LAST BIO QUIZ!!!!!!
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
Codon
segment of RNA coded for amino acids, made up of 3 bases
2
New cards
Why DNA replicates
needs to replicate to prevent errors and to enable splitting of cells
3
New cards
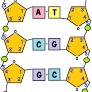
DNA Model
6 deoxyribose, 6 nitrogenous bases, 8 hydrogen bonds, phosphate
4
New cards
5’ to 3’ strand
when it goes up to down from 5’ to 3’
5
New cards
3’ to 5’
when it goes up to down from 3’ to 5’
6
New cards
Helicase
the unzipping enzyme, unzips DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds
7
New cards
DNA Polymerase
the builder, replicates DNA molecules and rebuilds DNA strands, if it makes a mistake a mutation occurs, proofreads DNA too
8
New cards
Primase
initializer, created primer to tell Polymerase where to start rebuilding
9
New cards
Ligase
the gluer, glues DNA fragments together again
10
New cards
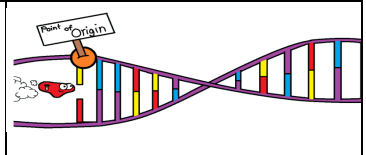
What is happening here?
At the origin, DNA helicase unwinds the DNA
11
New cards
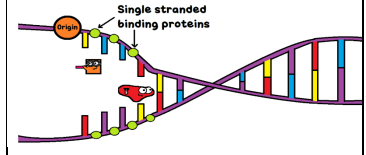
What is happening here?
Single Stranded Binding Proteins keep the DNA strands separated after being unwound.
12
New cards
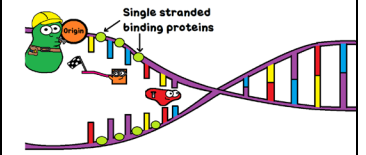
What is happening here?
Primase enters and indicates to DNA Polymerase where to begin DNA replication
13
New cards
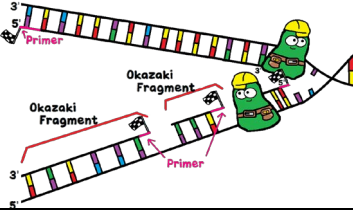
What is happening here?
DNA Polymerase must wait for DNA to unwind to replicate, creating the lagging strand. Leading strand is continuously replicated while lagging has pauses.
14
New cards
Lagging Strand
When DNA polymerase has to wait for DNA to unwind to replicate it, creating gaps later filled in, occur because DNA is antiparallel and replication only happens in 5’ to 3’ direction
15
New cards
Leading Strand
Continuously replicated throughout DNA replication
16
New cards
Central dogma
theory of flow of how we get our traits (DNA →RNA→Proteins)
17
New cards
Transcription
Process creating RNA from DNA, happens in nucleus
18
New cards
Translation
RNA to Proteins process, happens in ribosome
19
New cards
DNA v. RNA
DNA:
* Deoxyribose sugar
* Thymine instead of uracil
* Double stranded
RNA:
* Ribose sugar
* Uracil instead of thymine
* Single stranded
* Deoxyribose sugar
* Thymine instead of uracil
* Double stranded
RNA:
* Ribose sugar
* Uracil instead of thymine
* Single stranded
20
New cards
Nitrogenous bases binding in RNA
Adenine with **Uracil**, Cytosine with Guanine
21
New cards
DNA structure
includes phosphate, deoxyribose, nitrogenous base
22
New cards
semi-conservative
DNA replication creates this because the strands are half-old and half-new
23
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
hold nitrogen bases together
24
New cards
Anti-codon of tRNA
brings in amino acids
25
New cards
Replication
doubling DNA, occurs only in 5’ to 3’ direction