Optics Notes
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Grade 10 Optics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Light:
Form of energy which has properties of particles (photons) and waves.
Electromagnetic:
Light being made of oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
Wave:
Disturbance transferring energy from one point to another without transferring matter.
Crest:
Highest point on the wave.
Rest Position:
Level of water when there are no waves.
Amplitude:
The height of the wave from the rest position to the crest or the depth from the rest position to the trough.
Frequency:
Rate of repetition of a wave
When is more energy carried?
Larger the amplitude, the more energy carried and the higher frequency, the more energy the wave passes along.
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Range of all types of radiation that has electric and magnetic fields that travels in waves.
Additive Colour Theory of Light:
White light is composed of different colours (wavelengths) of light, White light is made of green, blue and red, a secondary colour is made by mixing TWO primary colours together.
Subtractive Colour Theory of Light:
When light strikes an object, some wavelengths of light reflect off the object while others are absorbed, colour visible to us is the reflected wavelengths, black and blue absorbs while white reflects (blue reflects itself only).
Primary Subtractive Colours:
Magenta, yellow, cyan
Secondary Subtractive Colours:
Red, green, blue.
How is light represented and what does it show?
Lines called rays which show the direction that light travels.
What are Ray diagrams used for?
Show the path that light takes after it leaves its source.
What does each ray end with?
Ends with an arrow to indicate the direction of travel.
Materials are classified according to?
How they transmit, absorb or reflect light.
How do transparent materials act?
They transmit light freely and absorb and reflect very little light.
How do translusent materials act?
They transmit some light but not enough to see through the material clearly.
How do opaque objects act?
Absorb and reflect light but do not transmit it.
Transmit:
Go through an object
Reflect:
Bounce off of an object
Absorb:
Soak up the light
What can ray diagrams explain?
The size and location of shadows and why some shadows are sharp while others have less distinct edges.
What does the size of the shadow depend on?
The size of the object blocking the light and its distance from the light source. Ex: The closer the object to the light source, the larger the shadow is.
Small light source =
sharp, well defined shadow
Large light source =
Fuzzy shadow because the object only partially blocks the light.
Umbra:
Part of the shadow where all light rays are blocked.
Penumbra:
The partially shaded outer region of the shadow that results from the light being partially blocked by an object.
Where do light rays come from?
Light sources that travel parallel to each other.
Regular Reflection:
The light rays strike a smooth surface, they reflect in the same direction (stay parallel).
Diffuse Reflection:
When light rays reflect off of an object with an uneven surface, they do not remain parallel, but are scattered in different directions.
Refraction:
The bending of light
Angles of light rays are always measured from a:
Normal line
The Laws of Reflections for Flat Surfaces:
The angle of incidence = the angle of reflection
Both the incident and reflected rays are in the same plane.
Plane mirror:
Any mirror that has a flat reflective surface.
When you look into a plane mirror, your image appears:
To be as far behind the mirror as you are in front of it.
Virtual Image:
Any image formed by rays that do not actually pass through the location of the image. Can not be projected on a screen.
Virtual rays are drawn as:
Dotted lines
Two types of curved mirrors:
Concave mirrors and convex mirrors.
Concave mirror:
Aka a converging mirror, has a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl and causes parallel rays to come to a focus.
More curved vs less curved:
More curved = focus is clearer
Less curved = focus is farther
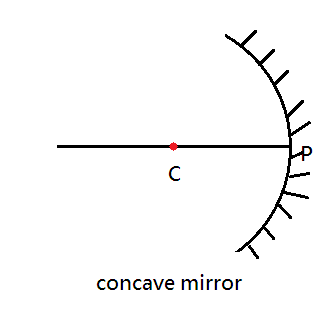
C (Centre of the curvature):
Centre of the sphere/cylinder from the mirror.
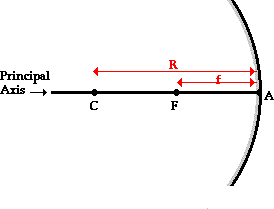
R (Radius of the curvature):
The distance from the centre of curvature to the mirror.
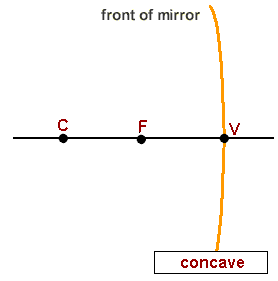
V (The vertex):
Geometric centre of the mirror.
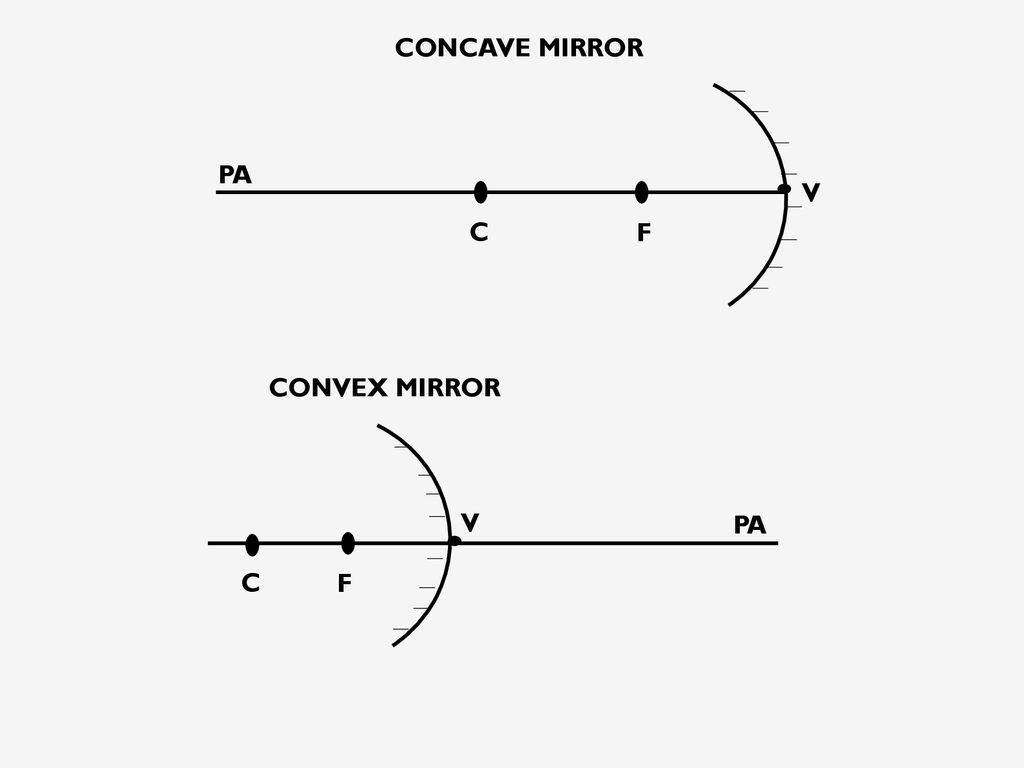
PA (Principal axis):
Line drawn through the vertex perpendicular to the surface.
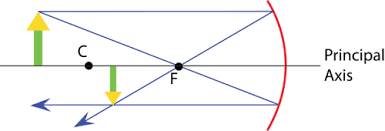
F (Focus):
Point where light rays parallel to the PA come together or diverge from.
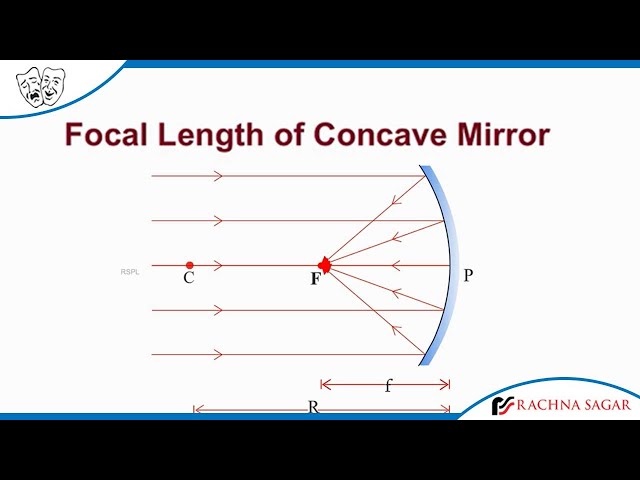
f (focal length):
Distance from vertex to focus measured along the principal axis.
What does the focal length of a mirror depend on?
How curved the mirror is.
The greater the curvature:
The shorter the focal length.
How are real images drawn?
Rays drawn in front of a mirror as solid lines.
Virtual:
Rays drawn behind a mirror and shown as dotted lines.
What image can be projected on a screen?
Real images.
Use of flashlight:
To produce a parallel beam (light to spread out/diverge).
Use of telescope:
To collect light from a distant source and focus it for viewing.
Use of cosmetic mirror:
To produce an enlarged image (makes images appear larger).
Use of headlights of a car:
To produce a parallel beam of light that is directed down or straight ahead (light to spread out/diverge).
Mirror Equation:
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
What mirrors have a positive focal length?
Concave Mirrors
What mirrors have a negative focal length?
Convex Mirrors
Anything in front of the mirror (real) is:
Concave
Anything behind the mirror (virtual) is:
Convex
Magnification Equation:
M = -di/do = hi/ho
Upright image:
Where M is positive
Upside down image:
Where M is negative
What is the incident ray (angle)?
A ray of light travelling towards and hitting a surface
When does light change speed?
When it enters a new medium causing a light to refract (bend)
Refracted Ray:
The light that is bent upon entering a second medium
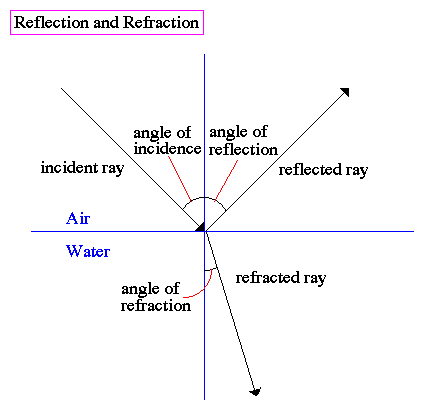
Angle of Refraction:
The angle between the normal and refracted ray.
Speed of light in a vacuum:
3.0 × 10^8 m/s (light travels around the earth 7 times in one second).
Variable for speed of light:
C
When does light refract?
When light travels and strikes a different medium either slowing it down or speeding it up.
Index of Refraction Formula:
n=c/v (n= index of refraction, c= velocity of light in a vacuum, v= velocity of light in a medium)
What unit does “n” have?
No units
If light travels from more dense to less dense, what happens?
It refracts away from the normal/bends outwards.
If light travels from less dense to more dense, what happens?
It refracts towards the normal/bends inwards.
Why does the light bend?
Because the light doesn’t hit the new medium all at once
What happens when the index of refraction is larger (denser medium)?
The speed of light decreases, causing it to bend towards the normal line.
What is the smallest index of refraction and in what object does it exist?
The smallest index of refraction is light in a vacuum with an index of 1.00
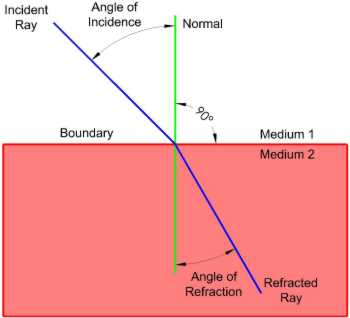
How is the angle of refraction measured?
From the normal line, drawn 90 degrees to the surface where the light ray crosses the boundary.
Dispersion:
The refraction of white light into separate wavelengths of colours.
Why does dispersion occur?
Refractive indices are wavelength dependent and different colours of light travel through a medium at difference speeds.
Explain how a rainbow works:
Through Refraction and Dispersion: When sunlight enters a water droplet, it slows down and changes direction. As light refracts in a water droplet, different wavelengths bend at slightly different angles.
Snell’s Law:
When a light ray strikes a new medium at 90 degrees (along the normal) its angle of incidence is 0 and the ray does not reflect
What happens to the refraction when the angle of incidence increases?
The refraction also increases
What two factors does the amount of refraction depend on?
The index of refraction and the angle of incidence
Snell’s Law Equation:
n1 sinθ1 = n2 sinθ2
What is n1?
Incident medium
What is θ1?
Incident angle
What is n2?
Refractive medium
What is θ2?
Refractive angle
Total internal reflection:
When light is reflected completely off the inside wall of a denser material rather than passing through the wall into a less dense medium.
What is the critical angle?
90 degrees
What is the refracted angle at the critical angle?
90 degrees and the refracted ray does not exit the material
What does the water-air boundary act as?
Acts as a mirror where light rays are reflected internally back into the water
When the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, the law of reflection holds true to what?
That the reflected angle becomes equal to the incident angle
What is the most important natural source of light?
The sun
Other natural sources of light include:
Plants, stars, fire, animals and lightning.
What is bioluminescence?
The ability of a plant or animal to produce light is called bioluminescence.
What is incandescent?
Light that is produced by an object, such as metal that is at very high temperature.