Tissues Surrounding the Teeth Lesson No.6
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Periodontium
Tissues that surround and support the teeth
Alveolar Process
The supporting suckets of the teeth
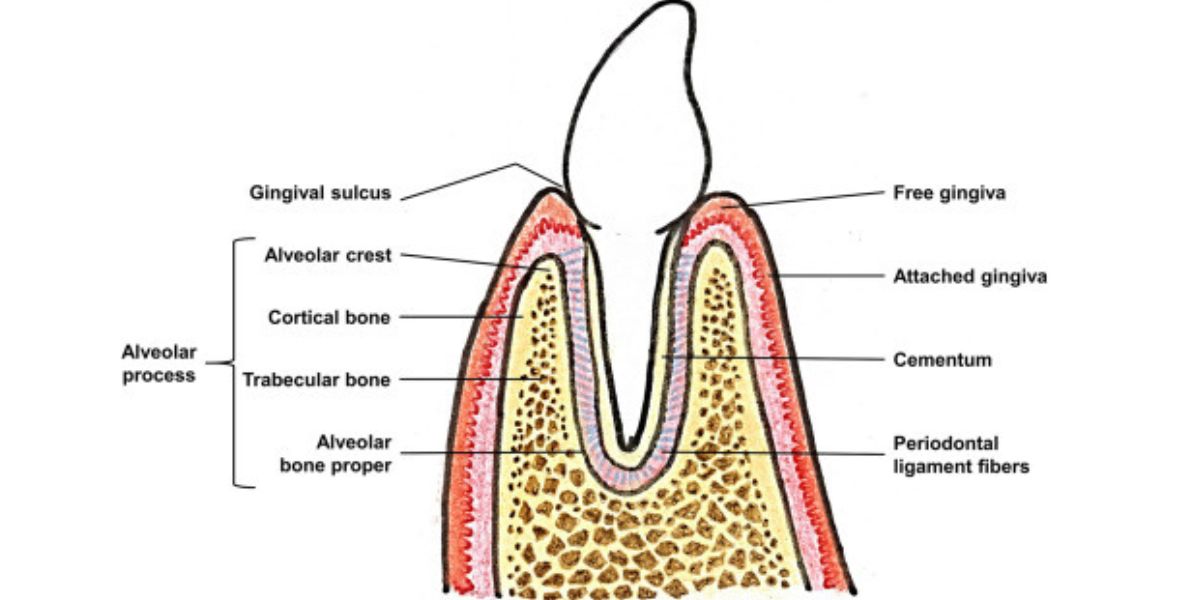
Cortical Plate
The alveolar process is made up of compact bone. The cortical plate provides strength for supporting bone and acts as an attachment for skeletal muscle
Lingual Plate
Inner plate
Facial or buccal plate
outer plate
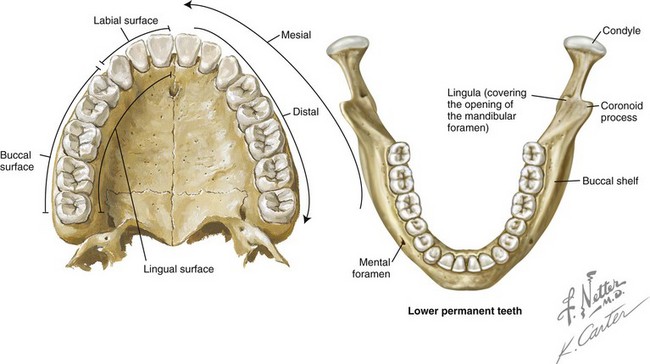
Periosteum
Covers the cortical plate also called fibrous sheath
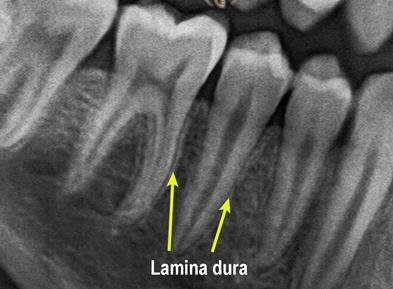
Lamina Dura
Also called the alveolar process proper, the cortical plate is attached directly to this
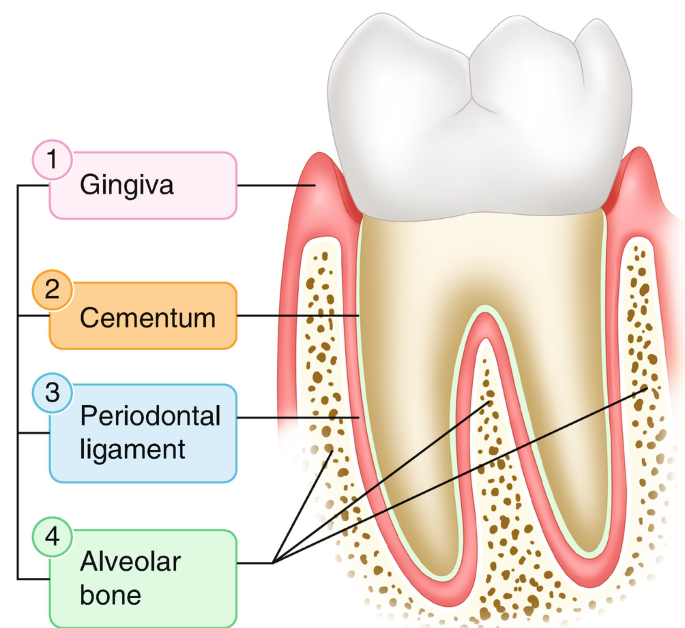
Periodontum Ligament (PDL)
A collection of fibers with the primary purpose of suspending the teeth within the alveolar process and supporting gingiva
Sharpey’s Fiber
Bundles collection of “principal fibers”
One end of these fibers is anchored into the cementum
Other end of the fibers are embedded within the bone
Able to withstand the stresses of a fully erupted functional tooth
Slight movement is permitted although these fibers are not elastic
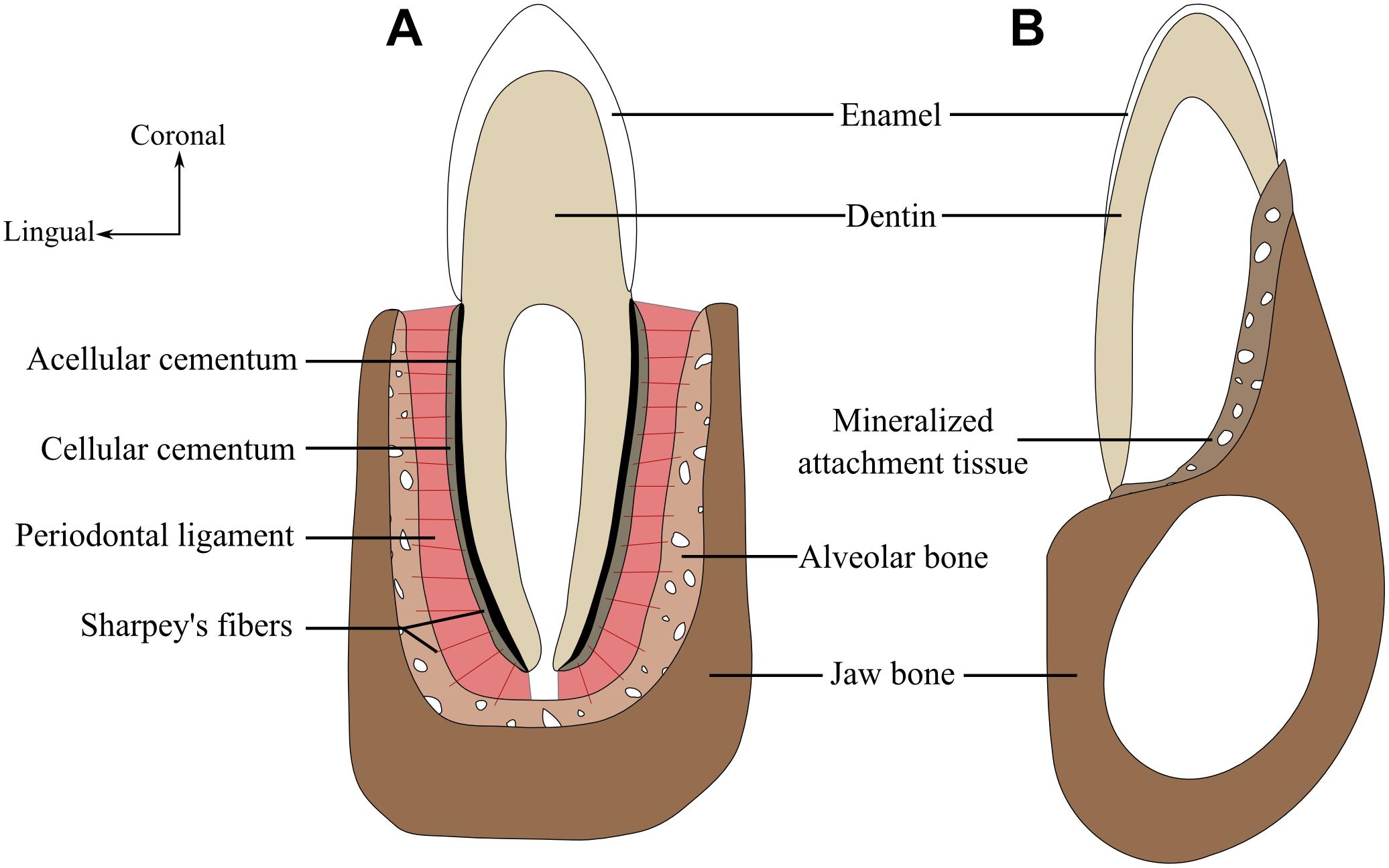
Principal Fibers
Serve to support the gingival tissue and suspend teeth within the alveolar process
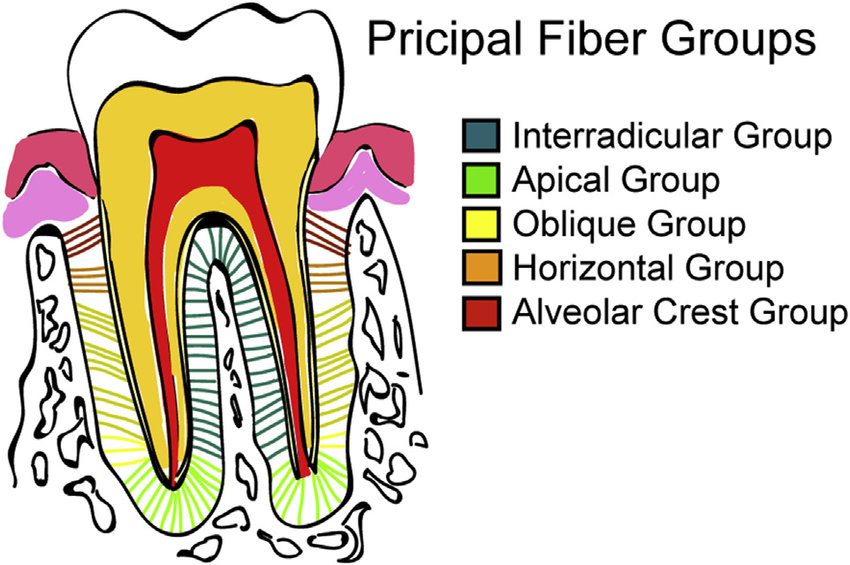
Different types of function cells found within PDL
Cementoblasts- for cementum
Osteoblasts- build bone
Fibroblasts- form fibrous tissue
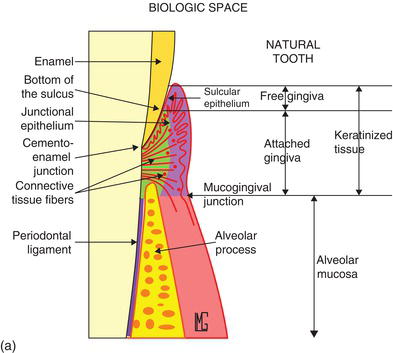
Gingiva
Also known as “gums”
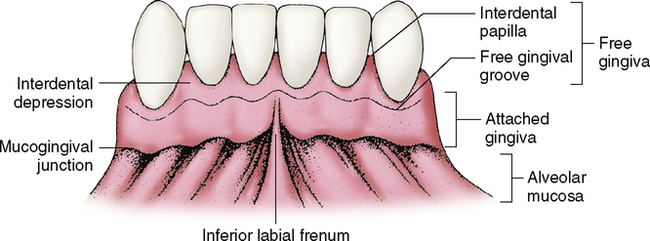
Free Gingiva
Moveable tissues that surrounds the crown of the tooth just above the CEJ of the tooth
Gingiva Crest
The peak of the free gingiva
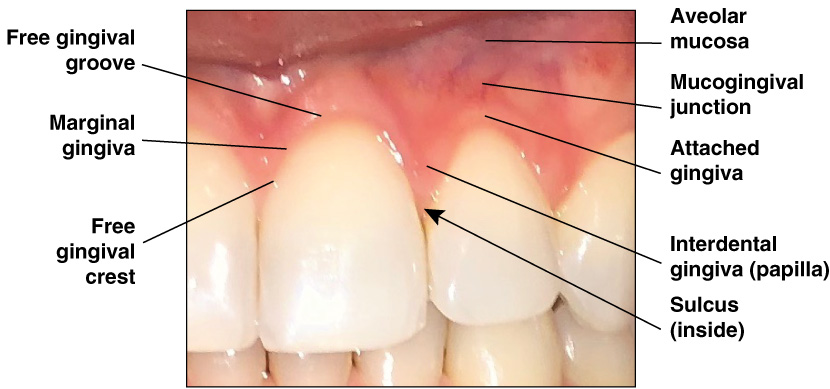
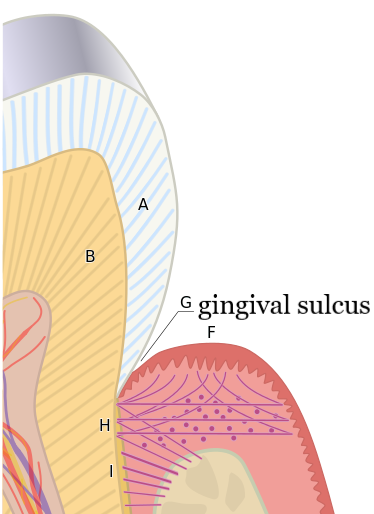
Gingiva Sulcus
The space that exists between the tooth and the free gingiva
Free Gingiva Groove
Located below the sulcus, this line separates the free gingiva and the attached gingiva
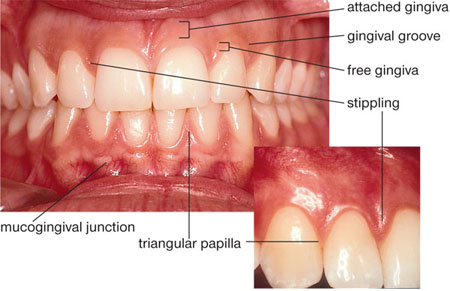
Interdental Papillae
Triangular shaped crests of gingival tissue located between the teeth. These crests of tissue consist of free and attached gingiva
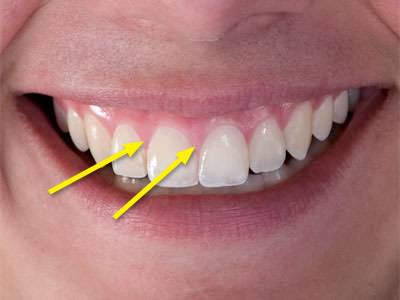
Attached Gingiva
The portion of the mucous membrane bound to the tooth and to the alveolar arches of the jaw