Chapter 14: Antimicrobial Drugs
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Antibacterial Drugs
Aka antibiotics
natural
Semisynthetic Drugs
Synthetic Drugs
Antifungal, Antiprotozoal, Antiviral drugs
Antibiotics
naturally occurring antimicrobials
Metabolic products of bacteria and fungi
Reduce competition for nutrients and space
Bacteria: Streptomyces and Bacillus
Molds: Penicillium and Cephalosporium
Selective Toxicity
The drug kills pathogens without damaging the host.
Becomes more difficult to achieve, and more side effects are seen when the infectious agent becomes more similar to the vertebrate host cell.
Antimicrobial Drugs
Disrupt the cellular processes or structures of bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.
Inhibit virus replication.
Cell Wall
Penicillin
DNA Synthesis
Fluoroquinolones
RNA Synthesis
Rifamycin
Plasma Membrane
Polymyxin B and Lipopeptide
Ribosomes
30S Subunit, 50S subunit
Metabolic Pathways
Folic Acid, Sulfonamides
Narrow-spectrum
Affects only a select group of microbes
Broad-spectrum
affects a more diverse range microbes.
Can kill good bacteria as well
Quick
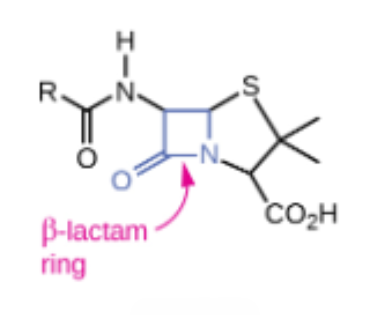
B-lactams
Block the synthesis of peptidoglycan, causing the cell wall to lyse.
All contain a highly reactive 3-C, 1-N ring
E.g. Penicillin and Cephalosporin
Penicillin
Semisynthetic ______
B-lactam antibacterial that was the first cell wall synthesis inhibitor developed
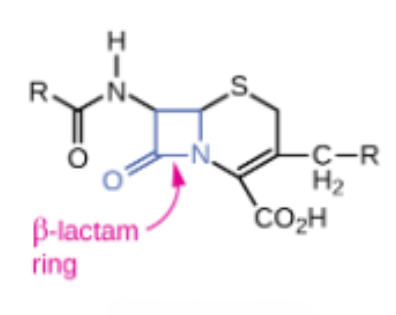
Cephalosporin
Semisynthetic ______
A group of cell wall synthesis inhibitors within the class of B-lactams
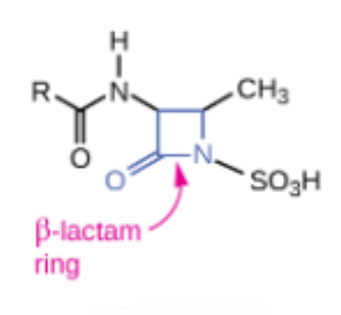
Monobactam
Semisynthetic ______
Interact directly with PBPs and inhibit transpeptidase activity
Inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls by binding to penicillin-binding proteins.
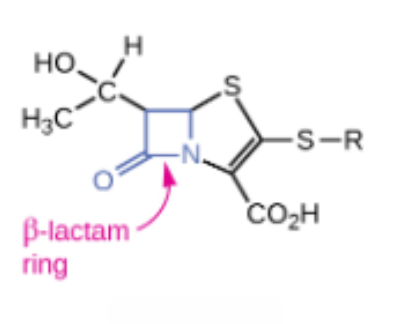
Carbapenem
Semisynthetic ______
Interact directly with PBPs and inhibit transpeptidase activity
Broad-spectrum antibiotics used to treat severe bacterial infections, particularly those resistant to other antibiotics
Methicillin
Interact directly with PBPs and inhibit transpeptidase activity
Narrow spectrum against gram positive bacteria only, including strains producing penillinase
Folic Acid synthesis
Inhibits the enzyme involved in production of dihydrofolic acid.
Sulfonamides
Sulfones
Broad Spectrum
Drug that targets many different types of microbes
Antiviral Drugs
Selective toxicity is almost impossible in viruses
Obligate intracellular parasites
Block Penetration into the host
Prevent Maturation of Viral Particles
Block replication, transcription, or translation or viral genetic material, viral uncoating.
Nucleotide analog
Synthetic compounds that resemble natural nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA and RNA.
Acyclovir
Herpesviruses
Ribavirin
A guanine analog
RSV, hemorrhagic fevers
Azidothymidine (AZT)
Thymine analog
HIV
Adaptive response to drugs
Due to genetic versatility or variation
Intrinsic and acquired through vertical gene transfer
Acquired Resistance
Spontaneous mutations in critical chromosomal genes
Acquisition of new genes or sets of genes via transfer from another species.
Superbugs
Group of pathogens that carry one or more resistance mechanisms, making them resistant to multiple antimicrobials.
Superinfection
Secondary infection that may develop as a result of long-term, broad-spectrum antimicrobial use.
Efflux Pump
Membrane proteins that help bacteria resist antibiotics by pumping them out of the cell
Fluoroquinolones
Aminoglycosides
Tetracyclines
B-lactams
Macrolides
Blocked Penetration
Occurs when bacteria become less permeable to antibiotics. This can happen when bacteria alter their outer membrane proteins or pump antibiotics out of the cell.
B-lactams
Tetracyclines
Fluoroquinolones
Inactivation of Enzymes
A mechanism that bacteria use to develop resistance to antibiotics. This can occur when bacteria evolve enzymes that modify or destroy the structure of antibiotics.
B-lactams
Aminoglycosides
Macrolids
Rifamycins
Target Modification
It occurs when the bacterial target protein that an antibiotic binds to is altered, preventing the antibiotic from effectively inhibiting bacterial growth.
Fluoroquinolones
Rifamycins
Vancomycin
B-lactams
Macrolides
Aminoglycosides
Antimicrobial Resistance
Misuse of antibiotics selects for resistant mutants
Using outdated or weakened antibiotics
Using antibiotics for the common cold and other inappropriate conditions
Using antibiotics in animal feed
Failing complete the prescribed regimen
Using someone else’s leftover prescription
Side Effects of Drugs
Direct damage to tissue due to toxicity of a drug.
Allergic reactions
Disruption in the balance of normal flora-superinfections possible.
Considerations in selecting an antimicrobial drug
Identify the microorganism causing the infection
Test the microorganism’s susceptibility (sensitivity) to various drugs in vitro when indicated.
The overall medical condition of the patient.
Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Test
Simple, rapid method for determining susceptibility and resistance of a bacterial pathogen to antibacterial drugs. The test involves drug-impregnated disks placed on an agar plate inoculated with a bacterial lawn.
Essential for groups of bacteria commonly showing resistance.
E-Test Diffusion Test
A quantitative method that measures how susceptible bacteria are to antimicrobial agents. Uses a plastic strip with a gradient of an antimicrobial agent to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the drug.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
The lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that prevents the growth of bacteria or fungi.
Smallest concentration of drug that visibly inhibits growth.