

Echinodermata Reproduction
mostly sexual reproduction, external fertilization; free-swimming larvae

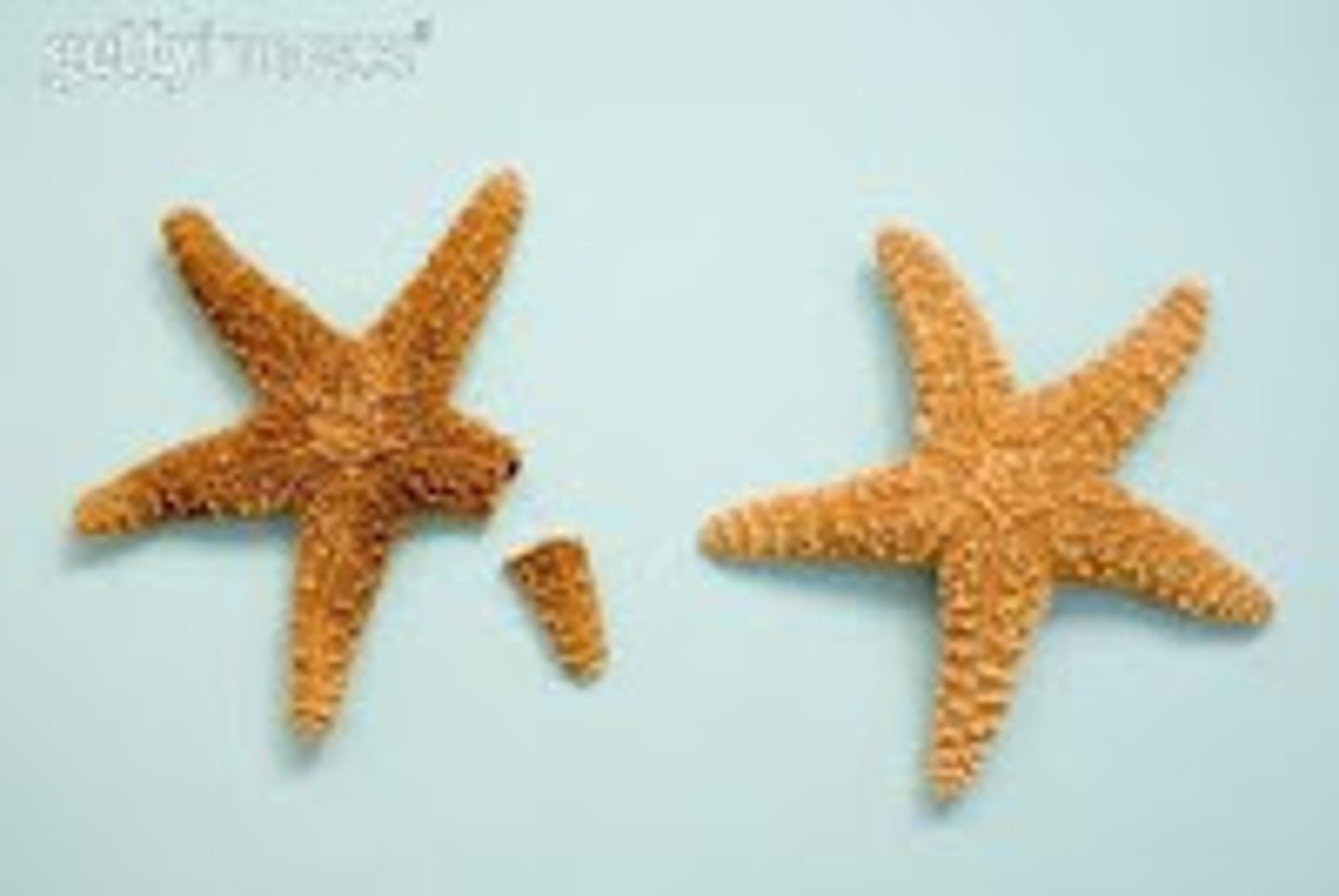
Asexual Reproduction in Echinoderms
can regenerate lost arms (common) or even an entire different organism if a portion of the central disc is present (only in certain species)

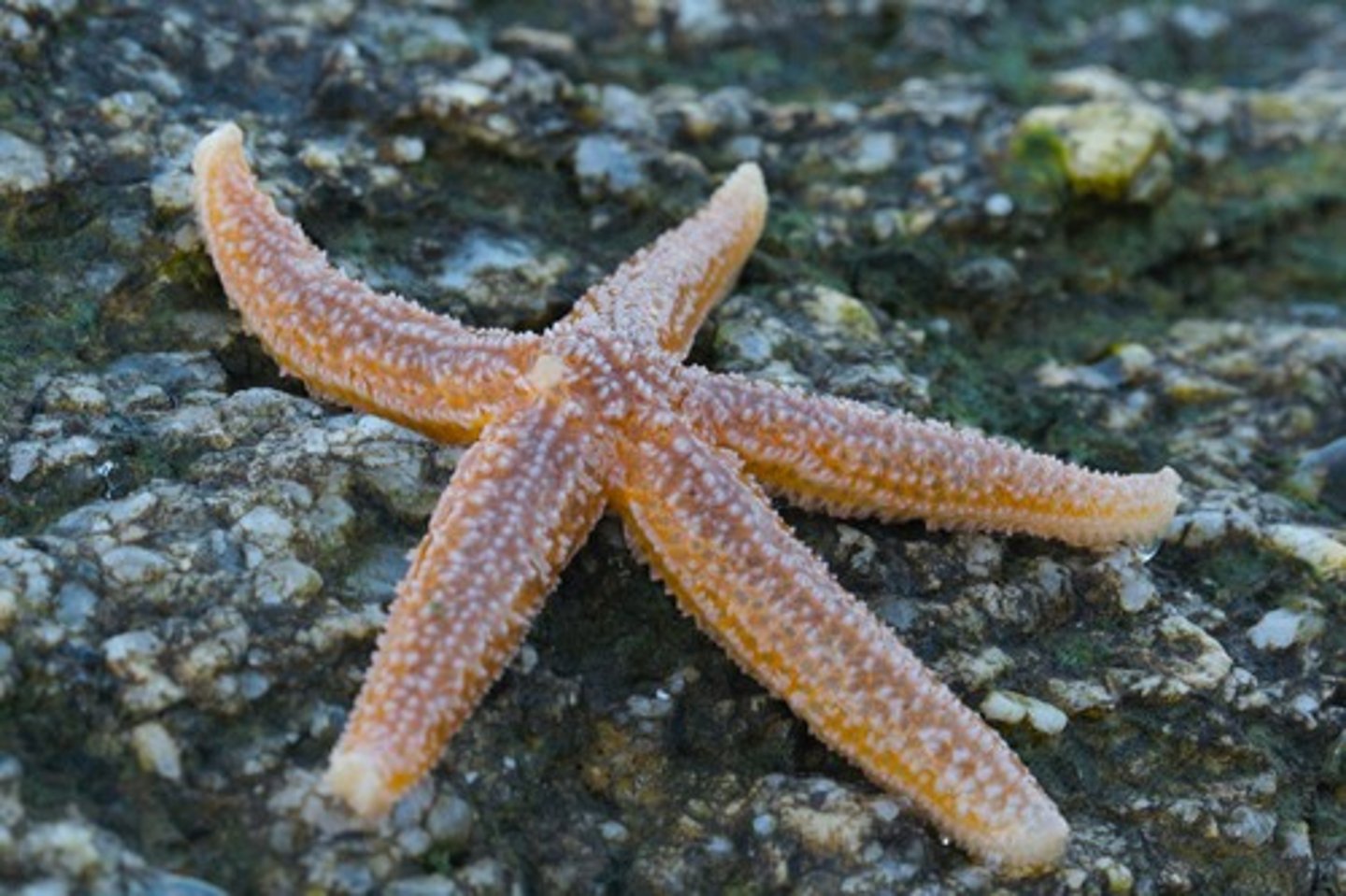
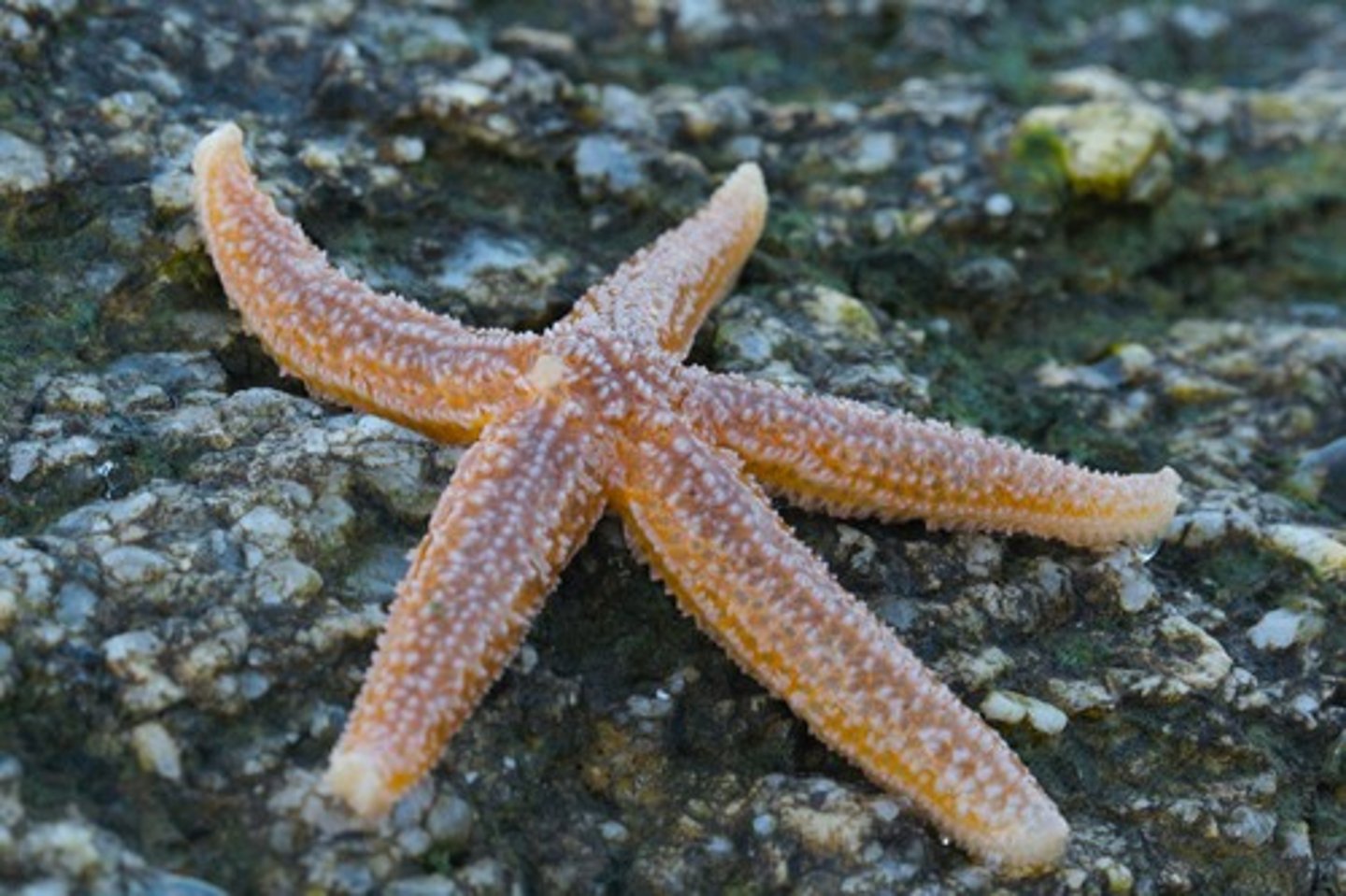
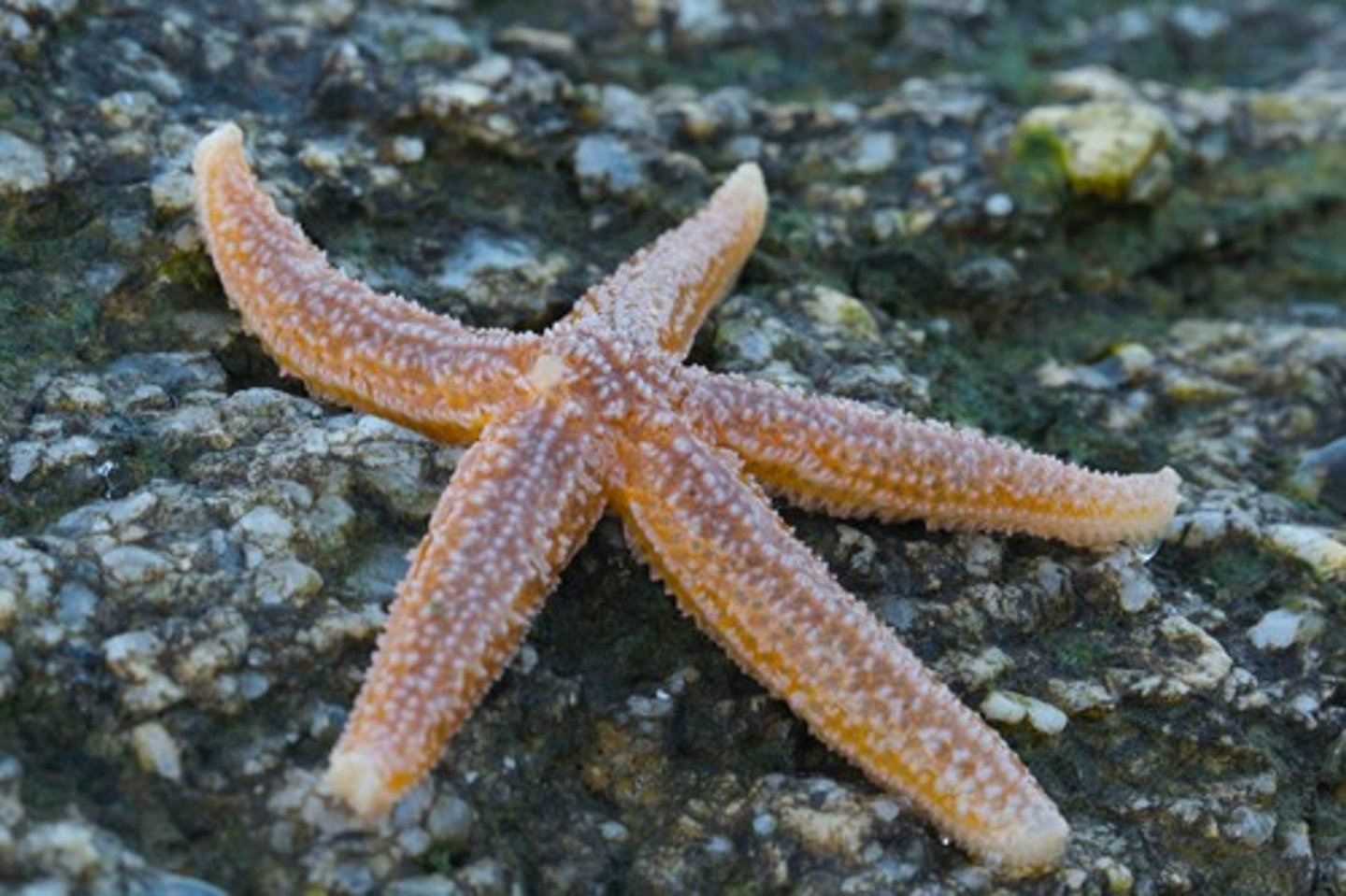
Class Asteroidea
Sea Stars; typically have 5 arms radiating from central disc, predators or scavengers; everts stomach into bivalves to weaken adductor muscles

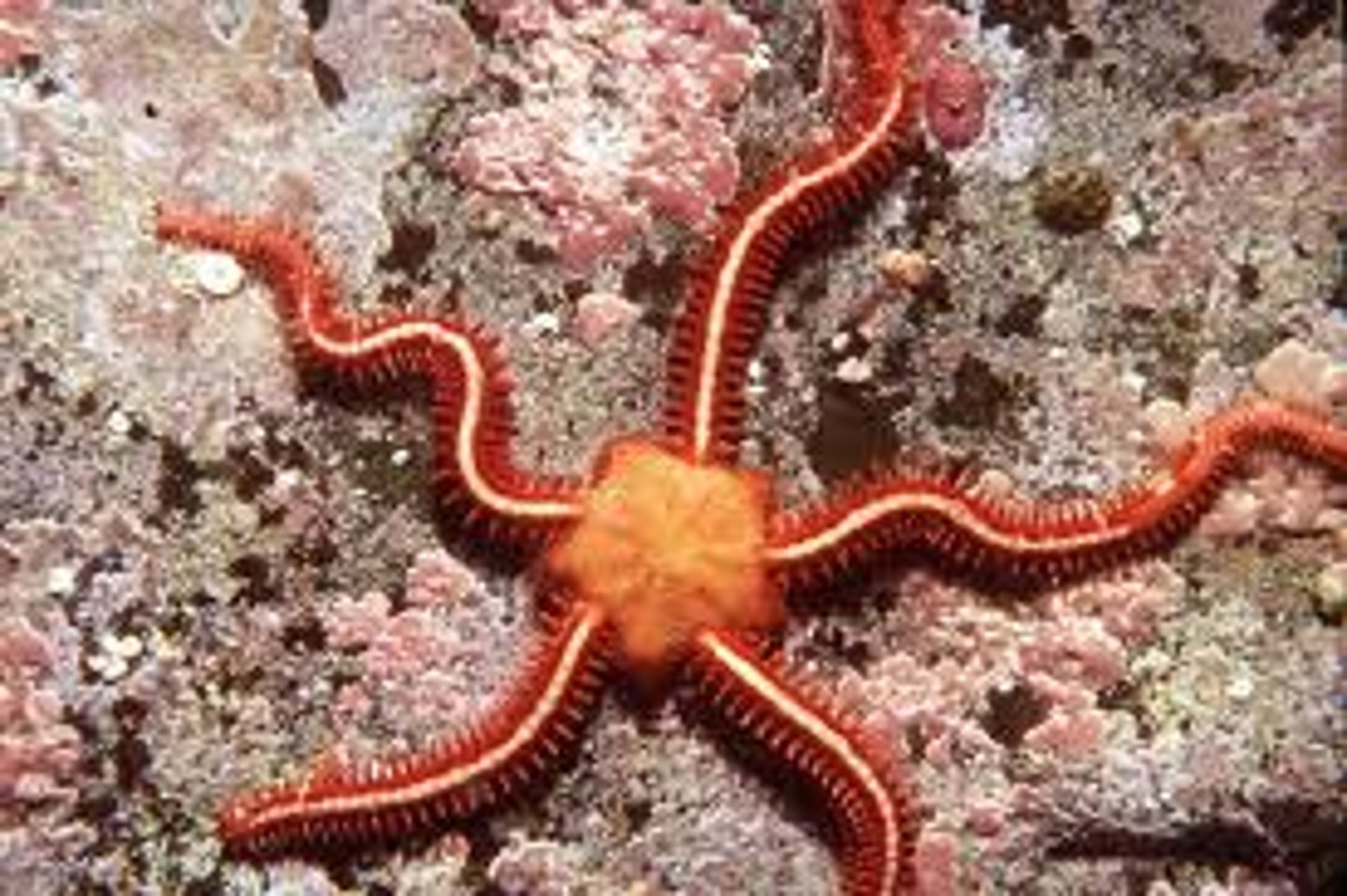
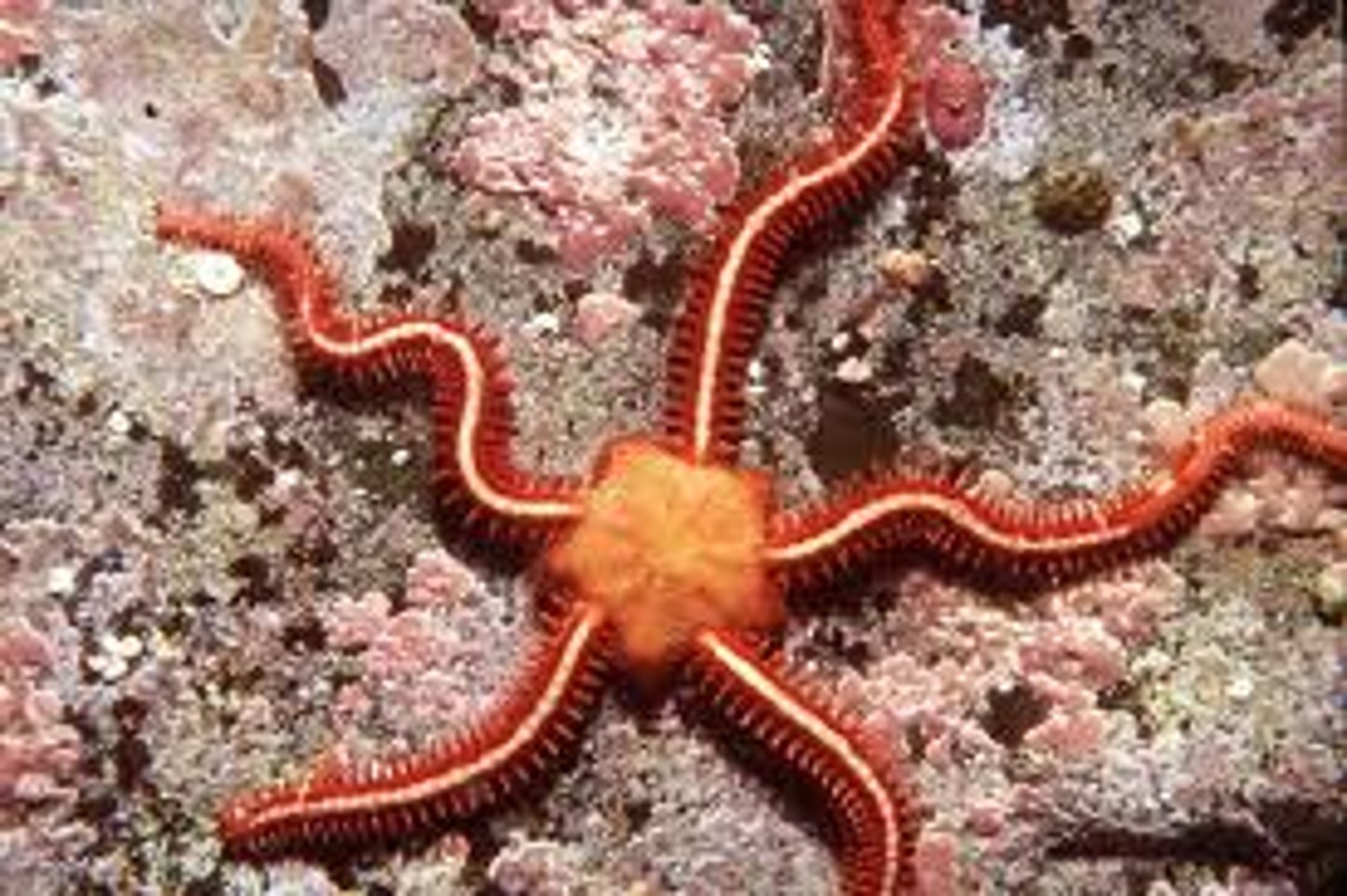
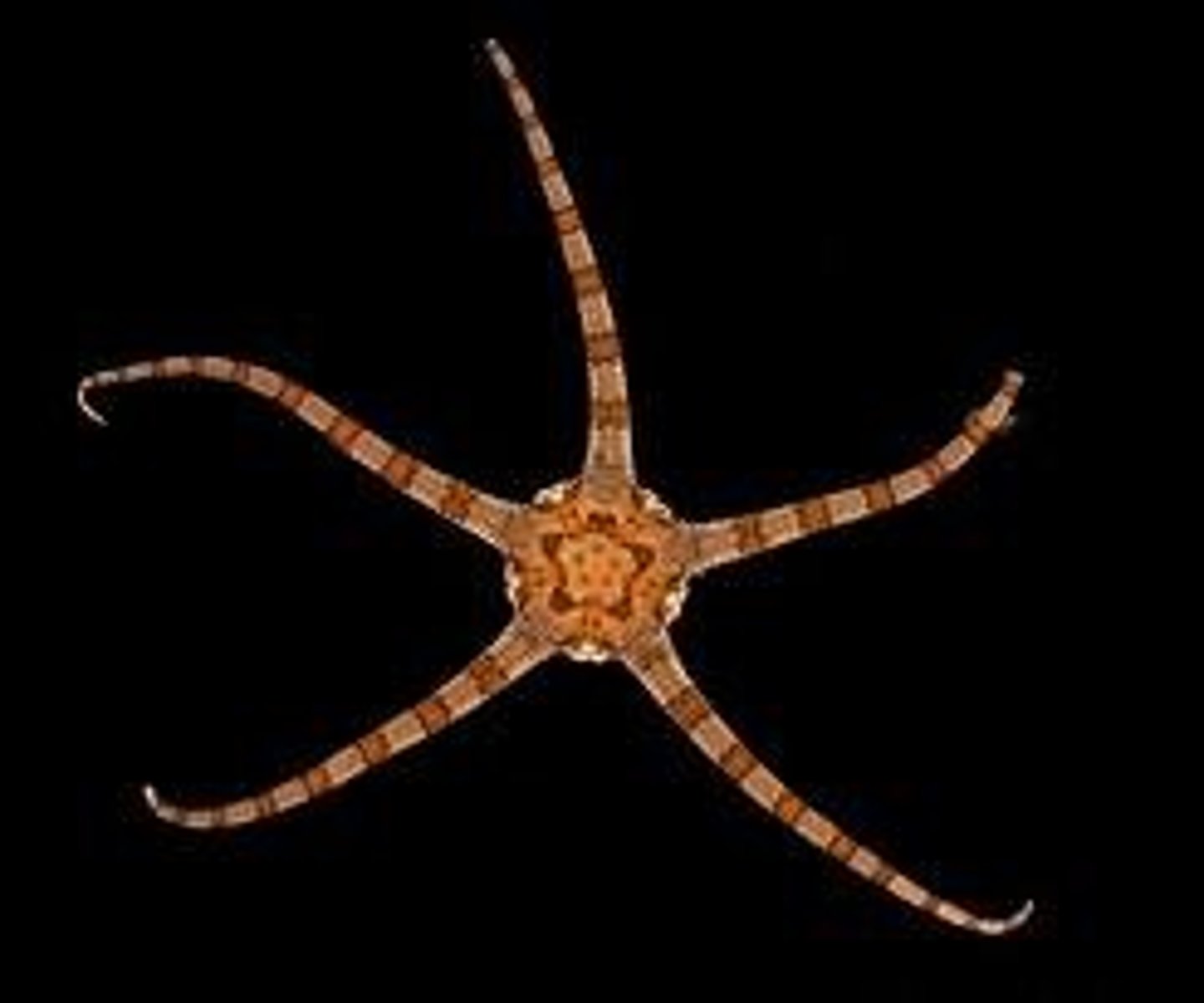
Class Ophiuroidea
Brittle stars and basket stars; largest echinoderm class; move arms in a snake-like motion

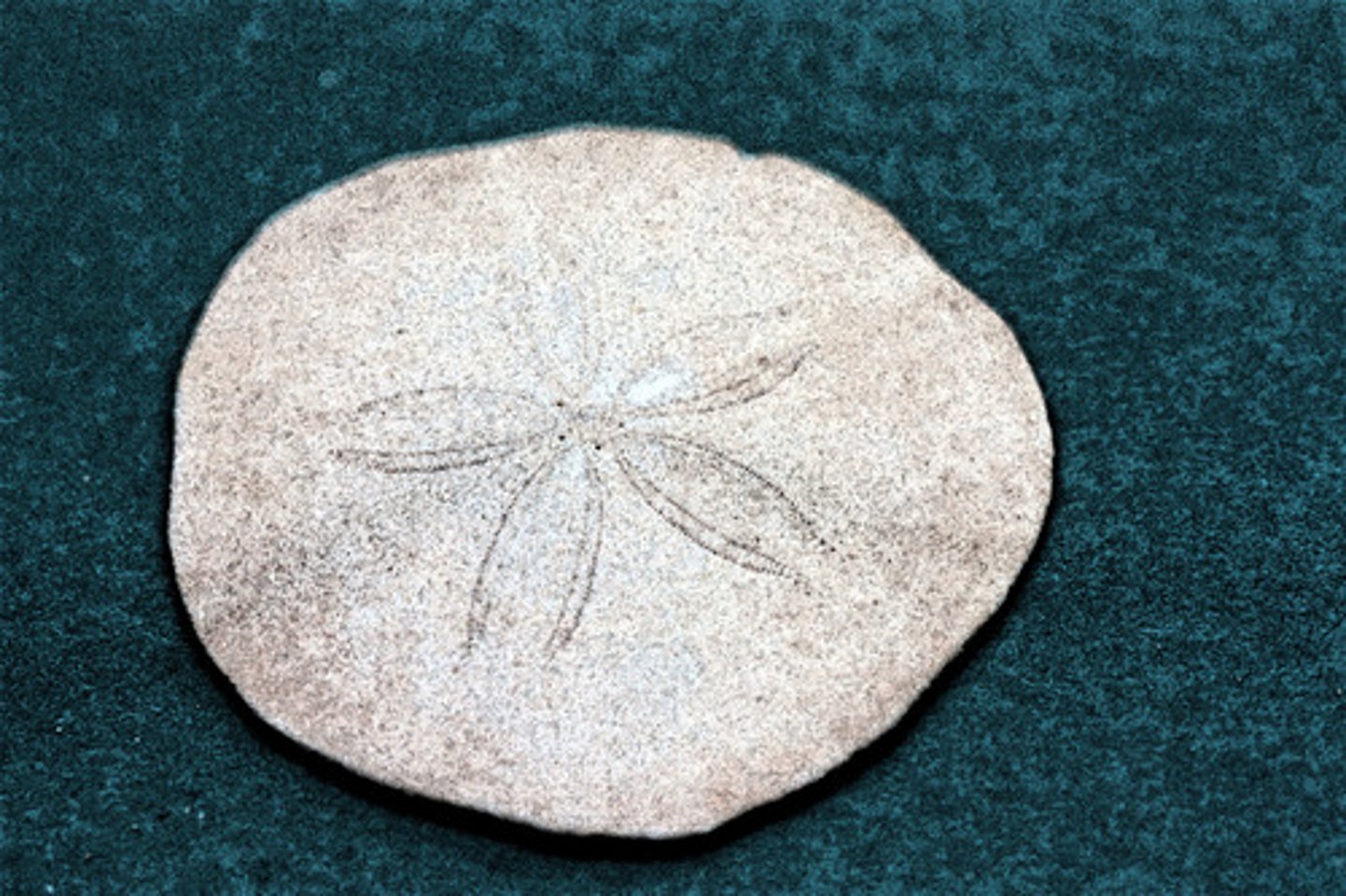
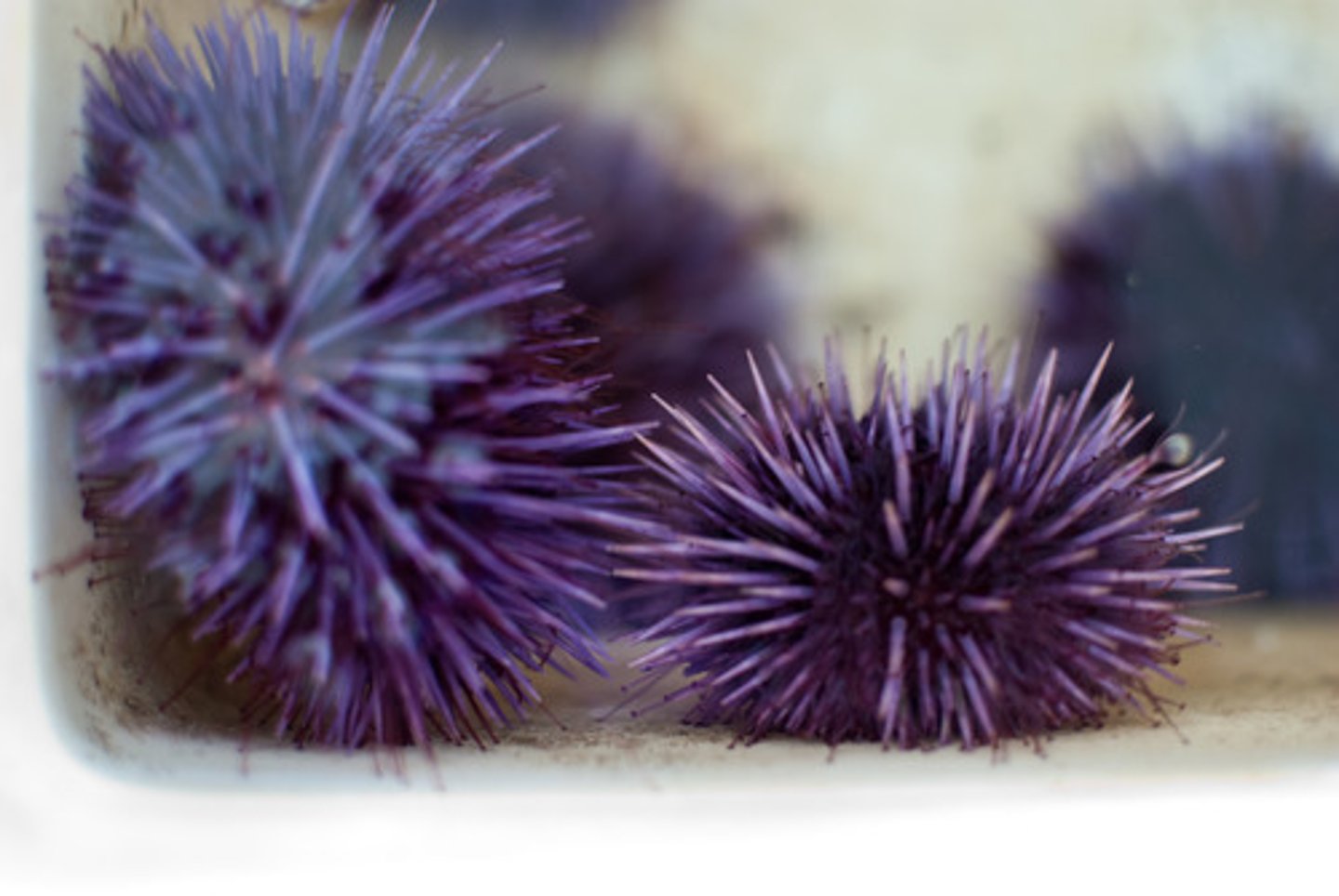
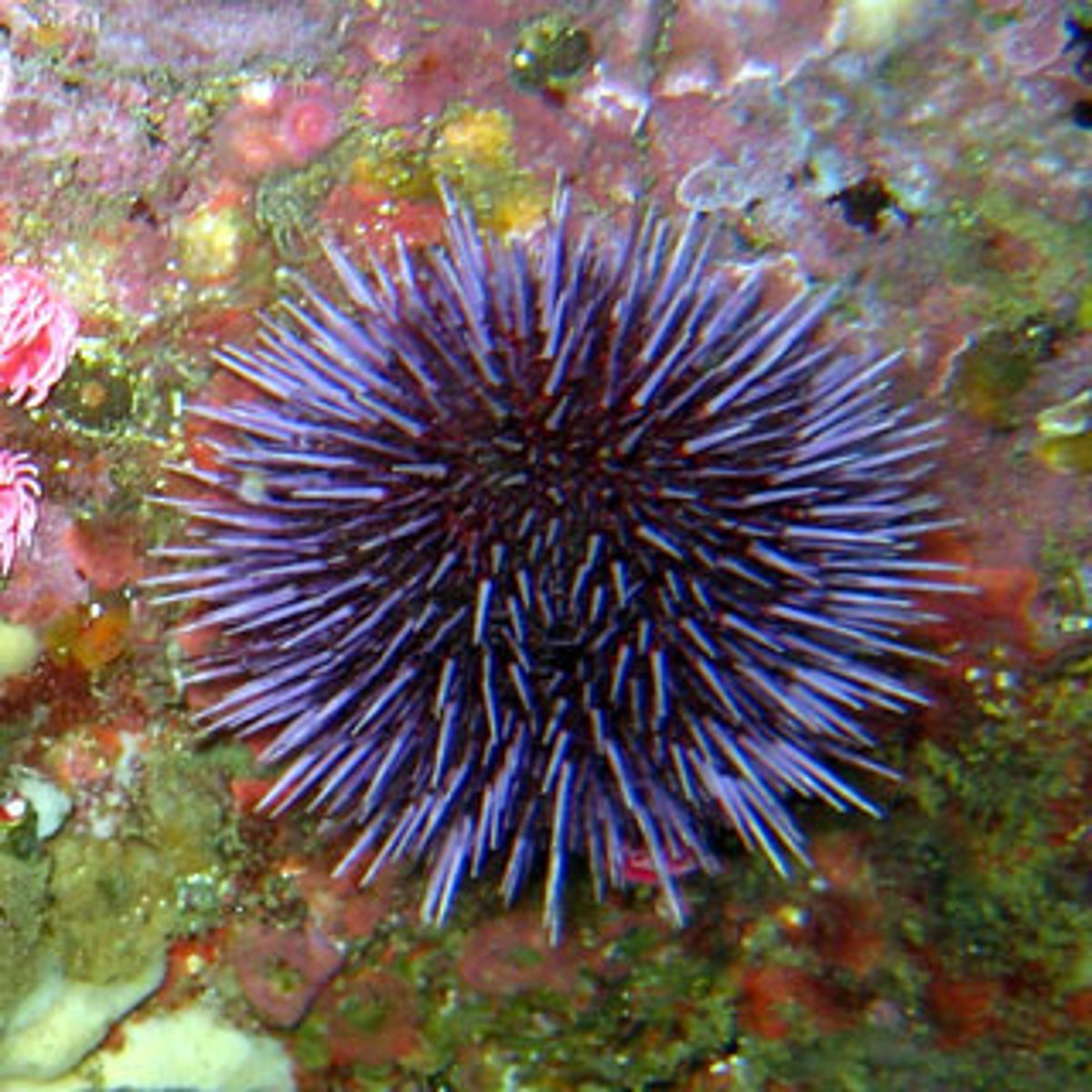
Class Echinoidea
Sand Dollars and Sea Urchins; have an endoskeleton fused into a test; no arms but show pentaradial symmetry; feed on algae, invertebrates, and detritus
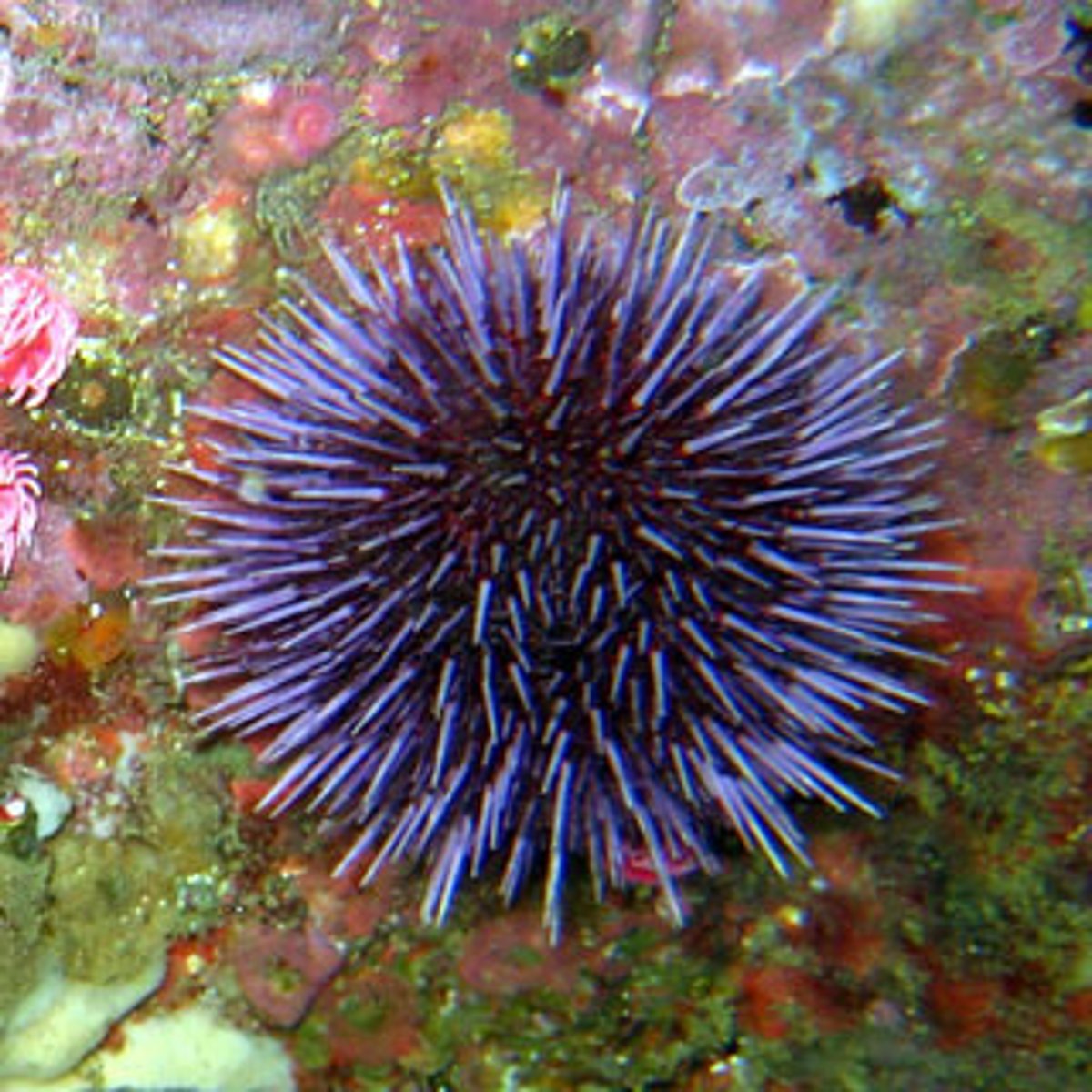

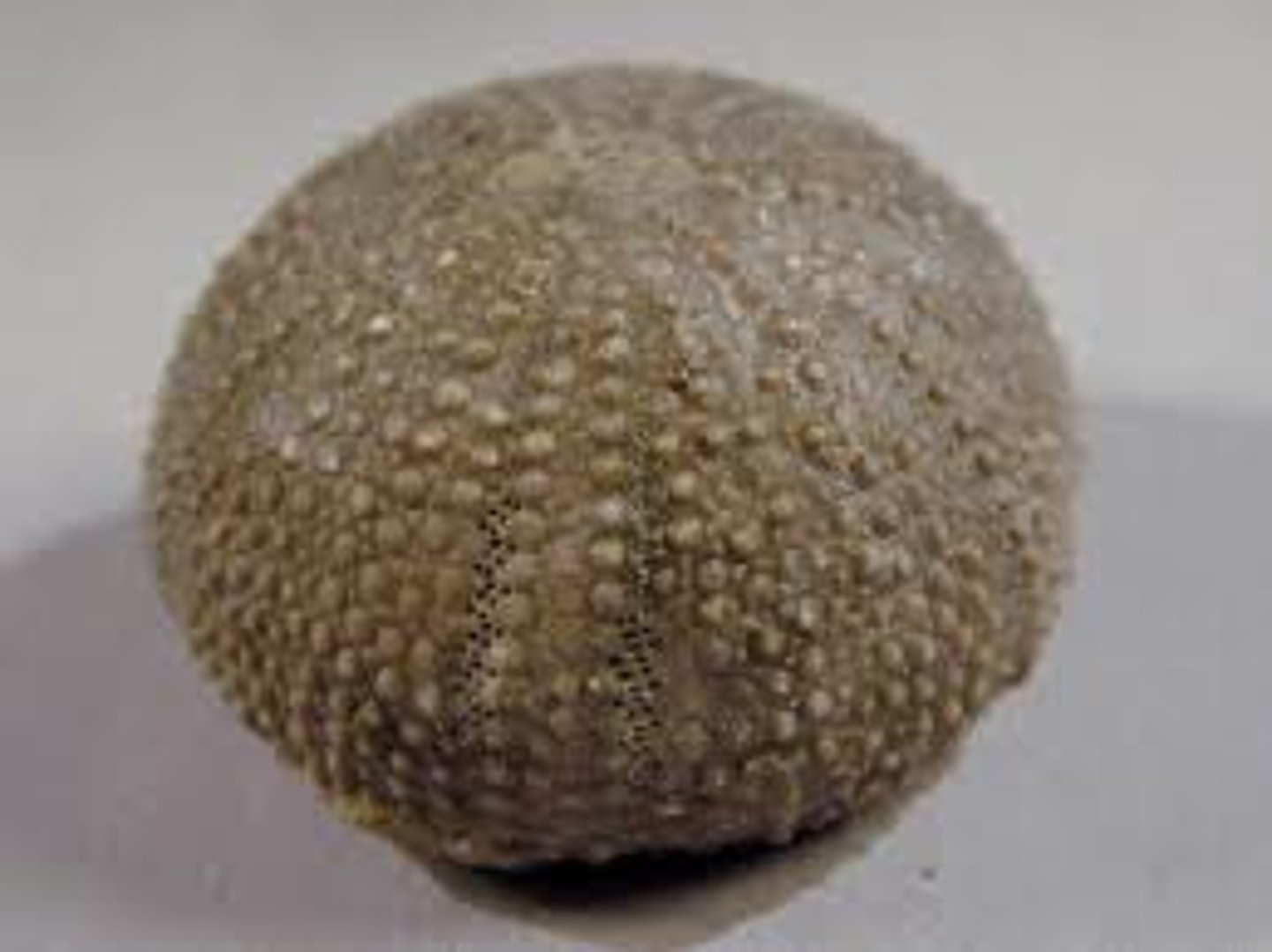
Test
solid, inflexible endoskeleton of urchins, ossicles fused together

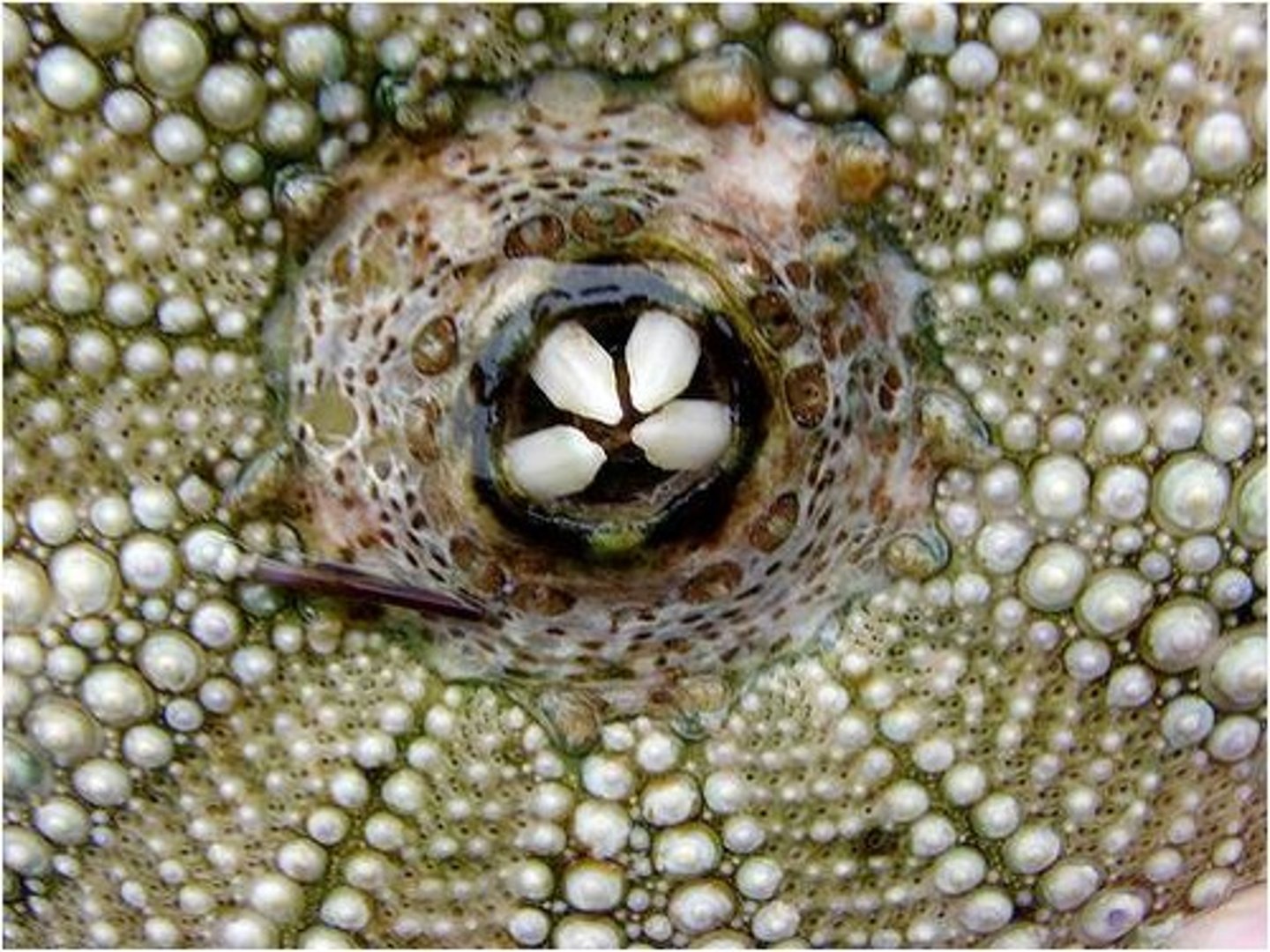
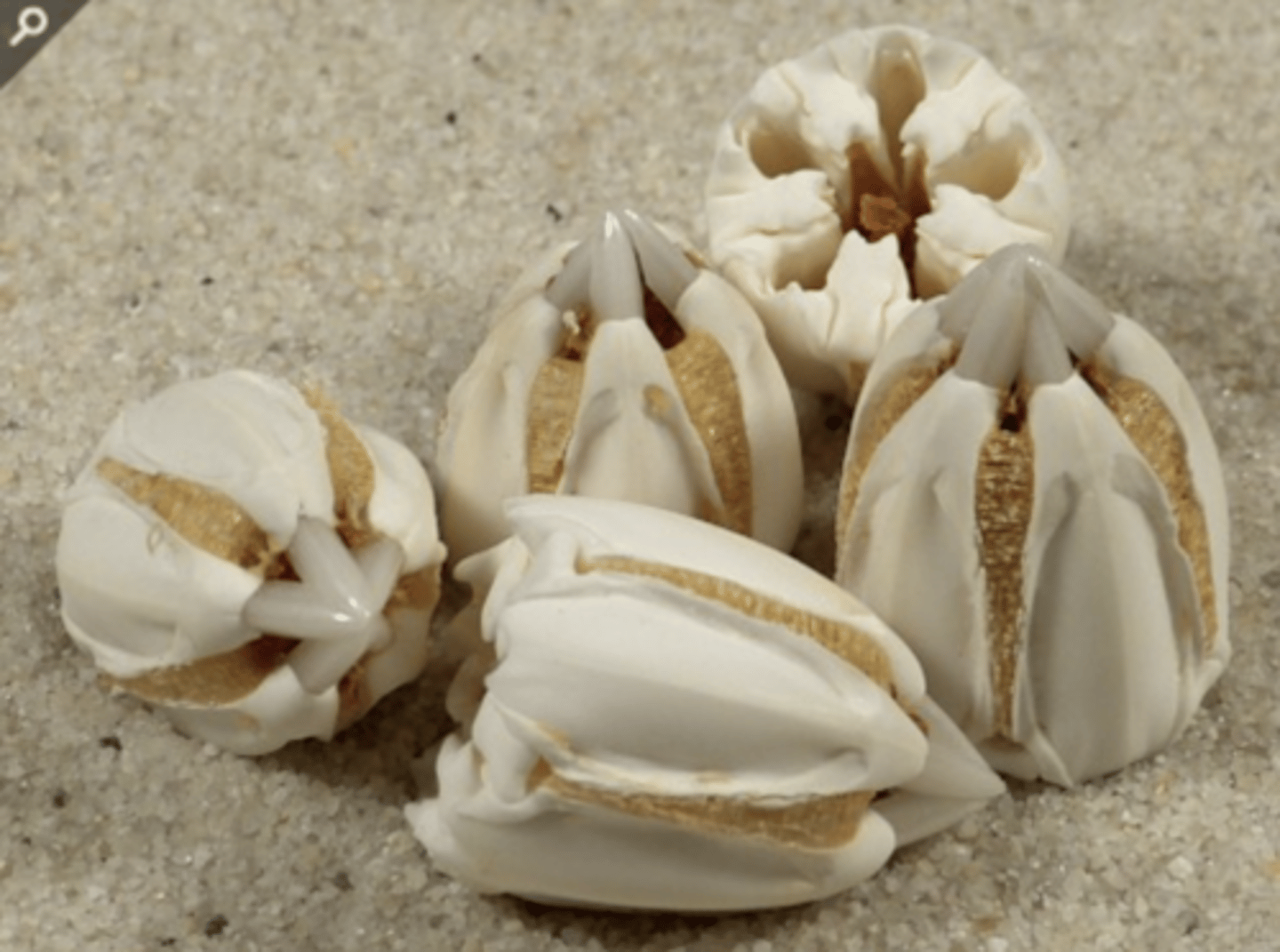
Aristotle's Lantern
the chewing mouth part of a sea urchin, made of ossicles and muscles, the tips of the teeth are very hard, teeth grow continuously

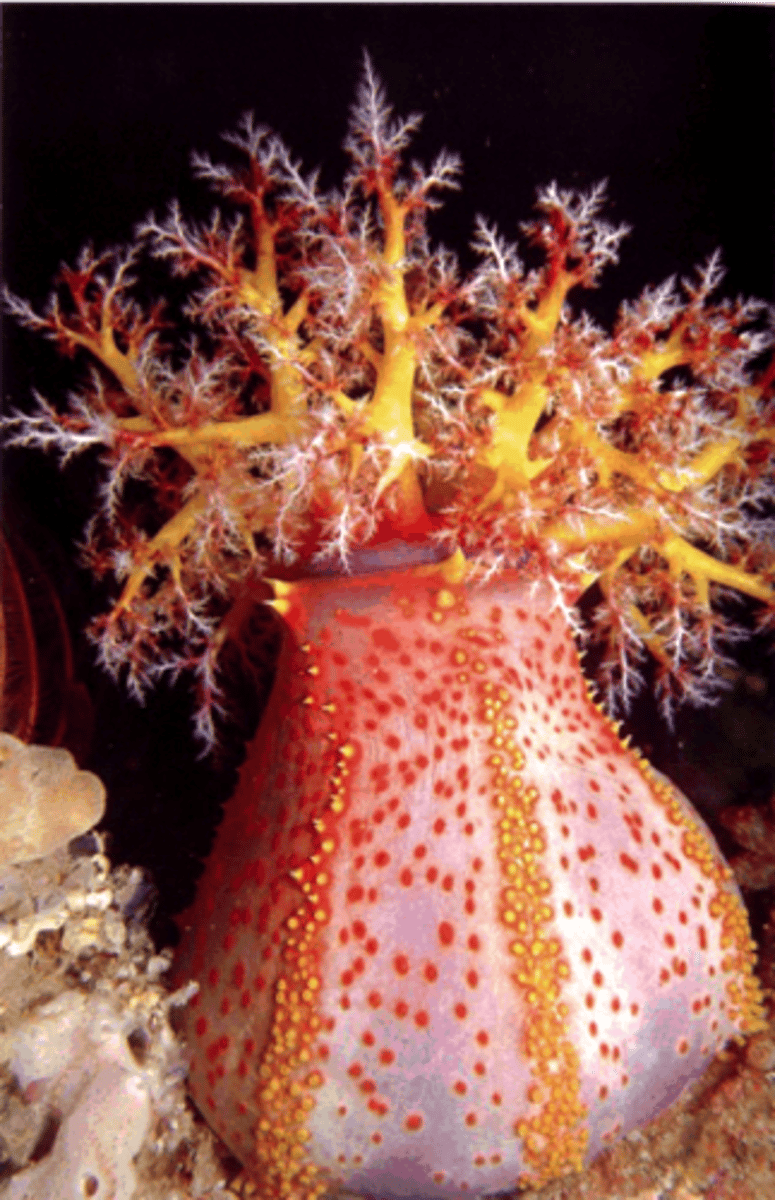
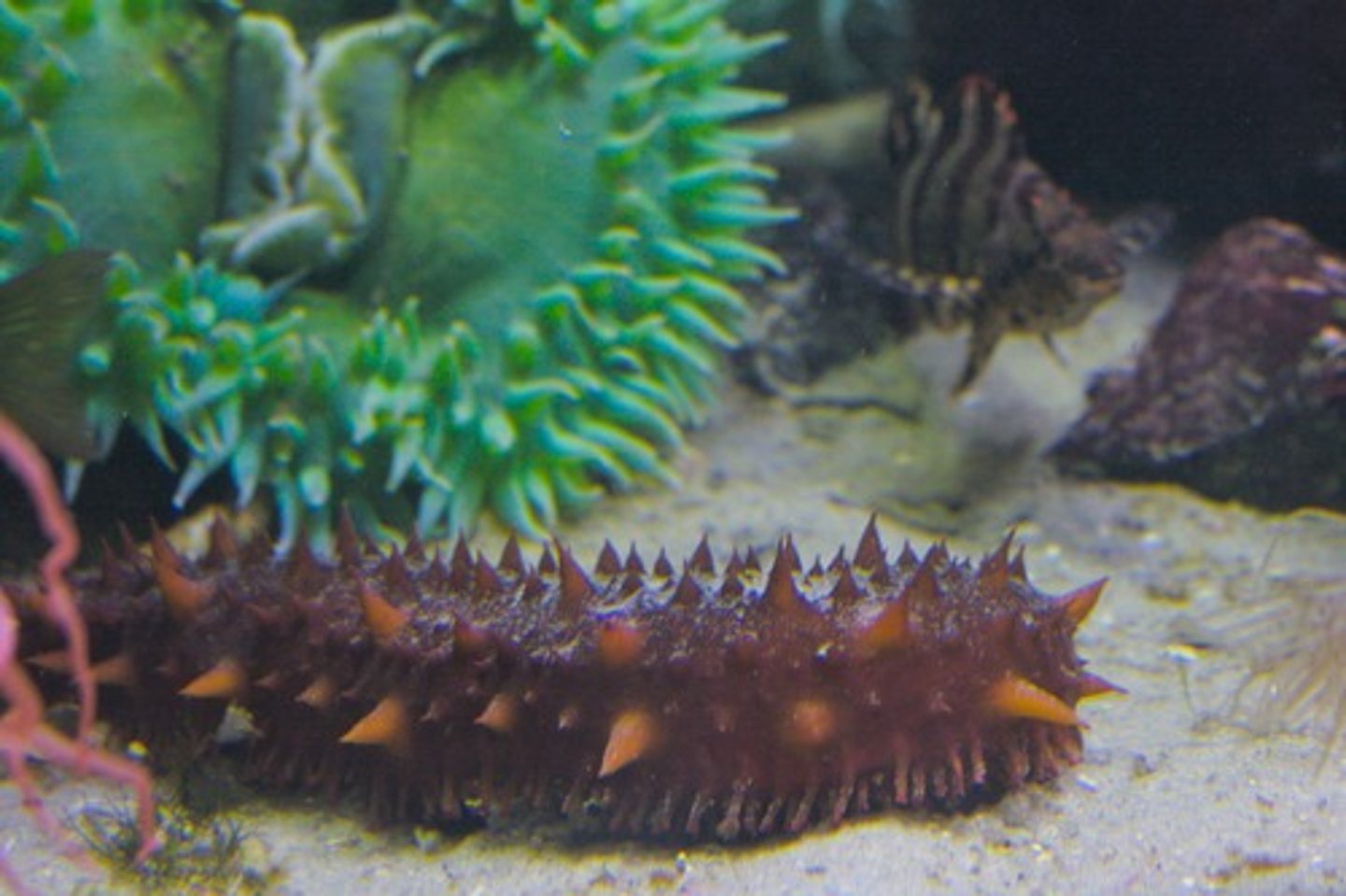
Class Holothuroidea
Sea Cucumbers; soft muscular body, elongated shape; lie on the bottom of the ocean floor; consume organic matter; tentacles around mouth; respiratory trees pump water through the body

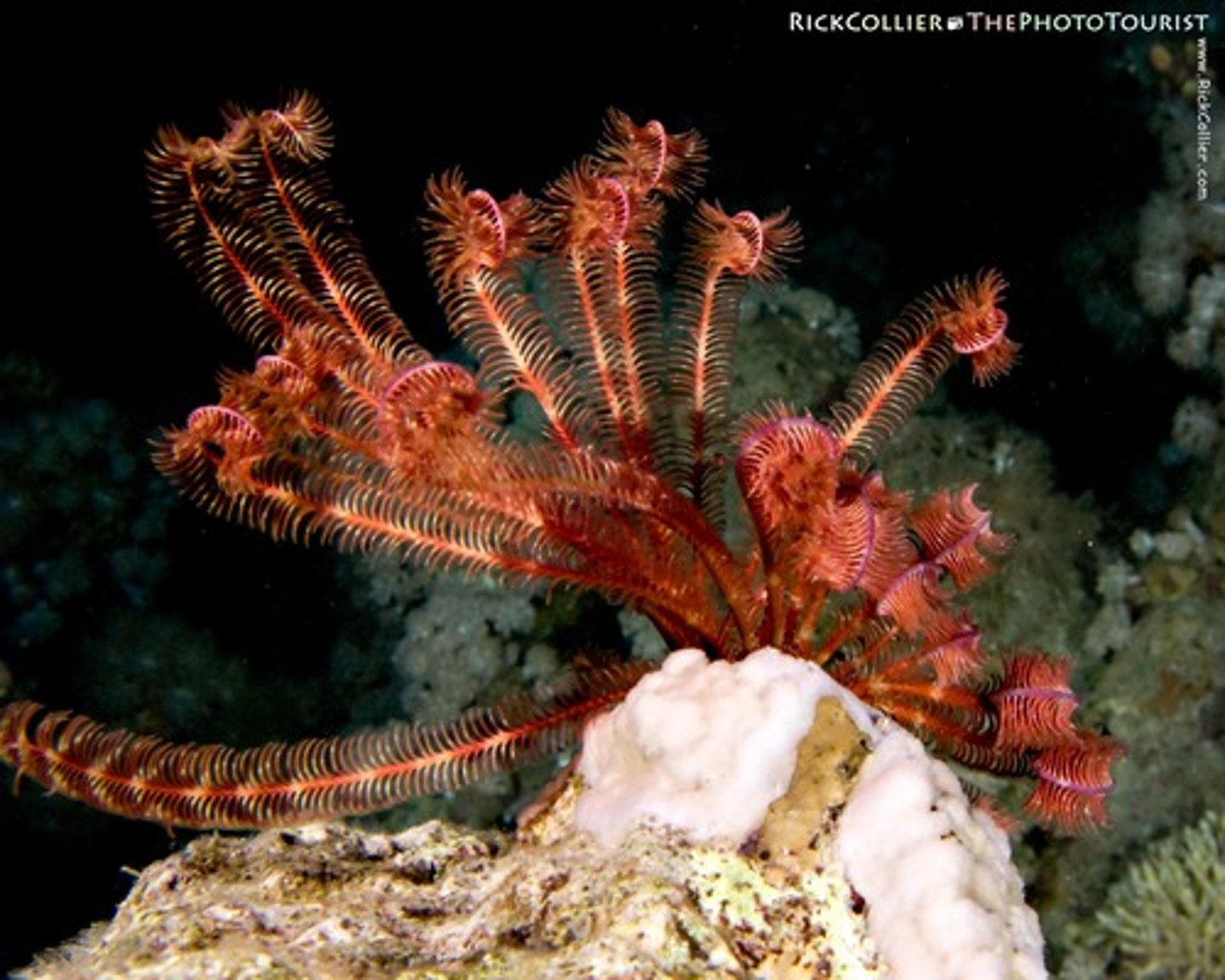
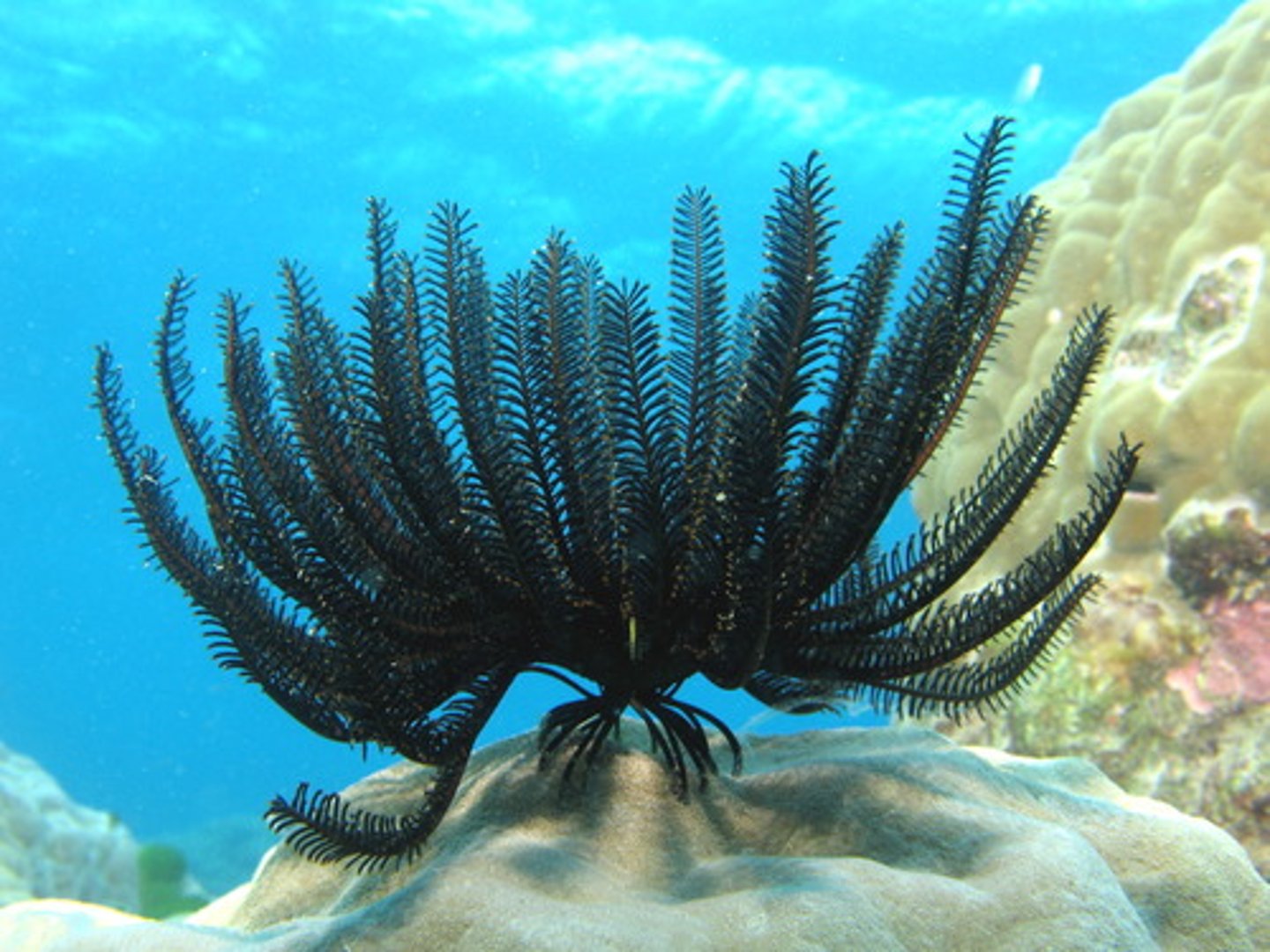
Class Crinoidea
Sea Lilies and Feather Stars; most primitive echinoderm class; Filter Feeders: Sea Lilies are stalked and sessile, Feather Stars swim and creep

Stone Canal
Connects the madreporite to the ring canal, named because it is reinforced with plates of CaCO3
ampulla
the bulb of the tube feet, muscular structure used to expand and contract the tube feet
Dioecious
Organisms with individual, or separate sexes, males and females

Ophiuroidea (photo)
This animal belongs to the class

Asteroidea (Photo)
This animal belongs to the class

Crinoidea (photo)
This animal belongs to the class

Holothuroidea (photo)
This animal belongs to the class

Echinoidea (Photo)
This animal belongs to the class

Autotomy
Defense mechanism where organism can severe a body part (usually an arm) and leave it behind to escape from a predator
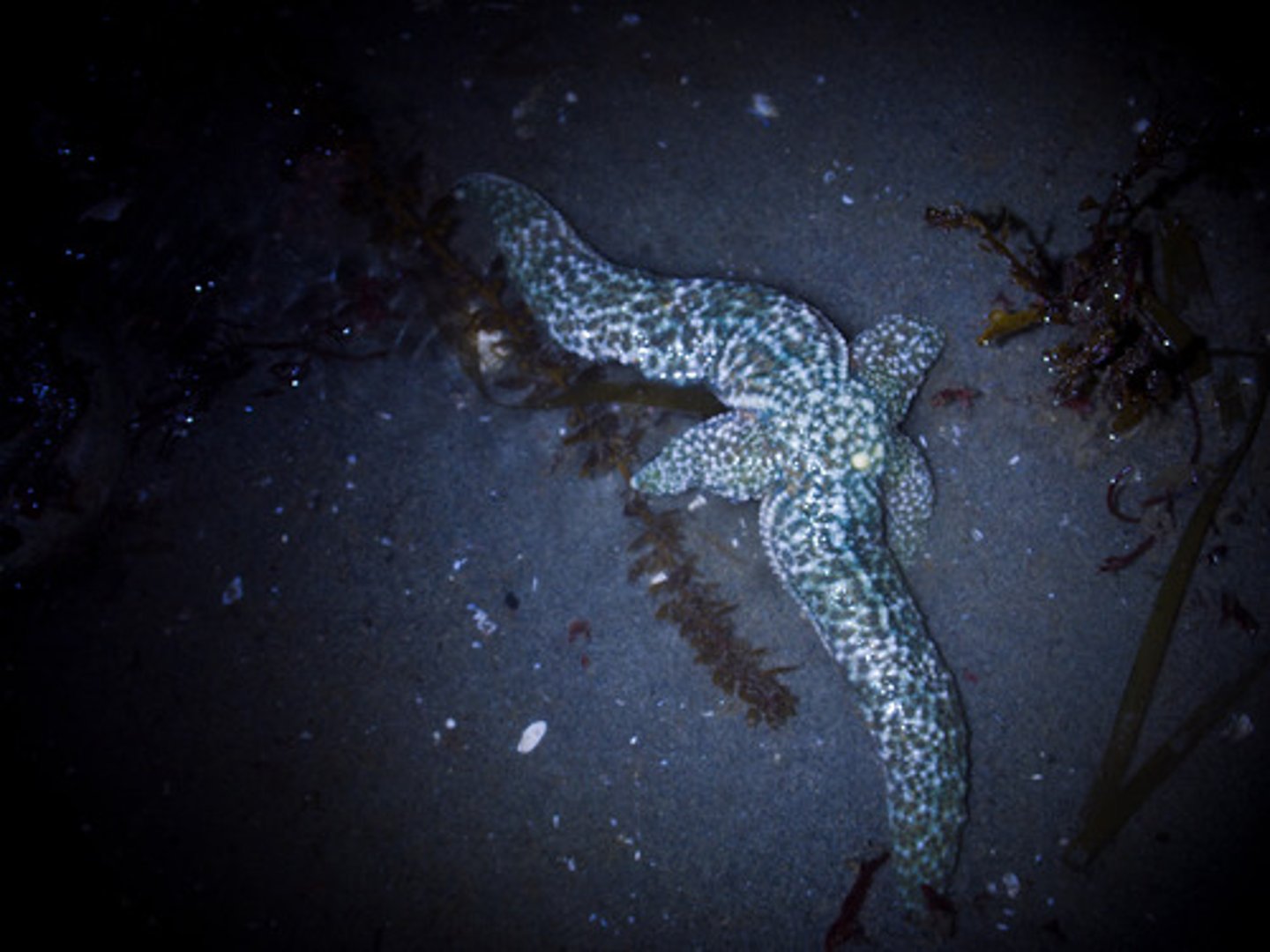

Evisceration
sea cucumbers eject internal organs to trap or deter a predator, involves liquifying and rupturing of connective tissue, all lost parts will eventually reform
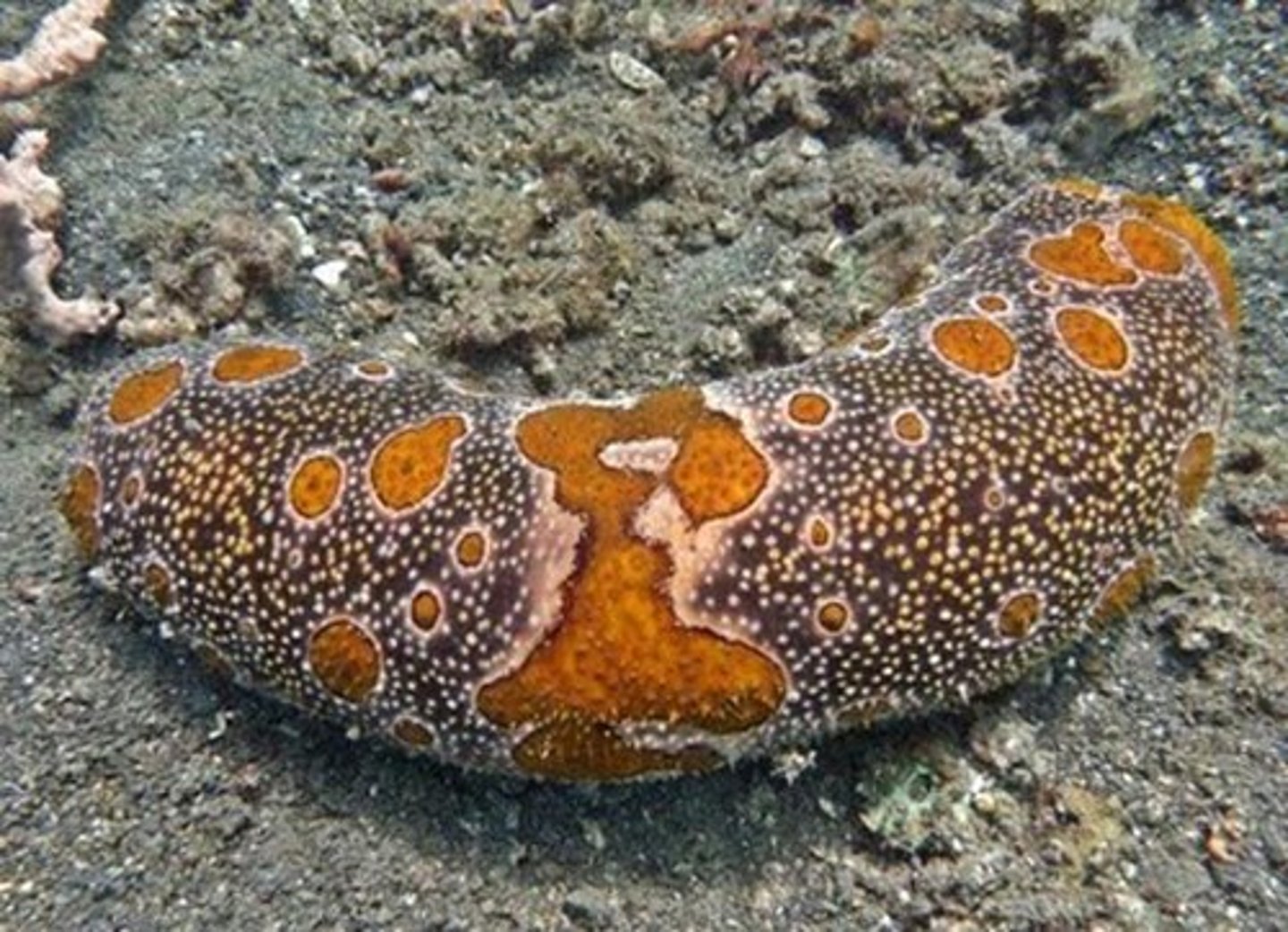

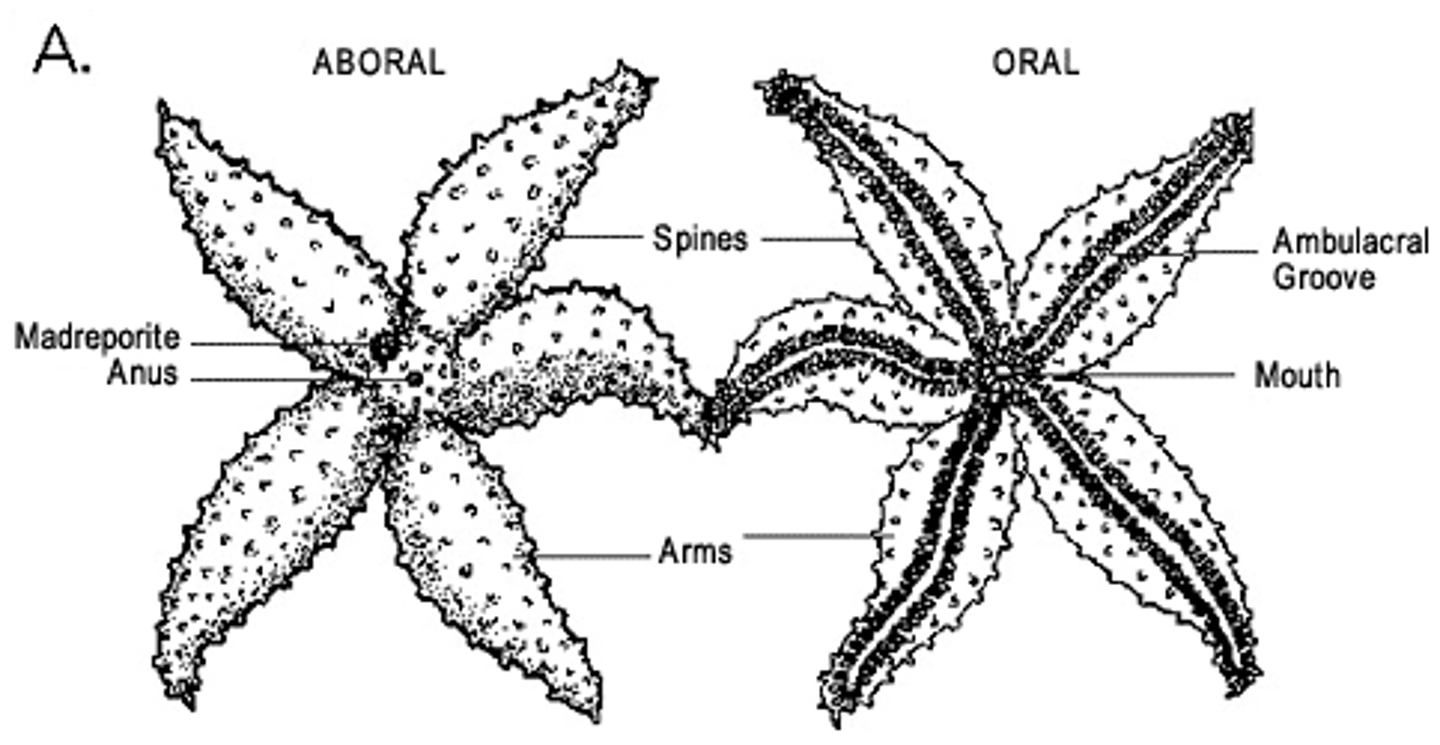
Oral
Side of organism where the mouth is found
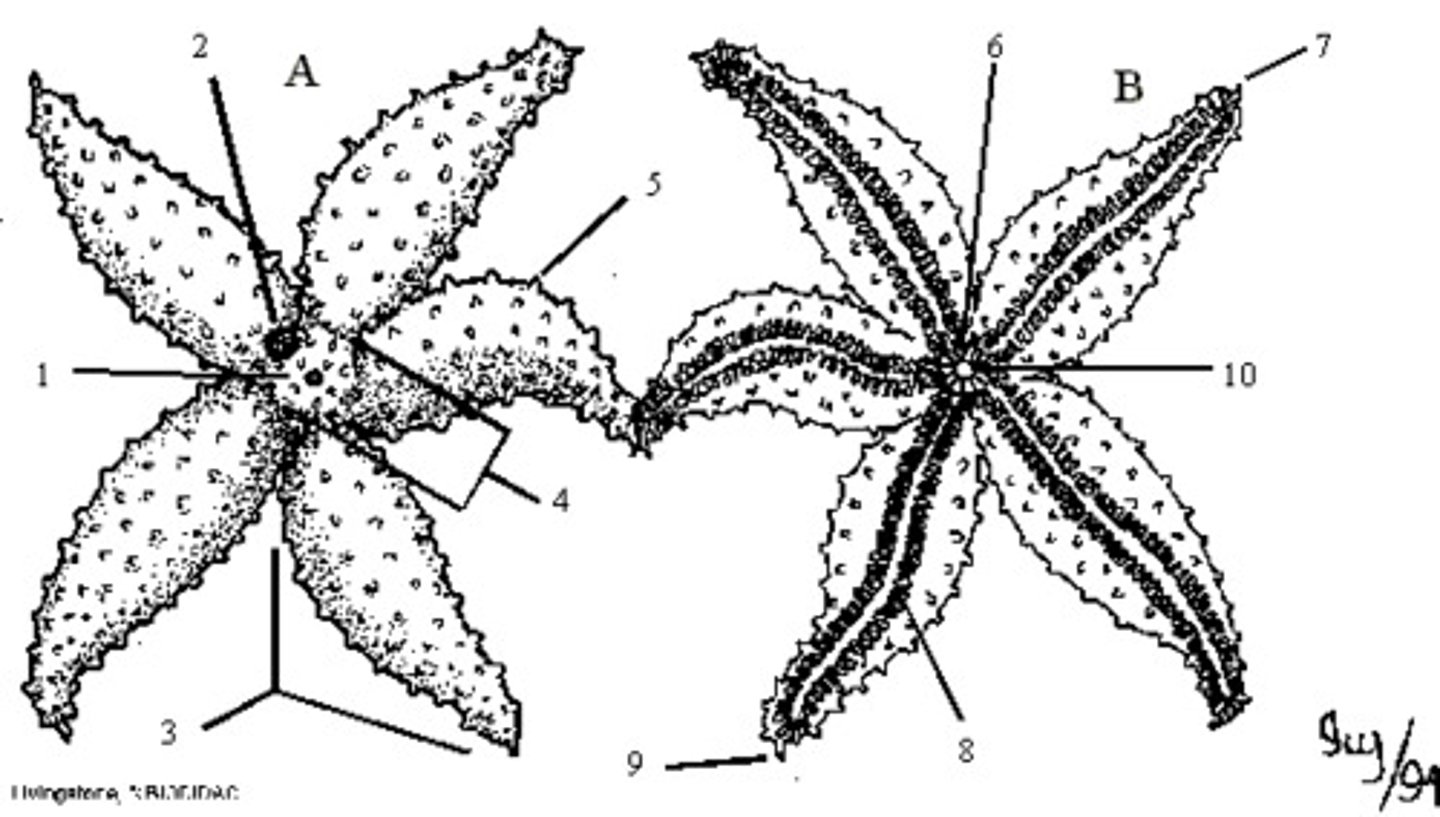
Aboral
Side of organism without a mouth
Literal meaning of the word echinoderm
spiny skin
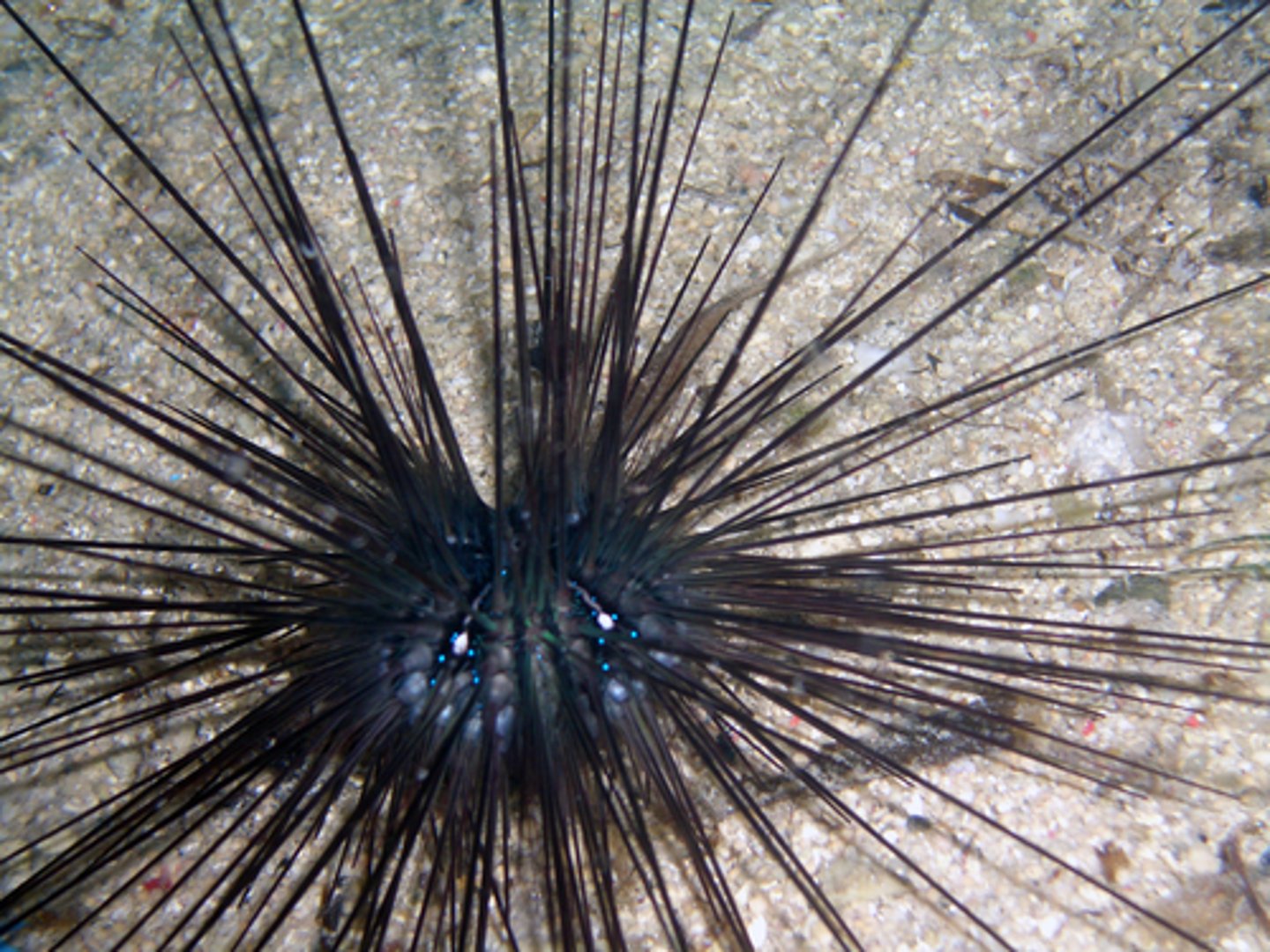

regeneration
Ability to regrow lost body parts
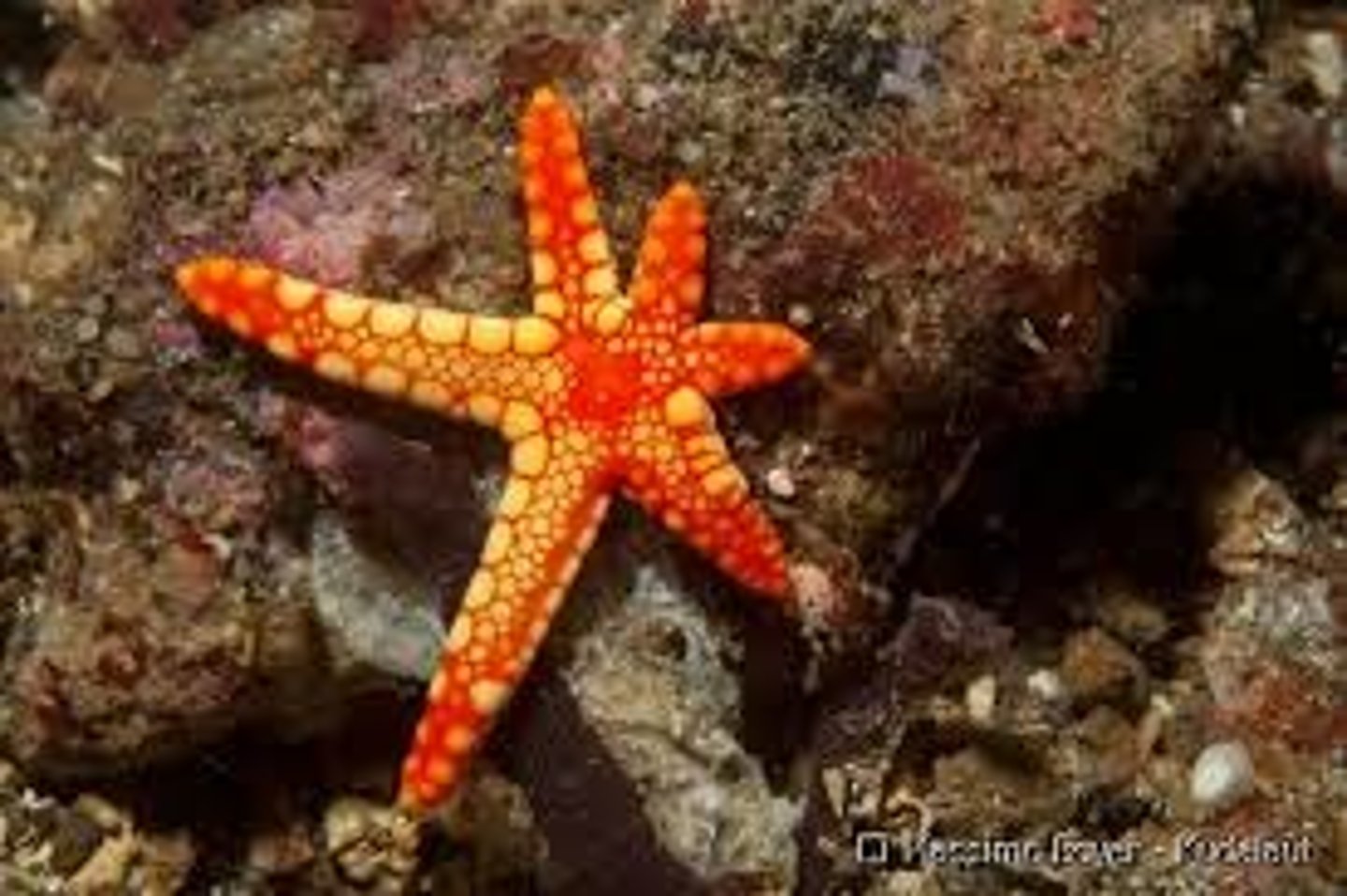

Central Disk
Portion of body from which the arms radiate

Cardiac stomach
positioned on the oral side and can be expelled for extracellular digestion
6
Number of Maine fishermen with active sea cucumber licenses
at least 66, but probably more
Number of sea cucumber species that are overexploited worldwide
Orange-footed cuke
Maine's only commercially important sea cucumber species
Catch tissue
Mutable connective tissue whose stiffness can be rapidly & dramatically altered, helps echinoderms stay in position without using much energy
Suction, ionic interactions, and gland that secretes adhesive substance
How tube feet attach to a solid surface
Picture of Aristotle's Lantern

Cilia
Line inside of water-vascular system and cause the water to circulate
85
Number of echinoderm species that are known to be toxic
Calcite crystals
Found on aboral surface of brittle stars, are lenses that focus light on nerves = "eyes"
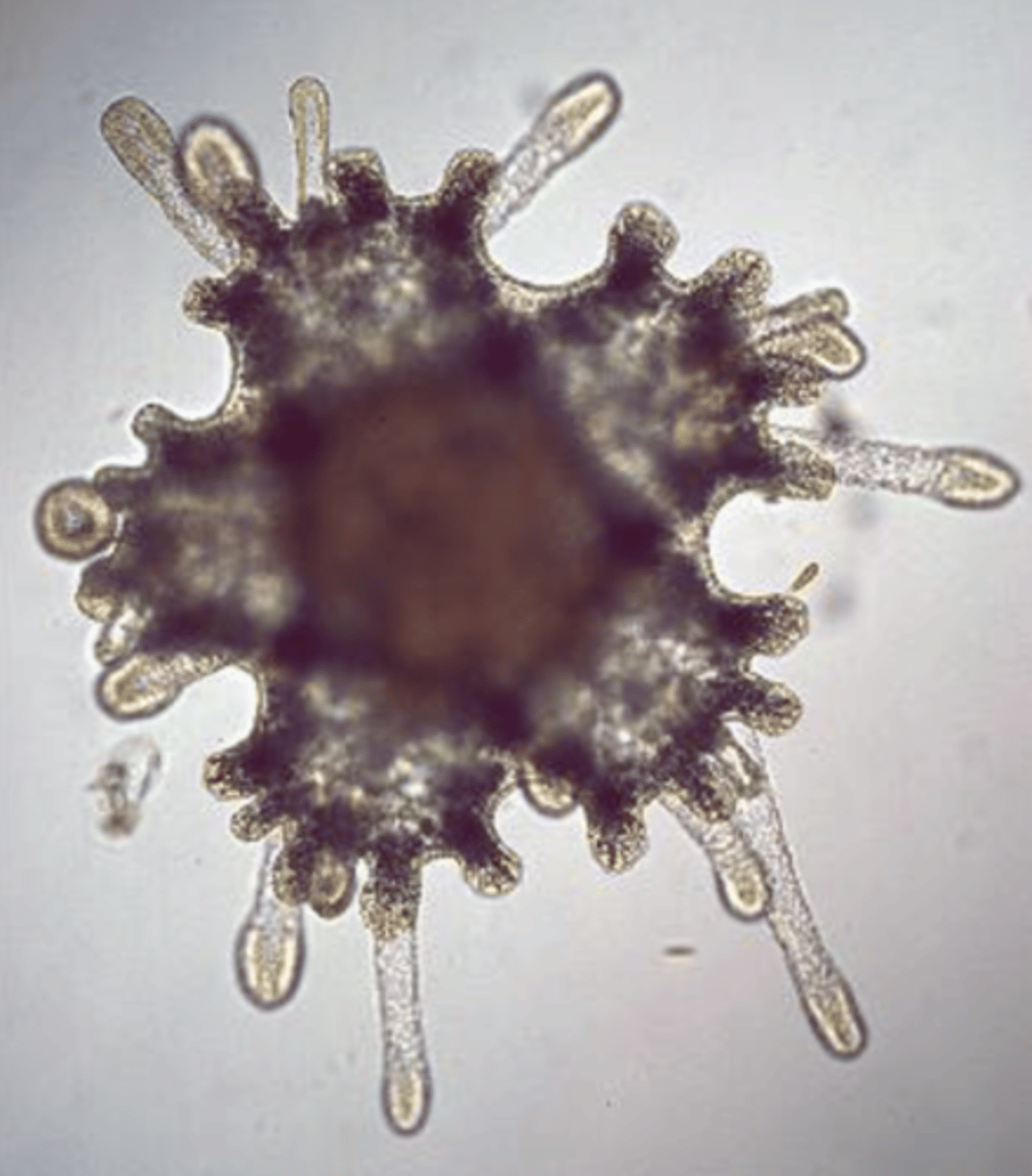
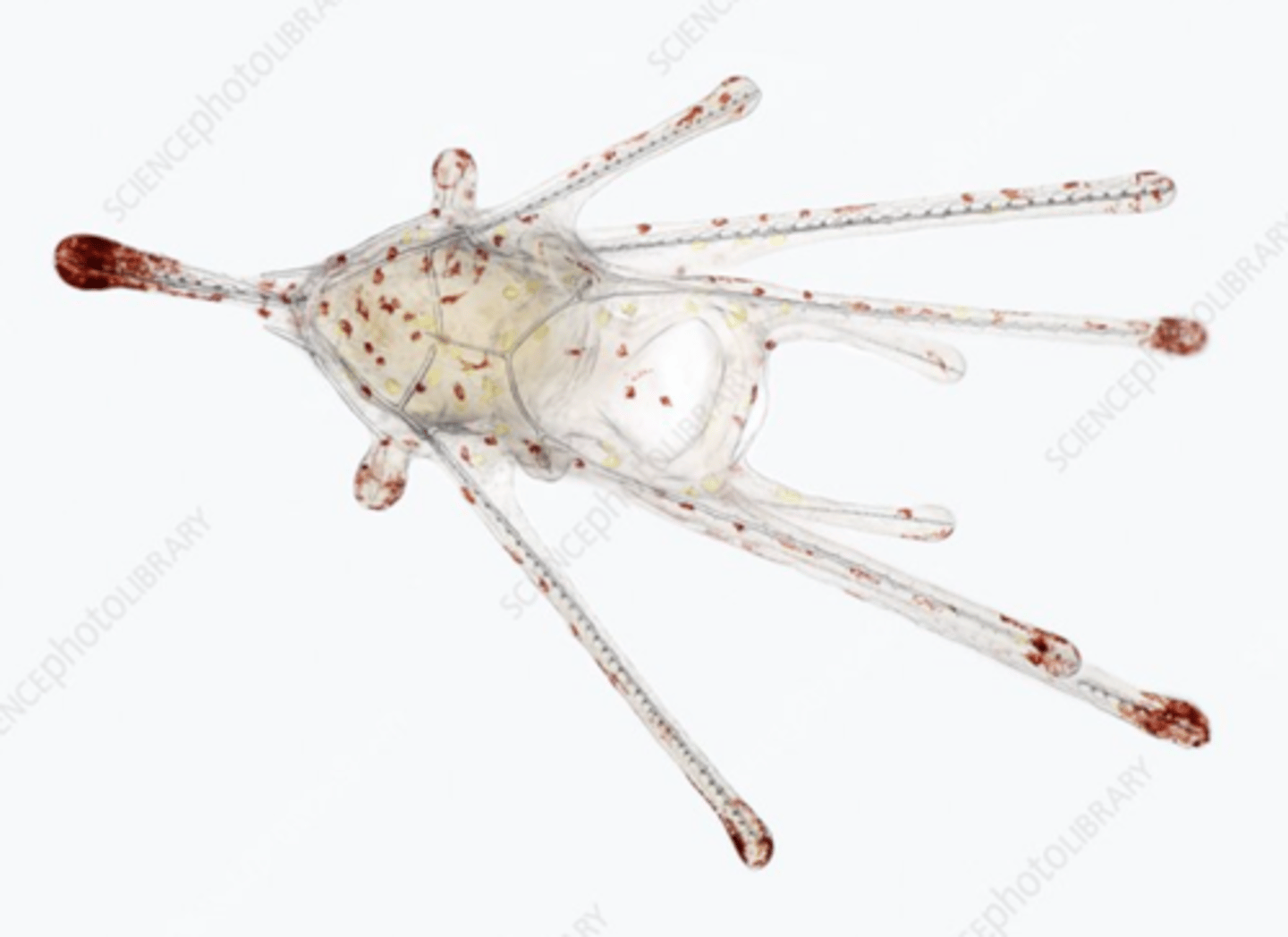
Picture of bipinnaria, early sea star larva
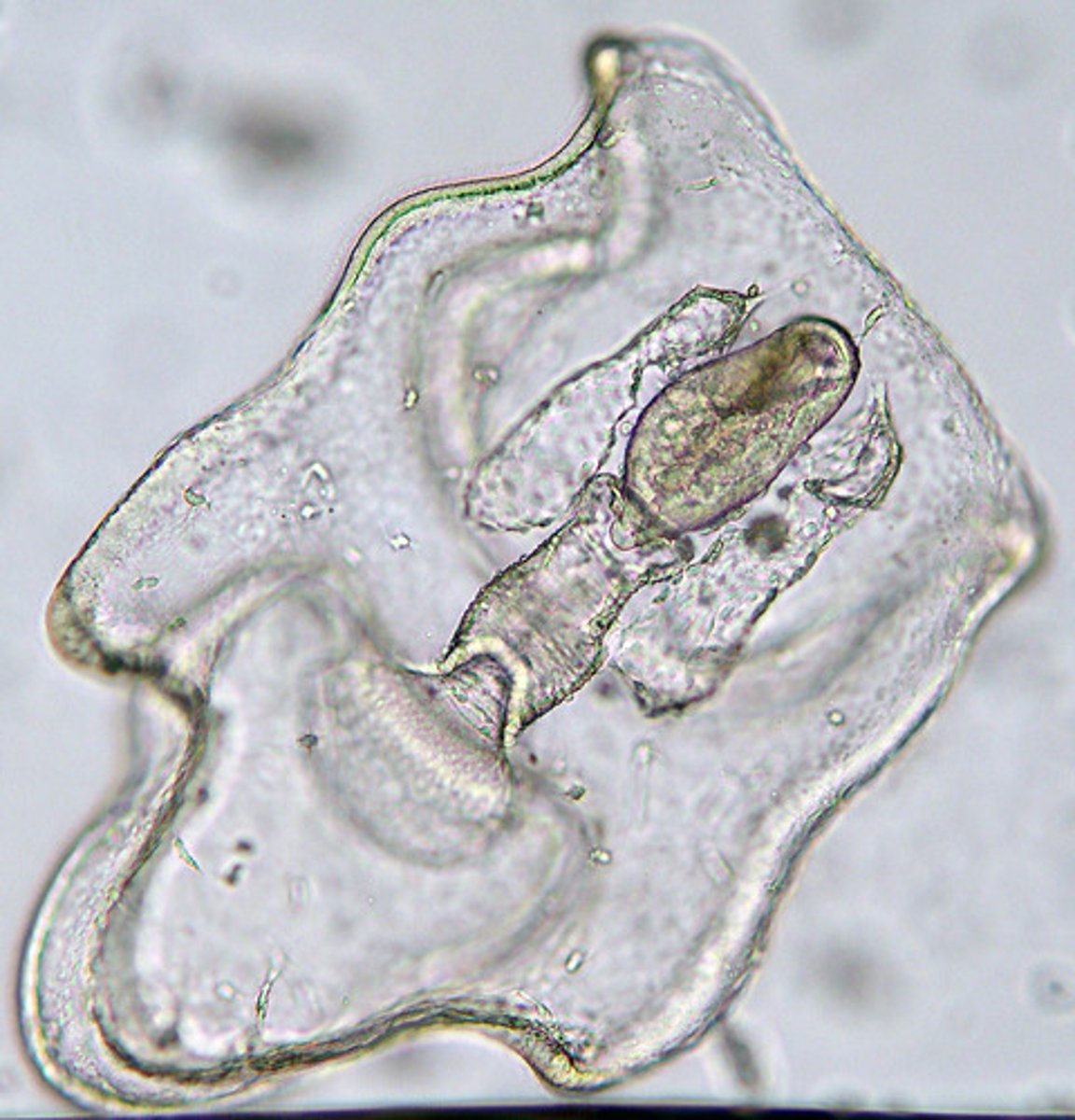
Digestive system only in the central disc, has a mouth, no anus, have multiple madreporites on the oral surface and slits called bursae, many hide during the day
What's odd, or unique, about brittle stars
Deposit feeders
Ingest sediments and remove organic material on and in the particles, capture small organisms in sediment
bivalves, sponges, gastropods, worms, and other echinoderms
What sea stars like to eat
Animals that belong to the phylum Echinodermata
sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sea lilies, and sea feathers
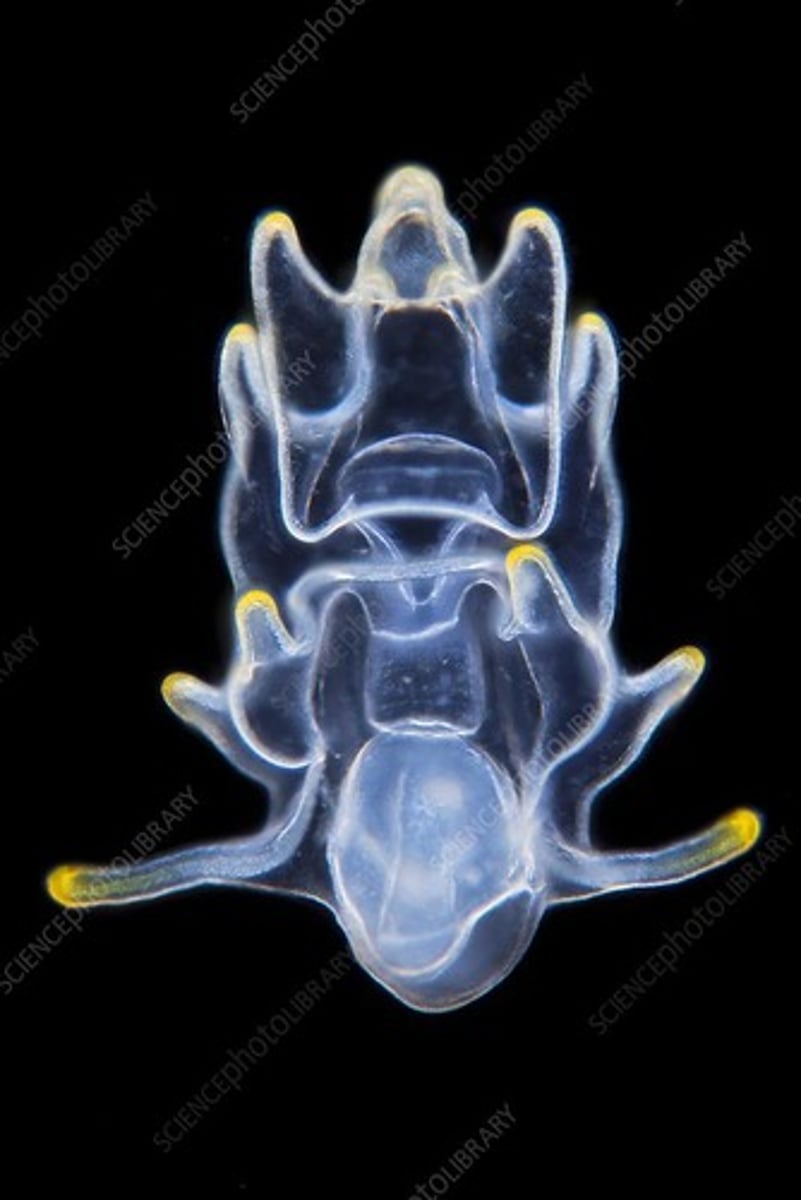
Picture of pluteus, larval urchin

Picture of ossicles in sea star skeleton

Picture of brachiolaria, later sea star larva
Picture of baby sea star, still pretty microscopic