Unit 2: Foundations of American Democracy Key Terms (Part 2)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Townshend Acts
This British law placed taxes on various common goods, including tea, glass, lead, and paper. It also allowed British soldiers to search colonists' homes for untaxed goods. The result was a boycott of British goods across the colonies.

Quartering Act
According to these laws, colonists were required to give British soldiers a room in their homes and provide them with food and other supplies.

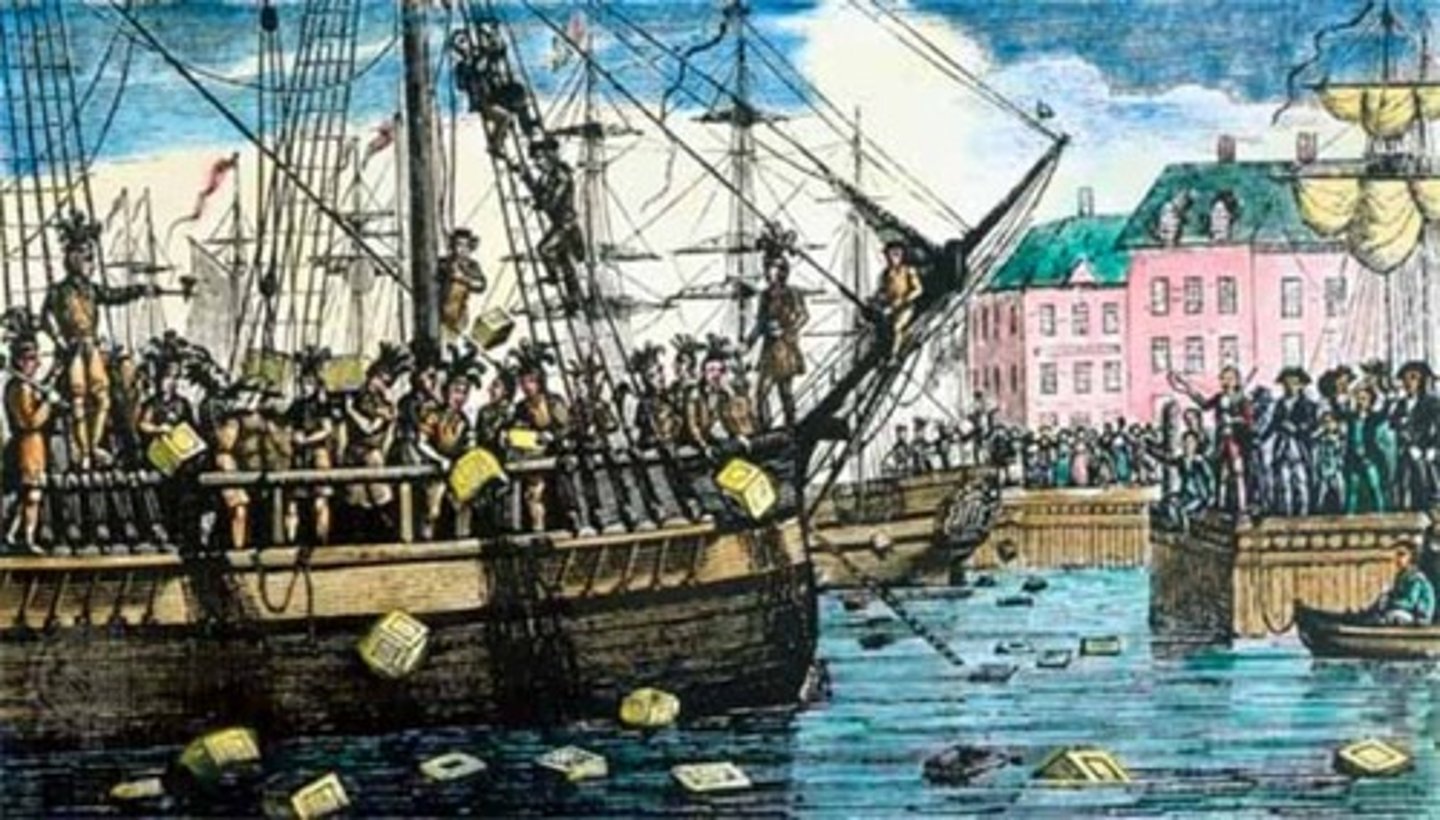
Boston Tea Party
In this event, the colonists protested British taxes and the monopoly of the British East India Company by dumping taxed tea into Boston Harbor.

Intolerable Acts
The British issued this law to punish the people of Boston for the Boston Tea Party. It included the closing of Boston Harbor as well as the banning of local government.

Proclamation of 1763
The British and colonists fought the French and Indian War to gain control of western lands from the French. After the British passed this rule after the war, they refused to allow colonists to settle in this land due to the cost of defending it.
Boston Massacre
After British soldiers opened fire on a group of Bostonians, the colonial leaders used this event as propaganda to turn people against Great Britain.
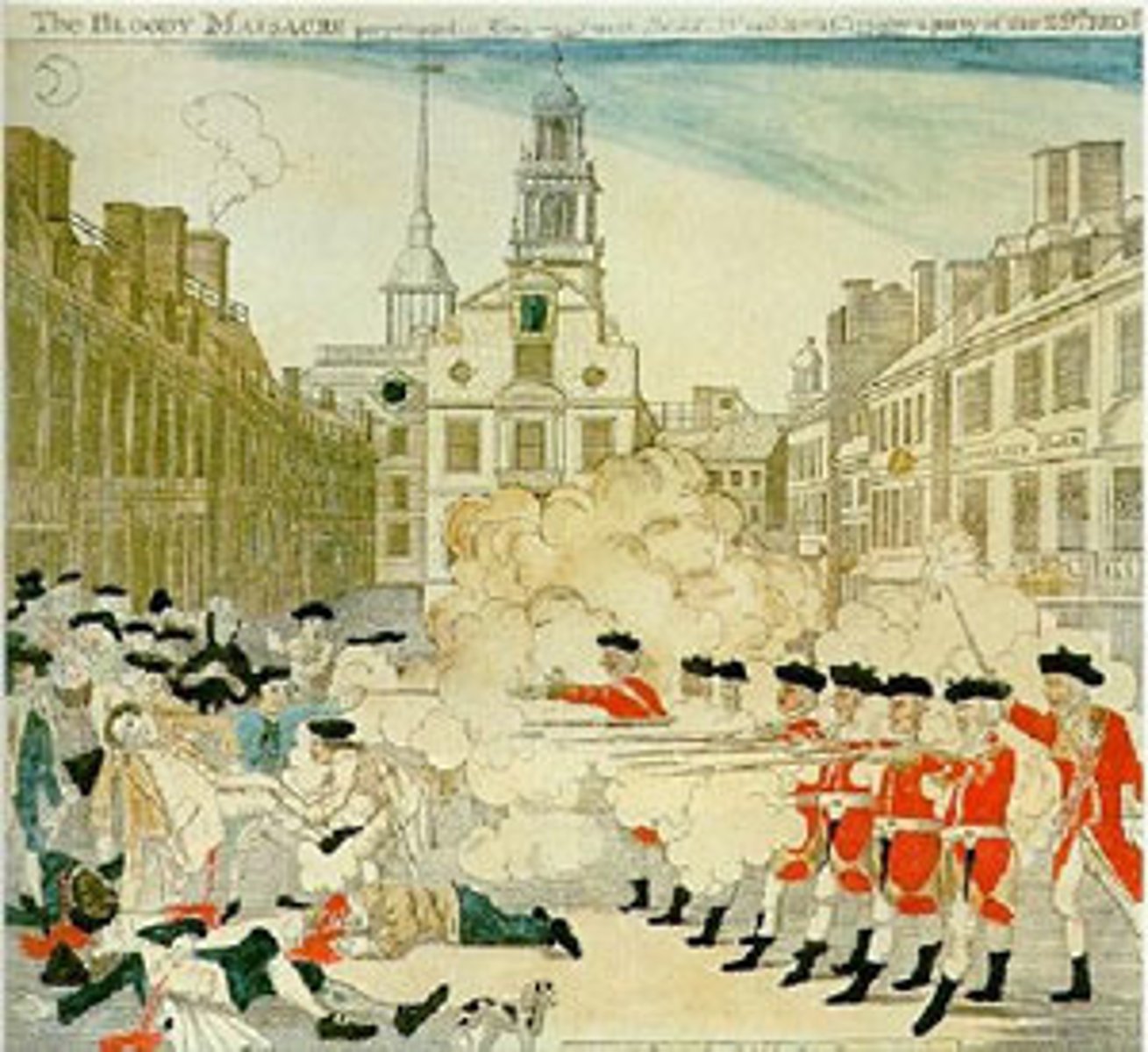

Battle of Lexington and Concord
This event unofficially began the war between the British and the 13 Colonies. While it is unknown who fired first, this important event is known in history as "The Shot Heard Round the World."

Stamp Act
This law taxed legal documents and other paper goods like newspapers. Colonists responded with boycotts, rallies, and even riots.

Sons of Liberty
This group of colonists was the leader of colonial protests and helped organize the resistance to British policies.

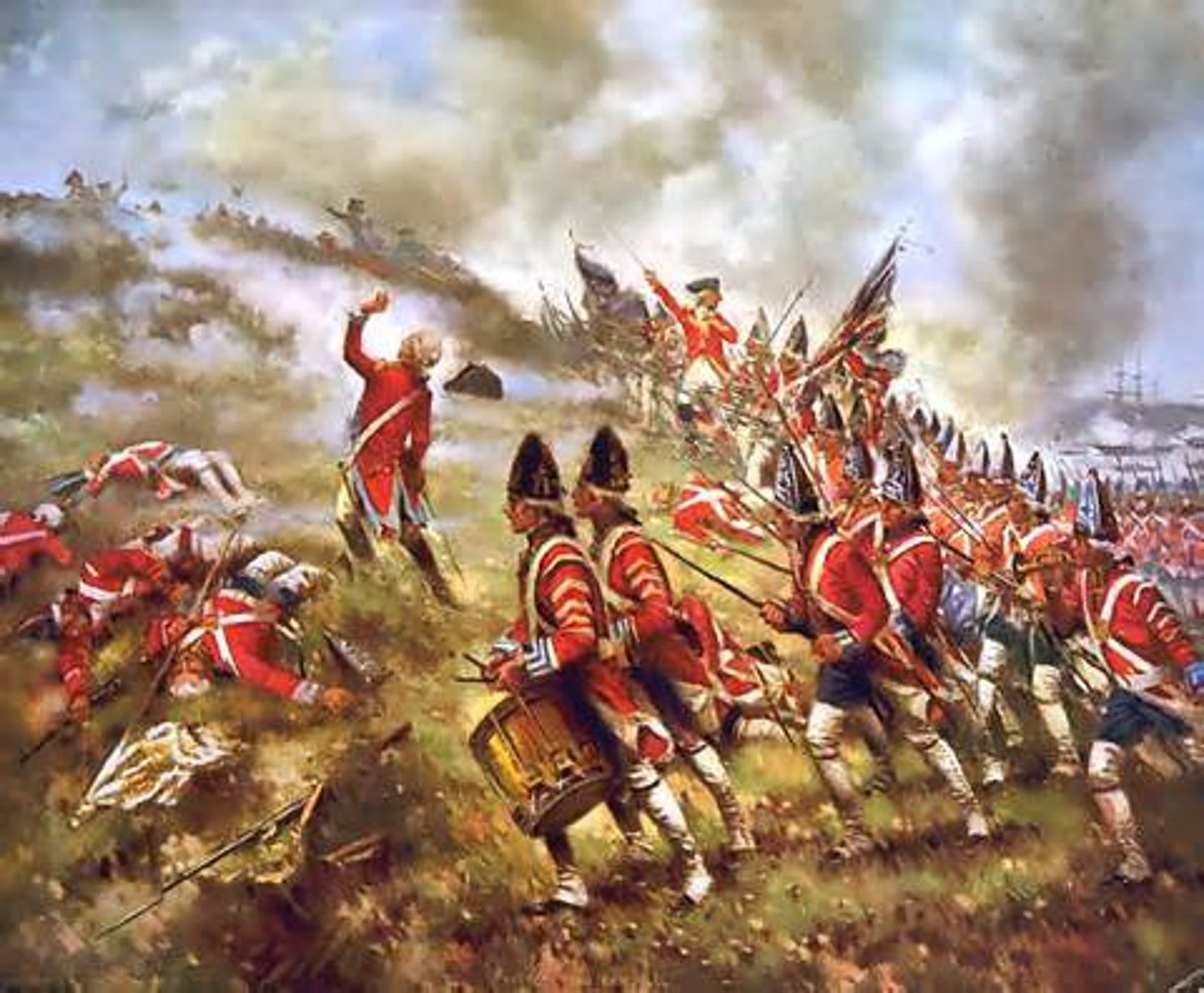
Battle of Bunker Hill
Although the war had not officially begun yet, this conflict is often considered the war's first major battle. Although the colonists lost, the battle showed the British that the Patriots were ready to fight.

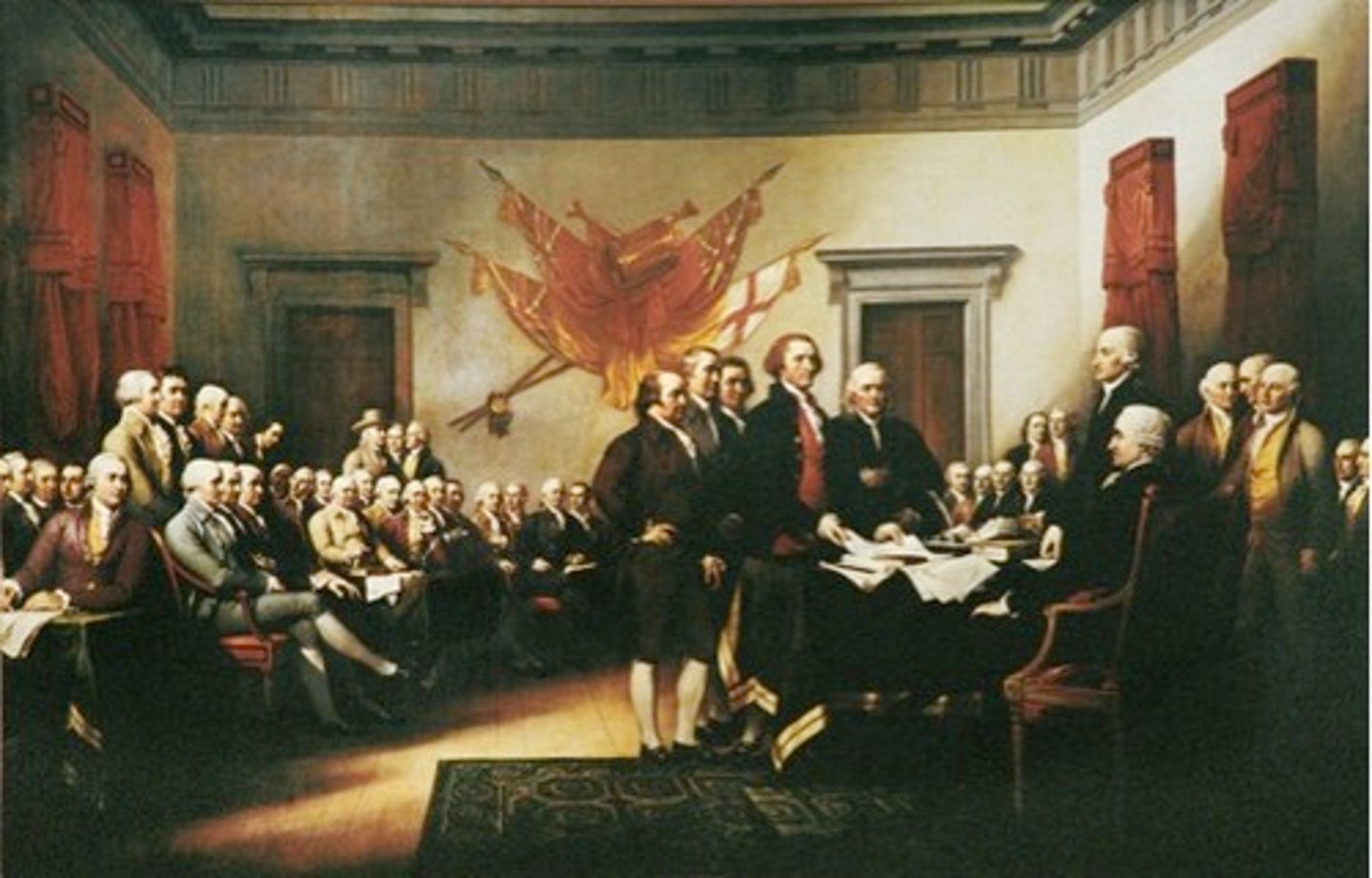
Declaration of Independence
A document stating that America is its own nation and free from the rule of Great Britain

protest
A statement or action expressing unhappiness about something

boycott
To refuse to buy goods to punish something or someone

demonstration
A group of people publicly sharing their feelings about a cause
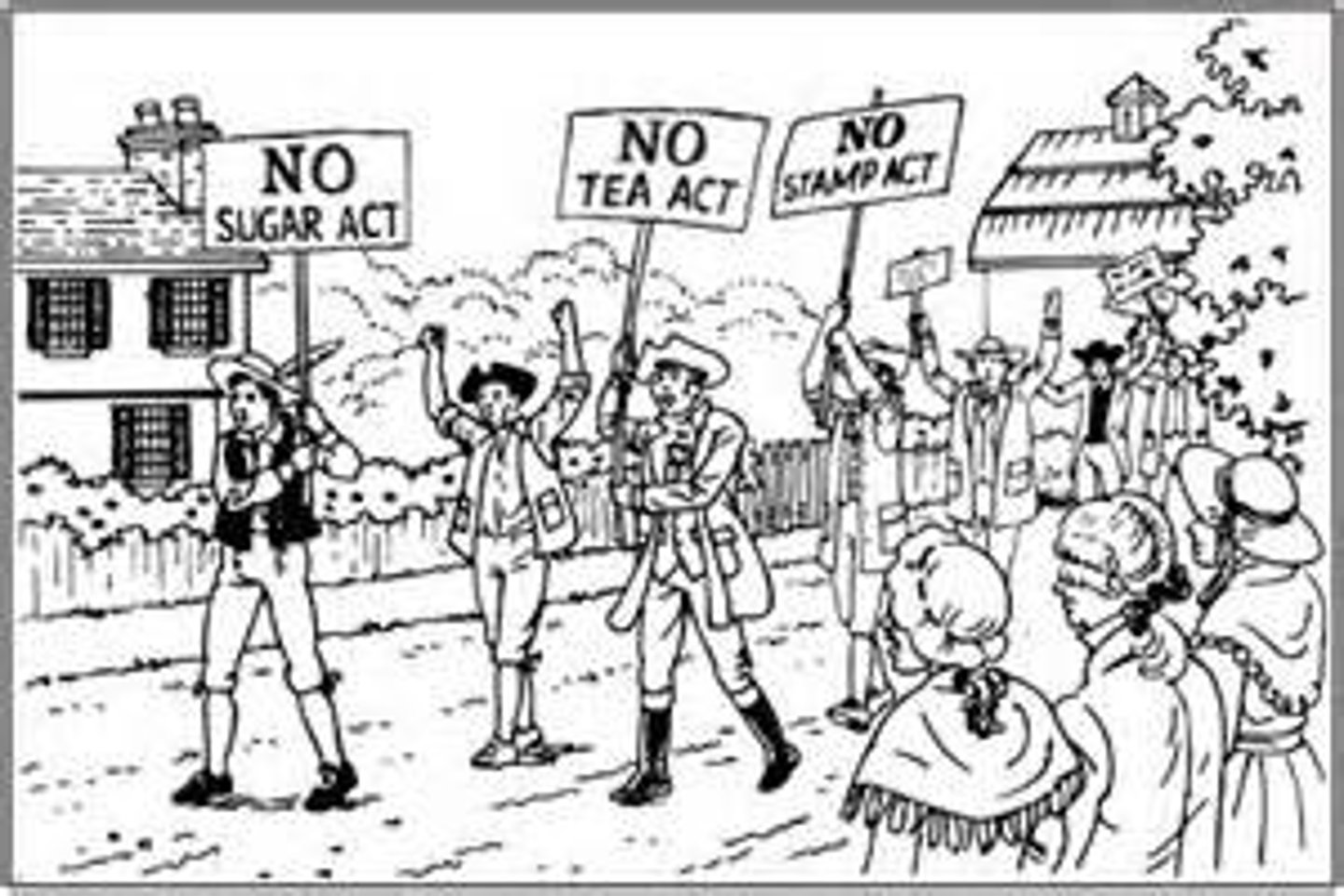

political cartoon
A visual that shows a point of view regarding an issue or individual.

propaganda
Information that expresses one, often biased point of view designed to persuade, a political advertisement.
George Washington
This individual was chosen as the head of the Continental Army to fight against Britain in the Revolutionary War.
Sam Adams
This individual became the leader of the Sons of Liberty and helped to turn colonist opinion against the British with his protests.