Comprehensive Study Flashcards for Westward Expansion Test - Key Terms and Definitions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
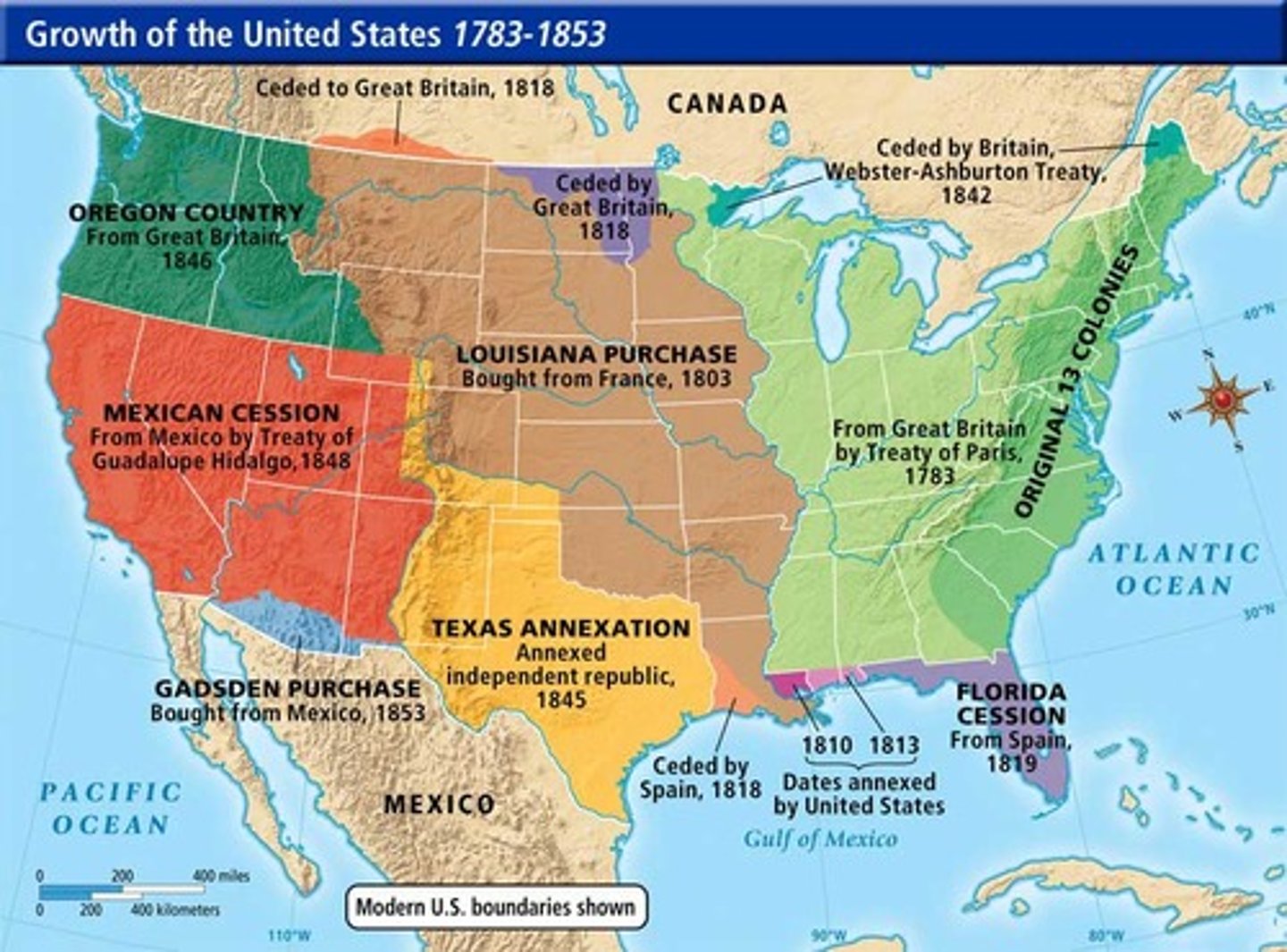
US Territorial Acquisitions Map
Study the map!
annex
to add a territory to a country (such an addition is called an annexation)
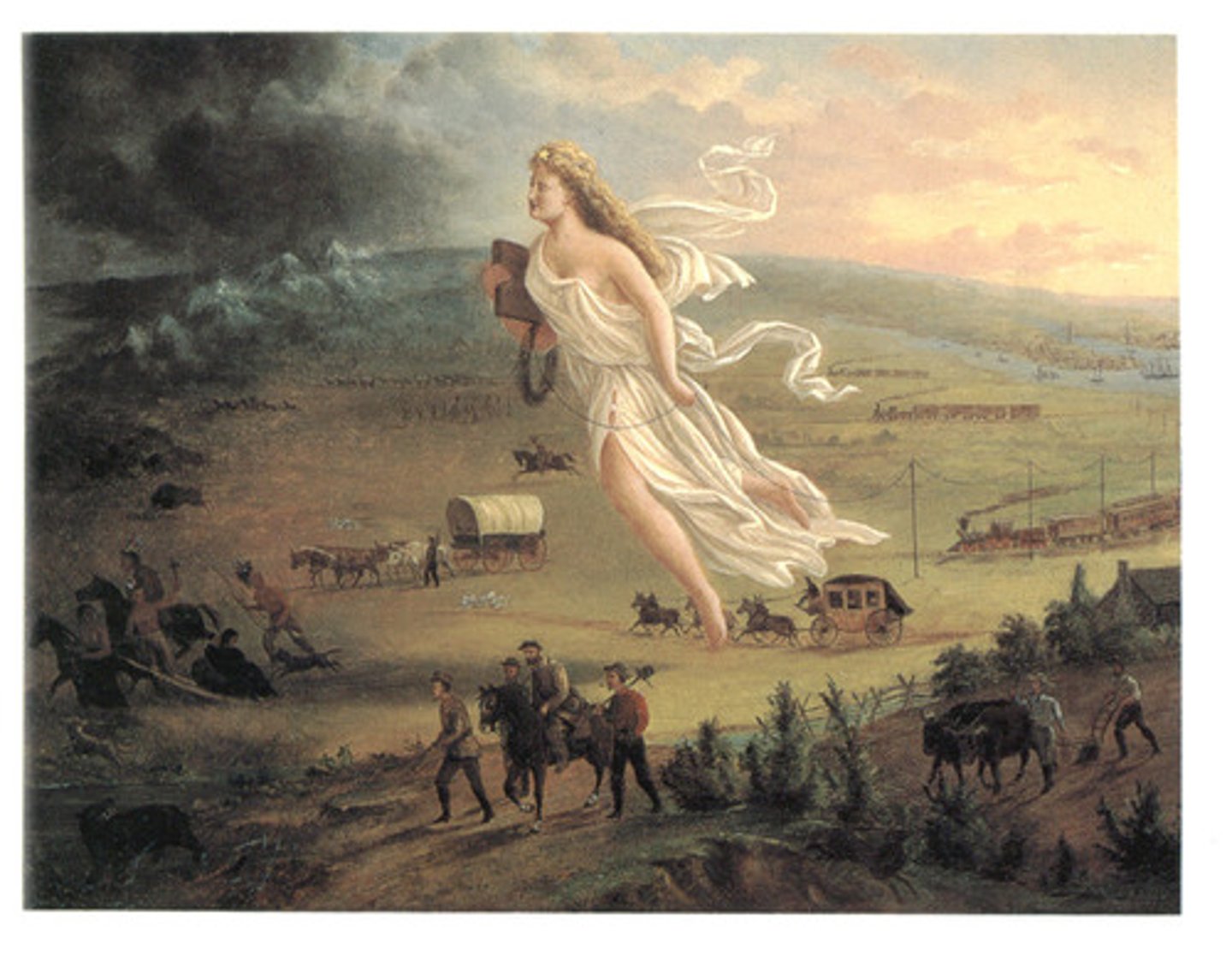
Manifest Destiny
Belief that it was God's will that the United States should spread across North America and bring American government, economy, culture, society, etc. to all those who lived there

John L. O'Sullivan
Newspaper editor who coined the term "manifest destiny"
Texas Revolution (1835-1836)
- Stephen Austin arrived in Texas just as Mexico declared its independence from Spain and took control of Texas
- When Stephen Austin asked for immigration to be reopened and for Texas to be made into its own Mexican state, Mexican General Santa Anna had him thrown in jail for promoting rebellion. After Austin was released in 1835, Texans rose up in revolt
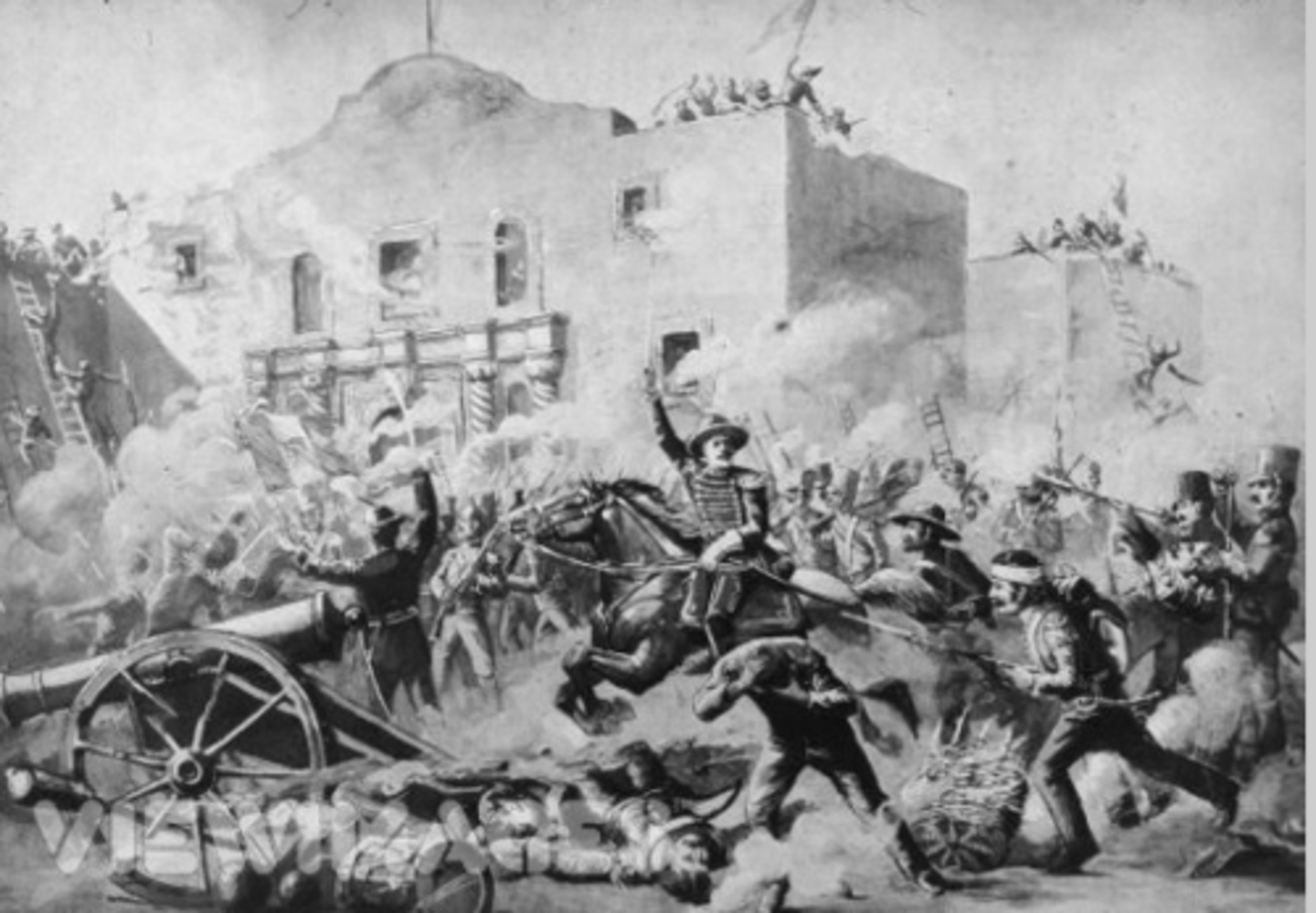
- General Santa Anna led the Mexican army to the Alamo in San Antonio, Texas and killed all the Texan soldiers there in March 1836
- Sam Houston led the Texan army to San Jacinto under the battle cry of "Remember the Alamo!" They captured Santa Anna and forced him to recognize Texan Independence
- Texas became an independent country from 1836-1845 called the Republic of Texas, or the "Lone Star Republic" because of the single star on its flag

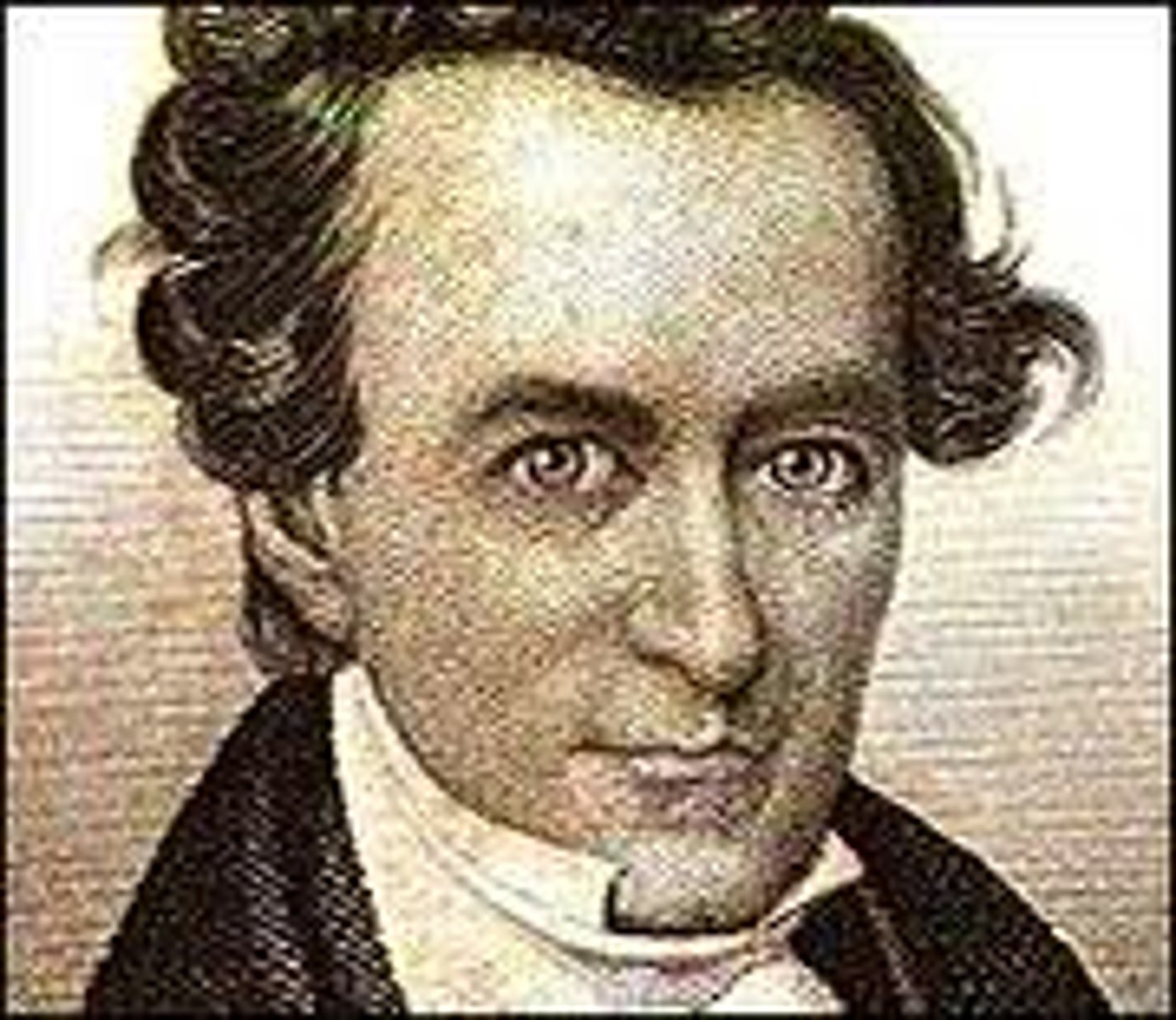
Stephen Austin
American leader who helped establish the Republic of Texas

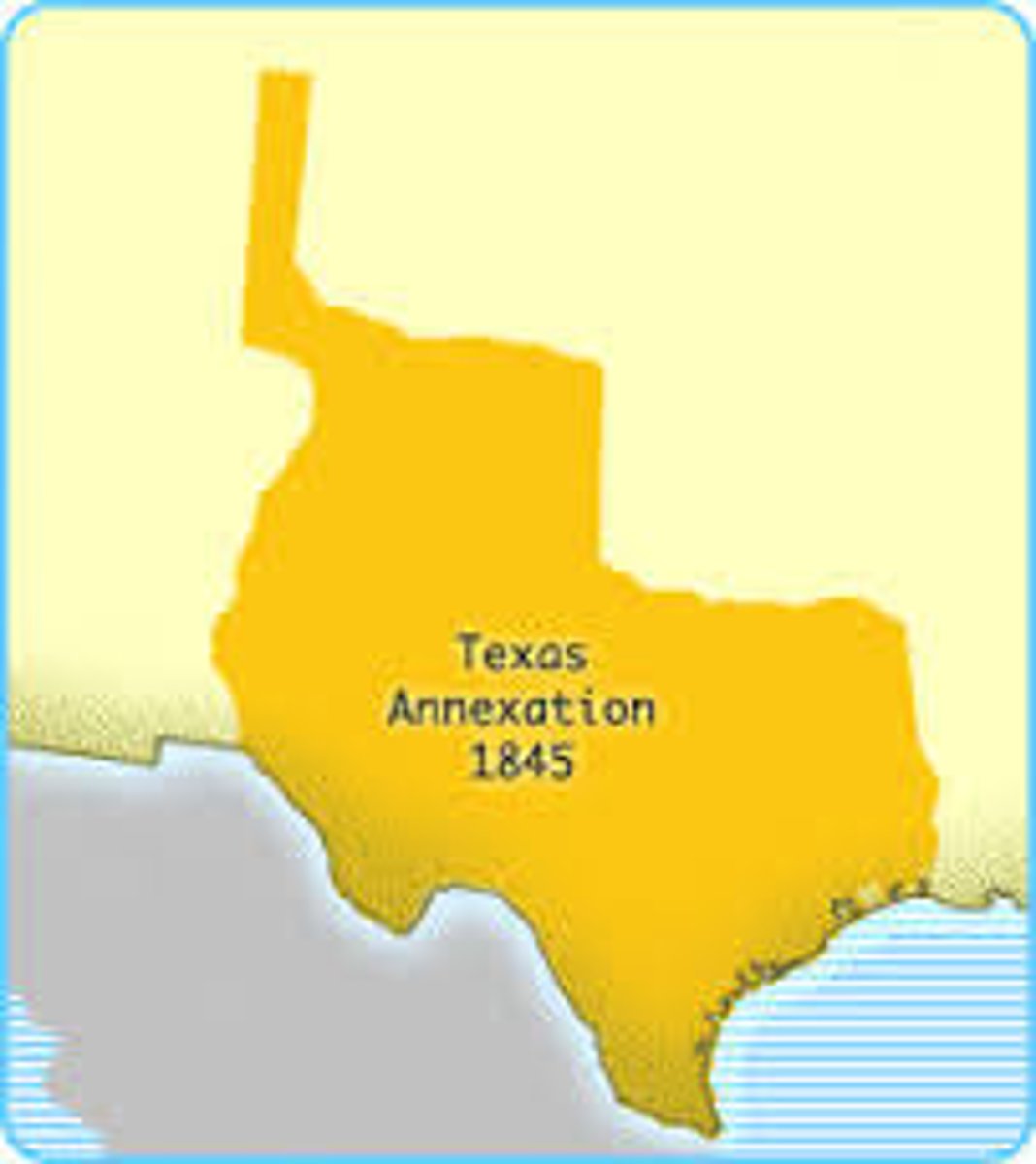
Texas Annexation (1845)
- While most Texans wanted Texas to become part of the United States, many Americans were divided on the issue of annexing Texas
- Since slavery was legal in Texas, Southerners were eager to add Texas as another slave state, while Northerners who opposed slavery did not
- After James K. Polk was elected president, Congress voted to annex Texas to the United States as the 28th state in 1845
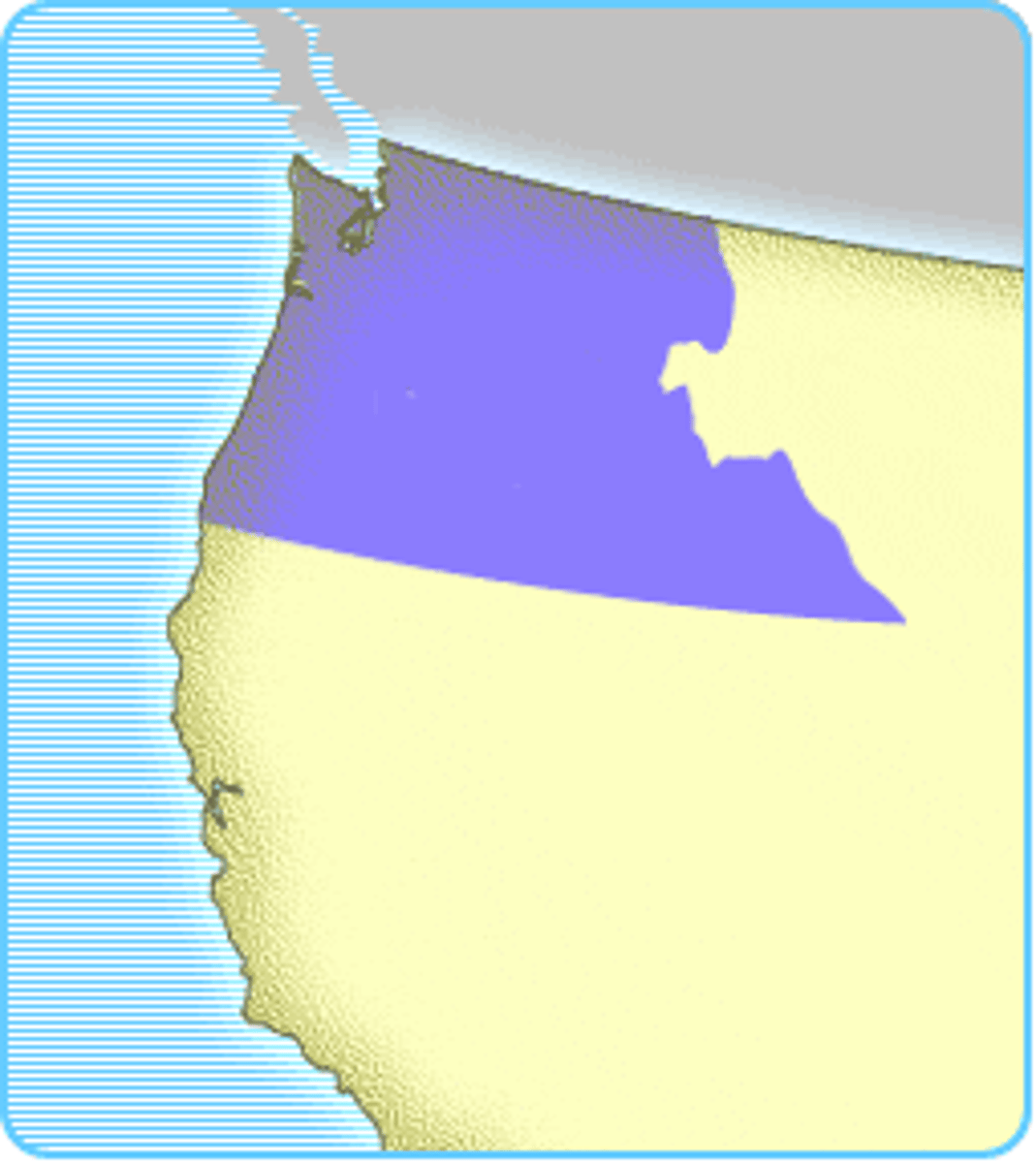
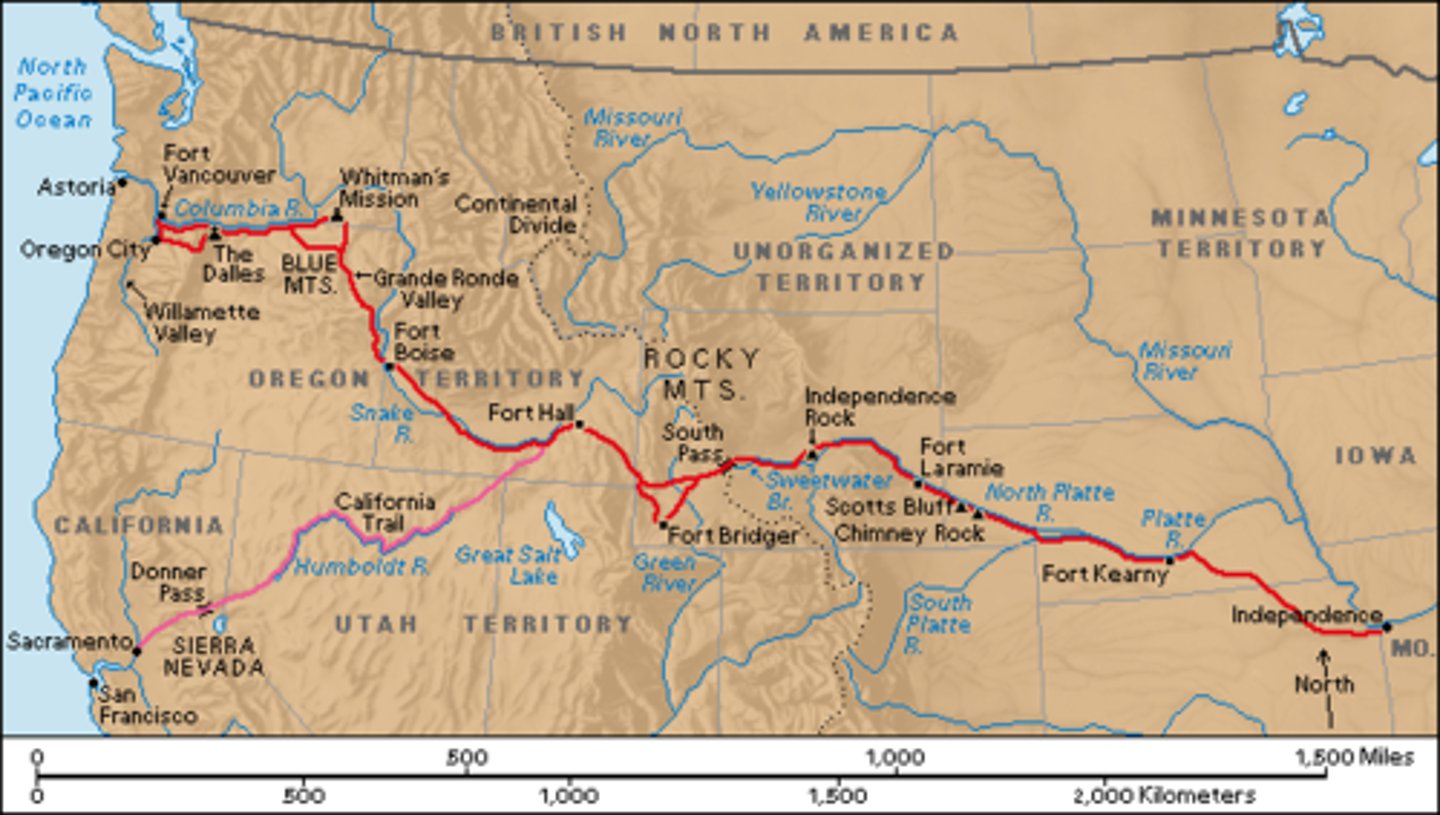
Oregon Country (1846)
- In 1825, both the United States and Great Britain claimed Oregon but agreed to a peaceful "joint occupation"
- The first American settlers to travel to Oregon were missionaries who hoped to spread Christianity to the Native American tribes living there
- They wrote letters home describing Oregon as a "pioneer's paradise" for its sunny weather, lack of disease, vast amount of trees, and available farmland
- In 1846, the United States agreed to split Oregon with Great Britain at the 49th parallel, which is the modern-day border between the US and Canada
Oregon Trail
Trail from Independence, Missouri to Oregon used by many pioneers during the 1840s
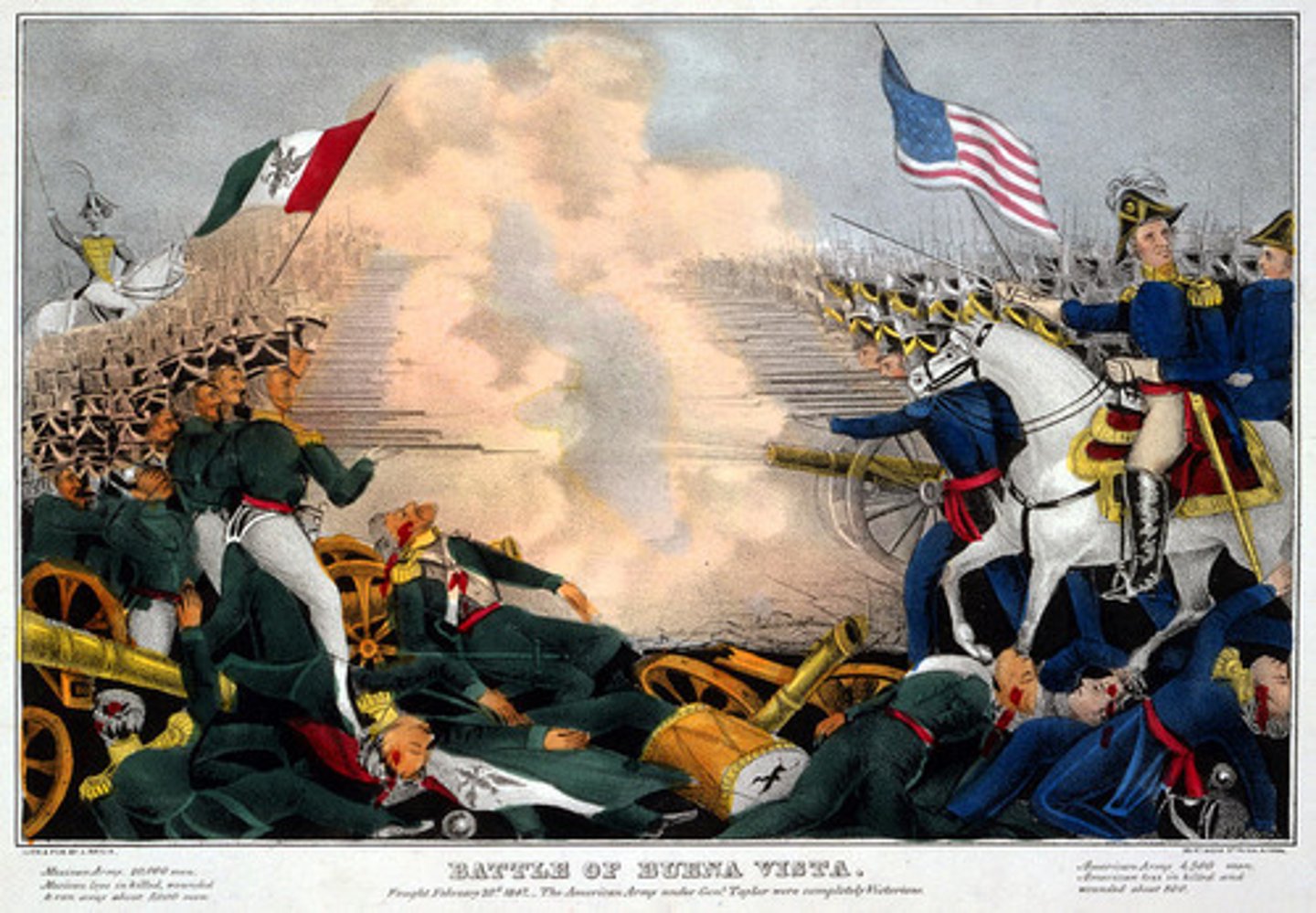
Mexican-American War (1846-1848)
- President James K. Polk attempted to purchase California and New Mexico from Mexico, but they were not interested in selling them
- Mexico considered the United States' annexation of Texas an act of war
- Mexico and Texas disagreed about where the southern border of Texas was
- Mexican soldiers fired on American troops patrolling the border along the Rio Grande River, which they considered to be Mexican territory
- The United States declared war on Mexico
- American Generals Zachary Taylor (who would later become president), and Winfield Scott invaded Mexico and were able to force the General Santa Anna and Mexican army to surrender after capturing Mexico City

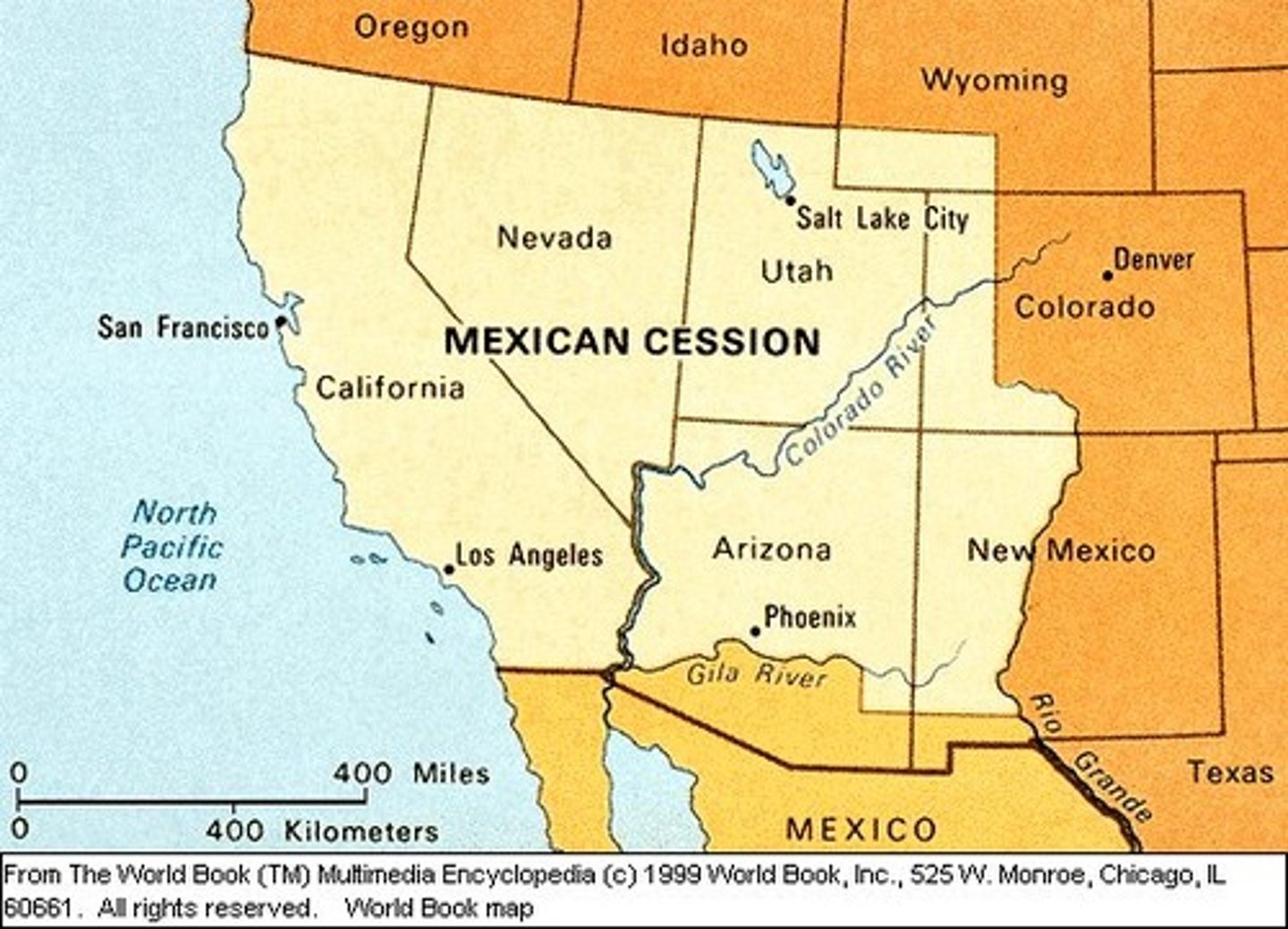
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848)
- Mexico gave up Texas and the Mexican Cession, which included the present-day states of California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico and parts of Colorado and Wyoming
- The United States agreed to pay Mexico $15 million
- The United States promised to protect Mexican citizens living in the Mexican Cession
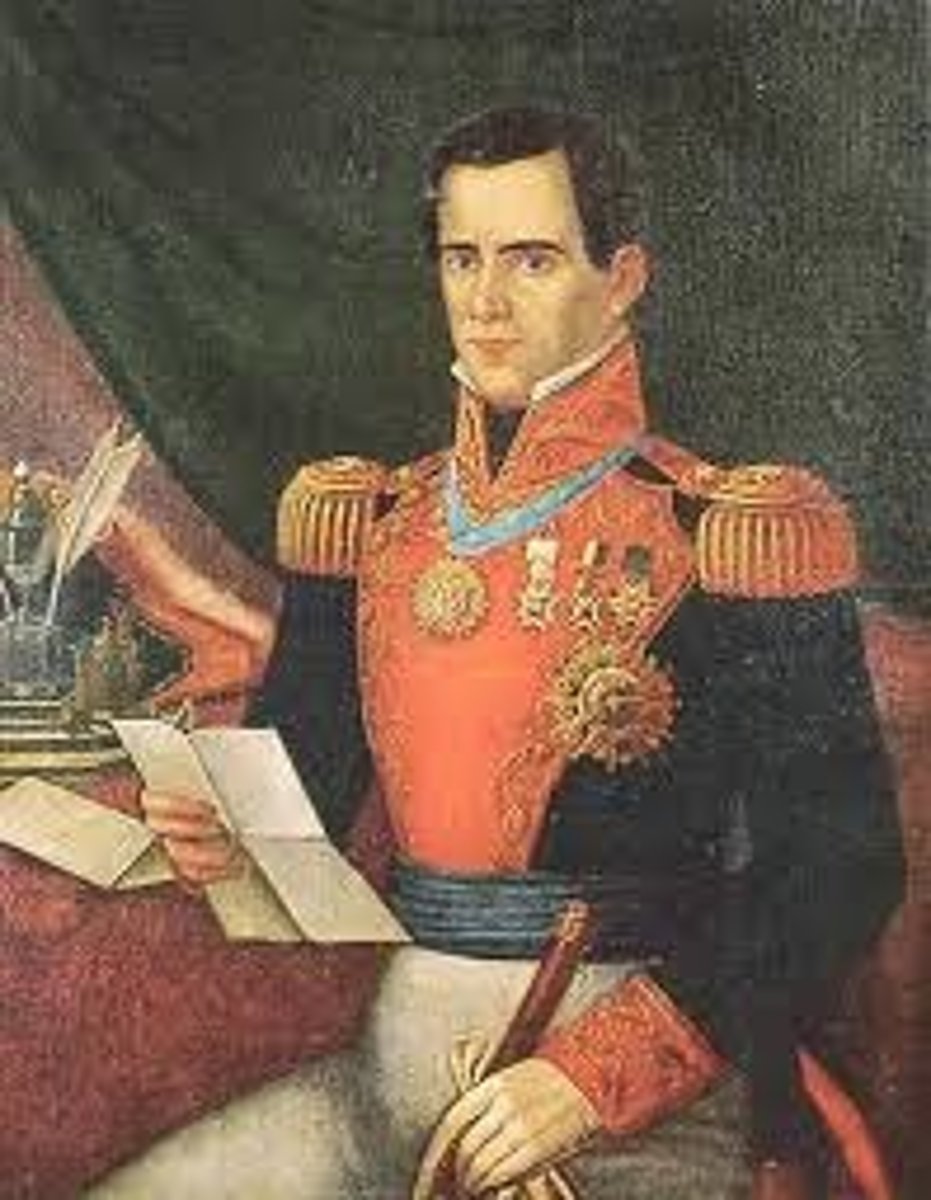
Antonio López de Santa Anna
Mexican general during the Texas Revolution and Mexican-American War

James K. Polk
President of the United States during the annexation of Texas, Oregon Treaty, and Mexican-American War

Zachary Taylor
American general during the Mexican-American War who later became President of the United States

Gadsden Purchase (1853)
- In 1853, James Gadsden arranged the purchase of a strip of land just south of the Mexican Cession for $10 million to build a railroad through the Southwest
- The acquisition of this land, known as the Gadsden Purchase, created the present-day border of the southwestern United States with Mexico

Californios
- Spanish-speaking soldiers and settlers
- Named many places in California today and introduced many of California's famous crops

Forty-Niners
- Mostly young, male Americans, but also people from Mexico, South America, Europe, Australia, and China who came to California in search of gold after it was discovered there in 1848
- The massive influx of people led to the deaths of many Native Americans and gave California enough people to become a state in 1850

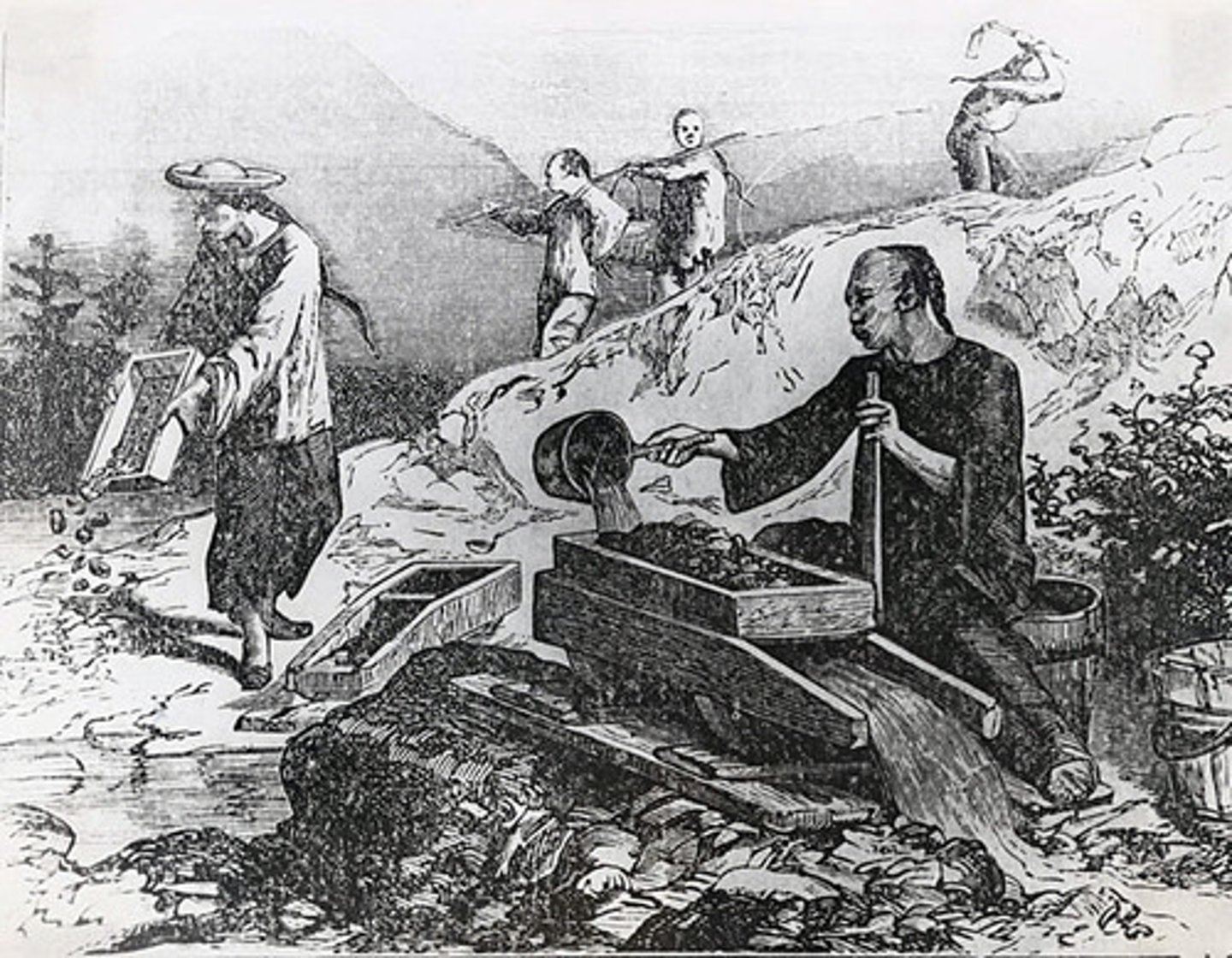
Chinese Immigrants
- Came across the Pacific Ocean to California
- Were often treated with prejudice and persecuted because they were from another country
- Mined gold, opened restaurants, laundries, and stores, drained swamps, and dug irrigation ditches
- Helped make California and the United States a more interesting place to live with their art, food, and music
persecuted
to cause a person or group to suffer

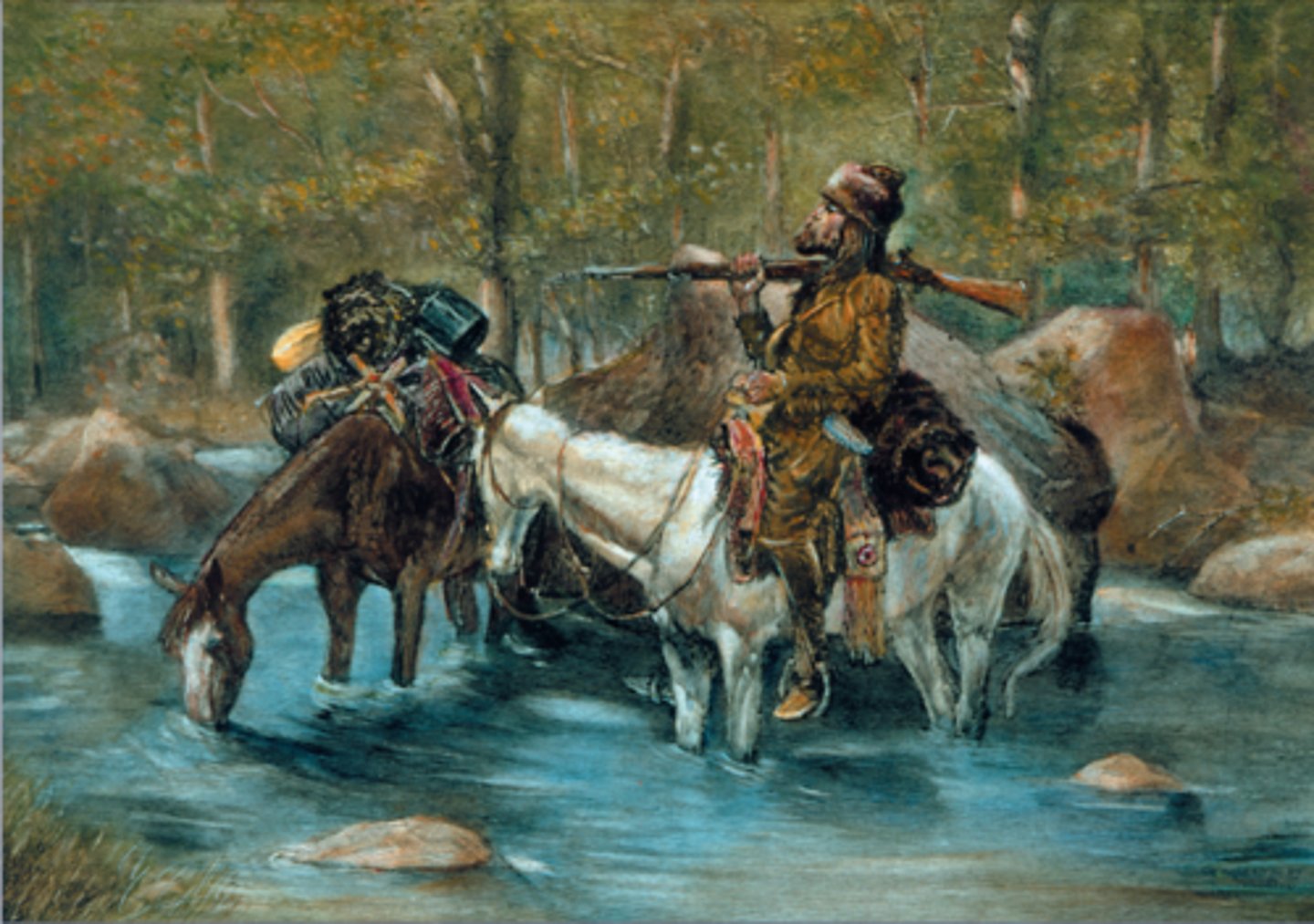
Mountain Men
- Fur trappers who would trap beavers then trade their furs for supplies
- They explored most of the West, and the routes they pioneered became the Oregon and California Trails

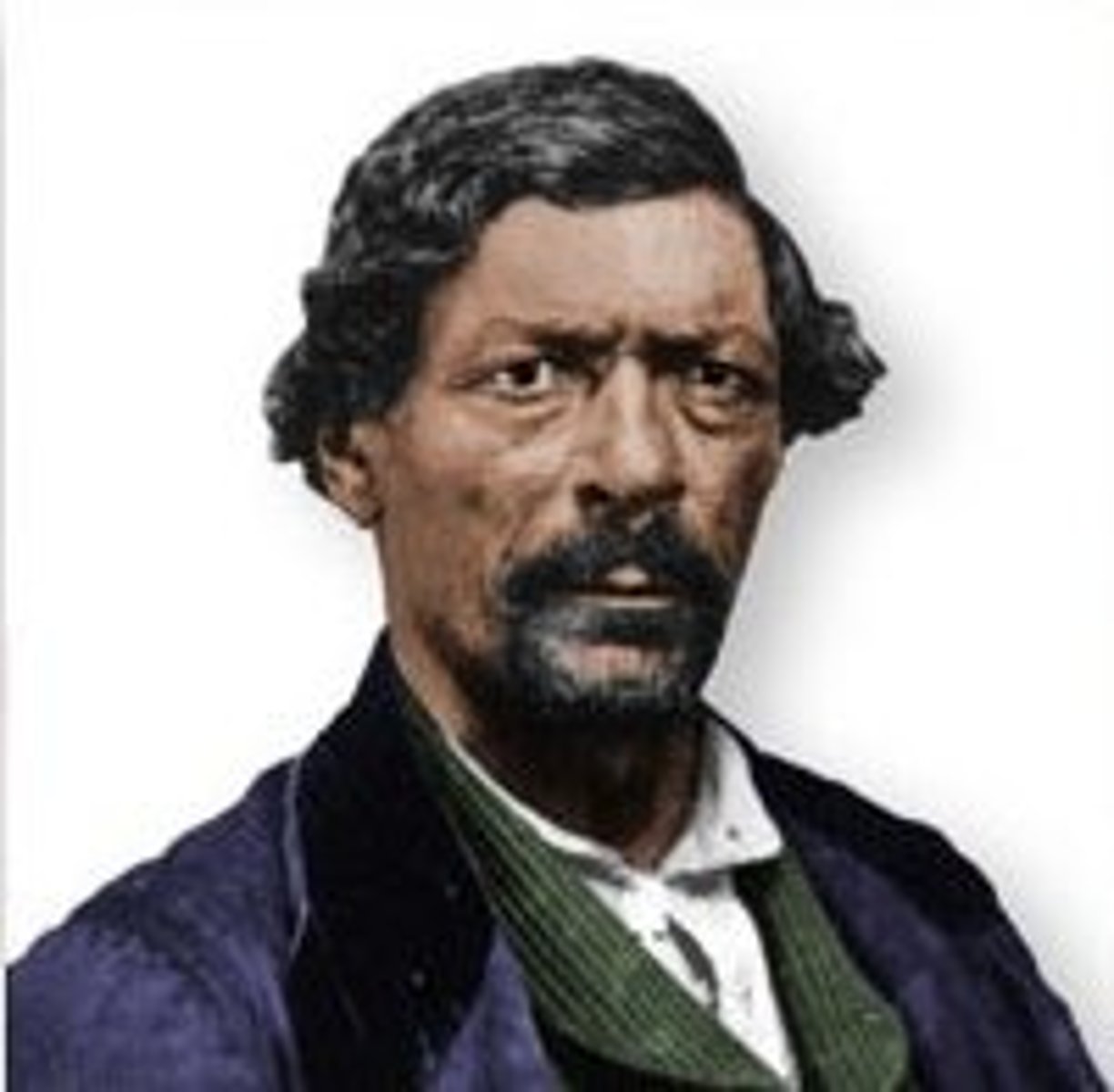
Jim Beckwourth
African-American fur trapper who was captured, adopted into the Crow Indian tribe, and later became their chief

Mormons
- Religious group founded in New York in 1830
- Mormons were persecuted because of their beliefs
- Under the leadership of Brigham Young, the Mormons traveled west and settled in Salt Lake City, Utah so they could freely practice their beliefs
- In Utah, they had to adapt to the hot and dry climate
- They learned new ways to farm, built dams, canals, and dug irrigation ditches to carry water from mountain streams to their farms in the valley

Brigham Young
Mormon leader who led the Mormons west to settle in Utah

irrigation
a system for bringing water to farmland by artificial means, such as using a dam to trap water and ditches to channel it to fields

Pioneer Women
- Women were expected to do the work they had done back home, such as cooking, washing clothes, and caring for the children, all while traveling 15 to 20 miles a day
- Women in the west gained the right to vote long before women in many states back East

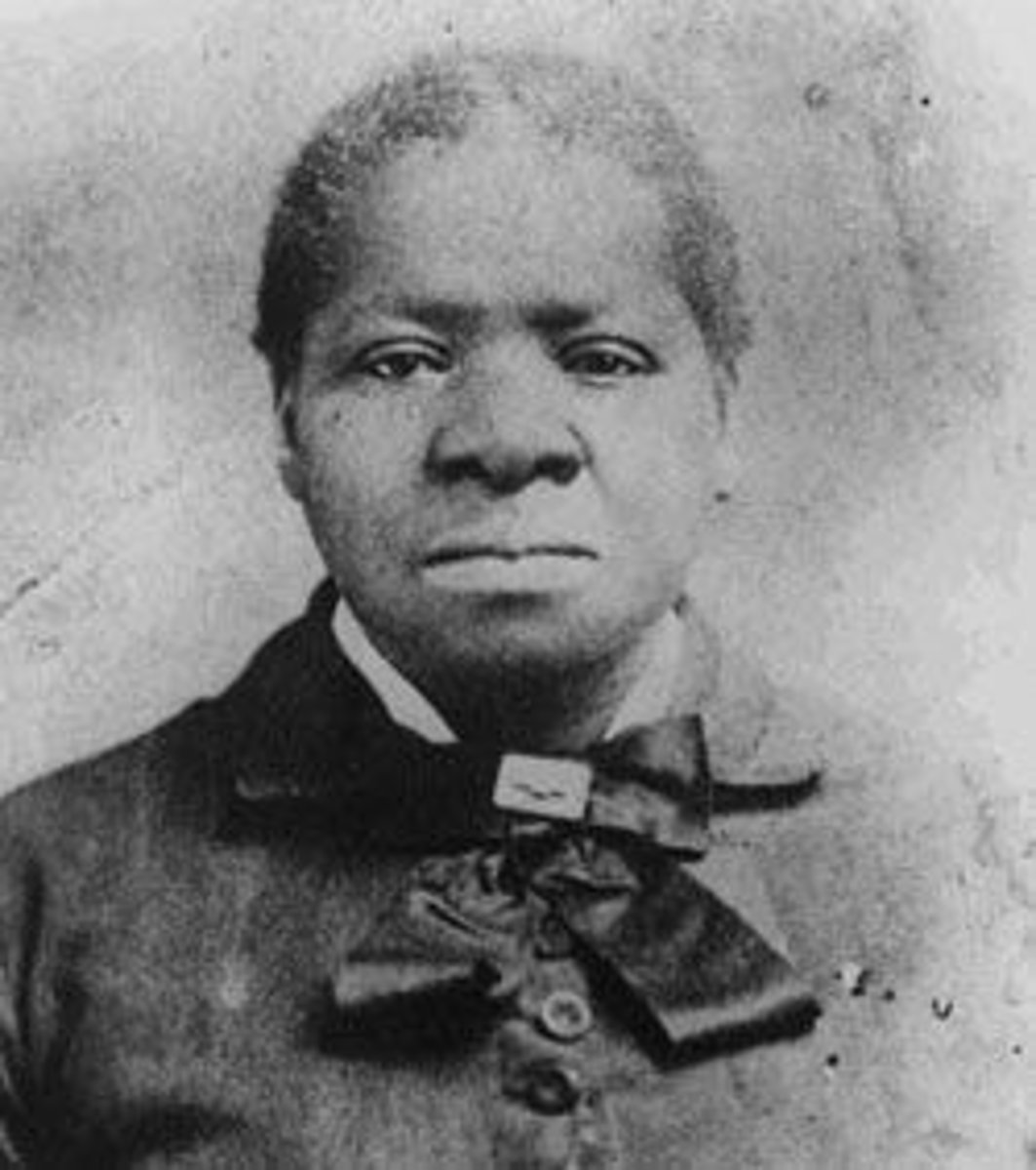
Biddy Mason
African American pioneer woman who won her freedom from slavery and settled in the West

Annie Bidwell
Pioneer woman who settled in the West and fought for women's right to vote

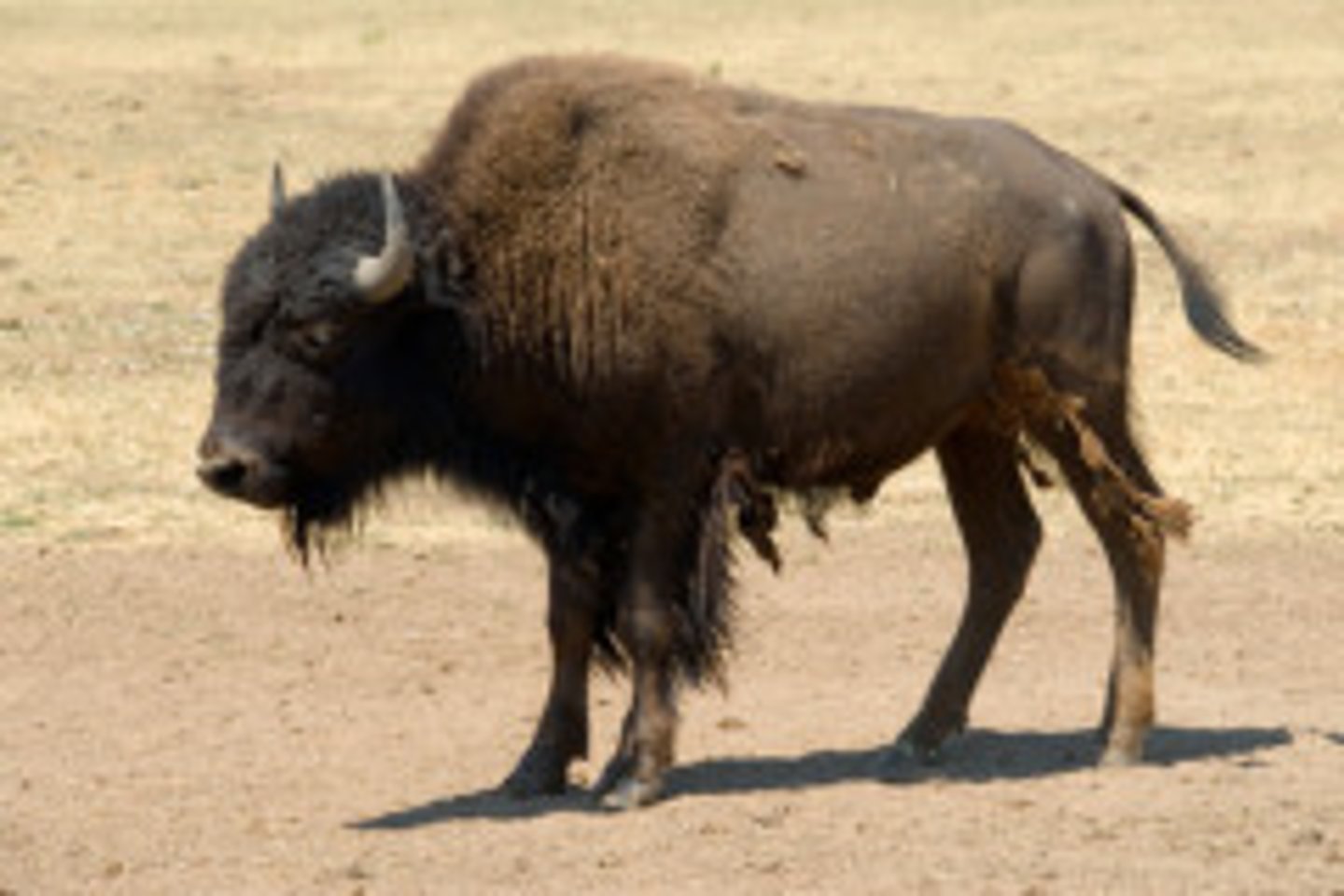
Buffalo
- An animal that was used by Native Americans in the Great Plains for food, shelter, clothing, tools, etc.
- As American settlers moved west, they killed off many of the buffalo until they went almost extinct

Treaties with Native Americans
US government attempted to make treaties with Native Americans to prevent fighting
Reservations
Many Native American tribes were pushed out of their lands and forced to move to reservations

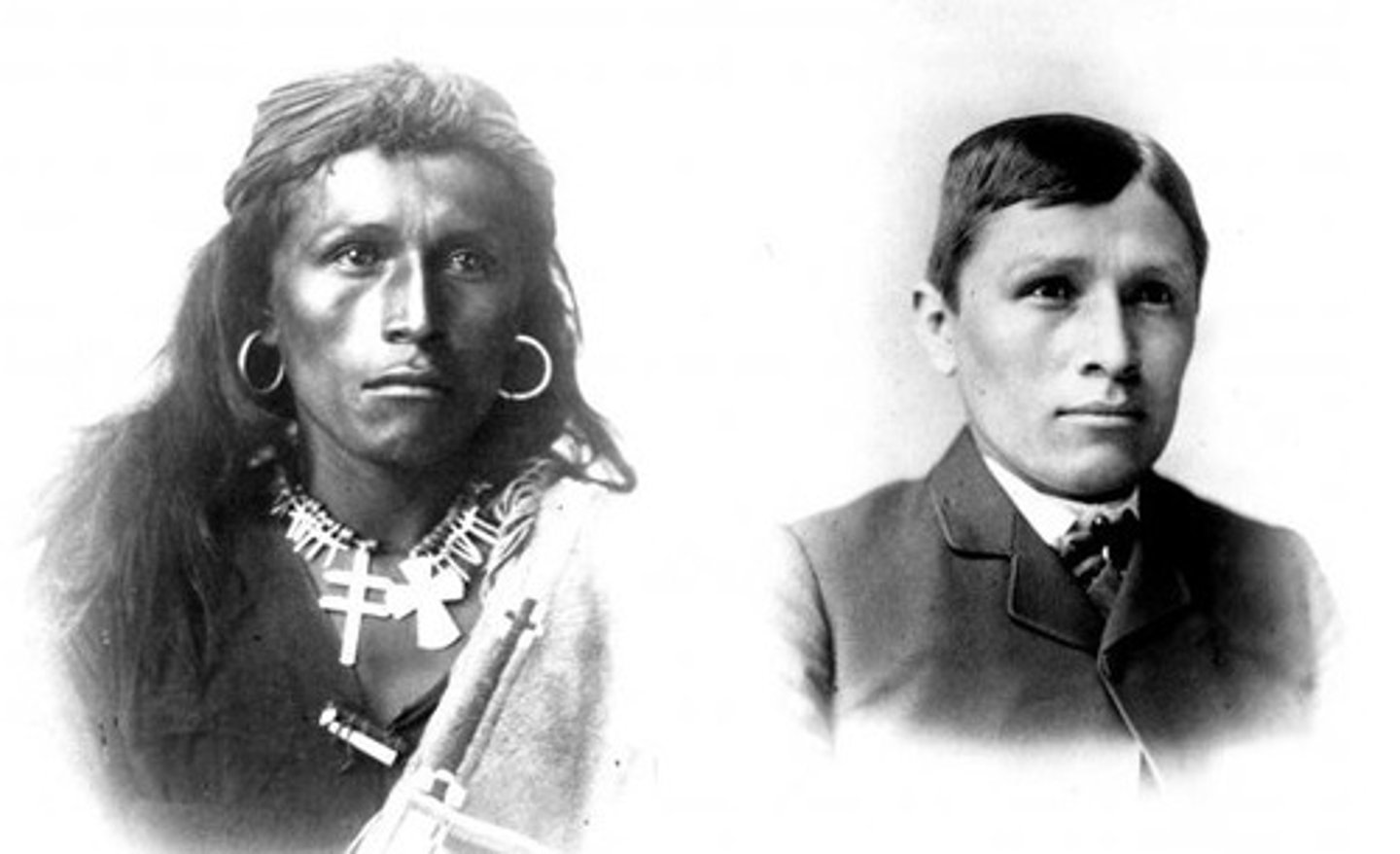
Assimilation
Reformers attempted to assimilate Native Americans into American culture by teaching them English, cutting their hair, having them dress like white people, etc. They also encouraged them to farm instead of hunt.

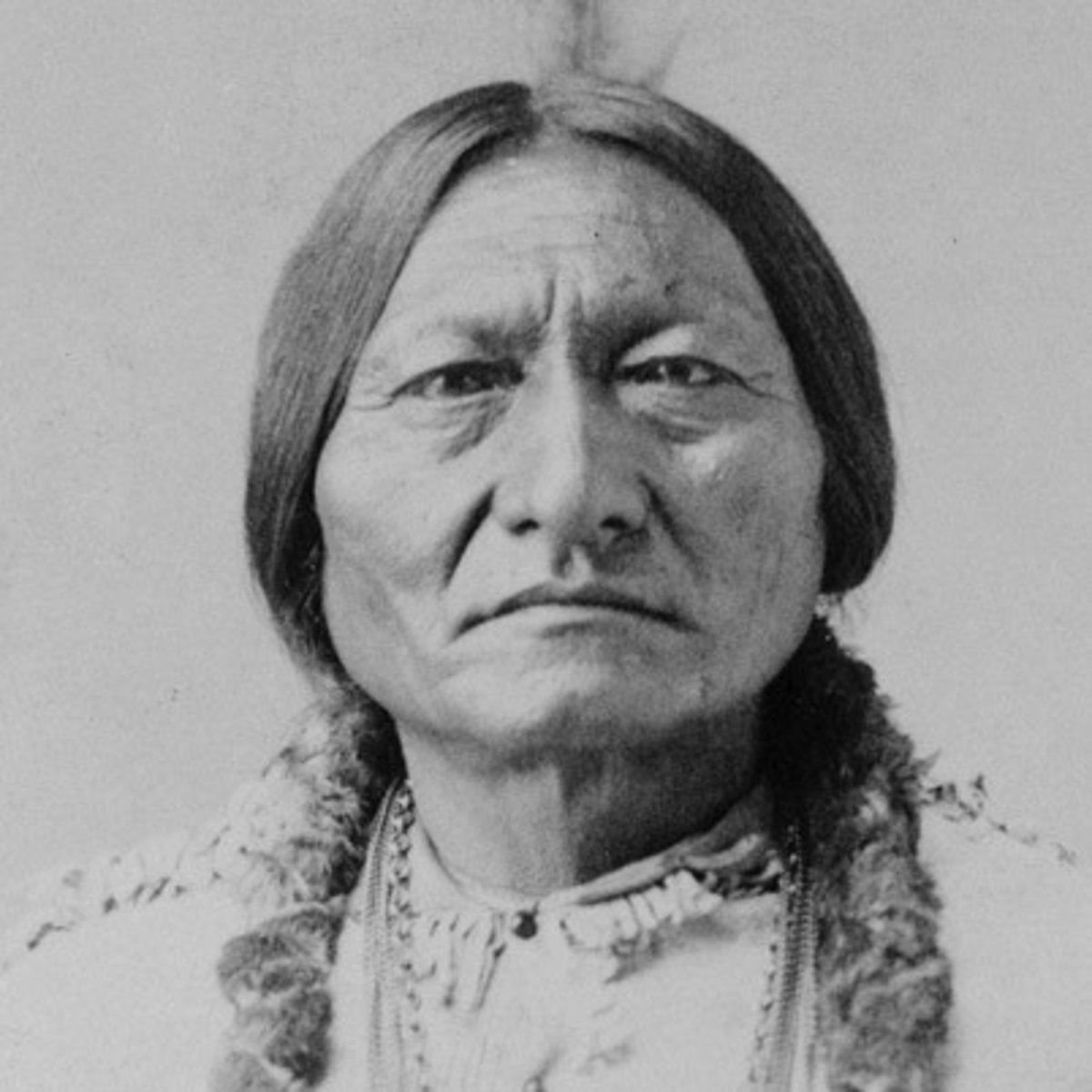
Sitting Bull
- Leader of the Lakota Sioux
- Refused to sell his people's land to the US government
- Defeated US troops led by George Armstrong Custer in the Battle of Little Bighorn

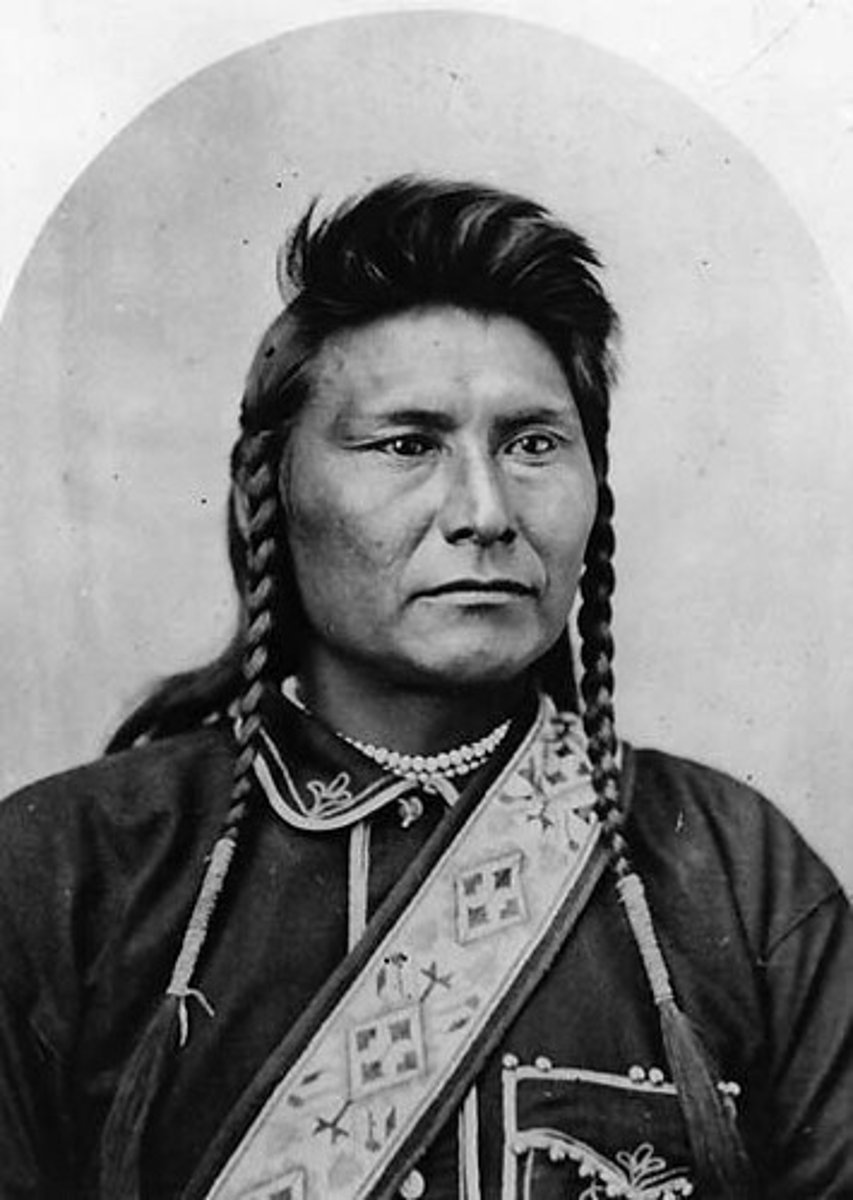
Chief Joseph
- Leader of the Nez Perce
- Refused to leave his lands in Oregon to go to a reservation in Idaho so he led 800 of his people in an attempt to escape to Canada
- Caught by the US army near the border of Canada and ordered his people not to fight
- Gave a famous speech where he said, "My heart is sick and sad. From where the sun now stands, I will fight no more forever."

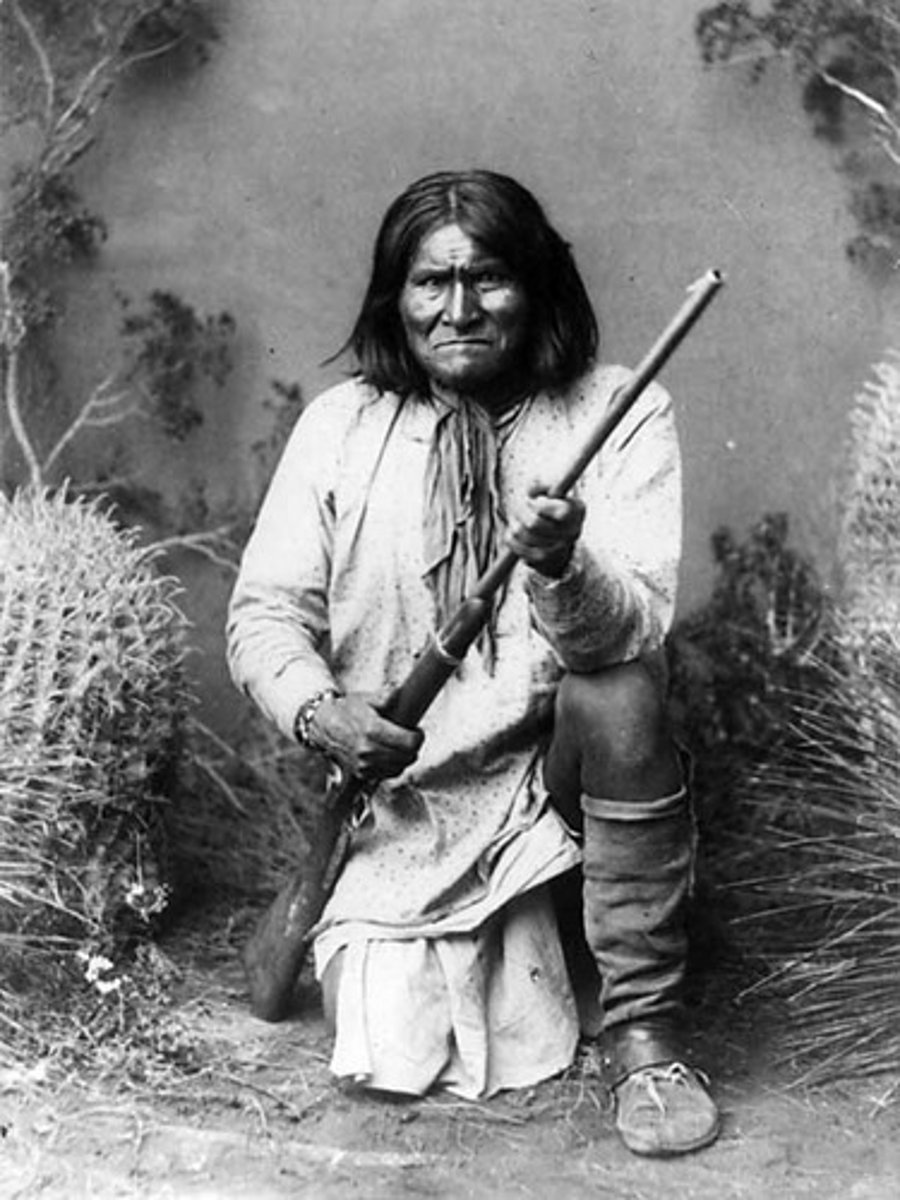
Geronimo
- Leader of the Apache
- Led raids on new US settlements in former Apache and Navajo lands
- Frustrated the US army for years, evading capture
- Last Native American to formally surrender to the US government

Battle of Wounded Knee
- The US Army arrived at a creek called Wounded Knee and demanded that the Sioux surrender their weapons
- A deaf Native American did not understand what was happening and when a soldier tried to take his gun away, a struggle began
- The gun went off and the soldiers opened fire, killing hundreds of Native Americans in the massacre
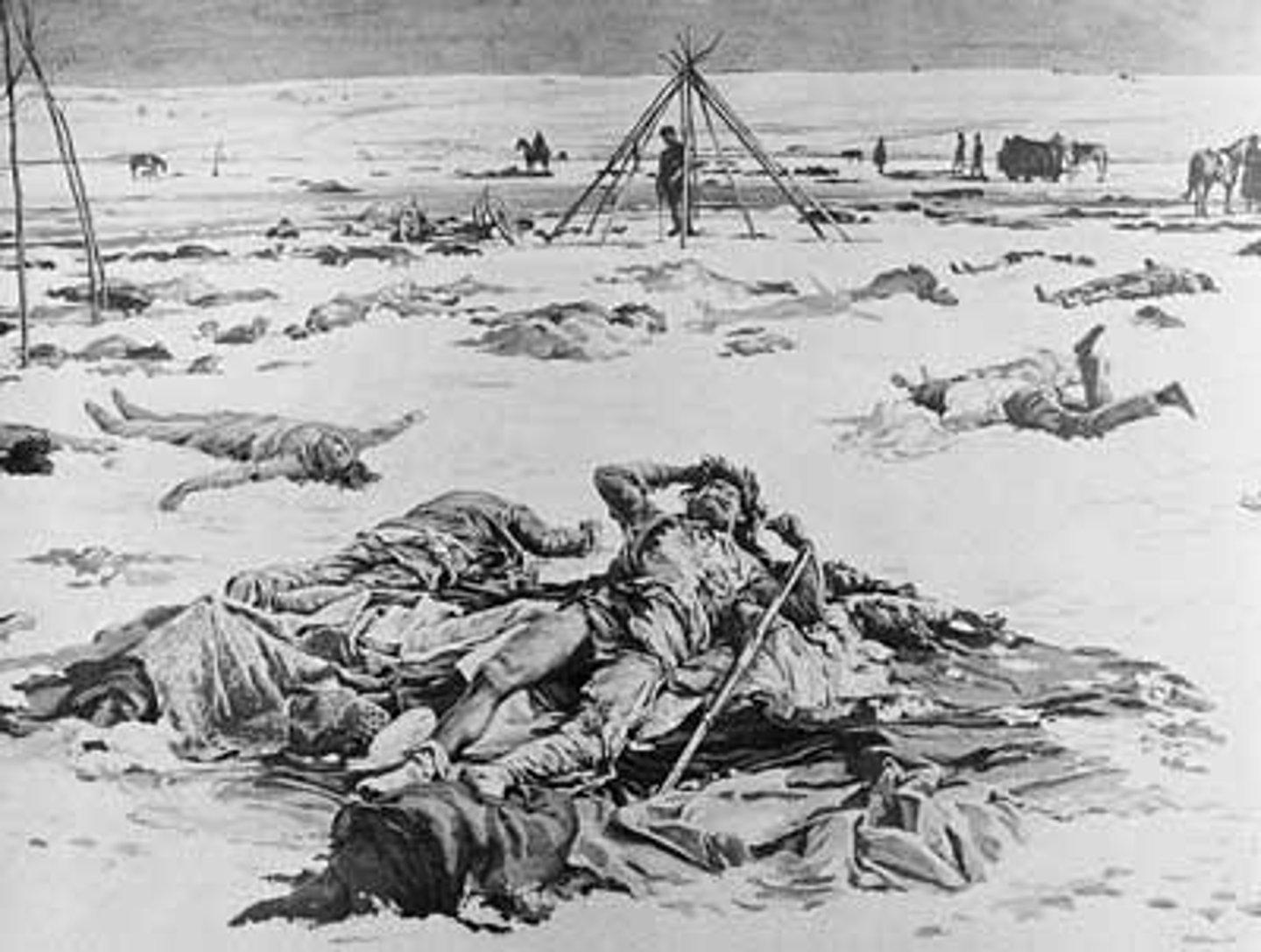

Westward expansion's effect on Native Americans
Many Native Americans were killed by warfare and diseases brought by the settlers who were moving west