Telescopes – Vocabulary List (9/2/2024, 9/8/2024, 9/16/2024)
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering telescope terms and definitions from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

27 Terms
astronomy
the study of all matter and energy in the universe.
universe
everything that exists to the best of our knowledge.
reflection
the redirection of a beam of light off a surface when it strikes the surface.
refraction
the bending of a beam of light as it passes from one material into another.
refracting telescope
a telescope that uses lenses to form an image.
reflecting telescope
a telescope that uses mirrors to form an image.
catadioptric
a telescope that uses both lenses and mirrors to form an image.
objective
the main mirror or lens of a telescope.
focal point
the point to which a central parallel beam of light from a distance point source is brought by the objective of a telescope.
focal plane (or image plane)
the plane to which several beams of parallel light from a distance extended object are brought by the objective of a telescope.
focal length
the distance from the objective to the focal point inside a telescope.
eyepiece
a lens placed after the image plane of a telescope to create parallel light so that the human eye is capable of focusing it.
magnification
the focal length of the telescope objective divided by the focal length of the eyepiece used.
Formula: magnification = focal length of obj. ÷ focal length of eyepiece
chromatic aberration
the failure of the different color components of visible light to form a common focus when using a simple biconvex lens.
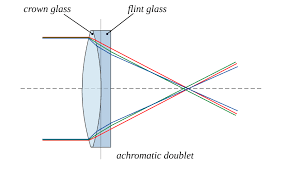
crown glass
a low-density glass. Solution to chromatic aberration.
flint glass
a high-density glass. Solution to chromatic aberration.
achromatic doublet
a lens formed by cementing crown glass and flint glass back-to-back to solve the chromatic aberration problem.
spherical aberration
the failure of light striking the edge of a spherically shaped optic (a mirror or lens) to form a common focus with light striking closer to the centerline.
The first image shows a correct lens
The second image shows a lens whose curve is incorrect.

Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope
a telescope that uses a spherical objective mirror and a corrector plate lens to solve the spherical aberration problem.
Cassegrain focus
when the focal plane of a telescope is located through a hole behind the objective mirror.
Airy disk
the actual pattern of light that is created at the focal point of a telescope by light from a distant point source.
resolution
the minimum angular separation between two distant point sources of light that can clearly be separated as such by a telescope.
north celestial pole
the imaginary point in the sky to which earth’s rotational axis points.
alt-azimuth mount
a telescope mount that uses two axes (one perpendicular and one parallel to the horizon) of tracking to compensate for Earth’s rotation.
equatorial mount (or polar mount)
a telescope mount that uses a single axis of tracking that is parallel to earth’s rotation axis to compensate for Earth’s rotation.
convection
the upward and downward movement of a fluid due to density differences caused by temperature differences between regions of the fluid.
seeing
a measure of the lack of twinkling (or lack of convection or lack of turbulence) of stars in the night sky when viewed from the earth’s surface.