MIDTERM Quiz Question Bank
1/157
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
basic characteristics of sociological theory
abstract
testable
explains, describes, predicts something about the social world
empirical
observable through the senses
positivism
understanding the world through science
operationalization
translation of theoretical ideas into methodological and real world observations
ideology
statements or beliefs about what the world ought to or should be
proposition
statement of the relationship between two concepts
sociological canon
theories thought to be the most valued, important ideas in sociology
sociological theory
oriented towards science and scientific testing. theories are developed and their validity is tested through scientific methods. often expressed in propositions.
sociological theory example
the more social ties a person has, the less likely they are to commit suicide or the less social ties a person has, the more likely they are to commit suicide.
social theory
oriented toward ideology, making statements about how the world could be or should be. politically motivated theory focusing upon consciousness raising and social change.
social theory examples
society is an iron cage of rationality - Max Weber
a new type of society has emerged, a disciplinary society of surveillance - Michel Foucault
everyday life is dominated by simulations - Jean Baudrillard
transformations in the 17th and 18th centuries that led to the development of sociological theory
scientific revolution
religious revolution
educational revolution
political revolution
industrial/technological revolution
economic revolution
urban revolution
revolution in social organization
feminist revolution
imperialism and colonialism
socio-political factors that affected the formation of sociological theory
sociological theory is itself political
privileges certain perspectives (i.e., race, gender, class, region, etc.)
proletariat & bourgeoisie
associated theorist: Karl Marx
associated theoretical tradition: conflict theory
(associated theorist) Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism
associated theorist: Max Weber
(associated theorist) society is symbolic interaction
associated theorist: George Herbert Mead
(associated theorist) social physics
associated theorist: Auguste Comte
(associated theorist) the division of labor in society
associated theorist: Emile Durkheim
(associated theorist) conspicuous consumption
associated theorist: Thorstein Veblen
(associated theorist) the stranger
associated theorist: Georg Simmel
(associated theorist) positivism
associated theorist: Auguste Comte
(associated theorist) mechanical solidarity
associated theorist: Emile Durkheim
(associated theorist) the means of production
associated theorist: Karl Marx
(associated theorist) social types and social forms
associated theorist: Georg Simmel
(associated theorist) collective effervescence
associated theorist: Emile Durkheim
(associated theorist) conflict can be functional
associated theorist: Georg Simmel
(associated theorist) class, status, power
associated theorist: Max Weber
(associated theorist) instead of focusing on production, business leaders focus on strategic financial strategies
associated theorist: Thorstein Veblen
(associated theorist) social control is self-control
associated theorist: George Herbert Mead
(associated theorist) had a silent debate with Marx
associated theorist: Max Weber
(associated theorist) the history of all society is the history of class conflict
associated theorist: Karl Marx
(associated theorist) conducted the first empirical study in sociology
associated theorist: Emile Durkheim
Suicide
(associated theorist) without language, we cannot have society
associated theorist: George Herbert Mead
(associated theorist) the blase attitude
associated theorist: Georg Simmel
(associated theorist) taking the role of the other
associated theorist: George Herbert Mead
(associated theorist) iron cage of rationality
associated theorist: Max Weber
(associated theorist) suicide
associated theorist: Emile Durkheim
(associated theorist) I, me, the generalized other
associated theorist: George Herbert Mead
(associated theorist) society is composed of exchange relationships
associated theorist: Georg Simmel
(associated theorist) bureaucracy
associated theorist: Max Weber
(associated theorist) economic class is the most important factor in understanding society
associated theorist: Karl Marx
(associated theorist) anomie
associated theorist: Emile Durkheim
(theoretical tradition) society is “like an organism”
associated theoretical tradition: functionalism
(theoretical tradition) the problem of intersubjectivity
associated theoretical tradition: phenomenology
(theoretical tradition) patriarchy is a primary system of domination
associated theoretical tradition: feminist theories
(theoretical tradition) systems of social inequality and stratification are main topics of investigation
associated theoretical tradition: conflict theory
(theoretical tradition) central topics include: the formation of identity and the nature of the self
associated theoretical tradition: symbolic interaction
(theoretical tradition) emphasis is on the whole and how parts contribute to the whole
associated theoretical tradition: functionalism
(theoretical tradition) interest convergence (Bell)
associated theoretical tradition: critical race theory
(theoretical tradition) maximizing gains and minimizing losses
associated theoretical tradition: exchange theory
(theoretical tradition) how do individuals create a sense of shared reality?
associated theoretical tradition: phenomenology
(theoretical tradition) interdependence and solidarity
associated theoretical tradition: functionalism
(theoretical tradition) the foundation of society is language
associated theoretical tradition: symbolic interaction
(theoretical tradition) intersectionality (Crenshaw)
associated theoretical tradition: feminist theories
(theoretical tradition) what is the basis for oppression in a society?
associated theoretical tradition: conflict theory
(theoretical tradition) focus is on the “means of mental production” instead of the “means of production”
associated theoretical tradition: critical theory
(theoretical tradition) it is through symbols that humans create society, meaning, and reality
associated theoretical tradition: symbolic interaction
(theoretical tradition) calls for inclusion of women’s voices
associated theoretical tradition: feminist theories
(theoretical tradition) counter-storytelling
associated theoretical tradition: critical race theory
(theoretical tradition) social life is composed of transactions controlled by a cost-benefit analysis
associated theoretical tradition: exchange theory
(theoretical tradition) emphasizes “lived experiences”
associated theoretical tradition: phenomenology
(theoretical tradition) the culture industry
associated theoretical tradition: critical theory
(theoretical tradition) standpoint epistemology
associated theoretical tradition: feminist theories
(theoretical tradition) race as a social construction
associated theoretical tradition: critical race theory
Parson’s theory of the unit act
actors are constrained by social conditions and cultural values
acts are not individual; they are very social
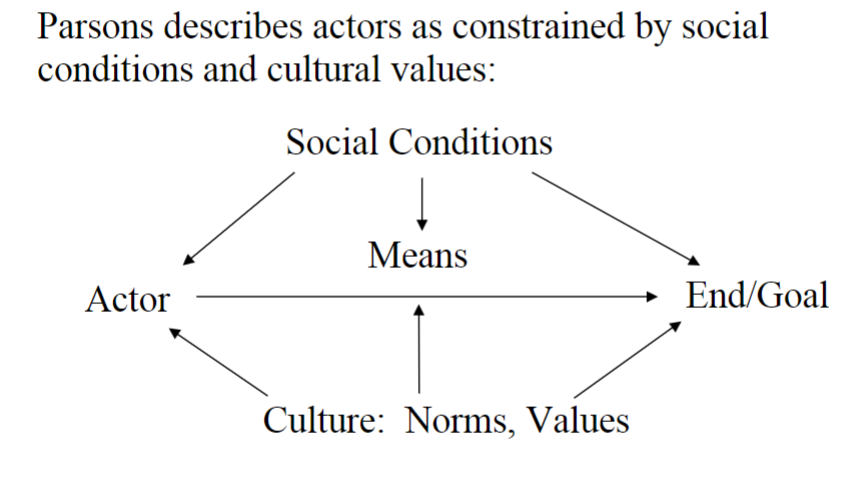
What makes Parsons’ theory of the unit act a sociological theory?
Parsons attempts to explain the act through a scientific approach that can be empirically observed/tested and analyzed in a social context. It is also presented as a proposition.
What are Parsons’ four functional imperatives that every social system has?
adaptation
goal attainment
integration
latency (pattern maintenance)
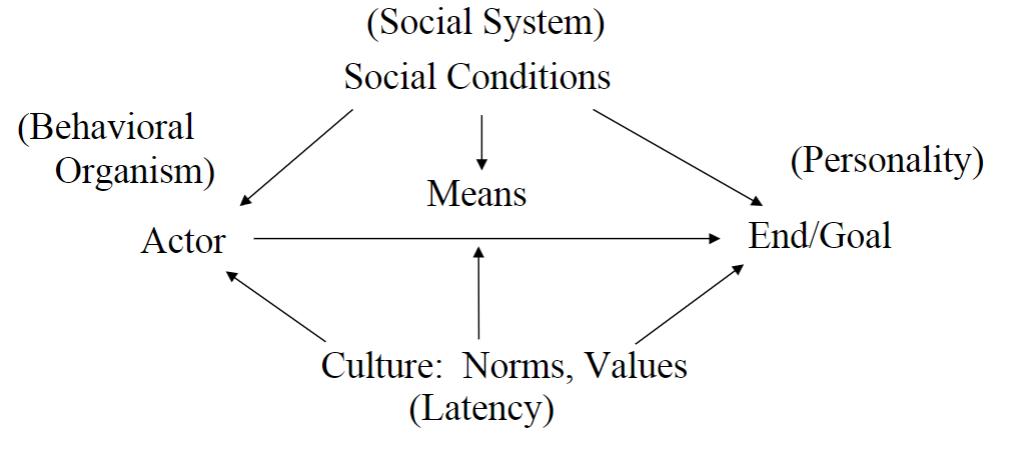
What are Parsons’ four action systems that help to solve the functional needs of a society?
behavioral organism
personality system
social system
cultural system
cultural system
patterned system of symbols, values, norms that create social integration
social system
organized around social structures (status-role complex)
behavioral organism
the material source of energy for the action systems
personality systems
provides the motivational (goal) orientation for the systems
Parsons’ theory of functional needs and their action systems
L[atency] = cultural system
I[ntegration] = social system
G[oal attainment] = personality system
A[daptation] = behavioral system
![<p>L[atency] = cultural system</p><p>I[ntegration] = social system</p><p>G[oal attainment] = personality system</p><p>A[daptation] = behavioral system</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/916b62d2-2da8-45a2-9e39-fb9b8155c554.png)
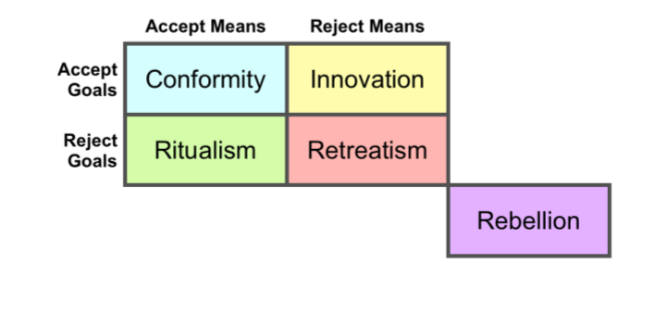
Merton’s strain theory
conformity: accepts means and goals
innovation: rejects means and accepts goals
ritualism: accepts means and rejects goals
retreatism: rejects means and goals
rebellion: new means and goals; challenges means and goals
How is Marx’s (conflict) theory a specific instance of Weber’s (conflict) theory?
Marx believes that economic class causes all aspects of stratification, so class creates social groups which then creates power groups (class —> status —> power).
Weber believes that class, status, and power are all distinct dimensions of stratification (class/status/power).
Ralf Dahrendorf critiques Marx’s theory of conflict by arguing that contemporary conflict is not organized around social class. Instead, it is organized around…
authority
Dahrendorf argues that tensions in the modern workplace are not primarily between owners and workers. Instead, they are between which two groups?
superordinates (order givers)
subordinates (order takers)
For Dahrendorf, every social setting has a social structure (status-role complex) as well as a distribution of power. What does Dahrendorf call these social structures?
imperatively coordinated association
Dahrendorf argues that group conflict emerges as a result of a conflict of interests. The structure of authority relations produces three groups…
quasi groups: unorganized but similar roles
interest groups: organized, united by interests [unions]
conflict groups: actively mobilized for interests [striking unions]
Parsons’ unit act that includes the action systems
actor = behavioral organism
goal = personality system
culture = cultural system
social conditions = social system
(theorist) imperatively coordinated associations
associated theorist: Ralf Dahrendorf
(theorist) contradictory class locations
associated theorist: Erik Olin Wright
(theorist) split labor market theory
associated theorist: Edna Bonacich
(theorist) the power elite
associated theorist: C. Wright Mills
(theorist) dual systems theory
associated theorist: Heidi Hartmann
(theorist) conflict shows itself in interaction
associated theorist: Randall Collins
(theorist) exploitation stems from control over production, labor power, and investments
associated theorist: Erik Olin Wright
(theorist) the cheerful robot
associated theorist: C. Wright Mills
(theorist) racial and ethnic divisions are exploited by employers to keep wages low
associated theorist: Edna Bonacich
(theorist) patriarchy and capitalism intersect
associated theorist: Heidi Hartmann
(theorist) quasi group, interest group, conflict group
associated theorist: Ralf Dahrendorf
(theorist) winners in conflict gain emotional energy
associated theorist: Randall Collins
More and more people in the US are earning college degrees.
What does this pattern do to the value of a college degree in the US?
What does Randall Collins call this process?
Credential inflation is as more people earn bachelor’s degrees, the less value it has. As a result, people need to have more credentials to qualify for the same positions.
limitations in Marx’s theory of conflict and how a contemporary theorist has worked to improve this limitation
Hartmann: the workers in Marx’s theory were only men, so she elaborated on the interconnection between capitalism and patriarchy through her dual systems theory
E.O.Wright: Marx (as generally articulated) did not account for a middle class who are both the oppressed and the exploiters in the labor system, contradictory class locations
groups who make up the power elite
corporate leaders
military leaders
political leaders
celebrities
stocks of knowledge
social recipes for making sense of and navigating the world
problem of intersubjectivity (def.)
how do we know that we share the same basic reality?
lifeworld
the everyday taken-for-granted world that human beings occupy
natural attitude
the world of common-sense assumptions we have about the world
Phenomenological theory argues that our experience of the world is separated into two different categories of experience…
lived (personally observed)
taken-for-granted (external knowledge)