NVHS AP Human Geography Unit 5
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
affluent
rich, wealthy
Annexation
Legal addition to land area of a city
(Addition of land to Chicago)
Bid-Rent Theory
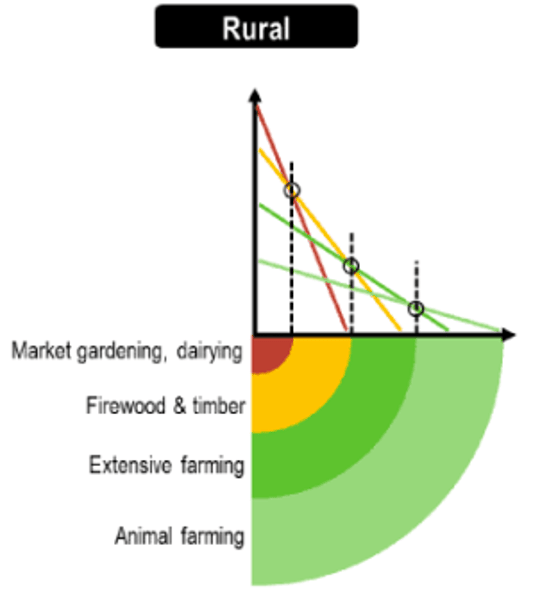
a geographical economic theory to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the CBD increases. (closer to CBD - Land more expensive)
Blockbusting
Illegal practice of inducing homeowners to sell their properties by telling them that a certain people of a certain race, national origin or religion are moving into the area
Borchert's epochs
5 epochs of transportation
The Sail-Wagon Epoch (1790-1830)
1st stage of transportation epochs, featured slow land/sea travel, such as wagons or sailboats
The Iron Horse Epoch (1830-1870)
2nd stage of transportation Epochs, featured steamboats, steam power, coal, and basic trains
The Steel Rail Epoch (1870-1920)
3rd stage of transportation Epochs, Featured advanced land transport such as high speed trains and rails. Ties into the Industrial revolution.
Auto-Air-Amenity Epoch (1920-1970)
4th stage of transportation Epochs, features gas engines, planes, cars, highways, and the development of suburbs.
Satellite-Electronics-Jet Propulsion Epoch (1970-present)
5th stage of transportation epochs, features jet propulsion, advanced electronics, rocketry, electric cars, and industrial planes/jets
Boomburbs
Rapidly growing suburban cities (Naperville)
brown fields
abandoned industrial sites that are contaminated to the point that new development is curtailed
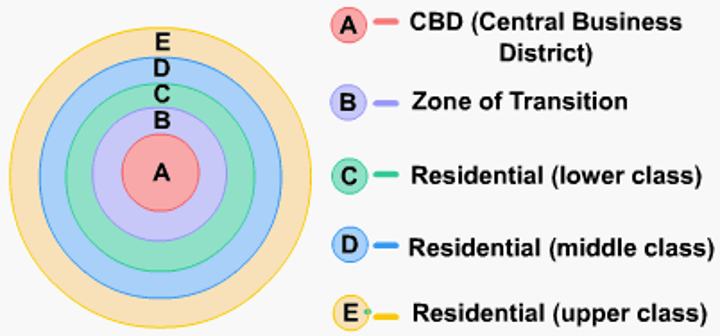
Burgess Concentric Zone Model (Rich, Poor, Industry, CBD)
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
Central Business District (CBD)
The downtown or nucleus of a city where retail stores, offices, and cultural activities are concentrated. (NYC)
central city
An urban settlement that has been legally incorporated into an independent, self-governing unit known as a municipality. (Chicago)
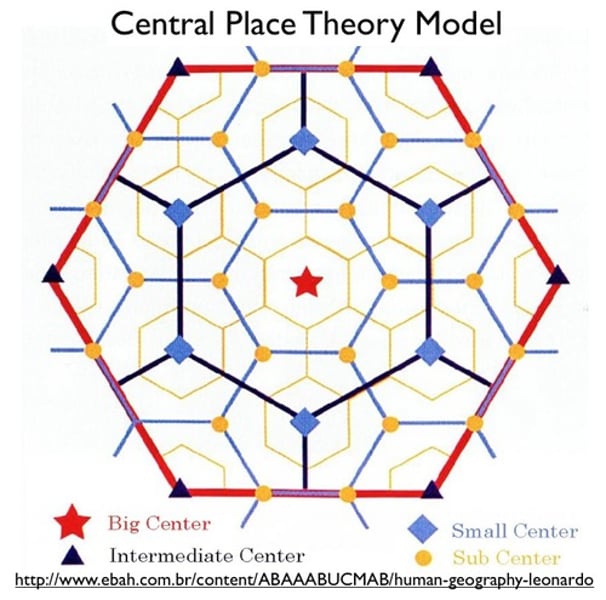
Christaller's Central Place Theory
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
Density Gradient
The change in density in an urban area from the center to outskirts.
Decentralization
The tendency of people or businesses and industry to locate outside the central city
Disamenity Zones
areas not connected to city services and under the control of drug lords and gangs (Favelas)
Edge City (Galactic City)
A large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area. (Tysons Corner, Virginia)
Ethnic segregation
The clustering together of people with similar ethnic or cultural characteristics into separate urban residential areas
Exurbs
Prosperous residential districts beyond the suburbs.
Filtering
a process of change in the use of a house, from single-family owner occupancy to abandonment
Food deserts
Areas where it is difficult to find affordable, healthy food options. (Certain areas of NYC)
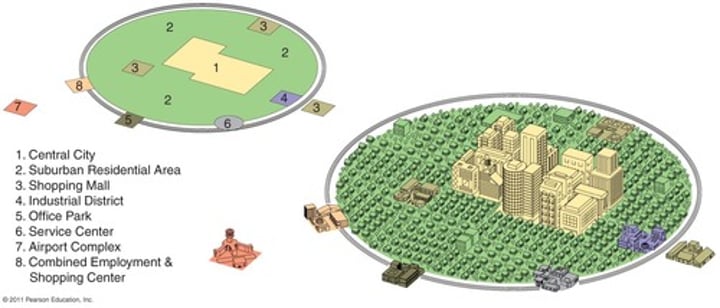
Galactic city model
last half of the twentieth century, represents the post-industrial city, many suburban CBDs have become specialized toward a particular sector
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area.
Gravity model
Predicts that the optimal location of a service is directly related to the number of people in the area and how far they must travel to access it.
Greenbelt
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.

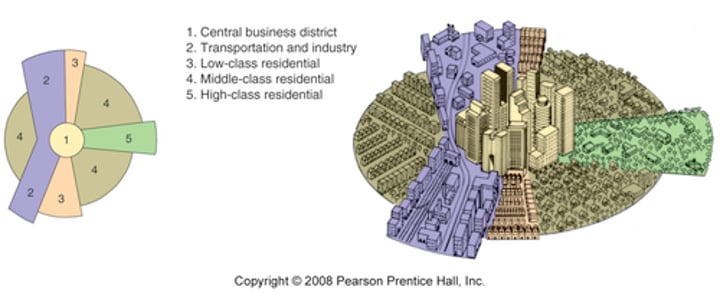
Hoyt Sector model (Rich, Poor, Industry, CBD)
the theory of urban structure that a city develops in a series of certain sectors, instead of rings.
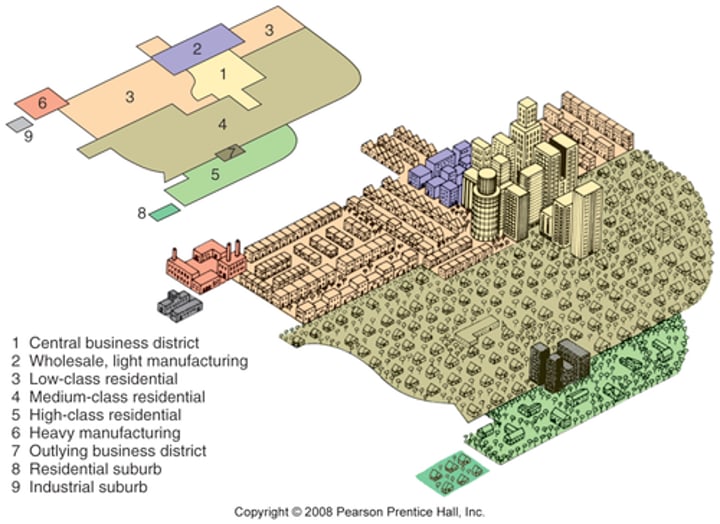
Multiple Nuclei Model (Rich, Poor, Industry, CBD)
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a collection of nodes of activities.
hinterland
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services. (A hinterland for a city could be smaller villages around it reliant on that city for certain services)
Inclusionary Zoning
Specifies inclusions within a development (Area must include a playground, or have affordable housing)
Infilling
The process by which population density in an urban center is increased by building on waste land or underused land.
informal settlements/squatter settlements
settlements by people who do not hold legal claims to the land their homes are built upon, not government endorsed
(favelas, Shantytowns, etc)
Infastructure
the basic framework of a system or city
Interdependence
A relationship between countries in which they rely on one another for resources, goods, or services
Market Area
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services.
Megacities
cities with more than 10 million people (Mexico City, Cairo)
Megapolis
a huge urban region formed when two or more metropolitan areas grow together (New York)
Metacities
cities with populations over 20 million (London, UK, Tokyo, etc)
metropolitan
having to do with a city and its surrounding communities
mixed-use zoning
zoning that permits multiple land uses in the same space or structure
(E.G. an area with both housing and commerce mixed in)
New Urbanism
Development of urban areas with walkable areas and sustainability in mind
The Law of the Primate City
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the largest settlement has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
range
maximum distance people are willing to travel to get a product or service
Rank size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
Redlining
A process by which banks draw lines on a map and refuse to lend money to purchase or improve property within the boundaries.
Service types
Consumer, Business, Public
site
The physical character of a place
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
Slow-growth cities
smart growth policies that concentrate growth in walkable urban centers to decrease sprawl
(sub)urban Sprawl
Rapid growth of urban/suburban areas
smart growth
Legislation and regulations to limit suburban sprawl and preserve farmland.
suburbinization
the movement from the city to the suburbs
Sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
threshold
minimum number of people needed for a business to operate
Transportation-oriented development
A mixed-use residential and commercial area designed to maximize access to public transport
urban blight
The degradation of the built and social environments of the city (Old, crumbling buildings littered streets, etc)
Urban cluster
an urban area with between 2,500 and 50,000 inhabitants
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements (hamlet, village, town, city, metropolis) according to their size and economic functions.
urban renewal
the clearing and rebuilding and redevelopment of urban slums
Urban revolution
the process by which small, kin-based, nonliterate agricultural villages were transformed into large, socially complex, urban societies
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities
Wallerstein's World Systems Theory
sees the world economy as a flexible core, periphery and semi-periphary
World Cities (Global Cities)
Centers of economic, culture, and political activity that are strongly interconnected and together control the global systems of finance and commerce (examples include: New York City, London, Tokyo, Sydney, Buenos Aires...)
World-regional models
models geographers have developed to describe cities outside of north America (Latin America, Africa, etc)
Latin American City Model (Rich, Poor, Industry, CBD)
Combines elements of Latin American Culture and globalization by combining radial sectors and concentric zones. Includes a thriving CBD with a commercial spine. The quality of houses decreases as one moves outward away from the CBD, and the areas of worse housing occurs in the Disamenity sectors.
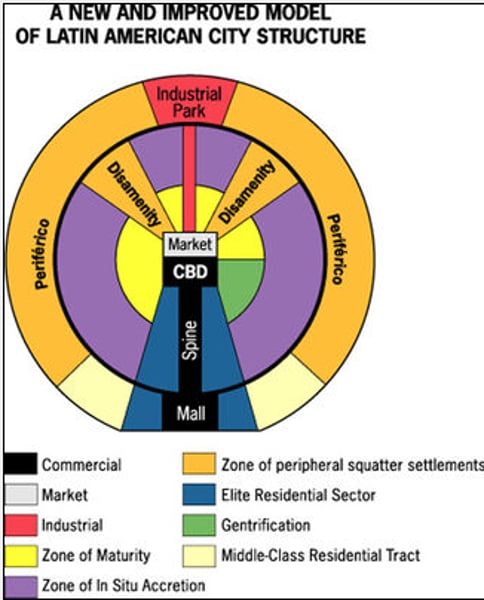
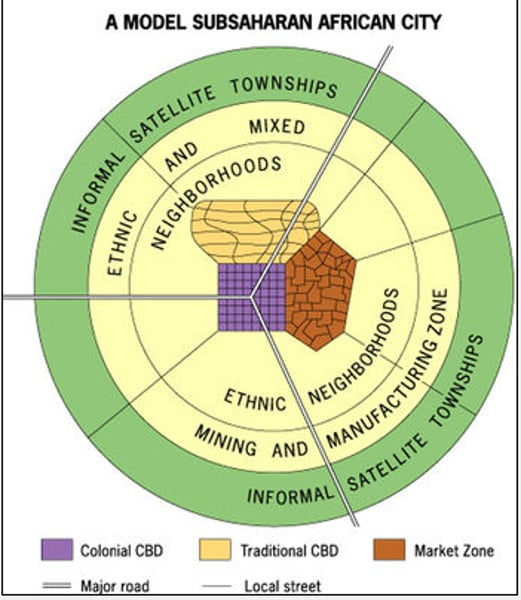
Africa Model (Rich, Poor, Industry, CBD)
Notable for containing 3 CBDs: A market, A colonial CBD, and a traditional CBD
Zones of Abandonment
areas that have been deserted in a city for economic or environmental reasons (Polluted or extremely poor reigon)
Zoning Ordinance
A law that limits the permitted uses of land and maximum density of development in a community.
Primary Sector (Services)
Deals with resource extraction, Agriculture and mining. Very few workers in US
Secondary sector (Services)
Deals with resource manufacturing and construction, few workers in US
Tertiary sector
the part of the economy that involves services rather than goods. 3 parts
Public (Government)
Consumer (Health, wholesale, retail)
Business (Finance, transport, professional services)
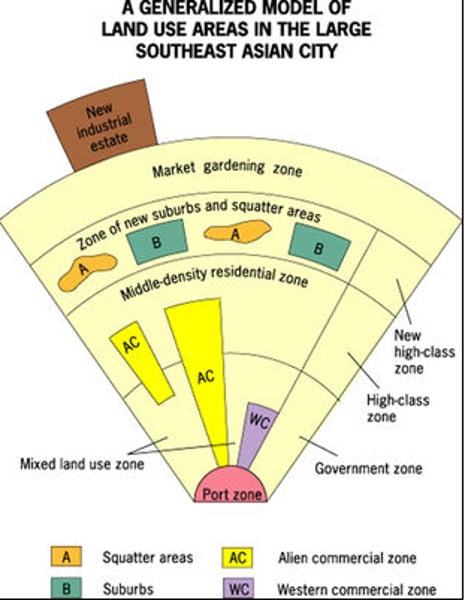
Southeast Asian Model (CBD, Rich, Poor, Industry)