Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System - Heart Physiology
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
auto-rhythmicity
The term for: generating rhythmic action potential independent of the nervous system
• the heart is auto-rhythmic
auto-rhythmicity
What triggers muscular contraction from initiating action potential between cardiac cells?
myocardial contractile cells and myocardial conducting cells
What are the two types of cardiac muscle cells
intercalated discs
What connects the contractile cells of the heart?
striated
Heart cells are marked with parallel bands; grooved
striated
Cardiac cells are ______, meaning they have actin, myosin, tropomyosin, and troponin
myocardial conducting cells
Which cardiac cell is
• neuron-like
• auto-rhythmic
• has a pace set by the fastest cell
myocardial conducting cells
What cardiac has the following components:
• sinoatrial node (SA)
• atrioventricular node (AV)
• atrioventricular bundle
• right and left bundle branches
• Purkinje fibers
the fastest one (first one to generate an action potential) → sinoatrial node (SA)
The components of conducting cells (i.e. SA, AV, Purkinje fibers, etc.) all generate an action potential, but which one sets the pace for the rest?
sinoatrial node (SA)
What is the fastest component of myocardial conducting cells to generate the first action potential?
sinoatrial node (SA)
What is known as the pacemaker node?
myocardial conducting cells
Action potential starts through what type of cardiac cell?
myocardial contractile cells
The action potential from the conducting cells spreads where?
tetany
What does it mean when the heart stays contracted?
the plateau phase from the slow Ca²⁺ channels and K⁺ channels opening
What prevents the heart from going into tetany?
electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)
What is the tracing of cardiac electrical activity?
• composite of conducting & contacting cells
typically 12
How many electrical leads are placed on a patient for an ECG/EKG
P wave
On the EKG tracing, what wave occurs first as a result of atrial depolarization?
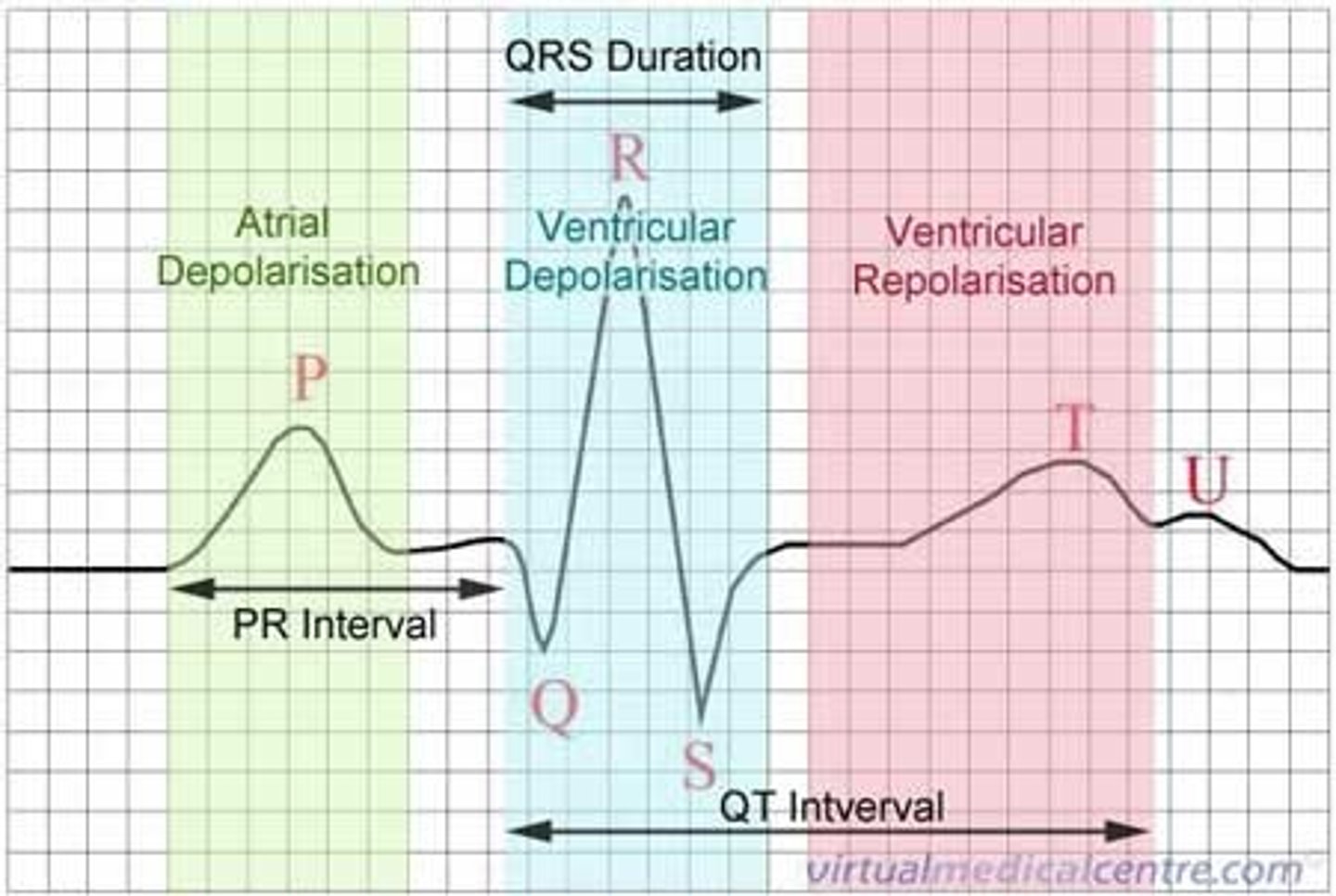
atrial depolarization
P wave results from this; this is when the SA node depolarizes, and it spreads throughthe atrial myocardium.
QRS complex
On the EKG tracing, what wave occurs first as a result of ventricular depolarization AND atrial repolarization?
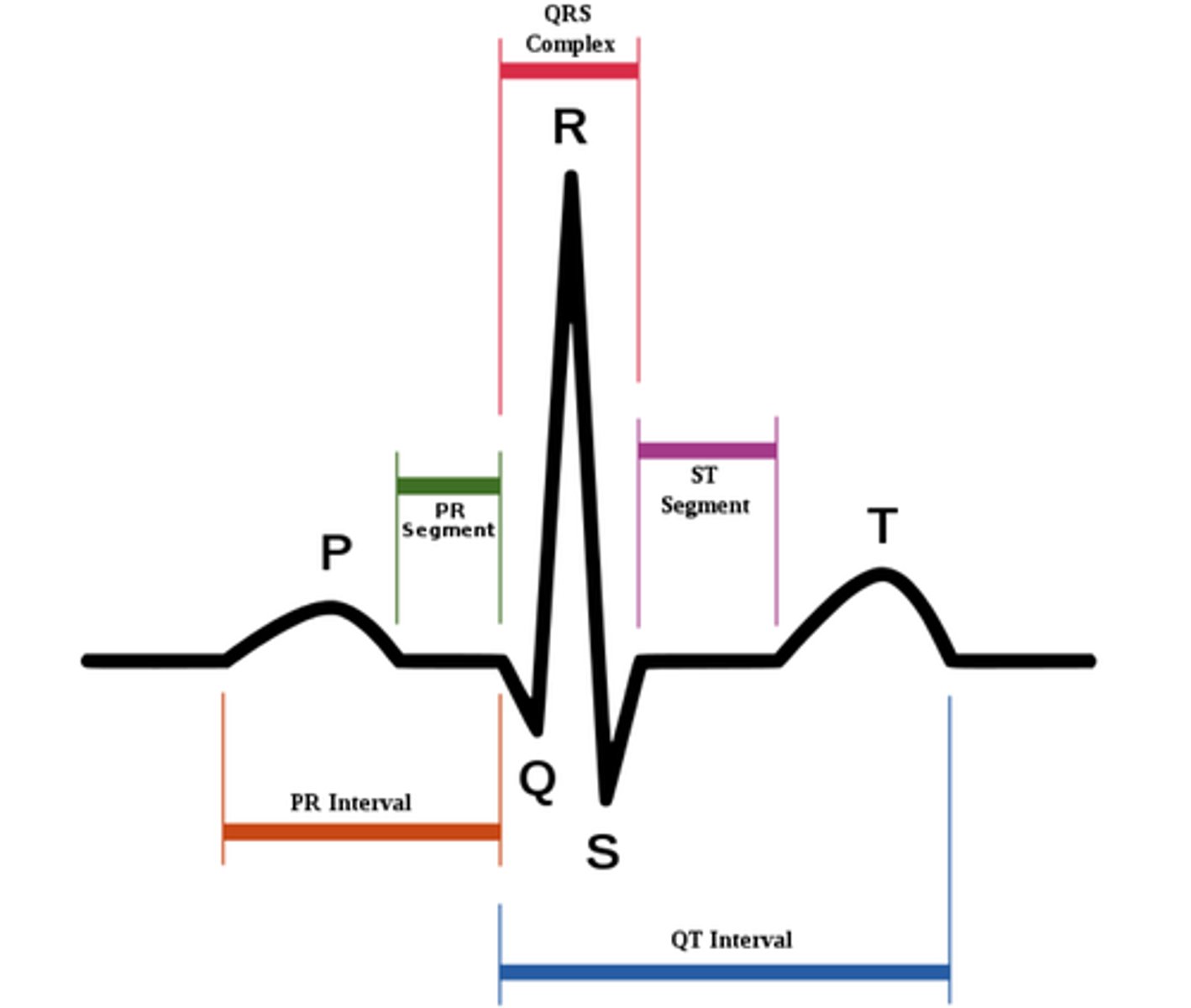
QRS complex
At what point of the EKG tracing do the atria repolarize?
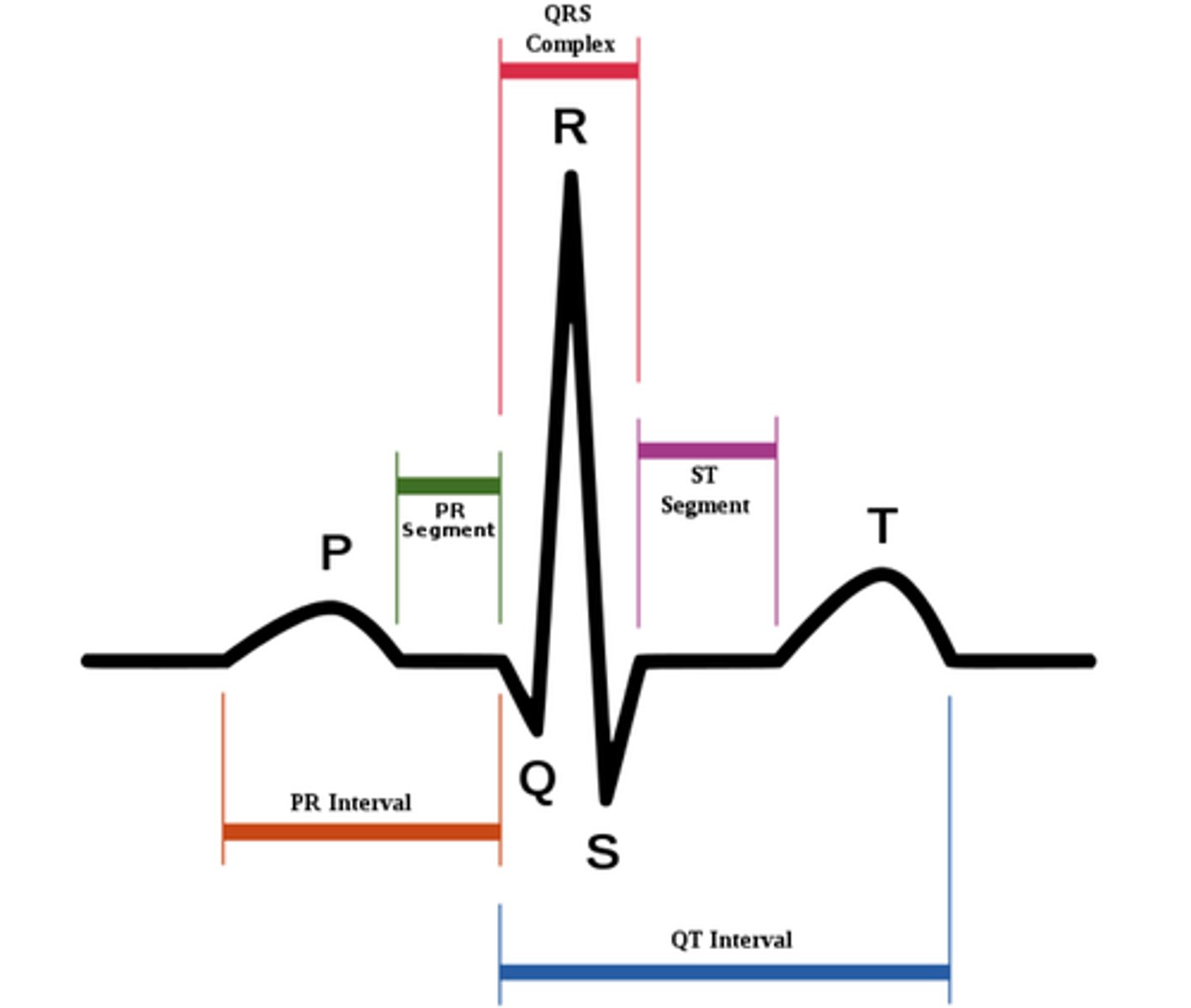
T wave
On the EKG tracing, what wave occurs first as a result of ventricular repolarization?
P-Q segment
On the EKG tracing, what is associated with atrial cells' plateau (atria are contracting)?
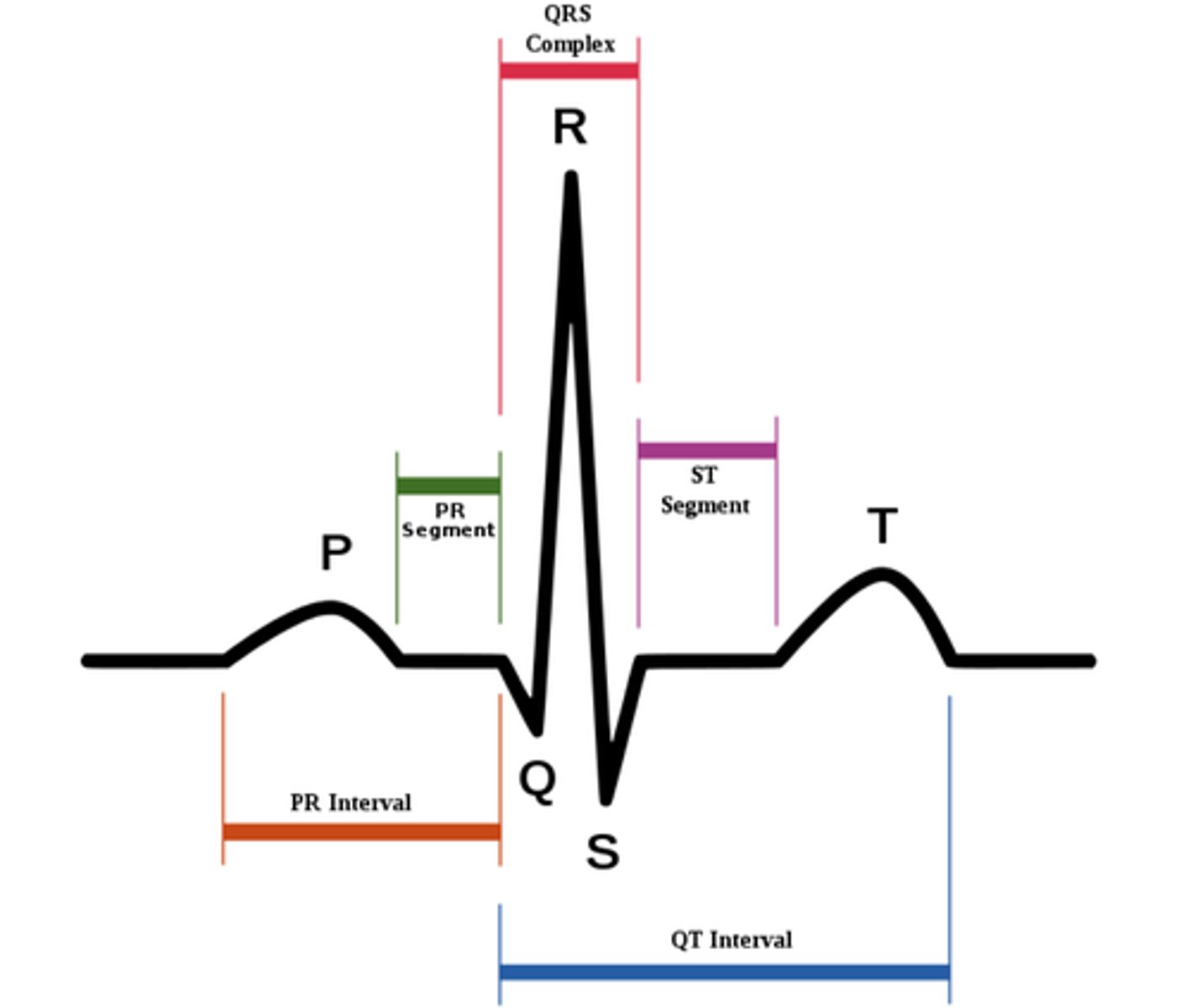
S-T segment
On the EKG tracing, what is associated with ventricular plateau (entire ventricular myocardium depolarized)
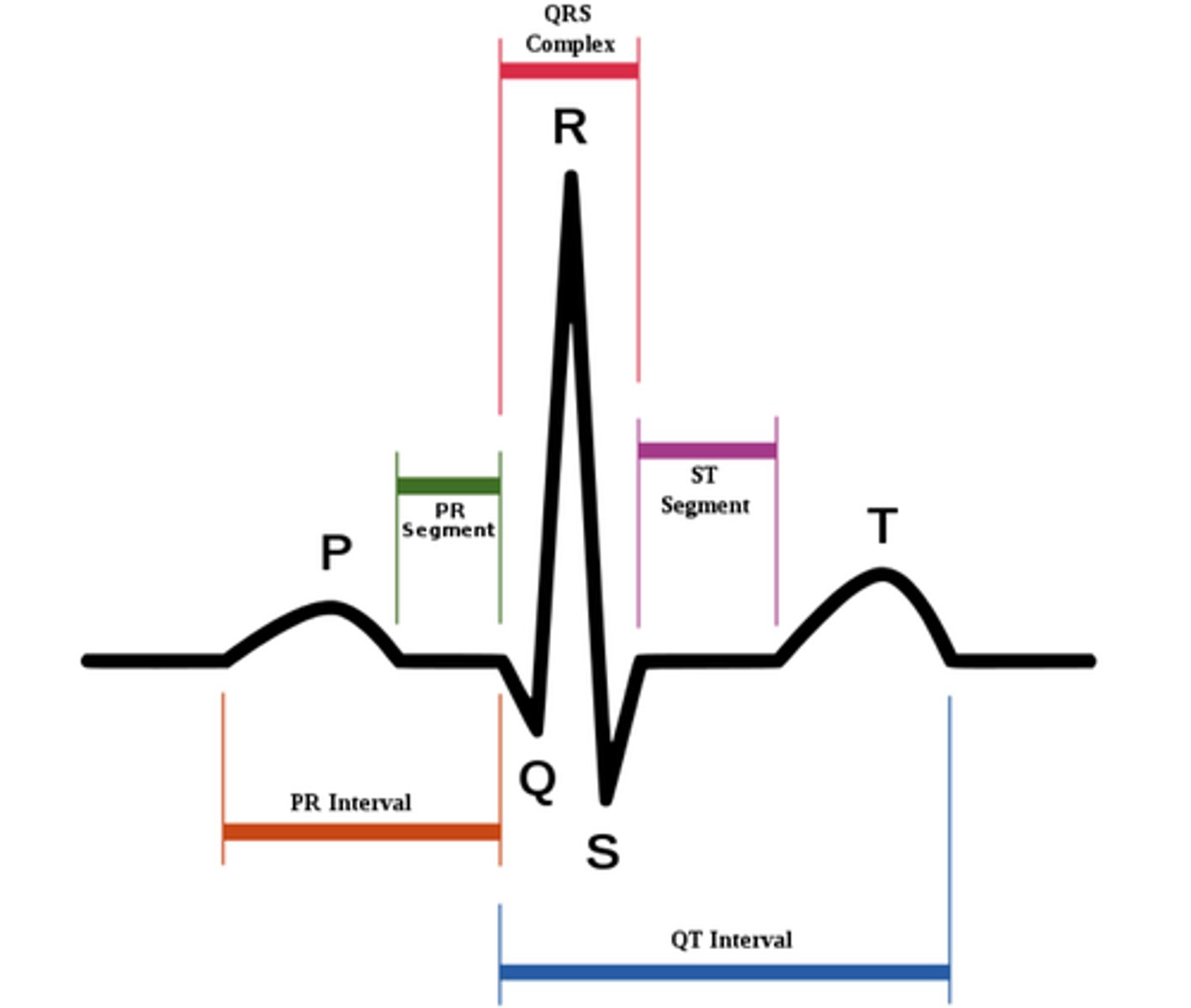
P-R interval
On the EKG tracing, what is the interval from the start of atrial depolarization to the start of the QRS complex?
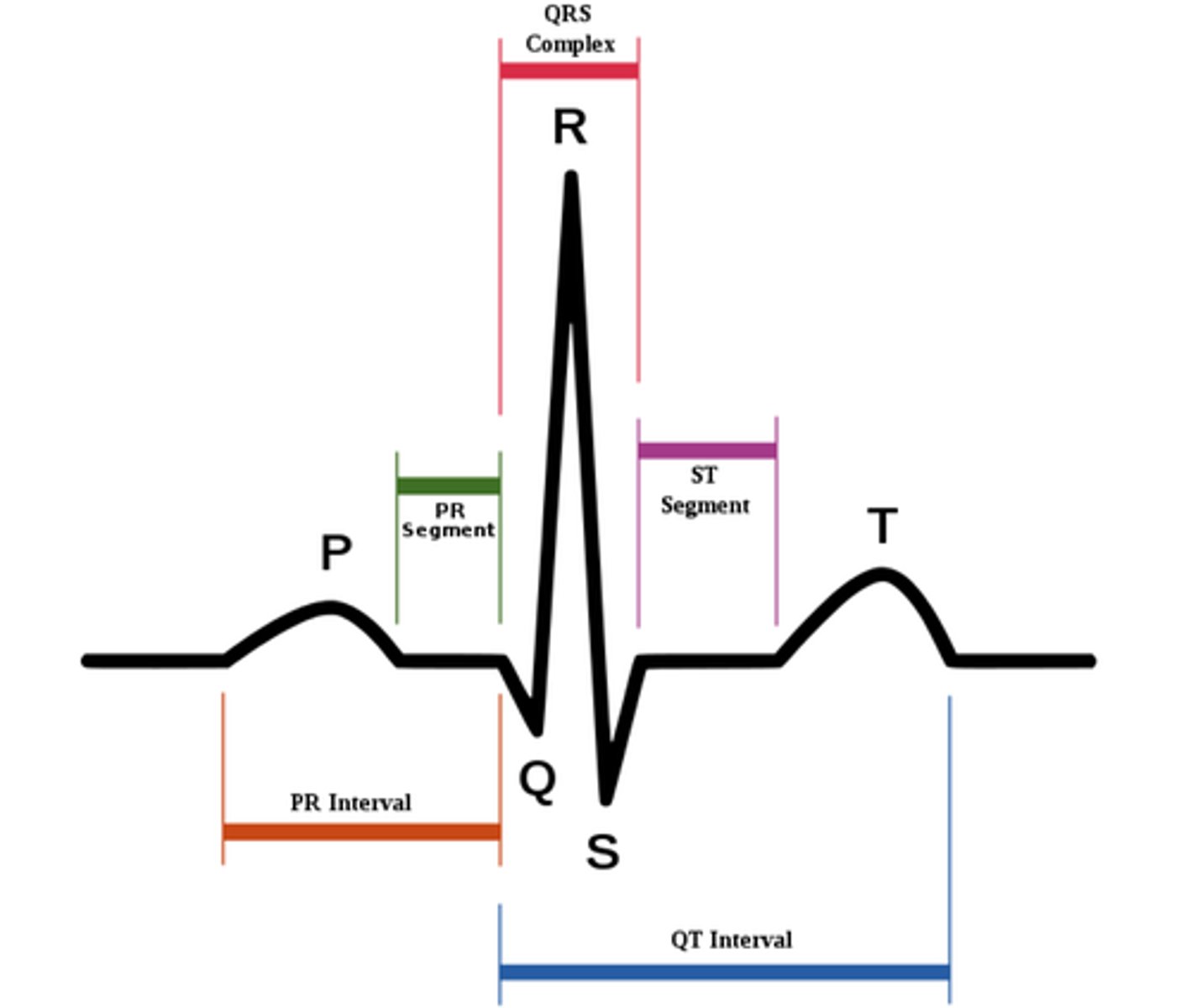
Q-T interval
On the EKG tracing, what is the interval that begins ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization?
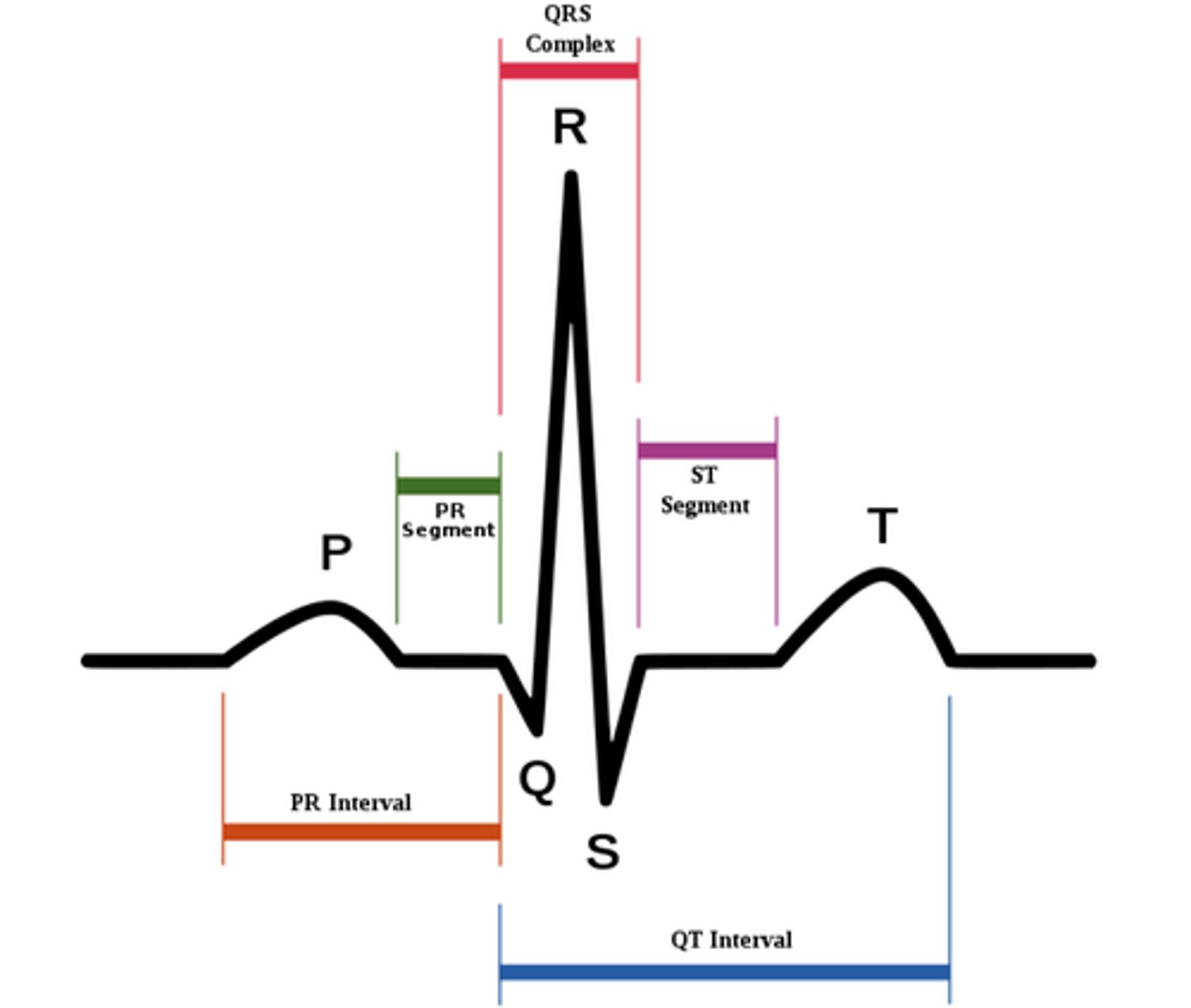
cardiac cycle
What is the sequence of events in one heartbeat?
systole
What is the contraction of the heart
diastole
What is the relaxation of the heart
ventricular filling
When does the cardiac cycle "begin"?
ventricular relaxation
When does the cardiac cycle "end"?
atrial systole
Depolarization of the atria leads to...
atrial diastole
Repolarization of the atria leads to...
stroke volume (SV)
What is the volume of blood that is ejeted out of the ventricles during ventricular contraction?
end diastolic volume (EDV)
What is the volume of blood in each ventricle at end of ventricular diastole
end systolic volume (ESV)
What is the volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after systole
S1 sound
What is the "lub" sound?
S1 sound
Which heart sound is caused by the closure of the atrioventricular (AV) valves?
mitral valve
What is the noisiest atrioventricular valve?
S2 sound
What is the "dub" sound?
S2 sound
Which heart sound is caused by the closure of the semilunar valves?
aortic valve
What is the noisiest semilunar valve?
S3 sound
Which heart sound is abnormal, caused from blood sloshing
(not tested)
S4 sound
Which heart sound is always abnormal, caused by blood pushing against the stiff left ventricle?
ECG tracing
What can be used to measure heart rate?
dysrhythmia
Define the diagnosis:
• an abnormal cardiac rhythm
bradycardia
Define the diagnosis:
• a type of dysrhthymia
• < 60 bpm
• abnormally slow resting heart rate
tachycardia
Define the diagnosis:
• a type of dysrhthymia
• > 100 bpm
• abnormally fast resting heart rate
heart block
Define the diagnosis:
• a type of dysrhthymia
• conduction system failure
•
fibrillation
Define the diagnosis:
• a type of dysrhthymia
• uncontrolled contractions
• "heart fluttering"
stroke volume (SV)
What is the volume of blood pumped forward with each ventricular contraction?
end diastolic volume (EDV) - end systolic volume (ESV)
What is the stroke volume equation (SV)?
ejection fraction (EF)
What is the measurement of the volume percentage of left ventricular contents ejected with each contraction?
stroke volume (SV) / end-diastolic volume (EDV)
What is the ejection fraction equation?
cardiac output
What is the volume of blood pumped by heart per minute?
HR x SV
What is the formula for cardiac output (CO)?
preload, contractility, afterload
What factors affect stroke volume (SV)
end diastolic volume (EDV)
Preload is directly proportional to _____________
Frank-Starling law
What's the rule where the greater the stretch, the stronger is the heart's contraction?
direct
Preload has a ____________ relationship with stroke volume
increases
If you increase preload... end diastolic volume ________, which _________ stroke volume (SV)
increases
If you increase duration of diastole... end diastolic volume ________, which _________ stroke volume (SV)
decreases
If the heart rate exceeds 160 bpm, the heart is beating to hard for the ventricles to fill with blood. This ________ stroke volume
decreases
If there is impaired venous return, this _________ stroke volume
direct
Contractility has a ________ relationship with stroke volume
increases
Stronger contractility ________ stroke volume
+ inotropic agents
What type of agents increase contractility?
What is the type of inotropic agent?
• increased Ca2+
• increased glucagon
• sympathetic stimulation
• digitalis
- inotropic agents
What type of agents decrease contractility?
- inotropic agents
What is the type of inotropic agent?
• increased K+ and H+
• sympathetic inhibition
• calcium channel blockers
afterload
What factor affecting SV is significant in HTN patients?
afterload
What is the resistance in the great vessels from accepting the blood that the vesicles are attempting to eject.
indirect
Afterload has a _______ relationship with stroke volume
heart rate (HR)
What is the number of beats per minute?
75 bpm
What is the normal heart rate?
< 60 bpm
What is the heart rate for someone with bradycardia?
> 100 bpm
What is the heart rate for someone with tachycardia?
+ chronotropic effects
What increases the heart rate?
- sympathetic stimulation
- nicotine, caffeine, thyroid hormone
- chronotropic effects
What decreases the heart rate?
- parasympathetic stimulation
- K+ and Ca2+ (hyper)
parasympathetic
Which nervous system sets the cardiac tone, in other words, slows down the pacemaker cells?
parasympathetic
Which nervous system DECREASES your heart rate?
sympathetic
Which nervous system INCREASES your heart rate?
sympathetic
Which nervous system increases the strength of contraction of the chambers in the heart?
coronary artery disease
Define the diagnosis
• The condition for atherosclerosis of coronary arteries
• Ischemia
• angina pectorsis
• depressed S-T segment
atherosclerosis
Define the diagnosis
• hardening of the arteries
ischemia
Define the diagnosis
• lack of blood supply
angina pectoris
Define the diagnosis
• chest pain that results when the heart does not get enough oxygen
myocardial infarction (MI)
Define the diagnosis
• heart attack
• cardiac muscle tissue death
• results in chest & left arm pain
• elevated S-T segments
• cardiac enzymes are elevated in the blood
heart failure
Define the diagnosis
• cardiac insufficiency
• a chronic condition in which the heart is unable to pump out all of the blood that it receives
• caused multiple things: cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis, chronic hypertension, myocardial infarction (MI)
right-sided heart failure
Define the diagnosis:
• systemic circulation back-up
• lower extremity edema
left-sided heart failure
Define the diagnosis:
• pulmonary circulation back-up
• pulmonary edema