HLTS 480- Special Sensory Systems
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
left
sensation on the right side of the body is delivered to the _________ side of the brain
spinal cord
afferent neurons from pain or temperature receptor cross over when they enter the ________ ________
brainstem
receptors for body movement, limb positions, fine touch discrimination, and pressure
pain, temperature
in the anterolateral system, afferent neurons from _________ or ___________ receptors cross over at the spinal cord
movement, positions, fine, pressure
in the dorsal column system, receptors for body _________________, limb _______________, ________ touch discrimination, and _______________
optical, neural
vision has a...
__________ component which focuses the visual image onto the receptor cells
____________ component which transforms the visual image into a pattern of graded and action potentials
visible light spectrum
the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye
lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
Sclera
white of the eye that blocks light
pupil
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
iris
a ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening
retina
location of photoreceptors
- extension of the optic nerve
optic disc
Region at the back of the eye where the optic nerve meets the retina
macula lutea
a yellowish central area of the retina that is rich in cones and that mediates clear detailed vision
- few blood vessels
fovea centralis
tiny pit or depression in the retina that is the region of clearest vision
inverted, backwards
When light enters the eye, the image is ___________ and _____________
Refraction
The bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another
ciliary muscles
muscle that pulls on the lens to change the light angles
- controls the opening of the pupil
converges
light _______________ right when it meets the retina in order for the image to be in focus
nearsighted
condition where the eyeball is too long
concave
nearsightedness is corrected by ___________ lenses
farsighted
condition where eyeball is too short
convex
farsightedness is corrected by __________ lenses
cones
the foveal centralis has a high concentration of ________ and a low concentration of _________ ___________
opthalmoscope
instrument used to examine the interior of the eye
hemorrhage
Excessive or profuse bleeding that can be seen as dark spots in an unhealthy eyeball
exudate
fluid, such as pus, that leaks out of an infected wound seen as light spots in an unhealthy eyeball
optic cup
the depression in the center of the optic disc
high
a cup:disc ratio exceeds 0.5 may indicate ________ intraocular pressure
glaucoma
increased intraocular pressure results in damage to the retina and optic nerve with loss of vision
oculomotor nerve
Cranial nerve III
- innervates the skeletal muscles that move the eye
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain
each
The right and left eye relay information to nerves that travel to ________ occipital lobes
right optic tract
Damage to _________ _________ _________
- loss of the left half of the field of vision of each eye
cross
damage to optic fibers that _________ at the optic chiasm
- loss of outer half of the visual field of each eye
left occipital lobe
damage to _______ ___________ ______
- loss of the right half of the field of vision of each eye
optic tract
leads from optic chiasma to terminate in lateral geniculate body
rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray
- used for low light vision
less
rods are _________ sensitive than cones
presbyopia
loss of elasticity in the lens with age
- causes need for reading glasses
cataract
clouding of the lens due to the dying of cells
- can replace lens surgically
macular degeneration
breakdown or thinning of the tissues in the macula, resulting in partial or complete loss of central vision
age related macular degeneration
form of macular degeneration occurring in approximately 30% of individuals over the age of 75
pitch
determined by the frequency of sound waves
loudness
determined by the amplitude of soundwaves
tympanic membrane
thin layer of proliferative skin cells separating the outer and middle ear
stapes
last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
- pushes on the oval window
Eustachian tube
A narrow tube between the middle ear and the throat that serves to equalize pressure on both sides of the eardrum
scala vestibuli
leads from oval window to apex of cochlea
scala tympani
extends from apex of cochlea to round window
helicotrema
connection of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani a the far end of the cochlear duct
cochlear duct
a fluid filled cavity within the cochlea that vibrates when sound waves strike it
vestibuli, basilar membrane, tympani
pressure waves travel through the perilymph of the scala ____________, vibrate the ___________ _____________ of the cochlear duct, and exit through the round window via the scala __________
basilar membrane
A structure that runs the length of the cochlea in the inner ear and holds the auditory receptors, called hair cells.
Organ of Corti
Center part of the cochlea, containing hair cells, canals, and membranes that ultimately cause the firing of receptor potentials
high, low
_______ frequency vibrations occur closer to the oval window, _____ frequency vibrations occur closer to the helicotrema
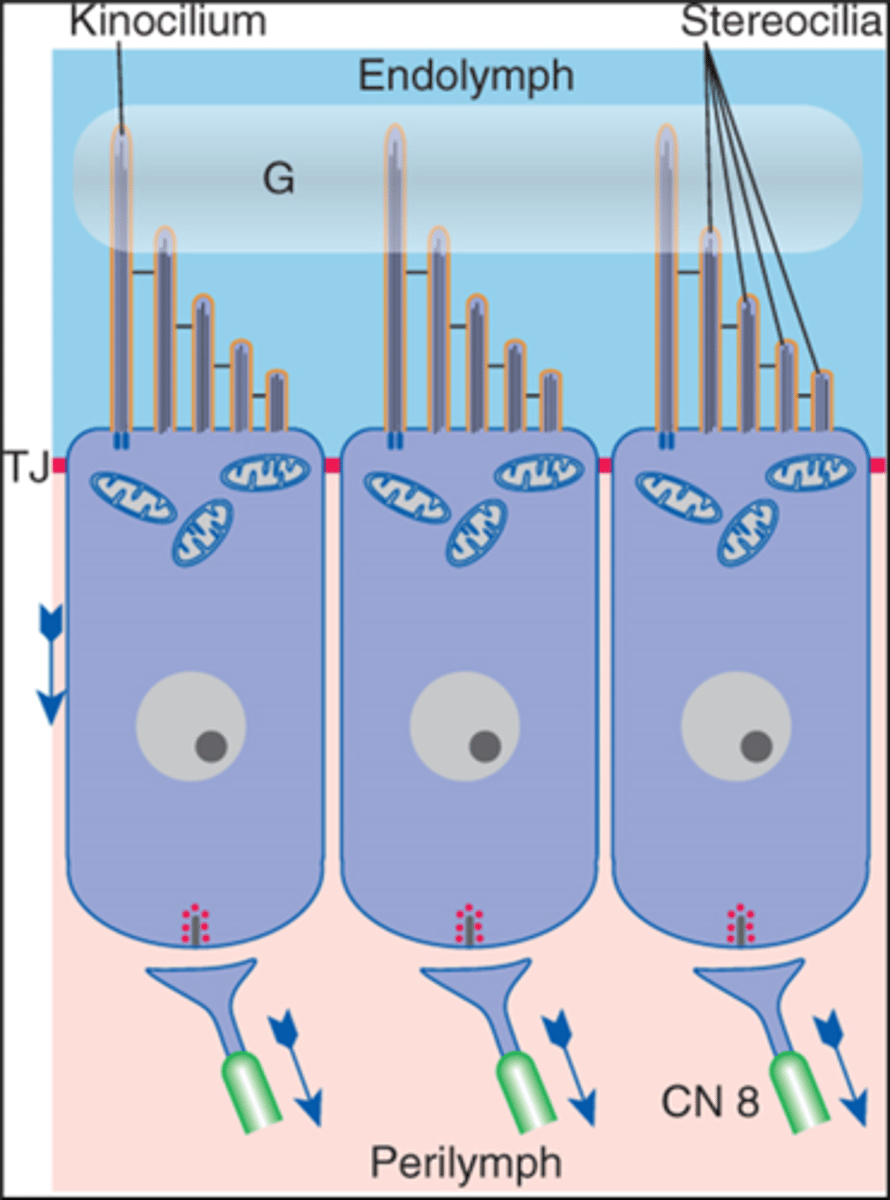
tip links, potassium, calcium, glutamate
in the organ of corti
1. stereocilia are bent toward the tallest member of a bundle
2. _____ ________ pull open mechanically gated gation channels
3. influx of _______________, which depolarizes the membrane
4. opens voltage gated _____________ channels near cell base
5. release ____________________
6. channels close by bending stereocilia in opposite direction
brainstem, thalamus, cortex, temporal
(vestibulo)cochlear nerve fibers synapse with interneurons in the _______________, travel through the ___________, before arriving at the auditory ____________ in the _____________ lobe
cochlear implant
a device for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve through electrodes threaded into the cochlea
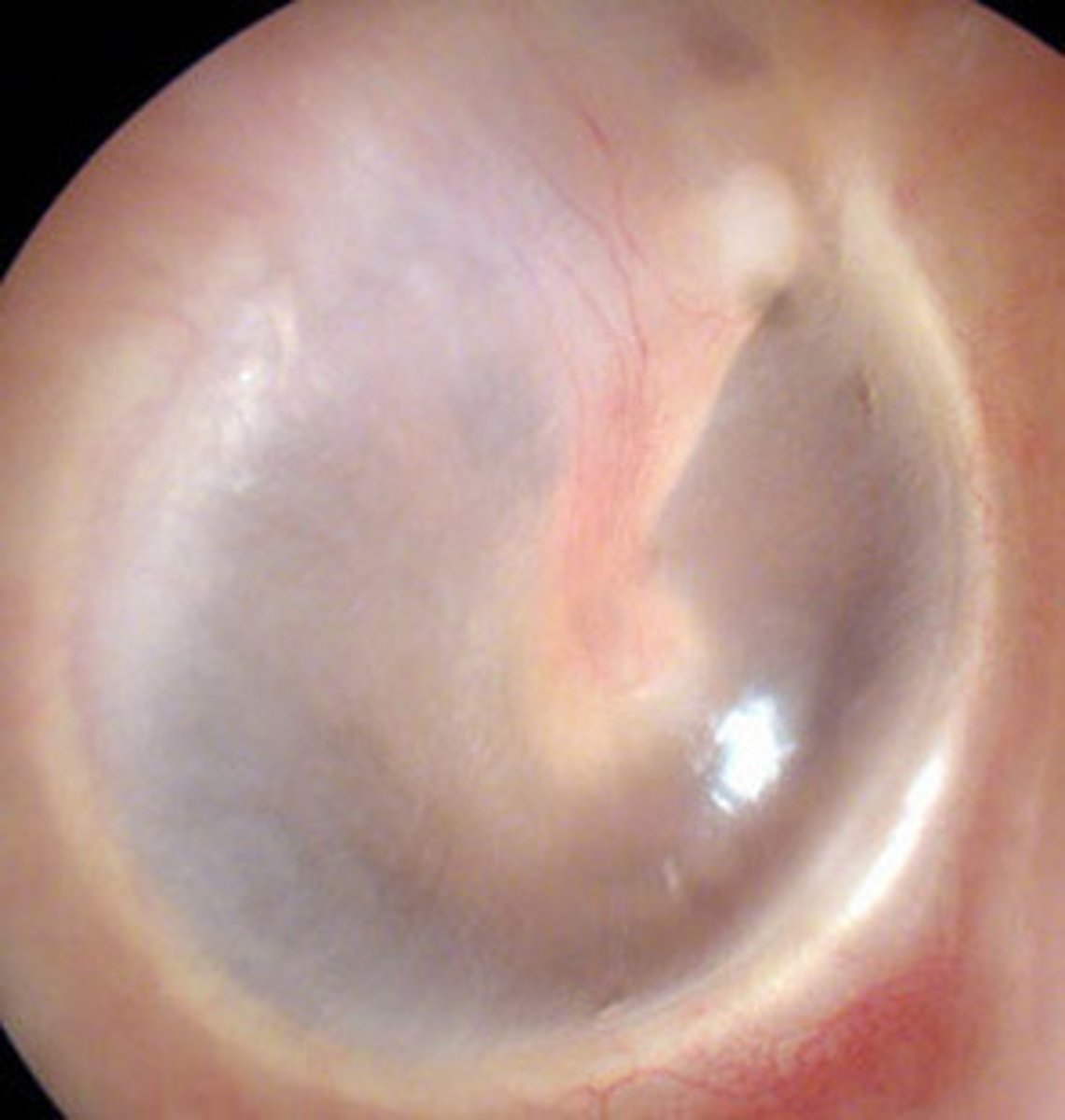
healthy tympanic membrane
- very thin
- almost transparent
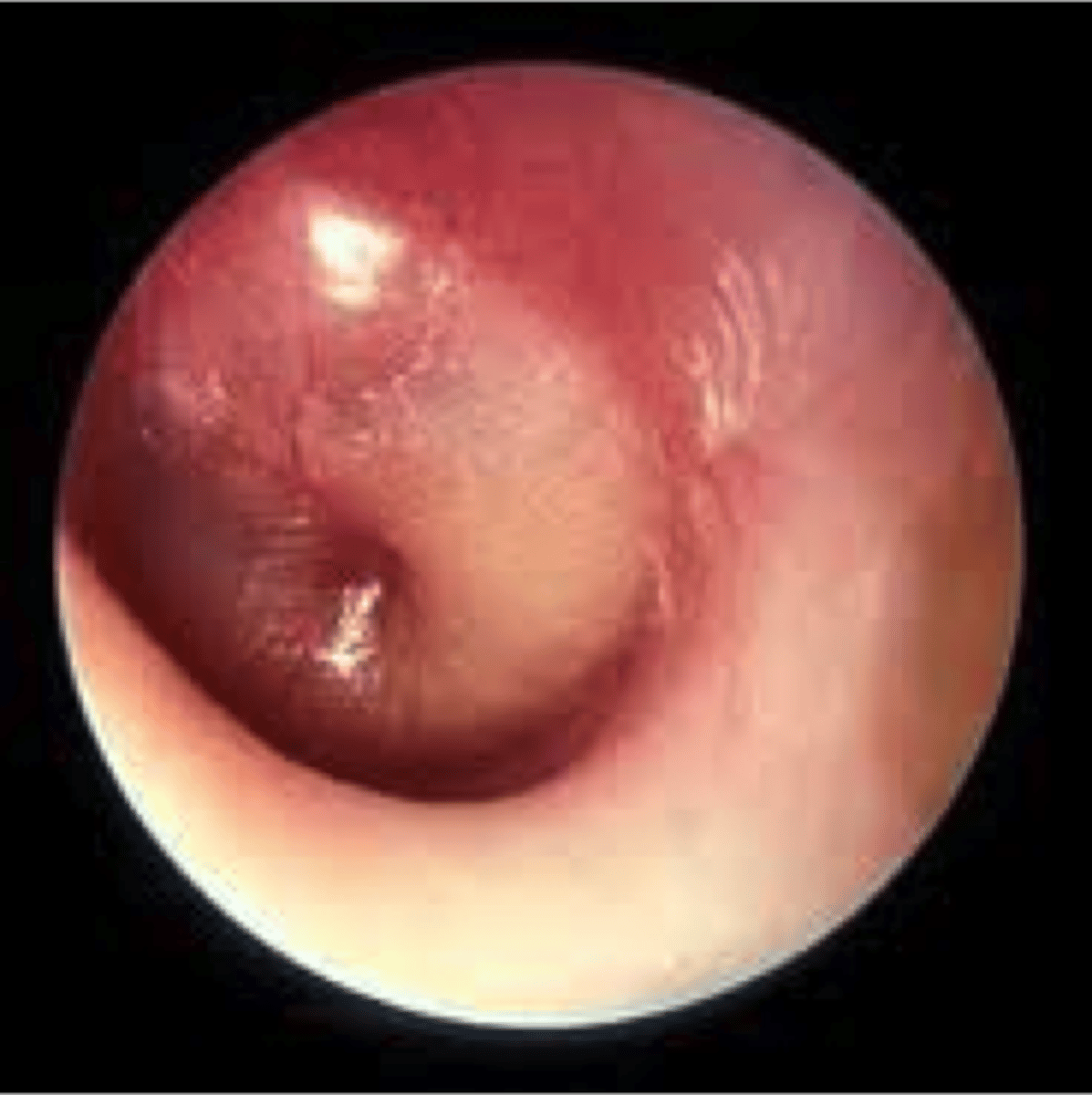
otitis media
technically inner ear infection on the slides
- inflamed and filled with fluid
india ink
marking tool to determine the growth pattern of skin cells in the tympanic membrane
vision, vestibular, proprioception, touch
since posture integrates _____________, __________ information, ________________, and touch (especially in the feet) it is difficult to find the origin of balance problems
semicircular canals
detect angular rotation of the head
- one canal for each axis
ampulla, cupula
is a structure in the vestibular system, providing the sense of spatial orientation, particularly with rotation
saccule, utricle
Fluid-filled sacs of the vestibular organ that inform the brain about the body's orientation
- location of your head in space
inertia, ampulla, stereocilia
Semicircular canals
1. head moves, and the hair cells of the cilia move with it
2. _____________ causes fluid in the semicircular duct to remain stationary
3. ______________ is pushed against the stationary fluid
4. ______________ bend causing depolarization or hyperpolarization
unstimulated, depolarization, hyperpolarization
semicircular canal hair cells
- ______________ hair cells release a baseline frequency of action potentials
- pushing the hair cells in one direction causes _________________, increasing the frequency
- pushing the hair cells in the other direction causes ____________________, decreasing the frequency
otolith
a calcium particle in the vestibule of the inner ear that adds extra weight to the lymph in th eutricle
vertigo
caused by the otoliths getting lodged
sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami
5 basic tastes
ligand
the gustatory system is ___________ stimulated (once they're dissolved in water)
glucose
stimulates sweet receptors
sodium
stimulates salty receptors
hydrogen ions
stimulates sour receptors
miscellaneous ligands
stimulated bitter receptors
glutamate
stimulates umami receptors
mucus
in order to smell something, the odorant must be dissolved in _______________
chemical senses
taste and smell